Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Rosa Muñoz-Cano and Version 2 by Vivi Li.
Adenosine is a nucleoside involved in the pathogenesis of allergic diseases. Its effects are mediated through its binding to G protein-coupled receptors: A1, A2a, A2b and A3. The receptors differ in the type of G protein they recruit, in the effect on adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity and the downstream signaling pathway triggered. Adenosine can produce both an enhancement and an inhibition of mast cell degranulation, indicating that adenosine effects on these receptors is controversial and remains to be clarified.
- adenosine
- adenosine receptors
- G protein
- mast cells
- allergic diseases
- asthma
1. Introduction
Adenosine is an endogenous purine nucleoside consisting of the union, through a glycosidic linkage, of an adenine with a sugar ribose (Figure 1) [1]. It is an intermediary metabolite that plays a vital role in the synthesis of nucleic acids and forms adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main component of the cellular energy, adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Adenosine is involved in various physiological and pathological functions including the modulation of inflammatory processes such as allergic diseases [2].
Figure 1. Structure of adenosine.
1.1. Synthesis and Degradation of Adenosine
Under physiological conditions, a low adenosine concentration (from 10 to 200 nM) is present in the extracellular space. However, under conditions of metabolic stress and in certain pathological situations, there is a significant elevation of adenosine concentration, reaching levels that can be as high as 100 µM [3][4][3,4].
Adenosine can be synthesized at intracellular and extracellular levels. In physiologic conditions adenosine is generated in the intracellular space while, under metabolically unfavorable conditions, extracellular generation is carried out. Intracellular synthesis is dependent on the dephosphorylation of AMP by 5′-nucleotidase or the hydrolysis of S-adenosyl-homocysteine (SAH) by SAH hydrolase [5] (Figure 2). Extracellular generation is carried out through a mechanism that involves the dephosphorylation of ATP, ADP, and AMP. The extracellular synthesis of adenosine is regulated by the sequential action of two enzymes on the cell surface: ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 (CD39) and 5′-ectonucleotidase (CD73). CD39 presents ATPase and ADPase activity and therefore can dephosphorylate both ATP and ADP, forming AMP. The last step for the generation of adenosine is carried out by CD73 through the dephosphorylation of AMP [6] (Figure 2). Since the adenosine precursors (ATP, ADP and AMP) are released by cells in situations of stress, inflammation and hypoxia, pathological situations will result in a large increase in the concentration of adenosine [7][8][7,8]. Similarly, the enzymes involved in their extracellular synthesis (CD39 and CD73) are overexpressed in some pathological situations, such as hypoxia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, resulting in increases of adenosine synthesis [9][10][11][9,10,11]. Finally, an attenuation of allergic airway inflammation has been observed in a CD39-/- mouse model [12].
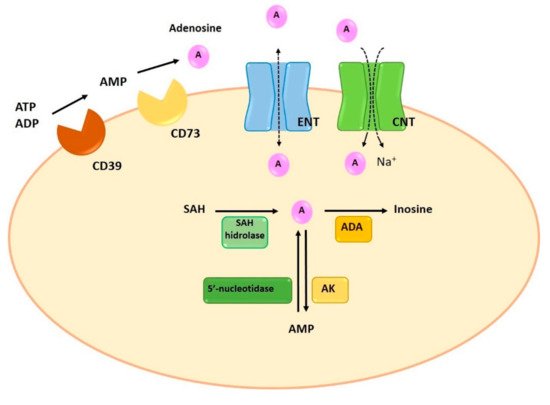
Figure 2. Synthesis, degradation and transport of adenosine. Intracellularly, adenosine is generated by dephosphorylation from AMP, by 5′-nucleotidase, or by hydrolysis of SAH, by SAH hydrolase. Extracellular adenosine generation is the result of the enzymatic activity of CD39 and CD73. ENT and CNT transporters allow the reuptake of adenosine. Finally, the adenosine is metabolized intracellularly by two enzymes, ADA and AK, which will produce inosine and AMP. ADA: adenosine deaminase; AK: adenosine kinase; AMP: adenosine monophosphate; CNT: concentrative nucleoside transporters; ENT: equilibrative nucleoside transporters; SAH: S-adenosyl-homocysteine.
Adenosine degradation is also involved in the final extracellular concentration of adenosine. This process can be performed in both, the extracellular and the intracellular space. Extracellularly, adenosine can be metabolized by the enzyme adenosine deaminase (ADA), which causes the deamination of adenosine into inosine. ADA can deaminate the adenosine when is anchored to the plasma membrane through its binds to membrane proteins such as CD26 [13]. However, the pathway that involves the activity of extracellular ADA is not the main way of adenosine degradation [14].
Normally, adenosine degradation takes place in the intracellular space. In fact, the adenosine present in the intracellular space can be directly metabolized while extracellular adenosine can suffer extracellular deamination by ADA or can be transferred to the intracellular compartment by specific transporters. The adenosine reuptaked to the intracellular compartment is rapidly metabolized through two metabolic pathways: ADA and adenosine kinase (AK). Similar to the extracellular metabolism, the enzymatic activity of ADA deaminates the adenosine to inosine. The second pathway involves the activity of AK, which phosphorylates adenosine and converts it into AMP [5] (Figure 2).
ADA activity has been related with some allergic diseases. A severe lung inflammation with eosinophilic airway infiltration and mast cell degranulation, features found in asthma patients, have been observed in an ADA-deficient mice model. Treatment with exogenous ADA, that reduced adenosine concentrations, resulted in the reversal of the inflammation [15]. Interestingly, an increase in inosine levels, which has been shown to increase RBL-2H3 rat basophil line degranulation through A3 AR activation [16], was also observed in a mouse model of allergic asthma, suggesting also the role of inosine in allergy inflammation [17].
1.2. Adenosine Transporters
Extracellularly, adenosine concentration is regulated by reuptake mechanisms through the action of two specific transporters: concentrative nucleoside transporters (CNTs) and equilibrative nucleoside transporters (ENTs) [18]. CNTs are active Na+-dependent transporters, mediate cell influx of nucleosides in the presence of an inwardly directed sodium gradient, against its concentration gradient. ENTs are passive bidirectional transporters which transport adenosine across the plasma membrane based on concentration gradients [19][20][19,20]. Despite both transporters participate in the regulation of adenosine extracellular concentration, it has been reported that ENTs are the most relevant transporters of adenosine, since they determine both the release and the reuptake of adenosine [9] (Figure 2).
2. Adenosine Receptors
Adenosine mediates its effects through activating G protein- coupled receptors (GPCRs). There are four types of adenosine receptors (ARs): A1, A2a, A2b and A3. All of them have a core domain which crosses the plasma membrane seven times, a 20–27 amino acids long helix and linked by three intracellular and three extracellular loops. The extracellular N- terminus presents one or more glycosylation sites, while the intracellular C-terminus has phosphorylation and palmitoylation sites, which have an important role for receptor internalization and desensitization [21]. ARs differ in the number of amino acids they present: A1 consists of 326 amino acids; A2a is the largest with 412 amino acids; A2b consists of 332 amino acids; and A3 presents 318 amino acids [22].
Adenosine receptors have different affinity for adenosine: A1 and A2a possess high affinity while A2b and A3 show relatively lower affinity [20]. In addition, as a general characteristic, receptors differ in the type of G protein they recruit, their effect on adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity and the downstream signaling pathway triggered. A1 and A3 are coupled to Gi and inhibit the activity of AC while A2a and A2b preferentially couple to Gs and increase cAMP levels by stimulation of AC [5][19][5,19] (Figure 3).
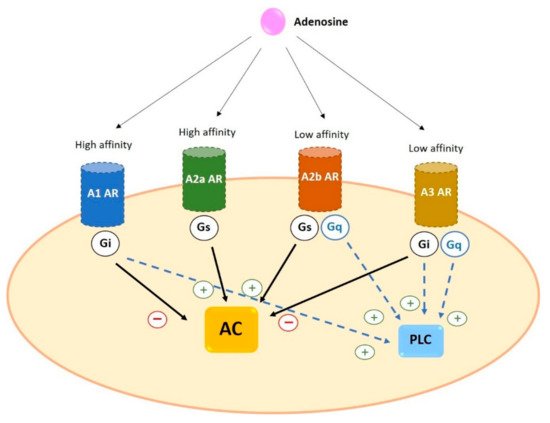

Figure 3. General characteristics of adenosine receptors. A1 and A2a ARs have a higher affinity for adenosine than A2b and A3 ARs. All four receptors trigger AC activation (via Gs) or inhibition (via Gi). In addition, some ARs can activate PLC coupling to Gq or through Gi. Black arrows indicate the effect on AC; blue dotted arrows indicate the effect on PLC. AC: adenylyl cyclase AR: adenosine receptors PLC: phospholipase C.
2.1. Expression of Adenosine Receptors in Human Cells
Adenosine receptors are widely distributed in human cells. These receptors play a role in diverse biological functions and show a broad spectrum of action [23]. The A1 receptor is the most conserved and it is expressed with the highest levels in the central nervous system (CNS), mainly in the neocortex, cerebellum, hippocampus, autonomic nerve terminals, spinal cord, and glial cells [24]. A1 is also found with high abundance in heart, kidney, adipose tissue, and pancreas [25]. Furthermore, and related to inflammatory airway diseases, it has been demonstrated that A1 is expressed in alveolar epithelial cells, airway smooth muscle cells, and several immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages and monocytes, where A1 enhances proinflammatory effects [7].
A2a is found in heart, lung, liver, nervous and immune system. High A2a levels are present in the striatum of the brain and the olfactory tubercle, lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, monocytes, and dendritic cells [21].
The highest levels of A2b are essentially found in the periphery, in the urinary blander, bowel, lung, vas deferens, and different cell types including, smooth muscle, alveolar epithelial, chromaffin and taste cells, as well as immune cells such as mast cells, neutrophils, dendritic, neutrophils and lymphocytes [3]. At the central level, the A2b is expressed in astrocytes, microglia and neurons [7].
A3 is expressed at the highest levels in lung, liver and immune cells. Lower levels have been reported in the heart and brain [5][26][5,26].
Expression of Adenosine Receptors in Human Basophils and Mast Cells
Mast cells and basophils play a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of allergic diseases through the secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators. Both types of cells are usually activated by the cross-linking of the allergen with its specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) and its binding to the high affinity IgE receptor (FcεRI) [27].
The ARs profile expression seems to be different when comparing mast cells with basophils. Moreover, different ARs expression has been reported depending on the source of the mast cells. For instance, it has been reported that human skin mast cells express all four receptors while human peripheral basophils express A2a, A2b and A3, but not A1 [28]. However, studies carried out in the human mast cell line LAD2 [29] and HMC-1 cells [30] demonstrated that both cell lines express A2a, A2b and A3, but not A1. In addition to the different expression profile, it has been reported differences in the level of expression. Gomez et al. demonstrated that A3 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in human lung mast cells was threefold higher than in skin mast cells, difference that may account for their disparity in the response to adenosine [31]. Muñoz-Cano et al. reported a higher expression of A3 in food anaphylaxis patients compared to health individuals, although the study was performed in whole blood samples where basophils, but not mast cells, are represented [32]. Similarly, using whole blood samples, polymorphisms of ADORA3 have been identified in patients with aspirin-induced urticaria [33], of ADORA1 and ADORA2A in aspirin-induced asthma [34], both in Korean population; ADA polymorphism have been observed in asthma patients from a Chinese Han population [35]. However, as far as we know, it has not been reported differences between healthy subjects and allergic patients in the adenosine receptor profile of basophils or mast cells [36].
2.2. Signal Transduction of Adenosine Receptors in Human Cells
2.2.1. A1
A1 is coupled to Gi/o protein. Its activation leads to inhibition of the AC, causing the reduction of intracellular production of cAMP. A1 also involves phospholipase C (PLC) activation and results in an increase in inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) and intracellular Ca2+ levels. High levels of Ca2+ stimulate protein kinase C (PKC) and other calcium-binding proteins [37]. In cardiac muscle and neurons, A1 can stimulate potassium channels and inhibit Q-, P- and N-type calcium channels. A1 activation is related to the phosphorylation of mitogen- activated protein kinases p38, ERK1/2, and JNK1/2 [7].
2.2.2. A2a
A2a binds to Gs protein and increases AC activity and cAMP production. The cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) is the main pathway, causing the phosphorylation and activation of several proteins such as the transcription factor cAMP- response element binding (CREB). Moreover, it has been reported that A2a is involved in the regulation of MAPK signaling [38].
2.2.3. A2b
A2b is coupled to Gs/q proteins. The main signaling pathway, through binding to Gs, involves the AC activation that leads to an increase in cAMP levels. As a result there is an activation of PKA by phosphorylation and others cAMP- dependent effectors such as Epac [3]. However, A2b can couple to Gq protein which mediates the activation of PLC [39] and resulting in Ca2+ mobilization. In addition, this type acts as stimulator of MAPK through phosphorylation of p38, ERK 1/2 and JNK 1/2 [7].
2.2.4. A3
A3 can couple to Gi protein to inhibit AC activity and decrease the level of cAMP. Moreover, A3 can also bind to Gq protein to stimulate PLC and increase intracellular concentration of Ca2+, action that can also be performed by Gβγ subunits. Furthermore, like other adenosine receptors, the A3 acts on MAPK and mediates the phosphorylation and activation of p38, ENK 1/2 and JNK 1/2 [40].
2.3. Desensitization of Adenosine Receptors
It has been reported that ARs can be desensitized due to the action of G protein-receptor kinases (GRKs) on the phosphorylation sites at the C-terminus of the GPCRs [41].
The activity of GRKs results in the internalization and desensitization when GPCRs are recruited from arrestins [41]. The A1, A2a, A2b and A3 have been shown to desensitize after stimulating with an agonist, but the rate of the desensitization depends on the AR type [42]: A3 desensitization is the fastest whereas A1 desensitization is the slowest [30][43][44][30,43,44]. Regulation of adenosine receptors is a complex process. Desensitization produces a reduction in the effects of adenosine receptors, which must be considered when designing possible agonists. For instance, the rapid desensitization of the A3 receptor suggests that an agonist could have the same effect as a specific antagonist [41].
3. Adenosine in Allergic Diseases
It has been suggested that adenosine is involved in the pathogenesis of allergic diseases such as asthma and urticaria. In fact, the studies focused in the analysis of the adenosine effect in patients suffering from asthma and urticaria suggested that adenosine play a role in these diseases. However, the results of the studies assessing the adenosine effects in mast cells and basophils are less conclusive.
In asthmatic patients, the inhalation of adenosine produces bronchoconstriction. However, this effect is not observed in healthy subjects [29]. In fact, it has been reported that the dysfunction of small airways plays a role in the dyspnea caused by adenosine in asthmatic patients [45]. Furthermore, high concentration of adenosine in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and condensation of exhaled air have been reported in asthmatic patients [46]. In line with these findings, Mao et al. demonstrated that patients with urticaria have higher levels of plasma adenosine compared to healthy subjects [47].
Studies performed in mast cells seems to support the role of adenosine in these allergic diseases. In the human mast cell line LAD2, stimulation of the FcεRI pathway was enhanced by the incubation with low concentrations (10 nM–2 µM) of the adenosine analog NECA, which acts non-selectively on receptors. However, the application of selective agonists did not show a significant increase in degranulation, suggesting that interaction between different receptors may play a role in the stimulation of the FcεRI pathway [48]. In line with these findings, it has been demonstrated that low concentrations (<1 µM) of adenosine increased the histamine release induced by FcεRI in mast cells derived from human lung. However, high adenosine concentrations (1000 µM) produced an inhibition of the action of FcεRI in the same cells [49]. Supporting these findings, Matsuo et al. have reported that histamine release was inhibited in peripheral human basophils and human skin mast cells by adenosine at 1–1000 µM and 1–100 µM, respectively [28].
It seems that the different response to adenosine may be related with the origin of mast cells. Adenosine at low concentration (1 µM) produced a potentiation of the response induced by FcεRI in lung but not in skin mast cells. On the other hand, high concentrations of adenosine (1000 µM) produced an inhibition of β-hexoaminidase release both in lung and skin mast cells. In this study the expression of the receptors was quantified, demonstrating that lung mast cells had A3 overexpressed, compared with skin mast cells. This different pattern of expression could explain, at least in part, the differential response when cells were incubated with adenosine [31].
3.1. Role of Specific Receptor Stimulation in Allergic Diseases
3.1.1. A1
Activation of this receptor induces both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects in allergic diseases. It has been reported a low presence of A1 in the lung [19] a no expression in human lung mast cells [31]. However, several studies suggested that A1 is involved in airway inflammatory diseases pathogenesis. It has been demonstrated that A1 is upregulated in both bronchial epithelium and smooth muscle of asthmatic patients. Moreover, it has been demonstrated that its activation produced bronchoconstriction [46]. Supporting this finding, studies performed in animal models have reported that adenosine and allergen exposition induce bronchoconstriction [50]. On the contrary, in a model of ischemia-reperfusion lung, A1 activation showed an anti-inflammatory effect by reducing the neutrophil chemotaxis and edema [51]. Indeed, a reduction of microvascular permeability and polymorphonuclear cell trafficking in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-damaged lung was also observed [19].
3.1.2. A2a
This receptor is characterized by its anti-inflammatory effects [19][52][19,52]. In A2a-/- mouse models, there was an increase in the accumulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum after treatment with an endotoxin compared to A2a +/+ [53], indicating its anti-inflammatory effects. In rats, pre-treatment with a A2a selective agonist (CGS21680) before cardiovascular bypass has been shown to dampen lung injury and inflammation [54]. In line with these findings, Alfaro TM et al. have demonstrated that CGS21680 produces an attenuation of the inflammatory response of human alveolar macrophages. In fact, the pro-inflammatory stimulus induced the expression of A2a in these cells [55]. Supporting this anti-inflammatory role, it has also been reported that CGS21680 treatment during allergen sensitization or re-exposure resulted in a decrease in IFN-γ as well as the accumulation of neutrophils, lymphocytes, and eosinophils in bronchoalveolar lavage [56]. Moreover, A2a upregulation has been also reported in monocytes from bronchoalveolar lavage of asthmatic compared to healthy subjects [57]. This finding suggests inflammatory environment seems to cause the overexpression and activation of A2a, which could attenuate the pathological situation.
Human lung mast cells have Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCa3.1, which are opened upon FcεRI activation, allowing calcium influx and degranulation [58]. A2a has been shown to inhibit the secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators induced by FcεRI pathway activation in mast cells, by means of closing KCa3.1 channels [59]. Likewise, CSG21680 has shown to inhibit C3a-induced activation in LAD2 by decreasing intracellular calcium influx [60].
Current treatments for some inflammatory lung diseases such as asthma are mostly based on glucocorticoids, although some patients have shown a poor response to these treatments and new therapies with A2a specific agonist may be a promising option. However, treatments with the specific agonists GW-328267 or UK-432097 have shown low efficacy [38].
3.1.3. A2b
The A2b receptor can bind to the Gs and Gq proteins, triggering both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory effects [7]. The anti-inflammatory effects have been demonstrated in human and animal models and several cell types. In an A2b-/- mouse model, an increase in FcεRI-induced mast cell activation was observed, suggesting the inhibitory role of this receptor [61]. In neutrophils, the activation of A2b inhibited their adhesion to endothelial cells while in macrophages and lymphocytes increased IL-10 production, inducing anti-inflammatory effects [19]. In this same line, it has been demonstrated that expression of A2b is induced when lung cells are exposed to pro-inflammatory stimuli. This mechanism would produce a damping of inflammation and lung protection [62][63][62,63]. Moreover, the use of the specific antagonist for A2b, MRS1754 increased the inflammatory effects induced by LPS [62][63][62,63]. Similarly, pharmacological treatment with the agonist BAY 60-6583 reduces lung inflammation and edema caused by acute lung injury induced by LPS in mice [62][64][62,64] and also decrease TNF-α levels [63]. For these anti-inflammatory effects, it has been suggested that BAY 60-6583 could be used as an add-on therapy in some glucocorticoid-resistant lung diseases [65].
On the contrary, several studies have demonstrated pro-inflammatory effects of A2b. The activation of this receptor in mast cells produces degranulation and secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β, IL-13, IL-3, IL-8 and IL-4 [19], leading to bronchoconstriction [50]. The use of a specific A2b antagonist, CVT-6883, attenuated inflammation and reduced bronchoconstriction [19][50][19,50]. Moreover, CVT-6883 treatment in a mice model based on multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced pulmonary fibrosis, reduces the levels of pro-fibrotic mediators [66]. In addition, treatment with another antagonist, GS6201, decreased the hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease [19]. Furthermore, the administration of the A2b antagonist ATL802 in lung injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion, attenuated inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokines release, improving lung function, decreasing resistance, blood pressure, and pulmonary vascular permeability [67].
3.1.4. A3
The activation of A3 is related with pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects depending on the cell type [7]. In the airways of asthmatics, A3 is found to be mainly expressed in eosinophils [50]. The activation of A3 induced the inhibition of eosinophil degranulation and chemotaxis. In fact, it has been hypothesized that the use of A3 agonists may be a useful therapeutic approach for eosinophil-dependent allergic diseases [5]. On the contrary, the activation of A3 in both rodent and human LAD2 mast cells enhanced degranulation induced by FcεRI activation [5][7][48][5,7,48]. Interestingly, low adenosine concentrations enhanced FcεRI-mediated degranulation in human lung, but not in skin mast cells. A3 overexpression in human lung mast cell may account for this differential effect [31]. In fact, the activation of A3 by a specific agonist, CI-IB-MECA, increased the expression of genes involved in vascular remodeling, such as IL-6, IL-8, and VEGF, and pro-fibrotic genes, such as osteopontin and amphiregulin, which leads to a worsening of asthma [30].
