Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Vivi Li and Version 1 by Tomasz M. Karpinski.
The incidence of fungal infections has been steadily increasing in recent years. Systemic mycoses are characterized by the highest mortality. At the same time, the frequency of infections caused by drug-resistant strains and new pathogens e.g., Candida auris increases. An alternative to medicines may be essential oils, which can have a broad antimicrobial spectrum. Rich in the essential oils are plants from the Lamiaceae family.
- Labiatae
- fungi
- Aspergillus
- Cryptococcus
- Penicillium
- dermatophytes
- β-caryophyllene
- sesquiterpene
- monoterpenes
- minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
1. Introduction
Fungal infections belong to the most often diseases of humans. It is estimated that about 1.7 billion people (25% of the population) have skin, nail, and hair fungal infections [1]. The development of most of these infections is affected by dermatophytes, namely Trichophyton spp., Microsporum spp., and Epidermophyton spp. [2]. Simultaneously, mucosal infections of the oral and genital tracts caused by Candida spp. are very common. About 0.13 billion of women suffer from vulvovaginal candidiasis. On the other hand, oral candidiases are common in babies and denture wearers. Fungi also cause life-threatening systemic infections, with mortality reaching >1.6 million, which is >3-fold more than malaria [3]. Among life-threatening fungal infections prevail cryptococcosis (Cryptococcus neoformans) with >1,000,000 cases and mortality rate 20–70%, candidiasis (Candida albicans) with >400,000 cases and mortality rate 46–75%, pneumocystosis (Pneumocystis jirovecii) with >400,000 cases and mortality rate 20–80%, and aspergillosis (Aspergillus fumigatus) with >200,000 cases and mortality rate 30–95% [1,4,5][1][4][5]. In Table 1 are presented diseases caused by some of the most often fungal pathogens among people.
| Superficial mycoses |
|
| Cutaneous and subcutaneous mycoses |
|
| Endemic mycoses |
|
| Opportunistic mycoses |
|
The big problem is growing drug-resistance amid fungi. Among Candida and Aspergillus species is observed resistance to azoles, e.g., to fluconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole. Some Candida species, especially C. glabrata and C. parapsilosis, can be echinocandin- and multidrug-resistant [8,9][8][9]. Acquired resistance to echinocandins has also been reported for yeasts C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. krusei, C. kefyr, C. lusitaniae, and C. dubliniensis [10] [10]. More than 3% of Aspergillus fumigatus isolates are resistant to one or more azoles [11]. Polyene resistance mainly concerns amphotericin B. Resistance to this drug is observed in Fusarium spp., Trichosporon spp., Aspergillus spp., and Sporothrix schenckii [12,13] [12][13]. Resistance to amphotericin B has also been reported for C. albicans, C. glabrata, and C. tropicalis [14,15,16] [14][15][16]. Cultures of some Candida species and Cryptococcus neoformans are presented in Figure 1.
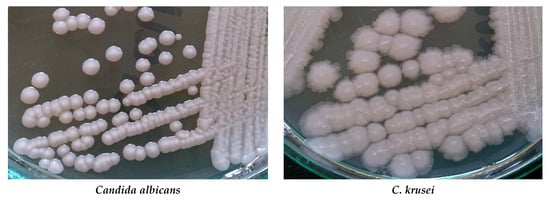
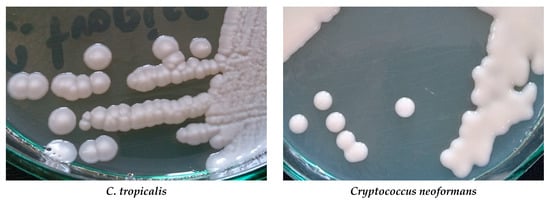
Figure 1. Cultures of selected yeast fungi on Sabouraud agar (Author of photos: Tomasz M. Karpiński).
The new epidemiological problem is C. auris, a multidrug-resistant organism first described in Japan in 2009 [17]. Recently, C. auris has been reported from 36 countries from six continents [18]. About 30% of isolates demonstrate reduced susceptibility to amphotericin B, and 5% can be resistant to the echinocandins [19,20][19][20]. The estimated mortality from C. auris fungemia range from 28% to 60% [21].
Fundamental issues are also the costs of treatment and hospitalization of patients with invasive fungal diseases. According to Drgona et al., all costs range from around €26,000 up to over €80,000 per patient [5].
2. Components of Essential Oils of Lamiaceae Family
The family Lamiaceae or Labiatae contains many valuable medicinal plants. In the family are 236 genera and between 6900 and 7200 species. To the most abundant genera belong Salvia (900 species), Scutellaria (360), Stachys (300), Plectranthus (300), Hyptis (280), Teucrium (250), Vitex (250), Thymus (220), and Nepeta (200). Lamiaceae plants rich in essential oils have great worth in natural medicine, pharmacology, cosmetology, and aromatherapy [25][22]. The essential oils are mostly present in leaves, however, they can be found in flowers, buds, fruits, seeds, rind, wood, or roots [26][23]. Essential oils are mixtures of volatile compounds, which are secondary plant metabolites. They play a role in the defense system of higher plants [27][24]. Essential oils may contain over 300 different compounds, mainly of molecular weight below 300 [28][25]. Some oils, e.g., obtained from Lavandula, Geranium, or Rosmarinus, contain 450 to 500 chemicals [29][26]. Among the active compounds of essential oils are various chemical classes, e.g., alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, esters, phenols, terpenes (monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes), and coumarins [30,31][27][28]. To the chemical components most commonly found as the main ingredients in essential oils, among plants presented in Table 2, include β-caryophyllene (41 plants), linalool (27 plants), limonene (26), β-pinene (25), 1,8-cineole (22), carvacrol (21), α-pinene (21), p-cymene (20), γ-terpinene (20), and thymol (20) (Figure 2). Sesquiterpene β-caryophyllene seems particularly important antifungal component in the Lamiaceae family. Its activity and its derivatives, such as caryophyllene oxide is well known [134,135,136][29][30][31]. According to Bona et al. [137][32], essential oils containing high concentrations of phenolic monoterpenes (e.g., carvacrol, p-cymene, thymol) have great antifungal activities. Rich in these substances are, among others Origanum and Thymus plants. Important antifungal chemicals often presented in Lamiaceae are also other monoterpenes as alcohol linalool and cyclic 1,8-cineole, limonene, pinenes, and terpinenes [138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41]. Table 1 shows that all of these antifungal substances are common in presented plants.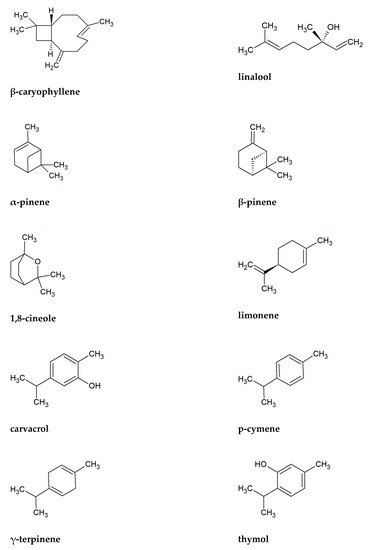
Figure 2. Chemical formulas of ten substances the most commonly found in essential oils of Lamiaceae plants presented in Table 1.
3. Antifungal Activity of Essential Oils of Lamiaceae Family
In Table 3 are shown the antifungal activities of selected Lamiaceae essential oils. More than half of the essential oils have good activity (<1000 µg/mL) against fungi. In some cases are observed significant discrepancies between different studies. An example could be the action of essential oils from Italian Calamintha nepeta against Candida albicans. In the work of Marongiu et al. [39][42], minimal inhibitory concentrations amounted to 1.25–2.5 µg/mL, while in Božović et al. [40][43] MICs were between 780 to 12,480 µg/mL. Differences may be related to the different biochemical composition of the examined essential oils. In results presented by Marongiu et al. [39] [42] the main components of essential oils were pulegone (39.9–64.4%), piperitenone oxide (2.5–19.1%) and piperitenone (6.4–7.7%), while in Božović et al. [40][43] three main substances were pulegone (37.7–84.7%), crysanthenone (1.3–33.9%) and menthone (0.5–35.4%). Some authors have described that the content of active substances varies depending on the season. In studies of Gonçalves et al. [60] [44] in Mentha cervina during the flowering phase in August amount of isomenthone and pulegone in essential oil amounted 8.7% and 75.1% respectively. Simultaneously, in the vegetative phase in February, the content of both components changed significantly and amounted to 77.0% for isomenthone and 12.9% for pulegone. Similarly, Al-Maskri et al. [75] [45] presented essential changes in some compounds of Ocimum basilicum essential oil between winter and summer. In the summer essential oil, there is significantly more of linalool, p-allylanisole and β-farnesene, and at the same time much less content of limonene and 1,8-cineole. In this work, a seasonal variation of chemical composition is directly related to other antifungal activities. It is particularly evident in action against Aspergillus niger, which was lower in the summer season. Zone of growth inhibition (ZOI) for winter essential oil was 21 mm and MIC > 50 µg/mL, while for summer essential oil-ZOI was 13 mm and MIC > 100 µg/mL [75][45]. Influence on the content of chemical substances in essential oils also has a method of obtaining them. Ćavar et al. [40] [43] compared the composition of oils obtained from Calamintha glandulosa using three methods: Hydrodistillation (HD), steam distillation (SD) and aqueous reflux extraction (ARE). For example, the level of menthone was 3.3% in ARE, 4.7% in HD, and 8.3% in SD method, while for shisofuran was only 0.1% in HD and SD, and even 9.7% in ARE [40][43]. Additionally, many other factors can affect antimicrobial activity, such as amount and concentration of inoculum, type of culture medium, pH of the medium and incubation time. All these factors can affect the value of MIC [145][40]. Differences are visible in Table 2. Generally, it can be assumed that the best activity (MICs < 100) have essential oils from Clinopodium spp. (excluding C. nepeta subsp. glandulosum and C. umbrosum), Lavandula spp., Mentha spp. (excluding M. piperita), Thymbra spp., and Thymus spp. (excluding T. migricus and T. vulgaris). The highest values of MICs are presented among others for Aeollanthus suaveolens, Agastache rugosa, Lepechinia mutica, Mentha × piperita, and Salvia sclarea. Simultaneously, some essential oils have a very different activity, and MIC values differ depending on the region, chemical composition, research methodology, etc. Significant variations can be observed even in Ocimum basilicum (MICs 1–10,000), O. sanctum (MICs 0.1–500), Origanum majorana (MICs 0.5–14,400) or in Thymus vulgaris (MICs 0.08–3600).Table 3. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of essential oils against fungi.
| Source of the Essential Oil | Targeted Fungus | MICs (µg/mL; µl/mL) | Reference(s) |
|---|
| Aeollanthus suaveolens |
| Mart. ex Spreng. = |
| A. heliotropioides |
| Oliv. | |||
| Candida albicans | 1200–5000 | [34] | |
| 1200–5000 | [46] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 5000 | [34] | |
| 5000 | [46] | ||
| Candida krusei | 2500 | [34] | |
| 2500 | [46] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 2500 | [ | |
| 2500 | |||
| 34 | ] | ||
| [ | 46] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1200 | [34] | |
| 1200 | [46] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 600–5000 | [34] | |
| 600–5000 | [46] | ||
| Agastache rugosa | |||
| (Fisch. and C.A.Mey.) Kuntze | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 10,000 | [153] | |
| 10,000 | [47] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 5000 | [153] | |
| 5000 | [47] | ||
| Blastoschizomyces capitatus | 5000 | [153] | |
| 5000 | [47] | ||
| Candida albicans | 28–5000 | [153,154] | |
| 28–5000 | [47][48] | ||
| Candida utilis | 5000 | [153] | |
| 5000 | [47] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 5000 | [153] | |
| 5000 | [47] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 10,000 | [153] | |
| 10,000 | [47] | ||
| Trichoderma viride | 5000 | [153] | |
| 5000 | [47] | ||
| Trichophyton erinacei | 780 | [153] | |
| 780 | [47] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 3120 | [153] | |
| 3120 | [47] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 1560 | [153] | |
| 1560 | [47] | ||
| Trichophyton schoenleinii | 1560 | [153] | |
| 1560 | [47] | ||
| Trichophyton soudanense | 1560 | [153] | |
| 1560 | [47] | ||
| Trichophyton tonsurans | 10,000 | [ | |
| 10,000 | |||
| 153 | ] | ||
| [ | 47] | ||
| Trichosporon mucoides | 5000 | [153] | |
| 5000 | [47] | ||
| Ballota nigra | |||
| subsp. | |||
| foetida | |||
| (Vis.) Hayek | |||
| Alternaria solani | 750 | [37] | |
| 750 | [49] | ||
| Botrytis cinerea | 600 | [37] | |
| 600 | [49] | ||
| Fusarium coeruleum | 350 | [37] | |
| 350 | [49] | ||
| Fusarium culmorum | 300 | [37] | |
| 300 | [49] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 300 | [37] | |
| 300 | [49] | ||
| Fusarium solani | 350 | [37] | |
| 350 | [49] | ||
| Fusarium sporotrichioides | 350 | [37] | |
| 350 | [49] | ||
| Fusarium tabacinum | 350 | [37] | |
| 350 | [49] | ||
| Fusarium verticillioides | 300 | [37] | |
| 300 | [49] | ||
| Clinopodium dalmaticum | |||
| (Benth.) Bräuchler and Heubl = | |||
| Micromeria dalmatica | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Cladosporium cladosporioides | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Fusarium tricinctum | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Penicilium ochrochloron | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Phomopsis helianthi | 0.2 | [38] | |
| 0.2 | [50] | ||
| Trichoderma viride | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Clinopodium nepeta | |||
| subsp. | |||
| glandulosum | |||
| (Req.) Govaerts = | |||
| Calamintha glandulosa | |||
| (Req.) Bentham = | |||
| Calamintha officinalis | |||
| Moench | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 1250 | [39] | |
| 1250 | [42] | ||
| Candida albicans | 2500 | [39] | |
| 2500 | [42] | ||
| Clinopodium nepeta | |||
| (L.) Kuntze = | |||
| Calamintha nepeta | |||
| (L.) Savi | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 1.25–10 | [41] | |
| 1.25–10 | [51] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 0.64–5 | [41] | |
| 0.64–5 | [51] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.32–10 | [41] | |
| 0.32–10 | [51] | ||
| Candida albicans | 1.25–12,480 | [41,42] | |
| 1.25–12,480 | [51][52] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 1.25–2.5 | [41] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [51] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1.25–2.5 | [41] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [51] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 1.25–2.5 | [41] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [51] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1.25–2.5 | [41] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [51] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 0.32–1.25 | [41] | |
| 0.32–1.25 | [51] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.64–2.5 | [41] | |
| 0.64–2.5 | [51] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.64–2.5 | [41] | |
| 0.64–2.5 | [51] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 1.25–5 | [41] | |
| 1.25–5 | [51] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.64–5 | [41] | |
| 0.64–5 | [51] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.64–5 | [41] | |
| 0.64–5 | [51] | ||
| Clinopodium thymifolium | |||
| (Scop.) Kuntze = | |||
| Micromeria thymifolia | |||
| (Scop.) Fritsch | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 2 | [38] | |
| 2 | [50] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 2 | [38] | |
| 2 | [50] | ||
| Cladosporium cladosporioides | 2 | [38] | |
| 2 | [50] | ||
| Fusarium tricinctum | 2 | [38] | |
| 2 | [50] | ||
| Penicillium ochrochloron | 2 | [ | |
| 2 | |||
| 38 | ] | ||
| [ | 50] | ||
| Phomopsis helianthi | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Trichoderma viride | 2 | [38] | |
| 2 | [50] | ||
| Clinopodium umbrosum | |||
| (M.Bieb.) Kuntze = | |||
| Calamintha umbrosa | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Alternaria solani | 3000 | [43] | |
| 3000 | [53] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 2000 | [43] | |
| 2000 | [53] | ||
| Helminthosporium maydis | 1500 | [43] | |
| 1500 | [53] | ||
| Dracocephalum heterophyllum | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Alternaria solani | 625 | [155] | |
| 625 | [54] | ||
| Candida albicans | 625–1000 | [44,155] | |
| 625–1000 | [55][54] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 2500 | [155] | |
| 2500 | [54] | ||
| Fusarium semitectum | 313 | [155] | |
| 313 | [54] | ||
| Hymenocrater longiflorus | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 480 | [45] | |
| 480 | [56] | ||
| Candida albicans | 240 | [45] | |
| 240 | [56] | ||
| Hyptis ovalifolia | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Microsporum canis | 15.6–1000 | [46,156] | |
| 15.6–1000 | [57][58] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 7.8–1000 | [46,156] | |
| 7.8–1000 | [57][58] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 15.6–1000 | [46,156] | |
| 15.6–1000 | [57][58] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 7.8–1000 | [46,156] | |
| 7.8–1000 | [57][58] | ||
| Hyssopus officinalis | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 52,200 | [47] | |
| 52,200 | [59] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 26,100 | [47] | |
| 26,100 | [59] | ||
| Aspergillus versicolor | 10,440 | [47] | |
| 10,440 | [59] | ||
| Candida albicans | 128–1000 | [44,48] | |
| 128–1000 | [55][60] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 512–1024 | [48] | |
| 512–1024 | [60] | ||
| Candida krusei | 128–256 | [48] | |
| 128–256 | [60] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 256–512 | [48] | |
| 256–512 | [60] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 512–1024 | [48] | |
| 512–1024 | [60] | ||
| Cladosporium cladosporioides | 10,440 | [47] | |
| 10,440 | [59] | ||
| Cladosporium fulvum | 26,100 | [47] | |
| 26,100 | [59] | ||
| Penicillium funiculosum | 52,200 | [47] | |
| 52,200 | [59] | ||
| Penicillium ochrochloron | 26,100 | [47] | |
| 26,100 | [59] | ||
| Trichoderma viride | 10,440 | [47] | |
| 10,440 | [59] | ||
| Lavandula angustifolia | |||
| Mill. | |||
| Candida albicans | 0.125–512 | [50,51,157] | |
| 0.125–512 | [61][62][63] | ||
| Malassezia furfur | >4 | [49] | |
| >4 | [64] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 1–512 | [49,51] | |
| 1–512 | [64][62] | ||
| Trichosporon beigelii | 2 | [49] | |
| 2 | [64] | ||
| Lavandula multifida | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 0.64 | [52] | |
| 0.64 | [65] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 0.32 | [52] | |
| 0.32 | [65] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.32 | [52] | |
| 0.32 | [65] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.32 | [ | |
| 0.32 | |||
| 52 | ] | ||
| [ | 65] | ||
| Candida guilliermondii | 0.32 | [52] | |
| 0.32 | [65] | ||
| Candida krusei | 0.64 | [52] | |
| 0.64 | [65] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 0.32 | [52] | |
| 0.32 | [65] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 0.32 | [52] | |
| 0.32 | [65] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Trichophyton verrucosum | 0.16 | [52] | |
| 0.16 | [65] | ||
| Lavandula pedunculata | |||
| (Miller) Cav. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 5–10 | [53] | |
| 5–10 | [66] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 2.5–5 | [53] | |
| 2.5–5 | [66] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 5 | [53] | |
| 5 | [66] | ||
| Candida albicans | 2.5 | [53] | |
| 2.5 | [66] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 1.25 | [53] | |
| 1.25 | [66] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1.25–2.5 | [53] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [66] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 2.5–5 | [53] | |
| 2.5–5 | [66] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1.25–2.5 | [53] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [66] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 0.32–1.25 | [ | |
| 0.32–1.25 | |||
| 53 | ] | ||
| [ | 66] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.32–0.64 | [53] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [66] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.32–1.25 | [53] | |
| 0.32–1.25 | [66] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.64–2.5 | [53] | |
| 0.64–2.5 | [66] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.64–1.25 | [53] | |
| 0.64–1.25 | [66] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.32–1.25 | [53] | |
| 0.32–1.25 | [66] | ||
| Lavandula stoechas | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 1.25–10 | [54] | |
| 1.25–10 | [67] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 0.64–1.25 | [54] | |
| 0.64–1.25 | [67] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.32–1.25 | [54] | |
| 0.32–1.25 | [67] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.64–512 | [51,54] | |
| 0.64–512 | [62][67] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 1.25 | [54] | |
| 1.25 | [67] | ||
| Candida krusei | 2.5 | [54] | |
| 2.5 | [67] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 2.5 | [54] | |
| 2.5 | [67] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 2.5 | [54] | |
| 2.5 | [67] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 0.64 | [54] | |
| 0.64 | [67] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.16–0.32 | [54] | |
| 0.16–0.32 | [67] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.16–0.64 | [ | |
| 0.16–0.64 | |||
| 54 | ] | ||
| [ | 67] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.32–0.64 | [54] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [67] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.32–0.64 | [54] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [67] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale | 0.16–0.64 | [54] | |
| 0.16–0.64 | [67] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.16–256 | [51,54] | |
| 0.16–256 | [62][67] | ||
| Trichophyton verrucosum | 0.32 | [54] | |
| 0.32 | [67] | ||
| Lavandula viridis | |||
| L’Her. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 5 | [55] | |
| 5 | [68] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 2.5 | [55] | |
| 2.5 | [68] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 2.5 | [55] | |
| 2.5 | [68] | ||
| Candida albicans | 1.25–2.5 | [55] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [68] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 0.64–1.25 | [55] | |
| 0.64–1.25 | [68] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1.25–2.5 | [55] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [68] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 1.25 | [55] | |
| 1.25 | [68] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1.25–2.5 | [55] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [68] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 0.64 | [55] | |
| 0.64 | [68] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.32 | [55] | |
| 0.32 | [68] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.32 | [ | |
| 0.32 | |||
| 55 | ] | ||
| [ | 68] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.64 | [55] | |
| 0.64 | [68] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.32–0.64 | [55] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [68] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale | 0.32–0.64 | [55] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [68] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.32 | [55] | |
| 0.32 | [68] | ||
| Trichophyton verrucosum | 0.32 | [55] | |
| 0.32 | [68] | ||
| Lepechinia mutica | |||
| (Benth.) Epling | |||
| Candida albicans | >9000 | [56] | |
| >9000 | [69] | ||
| Fusarium graminearum | >9000 | [56] | |
| >9000 | [69] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 2200–4500 | [56] | |
| 2200–4500 | [69] | ||
| Pyricularia oryzae | >9000 | [56] | |
| >9000 | [69] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 2200–4500 | [56] | |
| 2200–4500 | [69] | ||
| Marrubium vulgare | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | >1180 | [58] | |
| >1180 | [70] | ||
| Botrytis cinerea | >1100 | [58] | |
| >1100 | [70] | ||
| Fusarium solani | >1190 | [58] | |
| >1190 | [70] | ||
| Penicillium digitatum | >1120 | [58] | |
| >1120 | [70] | ||
| Melissa officinalis | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 313 | [158] | |
| 313 | [71] | ||
| Candida albicans | 30–313 | [59,158] | |
| 30–313 | [72][71] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 78 | [158] | |
| 78 | [71] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 30 | [ | |
| 30 | |||
| 59 | ] | ||
| [ | 72] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 30 | [59] | |
| 30 | [72] | ||
| Penicillium verrucosum | 125 | [159] | |
| 125 | [73] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. mentagrophytes | 15 | [59] | |
| 15 | [72] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 15 | [59] | |
| 15 | [72] | ||
| Trichophyton tonsurans | 15 | [59] | |
| 15 | [72] | ||
| Mentha cervina | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 2.5–5 | [60] | |
| 2.5–5 | [44] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Candida albicans | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 1.25 | [60] | |
| 1.25 | [44] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.64–1.25 | [60] | |
| 0.64–1.25 | [44] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 1.25 | [60] | |
| 1.25 | [44] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 1.25–2.5 | [60] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [44] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 1.25 | [60] | |
| 1.25 | [44] | ||
| Mentha | |||
| × | |||
| piperita | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 1450–5000 | [62,64] | |
| 1450–5000 | [74][75] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 625–10,000 | [64,158] | |
| 625–10,000 | [75][71] | ||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | 2500 | [64] | |
| 2500 | [75] | ||
| Candida albicans | 225–1125 | [63,158,160] | |
| 225–1125 | [76][71][77] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 225 | [62] | |
| 225 | [74] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 225–230 | [62] | |
| 225–230 | [74] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 313 | [158] | |
| 313 | [71] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 125 | [161] | |
| 125 | [78] | ||
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 1250 | [64] | |
| 1250 | [75] | ||
| Penicillium minioluteum | 2050–2200 | [62] | |
| 2050–2200 | [74] | ||
| Penicillium oxalicum | 1300–2050 | [62] | |
| 1300–2050 | [74] | ||
| Penicillium verrucosum | 2500 | [90] | |
| 2500 | [79] | ||
| Mentha pulegium | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.25–1.25 | [65,162] | |
| 0.25–1.25 | [80][81] | ||
| Aspergillus flavus | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.94–3.75 | [65,66,162,163] | |
| 0.94–3.75 | [80][82][81][83] | ||
| Candida bracarensis | 3.75 | [163] | |
| 3.75 | [83] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 1.25 | [ | |
| 1.25 | |||
| 162 | ] | ||
| [ | 81] | ||
| Candida krusei | 0.94–1.25 | [162,163] | |
| 0.94–1.25 | [81][83] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 0.64 | [162] | |
| 0.64 | [81] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 1.25–2.5 | [162] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [81] | ||
| Saccharomyces cervisiae | <0.3–0.94 | [66,163] | |
| <0.3–0.94 | [82][83] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 1.25–2.5 | [162] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [81] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale | 2.5 | [ | |
| 2.5 | |||
| 162 | ] | ||
| [ | 81] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Trichophyton verrucosum | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Mentha requienii | |||
| Bentham | |||
| Alternaria | spp. | >40 | [67] |
| spp. | >40 | [84] | |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | >60 | [67] | |
| >60 | [84] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.94–40 | [67,163] | |
| 0.94–40 | [84][83] | ||
| Candida bracarensis | 3.75 | [163] | |
| 3.75 | [83] | ||
| Candida krusei | 0.94 | [163] | |
| 0.94 | [83] | ||
| Fusarium spp. | >40 | [67] | |
| spp. | >40 | [84] | |
| Penicillum spp. | >60 | [67] | |
| spp. | >60 | [84] | |
| Rhodotorula spp. | 45 | [67] | |
| spp. | 45 | [84] | |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 0.94 | [163] | |
| 0.94 | [83] | ||
| Mentha spicata | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 0.64 | [ | |
| 0.64 | |||
| 162 | ] | ||
| [ | 81] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.64–313 | [158,162] | |
| 0.64–313 | [71][81] | ||
| Candida albicans | 1.25–625 | 162] | |
| 1.25–625 | |||
| [ | 51 | ,158, | |
| [ | 62][71][81] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 1.25 | [ | |
| 1.25 | |||
| 162 | ] | ||
| [ | 81] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 1.25 | [162] | |
| 1.25 | [81] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 0.32–313 | [158,162] | |
| 0.32–313 | [71][81] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.64 | [162] | |
| 0.64 | [81] | ||
| Fusarium graminearum | 2.5 | [164] | |
| 2.5 | [85] | ||
| Fusarium moniliforme | 2.5 | [164] | |
| 2.5 | [85] | ||
| Malassezia furfur | >4 | [49] | |
| >4 | [64] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.64–2 | [68,162] | |
| 0.64–2 | [86][81] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.64–3 | [162] | |
| 0.64–3 | [81] | ||
| Penicillium corylophilum | 0.625 | [165] | |
| 0.625 | [87] | ||
| Penicillium expansum | 2.5 | [ | |
| 2.5 | |||
| 164 | ] | ||
| [ | 85] | ||
| Trichophyton erinacei | 3 | [68] | |
| 3 | [86] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.64–3 | [68,162] | |
| 0.64–3 | [86][81] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale | 0.64 | [162] | |
| 0.64 | [81] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.25–512 | [49,51,162] | |
| 0.25–512 | [64][62][81] | ||
| Trichophyton terrestre | |||
| 3 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton verrucosum | 0.32 | [162] | |
| 0.32 | [81] | ||
| Trichosporon beigelii | 0.25 | [49] | |
| 0.25 | [64] | ||
| Mentha suaveolens | |||
| Ehrh. | |||
| Candida albicans | 0.34–1250 | [69,71,166] | |
| 0.34–1250 | [88][89][90] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 0.69–2.77 | [69] | |
| 0.69–2.77 | [88] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 300 | [167] | |
| 300 | [91] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 1250 | [167] | |
| 1250 | [91] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 1250 | [167] | |
| 1250 | [91] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 600–1250 | [167] | |
| 600–1250 | [91] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 5000 | [167] | |
| 5000 | [91] | ||
| Trichophyton violaceum | 600 | [167] | |
| 600 | [91] | ||
| Micromeria albanica | |||
| (Griseb. ex K. Maly) Silic | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.2 | [38] | |
| 0.2 | [50] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 0.2 | [38] | |
| 0.2 | [50] | ||
| Cladosporium cladosporioides | 0.2 | [38] | |
| 0.2 | [50] | ||
| Fusarium tricinctum | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Penicilium ochrochloron | 0.2 | [38] | |
| 0.2 | [50] | ||
| Phomopsis helianthi | 0.2 | [38] | |
| 0.2 | [50] | ||
| Trichoderma viride | 0.4 | [38] | |
| 0.4 | [50] | ||
| Moluccella spinosa | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 50 | [72] | |
| 50 | [92] | ||
| Candida albicans | 100 | [72] | |
| 100 | [92] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 100 | [72] | |
| 100 | [92] | ||
| Nepeta ciliaris | |||
| Benth. = | |||
| Nepeta leucophylla | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Alternaria solani | 3000 | [43] | |
| 3000 | [53] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.78 | [168] | |
| 0.78 | [93] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 1000 | [43] | |
| 1000 | [53] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.19 | [168] | |
| 0.19 | [93] | ||
| Helminthosporium maydis | 1500 | [43] | |
| 1500 | [53] | ||
| Nepeta clarkei | |||
| Hook. f. | |||
| Alternaria solani | 3000 | [43] | |
| 3000 | [53] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 2000 | [43] | |
| 2000 | [53] | ||
| Helminthosporium maydis | 2000 | [43] | |
| 2000 | [53] | ||
| Ocimum basilicum | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 10,000 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | >50 | [75] | |
| >50 | [45] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| >50–10,000 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| , | |||
| 75 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | |||
| 5000 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 30–625 | [ | ||
| 73 | |||
| , | |||
| 74 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida guilliermondii | |||
| 3.125–6.25 | [ | ||
| 76 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 313–1250 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| , | |||
| 169 | |||
| ] | |||
| Debaryomyces hansenii | |||
| 6.25 | [ | ||
| 76 | |||
| ] | |||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | |||
| 15 | [ | ||
| 74 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 1–15.2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| , | |||
| 74 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 3 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium chrysogenum | |||
| 10,000 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium italicum | >50 | [75] | |
| >50 | [45] | ||
| Rhizopus stolonifer | >50 | [75] | |
| >50 | [45] | ||
| Rhodotorula glutinis | 86 | [73] | |
| 86 | [94] | ||
| Trichophyton erinacei | |||
| 2.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 2.5–8.3 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| , | |||
| 74 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton terrestre | |||
| 3 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 28 | [73] | |
| 28 | [94] | ||
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe | 86 | [73] | |
| 86 | [94] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 8.3 | [ | ||
| 74 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton tonsurans | |||
| 8 | [ | ||
| 74 | |||
| ] | |||
| Yarrowia lypolytica | |||
| 57 | [ | ||
| 73 | |||
| ] | |||
| Ocimum × africanum | |||
| Lour. = | |||
| Ocimum | |||
| × | |||
| citriodorum | |||
| Candida guilliermondii | |||
| 3.125 | [ | ||
| 76 | |||
| ] | |||
| Debaryomyces hansenii | |||
| 1.56 | [ | ||
| 76 | |||
| ] | |||
| Ocimum campechianum | |||
| Mill. = | |||
| Ocimum micranthum | |||
| Willd. | |||
| Candida albicans | 69 | [73] | |
| 69 | [94] | ||
| Rhodotorula glutinis | 139 | [73] | |
| 139 | [94] | ||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 69 | [73] | |
| 69 | [94] | ||
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe | 104 | [73] | |
| 104 | [94] | ||
| Yarrowia lypolytica | 69 | [73] | |
| 69 | [94] | ||
| Ocimum forskolei | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 35.3–8600 | [ | ||
| 77 | |||
| , | |||
| 170 | |||
| ] | |||
| Ocimum gratissimum | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
| >1000 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 350–1500 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| , | |||
| 171 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida krusei | |||
| 750 | [ | ||
| 171 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida parapsilosis | |||
| 380 | [ | ||
| 171 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 1500 | [ | ||
| 171 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 250–300 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| , | |||
| 79 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium oxysporum f. | |||
| sp. | |||
| cubense | 62.5 | [80] | |
| 62.5 | [95] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum f. | |||
| sp. | |||
| lycopersici | 31.25 | [80] | |
| 31.25 | [95] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum f. | |||
| sp. | |||
| tracheiphilum | 62.5 | [ | |
| 62.5 | |||
| 80 | ] | ||
| [ | 95] | ||
| Fusarium solani | 62.5 | [80] | |
| 62.5 | [95] | ||
| Macrophomina phaseolina | 62.5–125 | [80] | |
| 62.5–125 | [95] | ||
| Malassezia pachydermatis | |||
| 300 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 200–500 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| , | |||
| 172 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 150–250 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| , | |||
| 172 | |||
| ] | |||
| Rhizoctonia solani | 31.25 | [80] | |
| 31.25 | [95] | ||
| Scopulariopsis brevicaulis | |||
| 400 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton interdigitale | |||
| 250 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 200–250 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| , | |||
| 172 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 150–250 | [ | ||
| 78 | |||
| , | |||
| 172 | |||
| ] | |||
| Ocimum tenuiflorum | |||
| L. = | |||
| Ocimum sanctum | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 300 | [ | ||
| 83 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 0.1–300 | [ | ||
| 81 | |||
| , | |||
| 82 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida glabrata | |||
| 0.15–300 | [ | ||
| 81 | |||
| , | |||
| 82 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida krusei | |||
| 0.35–450 | [ | ||
| 81 | |||
| , | |||
| 82 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida parapsilosis | |||
| 0.25–500 | [ | ||
| 81 | |||
| , | |||
| 82 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 0.1–300 | [ | ||
| 81 | |||
| , | |||
| 82 | |||
| ] | |||
| Origanum compactum | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Alternaria alternata | 300 | [84] | |
| 300 | [96] | ||
| Bipolaris oryzae | 300 | [84] | |
| 300 | [96] | ||
| Fusarium equiseti | 300 | [84] | |
| 300 | [96] | ||
| Fusarium graminearum | 300 | [84] | |
| 300 | [96] | ||
| Fusarium verticillioides | 300 | [84] | |
| 300 | [96] | ||
| Origanum majorana | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 450–650 | [ | ||
| 62 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 625 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Botrytis cinerea | |||
| 5000 | [ | ||
| 87 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 625 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 313 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium delphinoides | |||
| 1800–14,400 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium incarnatum-equiseti | |||
| 450–3600 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium napiforme | |||
| 3600–14,400 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium oxysporum | |||
| 900–3600 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium solani | |||
| 900–3600 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium verticillioides | |||
| 14,400 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 0.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium expansum | |||
| 10,000 | [ | ||
| 87 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium minioluteum | |||
| 400–500 | [ | ||
| 62 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium oxalicum | |||
| 350–400 | [ | ||
| 62 | |||
| ] | |||
| Sporothrix brasiliensis | |||
| ≤2250–9000 | [ | ||
| 86 | |||
| ] | |||
| Sporothrix schenckii | |||
| ≤2250–9000 | [ | ||
| 86 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton erinacei | |||
| 1 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 1.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton terrestre | |||
| 2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Origanum vulgare | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 0.64–2500 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| , | |||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
| 0.32–0.64 | [ | ||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 0.32–623 | [ | ||
| 62 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| , | |||
| 91 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | |||
| 470 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | |||
| 2500 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 0.32–700 | [ | ||
| 74 | |||
| , | |||
| 88 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| , | |||
| 91 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida glabrata | |||
| 350 | [ | ||
| 88 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida guillermondii | |||
| 0.64–1.25 | [ | ||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida krusei | |||
| 0.64–700 | [ | ||
| 88 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida parapsilosis | |||
| 0.64–170 | [ | ||
| 88 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 0.32–700 | [ | ||
| 88 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cladosporium | |||
| sp. | 0.05–0.3 | [ | |
| 173 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 0.16–78 | [ | ||
| 89 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | |||
| 0.32–2 | [ | ||
| 74 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium | |||
| sp. | 0.1–0.5 | [ | |
| 173 | |||
| ] | |||
| Malassezia furfur | |||
| 1–780 | [ | ||
| 49 | |||
| , | |||
| 174 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 0.025–2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| , | |||
| 74 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 0.025–1.25 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium | |||
| sp. | 0.1–0.5 | [ | |
| 173 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium chrysogenum | |||
| 625 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium corylophilum | |||
| 0.625 | [ | ||
| 165 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium funiculosum | |||
| 610 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium ochrochloron | |||
| 710 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium verrucosum | |||
| 1.1719 | [ | ||
| 90 | |||
| , | |||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 0.32–1.25 | [ | ||
| 74 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 0.16–1.25 | [ | ||
| 49 | |||
| , | |||
| 74 | |||
| , | |||
| 89 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton tonsurans | |||
| 1 | [ | ||
| 74 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichosporon beigelii | |||
| 0.25 | [ | ||
| 49 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton erinacei | |||
| 0.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 0.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton terrestre | |||
| 0.25 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Pogostemon cablin | |||
| (Blanco) Benth. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| >1500 | [ | ||
| 92 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 156 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus oryzae | |||
| >1500 | [ | ||
| 92 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 32–625 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| , | |||
| 175 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida krusei | |||
| 64–257 | [ | ||
| 175 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 32–257 | [ | ||
| 175 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 20 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Pogostemon heyneanus | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 6000 | [ | ||
| 176 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida glabrata | |||
| 6000 | [ | ||
| 176 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 10,000 | [ | ||
| 176 | |||
| ] | |||
| Premna microphylla | |||
| Turcz. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| >500 | [ | ||
| 94 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| >500 | [ | ||
| 94 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium oxysporum | |||
| >500 | [ | ||
| 94 | |||
| ] | |||
| Rosmarinus officinalis | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 330 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | |||
| 590 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 380–10,000 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| , | |||
| 98 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Botrytis cinerea | |||
| 2500 | [ | ||
| 87 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 30.2–1000 | [ | ||
| 51 | |||
| , | |||
| 91 | |||
| , | |||
| 96 | |||
| , | |||
| 98 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 313 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | |||
| 30 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 2.5–30.2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| , | |||
| 96 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 2.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium expansum | |||
| 5000 | [ | ||
| 87 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium ochrochloron | |||
| 470 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium funiculosum | |||
| 570 | [ | ||
| 91 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton erinacei | |||
| 1.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 5–15.3 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| , | |||
| 96 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 15–256 | [ | ||
| 51 | |||
| , | |||
| 96 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton terrestre | |||
| 5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton tonsurans | |||
| 15.2 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| ] | |||
| Salvia fruticosa | |||
| Miller | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 512 | [ | ||
| 51 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium oxysporum | |||
| f. sp. | |||
| dianthi | >2000 | [99] | |
| >2000 | [97] | ||
| Fusarium proliferatum | >2000 | [99] | |
| >2000 | [97] | ||
| Fusarium solani | |||
| f. sp. | |||
| cucurbitae | >2000 | [99] | |
| >2000 | [97] | ||
| Malassezia furfur | >4 | [99] | |
| >4 | [97] | ||
| Rhizoctonia solani | >2000 | [99] | |
| >2000 | [97] | ||
| Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | >2000 | [99] | |
| >2000 | [97] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 2–256 | [ | ||
| 49 | |||
| , | |||
| 99 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichosporon beigelii | |||
| 4 | [ | ||
| 49 | |||
| ] | |||
| Salvia mirzayanii | |||
| Rech. f. and Esfand | |||
| Candida albicans | 0.5–2 | [100] | |
| 0.5–2 | [98] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1 | [100] | |
| 1 | [98] | ||
| Candida dubliniensis | 0.06–0.5 | [100] | |
| 0.06–0.5 | [98] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 0.06–1 | [100] | |
| 0.06–1 | [98] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 0.25–1 | [100] | |
| 0.25–1 | [98] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 0.25–2 | [100] | |
| 0.25–2 | [98] | ||
| Trichosporon sp. | 1 | ||
| sp. | |||
| [ | 100 | ] | |
| 1 | [98] | ||
| Salvia officinalis | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 5–10 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
| 2.5–5 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 5–1250 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 2.5–2780 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| , | |||
| 101 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| , | |||
| 177 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida guillermondii | |||
| 1.25–2.5 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida krusei | |||
| 2.5–5 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida parapsilosis | |||
| 5 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 5 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 0.64–625 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | |||
| 0.64–100 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| , | |||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 1.25–100.2 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| , | |||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 1.25–2.5 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 1.25–60 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| , | |||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. interdigitale | |||
| 1.25 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 0.64–60 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| , | |||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton tonsurans | |||
| 60 | [ | ||
| 96 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton verrucosum | |||
| 1.25–2.5 | [ | ||
| 101 | |||
| ] | |||
| Salvia sclarea | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 1250 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 1250 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 313 | [ | ||
| 158 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium delphinoides | |||
| 1800–3600 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium incarnatum-equiseti | |||
| 1800–3600 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium napiforme | |||
| 1800–3600 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium oxysporum | |||
| 1800–3600 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium solani | |||
| 3600–7200 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium verticillioides | |||
| 1800 | [ | ||
| 85 | |||
| ] | |||
| Satureja hortensis | |||
| L. | |||
| Alternaria alternata | |||
| 62.5 | [ | ||
| 103 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 31.25–500 | [ | ||
| 103 | |||
| , | |||
| 104 | |||
| , | |||
| 117 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 471 | [117] | |
| 471 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 423 | [117] | |
| 423 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | 373 | [117] | |
| 373 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus terreus | 389 | [117] | |
| 389 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus variecolor | 125 | [103] | |
| 125 | [100] | ||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 200–400 | [ | ||
| 103 | |||
| , | |||
| 178 | |||
| ] | |||
| Fusarium culmorum | 125 | [103] | |
| 125 | [100] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 250 | [103] | |
| 250 | [100] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 62.5 | [103] | |
| 62.5 | [100] | ||
| Moniliania fructicola | 31.25 | [103] | |
| 31.25 | [100] | ||
| Penicillium spp. | 125 | [103] | |
| spp. | 125 | [100] | |
| Rhizoctonia solani | 125 | [103] | |
| 125 | [100] | ||
| Rhizopus spp. | 250 | [103] | |
| spp. | 250 | [100] | |
| Sclerotinia minor | 250 | [103] | |
| 250 | [100] | ||
| Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | 125 | [103] | |
| 125 | [100] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 62.5 | [103] | |
| 62.5 | [100] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 31.25 | [103] | |
| 31.25 | [100] | ||
| Satureja montana | |||
| L. | |||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 0.5 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton erinacei | |||
| 2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 2 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton terrestre | |||
| 3 | [ | ||
| 68 | |||
| ] | |||
| Satureja thymbra | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 25 | [ | ||
| 105 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
| 1.25–25 | [ | ||
| 105 | |||
| , | |||
| 179 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 2.5–25 | [ | ||
| 105 | |||
| , | |||
| 179 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | |||
| 2.5–25 | [ | ||
| 105 | |||
| , | |||
| 179 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus versicolor | |||
| 1.25 | [ | ||
| 179 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 25–128 | [ | ||
| 51 | |||
| , | |||
| 105 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium funiculosum | |||
| 2.5–25 | [ | ||
| 105 | |||
| , | |||
| 179 | |||
| ] | |||
| Penicillium ochrochloron | |||
| 1–1.25 | [ | ||
| 105 | |||
| , | |||
| 179 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichoderma viride | |||
| 1.25–25 | [ | ||
| 105 | |||
| , | |||
| 179 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 128 | [ | ||
| 51 | |||
| ] | |||
| Stachys cretica | |||
| L. | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 625 | [ | ||
| 106 | |||
| ] | |||
| Stachys officinalis | |||
| (L.) Trevis | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 2500 | [ | ||
| 107 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 5000 | [ | ||
| 107 | |||
| ] | |||
| Stachys pubescens | |||
| Ten. | |||
| Alternaria alternata | 1 | [108] | |
| 1 | [101] | ||
| Aspergillus flavus | 0–5 | [108] | |
| 0–5 | [101] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 1 | [108] | |
| 1 | [101] | ||
| Teucrium sauvagei | |||
| Le Houerou | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | >1000 | [109] | |
| >1000 | [102] | ||
| Candida albicans | >1000 | [109] | |
| >1000 | [102] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | >1000 | [109] | |
| >1000 | [102] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 850 | [109] | |
| 850 | [102] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 800 | [109] | |
| 800 | [102] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 900 | [109] | |
| 900 | [102] | ||
| Scopulariopsis brevicaulis | >1000 | [109] | |
| >1000 | [102] | ||
| Scytalidium dimidiatum | >1000 | [ | |
| >1000 | |||
| 109 | ] | ||
| [ | 102] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| var. | |||
| interdigitale | 950 | [109] | |
| 950 | [102] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| var. | |||
| mentagrophytes | 900 | [109] | |
| 900 | [102] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 800 | [109] | |
| 800 | [102] | ||
| Trichophyton soudanense | 800 | [109] | |
| 800 | [102] | ||
| Teucrium yemense | |||
| Deflers. | |||
| Aspergillus niger | 313 | [77] | |
| 313 | [103] | ||
| Botrytis cinerea | 313 | [77] | |
| 313 | [103] | ||
| Candida albicans | 1250 | [77] | |
| 1250 | [103] | ||
| Thymbra capitata | |||
| (L.) Cav. = | |||
| Thymus capitatus | |||
| (L.) Hoffmanns. and Link = | |||
| Coridothymus capitatus | |||
| (L.) Rchb.f. Solms | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 0.32 | [111] | |
| 0.32 | [104] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 0.16–0.32 | [111] | |
| 0.16–0.32 | [104] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.1–0.16 | [111,180] | |
| 0.1–0.16 | [104][105] | ||
| Aspergillus oryzae | 0.2 | [180] | |
| 0.2 | [105] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.16–128 | [51,110,111,112] | |
| 0.16–128 | [62][106][104][107] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 0.32 | [111,112] | |
| 0.32 | [104][107] | ||
| Candida guilliermondii | 0.16–0.32 | [111,112] | |
| 0.16–0.32 | [104][107] | ||
| Candida krusei | 0.32 | [111] | |
| 0.32 | [104] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 0.32 | [111,112] | |
| 0.32 | [104][107] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 0.32 | [111, | |
| 0.32 | |||
| 112 | ] | ||
| [ | 104][107] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.08 | [ | |
| 0.08 | |||
| 111 | ] | ||
| [ | 104] | ||
| Fusarium solani | 0.2 | [180] | |
| 0.2 | [105] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.08 | [111] | |
| 0.08 | [104] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.08 | [111] | |
| 0.08 | [104] | ||
| Penicillium digitatum | |||
| 0.5 | [ | ||
| 180 | |||
| ] | |||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.08 | [111] | |
| 0.08 | [104] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.16–64 | [51,111] | |
| 0.16–64 | [62][104] | ||
| Thymbra spicata | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 0.3 | [ | |
| 0.3 | |||
| 179 | ] | ||
| [ | 108 | ] | |
| Aspergillus niger | 0.6 | [179] | |
| 0.6 | [108] | ||
| Aspergillus versicolor | 0.3 | [179] | |
| 0.3 | [108] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 0.6 | [179] | |
| 0.6 | [108] | ||
| Candida albicans | 1.12–3750 | [51,113,114] | |
| 1.12–3750 | [62][109][110] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1.12 | [114] | |
| 1.12 | [110] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 0.6–1.12 | [114] | |
| 0.6–1.12 | [110] | ||
| Penicillium funiculosum | 0.3 | [179] | |
| 0.3 | [108] | ||
| Penicillium ochrochloron | 0.3 | [179] | |
| 0.3 | [108] | ||
| Trichoderma viride | 0.3 | [179] | |
| 0.3 | [108] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 64 | [ | |
| 64 | |||
| 51 | ] | ||
| [ | 62] | ||
| Thymus bovei | |||
| Benth. | |||
| Candida albicans | 250 | [ | |
| 250 | |||
| 115 | ] | ||
| [ | 111 | ] | |
| Thymus daenensis | |||
| Celak. | |||
| Alternaria alternata | >8 | [ | |
| >8 | |||
| 108 | ] | ||
| [ | 101 | ] | |
| Aspergillus flavus | 1 | [108] | |
| 1 | [101] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 4 | [108] | |
| 4 | [101] | ||
| Thymus kotschyanus | |||
| Boiss. and Hohen. | |||
| Alternaria alternata | 1 | [108] | |
| 1 | [101] | ||
| Aspergillus flavus | 0.5 | [108] | |
| 0.5 | [101] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 0–5 | [108] | |
| 0–5 | [101] | ||
| Thymus mastichina | |||
| (L.) L. | |||
| Candida albicans | 1.25–2.5 | [116] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [112] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 1.25–1.5 | [116] | |
| 1.25–1.5 | [112] | ||
| Candida guilliermondii | 1.25 | [116] | |
| 1.25 | [112] | ||
| Candida krusei | 1.25–2.5 | [116] | |
| 1.25–2.5 | [112] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 2.5–5 | [116] | |
| 2.5–5 | [112] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 2.5–10 | [116] | |
| 2.5–10 | [112] | ||
| Thymus migricus | |||
| Klokov et Des.-Shost. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 452 | [117] | |
| 452 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 460 | [117] | |
| 460 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 430 | [117] | |
| 430 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | 581 | [117] | |
| 581 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus terreus | 447 | [117] | |
| 447 | [99] | ||
| Thymus pulegioides | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 0.32 | [119] | |
| 0.32 | [113] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 0.16 | [119] | |
| 0.16 | [113] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.32 | [119] | |
| 0.32 | [113] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.32–0.64 | [119] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [113] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 0.32–0.64 | [119] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [113] | ||
| Candida guilliermondii | 0.32 | [119] | |
| 0.32 | [113] | ||
| Candida krusei | 0.32–0.64 | [119] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [113] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 0.64 | [ | |
| 0.64 | |||
| 119 | ] | ||
| [ | 113] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 0.32–0.64 | [119] | |
| 0.32–0.64 | [113] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.16 | [119] | |
| 0.16 | [113] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.16 | [119] | |
| 0.16 | [113] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.16 | [119] | |
| 0.16 | [113] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.16 | [119] | |
| 0.16 | [113] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.32 | [119] | |
| 0.32 | [113] | ||
| Thymus schimperi | |||
| Ronninger | |||
| Aspergillus minutus | 0.512–2 | [120] | |
| 0.512–2 | [114] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 0.16 | [181] | |
| 0.16 | [115] | ||
| Aspergillus tubingensis | 1–4 | [120] | |
| 1–4 | [114] | ||
| Beauveria bassiana | 0.128–1 | [120] | |
| 0.128–1 | [114] | ||
| Candida albicans | 0.16 | [181] | |
| 0.16 | [115] | ||
| Microsporum spp. | 0.08 | [181] | |
| spp. | 0.08 | [115] | |
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.128–1 | [120] | |
| 0.128–1 | [114] | ||
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 0.512–2 | [120] | |
| 0.512–2 | [114] | ||
| Rhodotorula spp. | 0.08 | ||
| spp. | |||
| [ | 181 | ] | |
| 0.08 | [115] | ||
| Tricophyton spp. | 0.08–0.31 | [181] | |
| spp. | 0.08–0.31 | [115] | |
| Verticillium sp. | 0.512–2 | [120] | |
| sp. | 0.512–2 | [114] | |
| Thymus serpyllum | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus carbonarius | 1.25 | [ | |
| 1.25 | |||
| 182 | ] | ||
| [ | 116 | ] | |
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 0.625 | [182] | |
| 0.625 | [116] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 2.5 | [182] | |
| 2.5 | [116] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.025 | [68] | |
| 0.025 | [86] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.25 | [68] | |
| 0.25 | [86] | ||
| Trichophyton erinacei | 0.1 | [68] | |
| 0.1 | [86] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.2 | [68] | |
| 0.2 | [86] | ||
| Trichophyton terrestre | 0.1 | [68] | |
| 0.1 | [86] | ||
| Thymus striatus | |||
| Vahl. | |||
| Alternaria alternata | 1 | [121] | |
| 1 | [117] | ||
| Aspergillus flavus | 1.5 | [121] | |
| 1.5 | [117] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 1 | [121] | |
| 1 | [117] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 1 | [121] | |
| 1 | [117] | ||
| Aspergillus terreus | 1 | [121] | |
| 1 | [117] | ||
| Aspergillus versicolor | 1 | [121] | |
| 1 | [117] | ||
| Cladosporium cladosporioides | 0.5 | [121] | |
| 0.5 | [117] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 1 | [121] | |
| 1 | [117] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 1.5 | [121] | |
| 1.5 | [117] | ||
| Penicillium funiculosum | 2 | [121] | |
| 2 | [117] | ||
| Penicillium ochrochloron | 2 | [121] | |
| 2 | [117] | ||
| Phomopsis helianthi | 0.5 | [121] | |
| 0.5 | [117] | ||
| Trichoderma viride | 2 | [121] | |
| 2 | [117] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 1 | [ | |
| 1 | |||
| 121 | ] | ||
| [ | 117] | ||
| Thymus vulgaris | |||
| L. | |||
| Absidia | spp. | 7 ± 4 | |
| spp. | |||
| [ | 122 | ] | |
| 7 ± 4 | [118] | ||
| Alternaria spp. | 9.4 ± 4.5 | [122] | |
| spp. | 9.4 ± 4.5 | [118] | |
| Alternaria alternata | 4.7–500 | [122, | |
| 4.7–500 | |||
| 183 | ] | ||
| [ | 118][119] | ||
| Aspergillus spp. | 3.2 | ||
| spp. | |||
| [ | 122 | ] | |
| 3.2 | [118] | ||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 9.35–1500 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| , | |||
| 104 | |||
| , | |||
| 122 | |||
| , | |||
| 125 | |||
| , | |||
| 184 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
| 144–1000 | [ | ||
| 124 | |||
| , | |||
| 184 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 9.35–1250 | [ | ||
| 64 | |||
| , | |||
| 122 | |||
| , | |||
| 158 | |||
| , | |||
| 184 | |||
| ] | |||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 2.5–750 | [164,184] | |
| 2.5–750 | [85][120] | ||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | 1250 | [64] | |
| 1250 | [75] | ||
| Aspergillus sulphureus | 10.88 ± 3.1 | [122] | |
| 10.88 ± 3.1 | [118] | ||
| Aspergillus versicolor | 9.6 ± 9.25 | [122] | |
| 9.6 ± 9.25 | [118] | ||
| Botrytis cinerea | |||
| 312 | [ | ||
| 87 | |||
| ] | |||
| Candida albicans | 0.16–313 | [73,74,116,158] | |
| 0.16–313 | [94][121][112][71] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 0.16–0.32 | [ | |
| 0.16–0.32 | |||
| 116 | ] | ||
| [ | 112] | ||
| Candida krusei | 0.08–0.16 | [116] | |
| 0.08–0.16 | [112] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 0.16 | [116] | |
| 0.16 | [112] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 0.16–0.32 | [116] | |
| 0.16–0.32 | [112] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 0.16–0.32 | [116] | |
| 0.16–0.32 | [112] | ||
| Chaetomium globosum | 1.6 | [122] | |
| 1.6 | [118] | ||
| Cladosporium spp. | 12.8 | [122] | |
| spp. | 12.8 | [118] | |
| Cladosporium sphaerospermum | 19.6 | [122] | |
| 19.6 | [118] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | 78 | [158] | |
| 78 | [71] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 4 | [74] | |
| 4 | [121] | ||
| Fusarium spp. | 62.5 | [185] | |
| spp. | 62.5 | [122] | |
| Fusarium delphinoides | 900–1800 | [85] | |
| 900–1800 | [123] | ||
| Fusarium incarnatum-equiseti | 450–3600 | [85] | |
| 450–3600 | [123] | ||
| Fusarium napiforme | 900 | [85] | |
| 900 | [123] | ||
| Fusarium oxysporum | 5–900 | [85,126] | |
| 5–900 | [123][124] | ||
| Fusarium solani | 1800–3600 | [85] | |
| 1800–3600 | [123] | ||
| Fusarium verticillioides | 900 | [85] | |
| 900 | [123] | ||
| Malassezia furfur | 920 | [174] | |
| 920 | [125] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 2.2 | [74] | |
| 2.2 | [121] | ||
| Mortierella spp. | 250 | [185] | |
| spp. | 250 | [122] | |
| Mucor spp. | 50.2 ± 8.4 | [122] | |
| spp. | 50.2 ± 8.4 | [118] | |
| Penicilium spp. | 18.95–500 | [122,185] | |
| spp. | 18.95–500 | [118][122] | |
| Penicilium brevicompactum | 19.6 | [122] | |
| 19.6 | [118] | ||
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 312.5–1750 | [64,184] | |
| 312.5–1750 | [75][120] | ||
| Penicilium chrysogenum | 19.6 | [122] | |
| 19.6 | [118] | ||
| Penicillium citrinum | 1250 | [184] | |
| 1250 | [120] | ||
| Penicillium expansum | 625 | [87] | |
| 625 | [126] | ||
| Penicillium griseofulvum | 19.6 | [122] | |
| 19.6 | [118] | ||
| Rhizopus spp. | 12.6 | [122] | |
| spp. | 12.6 | [118] | |
| Rhodotorula glutinis | 72 | [ | |
| 72 | |||
| 73 | ] | ||
| [ | 94] | ||
| Rhizopus oryzae | 256–512 | [123] | |
| 256–512 | [127] | ||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 72 | [73] | |
| 72 | [94] | ||
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe | 36 | [73] | |
| 36 | [94] | ||
| Stachybotrys chartarum | 6.2 | [122] | |
| 6.2 | [118] | ||
| Trichoderma spp. | 16.8 | [122] | |
| spp. | 16.8 | [118] | |
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 2.2 | [74] | |
| 2.2 | [121] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 2–72 | [74,124] | |
| 2–72 | [121][128] | ||
| Trichophyton tonsurans | 2.2 | [74] | |
| 2.2 | [121] | ||
| Ulocladium spp. | 5.45 ± 1.5 | ||
| spp. | |||
| [ | 122 | ] | |
| 5.45 ± 1.5 | [118] | ||
| Yarrowia lypolytica | 36 | [73] | |
| 36 | [94] | ||
| Thymus zygis | |||
| L. | |||
| Candida albicans | 0.16–0.32 | ||
| 0.16–0.32 | |||
| [ | 116 | ] | |
| [ | 112] | ||
| Candida glabrata | 0.32 | [116] | |
| 0.32 | [112] | ||
| Candida krusei | 0.16–0.32 | [116] | |
| 0.16–0.32 | [112] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | 0.16 | [116] | |
| 0.16 | [112] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 0.32 | [116] | |
| 0.32 | [112] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | 0.16–0.32 | [116] | |
| 0.16–0.32 | [112] | ||
| Penicillium corylophilum | 0.3125–0.625 | [165] | |
| 0.3125–0.625 | [87] | ||
| Vitex agnus-castus | |||
| L. | |||
| Candida albicans | 0.53–512 | [51,129] | |
| 0.53–512 | [62][129] | ||
| Candida dubliniensis | |||
| 0.27 | [129] | ||
| Candida famata | |||
| 2.13 | [129] | ||
| Candida glabrata | |||
| 0.27 | [129] | ||
| Candida krusei | |||
| 0.27 | [129] | ||
| Candida lusitaniae | |||
| 2.13 | [129] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | |||
| 1.06 | [129] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 0.13 | [129] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | 0.64–2.5 | [128] | |
| 0.64–2.5 | [130] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.64–5 | [128] | |
| 0.64–5 | [130] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 1.25–10 | [128] | |
| 1.25–10 | [130] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 1.25–10 | [128] | |
| 1.25–10 | [130] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.64–512 | [51,128] | |
| 0.64–512 | [62][130] | ||
| Zataria multiflora | |||
| Boiss. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 358 | [117] | |
| 358 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 358 | [117] | |
| 358 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 341 | [ | |
| 341 | |||
| 117 | ] | ||
| [ | 99] | ||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | 367 | [117] | |
| 367 | [99] | ||
| Aspergillus terreus | 447 | [117] | |
| 447 | [99] | ||
| Microsporum canis | 0.125–0.25 | [130] | |
| 0.125–0.25 | [131] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | 0.03–0.06 | [130] | |
| 0.03–0.06 | [131] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | 0.03 | [130] | |
| 0.03 | [131] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | 0.03–0.06 | [130] | |
| 0.03–0.06 | [131] | ||
| Trichophyton schoenleinii | 0.125–0.6 | [130] | |
| 0.125–0.6 | [131] | ||
| Ziziphora clinopodioides | |||
| Lam. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | 48.82 | [184,186] | |
| 48.82 | [120][132] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | 1750 | [184] | |
| 1750 | [120] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | 3000 | [184] | |
| 3000 | [120] | ||
| Aspergillus ochraceus | 1500 | [184] | |
| 1500 | [120] | ||
| Aspergillus parasiticus | 48.82 | [186] | |
| 48.82 | [132] | ||
| Penicillium chrysogenum | 3000 | [184] | |
| 3000 | [120] | ||
| Penicillium citrinum | 1750 | [184] | |
| 1750 | [120] | ||
| Ziziphora tenuior | |||
| L. | |||
| Aspergillus flavus | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | |||
| 0.64 | [133] | ||
| Aspergillus niger | |||
| 0.64 | [133] | ||
| Candida albicans | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Candida guillermondii | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Candida krusei | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Candida tropicalis | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Cryptococcus neoformans | |||
| 0.16 | [133] | ||
| Epidermophyton floccosum | |||
| 0.64 | [133] | ||
| Microsporum canis | |||
| 0.64–1.25 | [133] | ||
| Microsporum gypseum | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| 1.25 | [133] | ||
| Trichophyton mentagrophytes | |||
| var. | |||
| interdigitale | |||
| 1.254 | [133] | ||
| Trichophyton rubrum | |||
| 0.64 | [133] | ||
| Trichophyton verrucosum | |||
| 0.64 | [133] |
References
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden killers: Human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4.
- White, T.C.; Findley, K.; Dawson, T.L., Jr.; Scheynius, A.; Boekhout, T.; Cuomo, C.A.; Xu, J.; Saunders, C.W. Fungi on the skin: Dermatophytes and Malassezia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4.
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and multi-national prevalence of fungal diseases—estimate precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57.
- Park, B.J.; Wannemuehler, K.A.; Marston, B.J.; Govender, N.; Pappas, P.G.; Chiller, T.M. Estimation of the current global burden of cryptococcal meningitis among persons living with HIV/AIDS. AIDS 2009, 23, 525–530.
- Drgona, L.; Khachatryan, A.; Stephens, J.; Charbonneau, C.; Kantecki, M.; Haider, S.; Barnes, R. Clinical and economic burden of invasive fungal diseases in Europe: Focus on pre-emptive and empirical treatment of Aspergillus and Candida species. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 7–21.
- Murray, P.R.; Rosenthal, K.S.; Pfaller, M.A. Section 6. Mycology. In Medical Microbiology, 7th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 605–711.
- Reddy, K.R. Fungal infections (Mycoses): Dermatophytoses (Tinea, Ringworm). J. Gandaki Med. Coll. Nepal 2017, 10.
- Lortholary, O.; Desnos-Ollivier, M.; Sitbon, K.; Fontanet, A.; Bretagne, S.; Dromer, F. Recent exposure to caspofungin or fluconazole influences the epidemiology of candidemia: A prospective multicenter study involving 2,441 patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 532–538.
- Alexander, B.D.; Johnson, M.D.; Pfeiffer, C.D.; Jiménez-Ortigosa, C.; Catania, J.; Booker, R.; Castanheira, M.; Messer, S.A.; Perlin, D.S.; Pfaller, M.A. Increasing echinocandin resistance in Candida glabrata: Clinical failure correlates with presence of FKS mutations and elevated minimum inhibitory concentrations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1724–1732.
- Arendrup, M.C.; Perlin, D.S. Echinocandin resistance: An emerging clinical problem? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 27, 484–492.
- Van der Linden, J.W.; Arendrup, M.C.; Warris, A.; Lagrou, K.; Pelloux, H.; Hauser, P.M.; Chryssanthou, E.; Mellado, E.; Kidd, S.E.; Tortorano, A.M.; et al. Prospective multicenter international surveillance of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1041–1044.
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Rare and emerging opportunistic fungal pathogens: Concern for resistance beyond Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 4419–4431.
- Perlin, D.S.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. The global problem of antifungal resistance: Prevalence, mechanisms, and management. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e383–e392.
- Krcmery, V., Jr.; Spanik, S.; Kunova, A.; Trupl, J. Breakthrough fungemia appearing during empiric therapy with amphotericin B. Chemotherapy 1997, 43, 367–370.
- Hull, C.M.; Bader, O.; Parker, J.E.; Weig, M.; Gross, U.; Warrilow, A.G.; Kelly, D.E.; Kelly, S.L. Two clinical isolates of Candida glabrata exhibiting reduced sensitivity to amphotericin B both harbor mutations in ERG2. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6417–6421.
- Woods, R.A.; Bard, M.; Jackson, I.E.; Drutz, D.J. Resistance to polyene antibiotics and correlated sterol changes in two isolates of Candida tropicalis from a patient with an amphotericin B-resistant funguria. J. Infect. Dis. 1974, 129, 53–58.
- Satoh, K.; Makimura, K.; Hasumi, Y.; Nishiyama, Y.; Uchida, K.; Yamaguchi, H. Candida auris sp. nov, a novel ascomycetous yeast isolated from the external ear canal of an inpatient in a Japanese hospital. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 53, 41–44.
- Tracking Candida Auris. Case Count Updated as of July 31; 2019; CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/candida-auris/tracking-c-auris.html (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Lockhart, S.R.; Etienne, K.A.; Vallabhaneni, S.; Farooqi, J.; Chowdhary, A.; Govender, N.P.; Colombo, A.L.; Calvo, B.; Cuomo, C.A.; Desjardins, C.A.; et al. Simultaneous emergence of multidrug-resistant Candida auris on 3 continents confirmed by whole-genome sequencing and epidemiological analyses. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 134–140.
- Friedman, D.Z.P.; Schwartz, I.S. Emerging fungal infections: New patients, new patterns, and new pathogens. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 67.
- Hata, D.J.; Humphries, R.; Lockhart, S.R.; College of American Pathologists Microbiology Committee. Candida auris: An emerging yeast pathogen posing distinct challenges for laboratory diagnostics, treatment, and infection prevention. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019.
- Ramasubramania Raja, R. Medicinally potential plants of Labiatae (Lamiaceae) family: An overview. Res. J. Med. Plant. 2012, 6, 203–213.
- Carović-Stanko, K.; Petek, M.; Grdiša, M.; Pintar, J.; Bedeković, D.; Herak Ćustić, M.; Satovic, Z. Medicinal plants of the family Lamiaceae as functional foods—A review. Czech J. Food Sci. 2016, 34, 377–390.
- Radulović, N.S.; Blagojević, P.D.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.Z.; Stojanowić, N.M. Antimicrobial plant metabolites: Structural diversity and mechanism of action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 932–952.
- Vainstein, A.; Lewinsohn, E.; Pichersky, E.; Weiss, D. Floral fragrance. New inroads into an old commodity. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1383–1389.
- De Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential oils, Part III: Chemical composition. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 161–619.
- Piątkowska, E.; Rusiecka-Ziółkowska, J. Influence of essential oils on infectious agents. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 25, 989–995.
- Dhifi, W.; Bellili, S.; Jazi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Mnif, W. Essential oils’ chemical characterization and investigation of some biological activities: A critical review. Medicines 2016, 3, 25.
- Yang, D.; Michel, L.; Chaumont, J.P.; Millet-Clerc, J. Use of caryophyllene oxide as an antifungal agent in an in vitro experimental model of onychomycosis. Mycopathologia 1999, 148, 79–82.
- Dahham, S.S.; Tabana, Y.M.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ahamed, M.B.; Ezzat, M.O.; Majid, A.S.; Majid, A.M. The anticancer, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of the sesquiterpene β-caryophyllene from the essential oil of Aquilaria crassna. Molecules 2015, 20, 11808–11829.
- Selestino Neta, M.C.; Vittorazzi, C.; Guimarães, A.C.; Martins, J.D.; Fronza, M.; Endringer, D.C.; Scherer, R. Effects of β-caryophyllene and Murraya paniculata essential oil in the murine hepatoma cells and in the bacteria and fungi 24-h time-kill curve studies. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 190–197.
- Bona, E.; Cantamessa, S.; Pavan, M.; Novello, G.; Massa, N.; Rocchetti, A.; Berta, G.; Gamalero, E. Sensitivity of Candida albicans to essential oils: Are they an alternative to antifungal agents? J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1530–1545.
- Kordali, S.; Cakir, A.; Ozer, H.; Cakmakci, R.; Kesdek, M.; Mete, E. Antifungal, phytotoxic and insecticidal properties of essential oil isolated from Turkish Origanum acutidens and its three components, carvacrol, thymol and p-cymene. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8788–8795.
- Marei, G.I.K.; Abdel Rasoul, M.A.; Abdelgaleil, S.A.M. Comparative antifungal activities and biochemical effects of monoterpenes on plant pathogenic fungi. Pesticide Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 103, 56–61.
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Sharifzadeh, A.; Shokri, H.; Khosravi, A.R.; Abbaszadeh, A. Antifungal efficacy of thymol, carvacrol, eugenol and menthol as alternative agents to control the growth of food-relevant fungi. J. Mycol. Med. 2014, 24, e51–e56.
- Rivera-Yañez, C.R.; Terrazas, L.I.; Jimenez-Estrada, M.; Campos, J.E.; Flores-Ortiz, C.M.; Hernandez, L.B.; Cruz-Sanchez, T.; Garrido-Fariña, G.I.; Rodriguez-Monroy, M.A.; Canales-Martinez, M.M. Anti-Candida activity of Bursera morelensis Ramirez essential oil and two compounds, α-pinene and γ-terpinene—an in vitro study. Molecules 2017, 22, 95.
- de Oliveira Lima, M.I.; Araújo de Medeiros, A.C.; Souza Silva, K.V.; Cardoso, G.N.; de Oliveira Lima, E.; de Oliveira Pereira, F. Investigation of the antifungal potential of linalool against clinical isolates of fluconazole resistant Trichophyton rubrum. J. Mycol. Med. 2017, 27, 195–202.
- de Macêdo Andrade, A.C.; Rosalen, P.L.; Freires, I.A.; Scotti, L.; Scotti, M.T.; Aquino, S.G.; de Castro, R.D. Antifungal activity, mode of action, docking prediction and anti-biofilm effects of (+)-β-pinene enantiomers against Candida spp. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 2481–2490.
- Wang, K.; Jiang, S.; Pu, T.; Fan, L.; Su, F.; Ye, M. Antifungal activity of phenolic monoterpenes and structure-related compounds against plant pathogenic fungi. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1423–1430.
- Shi, Y.; Si, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Shang, S.; Song, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liao, S. Derivatization of natural compound β-pinene enhances its in vitro antifungal activity against plant pathogens. Molecules 2019, 24, 3144.
- Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.A.; Kasprzak, K.; Oniszczuk, T.; Oniszczuk, A. Natural monoterpenes: Much more than only a scent. Chem. Biodiv. 2019, 16, e19004.
- Monforte, M.T.; Tzakou, O.; Nostro, A.; Zimbalatti, V.; Galati, E.M. Chemical composition and biological activities of Calamintha officinalis Moench essential oil. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 297–303.
- Ćavar, S.; Vidic, D.; Maksimović, M. Volatile constituents, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant activity of Calamintha glandulosa (Req.) Bentham. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 1758–1764.
- Gonçalves, M.J.; Vicente, A.M.; Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L. Composition and antifungal activity of the essential oil of Mentha cervina from Portugal. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 867–871.
- Al-Maskri, A.Y.; Hanif, M.A.; Al-Maskari, M.Y.; Abraham, A.S.; Al-sabahi, J.N.; Al-Mantheri, O. Essential oil from Ocimum basilicum (Omani Basil): A desert crop. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1487–1490.
- Ngo Mback, M.N.; Agnaniet, H.; Nguimatsia, F.; Jazet Dongmo, P.M.; Hzounda Fokou, J.B.; Bakarnga-Via, I.; Fekam Boyom, F.; Menut, C. Optimization of antifungal activity of Aeollanthus heliotropioides oliv essential oil and Time Kill Kinetic Assay. J. Mycol. Med. 2016, 26, 233–243.
- Shin, S.; Kang, C.A. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Agastache rugosa Kuntze and its synergism with ketoconazole. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 111–115.
- Gong, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Kasimu, R. Microscopic identification and in vitro activity of Agastache rugosa (Fisch. et Mey) from Xinjiang, China. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 95.
- Fraternale, D.; Ricci, D. Essential oil composition and antifungal activity of aerial parts of Ballota nigra ssp foetida collected at flowering and fruiting times. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1015–1018.
- Marinković, B.; Marin, P.D.; Knezević-Vukcević, J.; Soković, M.D.; Brkić, D. Activity of essential oils of three Micromeria species (Lamiaceae) against micromycetes and bacteria. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 336–339.
- Marongiu, B.; Piras, A.; Porcedda, S.; Falconieri, D.; Maxia, A.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L. Chemical composition and biological assays of essential oils of Calamintha nepeta (L.) Savi subsp. nepeta (Lamiaceae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 1734–1742.
- Božović, M.; Garzoli, S.; Sabatino, M.; Pepi, F.; Baldisserotto, A.; Andreotti, E.; Romagnoli, C.; Mai, A.; Manfredini, S.; Ragno, R. Essential oil extraction, chemical analysis and anti-Candida activity of Calamintha nepeta (L.) Savi subsp. landulosa (Req.) Ball—New approaches. Molecules 2017, 22, 203.
- Kumar, V.; Mathela, C.S.; Tewari, A.K.; Bisht, K.S. In vitro inhibition activity of essential oils from some Lamiaceae species against phytopathogenic fungi. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 114, 67–71.
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Yun, T.; Fu, Y.; Liu, C.; Gong, B.; Neng, B. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the essential oil of Tibetan herbal medicine Dracocephalum heterophyllum Benth. Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 22, 1–11.
- Stappen, I.; Wanner, J.; Tabanca, N.; Wedge, D.E.; Ali, A.; Kaul, V.K.; Lal, B.; Jaitak, V.; Gochev, V.K.; Schmidt, E.; et al. Chemical composition and biological activity of essential oils of Dracocephalum heterophyllum and Hyssopus officinalis from Western Himalaya. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 133–138.
- Ahmadi, F.; Sadeghi, S.; Modarresi, M.; Abiri, R.; Mikaeli, A. Chemical composition, in vitro anti-microbial, antifungal an d antioxidant activities of the essential oil and methanolic extract of Hymenocrater longiflorus Benth., of Iran. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1137–1144.
- De Oliveira, C.M.A.; Silva, M.R.R.; Kato, L.; da Silva, C.C.; Ferreira, H.D.; Souza, L.K.H. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of the essential oil of Hyptis ovalifolia Benth. (Lamiaceae). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2004, 15, 756–759.
- Souza, L.K.; de Oliveira, C.M.; Ferri, P.H.; de Oliveira Júnior, J.G.; de Souza Júnior, A.H.; Fernandes Ode, F.; Silva Mdo, R. Antimicrobial activity of Hyptis ovalifolia towards dermatophytes. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2003, 98, 963–965.
- Džamić, A.M.; Soković, M.D.; Novaković, M.; Jadranin, M.; Ristić, M.S.; Tešević, V.; Marin, P.D. Composition, antifungal and antioxidant properties of Hyssopus officinalis L. subsp. pilifer (Pant.) Murb. essential oil and deodorized extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 51, 401–407.
- Hristova, Y.; Wanner, J.; Jirovetz, L.; Stappen, I.; Iliev, I.; Gochev, V. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of essential oil of Hyssopus officinalis L. from Bulgaria against clinical isolates of Candida species. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 592–601.
- D’Auria, F.D.; Tecca, M.; Strippoli, V.; Salvatore, G.; Battinelli, L.; Mazzanti, G. Antifungal activity of Lavandula angustifolia essential oil against Candida albicans yeast and mycelial form. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, 391–396.
- Khoury, M.; Stien, D.; Eparvier, V.; Ouaini, N.; El Beyrouthy, M. Report on the medicinal use of eleven Lamiaceae species in Lebanon and rationalization of their antimicrobial potential by examination of the chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of their essential oils. Evid. Based Compl. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016.
- Dolatabadi, S.; Salari, Z.; Mahboubi, M. Antifungal effects of Ziziphora tenuior, Lavandula angustifolia, Cuminum cyminum essential oils against clinical isolates of Candida albicans from women suffering from vulvovaginal candidiasis. Infect 2019, 23, 222–226.
- Adam, K.; Sivropoulou, A.; Kokkini, S.; Lanaras, T.; Arsenakis, M. Antifungal activities of Origanum vulgare subsp. hirtum, Mentha spicata, Lavandula angustifolia, and Salvia fruticosa essential oils against human pathogenic fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1739–1745.
- Zuzarte, M.; Vale-Silva, L.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Vaz, S.; Canhoto, J.; Pinto, E.; Salgueiro, L. Antifungal activity of phenolic-rich Lavandula multifida L. essential oil. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 1359–1366.
- Zuzarte, M.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Dinis, A.M.; Canhoto, J.M.; Salgueiro, L.R. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of the essential oils of Lavandula pedunculata (Miller) Cav. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1283–1292.
- Zuzarte, M.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cruz, M.T.; Cavaleiro, C.; Canhoto, J.; Vaz, S.; Pinto, E.; Salgueiro, L. Lavandula luisieri essential oil as a source of antifungal drugs. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1505–1510.
- Zuzarte, M.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Canhoto, J.; Vale-Silva, L.; Silva, M.J.; Pinto, E.; Salgueiro, L. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of the essential oils of Lavandula viridis L’Her. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 612–618.
- Ramírez, J.; Gilardoni, G.; Jácome, M.; Montesinos, J.; Rodolfi, M.; Guglielminetti, M.L.; Cagliero, C.; Bicchi, C.; Vidari, G. Chemical composition, enantiomeric analysis, AEDA sensorial evaluation and antifungal activity of the essential oil from the Ecuadorian plant Lepechinia mutica Benth (Lamiaceae). Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700292.
- Zarai, Z.; Kadri, A.; Ben Chobba, I.; Ben Mansour, R.; Bekir, A.; Mejdoub, H.; Gharsallah, N. The in-vitro evaluation of antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic properties of Marrubium vulgare L. essential oil grown in Tunisia. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 161.
- Powers, C.N.; Osier, J.L.; McFeeters, R.L.; Brazell, C.B.; Olsen, E.L.; Moriarity, D.M.; Satyal, P.; Setzer, W.N. Antifungal and cytotoxic activities of sixty commercially-available essential oils. Molecules 2018, 23, 1549.
- Mimica-Dukic, N.; Bozin, B.; Sokovic, M.; Simin, N. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Melissa officinalis L. (Lamiaceae) essential oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2485–2489.
- Ozcakmak, S.; Dervisoglu, M.; Yilmaz, A. Antifungal activity of lemon balm and sage essential oils on the growth of ochratoxigenic Penicillium verrucosum. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 3079–3084.
- Camiletti, B.X.; Asensio, C.M.; Pecci Mde, L.; Lucini, E.I. Natural control of corn postharvest fungi Aspergillus flavus and Penicillium sp. using essential oils from plants grown in Argentina. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M2499–M2506.
- Hossain, F.; Follett, P.; Dang Vu, K.; Harich, M.; Salmieri, S.; Lacroix, M. Evidence for synergistic activity of plant-derived essential oils against fungal pathogens of food. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 24–30.
- Samber, N.; Khan, A.; Varma, A.; Manzoor, N. Synergistic anti-candidal activity and mode of action of Mentha piperita essential oil and its major components. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1496–1504.
- Tyagi, A.K.; Malik, A. Liquid and vapour-phase antifungal activities of selected essential oils against Candida albicans: Microscopic observations and chemical characterization of Cymbopogon citratus. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 65.
- Sharma, A.; Rajendran, S.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, S.; Kundu, B. Antifungal activities of selected essential oils against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici 1322, with emphasis on Syzygium aromaticum essential oil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 308–313.
- Jeršek, B.; Poklar Ulrih, N.; Skrt, M.; Gavarić, N.; Božin, B.; Smole Možina, S. Effects of selected essential oils on the growth and production of ochratoxin A by Penicillium verrucosum. Arhiv Higijenu i Toksikologiju 2014, 65, 199–208.
- Mahboubi, M.; Haghi, G. Antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of Mentha pulegium L. essential oil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 325–327.
- Piras, A.; Porcedda, S.; Falconieri, D.; Maxia, A.; Gonçalves, M.; Cavaleiro, C.; Salgueiro, L. Antifungal activity of essential oil from Mentha spicata L. and Mentha pulegium L. growing wild in Sardinia island (Italy). Nat. Prod. Res. 2019.
- Abdelli, M.; Moghrani, H.; Aboun, A.; Maachi, R. Algerian Mentha pulegium L. leaves essential oil: Chemical composition, antimicrobial, insecticidal and antioxidant activities. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 197–205.
- Fancello, F.; Zara, S.; Petretto, G.L.; Chessa, M.; Addis, R.; Rourke, J.P.; Pintore, G. Essential oils from three species of Mentha harvested in Sardinia: Chemical characterization and evaluation of their biological activity. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1751–1761.
- Chessa, M.; Sias, A.; Piana, A.; Mangano, G.S.; Petretto, G.L.; Masia, M.D.; Tirillini, B.; Pintore, G. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oil from Mentha requienii Bentham. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 93–99.
- Houicher, A.; Hechachna, H.; Teldji, H.; Ozogul, F. In vitro study of the antifungal activity of essential oils obtained from Mentha spicata, Thymus vulgaris, and Laurus nobilis. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2016, 8, 99–106.
- Nardoni, S.; Giovanelli, S.; Pistelli, L.; Mugnaini, L.; Profili, G.; Pisseri, F.; Mancianti, F. In vitro activity of twenty commercially available, plant-derived essential oils against selected dermatophyte species. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1473–1478.
- Ji, H.; Kim, H.; Beuchat, L.R.; Ryu, J.H. Synergistic antimicrobial activities of essential oil vapours against Penicillium corylophilum on a laboratory medium and beef jerky. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 291, 104–110.
- Oumzil, H.; Ghoulami, S.; Rhajaoui, M.; Ilidrissi, A.; Fkih-Tetouani, S.; Faid, M.; Benjouad, A. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of essential oils of Mentha suaveolens. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 727–731.
- Garzoli, S.; Pirolli, A.; Vavala, E.; Di Sotto, A.; Sartorelli, G.; Božović, M.; Angiolella, L.; Mazzanti, G.; Pepi, F.; Ragno, R. Multidisciplinary approach to determine the optimal time and period for extracting the essential oil from Mentha suaveolens Ehrh. Molecules 2015, 20, 9640–9655.
- Pietrella, D.; Angiolella, L.; Vavala, E.; Rachini, A.; Mondello, F.; Ragno, R.; Bistoni, F.; Vecchiarelli, A. Beneficial effect of Mentha suaveolens essential oil in the treatment of vaginal candidiasis assessed by real-time monitoring of infection. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 18.
- Angiolella, L.; Vavala, E.; Sivric, S.; D’Auria, F.D.; Ragno, R. In vitro activity of Mentha suaveolens essential oil against Cryptococcus neoformans and dermatophytes. Int. J. Essent. Oil Ther. 2010, 4, 35–36.
- Casiglia, S.; Jemia, M.B.; Riccobono, L.; Bruno, M.; Scandolera, E.; Senatore, F. Chemical composition of the essential oil of Moluccella spinosa L. (Lamiaceae) collected wild in Sicily and its activity on microorganisms affecting historical textiles. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1201–1206.
- Bisht, D.S.; Padalia, R.C.; Singh, L.; Pande, V.; Lal, P.; Mathela, C.S. Constituents and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of six Himalayan Nepeta species. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2010, 75, 739–747.
- Sacchetti, G.; Medici, A.; Maietti, S.; Radice, M.; Muzzoli, M.; Manfredini, S.; Braccioli, E.; Bruni, R. Composition and functional properties of the essential oil of amazonian basil, Ocimum micranthum Willd., Labiatae in comparison with commercial essential oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3486–3491.
- Mohr, F.B.; Lermen, C.; Gazim, Z.C.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Alberton, O. Antifungal activity, yield, and composition of Ocimum gratissimum essential oil. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16.
- Santamarina, M.P.; Roselló, J.; Sempere, F.; Giménez, S.; Blázquez, M.A. Commercial Origanum compactum Benth. and Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume essential oils against natural mycoflora in Valencia rice. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2215–2258.
- Pitarokili, D.; Tzakou, O.; Loukis, A.; Harvala, C. Volatile metabolites from Salvia fruticosa as antifungal agents in soilborne pathogens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3294–3301.
- Zomorodian, K.; Moein, M.; Pakshir, K.; Karami, F.; Sabahi, Z. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activities of the essential oil from Salvia mirzayanii leaves. J. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 22, 770–776.
- Alizadeh, A.; Zamani, E.; Sharaifi, R.; Javan-Nikkhah, M.; Nazari, S. Antifungal activity of some essential oils against toxigenic Aspergillus species. Commun. Agric. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2010, 75, 761–767.
- Güllüce, M.; Sökmen, M.; Daferera, D.; Ağar, G.; Ozkan, H.; Kartal, N.; Polissiou, M.; Sökmen, A.; Sahin, F. In vitro antibacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant activities of the essential oil and methanol extracts of herbal parts and callus cultures of Satureja hortensis L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3958–3965.
- Mohammadi, A.; Nazari, H.; Imani, S.; Amrollahi, H. Antifungal activities and chemical composition of some medicinal plants. J. Mycol. Med. 2014, 24, e1–e8.
- Salah, K.B.; Mahjoub, M.A.; Chaumont, J.P.; Michel, L.; Millet-Clerc, J.; Chraeif, I.; Ammar, S.; Mighri, Z.; Aouni, M. Chemical composition and in vitro antifungal and antioxidant activity of the essential oil and methanolic extract of Teucrium sauvagei Le Houerou. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 1089–1097.
- Ali, N.A.A.; Chhetri, B.K.; Dosoky, N.S.; Shari, K.; Al-Fahad, A.J.A.; Wessjohann, L.; Setzer, W.N. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities of Ocimum forskolei and Teucrium yemense (Lamiaceae) essential oils. Medicines 2017, 4, 17.
- Salgueiro, L.R.; Pinto, E.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Rodrigues, A.G.; Palmeira, A.; Tavares, C.; Costa-de-Oliveira, S.; Martinez-de-Oliveira, J. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of the essential oil of Thymbra capitata. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 572–575.
- Tabti, L.; Dib Mel, A.; Gaouar, N.; Samira, B.; Tabti, B. Antioxidant and antifungal activity of extracts of the aerial parts of Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoffmanns against four phytopathogenic fungi of Citrus sinensis. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2014, 9, 49–54.
- Goren, A.C.; Bilsel, G.; Bilsel, M.; Demir, H.; Kocabaş, E.E. Analysis of essential oil of Coridothymus capitatus (L.) and its antibacterial and antifungal activity. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 2003, 58, 687–690.
- Palmeira-de-Oliveira, A.; Gaspar, C.; Palmeira-de-Oliveira, R.; Silva-Dias, A.; Salgueiro, L.; Cavaleiro, C.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Martinez-de-Oliveira, J.; Queiroz, J.A.; Rodrigues, A.G. The anti-Candida activity of Thymbra capitata essential oil: Effect upon pre-formed biofilm. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 379–383.
- Marković, T.; Chatzopoulou, P.; Šiljegović, J.; Nikolić, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Ćirić, A.; Soković, M. Chemical analysis and antimicrobial activities of the essential oils of Satureja thymbra L. and Thymbra spicata L. and their main components. Arch. Biol. Sci. Belgrade 2011, 63, 457–464.
- Kiliç, T. Analysis of essential oil composition of Thymbra spicata var. spicata: Antifungal, antibacterial and antimycobacterial activities. Z. Naturforsch. C 2006, 61, 324–328.
- Unlü, M.; Vardar-Unlü, G.; Vural, N.; Dönmez, E.; Ozbaş, Z.Y. Chemical composition, antibacterial and antifungal activity of the essential oil of Thymbra spicata L. from Turkey. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 572–579.
- Jaradat, N.; Adwan, L.; Kaibni, S.; Shraim, N.; Zaid, A.N. Chemical composition, anthelmintic, antibacterial and antioxidant effects of Thymus bovei essential oil. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 418.
- Pina-Vaz, C.; Gonçalves Rodrigues, A.; Pinto, E.; Costa-de-Oliveira, S.; Tavares, C.; Salgueiro, L.; Cavaleiro, C.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Martinez-de-Oliveira, J. Antifungal activity of Thymus oils and their major compounds. J. Eur. Acad Dermatol. Venereol. 2004, 18, 73–78.
- Pinto, E.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Salgueiro, L.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Costa-de-Oliveira, S.; Cavaleiro, C.; Palmeira, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Martinez-de-Oliveira, J. Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Thymus pulegioides on Candida, Aspergillus and dermatophyte species. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 1367–1373.
- Pagiotti, R.; Angelini, P.; Rubini, A.; Tirillini, B.; Granetti, B.; Venanzoni, R. Identification and characterisation of human pathogenic filamentous fungi and susceptibility to Thymus schimperi essential oil. Mycoses 2011, 54, e364–e376.
- Nasir, M.; Tafess, K.; Abate, D. Antimicrobial potential of the Ethiopian Thymus schimperi essential oil in comparison with others against certain fungal and bacterial species. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 260.
- Sokolić-Mihalak, D.; Frece, J.; Slavica, A.; Delaš, F.; Pavlović, H.; Markov, K. The effects of wild thyme (Thymus serpyllum L.) essential oil components against ochratoxin-producing Aspergilli. Arhiv za Higijenu i Toksikologiju 2012, 63, 457–462.
- Couladis, M.; Tzakou, O.; Kujundzic, S.; Sokovic, M.; Mimica-Dukic, N. Chemical analysis and antifungal activity of Thymus striatus. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 40–42.
- Segvić Klarić, M.; Kosalec, I.; Mastelić, J.; Piecková, E.; Pepeljnak, S. Antifungal activity of thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) essential oil and thymol against moulds from damp dwellings. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 44, 36–42.
- Perina, F.J.; Amaral, D.C.; Fernandes, R.S.; Labory, C.R.; Teixeira, G.A.; Alves, E. Thymus vulgaris essential oil and thymol against Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler: Effects on growth, viability, early infection and cellular mode of action. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 1371–1378.
- Sharifzadeh, A.; Javan, A.J.; Shokri, H.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Keykhosravy, K. Evaluation of antioxidant and antifungal properties of the traditional plants against foodborne fungal pathogens. J. Mycol. Med. 2016, 26, e11–e17.
- Bozin, B.; Mimica-Dukic, N.; Simin, N.; Anackov, G. Characterization of the volatile composition of essential oils of some Lamiaceae spices and the antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the entire oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1822–1828.
- Liu, J.; Sui, G.; He, Y.; Liu, D.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, W. Prolonging storage time of baby ginger by using a sand-based storage medium and essential oil treatment. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, M593–M599.
- Homa, M.; Fekete, I.P.; Böszörményi, A.; Singh, Y.R.; Selvam, K.P.; Shobana, C.S.; Manikandan, P.; Kredics, L.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Galgóczy, L. Antifungal effect of essential oils against Fusarium keratitis isolates. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 1277–1284.
- Divband, K.; Shokri, H.; Khosravi, A.R. Down-regulatory effect of Thymus vulgaris L. on growth and Tri4 gene expression in Fusarium oxysporum strains. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 104, 1–5
- Vinciguerra, V.; Rojas, F.; Tedesco, V.; Giusiano, G.; Angiolella, L. Chemical characterization and antifungal activity of Origanum vulgare, Thymus vulgaris essential oils and carvacrol against Malassezia furfur. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 33, 3273–3277.
- Nikkhah, M.; Hashemi, M.; Habibi Najafi, M.B.; Farhoosh, R. Synergistic effects of some essential oils against fungal spoilage on pear fruit. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 257, 285–294.
- De Lira Mota, K.S.; de Oliveira Pereira, F.; de Oliveira, W.A.; Lima, I.O.; de Oliveira Lima, E. Antifungal activity of Thymus vulgaris L. essential oil and its constituent phytochemicals against Rhizopus oryzae: Interaction with ergosterol. Molecules 2012, 17, 14418–14433.
- Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Cameotra, S.S. Carum copticum and Thymus vulgaris oils inhibit virulence in Trichophyton rubrum and Aspergillus spp. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 523–531.
- Asdadi, A.; Hamdouch, A.; Oukacha, A.; Moutaj, R.; Gharby, S.; Harhar, H.; El Hadek, M.; Chebli, B.; Idrissi Hassani, L.M. Study on chemical analysis, antioxidant and in vitro antifungal activities of essential oil from wild Vitex agnus-castus L. seeds growing in area of Argan Tree of Morocco against clinical strains of Candida responsible for nosocomial infections. J. Mycol. Med. 2015, 25, e118–e127.
- Marongiu, B.; Piras, A.; Porcedda, S.; Falconieri, D.; Goncalves, M.J.; Salgueiro, L.; Maxia, A.; Lai, R. Extraction, separation and isolation of volatiles from Vitex agnus-castus L. (Verbenaceae) wild species of Sardinia, Italy, by supercritical CO2. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 569–579.
- Mahboubi, M.; Heidary Tabar, R.; Mahdizadeh, E. The anti-dermatophyte activity of Zataria multiflora essential oils. J. Mycol. Med. 2017, 27, 232–237.
- Moghadam, H.D.; Sani, A.M.; Sangatash, M.M. Antifungal activity of essential oil of Ziziphora clinopodioides and the inhibition of aflatoxin B1 production in maize grain. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 493–499.
- Abu-Darwish, M.S.; Cabral, C.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Cruz, M.T.; Paoli, M.; Tomi, F.; Efferth, T.; Salgueiro, L. Ziziphora tenuior L. essential oil from Dana Biosphere Reserve (Southern Jordan); Chemical characterization and assessment of biological activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 963–970.
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253.
- Helal, G.A.; Sarhan, M.M.; Abu Shahla, A.N.K.; Abou El-Khair, E.K. Effects of Cymbopogon citratus L. essential oil on the growth, lipid content and morphogenesis of Aspergillus niger ML2-strain. J. Basic Microbiol. 2006, 46, 456–469.
- Rammanee, K.; Hongpattarakere, T. Effects of tropical citrus essential oils on growth, aflatoxin production, and ultrastructure alterations of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 1050–1059.
- Hyldgaard, M.; Mygind, T.; Meyer, R.L. Essential oils in food preservation: Mode of action, synergies, and interactions with food matrix components. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 1–24.
- Basak, S.; Guha, P. A review on antifungal activity and mode of action of essential oils and their delivery as nano-sized oil droplets in food system. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4701–4710.
- Tariq, S.; Wani, S.; Rasool, W.; Shafi, K.; Bhat, M.A.; Prabhakar, A.; Shalla, A.H.; Rather, M.A. A comprehensive review of the antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral potential of essential oils and their chemical constituents against drug-resistant microbial pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 134.
More
