Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer is a prevailing global health disease with a high incidence rate which varies by region. It is a huge economic burden on health care providers. GI cancer affects different organs in the body such as the gastric organs, colon, esophagus, intestine, and pancreas. Phytochemicals are non-nutritive bioactive secondary compounds abundantly found in fruits, grains, and vegetables. Consumption of phytochemicals may protect against chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disease, and cancer. Multiple studies have assessed the chemoprotective effect of selected phytochemicals in GI cancer, offering support to their potential towards reducing the pathogenesis of the disease.The aim of this review is to summarize the current knowledge addressing the anti-cancerous effects of selected dietary phytochemicals on GI cancer and their molecular activities on selected mechanisms, i.e., nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-B), detoxification enzymes, adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK), wingless-related integration site/-catenin (wingless-related integration site (Wnt)-catenin, cell apoptosis, phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/ protein kinase B AKT/ mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Overall, phytochemicals improve cancer prognosis through the downregulation of -catenin phosphorylation, therefore enhancing apoptosis, and upregulation of the AMPK pathway, which supports cellular homeostasis. Nevertheless, more studies are needed to provide a better understanding of the mechanism of cancer treatment using phytochemicals and possible side effects associated with this approach.
- phytochemical
- gastrointestinal cancer
- intestinal cancer
- apoptosis
- anti-cancerous effects
1. Gastrointestinal Cancer and Phytochemicals
1.1. Gastrointestinal Cancer
1.2. Colorectal Cancer
1.3. Esophageal Cancer
1.4. Diet and Microbial Metabolites
2. Anti-Cancerous Effects of Selected Phytochemicals
2.1. Carotenoids
2.1.1. Lutein
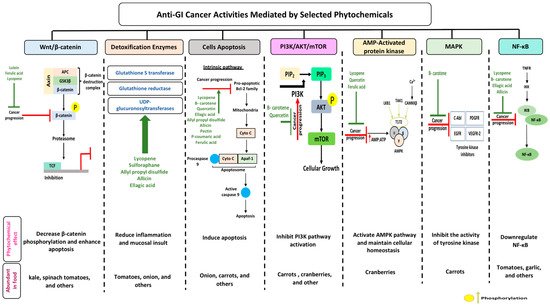
2.1.2. Lycopene
2.2. Proanthocyanidins
2.2.1. Quercetin
2.2.2. Ellagic Acid
2.3. Organosulfur Compounds
2.3.1. Allicin
2.3.2. Allyl Propyl Disulfide
2.3.3. Asparagusic Acid
2.3.4. Sulforaphane
| Phytochemical Subclass | Phytochemical and Structure | Dietary Source | Conversion Reaction | Metabolites Produced | Mechanism of Action | Model Used | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In Vitro | |||||||
| Carotenoids | Lutein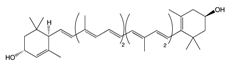 |
Egg yolk, kale, spinach, parsley, and peas | Oxidation | 3′-dehydro-lutein |
|
|
|
[42][46][74,78] |
Lycopene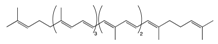 |
Tomato, guava, papaya, grapefruit, and watermelon | Auto-oxidation Radical-mediated oxidation | Apo-10′-lycopenoids |
|
|
|
[54][57][86,89] | |
β-Carotene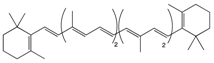 |
Carrot | Oxidation | Falcarindiol 6-methoxymellein |
|
|
|
[129][130][131][97,98,99] | |
| Pro-anthocy-anidins | Quercetin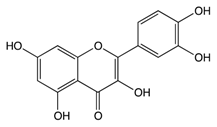 |
Cranberry | Sulfation Conjugation | 3-(4hydroxyphenyl) -propionic acid hippuric acid catechol-O-sulfate |
|
|
|
[68][108[69],109] |
Ellagic Acid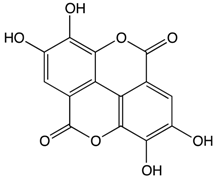 |
Bilberry | Glucuronidation O-methylation |
Peonidin-3-galactoside |
|
|
|
[80][81][120,121] | |
| Organosulfur Compounds | Allicin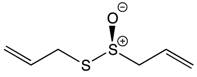 |
Garlic | Oxidation Hydrolysis | Allyl methyl sulfide (AMS) Allyl methyl sulfoxide (AMSO) Allyl methyl sulfone (AMSO2) |
|
|
|
[95][135[96],136] |
Allyl propyl disulfide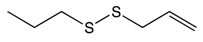 |
Onion | Reduction | Quercetin 3,4‘-diglucoside Quercetin 4‘-glucoside |
|
|
[106][107][146,147] | ||
Asparagusic acid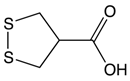 |
Asparagus | Sulfation | Asparagus polysaccharide dimethyl sulfide |
|
|
[112][113][152,153] | ||
Sulforaphane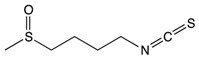 |
Broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprout, and cauliflower | Hydrolysis | Thiocyanates Isothiocyanates Epithionitrile nitrile |
|
|
[124][125][164,165] | ||
| Other Phytochemicals | Pectin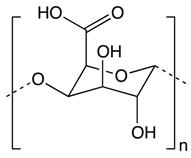 |
Apples, plums, oranges, and gooseberries | Colonic fermentation | Butyrate |
|
|
|
[132][169[133],170] |
Curcumin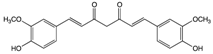 |
Ginger | Hydrolysis | Curcumin glucuronide Curcumin sulfate |
|
|
[134][135][183,184] | ||
p-Couramic acid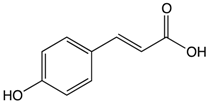 |
Navy beans | Hydrolysis | N-methylpipecolate 2-aminoadipate Piperidine Vanillate |
|
|
[136][189[137],190] | ||
Ferulic acid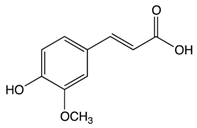 |
Rice bran | Colonic fermentation | Tryptophan α-ketoglutarate γ-tocopherol/β-tocopherol γ-tocotrienol |
|
|
|
[138][139][201,202] | |
