The p53 tumor suppressor plays a pivotal role in cancer and infectious disease. Many oncology treatments are now calling on immunotherapy approaches, and scores of studies have investigated the role of p53 antibodies in cancer diagnosis and therapy. This review summarizes the current knowledge from the preliminary evidence that suggests a potential role of p53 as an antigen in the adaptive immune response and a monitoring key role of the innate immune system, thereby speculating on the idea that mutant p53 antigens serve as a druggable target in immunotherapy. Except in a few cases, the vast majority of published work on p53 antibodies in cancer patients use wild-type p53 as the antigen to detect these antibodies and it is unclear that they can recognize p53 mutants carried by cancer patients at all. We envision that an antibody targeting a specific mutant p53 will be effective therapeutically against the cancer carrying the exact mutant p53. Thus, novel antibodies targeting mutant p53, but not the wild-type isoform, should be pursued in preclincial and clinical studies.
- p53
- serum antibodies
- tumor-suppressor
- immunoncology
- cancer
1. Discovery of p53
Approximately 70 years ago, several DNA viruses such as adenovirus, human Epstein–Barr virus, polyoma and SV40 were found to be able to cause tumors in humans and rodents [1]. In all of these cases, the viral proteins which stem from the viral genome—either integrated into a chromosome or as plasmid—were observed to be involved in tumor promotion, formation and maintenance [2][3][4]. These viral proteins—subsequently named tumor antigens (TA)—were recognized by the immune system and the different antibodies were found to target them specifically [5]. Given this scenario, in 1979, four different groups in England, the United States, and France nearly simultaneously discovered the p53 protein in normal and cancerous cells, testing the serum from animals with spontaneously derived or SV40 virus-induced tumors [6][7][8][9]. Among these four studies, the same 53kD protein (called p53) was detected—and confirmed with peptide maps—in SV40-transformed cells and malignant cells that are not transformed by a virus, whereas decreased p53 levels were observed in uninfected normal cells. Malignant cells that were not transformed by any virus also had increased levels of p53, suggesting that the SV40 tumor antigen, a well-known factor for the tumor initiation and progression, binds to p53 and raises its concentration above its normal levels in control healthy cells [10]. These preliminary results paved the way for a vast number of studies on the role of cellular protein p53 in the cancer biology field, leading to the discovery that p53 mutations are the most common genetic alteration in human cancers.
2.
Tumor Suppression Role
p53 has a unique and unequivocal tumor suppression role, which has been confirmed by the cancer susceptibility of individuals affected by Li–Fraumeni syndrome, the p53 inactivation in most sporadic human cancers, and the spontaneous tumorigenesis in mice with the p53 gene knocked out [11]. During tumor development, inherited and/or sporadic TP53 genetic missense mutations are normally followed by a loss of heterozygosity (LOH), turning into an entire p53 deficiency. It seems there is a selective advantage towards the loss of the remaining allele of the wild-type p53 (p53-wt) gene [12][13][14]. The loss of p53 gives way to the initiation and progression of malignancies, which are generally characterised by more malignant features such as intensified invasiveness and metastatic capability, genetic instability and poor cellular differentiation [15][16][17][18]. In all likelihood, these outcomes are given not only by the loss-of-function (LOF) of wild-type p53 (p53-wt) but also by the tumorigenic gain-of-function (GOF) features of some p53 mutants (p53-mut) described later.
p53 is known as the “guardian of the genome” thanks to its capacity to respond to outside stresses, which promotes transient or permanent cycle arrest and apoptosis, following different stress factors including hypoxia, DNA impairment, oxidative stress, hyperproliferative signals, nutrient shortage [19][20][21]. p53 supports tumor suppression through its roles as transcription factor and mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (to trigger apoptosis) and, indeed, the most investigated biological activity of p53 is its transcriptional activator role [17].
3.
Transcriptional Role of p53, Relevant Mutations and the Mutant p53 GOF
In common with other transcription factors, p53 is composed of three distinct domains, which are responsible for oligomerization, transcriptional activation and sequence-specific DNA-binding [22][23]. Although the carboxy-terminal domain has been shown to play a pivotal role for the tetramerization of p53 monomers—which, in turn, triggers transcriptional activation—approximately 30% of TP53 mutations in human malignancies occur in six “hotspot” amino acid residues within the DNA-binding domain (R175, G245, R248, R249, R273 and R282). Such alterations in malignancies highlight the crucial role of p53 as a transcription factor in tumor suppression [24][25]. Together with the well-established tumorigenic promotion via loss of p53-wt function, the retained p53-mut is also thought to promote tumorigenesis via GOF properties and a dominant negative effect on the p53-wt protein [19][26]. After showing malignant characteristics such as increased survival and invasiveness, a poor differentiation rate and proliferation in preliminary cell culture studies, the GOF of tumor-derived p53-mut was corroborated by knock-in mice studies. In these studies, different mice strains harboring equivalent human tumor p53-mut (e.g., p53
273H
R248Q
R248W
175H
G245S) reported a shorter tumor latency, a wider tumor spectrum and a higher rate of metastasis, supporting the concept that p53-mut actively sustains cancer development and progression [13][17][28][29][30]. p53 GOF could be attributable to an increase in the interaction with other transcriptional factors such as the vitamin D receptor (VDR), the nuclear factor Υ (NFΥ) and p63 and p73 [31][32], resulting in the alteration or inhibition of the DNA-binding capacity of these transcription factors [33][34]. Lastly, p53-mut has been observed to interact with the Nijmegen breakage syndrome protein 1 (NBS1), Meiotic Recombination 11 (MRE11) and DNA repair protein RAD50 (RAD50), to make a complex (NBS1-MRE11-RAD50) and impair the DNA damage signalling [35][36].
p53 Degradation and Accumulation
The p53 transcription factor is part of an autoregulatory loop where p53 protein promotes the expression of Mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) protein, which, in turn, polyubiquitinates the p53 protein and supports its degradation [10][37]. Yue et al. showed that BAG family molecular chaperon regulator 2 (BAG2) binds to p53-mut and translocates it into the nucleus to inhibit the interaction between MDM2 and p53, thus blocking the MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53. They further reported that the DBD of the p53-mut and the BAG domain of the BAG2 are essential for the BAG2-p53-mut interaction. Noteworthily, different models expressing p53-mut, that lacked the main sites for p53 ubiquitination by MDM2, still showed a normal half-life and stabilization for p53 under stress conditions [38][39]. In fact, there are alternative pathways involved in the degradation of p53. Benchimol et al. showed, for the first time, that MDM2 is not the only E-3 ligase capable of controlling p53 ubiquitination [40]. There are many different E3 ligases targeting p53 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation and their description is out of the scope of this review. For a more thorough description of such molecules involved in p53 degradation we refer to tailored reviews [41][42]. Briefly, the following are E-3 ligases involved in p53 ubiquitin-mediated degradation that mediate the K48-linked polyubiquitination of p53, marking the protein for proteosomal degradation: MDM2, Fogol Caspase Recruitment Domain-Containing protein 16 (COP1) and Ring Finger And CHY Zinc Finger Domain Containing 1 (Pirh2), as well as Tripartite Motif Containing 24 (TRIM24) [43], TOP1 Binding Arginine/Serine Rich Protein (TOPORS) [44], WW Domain Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 1 (WWP1) [45], ADP ribosylation factor–Protein oikybromo-1 (ARF-BP1) [46], Ubiquitin-conjugation enzyme E2 13 (Ubc13) [47], Human Herpes Virus Infected Cell Polupeptide 0 (ICP0) [48], Cell Division Cycle And Apoptosis Regulator 1 (CARP1/2) [49], Cullin 7 (CUL7) [50], Synoviolin (SYVN) [51], E4F Transcription Factor 1 (E4F1) [52], STIP1 Homology And U-Box Containing Protein 1 (CHIP) [53], E4orf6 and E1B55K [54], MSL Complex Subunit 2 (MSL2) [55], F-Box Protein 42 (JFK) [56] and Makorin Ring Finger Protein 1 (MKRN1) [56]. Notably, mono- or K63-linked polyubiquitination is linked to other functions besides ubiquitination, such as nuclear and cytosolic localization, alterations of p53 transcriptional levels. Nuclear export is induced by conjugating with ubiquitin by MDM2, MSL2 and WWP1; ICP0 was shown to accumulate ubiquitin p53 at nuclear foci; E4F1, was shown to active cell-cycle arrest at G0/G1 after mono-di or tri- ubiquitinating p53; CUL7 was shown to mono- or deubiquitinate p53 to repress p53 transcriptional activity by unknown mechanisms [45][48][50][52][55]. Therefore, there are different mechanisms by E3 ligases to fine-tune the levels of p53 in cells. However, none of these E3 ligases has been studied in detail as much as MDM2. p53 mutated proteins do not activate the expression of MDM2. In consequence, such mechanisms of degradation do not occur in p53-mut where MDM2 levels are very low [57]. Therefore, this has been postulated as an explanation of why only p53-mut bearing patients result in the formation of p53 antibodies (p53-Abs).
The accumulation of p53 can be triggered by many mechanisms, such as stress signals, DNA damage, nucleotide deprivation, DNA damage, mitogenic or oncogenic activation viral infection, heat shock proteins like HSP70/HSP40/HSP90, which, in cancer cells, form a multi-chaperone complex around p53-mut facilitating the unfolding of the p53-mut and its spontaneous folding to another conformation with different energy minimum [58][59][60] (
Figure 1). In addition, the activity of p53 can be further enhanced by post-translational modifications working as positive or negative regulators [6][58][61][62].
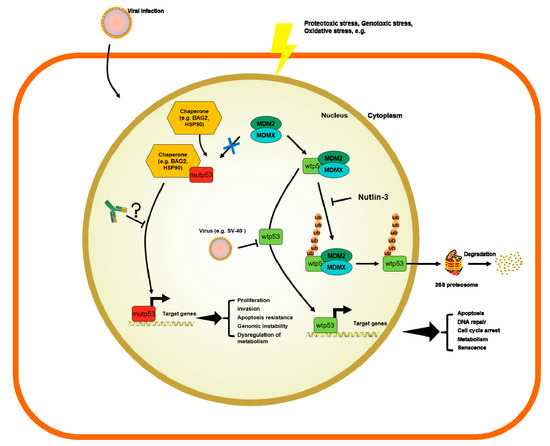

Figure 1. Mechanisms of regulation of wild-type p53 (p53-wt) and p53 mutants (p53-mut) and the potential role of p53 antibodies (p53-Abs).
4.) p53-Abs measurements and specificity
There are several methods for the measurement of p53-Abs from specimens, such as ELISA [63][64][84,85], Western blot or Immunoprecipitation[65][66][86,87], possibly explaining why results are different in the literature regarding the frequency of p53-Abs. Additionally there are different types of epitopes recognized by these assays. The p53-Abs usually recognizes immunodominant epitopes found in the COOH and NH2 termini of p53. Therefore it is crucial to have valid systems recognizing the entire p53 protein, looking at both sides [67][88].
The structure of p53 has been already been established by X-ray crystallography. The protein has a central region made of 102-292 amino acids[89]. This includes two β-sheets antiparallel motifs made of 4 and 5 β-strands, respectively. Moreover, these strands form a structure that keeps together the protein: 1) LSH with and α-helix, three β-strands and the L1 loop; 2) L2 loop with smaller helix; 3) L3 loop made of turns. The region involved in the DNA interaction is the LSH motif and L3 helix. According to Suossi et al, these two loops stabilize the protein structure by binding with each other by a zinc atom connected to Cys176 and His179 on the L2 loop and Cys278 and Cys242 on the L3 loop [68][69][90,91]. Additionally the central region of p53-wt is held in a compact conformation by two antiparallel β-sheets. This specific conformation is hydrophobic and poorly immunogenic [68][90]. Some key epitope residues used by anti-p53 Abs correspond to those needed for the MDM2 interaction with NH2 terminus of p53 [7].
p53 antibodies could be specific to at least one conformation of p53-mut. Interestingly, there are some publications showing that p53-Abs are able to recognize not only the p53-mut but also the p53-wt[92–94] [70][71][72] . The epitopes of human p53 were precisely mapped [73][95]. From the analysis of more than 200 sera it was possible to evince that the immune-dominant epitopes were on the COOH terminus of human p53 and a much less extent very few antibodies recognized the human p53 central region [71][73][74][75][93,95–97].
5.) p53-Abs in Cancer Patients
The first population study looking at s-p53-Abs produced by human cancer patients relates back to 1982, where it was demonstrated that p53-Abs were found in 10% of the sera of breast cancer women [66][98]. More studies on various cancers came afterwards proving that in about 30% of different types of cancers p53-Abs were detected [69][91].
The s-p53-Abs has been found in patients with head and neck cancer, ovarian cancer ascites’ fluids, pancreatic, colon and lung tumors pleural effusions, and saliva from oral cancer patients [69][76][77][78][79][91,99–102]. As expected, there is a high correlation between the s-p53-Ab and the frequency of p53 gene alterations in the tumors [63][70][77][78][80][81][84,92,100,101,103,104]. In mesothelioma and prostate cases where p53-mut were low, the presence of s-p53-Abs was low [82][105]. Tavassoli et al showed that p53 was detected in both saliva and sera of 29 oral SCC patients [78][101]. Angelopoulou et al analysed 96 ascites fluids from women with primary ovarian cancer for s-p53-Abs. They showed that autoantibodies were present in both serum and ascites of 6/30 patients; of them 22 were negative for auto-antibodies in either serum or ascites, and 2 had them only in the serum [77][100].
Suoussi et al made a meta-analysis of 18 clinical studies, pulling down 9,489 patients with cancer and discovered that the s-p53-Abs were a marker for patients with neoplasia (p< 10-4) [69][91]. There was a significant correlation between s-p53-Abs and p53 mutations and various types of cancer. Interestingly, cancers that did not have p53-mut, specifically testicular carcinoma [83][84][106,107], hepatoma [85][108] and melanoma [86][87][109,110] were also negative for p53-Abs. On the other hand, most cancers with high rate of p53-mut have also a high frequency of s-p53-Abs, except for glioma with high p53-mut[111] [88] and low rate of s-p53-Abs [88][89][111,112]. In a glioblastoma cohort of 60 patients, 24 of them had p53-mut, but none of them had s-p53-Abs. This could be due to the lack of the p53 immune response in the brain (an immunoprivileged organ), preventing the production of s-p53-Abs.
Roughly, about 20-40% of p53-mut patients had the s-p53-Abs in the sera. It is worthy to mention that despite similar tumors, p53-mut and its accumulation, it is not a rule that all these patients are positive for s-p53-Abs [90][91][92][93][113–116]. There must be other factors that come into play in the production of s-p53-Abs that future research could unravel.
6.) Prognostic Value of p53-Abs in Cancer Patients
Many studies have been conducted to evaluate the clinical utility of s-p53-Abs. In Breast Cancer (BC), there are several studies showing that s-p53-Abs correlated with high grades of the tumor and in hormone negative steroid hormones they were not expressed [66][71][94][95][64][87,93,117–119]. Lenner et al showed in 353 BC patients that the presence of a high concentration of s-p53-Abs correlated significantly with worse survival (p=0.003) [96][120]. Likewise Peyrat et al showed in 165 BC patients that overall survival was worse in patients with s-p53-Abs (p<0.0005) [95][118].
Of note, Willsher et al in 82 BC patients did not find any correlation[97][121]. Porzsolt et al in 50 BC patients showed that p53-Abs were present in BC patients with a good prognosis [98][122]. On the contrary, Generali et al showed the association with the absence of ER expression and p53 expression, supporting its negative predictive role. Moreover, hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is directly linked to the p53-mut in BC (noteworthy, the routine immunohistochemical procedures usually detect the mutated form); it leads to the inhibition of tumor apoptosis with a negative impact on treatment response in BC [99][123]. In colorectal cancer (CRC), few initial studies demonstrated that s-p53-Abs correlated with worse survival [80][81][100][103,104,124]. In fact Kressner et al showed in 184 CRC patients that s-p53-Abs correlated with shorter survival. However, the latter data did not reach the same statistical significance when Duke’s stage was taken into consideration in the analysis model [100][124]. Houbiers et al conducted a post-operative study in 255 CRC patients using ELISA. The group showed that 25.5% of the patients were s-p53-Abs positive. The presence of such antibodies significantly correlated with prognostic factors, like tumor shape, histological grade, angiogenesis and Quetelet Index (p= 0.02, p=0.04, p=0.02 and p=0.01, respectively). Moreover, in 64 of the CRC patients, who were at stage A or B1, the positivity to s-p53-Abs significantly correlated with decreased overall survival and disease-free survival (p=0.04 for both) [81][104]. On the contrary more recently, Kunizaki et al in 170 CRC observed that serum s-p53-Abs did not correlate with overall survival [101][125]. Angelopoulou et al study made of 229 CRC patients that 53 (23%) of the patients were s-p53-Abs positive and that the concentration of s-p53-Abs changed during disease progression or regression reflecting the disease stage. Although their data failed to reach statistical significance, they postulated an interesting hypothesis that s-p53Abs could be used to monitor CRC disease progression [80][103]. However, Tokunaga et al with 244 CRC patients more recently observed that serum s-p53-Abs were not able to predict patients prognosis (p=0.788) [102][126].
Also in lung cancer, there are controversies regarding the clinical utility of s-p53-Abs. In fact while in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC) the antibodies associated with worse survival [103][104][105][127–129], in Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (SCLC) Zalcman et al observed in 97 SCLC patients that patients with s-p53-Abs had a worse survival compared to patients without the s-p53-Abs (p=0.014) [106][130]. Other groups corroborated such findings. On the contrary, Murray et al showed in 231 SCLC that in those patients having elevated s-p53-abs levels had a better survival compared to patients with lower levels of the antibody. In fact, by setting through ELISA a strong level of p53 positivity to a score up to 5, the authors observed that p53-Abs positive patients had a median survival of 11 months vs. 8 months of the patients that did not have the antibody. p53Abs appeared to be an independent prognostic factor in this study (p=0.02) [57][131]. Moreover, Mack et al detected in 180 lung cancer patients that there was a significant correlation between p53-Abs positivity and a shorter survival of NSCLC patients (p=0.01) [107][132]. More recently, Mattioni et al conducted a study made of 201 lung cancer patients corroborating what is the knowledge about NSCLC. In fact the authors demonstrated that in NSCLC patients with lower levels of s-p53-Abs survived significantly longer than patients with higher levels of s-p53-Abs (p=0.049). On the same line, the same publication additionally showed that patients with squamous cell carcinoma (excluding adenocaricinoma) with lower levels of s-p53-Abs survived significantly longer compared to patients with higher levels of s-p53Abs (p=0.044) [79][102].
Another series of surprising data come from oral cancer. There were two initial studies proving that s-p53-Abs expression correlated with worse survival of patients [80][81][103,104]. Bourhis et al in 80 of oral cancer patients who were s-p53-Abs positive evinced that the s-p53-Abs expression correlated with a higher risk of tumor relapse and death (p=0.003 and p=0.03, respectively) [108][133]. Werner et al in 149 conducted a clinical study made of head and neck cancer patients who received surgery and radiation therapy. In line with what observed by the former group, the latter group detected in the 17 seropositive for s-p53-Abs patients (44.7%) that they failed to respond to the therapy; whereas only 8 of the seronegative patients for the s-p53-Abs failed to respond to therapy (21.1%) [109][134]. Later on, on the same line as the previous two groups, Gottschlich et al with 109 head and neck cancer patients observed that s-p53-abs correlated with worse outcomes, although the authors did not show any statistical significance in their data [110][135]. Successively, Shimada et al detected in 258 oesophageal cancer patients that s-p53-Abs (p < 0.001; HR: 10.6 2; 95%CI:.76-40.00) and S-CRP were independent prognostic factors [111][136]. To corroborate these findings, later on Sainger et al observed that the s-p53-Abs positivity correlated with lymph node metastasis, advanced disease and well-differentiated tumors [112][137]. Most recently, Kunizaki et al attested in 133 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma the high levels of both S-p53Ab and SCC-Ag in patients correlated with significantly lower survival compared to patients with elevated and patients with elevated levels of only one or neither of these factors (p=0.009) [113][138]. Furthermore, s-p53-Abs positivity strongly correlated with poor outcome from treatment in in the 60 oral precancerous treated patients.
The updated list of all the clinical studies evincing the prognostic value of s-p53-Abs in all the cancer types is summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Clinical studies investigating the prognostic value of s-p53-Abs in cancer.
|
Study |
Methods and patients |
Prognostic or Predictive Outcomes |
Reference |
|||
|
Kunizaki et al 2018 |
S-p53Ab, SCC-Ag, CEA
Antibody for p53-wt
133 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients |
The presence of both S-p53Ab and SCC-Ag in patients correlated with significantly lower survival compared to patients with elevated and patients with elevated levels of only one or neither of these factors (p=0.009). |
[113][138] |
|||
|
Kunizaki et al 2017 |
S-p53Ab
Detected with anti-p53 detection kit MESACUP anti-p53 Test
Antibody for p53-wt
208 GC patients
|
Did not observe any significant correlation between S-p53Ab in GC and overall survival (hazard ratio(HR)=2.052; 95% confidence interval(CI)= 0.891-4.726; p=0.091).
Conversely, Cox regression analysis revealed that a high level of CA19-9 was an independent prognostic factor for GC (hazard ratio(HR)=3.864; 95% confidence interval(CI)= 1.248-11.959; p=0.019). |
[114][139] |
|||
|
Tokunaga et al 2017 |
CEA, CA19-9, S-P53Ab
Antibody for p53-wt
244 CRC patients |
S-P53Ab had no power to predict the prognosis (P = 0.786).
Combined CEA and CA19-9 positivity was an exclusive independent prognostic factor (P = 0.034). |
[102][140] |
|||
|
Kunizaki et al 2016 |
S-p53Ab, CEA
ELISA. Antibody for p53-wt
170 CRC patients |
Positivity for s-p53Ab in CRC did not correlate with overall survival.
Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed significant differences between patients with elevated s-p53Ab and CEA and those with elevated levels of either one or neither of these factors (p<0.001). |
[101][125] |
|||
|
Mattioni et al 2015 |
s-p53-Abs
ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt Direct Sequencing was used to detect mutations: Mutant and Wild type antibodies: 9 patients with p53-wt and 3 patients with p53 deletions
201 NSCLC patients |
Patients with lower levels of p53Abs survived significantly longer than patients with higher levels of p53Abs (p=0.049) |
[79][102] |
|||
|
Anderson et al 2010 |
s-p53Ab
ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
Invasive serous OC (n = 60), nonserous ovarian cancers (n = 30), and women with benign disease (n = 30).
|
p53-Ab did not significantly improve the detection of cases [area under the curve (AUC), 0.69] or the discrimination of benign versus malignant disease (AUC, 0.64) compared with CA 125 (AUC, 0.99) or HE4 (AUC, 0.98). In multivariate analysis among cases, p53-AAb correlated only with a family history of breast cancer (P = 0.01). |
[115][141] |
|||
|
Atta et al 2008 |
s-p53Ab
ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt.
41 HCC, 26 Liver cirrhosis, 29 healthy controls
|
Our results revealed that anti-p53 has a positive significant correlation with AFP (p=0.002), severity of liver disease [Child Pugh score (p=0.02) and MELD score (p=0.0003)], tumor size (p<0.0001), tumor number (p=0.003) and tumor staging systems [Okuda (p=0.04), CLIP (p=0.006) and Tokyo (p<0.0001)]. Also, our results revealed that s-p53-Abs had a significant association with overall survival of patients with HCC (p=0.019) with a shorter survival time in anti-p53 positive status patients and with higher s-p53-Abs levels within 19 months follow up |
[116][142] |
|||
|
Mattioni et al 2007 |
S-p53-Abs
Levels of p53-mut were determined with a selective, quantitative ELISA kit (Cambridge, Oncogene, USA)
111 GC patients 64 healthy donors
|
The survival time of serum-positive patients was significantly longer than that of patients with low/negative serum levels, with a survival rate of 41.2% and 14.9%, respectively, over 48 months (p<0.05). |
[117][143] |
|||
|
Lawniczak et al 2007 |
S-p53-Abs
ELISA
71 GC patients
|
The presence of p53-Abs was connected with intestinal tumor type (p < 0.05) and older age (p = 0.0035).
|
[118][144] |
|||
|
Akere et al 2007 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
41 HCC patients 45 controls
|
There is a low prevalence of serum anti-p53 in our study population, and this is commoner in men. It is also present in the control group and therefore may not be useful as a diagnostic tool in this study population.
|
[119][145] |
|||
|
Sainger et al 2006 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
60 oral precancerous patients, 75 untreated oral cancer patients, and 86 follow-up blood samples of the oral cancer patients. 55 healthy controls,
|
The s-p53-Abs positivity correlated with lymph node metastasis, advanced disease and well-differentiated tumors.
Furthermore, p53-Abs positivity strongly correlated with poor outcome from treatment in in the 60 oral precanecours treated patients.
|
[112][137] |
|||
|
Goodell et al 2006 |
S-p53-Abs
ELISA. Antibodies against p53K132Q (c.394A>C).
104 ovarian cancer patients
|
Patients with s-p53Abs recognizing the mutated protein showed a significantly higher survival compared to patients without antibody (p=0.01) |
[120][146] |
|||
|
Gumus et al 2004 |
S-p53-Abs
ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
76 urinary bladder cancer patients |
There was an association between the presence of s-p53-Abs and tumor p53 gene overexpression (P = 0.001)
|
[121][147] |
|||
|
Shimada H et al 2003 |
S-p53-Abs, C-reactive
ELISA Antibodies for p53-wt
258 oesophageal cancer patients |
s-p53-Abs (p < 0.001; HR: 10.6 2; 95%CI:.76-40.00) and S-CRP were independent prognostic factors. |
[111][136] |
|||
|
Hødgall et al 2002 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA Antibodies for p53-wt
193 OC patients 34 borderline OC 86 healthy controls
|
No significant associations were found between p53 AAb and clinical stage, age, histological subtype and radicality after primary surgery. |
[122][148] |
|||
|
Parasole et al 2001 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
80 HCC patients
|
anti-p53 was not useful as prognostic factors
|
[123][149] |
|||
|
Tangkijvanich et al 2000 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
121 HCC patients |
There were no differences between groups with regard to age, sex, viral markers (HBsAg or anti-HCV), severity of liver disease and tumor advancement. The median survival rates for patients positive and negative for s-p53-Abs were 4.0 and 3.0 months, respectively (p = 0.443, by log-rank test). |
[124][150] |
|||
|
Sitruk et al 2000 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA
159 HCC patients |
Detection of s-p53-Abs was significantly correlated with the presence of a multinodular or infiltrative tumor (P<0.03)
|
[125][151] |
|||
|
Zalcman et al 2000 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
97 SCLC patients |
Patients with limited-stage SCLC and p53-Ab had a median survival time of 10 months, whereas limited-stage SCLC patients without p53-Ab had a 17-month median survival time (p = 0.014). |
[106][130]
|
|||
|
Murray et al 2000 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
231 SCLC patients |
High levels of p53-Abs correlated with worse survival compared to patients with lower levels of the antibodies (p = 0.02). |
[57]
|
|||
|
Gottschlich et al 2000 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
109 head and neck cancer patients |
p53-seropositive for the p53-Abs patients showed a correlation with clinical outcome.
|
[110][135] |
|||
|
Mack et al 2000 |
S-p53-Abs Immunofluorescence. Antibodies against p53 R273H (c.818G>A).
35 SCLC patients 99 NSCLC patients
|
There was no correlation between p53-Abs status in SCLC, but the presence of these antibodies and a significant correlation with shorter survival in NSCLC (p=0.01).
|
[107][132] |
|||
|
Lenner et al 1999 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
353 BC patients |
There was a significant negative correlation between presence of s-p53-Abs and survival (P= 0.003)
|
[96][120]
|
|||
|
Kressner et al 1998 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
184 CRC patients |
p53-Abs correlated with shorter survival (p=0.02) |
[100][124] |
|||
|
Werner et al 1997 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
143 oral cancer patients |
the presence of the p53-Ab significantly correlated with more local tumor recurrences and deaths tumor compared to the other group of p53-Ab negative patients (p<0.05) |
[109][134]
|
|||
|
Angelopoulou et al 1997 |
anti-p53 antibodies
ELISA. c.742C>T p.R248W
229 CRC patients |
p53Abs did not significantly correlate with survival |
[80][103] |
|||
|
Bourhis et al 1996 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt. They previously showed a correlation between their ELISA p53-wt antibodies with the presence of p53-mut gene[105].
90 oral cancer patients |
p53-Abs expression correlated with a higher risk of tumor relapse and death (p=0.003 and p=0.03, respectively) |
[108][133]
|
|||
|
Willsher et al 1996 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA Antibodies for soluble p53 with 132 amino acids deletions from N-terminus.
82 BC patients |
Did not find any correlation |
[97][121] |
|||
|
Peyrat et al 1995 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt.
165 BC patients |
Overall survival was significantly worse in patients with s-p53-Abs compared to patients without the s-p53-Abs (p<0.0005). |
[95][118]
|
|||
|
Houbiers et al 1995 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies for p53-wt
255 CRC patients |
Overall survival and Disease Free Survival were significantly worse in patients with s-p53-Abs compared to patients without the s-p53-Abs (p=0.04 for both). |
[81][152] |
|||
|
Porzsolt et al 1994 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibodies against p53R273H (c.818G>A).
50 BC patients |
s-p53-Abs were higher in BC patients with high risk vs patients with low risk. The difference was not statistically significant (p=0.15) |
[98][122] |
|||
|
Volkmann et al 1993 |
S-p53-Abs ELISA. Antibody PAb 1801 against p53-wt and p53-mut. Epitope amino acids 32-79
80 BC patients |
s-p53-Abs correlated with better prognosis compared to patients without the antibodies (p<0.00003 ) |
[126][153] |
|||
Abbreviations: breast cancer, BC; hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC; gastric cancer, GC; serum p53 antibodies, s-p53-Abs; small cell lung carcinoma, SCLC; p53 wild-type, p53-wt; p53 mutant, p53-mut; Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
7.) Discussions and Future Directions
The role of p53-Abs is becoming increasingly important in an era where immune-oncology is advancing at a great speed. Firstly, it is known that infection by SV40 and any other virus stresses the cell and that the infecting viruses avoid cell death by elaborating the following mechanisms: they inhibit p53-wt protein and they inhibit the Rb protein, which is needed to block apopotosis and cell cycle arrest. Secondly, in many cancer cells, from viral and no-viral origin, p53-mut is expressed at very high levels. The p53-mut is unable to bind to DNA to promote the transcription of MDM2 and other p53 transactivational targets and it is therefore not regulated by the same autoregulatory loop of p53-wt. As a direct consequence this leads to its expressed at very high levels in cancer cells, where they work as dominant negative proteins to p53-wt. As an indirect consequence, the accumulated p53-mut serves as an antigen. Finally these p53-mut antigens drive the adaptive immune system to recognize such antigens and produce antibodies that may kill the cancer cells with p53-mut or normal cells with p53-wt. Worth to say that the studies investigating the prognostic role of p53-Abs still remain controversial; and it appears to be tissue-specific. Most interestingly, we have reported here a full updated list of studies on the prognostic value of s-p53-Abs in cancer from published literature (Table 1). Except in a few cases, the vast majority of these studies use p53-wt as the antigen to detect s-p53-Abs in cancer patients and it is unclear that these s-p53-Abs can recognize p53-mut at all. In an historic epoch that has been contemplating the advancement of targeted therapies to meet specific therapeutic needs of cancer patients, it would be of paramount importance to know whether the ELISA assays, designed for recognition of s-p53-Abs, can recognize p53-mut. This review tries to summarize to the best of our knowledge such notion in Table 1. Having methods to detect specific p53-Abs recognizing specific p53-mut could become pivotal in future studies trying to better understand their prognostic value. Moreover, antibodies against specific p53-mut could be directly used for future therapies, which is something p53 biologists would like to further investigate. Sabapathy and colleagues have put this idea into practice by developing mouse monoclonal antibodies against p53 hotspot mutants, R175H, R248Q, and R273H[154], yet the therapeutic effacicy has not been reported.
Of note, expressions of PD-L1 and p53 correlated in various types of cancers[155–159]. Additionally p53-mut downmodulates the expression of PD-L1 through microRNA-34[155]. For such reasons, it would be also interesting in future experiments to investigate the efficacy of p53-Abs recognizing p53-mut in combination with checkpoint inhibitors against PD-L1.
In conclusion, there are s-p53-Abs in a significant portion of cancer patients (mostly observed by ELISA) and only in a small fraction of these studies, the presence of s-p53-Abs predicts better survival. Virtually all s-p53-Abs are detected using p53-wt as an antigen. One thing we do not currently know, but hope that an antibody targeting a specific p53-mut will be effective in therapeutics against the cancer carrying the exact p53-mut. In fact, s-p53-Abs from cancer patients may target both p53-wt and p53-mut. Novel antibodies targeting p53-mut, but not p53-wt, should be pursued in pre- and clinical trials.
8). References
- Levine, A.J. Transformation-associated tumor antigens. Adv. Cancer Res. 1982, 37, 75–109.
- Levine, A.J. Oncogenes of DNA tumor viruses. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 493–6.
- Werness, B.A.; Levine, A.J.; Howley, P.M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science (80-. ). 1990, 248, 76–79.
- Scheffner, M.; Werness, B.A.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Levine, A.J.; Howley, P.M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 1990, 63, 1129–1136.
- Tevethia, S.S.; Lewis, A.J.; Campbell, A.E.; Tevethia, M.J.; Rigby, P.W.J. Simian virus 40 specific cytotoxic lymphocyte clones localize two distinct TSTA sites on cells synthesizing a 48 kD SV40 T antigen. Virology 1984, 133, 443–447.
- DeLeo, A.B.; Jay, G.; Appella, E.; Dubois, G.C.; Law, L.W.; Old, L.J. Detection of a transformation-related antigen in chemically induced sarcomas and other transformed cells of the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1979, 76, 2420–2424.
- Kress, M.; May, E.; Cassingena, R.; May, P. Simian virus 40-transformed cells express new species of proteins precipitable by anti-simian virus 40 tumor serum. J. Virol. 1979, 31, 472–483.
- Lane, D.P.; Crawford, L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SY40-transformed cells [19]. Nature 1979, 278, 261–263.
- Linzer, D.I.H.; Levine, A.J. Characterization of a 54K Dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell 1979, 17, 43–52.
- Levine, A.J. P53 and the immune response: 40 years of exploration—a plan for the future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21.
- Sabapathy, K.; Lane, D.P. Understanding p53 functions through p53 antibodies. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 317–329.
- Olivier, M.; Taniere, P. Somatic mutations in cancer prognosis and prediction: Lessons from TP53 and EGFR genes. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2011, 23, 88–92.
- Rivlin, N.; Brosh, R.; Oren, M.; Rotter, V. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Important milestones at the various steps of tumorigenesis. Genes and Cancer 2011, 2, 466–474.
- Donnelly, M.P.; Li, J.; Hwang, P.M. Mitochondrial stress delays tumorigenesis in a Li-Fraumeni syndrome mouse model. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 115–117.
- Levine, A.J.; Puzio-Kuter, A.M.; Chan, C.S.; Hainaut, P. The role of the p53 protein in stem-cell biology and epigenetic regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6.
- Amelio, I.; Melino, G. Context is everything : extrinsic signalling and gain-of-function p53 mutants. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 16.
- Pfister, N.T.; Prives, C. Transcriptional regulation by wild-type and cancer-related mutant forms of p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7.
- Lane, D.P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 1992, 358, 15–6.
- Beckerman, R.; Prives, C. Transcriptional regulation by p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2.
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell 2009, 137, 413–31.
- Friedman, P.N.; Chen, X.; Bargonetti, J.; Prives, C. The p53 protein is an unusually shaped tetramer that binds directly to DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1993, 90, 3319–3323.
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2.
- Dittmer, D.; Pati, S.; Zambetti, G.; Chu, S.; Teresky, A.K.; Moore, M.; Finlay, C.; Levine, A.J. Gain of function mutations in p53. Nat. Genet. 1993, 4, 42–6.
- Song, H.; Hollstein, M.; Xu, Y. p53 gain-of-function cancer mutants induce genetic instability by inactivating ATM. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 573–580.
- Liu, D.P.; Song, H.; Xu, Y. A common gain of function of p53 cancer mutants in inducing genetic instability. Oncogene 2010, 29, 949–956.
- Hanel, W.; Marchenko, N.; Xu, S.; Xiaofeng Yu, S.; Weng, W.; Moll, U. Two hot spot mutant p53 mouse models display differential gain of function in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 898–909.
- Heinlein, C.; Krepulat, F.; Löhler, J.; Speidel, D.; Deppert, W.; Tolstonog, G. V. Mutant p53R270H gain of function phenotype in a mouse model for oncogene-induced mammary carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1701–1709.
- Brosh, R.; Rotter, V. When mutants gain new powers: News from the mutant p53 field. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 701–713.
- Stambolsky, P.; Tabach, Y.; Fontemaggi, G.; Weisz, L.; Maor-Aloni, R.; Sigfried, Z.; Shiff, I.; Kogan, I.; Shay, M.; Kalo, E.; et al. Modulation of the Vitamin D3 Response by Cancer-Associated Mutant p53. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 273–285.
- Liu, K.; Ling, S.; Lin, W.-C. TopBP1 Mediates Mutant p53 Gain of Function through NF-Y and p63/p73. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 4464–4481.
- Gaiddon, C.; Lokshin, M.; Ahn, J.; Zhang, T.; Prives, C. A Subset of Tumor-Derived Mutant Forms of p53 Down-Regulate p63 and p73 through a Direct Interaction with the p53 Core Domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1874–1887.
- Yamamoto, S.; Iwakuma, T. Regulators of oncogenic mutant TP53 gain of function. Cancers (Basel). 2019, 11.
- Pitolli, C.; Wang, Y.; Mancini, M.; Shi, Y.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. Do mutations turn p53 into an oncogene? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20.
- Roszkowska, K.A.; Gizinski, S.; Sady, M.; Gajewski, Z.; Olszewski, M.B. Gain-of-function mutations in p53 in cancer invasiveness and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21.
- Wu, X.; Bayle, J.H.; Olson, D.; Levine, A.J. The p53-mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1126–1132.
- Feng, L.; Lin, T.; Uranishi, H.; Gu, W.; Xu, Y. Functional Analysis of the Roles of Posttranslational Modifications at the p53 C Terminus in Regulating p53 Stability and Activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 5389–5395.
- Krummel, K.A.; Lee, C.J.; Toledo, F.; Wahl, G.M. The C-terminal lysines fine-tune P53 stress responses in a mouse model but are not required for stability control or transactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2005, 102, 10188–10193.
- Leng, R.P.; Lin, Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, H.; Lemmers, B.; Chung, S.; Parant, J.M.; Lozano, G.; Hakem, R.; Benchimol, S. Pirh2, a p53-induced ubiquitin-protein ligase, promotes p53 degradation. Cell 2003, 112, 779–791.
- Jain, A.K.; Barton, M.C. Making sense of ubiquitin ligases that regulate p53. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 665–672.
- Sane, S.; Rezvani, K. Essential roles of E3 ubiquitin ligases in p53 regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18.
- Allton, K.; Jain, A.K.; Herz, H.M.; Tsai, W.W.; Sung, Y.J.; Qin, J.; Bergmann, A.; Johnson, R.L.; Barton, M.C. Trim24 targets endogenous p53 for degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 11612–11616.
- Rajendra, R.; Malegaonkar, D.; Pungaliya, P.; Marshall, H.; Rasheed, Z.; Brownell, J.; Liu, L.F.; Lutzker, S.; Saleem, A.; Rubin, E.H. Topors functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase with specific E2 enzymes and ubiquitinates p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 36440–36444.
- Laine, A.; Ronai, Z. Regulation of p53 localization and transcription by the HECT domain E3 ligase WWP1. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1477–1483.
- Chen, D.; Kon, N.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Qin, J.; Gu, W. ARF-BP1/mule is a critical mediator of the ARF tumor suppressor. Cell 2005, 121, 1071–1083.
- Laine, A.; Topisirovic, I.; Zhai, D.; Reed, J.C.; Borden, K.L.B.; Ronai, Z. Regulation of p53 localization and activity by Ubc13. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 8901–13.
- Boutell, C.; Everett, R.D. The herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) regulatory protein ICP0 interacts with and ubiquitinates p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36596–36602.
- Yang, W.; Rozan, L.M.; McDonald, E.R.; Navaraj, A.; Liu, J.J.; Matthew, E.M.; Wang, W.; Dicker, D.T.; El-Deiry, W.S. CARPs are ubiquitin ligases that promote MDM2-independent p53 and phospho-p53ser20 degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3273–3281.
- Andrews, P.; He, Y.J.; Xiong, Y. Cytoplasmic localized ubiquitin ligase cullin 7 binds to p53 and promotes cell growth by antagonizing p53 function. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4534–4548.
- Yamasaki, S.; Yagishita, N.; Sasaki, T.; Nakazawa, M.; Kato, Y.; Yamadera, T.; Bae, E.; Toriyama, S.; Ikeda, R.; Zhang, L.; et al. Cytoplasmic destruction of p53 by the endoplasmic reticulum-resident ubiquitin ligase “Synoviolin.” EMBO J. 2007, 26, 113–122.
- Le Cam, L.; Linares, L.K.; Paul, C.; Julien, E.; Lacroix, M.; Hatchi, E.; Triboulet, R.; Bossis, G.; Shmueli, A.; Rodriguez, M.S.; et al. E4F1 Is an Atypical Ubiquitin Ligase that Modulates p53 Effector Functions Independently of Degradation. Cell 2006, 127, 775–788.
- Esser, C.; Scheffner, M.; Höhfeld, J. The chaperone-associated ubiquitin ligase CHIP is able to target p53 for proteasomal degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27443–27448.
- Querido, E.; Blanchette, P.; Yan, Q.; Kamura, T.; Morrison, M.; Boivin, D.; Kaelin, W.G.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W.; Branton, P.E. Degradation of p53 by adenovirus E4orf6 and E1B55K proteins occurs via a novel mechanism involving a Cullin-containing complex. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 3104–3117.
- Kruse, J.P.; Gu, W. MSL2 promotes Mdm2-independent cytoplasmic localization of p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3250–3263.
- Sun, L.; Shi, L.; Li, W.; Yu, W.; Liang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Yao, X.; et al. JFK, a Kelch domain-containing F-box protein, links the SCF complex to p53 regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 10195–10200.
- Phillips, A.; Teunisse, A.; Lam, S.; Lodder, K.; Darley, M.; Emaduddin, M.; Wolf, A.; Richter, J.; De Lange, J.; Vries, M.V. De; et al. HDMX-L is expressed from a functional p53-responsive promoter in the first intron of the HDMX gene and participates in an autoregulatory feedback loop to control p53 activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29111–29127.
- Yue, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Feng, Z.; et al. BAG2 promotes tumorigenesis through enhancing mutant p53 protein levels and function. Elife 2015, 4, 1–23.
- Murray, P. V.; Soussi, T.; O’Brien, M.E.R.; Smith, I.E.; Brossault, S.; Norton, A.; Ashley, S.; Tavassoli, M. Serum p53 antibodies: Predictors of survival in small-cell lung cancer? Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1418–1424.
- Rosenthal, R.; Cadieux, E.L.; Salgado, R.; Bakir, M. Al; Moore, D.A.; Hiley, C.T.; Lund, T.; Tanić, M.; Reading, J.L.; Joshi, K.; et al. Neoantigen-directed immune escape in lung cancer evolution. Nature 2019, 567, 479–485.
- Smyth, M.J.; Thia, K.Y.T.; Street, S.E.A.; Cretney, E.; Trapani, J.A.; Taniguchi, M.; Kawano, T.; Pelikan, S.B.; Crowe, N.Y.; Godfrey, D.I. Differential tumor surveillance by natural killer (NK) and NKT cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 661–668.
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452.
- Blagih, J.; Zani, F.; Chakravarty, P.; Hennequart, M.; Pilley, S.; Hobor, S.; Hock, A.K.; Walton, J.B.; Morton, J.P.; Gronroos, E.; et al. Cancer-Specific Loss of p53 Leads to a Modulation of Myeloid and T Cell Responses. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 481-496.e6.
- Wang, B.; Niu, D.; Lai, L.; Ren, E.C. P53 increases MHC class i expression by upregulating the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2359.
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 153–167.
- Freeman, G.J.; Long, A.J.; Iwai, Y.; Bourque, K.; Chernova, T.; Nishimura, H.; Fitz, L.J.; Malenkovich, N.; Okazaki, T.; Byrne, M.C.; et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1027–1034.
- Blasius, A.L.; Beutler, B. Intracellular Toll-like Receptors. Immunity 2010, 32, 305–315.
- Shatz, M.; Menendez, D.; Resnick, M.A. The human TLR innate immune gene family is differentially influenced by DNA stress and p53 status in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3949–3957.
- Menendez, D.; Lowe, J.M.; Snipe, J.; Resnick, M.A. Ligand dependent restoration of human TLR3 signaling and death in p53 mutant cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61630–61642.
- Shatz, M.; Shats, I.; Menendez, D.; Resnick, M.A. p53 amplifies Toll-like receptor 5 response in human primary and cancer cells through interaction with multiple signal transduction pathways. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16963–16980.
- Blagih, J.; Buck, M.D.; Vousden, K.H. p53, cancer and the immune response. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133.
- Wörmann, S.M.; Song, L.; Ai, J.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Kurkowski, M.U.; Görgülü, K.; Ruess, D.; Campbell, A.; Doglioni, C.; Jodrell, D.; et al. Loss of P53 Function Activates JAK2–STAT3 Signaling to Promote Pancreatic Tumor Growth, Stroma Modification, and Gemcitabine Resistance in Mice and Is Associated With Patient Survival. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 180-193.e12.
- Wellenstein, M.D.; Coffelt, S.B.; Duits, D.E.M.; van Miltenburg, M.H.; Slagter, M.; de Rink, I.; Henneman, L.; Kas, S.M.; Prekovic, S.; Hau, C.S.; et al. Loss of p53 triggers WNT-dependent systemic inflammation to drive breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2019, 572, 538–542.
- Walton, J.; Blagih, J.; Ennis, D.; Leung, E.; Dowson, S.; Farquharson, M.; Tookman, L.A.; Orange, C.; Athineos, D.; Mason, S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Trp53 and Brca2 knockout to generate improved murine models of ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6118–6129.
- Bezzi, M.; Seitzer, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Reschke, M.; Chen, M.; Wang, G.; Mitchell, C.; Ng, C.; Katon, J.; Lunardi, A.; et al. Diverse genetic-driven immune landscapes dictate tumor progression through distinct mechanisms. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 165–175.
- Ruddell, A.; Kelly-Spratt, K.S.; Furuya, M.; Parghi, S.S.; Kemp, C.J. p19/Arf and p53 suppress sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and carcinoma metastasis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3145–3155.
- Candido, J.B.; Morton, J.P.; Bailey, P.; Campbell, A.D.; Karim, S.A.; Jamieson, T.; Lapienyte, L.; Gopinathan, A.; Clark, W.; McGhee, E.J.; et al. CSF1R+ Macrophages Sustain Pancreatic Tumor Growth through T Cell Suppression and Maintenance of Key Gene Programs that Define the Squamous Subtype. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1448–1460.
- Zhu, Y.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Meyer, M.A.; Nywening, T.M.; West, B.L.; Luo, J.; Wang-Gillam, A.; Goedegebuure, S.P.; Linehan, D.C.; De Nardo, D.G. CSF1/CSF1R blockade reprograms tumor-infiltrating macrophages and improves response to T-cell checkpoint immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer models. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5057–5069.
- Bailey, J.M.; Hendley, A.M.; Lafaro, K.J.; Pruski, M.A.; Jones, N.C.; Alsina, J.; Younes, M.; Maitra, A.; McAllister, F.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; et al. P53 mutations cooperate with oncogenic Kras to promote adenocarcinoma from pancreatic ductal cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4282–4288.
- Rachmawati, M.; Yulianti, H.; Hernowo, B.S.; Suryanti, S.; Wijaya, I.; Rahadiani, N.; Heriyanto, D.S.; Irianiwati, I. The Correlation of KRAS Gene Expression and P53 Immunoexpression In Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 1940–1945.
- Coppé, J.-P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Campisi, J. Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotypes Reveal Cell-Nonautonomous Functions of Oncogenic RAS and the p53 Tumor Suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e301.
- Rufini, A.; Tucci, P.; Celardo, I.; Melino, G. Senescence and aging: The critical roles of p53. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5129–5143.
- Lessel, D.; Wu, D.; Trujillo, C.; Ramezani, T.; Lessel, I.; Alwasiyah, M.K.; Saha, B.; Hisama, F.M.; Rading, K.; Goebel, I.; et al. Dysfunction of the MDM2/p53 axis is linked to premature aging. In Proceedings of the Journal of Clinical Investigation; American Society for Clinical Investigation, 2017; Vol. 127, pp. 3598–3608.
- Donehower, L.A. Does p53 affect organismal aging? J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 192, 23–33.
- Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Cao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H. Extraordinary GU-rich single-strand RNA identified from SARS coronavirus contributes an excessive innate immune response. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 88–95.
- Lubin, R.; Schlichtholz, B.; Teillaud, J.L.; Garay, E.; Bussel, A.; Wild, C.P. p53 antibodies in patients with various types of cancer: assay, identification, and characterization. Clin. Cancer Res. 1995, 1, 1463–9.
- Angelopoulou, K.; Diamandis, E.P.; Sutherland, D.J.A.; Kellen, J.A.; Bunting, P.S. Prevalence of serum antibodies against the p53 tumor suppressor gene protein in various cancers. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 58, 480–487.
- De Fromentel, C.C.; Chandrasekaran, K.; May, P.; May‐Levin, F.; Mouriesse, H.; Lemerle, J. Presence of circulating antibodies against cellular protein p53 in a notable proportion of children with B‐cell lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 1987, 39, 185–189.
- Crawford, L. V.; Pim, D.C.; Bulbrook, R.D. Detection of antibodies against the cellular protein p53 in sera from patients with breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1982, 30, 403–408.
- Bennett, W.P.; Colby, T. V.; Travis, W.D.; Borkowski, A.; Jones, R.T.; Lane, D.P.; Metcalf, R.A.; Samet, J.M.; Takeshima, Y.; Gu, J.R.; et al. p53 Protein Accumulates Frequently in Early Bronchial Neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 4817–4822.
- Cho, Y.; Gorina, S.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Pavletich, N.P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: Understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science (80-. ). 1994, 265, 346–355.
- Legros, Y.; Meyer, A.; Ory, K.; Soussi, T. Mutations in p53 produce a common conformational effect that can be detected with a panel of monoclonal antibodies directed toward the central part of the p53 protein. Oncogene 1994, 9, 3689–94.
- Soussi, T. p53 Antibodies in the sera of patients with various types of cancer: A review. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1777–1788.
- Davidoff, A.M.; Dirk Iglehart, J.; Marks, J.R. Immune response to p53 is dependent upon p53/HSP70 complexes in breast cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1992, 89, 3439–3442.
- Schlichtholz, B.; Legros, Y.; Gillet, D.; Gaillard, C.; Marty, M.; Lane, D.; Calvo, F.; Soussi, T. The immune response to p53 in breast cancer patients is directed against immunodominant epitopes unrelated to the mutational hot spot. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 6380–4.
- Labrecque, S.; Naor, N.; Thomson, D.; Matlashewski2, G. Analysis of the Anti-p53 Antibody Response in Cancer Patients1; 1993; Vol. 53;.
- Janin, N.; Bressac, B.; Hirsch, A. Analysis of p53 Antibodies in Patients with Various Cancers Define B-Cell Epitopes of Human p53: Distribution on Primary Structure and Exposure on Protein Surface. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 5872–5876.
- Schlichtholz, B.; Trédaniel, J.; Lubin, R.; Zalcman, G.; Hirsch, A.; Soussi, T. Analyses of p53 antibodies in sera of patients with lung carcinoma define immunodominant regions in the p53 protein. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 69, 809–16.
- Vennegoor, C.J.G.; Nijman, H.W.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Vernie, L.; Verstraeten, R.A.; von Mensdorff-Pouilly, S.; Hilgers, J.; Verheijen, R.H.; Kast, W.M.; Melief, C.J.; et al. Autoantibodies to p53 in ovarian cancer patients and healthy women: a comparison between whole p53 protein and 18-mer peptides for screening purposes. Cancer Lett. 1997, 116, 93–101.
- Crawford, L. V.; Pim, D.C.; Bulbrook, R.D. Detection of antibodies against the cellular protein p53 in sera from patients with breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1982, 30, 403–408.
- Munker, R.; Stötzer, O.; Darsow, M.; Classen, S.; Lebeau, A.; Wilmanns, W. Autoantibodies against p53 are not increased in human ascites and pleural effusions. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1996, 42, 200–201.
- Angelopoulou, K.; Diamandis, E.P. Detection of the TP53 tumour suppressor gene product and p53 auto-antibodies in the ascites of women with ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Part A 1997, 33, 115–121.
- Tavassoli, M.; Brunel, N.; Maher, R.; Johnson, N.W.; Soussi, T. p53 antibodies in the saliva of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Int. J. cancer 1998, 78, 390–1.
- Mattioni, M.; Soddu, S.; Prodosmo, A.; Visca, P.; Conti, S.; Alessandrini, G.; Facciolo, F.; Strigari, L. Prognostic role of serum p53 antibodies in lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 148.
- Angelopoulou, K.; Stratis, M.; Diamandis, E.P. Humoral immune response against p53 protein in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. cancer 1997, 70, 46–51.
- Houbiers, J.G.A.; van der Burg, S.H.; van de Watering, L.M.G.; Tollenaar, R.A.E.M.; Brand, A.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Melief, C.J.M. Antibodies against p53 are associated with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 637–641.
- Lubin, R.; Schlichtholz, B.; Teillaud, J.L.; Garay, E.; Bussel, A.; Wild, C.P.; Soussi, T. p53 Antibodies in Patients with Various Types of Cancer: Assay, Identification, and Characterization. Clin. Cancer Res. 1995, 1, 1463–1469.
- Malkin, D.; Gallie, B.L.; Buchanan, J. Mutations of the p53 Gene Do Not Occur in Testis Cancer. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3574–3578.
- M, F.; T, S.; Y, I.; DJ, S.; HP, K. Mutations of the p53 gene are not detectable in human testicular tumors. Mod. Pathol. 1994, 7, 435–439.
- Puisieux, A.; Galvin, K.; Troalen, F.; Bressac, B.; Marcais, C.; Galun, E.; Ponchel, F.; Yakicier, C.; Ji, J.; Ozturk, M. Retinoblastoma and p53 tumor suppressor genes in human hepatoma cell lines. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 1407–1413.
- Lübbe, J.; Reichel, M.; Burg, G.; Kleihues, P. Absence of p53 gene mutations in cutaneous melanoma. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 819–821.
- Luca, M.; Lenzi, R.; Leejackson, D.; Gutman, M.; Fidler, I.; Bareli, M. P53 mutations are infrequent and do not correlate with the metastatic potential of human-melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 1993, 3, 19–22.
- Ohgaki, H.; Eibl, R.H.; Reichel, M.B.; Mariani, L.; Petersen, I.; Höll, T.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Schwab, M.; Gehring, M. Mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in neoplasms of the human nervous system. Mol. Carcinog. 1993, 8, 74–80.
- Rainov, N.G.; Dobberstein, K.U.; Fittkau, M.; Bahn, H.; Holzhausen, H.J.; Gantchev, L.; Burkert, W. Absence of p53 autoantibodies in sera from glioma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 1995, 1, 775–81.
- Winter, S.F.; Sekido, Y.; Minna, J.D.; Mcintire, D.; Johnson, B.E.; Gazdar, A.F.; Carbone, D.P. Antibodies against autologous tumor cell proteins in patients with small-cell lung cancer: Association with improved survival. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 2012–2018.
- Cawley, H.M.; Meltzer, S.J.; De Benedetti, V.M.G.; Hollstein, M.C.; Muehlbauer, K.R.; Liang, L.; Bennett, W.P.; Souza, R.F.; Greenwald, B.D.; Cottrell, J.; et al. Anti-p53 antibodies in patients with Barrett’s esophagus or esophageal carcinoma can predate cancer diagnosis. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 19–27.
- Hammel, P.; Leroy-Viard, K.; Chaumette, M.T.; Villaudy, J.; Falzone, M.C.; Rouillard, D.; Hamelin, R.; Boissier, B.; Remvikos, Y. Correlations between p53-protein accumulation, serum antibodies and gene mutation in colorectal cancer. Int. J. cancer 1999, 81, 712–8.
- von Brevern, M.C.; Hollstein, M.C.; Cawley, H.M.; De Benedetti, V.M.; Bennett, W.P.; Liang, L.; He, A.G.; Zhu, S.M.; Tursz, T.; Janin, N.; et al. Circulating anti-p53 antibodies in esophageal cancer patients are found predominantly in individuals with p53 core domain mutations in their tumors. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4917–21.
- Mudenda, B.; Green, J.A.; Green, B.; Jenkins, J.R.; Robertson, L.; Tarunina, M.; Leinster, S.J. The relationship between serum p53 autoantibodies and characteristics of human breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 69, 1115–1119.
- Peyrat, J.P.; Fournier, J.; Bonneterre, J.; Vanlemmens, L.; Lubin, R.; Soussi, T. Prognostic significance of circulating P53 antibodies in patients undergoing surgery for locoregional breast cancer. Lancet 1995, 345, 621–622.
- Angelopoulou, K.; Diamandis, E.P.; Sutherland, D.J.A.; Kellen, J.A.; Bunting, P.S. Prevalence of serum antibodies against the p53 tumor suppressor gene protein in various cancers. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 58, 480–487.
- Lenner, P.; Wiklund, F.; Emdin, S.O.; Arnerlöv, C.; Eklund, C.; Hallmans, G.; Zentgraf, H.; Dillner, J. Serum antibodies against p53 in relation to cancer risk and prognosis in breast cancer: A population-based epidemiological study. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 927–932.
- Willsher, P.C.; Pinder, S.E.; Robertson, L.; Nicholson, R.I.; Ellis, I.O.; Bell, J.A.; Blamey, R.W.; Green, J.A.; Robertson, J.F. The significance of p53 autoantibodies in the serum of patients with breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 16, 927–30.
- Porzsolt, F.; Schmid, M.; Höher, D.; Muche, R.; Gaus, W.; Montenarh, M. Biologic Relevance of Auto-Anti bodies against p53 in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 1994, 17, 402–408.
- Generali, D.; Fox, S.B.; Berruti, A.; Brizzi, M.P.; Campo, L.; Bonardi, S.; Wigfield, S.M.; Bruzzi, P.; Bersiga, A.; Allevi, G.; et al. Role of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in prediction of the efficacy and outcome of primary epirubicin/tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 921–930.
- Kressner, U.; Glimelius, B.; Bergström, R.; Påhlman, L.; Larsson, A.; Lindmark, G. Increased serum p53 antibody levels indicate poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 1848–1851.
- Kunizaki, M.; Sawai, T.; Takeshita, H.; Tominaga, T.; Hidaka, S.; To, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Hamamoto, R.; Nanashima, A.; Nagayasu, T. Clinical Value of Serum p53 Antibody in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 4171–5.
- Tokunaga, R.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Yoshida, N.; Baba, H. The utility of tumor marker combination, including serum P53 antibody, in colorectal cancer treatment. Surg. Today 2017, 47, 636–642.
- Komiya, T.; Hirashima, T.; Takada, M.; Masuda, N.; Yasumitsu, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Hosono, Y.; Kikui, M.; Tsuji, S.; Fukuoka, M.; et al. Prognostic significance of serum p53 antibodies in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Anticancer Res. 17, 3721–4.
- Lai, C.L.; Tsai, C.M.; Tsai, T.T.; Kuo, B.I.; Chang, K.T.; Fu, H.T.; Perng, R.P.; Chen, J.Y. Presence of serum anti-p53 antibodies is associated with pleural effusion and poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 3025–30.
- Laudanski, J.; Burzykowski, T.; Niklinska, W.; Chyczewski, K.; Furman, M.; Niklinski, J. Prognostic value of serum p53 antibodies in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 1998, 22, 191–200.
- Zalcman, G.; Trédaniel, J.; Schlichtholz, B.; Urban, T.; Milleron, B.; Lubin, R.; Meignin, V.; Couderc, L.; Hirsch, A.; Soussi, T. Prognostic significance of serum p53 antibodies in patients with limited‐stage small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 89, 81–86.
- Murray, P. V.; Soussi, T.; O’Brien, M.E.R.; Smith, I.E.; Brossault, S.; Norton, A.; Ashley, S.; Tavassoli, M. Serum p53 antibodies: Predictors of survival in small-cell lung cancer? Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1418–1424.
- Mack, U.; Ukena, D.; Montenarh, M.; Sybrecht, G.W. Serum anti-p53 antibodies in patients with lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2000, 7, 669–674.
- Bourhis, J.; Lubin, R.; Roche, B.; Koscielny, S.; Bosq, J.; Dubois, I.; Talbot, M.; Marandas, P.; Schwaab, G.; Wibault, P.; et al. Analysis of p53 serum antibodies in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1996, 88, 1228–33.
- Werner, J.A.; Gottschlich, S.; Folz, B.J.; Goeroegh, T.; Lippert, B.M.; Maass, J.D.; Rudert, H. p53 serum antibodies as prognostic indicator in head and neck cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1997, 44, 112–116.
- Gottschlich, S.; Maune, S.; Maass, J.D.; Görögh, T.; Hoffmann, M.; Hoffmann-Fazel, A.; Meyer, J.; Werner, J.A.; Rudert, H. Serum p53 autoantibodies in the follow-up of head and neck cancer patients. Oncology 2000, 59, 31–35.
- Shimada, H.; Kitabayashi, H.; Nabeya, Y.; Okazumi, S.I.; Matsubara, H.; Funami, Y.; Miyazawa, Y.; Shiratori, T.; Uno, T.; Itoh, H.; et al. Treatment response and prognosis of patients after recurrence of esophageal cancer. Surgery 2003, 133, 24–31.
- Sainger, R.N.S.; Shah, M.H.; Desai, A.A.; Shukla, S.N.; Shah, P.M.; Telang, S.D.; Patel, P.S. Clinical significance of serum p53 antibodies in oral cancer. Tumori 92, 134–9.
- Kunizaki, M.; Hamasaki, K.; Wakata, K.; Tobinaga, S.; Sumida, Y.; Hidaka, S.; Yasutake, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamasaki, T.; et al. Clinical value of serum p53 antibody in the diagnosis and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 1807–1813.
- Kunizaki, M.; Fukuda, A.; Wakata, K.; Tominaga, T.; Nonaka, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Sumida, Y.; Hidaka, S.; Yasutake, T.; et al. Clinical significance of serum p53 antibody in the early detection and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1979–1984.
- Tokunaga, R.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Yoshida, N.; Baba, H. The utility of tumor marker combination, including serum P53 antibody, in colorectal cancer treatment. Surg. Today 2017, 47, 636–642.
- Anderson, K.S.; Wong, J.; Vitonis, A.; Crum, C.P.; Sluss, P.M.; LaBaer, J.; Cramer, D. p53 autoantibodies as potential detection and prognostic biomarkers in serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2010, 19, 859–868.
- Atta, M.M.; El-Masry, S.A.; Abdel-Hameed, M.; Baiomy, H.A.; Ramadan, N.E. Value of serum anti-p53 antibodies as a prognostic factor in Egyptian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 1131–1139.
- Mattioni, M.; Soddu, S.; Porrello, A.; D’Alessandro, R.; Spila, A.; Guadagni, F. Serum anti-p53 antibodies as a useful marker for prognosis of gastric carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Markers 22, 302–6.
- Lawniczak, M.; Bielicki, D.; Sulzyc-Bielicka, V.; Marlicz, K.; Starzyńska, T. [Serum anti-p53 antibodies in gastric cancer patients]. Pol. Merkur. Lekarski 2007, 23, 192–5.
- Akere, A.; Otegbayo, J.A. Evaluation of the pattern and prognostic implications of anti-p53 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Singapore Med. J. 2007, 48, 41–4.
- Goodell, V.; Salazar, L.G.; Urban, N.; Drescher, C.W.; Gray, H.; Swensen, R.E.; McIntosh, M.W.; Disis, M.L. Antibody immunity to the p53 oncogenic protein is a prognostic indicator in ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 762–768.
- Gumus, E.; Erdamar, S.; Demirel, G.; Horasanli, K.; Kendirci, M.; Miroglu, C. Association of positive serum anti-p53 antibodies with poor prognosis in bladder cancer patients. Int. J. Urol. 2004, 11, 1070–1077.
- Høgdall, E.V.S.; Høgdall, C.K.; Blaakaer, J.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Glud, E.; Christensen, L.; Bock, J.E.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Wiik, A.; Kjaer, S.K. P53 autoantibodies in sera from Danish ovarian cancer patients and their correlation with clinical data and prognosis. APMIS 2002, 110, 545–553.
- Parasole, R.; Izzo, F.; Perrone, F.; Pignata, S.; Galati, M.G.; Leonardi, E.; Castiglione, F.; Orlando, R.; Castello, G.; Esposito, G.; et al. Prognostic value of serum biological markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 3504–9.
- Tangkijvanich, P.; Janchai, A.; Charuruks, N.; Kullavanijaya, P.; Theamboonlers, A.; Hirsch, P.; Poovorawan, Y. Clinical associations and prognostic significance of serum anti-p53 antibodies in Thai patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pacific J. allergy Immunol. 2000, 18, 237–43.
- Sitruk, V.; Vaysse, J.; Chevret, S.; Ganne-Carrie, N.; Christidis, C.; Trinchet, J.; Beaugrand, M. [Prevalence and prognostic value of serum anti-p53 antibodies in hepatocellular carcinoma. A study of 159 patients]. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2000, 24, 1159–63.
- Houbiers, J.G.A.; van der Burg, S.H.; van de Watering, L.M.G.; Tollenaar, R.A.E.M.; Brand, A.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Melief, C.J.M. Antibodies against p53 are associated with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 637–641.
- Volkmann, M.; Müller, M.; Hofmann, W.J.; Meyer, M.; Hagelstein, J.; Räth, U.; Kommerell, B.; Zentgraf, H.; Galle, P.R. The humoral immune response to p53 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma is specific for malignancy and independent of the alpha-fetoprotein status. Hepatology 1993, 18, 559–65.
- Hwang, L.A.; Phang, B.H.; Liew, O.W.; Iqbal, J.; Koh, X.H.; Koh, X.Y.; Othman, R.; Xue, Y.; Richards, A.M.; Lane, D.P.; et al. Monoclonal Antibodies against Specific p53 Hotspot Mutants as Potential Tools for Precision Medicine. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 299–312.
- Cortez, M.A.; Ivan, C.; Valdecanas, D.; Wang, X.; Peltier, H.J.; Ye, Y.; Araujo, L.; Carbone, D.P.; Shilo, K.; Giri, D.K.; et al. PDL1 Regulation by p53 via miR-34. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108.
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, C.-L.; Xian, J.; Ye, Q.; Qin, X.; Tan, Y.-W.; Cao, Y.-D. <p>Positive correlation between programmed death ligand-1 and p53 in triple-negative breast cancer</p>. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2019, Volume 12, 7193–7201.
- Tojyo, I.; Shintani, Y.; Nakanishi, T.; Okamoto, K.; Hiraishi, Y.; Fujita, S.; Enaka, M.; Sato, F.; Muragaki, Y. PD-L1 expression correlated with p53 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 41.
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.H. Correlation between Programmed Death-1 Ligand-1 and p53 in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Chin. Med. J. (Engl). 2018, 131, 990–993.
- Yu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, F.; Lin, Y. Bin; Wang, W.D.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Cai, L. Correlation and prognostic significance of PD-L1 and P53 expression in resected primary pulmonary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 1891–1902.
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access
article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution
(CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
