Alkaloids are an important group of specialized nitrogen metabolites with a wide range of biochemical and pharmacological effects. Since the first publication on lycorine in 1877, more than 650 alkaloids have been extracted from Amaryllidaceae bulbous plants and clustered together as the Amaryllidaceae alkaloids (AAs) family.
- Amaryllidaceae alkaloids
- specialized metabolism
- biosynthesis
- antitumor
- anti-cholinesterase
- antiviral
- antiparasitic
1. Classification of Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids
To date, more than 650 AAs have been reported, and their chemical library is still expanding [1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14]. Although diverse in structure, this plethora of AAs are categorized together as they share a common initial synthesis pathway. In previous literature, large numbers of AAs have been classified into different groups according to chemical characteristics, e.g., molecular skeleton and ring structure [1][15][16][17]. For this review, AAs were classified into 10 main groups instead, following a biochemical classification based on biogenetic lineage and ring type, to easily track the biosynthetic pathways [18] (
,
). For example, haemanthamine and crinine were grouped together with respect to their biosynthetic origin and ring type even if they were previously categorized separately [19]. Some AAs with ring types different than those of group I to IX were classified in group X (or other-types) because they follow distinct biogenetic pathway, or because we cannot clearly indicate their biosynthetic origin (
). Galanthindole contains a non-fused indole ring and might represent an artifact of homolycorine- or of pretazettine-type derivatives [20]. Ismine is considered to be a catabolic product from the haemanthamine-type skeleton, thus not a specific type of AA [21]. The latter examples demand further investigation on biogenetic origin and are not yet included on any particular type of AA.
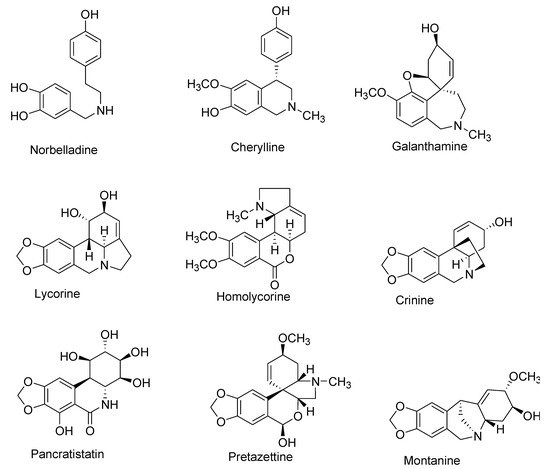
Representative Amaryllidaceae alkaloid structure for the main Amaryllidaceae alkaloid (AA)-types.
| Number | Type Name | Ring-Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Norbelladine | N | -(3,4-Dioxybenzyl)-4-oxyphenethylamine |
| II | Cherylline | Tetrahydroisoquinoline | |
| III | Galantamine | 6H-Benzof,f]-2-benzazepine | |
| IV | Lycorine | Pyrrolo[d,e]phenanthridine | |
| V | Homolycorine | 2-Benzopyrano-[3,4-g]indole | |
| VI | Crinine | 5,10b-Ethanophenanthridine | |
| VII | Narciclasine | Lycoricidine | |
| VIII | Pretazettine | 2-Benzopyrano [3,4-c]indole | |
| IX | Montanine | 5,11-Methanomorphanthridine | |
| X | Other | Different ring types and biogenetic origin |
Main types of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids grouped according to their ring type and biosynthetic origin.
Some types of AA, such as plicamine and secoplicamine, are extracted in trace amounts exclusively from specific Amaryllidaceae species, such as Zephyranthes, but are classified in type X as they are rare, dinitrogenous members of AA, with a distinct biosynthetic linage [21][22][23][24]. Mesembrine alkaloids (also known as sceletium) have a distinct biosynthetic pathway, without norbelladine as key intermediate, they are usually extracted from Aizoaceae, but can be collected from several species of Amaryllidaceae [10]. Here, we concentrated exclusively on AAs that were discovered since 2015; hence, some alkaloids families are not represented.
2. Biosynthesis of Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids
Biosynthesis of AAs with their diverse and complex carbon skeleton involves a sequence of biochemical reactions such as oxidation, reduction, hydroxylation, methylation, phenol-phenol coupling, and oxide bridge formation. Although the complete AA biosynthetic pathway has not yet been elucidated, several steps with catalyzing enzymes can be predicted on the basis of the reaction types and enzyme families [25][18][26][27]. Here, we briefly discuss the AAs biosynthesis pathway and the enzymes involved.
Although novel AAs are still being discovered, radiolabeling experiments demonstrated that they all share a common biochemical pathway with a key intermediate; norbelladine, which is subsequently
-methylated, and then undergoes cyclization to give diverse basic skeletons of AAs (
;
) [28][29][30][31][32][33][34]. Norbelladine originates from the condensation of tyramine and 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde (3,4-DHBA), molecules derived from the aromatic amino acids
-tyrosine and
-phenylalanine, respectively (
). The enzyme responsible for tyramine biosynthesis is the tyrosine decarboxylase (TYDC) (
). Two gene transcript variants of TYDC, named
and
, were identified from the transcriptome of different Amaryllidaceae species including
.
[35],
[36],
[37], and
[38].
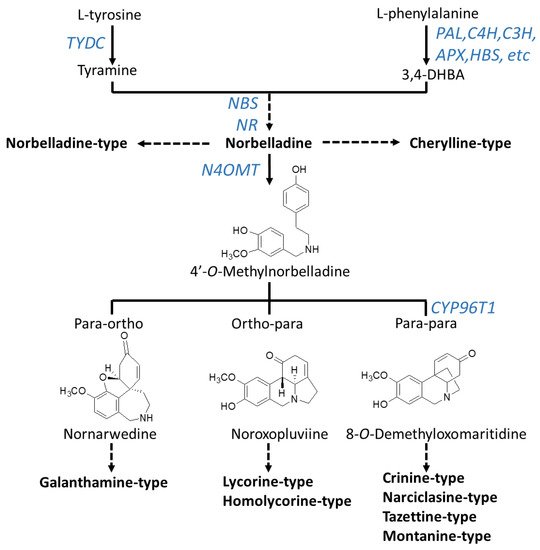
Biosynthesis pathway to major types of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids. Arrows without labeling reflect chemical reactions that have not been enzymatically characterized. Enzymes that have been identified are labeled in blue. A solid arrow symbolizes one enzymatic step whereas a broken arrow shows multiple enzymatic reactions. Chemical structures of precursors were added to clarify the regioselective phenol-phenol’ coupling reaction. Enzyme abbreviations: PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; C3H, coumarate 3-hydroxylase; APX, ascorbate peroxidase; HBS, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde synthase; TYDC, tyrosine decarboxylase; NBS, norbelladine synthase; NR, noroxomaritidine reductase; CYP96T1, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase 96T1.
The pathway leading to 3,4-DHBA from
phenylalanine involves a series of reactions known as the phenylpropanoid pathway which is phylogenetically spread in most plant species. In Amaryllidaceae, using precursor feeding experiments, it was reported that
-cinnamic acid,
-coumaric acid, and caffeic acid were intermediate products that ultimately led to 3,4-DHBA [39][40]. Specifically,
phenylalanine is converted to
-cinnamic acid by the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) (
). Several
gene transcripts were identified and characterized from different species of Amaryllidaceae [35][36][37][41][42][43]. Interestingly, two main phylogenetic
clusters were identified; the first one contained
transcripts ubiquitously expressed in Amaryllidaceae whereas the second cluster contained
transcripts with expression highest and correlating with organs where AAs accumulated [18]. This indicates that different
transcripts encode enzymes with distinct functions in the phenylpropanoid pathway and it suggests the role of the latter cluster in AA biosynthesis. Next,
-cinnamic acid is hydroxylated to form
-coumaric acid by the cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H), a cytochrome P450 of the CYP73 subfamily (cinnamate 4-hydroxylase, C4H) [44][45]. Transcripts encoding C4H were reported from several Amaryllidaceae species [35][36][37][43] including
from
, which was characterized as producing a region-specific 4-hydroxylation of
-cinnamic acid [43]. The reactions catalyzed by PAL and C4H are also crucial steps in the biosynthesis of many phenylpropanoids such as flavonoids, linins, coumarins and stilbenes. From there, the enzymes and order of reactions leading to 3,4-DHBA are not known however it is hypothesized that it may involve the CYP98A3 named coumarate 3-hydroxylase (C3H) and/or the ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and/or the 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde synthase (HBS) [18] (
). A few studies have reported on the presence of phenolic acids such as caffeic,
-coumaric, and ferulic acids in
,
and
[46][47][48]. In addition, 3,4-DHBA was detected in plants outside the Amaryllidaceae family [49]. Collectively, this suggest that the initial reactions and enzymes of the phenylpropanoid pathway participate in the synthesis of the AA precursor 3,4-DHBA.
The condensation of tyramine and 3,4-DHBA leads to the formation of norbelladine catalyzed by the norbelladine synthase (NBS) and/or the noroxomaritidine reductase (NR) or a combination of these enzymes [50][51]. Norbelladine is the precursor to all AAs. For example, norbelladine can undergo different biochemical reactions such as methylation, hydroxylation, dehydration, cyclization and tautomerization to form cherylline-type AAs (
). Alternatively, norbelladine can be methylated by the norbelladine 4′-
-methyltransferase (N4OMT) to form 4′-
-methylnorbelladine [52]. 4′-
-methylnorbelladine cyclization in a regioselective phenol-phenol oxidative coupling forms the ortho-para’, para-para’ or para-ortho’ C-C coupled producing the various structural types of AAs (
). The para-ortho’ C-C coupling leads to galantamine-type AAs whereas the ortho-para’ phenol coupling elaborates lycorine- and homolycorine-types of AAs (
). The para-para phenol-phenol’ coupling reaction produces the crinine-, narciclasine-, tazettine- and montanine-types of AAs. A cytochrome P450 sequence was identified through comparative transcriptomics of
sp.
,
sp., and
. Through heterologous expression and characterization, CYP96T1 formed the products (10b
,4a
)-noroxomaritidine and (10b
,4a
)-noroxomaritidine from 4′-
-methylnorbelladine supporting its involvement as a para-para’ C-C phenol coupling cytochrome P450 [53].
The core skeletons obtained from norbelladine, methylnorbelladine, and the phenol coupling steps form the basis of AA diversity. A complex network of enzyme catalyzing various types of reactions, such as C-C and C-O bond formations,
- and
-methylations, demethylations, hydroxylations, oxidations and reductions, yield the several hundred of structurally related AAs. Only a few of these enzymes are known to date and they are reported in
.
3. Pharmacological Properties of Novel Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids
The pharmacological properties of the newly discovered AAs (
–
) were assessed when isolated in sufficient amount. AAs display a wide range of biological activities, including cytotoxicity, effects on the central nervous systems (CNS), anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-parasitic, larvicidal, and antioxidant activities.
3.1. Antitumoral Cytotoxic Activity
Lycorine is the most abundantly found AA, it belongs to the pyrrolo[
]phenanthridine subgroup. The biological effects of lycorine have been known for many years, and lycorine is still being investigated for a variety of therapeutic application, in particular as anticancer agent showing promising activity against tumors with dismal prognoses [54][55]. The structure–activity relationship (SAR) of lycorine and its derivatives has been evaluated using human leukemia T cells (Jurkat). The results showed that the free 1,2-diol functionality in the C-ring is required to induce apoptosis [56]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that the presence of the unaltered diol functionality in the C-ring in its original configuration in lycorine series, the stereochemistry of the C/D ring junction and the conformational freedom of the C-ring were required for the anticancer activity [54]. 4′-
,
dimethylnorbelladine
oxide (
) displayed a weak cytotoxicity activity against the human colon cancer cell line HCT116 at concentration ranging from 10
M and 10
M [57].
Among the new lycorine-type alkaloids, (+)-1-hydroxy-ungeremine (
) was evaluated for its cytotoxic potential against BEN-MEN-1 (meningioma), CCF-STTG1 (astrocytoma), CHG-5 (glioma), SHG-44 (glioma), U251 (glioma), HL-60 (human myeloid leukemia), SMMC-7721 (hepatocellular carcinoma), and W480 (colon cancer) cell lines and exhibited the most potent cytotoxicity against all tested tumor cell lines except BEN-MEN-1, with IC
values ranging from 9.4 to 11.8 μM [58]. Pseudolycorine
-oxide (
) was inactive against human cervical cancer (SiHa) and human epidermoid carcinoma (KB) cells [59].
Among the homolycorine-type alkaloids, (+)-2-hydroxy-8-demethyl-homolycorine-α-
-oxide (
) had no significant cytotoxic activity (IC
> 80 μM) against BEN-MEN-1 (meningioma), CCF-STTG1 (astrocytoma), CHG-5 (glioma), SHG-44 (glioma), U251 (glioma), HL-60 (human myeloid leukemia), SMMC-7721 (hepatocellular carcinoma), and W480 (colon cancer) cell lines [58]. Lycoranines E and F (
and
) showed moderate cytotoxicity against A549 (human lung carcinoma) and LoVo (human colon carcinoma) cells lines with IC
> 20 μM [60]. 2α-10bα-Dihydroxy-9-
-demethylhomolycorine (
) showed significant cytotoxicity against the HCT-116 (colon adenocarcinoma), OVCAR-8 (ovarian carcinoma) and SF-295 (glioblastoma) cell lines with IC
values 11.69, 15.11, and 16.31 μM respectively [61].
Numerous additional types of AAs displayed interesting anti-cancer activity. Of the cherylline-type, gigantellinine (
) had a weak but significant cytotoxicity at 400 μM against breast cancer cell line MCF-7, while gigantelline (
) showed no cytotoxicity at the same concentration [62]. Crinine-derivatives (+)-6β-acetyl-8-hydroxy-9-methoxy-crinamine (
) showed significant cytotoxicity against HL-60 (IC
< 10 μM), and moderate cytotoxicity against astrocytoma and glioma cell lines, CCF-STTG1, CHG-5, SHG- 44 and U251 (10 μM < IC
≤ 30 μM) [58]. The cleavage between C-1 and C-13 and the hydroxyl at C-6′ in crinine alkaloid skeleton might be essential to their bioactivity [63]. Crijaponine A (
) was inactive towards both human epithelial carcinoma HeLa and HL-60 cell lines (IC
> 60 μM) [64]. 6α-Methoxyundulatine (
), 6α-methoxycrinamidine (
), and undulatine
-oxide (
) did not show significant cytotoxicity against the KB (derived from a human carcinoma of the naropharynx), HepG2 (human liver cancer), MCF7 (breast cancer), SK-Mel2 (melanoma), and LNCaP (human prostate) cancer cell lines with IC
> 100 μM [65]. 1,4-Dihydroxy-3-methoxy powellan (
) displayed an IC
> 60 μM against the A2780 human ovarian cancer cell line [66]. Gigancrinine (
) showed no cytotoxicity at 400 μM against breast cancer cell line MCF-7 [62]. 3-
-Methyl-
-vittatine (
) did not shown any cytotoxicity against MCF7, TK10 and UACC62 cancer cell lines [67]. Narciclasine-4-
β
xylopyranoside (
), a narciclasine-type was inactive against KB and SiHa cell lines at all the concentrations [68]. Jonquailine (
), a pretazettine-tye, showed significant antiproliferative activities against cells derived from glioblastoma (U87, U373, and Hs683), melanoma (SKMEL-28), uterine sarcoma (MES-SA and MES-SA/Dx5), and lung carcinoma (A549, H1993 and H2073) with IC
values ranging from 1 to 85 μM [69]. Moreover, (
) showed synergic effects with paclitaxel in its anti-proliferative action against lung carcimoma drug-resistant H1993 and H2073 cells in a dose-dependent manner with IC
values between 0.39 and 100 μM. The SAR of (
) suggested that hydroxylation of C-8 was required for its anticancer activity [69].
Among cripowellin-type AAs, 4,8-dimethoxy-cripowellin C (
), 4,8-dimethoxy-cripowellin D (
), 9-methoxy-cripowellin B (
), and 4-methoxy-8-hydroxy-cripowellin B (
) showed impressive cytotoxicity against seven lung cancer cell lines (A549, H446, H460, H292, 95-D, and SPCA-1) with IC
< 30 nM, with (
) and (
) being more active than (
) and (
). Cripowellin C (
) and cripowellin D (
) were efficiently cytotoxic against the A2780 human ovarian cancer cell line with IC
values of 25 ± 2, and 28 ± 1 nM, respectively [70].
Other-type of AA (+)-
-methoxylcarbonyl-2-demethyl-isocorydione (
) exhibited strong cytotoxic against all tested tumor cell lines (astrocytoma, glioma, human myeloid leukemia, hepatocellular carcinoma, colon cancer) except meningioma (BEN-MEN-1), with IC
values of 9.2–12.8 μM [58]. Zephycandidine A (
) was cytotoxic for five cancer cell lines, HL-60, A549, MCF-7, colon cancer SW480 (colon cancer), and hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC- 7721 (hepatocellular carcinoma), with IC
values of 1.98, 6.49, 3.44, 6.27, and 7.03 μM, respectively. Moreover, zephycandidine A (
) showed weak cytotoxicity against the normal Beas-2B cell line (IC
= 20.08 μM) with selectivity index as high as 10 when compared normal Beas-2B cell line, via activation of caspase-3, upregulation of Bax, down-regulation of Bcl-2, and degradation of PARP expression [71]. Hymenolitatine (
) showed weak cytotoxic activity against four cancer cell lines, HepG-2, LoVo, Hela, and A549, with IC
values of 75.19, 69.81, 96.37, and 102.53 μM, respectively [72]. Cripowellin-form (
–
) and Zephycandidine A (
) belonging to the other-type of AA may be potential targets for further anticancer investigations.
3.2. Effects on the Central Nervous System (CNS)
Several enzymes of the CNS are interesting drug targets. AChE is a serine protease located at neuromuscular junctions, in cholinergic synapses of the central nervous system and in red blood cells [73][74][75]. The enzyme catalyzes the rapid hydrolysis and inactivation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into acetate and choline to enable cholinergic neurons to return to their resting state. Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) can also hydrolyze acetylcholinesterase into acetate and choline. BChE is produced by the liver and detected in the plasma. Changes in its plasmatic levels can indicate of liver dysfunction. BChE is also expressed in neurons of the CNS [76].
In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), AChE is overly active, and the consequential lower level of acetylcholine in the brain cause weakened neurotransmission [77]. Similarly, BChE deregulation is measured in the brain of individuals suffering from AD. Malfunction of the cholinergic system may be pharmacologically tackled via AChE inhibitors that ameliorate the cholinergic deficit at early stages of the disease and reduce progression. In addition, glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a ubiquitous serine/threonine kinase, implicated in AD, which can trigger abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau protein, which is believed to be a critical event in neurofibrilary tangle formation. Thus, GSK-3 inhibition represents an attractive drug target for AD and other neurodegenerative disorders [78]. Finally, prolyloligopeptidase (POP) is a cytosolic serine peptidase widely distributed in the organs of the body, including the brain, which cleaves peptide bonds at the carboxyl end of proline [79][80]. Previous studies have shown that POP inhibitors are efficient anti-dementia drugs [81][82].
The AA galantamine, donepezil and rivastigmine are potent reversible inhibitors of AChE approved for the symptomatic treatment of AD [83][84]. Since cholinesterase enzyme inhibitors are first generation drugs for AD, AChE and BChE are the most targeted enzymes at the moment.
Galantamine derivative sanguinine is ten times more active than galantamine whereas 11-hydroxygalantamine exhibits inhibitory activity similar to that of galantamine. The extra or protected hydroxyl group in its allylic position in (R
) may be required for the activities [85]. SAR of galantamine and its derivatives was comprehensively reviewed elsewhere [16].
Among the six new galantamine-type alkaloids only 9-de-
-methyl-
β-hydroxygalantamine (
) showed a weak AChE inhibitory activity with IC
value 168.7 μM. The SAR of new galantamine derivatives alkaloids (
