Lymph node structural organization is reported to be governed by the stromal cells. Fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs), a subset of the stromal cells found inusually found and isolated from the T lymphocyte regioncell zone of lymph nodes (LNs) and other secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs), have , have recently been described as much more than structural cells.
FRCs are described to be organized in a conduit system called the “reticular fiber network”, responsible for transferring antigens from tissue to T cell zones in LNs and for controlling the conduit matrix deposition during lymph node expansionple structural cells.
- fibroblastic reticular cells
- T cells
- lymph nodes
1. Overview
Fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs), usually found and isolated from the T cell zone of lymph nodes, have recently been described as much more than simple structural cells. Originally, these cells were described to form a conduit system called the “reticular fiber network” and for being responsible for transferring the lymph fluid drained from tissues through afferent lymphatic vessels to the T cell zone. However, nowadays, these cells are described as being capable of secreting several cytokines and chemokines and possessing the ability to interfere with the immune response, improving it, and also controlling lymphocyte proliferation. Here, we performed a systematic review of the several methods employed to investigate the mechanisms used by fibroblastic reticular cells to control the immune response, as well as their ability in determining the fate of T cells. We searched articles indexed and published in the last five years, between 2016 and 2020, in PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane, following the PRISMA guidelines. We found 175 articles published in the literature using our searching strategies, but only 24 articles fulfilled our inclusion criteria and are discussed here. Other articles important in the built knowledge of FRCs were included in the introduction and discussion. The studies selected for this review used different strategies in order to access the contribution of FRCs to different mechanisms involved in the immune response: 21% evaluated viral infection in this context, 13% used a model of autoimmunity, 8% used a model of GvHD or cancer, 4% used a model of Ischemic-reperfusion injury (IRI). Another four studies just targeted a particular signaling pathway, such as MHC II expression, FRC microvesicles, FRC secretion of IL-15, FRC network, or ablation of the lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-producing ectoenzyme autotaxin. In conclusion, our review shows the strategies used by several studies to isolate and culture fibroblastic reticular cells, the models chosen by each one, and dissects their main findings and implications in homeostasis and disease.
2. Background
3. Conclusions
| Ref. | Year | Host | Interventions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Genotype | Age (Weeks) | Gender | Type | Time (Days) | ||
| Ref. | Lymph Node Region | Digestion Type | Digestion Solution | FRC Culture Medium + Supplement | FRC Immunophenotypic Characterization | Technique for Cell Separation | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aparicio-Domingo et al. [18] | 2020 | Mice C57BL/6J | IL-33gfp/gfp; IL-33gfp/+ | 7–19 | M | LCMV clone 13 and WE virus; tamoxifen | Single dose; 6 (3/week) |
| Dertschnig et al. [19] | 2020 | Mice C57BL/6 | Female to male bone marrow transplant model (BMT), T cell-depleted, plus transgenic TCR-CD8 MataHari (Mh) | NR | M | ||
| Brown et al. [ | |||||||
| 24 | |||||||
| Mice BALB/c | |||||||
| Aparicio-Domingo et al. [18] | Axillary; brachial; inguinal | Enzymatic | Collagenase IV; DNase I; CaCl2 | DMEM (2% FCS) | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sortingDexamethasone; DT; Gy irradiation | |
| CD4, CD8, B220, CD44 | |||||||
| Ref. | Trial Types | Study Target | Time of Intervention | Main Performed Evaluations | Results | FRC Role in Immune Response | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3; 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ] | LN | CD8+ T cells | Non selection performed | DMEM (2% FCS) | CD45, CD8α, CD4, TRCαβ | |||||||||||||||
| Aparicio-Domingo et al. [18] | IL-33-GFP reporter mice | LCMV | 3 days/w for 2 weeks |
FC and RNA sequencing | FRC is one important IL-33 source in LNs, vital for driving acute and chronic antiviral T cell responses. | Anti-viral response>94 | Dertschnig et al. [19] | LN | T cells | CD3 negative selection followed by CD4 and CD8α positive selection (MicroBeads—Myltenyi) |
NR | |||||||||
| Dertschnig et al. [ | CD45, CD45.1, CD3, CD4, CD8α, CD62L, CD44, CD69, CD127, Vα2, Vβ5 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 19] | FRC and DC ablation in vivo; identification of PTA regulatory genes; BTM model induction | GvHD | 2 weeks | FC, RNA sequencing, confocal microscopy | The loss of PTA presentation by FRCs during GVHD leads to permanent damage in their networks in lymphoid tissues. | Control of peripheral tolerance | Eom et al. [20] | 2020 | Human | Eom et al. [20] | LN | NAMetastatic melanoma and surgery | NA | NA | NA | NANA | ||||
| NA | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Eom et al. [20 | CD45, CD3, CD8 | |||||||||||||||||||
| ] | Identification of distinctive subpopulations of CD90+ SCs present in melanoma-infiltrated LNs |
Melanoma | NA | FC, gene expression | There are several distinct subsets of FRCs present in melanoma-infiltrated LNs. These FRCs may be related to cancer metastasis invasion and progression by avoiding T cells through secreted factors. | Lymph node invasion metastasis and its correlation with FRC gene expression. | Gonzalez et al. [21] | Gonzalez et al. [21] | Spleen | CD8+ T cells | CD8 isolation by negative selection (Microbeads—MojoSort) | |||||||||
| Gonzalez et al. [21]2020 | Mice (NOD/ShiLtJ, NOR/LtJ, and NOD.CgTg); Human | Type 1 diabetes |
12 | F | NA | Tissue-engineered stromal reticula and FRC/T cell co-culture | Type 1 NA |
|||||||||||||
| NR | diabetes | NA | CD45, CD8, CD44, CD25 | |||||||||||||||||
| FC, immunofluorescence, imaging | FRCs modulate their interactions with autoreactive T cells by remodeling their reticular network in LNs. FRC with decreased contractility through gp38 downregulation, can loosen/relax their network, potentially decreasing FRC tolerogenic interactions with autoreactive T cells and promoting their escape from peripheral regulation in LNs. | Role of FRCs on tolerance and T1D | Knop et al. [22] | 2020 | Mice C57BL/6N and ROSA26RFP | IL-7−/−, PGK-Cre, FLPO, RAG1−/−, Thy1.1+ OT-I | NR | NR | NA | NA | ||||||||||
| Knop et al. [22] | LN; spleen | T cells and NK | CD8α positive selection (MicroBeads—Myltenyi) | CD45, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD8α, CD62L, Bcl-2, CD127, Nk1.1, RORγt | ||||||||||||||||
| Knop et al. [22] | IL-7fl/fl mice and adoptive T cell transfer | NA | NA | FC | IL7, produced by LN FRCs-regulated T cell homeostasis, is crucial for TCM maintenance. | IL7 produced by LN FRCs is crucial for TCM | Perez-Shibayama et al. [23] | 2020 | Mice C57BL/6 | CCL19-Cre IFNARfl/fl | 8–10 | NR | LCMV Armstrong | NR | ||||||
| maintenance | Perez-Shibayama et al. [23] | LN; spleen | T cell subsets and exhaustion | No selection performed | RPMI | CD45.1, CD45.2, CD45R, CD8α, CD8β, CD3e, CD44 CD62L, PD-1, PDL1 | Brown et al. [ | |||||||||||||
| Perez-Shibayama et al. [23] | LCMV-infected mice, FRC ex vivo restimulation and cytokine production | LCMV Armstrong | 8 d | FC | IFNAR-dependent shift of FRC subsets toward an immunoregulatory state reduces exhaustive CD8+ T cell activation. | IFN type 1 influences FRC peripheral tolerance | 24] | ]2019 | Mice C57BL/6 | IL-6−/−; NOS2−/− | 5–12 | M | PR8-GP33-41, LCMV, influenza, OT-1 T cells with OVA | NR | ||||||
| NR | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; DNase I; Dispase | α-MEM | Brown et al. [CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | 24>95 | ] | LN | CD8+ T cells | CD8α positive selection (MicroBeads—Myltenyi) | RPMI; α-MEM | CD45.1, CD45.2, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD275, CD28, CD44 | Kasinath et al. [25] | 2019 | Mice CD-1 IGS or C57BL/6 or C57BL/6J | CCL19-Cre iDTR | 8–10 | M | Nephrotoxic serum (NTS); DT | 3 |
| Kelch et al. [26] | 2019 | Mice C57BL/6J | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brown et al. [24] | NA | 9–22 | M | NA | NA | |||||||||||||||
| FRC/T cell co-cultures | Influenza and LCMV infection | NR | FC and RNA sequencing | FRCs play a role over restricting T cell expansion—they can also outline the fate and function of CD8+ T cells through their IL-6 production. | Majumder et al. [27] | 2019 | Mice C57BL/6 | IL-17A−/−; IL-17RAfl/fl; OT-II, ACT1−/−; CCL19-Cre; IL23R−/−; Regnase1+/- | 6–12 | M-F | MOG with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, pertussis toxin on/OT-II CD4+ T cells with OVA/DSS | 2 | ||||||||
| Masters et al. [28] | 2019 | Mice C57BL/6 | RAG−/−; CD45.1 | 2–4 m and 19–21 m | M | Influenza | NR | |||||||||||||
| FRCs influence the CD8 T cells fate | Kasinath et al. [25] | LN; spleen | CD4+ T cells | No selection performed | NR | CD45, CD3, CD4, CD44, CD62L, IL-17A | Schaeuble et al. [29] | 2019 | Mice C57BL/6 | NOS2−/−; OT-1; COX2−/−, COX2ΔCCL19Cre, and ROSA26-EYFPCCL19Cre | ≥6 | NR | OVA and poly (I:C) | 4 | ||||||
| Dubrot et al. [30] | 2018 | Mice C57BL/6 | CIITA−/−; pIV−/−; K14 TGP IVKO; RAG2−/− PROX-1-Cre MHC-IIfl | >12m | NR | Tamoxifen; IFN-γ and FTY720 | 4 (Twice/day); 6 | |||||||||||||
| Knoblich et al. [31] | 2018 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kasinath et al. [25] | Mouse FRC depletion and treatment with anti-PDPN antibody | Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (GN) | 3 d | FC and gene expression | Removal of kidney-draining lymph nodes, depletion of fibroblastic reticular cells, and treatment with anti-podoplanin antibodies each resulted in the reduction of kidney injury in GN. | Kelch et al. [26] | LN | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||
| Role of FRCs and PDPN expression in GN | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kelch et al. [26] | 3D imaging and topological mapping | NA | NA | EVIS imaging and confocal microscopy | T cell zones showed homogeneous branching, conduit density was significantly higher in the superficial T cell zone compared with the deep zone. Although the biological significance of this structural segregation is still unclear, independent reports have pointed to an asymmetry in cell positioning in both zones. Naive T cells tend to occupy the deep TCZ, whereas memory T cells preferentially locate to the superficial zones, and innate effector cells can often be found in the interfollicular regions. |
FRC conduits and their distribution inside LNs | Majumder et al. [27] | LN | T and B cells | NR | ||||||||||
| Majumder et al. [27 | NR | ] | Metabolic assay | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis | 7 d | FC, immunoblotting, siRNA transfection | During Th17 differentiation in LNs, IL-17 signals to FRCs and impacts LN stromal organization by promoting FRC activation through a switch on their phenotype from quiescence to highly metabolic. | FRCs are impacted by metabolic alterations driven by IL-17 | ||||||||||||
| Masters et al. [28] | FRC-mediated T cell proliferation inhibition and T cell survival assays | Aging and influenza infection | NR | FC | Age-related changes in LN stromal cells may have the largest impact on the initiation of the immune response to influenza infection, and may be a factor contributing to delayed T cell responses to this virus. | Aging impacts the adaptive anti-viral immune response initiation in LN | Human | Cadaveric donors | NA | NA | NAFOXP3hCD2xRAG2−/− xD011.10 | NR | M-F | NA | NA | |||||
| Valencia et al. [36] | 2017 | Human | Brain-dead organ donors | NA | M-F | NA | NA | |||||||||||||
| Yu, M. et al. [37] | 2017 | Mice C57BL/6 and Human | PTGS2Y385F/Y385F; OVA-specific CD8 (OT-I); CD4 (OT-II) | 4–6 | NR | DC-vaccine | 1.5 | |||||||||||||
| Gil-Cruz et al. [38] | 2016 | Mice C57BL/6N or C57BL/6N-Tg or R26R-EYFP | Myd88−/−; TLR7−/−; CCL19-Cre | 8–10 | NR | MHV A59; Citrobacter rodentium | 12; 6 | |||||||||||||
| Novkovic et al. [39] | 2016 | Mice C57BL/6N or C57BL/6N-Tg | CCL19-Cre; iDTR | 6–9 | NR | DT | 3 and 5 | |||||||||||||
| Dertschnig et al. [19] | Peripheral; mesenteric | Enzymatic | DNase; Liberase | NC | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | NR | |||||||||||||
| Eom et al. [20] | Axillary; inguinal; cervical; mesenteric; mediastinum | Enzymatic | DNase I; Liberase DH | RPMI-1640 | CD45, CD31, PDPN | NR | NR | |||||||||||||
| Gonzalez et al. [21] | Skin-draining (brachial; axillary; inguinal); Pancreatic | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; DNase I; Dispase II | NR | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | NR | |||||||||||||
| Knop et al. [22] | Peripheral; mesenteric | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; Dispase II; DNase I; Latrunculin B | RPMI-1640 | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | >73.3 | |||||||||||||
| Perez-Shibayama et al. [23] | Inguinal | Enzymatic | Collagenase F; DNase I | RPMI | NR | NR | NR | Royer et al. [40] | 2016 | Mice C57BL/6 or Gbt-1.1 | CXCL10−/−; CXCR3−/−; STING−/−; CD18−/− | 6–12 | M-F | HSV-1 | NR | |||||
| Takeda et al. [41] | 2016 | Mice C57BL/6J | LPAR2−/−; ENPP2-flox, CCCL19-Cre, LPAR5−/− | |||||||||||||||||
| Kasinath et al. [25] | Kidney | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||||
| Kelch et al. [26] | Popliteal; mesenteric; Inguinal | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||||
| Majumder et al. [27] | Mesenteric; inguinal | Enzymatic | DNase I; Liberase; Dispase | RPMI | CD45; CD31; PDPN; | Microbeads isolation | >98 | |||||||||||||
| Masters et al. [28] | Mesenteric; popliteal |
Enzymatic | Liberase TL; Benzonuclease | RPMI-1640 | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Microbeads isolation | >90 | |||||||||||||
| Schaeuble et al. [29] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Schaeuble et al. [29Peripheral (axillary, brachial, inguinal) | ] | Nos2Enzymatic | −/−Collagenase IV; DNase I | DMEM (2% FCS) | , COX2−/−CD45; CD31; PDPN | mice and FRC/T cell co-cultureMicrobeads isolation | ≥90 | |||||||||||||
| COX/Prostaglandin E2 pathway | 4 d | FC | FRCs constitutively express high levels of COX2 and its product PGE2, thereby identified as a mechanism of T cell proliferation control. | PGE2 and COX2 pathways in FRCs are implicated in the control of T cell proliferation | Dubrot et al. [30] | Skin-draining | Enzymatic | Collagenase D; DNase I | HBSS | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | NR | NA | |||||||
| Dubrot et al. [30] | Adoptive transfer T cells in RAG−/− mice and Treg suppression assay | MHC II-induced expression by FRC and LEC and its impact on autoimmunity | 5 d | FC | LNSCs inhibit autoreactive T-cell responses by directly presenting antigens through endogenous MHCII molecules. | Control of peripheral tolerance in autoimmunity | Knoblich et al. [31] | NR | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; DNase I; Dispase | α-MEM (10% FBS) | CD45; PDPN | NR | 99 | ||||||
| Knoblich et al. [31] | T cell and CAR T cell activation assay | COX/Prostaglandin E2, iNOS, IDO and TGF-β pathways in FRCs, | NA | FC and RNA sequencing | Maaraouf et al. [32] | |||||||||||||||
| Maaraouf et al. [322018 | ] | KidneyMice C57BL/6 | CCL19-Cre; iDTR; RAG1−/− | NR | NR | DT; LTβr-Ig | 1; 2 | |||||||||||||
| FRCs block proliferation and modulate differentiation of newly activated naïve human T cells, without requiring T cell feedback. | FRCs used several pathways to control T cell proliferation | |||||||||||||||||||
| Maaraouf et al. [32] | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; DNase I; Dispase II | DMEM (10% FBS) | FRC labeling and injection into mice | Ischemic-reperfusion injury (IRI)CD45; CD31; PDPN | NR | NR | NR | FC, electron and confocal microscopy | Depletion of FRCs reduced T cell activation in the kidney LNs and ameliorated renal injury in acute IRI. | Role of FRCs in IRI | Chung et al. [33] | 2017 | Mice BALB/c or C57BL/6 | ||||||
| Chung et al. [33 | TgMx1-Cre; DLL1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chung et al. [33] | fl/fl | ; DLL4fl/fl; NOTCH2fl/fl; RAG1−/− | 6–10 or 8–12 | M-F | FRC/T cell co-culturepoly (I:C)/8.5-9 Gy; poly (I:C)/6 Gy irradiation |
0.16; 0.12 | ||||||||||||||
| ] | Peripheral (cervical, axial, brachial, inguinal) | GvHD | 4 h and 3 h | FC | FRCs delivered NOTCH signals to donor alloreactive T cells at early stages after allo-BMT to program the pathogenicity of these T cells. | Role of FRC NOTCH-signaling in activating alloreactive T cells | ||||||||||||||
| Gao et al. [34] | FRC expression and secretion of Interleukin 7 | Tumor-draining LNs | NA | FC | LN tumor-infiltrating cells decreased the FRC population and IL-7 secretion, leading to declined numbers of T cells in TDLNs. This may partly explain the weakened ability of immune surveillance in TDLNs. | Role of IL-7 secretion by FRCs and its impact on tumor-draining LNs | ||||||||||||||
| Pazstoi et al. [35] | Treg induction in presence of FRC microvesicles. | FRC microvesicles (MVEs) | NA | FC and RNA sequencing | Stromal cells originating from LNs contributed to peripheral tolerance by fostering de novo Treg induction by MVEs carrying high levels of TGF-β. | Role of FRC MVEs in inducing peripheral tolerance | ||||||||||||||
| Valencia et al. [36] | FRC/T cell co-culture | COX 2/Prostaglandin E2, iNOS, IDO and TGF-β pathways in FRCs | 6 h | FC | COX2 expression was detected in human FRCs but was not considerably upregulated after inflammatory stimulation, concluding that human and murine FRCs would regulate T lymphocytes responses using different mechanisms. | Role of FRCs integrating innate and adaptive immune responses and balancing tolerance and immunogenicity | ||||||||||||||
| Yu, M. et al. [37] | FRC/T cell co-culture | COX 2/Prostaglandin E2 pathway in FRCs | NA | FC, WB | Hyperactivity of COX-2/PGE2 pathways in FRCs is a mechanism that maintains peripheral T cell tolerance during homeostasis. | PGE2 and COX2 pathways in FRCs are implicated in the control of T cell proliferation. | ||||||||||||||
| Gil-Cruz et al. [38] | ILC1 and NK cells regulation | FRC secretion of IL-15 | 3 h | FC | FRC secretion of IL-15 regulates homeostatic ILC1 and NK cell maintenance. | Role of FRCs in innate in immunity | ||||||||||||||
| Novkovic et al. [39] | Royer et al. [40] | Mandibular | Mechanical disruption | NR | RPMI-1640 (10% FBS) | NR | NR | NR | ||||||||||||
| Takeda et al. [41] | Mesenteric; peripheral; brachial | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; Dispase; DNase I | RPMI-1640 | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | NR |
| Ref. | Source of Cells | Cell Type | Separation Technique | Immune Cell Preservation Solution and Supplementation | Immune Cell Immunophenotypic Characterization | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aparicio-Domingo et al. [18 | |||||||||||||||
| RPMI | |||||||||||||||
| CD45, CD45.2, CD4, B220, IL-17A, IL-17R | |||||||||||||||
| Masters et al. [ | |||||||||||||||
| 28 | |||||||||||||||
| ] | LN; peripheral blood | CD8+ T | CD8 isolation by negative selection (Microbeads—MojoSort) | NR | CD45, CD45.1, CD45.2, CD69, CD8α | ||||||||||
| Schaeuble et al. [29] | LN; spleen | T cells | No selection performed | RPMI | CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8α, CD44, CD62L, CD279, FoxP3, CD25 | ||||||||||
| Dubrot et al. [30] | LN; spleen | T cells, B cells, Treg, and DC | Pan T isolation by negative selection (MicroBeads—Myltenyi) |
NR | CD45, CD44, CD3, CD4, CD8α, FOXp3, Ly5.1, CD11b, CD19, CD25, CD62L, PDCA-1, PD-1, IL-17, IFNγR | ||||||||||
| Knoblich et al. [31] | LN; tonsils | T cells | Pan T isolation by negative selection (MicroBeads—Myltenyi) |
NR | CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD62L, CD27, CD45RO, CD25 | ||||||||||
| Maaraouf et al. [32] | Spleen | T cells | Pan T isolation by negative selection (MicroBeads—Myltenyi) |
NR | CD45, CD4 | Enzymatic | Collagenase IV; DNase I | DMEM (2% FBS) | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | |||||
| Chung et al. [ | NR | 33] | Spleen; peripheral blood | T cells, B cells, FDCs, Treg, and DCs | T cell Thy.1 selection (Microbeads—StemCells Technologies) |
NA | CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8, FOXp3, CD157, CD19, B220, CD44, CD62L, CD11c, CD11b, CD169, CD21/35, F4/80, TCRβ | Gao et al. [34] | 2017 | Mice C57BL/6 and Human | Colon cancer | 6 | F | Lewis Long carcinoma cells | NA |
| Gao et al. [34] | Inguinal | Enzymatic | Collagenase IV; DNase I | RPMI-1640 (2% FBS) | |||||||||||
| Gao et al. [ | CD45; CD31; PDPN | 34] | LN | T cells | NRNA | NRNA | CD45, CD4, CD8 | Pazstoi et al. [35] | |||||||
| Pazstoi et al. [35]2017 | Mesenteric | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; Dispase; DNase I | RPMI-1640 | CD45; CD31; PDPN | Cell sorting | 91–97 | ||||||||
| Pazstoi et al. [35] | LN | T cells | CD4 positive selection (Microbeads—Myltenyi) |
EX VIVO | CD45, CD45.2, CD4, CD2, CD9, CD24, CD25, CD63 | Valencia et al. [36] | Mesenteric | Mechanical disruption | NR | RPMI-1640 | CD45, CD31, PDPN | NR | |||
| Valencia et al. [ | NR | ||||||||||||||
| 36] | LN | CD4+ T cells | CD4 naïve T cell negative selection (Microbeads—Myltenyi) |
RPMI (10% FCS) | CD45, CD44, CD4 | Yu, M. et al. [37] | Axillary; brachial; inguinal | ||||||||
| Yu, M. et al. [37 | Enzymatic | ] | LNCollagenase P; Dispase; DNase I | DMEM (10% FBS) | T cells | Pan T cell negative selection (Microbeads—StemCells Technologies)CD45; CD31; PDPN |
Cell sorting | >95 | |||||||
| RPMI (10% FBS) | CD45, CD45.1, CD45.2, CD3, CD4, CD8α, CD25, CD69, CD44 | Gil-Cruz et al. [38] | Mesenteric | Enzymatic | |||||||||||
| Gil-Cruz et al. [38] | PP; LN | T cells, B cells, NK cells, Treg, and ILCsCollagenase D; DNase I | RPMI-1640 (2% FCS) | CD45; CD31; PDPN | NR | RPMI (10% FCS)Cell sorting | CD45, CD3e, CD4, CD8α, EOMES, FoxP3, B220, CD19, CD127, CD62L, CD44, CD69, F4/80, IL-17A, IL-7Rα, GATA3, RORγt, IL-15RαIL-15Rβ, NKp46, NK1.1NR | ||||||||
| Novkovic et al. [39] | Inguinal | Enzymatic | Collagenase P; DNase I | RPMI (2% FCS) | PDPN | NA | |||||||||
| Novkovic et al. [39] | LN; Spleen | DCs and T cells | NRNA | RPMI (2% FCS) | CD45, CD3, CD8, CD4, CD11c, MHCII | ||||||||||
| FRC network topological analysis | FRC network | NA | Intravital TPM with morphometric 3D reconstitution analysis. | Physical scaffold of LNs formed by the FRC network is critical for the maintenance of LN functionality. | FRC network disruption impacts the immune response | Royer et al. [40] | SLOs | CD8+ T cells | CD8 positive selection (Microbeads—Myltenyi) | RPMI (10% FBS) | CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8 | ||||
| Royer et al. [40] | Adoptive transfer of T cells and T cell response to herpesvirus-associated lymphadenitis | HSV-1 | 4 h | FC | Dissemination of the virus to secondary lymphoid organs impairs HSV-specific CD8+ T cell responses by driving pathological alterations to the FRCs conduit system, resulting in fewer HSV-specific CD8+ T cells in circulation. | Role of FRC in virus-specific T CD8 response | ; LPAR6−/− | 8–12 | NR | CD4+ T cells labeled with CMTMR; LTβR-Fc | 0.6; 1.04; 28 |
| Takeda et al. [ | ||||
| 41 | ||||
| ] | ||||
| LN; Spleen | ||||
| T cells, B cells | ||||
| Takeda et al. [ | ||||
| 41 | ||||
| CD4 naïve T cell negative selection | ||||
| (Microbeads—Myltenyi) | ||||
| RPMI | ||||
| ] | ||||
| Lymphocyte migration | ||||
| Ablation of LPA-producing ectoenzyme autotaxin in FRCs | NA | FC, IMS, Intravital TPM | LPA produced by LN FRCs acts locally to LPA2 to induce T cell motility. | Role of FRCs in T cell local migration |
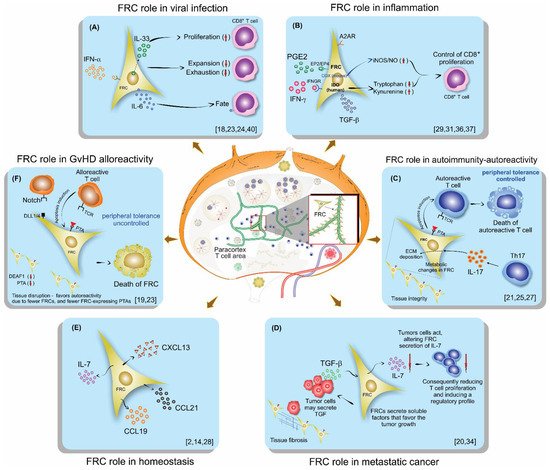
References
- Denton, A.E.; Carr, E.J.; Magiera, L.P.; Watts, A.J.B.; Fearon, D.T. Embryonic FAP+ lymphoid tissue organizer cells generate the reticular network of adult lymph nodes. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2242–2252.
- Link, A.; Vogt, T.K.; Favre, S.; Britschgi, M.R.; Acha-Orbea, H.; Hinz, B.; Cyster, J.G.; Luther, S.A. Fibroblastic reticular cells in lymph nodes regulate the homeostasis of naive T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1255–1265.
- Sixt, M.; Kanazawa, N.; Selg, M.; Samson, T.; Roos, G.; Reinhardt, D.P.; Pabst, R.; Lutz, M.B.; Sorokin, L. The conduit system transports soluble antigens from the afferent lymph to resident dendritic cells in the T cell area of the lymph node. Immunity 2005, 22, 19–29.
- Martinez, V.G.; Pankova, V.; Krasny, L.; Singh, T.; Makris, S.; White, I.J.; Benjamin, A.C.; Dertschnig, S.; Horsnell, H.L.; Kriston-Vizi, J.; et al. Fibroblastic Reticular Cells Control Conduit Matrix Deposition during Lymph Node Expansion. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2810–2822.
- Luther, S.A.; Vogt, T.K.; Siegert, S. Guiding blind T cells and dendritic cells: A closer look at fibroblastic reticular cells found within lymph node T zones. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 138, 9–11.
- Mueller, S.N.; Ahmed, R. Lymphoid stroma in the initiation and control of immune responses. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 224, 284–294.
- Alvarenga, H.G.; Marti, L. Multifunctional Roles of Reticular Fibroblastic Cells: More Than Meets the Eye? J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 402038.
- Fletcher, A.L.; Acton, S.E.; Knoblich, K. Lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 350–361.
- Severino, P.; Palomino, D.T.; Alvarenga, H.; Almeida, C.B.; Pasqualim, D.C.; Cury, A.; Salvalaggio, P.R.; De Vasconcelos Macedo, A.L.; Andrade, M.C.; Aloia, T.; et al. Human Lymph Node-Derived Fibroblastic and Double-Negative Reticular Cells Alter Their Chemokines and Cytokines Expression Profile Following Inflammatory Stimuli. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 141.
- Vega, F.; Coombes, K.R.; Thomazy, V.A.; Patel, K.; Lang, W.; Jones, D. Tissue-specific function of lymph node fibroblastic reticulum cells. Pathobiol. J. Immunopathol. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 73, 71–81.
- Frontera, V.; Arcangeli, M.L.; Zimmerli, C.; Bardin, F.; Obrados, E.; Audebert, S.; Bajenoff, M.; Borg, J.P.; Aurrand-Lions, M. Cutting edge: JAM-C controls homeostatic chemokine secretion in lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells expressing thrombomodulin. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 603–607.
- Kaldjian, E.P.; Gretz, J.E.; Anderson, A.O.; Shi, Y.; Shaw, S. Spatial and molecular organization of lymph node T cell cortex: A labyrinthine cavity bounded by an epithelium-like monolayer of fibroblastic reticular cells anchored to basement membrane-like extracellular matrix. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 1243–1253.
- Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Malhotra, D.; Fletcher, A.L.; Acton, S.E.; Elpek, K.G.; Tayalia, P.; Collier, A.-r.; Turley, S.J. Regulated release of nitric oxide by nonhematopoietic stroma controls expansion of the activated T cell pool in lymph nodes. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1096–1104.
- Fletcher, A.L.; Malhotra, D.; Turley, S.J. Lymph node stroma broaden the peripheral tolerance paradigm. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 12–18.
- Gardner, J.M.; Devoss, J.J.; Friedman, R.S.; Wong, D.J.; Tan, Y.X.; Zhou, X.; Johannes, K.P.; Su, M.A.; Chang, H.Y.; Krummel, M.F.; et al. Deletional tolerance mediated by extrathymic Aire-expressing cells. Science 2008, 321, 843–847.
- Nadafi, R.; Gago de Graça, C.; Keuning, E.D.; Koning, J.J.; de Kivit, S.; Konijn, T.; Henri, S.; Borst, J.; Reijmers, R.M.; van Baarsen, L.G.M.; et al. Lymph Node Stromal Cells Generate Antigen-Specific Regulatory T Cells and Control Autoreactive T and B Cell Responses. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4110–4123.
- Krausgruber, T.; Fortelny, N.; Fife-Gernedl, V.; Senekowitsch, M.; Schuster, L.C.; Lercher, A.; Nemc, A.; Schmidl, C.; Rendeiro, A.F.; Bergthaler, A.; et al. Structural cells are key regulators of organ-specific immune responses. Nature 2020, 583, 296–302.
- Aparicio-Domingo, P.; Cannelle, H.; Buechler, M.B.; Nguyen, S.; Kallert, S.M.; Favre, S.; Alouche, N.; Papazian, N.; Ludewig, B.; Cupedo, T.; et al. Fibroblast-derived IL-33 is dispensable for lymph node homeostasis but critical for CD8 T-cell responses to acute and chronic viral infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 51, 76–90.
- Dertschnig, S.; Evans, P.; Santos, E.S.P.; Manzo, T.; Ferrer, I.R.; Stauss, H.J.; Bennett, C.L.; Chakraverty, R. Graft-versus-host disease reduces lymph node display of tissue-restricted self-antigens and promotes autoimmunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1896–1911.
- Eom, J.; Park, S.M.; Feisst, V.; Chen, C.J.J.; Mathy, J.E.; McIntosh, J.D.; Angel, C.E.; Bartlett, A.; Martin, R.; Mathy, J.A.; et al. Distinctive Subpopulations of Stromal Cells Are Present in Human Lymph Nodes Infiltrated with Melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 990–1003.
- Gonzalez Badillo, F.; Zisi Tegou, F.; Masina, R.; Wright, S.; Scully, M.; Harwell, L.; Lupp, M.; Postigo-Fernandez, J.; Creusot, R.J.; Tomei, A.A. Tissue-Engineered Stromal Reticula to Study Lymph Node Fibroblastic Reticular Cells in Type I Diabetes. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2020, 13, 419–434.
- Knop, L.; Deiser, K.; Bank, U.; Witte, A.; Mohr, J.; Philipsen, L.; Fehling, H.J.; Müller, A.J.; Kalinke, U.; Schüler, T. IL-7 derived from lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells is dispensable for naive T cell homeostasis but crucial for central memory T cell survival. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 846–857.
- Perez-Shibayama, C.; Islander, U.; Lütge, M.; Cheng, H.W.; Onder, L.; Ring, S.S.; de Martin, A.; Novkovic, M.; Colston, J.; Gil-Cruz, C.; et al. Type I interferon signaling in fibroblastic reticular cells prevents exhaustive activation of antiviral CD8+ T cells. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5.
- Brown, F.D.; Sen, D.R.; LaFleur, M.W.; Godec, J.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Schildberg, F.A.; Kim, H.J.; Yates, K.B.; Ricoult, S.J.H.; Bi, K.; et al. Fibroblastic reticular cells enhance T cell metabolism and survival via epigenetic remodeling. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1668–1680.
- Kasinath, V.; Yilmam, O.A.; Uehara, M.; Jiang, L.; Ordikhani, F.; Li, X.; Salant, D.J.; Abdi, R. Activation of fibroblastic reticular cells in kidney lymph node during crescentic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 310–320.
- Kelch, I.D.; Bogle, G.; Sands, G.B.; Phillips, A.R.J.; LeGrice, I.J.; Dunbar, P.R. High-resolution 3D imaging and topological mapping of the lymph node conduit system. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000486.
- Majumder, S.; Amatya, N.; Revu, S.; Jawale, C.V.; Wu, D.; Rittenhouse, N.; Menk, A.; Kupul, S.; Du, F.; Raphael, I.; et al. IL-17 metabolically reprograms activated fibroblastic reticular cells for proliferation and survival. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 534–545.
- Masters, A.R.; Hall, A.; Bartley, J.M.; Keilich, S.R.; Lorenzo, E.C.; Jellison, E.R.; Puddington, L.; Haynes, L. Assessment of Lymph Node Stromal Cells as an Underlying Factor in Age-Related Immune Impairment. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 1734–1743.
- Schaeuble, K.; Cannelle, H.; Favre, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Oberle, S.G.; Speiser, D.E.; Zehn, D.; Luther, S.A. Attenuation of chronic antiviral T-cell responses through constitutive COX2-dependent prostanoid synthesis by lymph node fibroblasts. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000072.
- Dubrot, J.; Duraes, F.V.; Harlé, G.; Schlaeppi, A.; Brighouse, D.; Madelon, N.; Göpfert, C.; Stokar-Regenscheit, N.; Acha-Orbea, H.; Reith, W.; et al. Absence of MHC-II expression by lymph node stromal cells results in autoimmunity. Life Sci. Alliance 2018, 1, e201800164.
- Knoblich, K.; Cruz Migoni, S.; Siew, S.M.; Jinks, E.; Kaul, B.; Jeffery, H.C.; Baker, A.T.; Suliman, M.; Vrzalikova, K.; Mehenna, H.; et al. The human lymph node microenvironment unilaterally regulates T-cell activation and differentiation. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2005046.
- Maarouf, O.H.; Uehara, M.; Kasinath, V.; Solhjou, Z.; Banouni, N.; Bahmani, B.; Jiang, L.; Yilmam, O.A.; Guleria, I.; Lovitch, S.B.; et al. Repetitive ischemic injuries to the kidneys result in lymph node fibrosis and impaired healing. JCI Insight 2018, 3.
- Chung, J.; Ebens, C.L.; Perkey, E.; Radojcic, V.; Koch, U.; Scarpellino, L.; Tong, A.; Allen, F.; Wood, S.; Feng, J.; et al. Fibroblastic niches prime T cell alloimmunity through Delta-like Notch ligands. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1574–1588.
- Gao, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Guo, B.; Zhu, B. Disrupted fibroblastic reticular cells and interleukin-7 expression in tumor draining lymph nodes. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2954–2960.
- Pasztoi, M.; Pezoldt, J.; Beckstette, M.; Lipps, C.; Wirth, D.; Rohde, M.; Paloczi, K.; Buzas, E.I.; Huehn, J. Mesenteric lymph node stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles contribute to peripheral de novo induction of Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 2142–2152.
- Valencia, J.; Jiménez, E.; Martínez, V.G.; Del Amo, B.G.; Hidalgo, L.; Entrena, A.; Fernández-Sevilla, L.M.; Del Río, F.; Varas, A.; Vicente, Á.; et al. Characterization of human fibroblastic reticular cells as potential immunotherapeutic tools. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 640–653.
- Yu, M.; Guo, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Yang, W.; Bollag, R.; Cui, Y. Fibroblastic reticular cells of the lymphoid tissues modulate T cell activation threshold during homeostasis via hyperactive cyclooxygenase-2/prostaglandin E(2) axis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3350.
- Gil-Cruz, C.; Perez-Shibayama, C.; Onder, L.; Chai, Q.; Cupovic, J.; Cheng, H.W.; Novkovic, M.; Lang, P.A.; Geuking, M.B.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. Fibroblastic reticular cells regulate intestinal inflammation via IL-15-mediated control of group 1 ILCs. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1388–1396.
- Novkovic, M.; Onder, L.; Cupovic, J.; Abe, J.; Bomze, D.; Cremasco, V.; Scandella, E.; Stein, J.V.; Bocharov, G.; Turley, S.J.; et al. Topological Small-World Organization of the Fibroblastic Reticular Cell Network Determines Lymph Node Functionality. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002515.
- Royer, D.J.; Conrady, C.D.; Carr, D.J. Herpesvirus-Associated Lymphadenitis Distorts Fibroblastic Reticular Cell Microarchitecture and Attenuates CD8 T Cell Responses to Neurotropic Infection in Mice Lacking the STING-IFNα/β Defense Pathways. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2338–2352.
- Takeda, A.; Kobayashi, D.; Aoi, K.; Sasaki, N.; Sugiura, Y.; Igarashi, H.; Tohya, K.; Inoue, A.; Hata, E.; Akahoshi, N.; et al. Fibroblastic reticular cell-derived lysophosphatidic acid regulates confined intranodal T-cell motility. eLife 2016, 5, e10561.
- Krishnamurty, A.T.; Turley, S.J. Lymph node stromal cells: Cartographers of the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 369–380.
- Talemi, S.R.; Höfer, T. Antiviral interferon response at single-cell resolution. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 285, 72–80.
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457.
- Chai, Q.; Onder, L.; Scandella, E.; Gil-Cruz, C.; Perez-Shibayama, C.; Cupovic, J.; Danuser, R.; Sparwasser, T.; Luther, S.A.; Thiel, V.; et al. Maturation of lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells from myofibroblastic precursors is critical for antiviral immunity. Immunity 2013, 38, 1013–1024.
- Thompson, H.L.; Smithey, M.J.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Jeftić, I.; Jergović, M.; White, S.E.; Currier, N.; Lang, A.M.; Okoye, A.; Park, B.; et al. Lymph nodes as barriers to T-cell rejuvenation in aging mice and nonhuman primates. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12865.
- Mueller, S.N.; Matloubian, M.; Clemens, D.M.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Gangappa, S.; Larsen, C.P.; Ahmed, R. Viral targeting of fibroblastic reticular cells contributes to immunosuppression and persistence during chronic infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15430–15435.
- Zeng, M.; Smith, A.J.; Wietgrefe, S.W.; Southern, P.J.; Schacker, T.W.; Reilly, C.S.; Estes, J.D.; Burton, G.F.; Silvestri, G.; Lifson, J.D.; et al. Cumulative mechanisms of lymphoid tissue fibrosis and T cell depletion in HIV-1 and SIV infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 998–1008.
- Malhotra, D.; Fletcher, A.L.; Turley, S.J. Stromal and hematopoietic cells in secondary lymphoid organs: Partners in immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 251, 160–176.
- Siegert, S.; Luther, S.A. Positive and negative regulation of T cell responses by fibroblastic reticular cells within paracortical regions of lymph nodes. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 285.
- Postigo-Fernandez, J.; Farber, D.L.; Creusot, R.J. Phenotypic alterations in pancreatic lymph node stromal cells from human donors with type 1 diabetes and NOD mice. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2040–2051.
