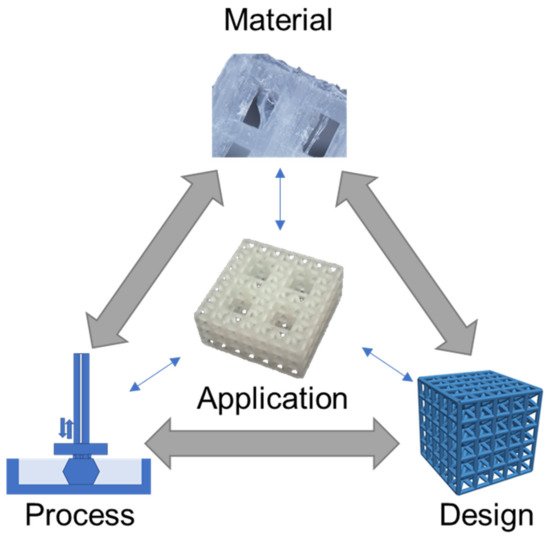
Polymer 3D printing is an emerging technology with recent research translating towards increased use in diverse industries. The polymer 3D printing process works by depositing a polymer in a directed fashion to form a completed part, generally through layer by layer deposition. Polymer printing is advantageous because it enables printing low-cost functional parts with diverse properties and capabilities. An important aspect polymer 3D printing is the consideration of materials, processes, and design strategies that all influence a parts performance. Research in materials has led to the development of polymers with advantageous characteristics for mechanics and biocompatibility, with tuning of mechanical properties achieved by altering printing process parameters. Suitable polymer printing processes include extrusion, resin, and powder 3D printing, which enable directed material deposition for the design of advantageous and customized architectures. Through careful consideration of material, process, and design it is possible to create a 3D printed polymer part of complex geometry that is tuned for a specific application on a per-print basis.
1. Introduction
Polymer 3D (three-dimensional) printing has advanced rapidly in recent years with many areas of research now translating to engineered products, especially in medical fields [1][2][3][4]. Polymer printing is advantageous for a broad range of medical areas that benefit from the diversity of polymer material characteristics and processing approaches [5][6][7][8]. 3D printing is a highly desirable fabrication approach because it enables the construction of designs with complex geometries and architectures that are not possible with conventional manufacturing processes. For instance, tissue scaffold structures fabricated with polyjet and stereolithography printing can achieve hierarchical forms that mimic bone, thereby providing a mechanical and biological niche to support tissue regeneration [9][10]. Additionally, the selection of polymers has advantages over metal printing approaches, that result in metal implants that do not degrade in the body and lead to mechanical issues such as stress shielding [11]. In areas of safety equipment, polymer-printed lattices achieve efficient energy absorption with a rapid fabrication process that bypasses the supply chain limitations of bulk manufacturing [12][13]. Polymer printing is possible using extrusion, resin, and powder 3D printing processes that provide versatility for material selection and supporting designs with diverse architectures, responses, and layouts [14][15]. Because of the large design space offered by 3D polymer printing, and its opportunities for improving medical applications, we carried out a critical review by considering recent advances in materials, processes, and design strategies that all influence an application’s outcome [16], as illustrated in
Polymer 3D (three-dimensional) printing has advanced rapidly in recent years with many areas of research now translating to engineered products, especially in medical fields [1,2,3,4]. Polymer printing is advantageous for a broad range of medical areas that benefit from the diversity of polymer material characteristics and processing approaches [5,6,7,8]. 3D printing is a highly desirable fabrication approach because it enables the construction of designs with complex geometries and architectures that are not possible with conventional manufacturing processes. For instance, tissue scaffold structures fabricated with polyjet and stereolithography printing can achieve hierarchical forms that mimic bone, thereby providing a mechanical and biological niche to support tissue regeneration [9,10]. Additionally, the selection of polymers has advantages over metal printing approaches, that result in metal implants that do not degrade in the body and lead to mechanical issues such as stress shielding [11]. In areas of safety equipment, polymer-printed lattices achieve efficient energy absorption with a rapid fabrication process that bypasses the supply chain limitations of bulk manufacturing [12,13]. Polymer printing is possible using extrusion, resin, and powder 3D printing processes that provide versatility for material selection and supporting designs with diverse architectures, responses, and layouts [14,15]. Because of the large design space offered by 3D polymer printing, and its opportunities for improving medical applications, we carried out a critical review by considering recent advances in materials, processes, and design strategies that all influence an application’s outcome [16], as illustrated in for a tissue scaffold example.
Figure 1.
Material, process, and design considerations for medical applications, illustrated for a tissue scaffold example [17]. Images adapted with permission.
The
schematic highlights a hierarchical tissue scaffold constructed from beam-based unit cells with interconnected considerations in materials, process, and design for ensuring appropriate mechanical and biological functioning [17]. In this example, a design strategy for mimicking the hierarchical structure of bone largely drove the need for a suitable printing process and material selection to support the application. The material choice was dictated by a need for appropriate stiffness to ensure structural integrity while retaining biocompatibility to promote tissue growth, which was fulfilled with a methacrylic acid-based polymer. The printing process requires the formation of layers for building the complicated hierarchical truss structure, which was achieved by stereolithography printing. However, once these factors are selected, there is a need to iterate and refine the structure’s design based on performance variability attributed to uncertainty and part variation in the 3D printing process [9][18].
schematic highlights a hierarchical tissue scaffold constructed from beam-based unit cells with interconnected considerations in materials, process, and design for ensuring appropriate mechanical and biological functioning [17]. In this example, a design strategy for mimicking the hierarchical structure of bone largely drove the need for a suitable printing process and material selection to support the application. The material choice was dictated by a need for appropriate stiffness to ensure structural integrity while retaining biocompatibility to promote tissue growth, which was fulfilled with a methacrylic acid-based polymer. The printing process requires the formation of layers for building the complicated hierarchical truss structure, which was achieved by stereolithography printing. However, once these factors are selected, there is a need to iterate and refine the structure’s design based on performance variability attributed to uncertainty and part variation in the 3D printing process [9,18].
Comparative studies for tissue scaffolds can achieve widely different design strategies based on different material/printing process decisions. For instance, tissue scaffolds constructed from polycaprolactone (PCL) using fused deposition modeling have more compliant structures with biodegradability, while titanium scaffolds printed with selective laser sintering have a higher stiffness, but no biodegradability [19][20]. These choices then influence the scaffold’s topological design, since it is generally not feasible to print polycaprolactone as a truss-based structure, whereas selective laser sintering processes are able to produce titanium in forms to achieve mechanically efficient truss-based structures that promote high porosity for large void volumes for tissue growth.
Comparative studies for tissue scaffolds can achieve widely different design strategies based on different material/printing process decisions. For instance, tissue scaffolds constructed from polycaprolactone (PCL) using fused deposition modeling have more compliant structures with biodegradability, while titanium scaffolds printed with selective laser sintering have a higher stiffness, but no biodegradability [19,20]. These choices then influence the scaffold’s topological design, since it is generally not feasible to print polycaprolactone as a truss-based structure, whereas selective laser sintering processes are able to produce titanium in forms to achieve mechanically efficient truss-based structures that promote high porosity for large void volumes for tissue growth.
Generally, decisions across material, process, and design strategies occur in a nonlinear and integrated fashion that requires careful consideration and knowledge of their relation to an application. Here, materials, process, and design strategies for polymer printing are reviewed in the context of medical applications, with a critical assessment for how each of these decision factors influence applications and one another. Initially, materials are reviewed to highlight their capabilities and properties, with data presented to compare diverse materials available for mechanical applications. Reviews on printing processes include extrusion, resin, and powder printing, which are among the most common approaches for polymer printing, with considerations for how processing influences part fidelity and functionality. The investigation of design strategies provides an overview for organizing processed materials that is advantageous for tuning application performance. Considered applications include prosthetics, safety equipment, and drug delivery, which provide context for how fundamental research in these areas translates to medical scenarios.
2. Material Capabilities
Material capabilities of polymers for 3D printing are informed by their molecular structures, and also depend on a material’s processing during printing. The selection of materials for design applications is often conducted by considering measurable properties, such as mechanical properties, with ranges based on processing and testing methods that provide further complications in predicting part performance during the system design.
2.1. Material Structure
There is a broad range of polymer materials for 3D printing, with capabilities informed from their molecular structure, with polymers processed in different manners for each printing process. In extrusion processes, thermoplastics are commonly used for 3D printing where they are melted for extrusion followed by hardening after deposition [21]. For example, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a common thermoplastic that exhibits favorable impact strength and improved chemical resistance compared to pure polystyrene [22]. The properties of ABS are tunable based on the ratio of its three monomers, for instance, its density may range from 1.05 mg/m 3
to 1.07 mg/m
3
with resulting tensile moduli from 2.5 GPa to 2.7 GPa. Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA) is an alternative to ABS with improved heat resistance and exceptional ultraviolet stability [23], while polylactic acid (PLA) is another popular thermoplastic with biocompatibility but a lower glass transition temperature.
PLA is also suitable for further types of printing processes, such as resin curing with stereolithography [24], which enables the construction of more complex part architectures than is generally possible with extrusion processes. Although PLA is biocompatible, there is some concern for toxicity in stereolithography printed PLA because of the addition of photopolymers to the resin solution, which is necessary for cross-linking monomers to form polymers in the presence of ultraviolet light. However, when properly printed and post-processed, resin curing processes have been demonstrated as safe for medical applications, depending on the particular combination of chemical components [25]. These considerations for linking the chemical structure of a polymer to its functioning and printing are essential in pairing printing processes with materials to achieve a desired set of properties for a specified application.
2.2. Material Properties
There are diverse material properties necessitated by medical applications that are achievable through 3D printing. Often, medical applications drive the need for specific material capabilities, such as the need for energy absorbing materials in impact resistance, multicolored parts with suitable textures for modeling surgical anatomies, or specified material properties to mimic biological tissues.
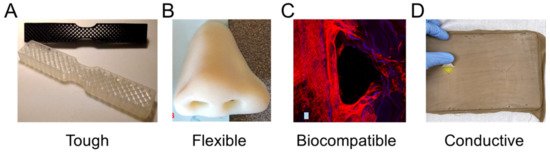
highlights recent research in medical polymer materials with a focus on mechanical capabilities for toughness [26][27] and flexibility [28][29], biological capabilities for biocompatibility [24][30], and further capabilities such as electrical conductivity [31][32].
highlights recent research in medical polymer materials with a focus on mechanical capabilities for toughness [26,27] and flexibility [28,29], biological capabilities for biocompatibility [24,30], and further capabilities such as electrical conductivity [31,32].
Figure 2.
Materials with highlighted properties for (
A
B
C
) biocompatibility [30], and ( D
) conductivity [31]. Images adapted with permission.
Toughness in a material refers to its capability to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing, which is calculated from a combination of the material’s strength and ductility. Recently, a 3D-printed tensile bar with crosshatch structures was printed from a tough polyurethane material with comparisons including physically cross-linked Carbothane AC-4095A in pellet form and chemically cross-linked polyurethane with 68A hardness in liquid resin form (
A) [26]. Results demonstrated elastomeric polyurethanes are relatively tolerant of architectures and notches, which also promotes their use in a variety of design strategies. A further example of toughness for biomedical materials was demonstrated with a methacrylic polymer printed using the resin curing process with a tensile strength of 41 MPa and a general elongation up to 50% before breaking [27]. The material was used for printing a shaft coupling for an assembly without any post-treatment necessary due to the high accuracy of the printing process.
Flexible materials have been constructed recently that are useful as prosthetics, and enable the optimization of a specified form for a person’s unique physiology through scanning and fitting technologies (
B) [28]. The patient of interest for the study was 27 years old and had a topographic scan of their face that used 3D mapping software to print the nose shape using a Stratasys polyjet printer with TangoPlus flexible material. The TangoPlus material had a 26 to 28 Shore A Hardness, 0.8 to 1.5 MPa tensile strength, and 2 to 4 kg/cm tear resistance, while having a feel similar to rubber. Recoloring was necessary to match the patient’s skin tone. Flexible materials have also been used to print complex structures, such as an Eiffel tower model printed with temperature-stimulated flexible polymer printed using stereolithography [29]. The model distorts at lower temperature and as the temperature increases to 70 °C, the print regains its original form. This temperature-dependent functionality provides possibilities for medical applications with heat-initiated actuation, which could be initiated by body heat or devices.
Biocompatibility is a necessary material property for printed devices that interact with the body, such as hearing aids and retainers, or are implanted in vivo, such as artificial joints or tissue scaffolds. Depending on the application, biocompatibility can have differing criteria, but generally refers to the need for the material to do no harm to the body while facilitating its intended function. For tissue scaffolds, biocompatibility typically refers to a need for non-cytotoxicity, biodegradability, and promotion of tissue growth. Polyjet printing uses Stratasys MED610 material, which is an acrylic-based polymer that has recently had success for printing tissue scaffolds of complex topologies (
C) [30]. Biological testing was conducted by measuring cell viability using Saos-2 cells that survived, with no difference between the 3D-printed materials and controls after 48 h. Further testing demonstrated growth on tissue scaffold surfaces; however, the growth was limited compared to other tissue engineering materials. An alternative approach is the use of stereolithography for 3D-printed lattices using polylactic acid that can reliably form lattice structures with microscale features [24]. Further testing is required to determine the benefits of 3D-printed polymers to conventional tissue engineering approaches; however, polymers provide immediate advantages over metals due to their ability to degrade safely in vivo.
Electrical conductance is another material property that is useful for medical applications and has been used for fabricated, sensorized tissue analogues through the 3D printing of an organogel. The technology was used to create a suture training pad fabricated with embedded piezoresistive strain sensors and conductive threads as electrodes to quantify the performance of the trainee (
D) [31]. Fabrication steps included fixing nylon fabric to the bottom of a PLA mold, then pouring and curing skin-colored liquid PDMS, inserting conductive threads into the 3D-printed organogel, encapsulating sensors, adding a fat layer, and cutting the sample to form a suture pad. Further polymer electrical conductivity has been demonstrated with thermoplastics mixed with conductive carbon black fillers for 3D printing a chess rookie that enables turning on an LED light [32]. These printing capabilities enable new types of design applications that could provide feedback in different medical scenarios through embedding sensors in fabricated designs, possibly activating when certain mechanical triggers are reached.
2.3. Material Capabilities
Properties of 3D-printed parts are dependent on both their material structure and printing process, and therefore require extensive testing of combinations of materials/process parameters to determine material capabilities for a given application [33]. For instance, a part’s mechanical response when fabricated with fused deposition modeling is alterable based on the printed layer thickness, processing temperature, and orientation [34][35]. In
Properties of 3D-printed parts are dependent on both their material structure and printing process, and therefore require extensive testing of combinations of materials/process parameters to determine material capabilities for a given application [33]. For instance, a part’s mechanical response when fabricated with fused deposition modeling is alterable based on the printed layer thickness, processing temperature, and orientation [34,35]. In a summary is provided that highlights the measured mechanical properties of some common polymer 3D-printed materials tested as solid samples; additional notes in the table provide context for how testing was carried out to provide ranges of process-dependent properties. Material properties include strength- and stiffness-related metrics that are key properties for selecting suitable materials in mechanical applications.
Table 1. Measured 3D-printed part properties organized by material and printing process. Further details included to provide relevant context.
Measured 3D-printed part properties organized by material and printing process. Further details included to provide relevant context.
| Material |
Printing Process |
Measured Properties |
References |
| Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 35 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 1300 MPa. |
[36] |
| Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 27–31 MPa;
Layer height: 0.05–0.14 mm;
Processed at 210–240 °C. |
[34] |
| Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 15–38 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 1220–1430 MPa;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[35] |
| Polycarbonate (PC) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 37 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 1000 MPa. |
[36] |
Polycarbonate (PC);
Biomaterial blend |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 35–65 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 2100 MPa;
Nozzle Temperature: 240–270 °C;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[35] |
Polycarbonate (PC);
Fossil-fuel blend |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 28–62 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 1300–1500 MPa;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[35] |
| Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 58–85 MPa
Elastic Modulus: 3000–4100 MPa;
Temperature dependent. |
[37] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 36–40 MPa;
Layer Height: 0.05–0.14 mm;
Processed at 210–240 °C. |
[34] |
| Polylactic acid (PLA) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Ultimate Strength: 265 MPa;
Yield Strength: 205 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 4400 MPa;
Compression Testing. |
[38] |
| Polylactic acid (PLA) |
Fused deposition modeling |
Tensile Strength: 28–56 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 2000 MPa;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[35] |
| Polyamide 12 (Nylon) |
Multi jet fusion |
Tensile Strength: 47–48 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 1150–1250 MPa;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[39] |
Acrylic-based
(Stratasys: MED 610) |
Polyjet |
Elastic Modulus: 1860–2120 MPa;
Compression Testing;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[9] |
Epoxy-based
(DSM Somos, Inc: Watershed XC 11122) |
Stereolithography |
Tensile Strength: 37–48 MPa;
Elastic Modulus: 2040–2400 MPa;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[40] |
| Methacrylic Acid (EnvisionTEC: E-Shell 600) |
Stereolithography |
Elastic Modulus: 1400–1620 MPa;
Compression Testing;
Orientations of 0° to 90°. |
[16] |
| Methacrylic Acid (Formlabs: Dental SG) |
Stereolithography |
Elastic Modulus: 1670 MPa;
Compression Testing. |
[17] |
In
In
, multiple studies are reported for comparisons of ABS materials that all demonstrated similar, but slightly different mechanical properties [34][35][36], such as tensile strength ranging from 15 MPa to 38 MPa. These differences are accounted for in part because of the different processing temperatures and printing parameters used to construct parts, the slightly different proportions of monomers in ABS’s structure, and the tested part’s orientation. For instance, the low tensile strength measurement of 15 MPa for ABS was due to testing in the transverse loading direction compared to the higher measurements of tensile strength closer to 30 MPa based on the build layer orientation. Similar differences were observed for polycarbonate materials based on their processing and chemicals used to manufacture the material [35][36]. One study concluded that a blend of polycarbonate referred to as a bio-based polycarbonate had a slightly higher strength of 65 MPa and significantly higher elastic modulus of 2100 MPa than a polycarbonate manufactured using fossil fuels with 62 MPa strength and 1500 MPa elastic modulus [35]. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and polylactic acid (PLA) are commonly used biocompatible materials with relatively high mechanical strength and stiffness among polymers, and are also manufacturable with fused deposition modeling [37][38]. PEEK is generally the more expensive of the two materials with an elastic modulus up to 4100 MPa, while PLA has an elastic modulus of 4400 MPa; both are the highest values among the surveyed
, multiple studies are reported for comparisons of ABS materials that all demonstrated similar, but slightly different mechanical properties [34,35,36], such as tensile strength ranging from 15 MPa to 38 MPa. These differences are accounted for in part because of the different processing temperatures and printing parameters used to construct parts, the slightly different proportions of monomers in ABS’s structure, and the tested part’s orientation. For instance, the low tensile strength measurement of 15 MPa for ABS was due to testing in the transverse loading direction compared to the higher measurements of tensile strength closer to 30 MPa based on the build layer orientation. Similar differences were observed for polycarbonate materials based on their processing and chemicals used to manufacture the material [35,36]. One study concluded that a blend of polycarbonate referred to as a bio-based polycarbonate had a slightly higher strength of 65 MPa and significantly higher elastic modulus of 2100 MPa than a polycarbonate manufactured using fossil fuels with 62 MPa strength and 1500 MPa elastic modulus [35]. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and polylactic acid (PLA) are commonly used biocompatible materials with relatively high mechanical strength and stiffness among polymers, and are also manufacturable with fused deposition modeling [37,38]. PEEK is generally the more expensive of the two materials with an elastic modulus up to 4100 MPa, while PLA has an elastic modulus of 4400 MPa; both are the highest values among the surveyed materials.
Numerous 3D-printed biocompatible materials have been recently investigated for use as bone tissue scaffolds, with several methacrylic/acrylic-based materials included as examples in
[9][16][17]. These materials were printed with varied resin curing processes and all demonstrated similar elastic moduli around 1500 MPa to 2000 MPa, with some dependency on build orientation. In comparison to the fused deposition modeling parts, these resin prints have a lower stiffness, although their stiffness is tunable based on the curing time per layer and post-processing curing time that has been demonstrated for lattice structures [16]. Overall, the highlighted materials from
[9,16,17]. These materials were printed with varied resin curing processes and all demonstrated similar elastic moduli around 1500 MPa to 2000 MPa, with some dependency on build orientation. In comparison to the fused deposition modeling parts, these resin prints have a lower stiffness, although their stiffness is tunable based on the curing time per layer and post-processing curing time that has been demonstrated for lattice structures [16]. Overall, the highlighted materials from demonstrate how a single material can achieve varied properties based on its processing, and that varied processes enable material selection with similar property ranges. Further considerations for selecting a material/process combination are fabrication accuracies and consistency, which further add complexity to design decisions when selecting a 3D printing approach for a given application.
3. Printing Processes
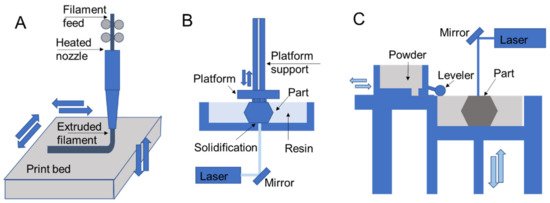
The most common techniques for polymer 3D printing include extrusion-, resin-, and powder-based processes (
) [1]. Each type of process enables the additive deposition of layers to form parts and carries out fabrication using unique processing steps that restrict processes to different material selections and capabilities to form designs.
Figure 3.
3D printing schematics for (
A
) fused deposition modeling, (
B
) stereolithography, and (
C
) selective laser sintering that are representative of extrusion, resin, and powder processes, respectively.
In extrusion processes such as fused deposition modeling, the material is melted and extruded through a nozzle where it is directed for deposition to form part layers (
A) [39][40]. The filament feed generates nozzle pressure that is used to control material flow during part construction. In direct ink writing, which is another extrusion process, material is pushed through a nozzle according to an applied external shear stress such as air pressure or piston movements [41]. Resin 3D printing relies on applying ultraviolet light in specified patterns to form a part layer by layer by curing deposited liquid resin, which is commonly used for stereolithography printing [42][43]. In direct laser writing, ultraviolet light is directed towards a vat of photosensitive resin to form solid layers with a moving build platform (
A) [41,42]. The filament feed generates nozzle pressure that is used to control material flow during part construction. In direct ink writing, which is another extrusion process, material is pushed through a nozzle according to an applied external shear stress such as air pressure or piston movements [43]. Resin 3D printing relies on applying ultraviolet light in specified patterns to form a part layer by layer by curing deposited liquid resin, which is commonly used for stereolithography printing [44,45]. In direct laser writing, ultraviolet light is directed towards a vat of photosensitive resin to form solid layers with a moving build platform ( B). Resin curing also occurs in polyjet printing, with the deposition of ink/resin on a surface with subsequent ultraviolet curing [9][17]. Powder 3D printing relies on fusing powders of a selected material using lasers in selective laser sintering [44][45] (
B). Resin curing also occurs in polyjet printing, with the deposition of ink/resin on a surface with subsequent ultraviolet curing [9,17]. Powder 3D printing relies on fusing powders of a selected material using lasers in selective laser sintering [46,47] ( C) or by chemical means in binder jetting. In these processes a bed of powder is solidified and replenished layer by layer to form a part.
3.1. Extrusion
Among extrusion 3D printing processes, fused deposition modeling is the most commonly used (
A) [39][40]. In fused deposition modeling material is fed into the printer as a continuous filament. The extruder body is heated to melt the filament that is extruded by the pressure generated by the filament feed. After filament extrusion, the filament cools down and solidifies to form a solid geometry. Some of the most common printing materials for fused deposition modeling are polylactic acid (PLA), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). Support materials are also available that are removed during post-processing and include water-dissolvable materials such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), breakaway materials, and wax. The performance of the printed parts depends on material selection and process parameters such as layer thickness, build orientation, raster angle, infill density, nozzle temperature, and printing speed [46]. In fused deposition modeling, the nozzle temperature is generally maintained at a few degrees higher than the melting point of the polymer, since further increasing the nozzle temperatures may affect the performance for materials like PEEK and polyetherimide (PEI). It has been reported that the elongation percentage before failure and impact strength of a PEI part starts reducing when the temperature increases beyond an optimal nozzle temperature [47]. On the other hand, lower temperatures may result in extrusion difficulty and poor print quality due to the formation of porous volumes between the layers [47]. Additionally, layer size presents trade-offs in print resolution, part performance, and printing speed while resulting in variable amounts of anisotropy in final part properties introduced by patterning of layers in specified directions.
A) [41,42]. In fused deposition modeling material is fed into the printer as a continuous filament. The extruder body is heated to melt the filament that is extruded by the pressure generated by the filament feed. After filament extrusion, the filament cools down and solidifies to form a solid geometry. Some of the most common printing materials for fused deposition modeling are polylactic acid (PLA), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). Support materials are also available that are removed during post-processing and include water-dissolvable materials such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), breakaway materials, and wax. The performance of the printed parts depends on material selection and process parameters such as layer thickness, build orientation, raster angle, infill density, nozzle temperature, and printing speed [48]. In fused deposition modeling, the nozzle temperature is generally maintained at a few degrees higher than the melting point of the polymer, since further increasing the nozzle temperatures may affect the performance for materials like PEEK and polyetherimide (PEI). It has been reported that the elongation percentage before failure and impact strength of a PEI part starts reducing when the temperature increases beyond an optimal nozzle temperature [49]. On the other hand, lower temperatures may result in extrusion difficulty and poor print quality due to the formation of porous volumes between the layers [49]. Additionally, layer size presents trade-offs in print resolution, part performance, and printing speed while resulting in variable amounts of anisotropy in final part properties introduced by patterning of layers in specified directions.
Direct ink writing, also known as robocasting, is another extrusion 3D printing process that avoids the heating requirements of fused deposition modeling, and rather deposits a shear, thinning viscoelastic material via a nozzle by applying external shear stress [48][49][50]. Since the process enables printing in ambient conditions, it is ideal for printing soft materials. As the shear stress increases, the viscosity of the ink reduces and enables extrusion through the nozzle. As the ink is extruded, it regains its viscosity to form a 3D structure. The filaments are stacked to additively form the final part. The printed part is cured in a different environment as per the material requirement. Direct ink writing is used to print different materials including bio-inks [41], fiber-suspended inks [48][51], electro/magnetic inks [52], and multi-material inks [53]. The capability of printing different materials in direct ink writing has made it possible to produce designs for diverse applications [48][50]. Some of the most widely used polymers for direct ink writing are polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), thermoplastics, and epoxy. The major factors in determining the printability are the viscosity and shear thinning property of the material.
Direct ink writing, also known as robocasting, is another extrusion 3D printing process that avoids the heating requirements of fused deposition modeling, and rather deposits a shear, thinning viscoelastic material via a nozzle by applying external shear stress [50,51,52]. Since the process enables printing in ambient conditions, it is ideal for printing soft materials. As the shear stress increases, the viscosity of the ink reduces and enables extrusion through the nozzle. As the ink is extruded, it regains its viscosity to form a 3D structure. The filaments are stacked to additively form the final part. The printed part is cured in a different environment as per the material requirement. Direct ink writing is used to print different materials including bio-inks [43], fiber-suspended inks [50,53], electro/magnetic inks [54], and multi-material inks [55]. The capability of printing different materials in direct ink writing has made it possible to produce designs for diverse applications [50,52]. Some of the most widely used polymers for direct ink writing are polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), thermoplastics, and epoxy. The major factors in determining the printability are the viscosity and shear thinning property of the material.
3.2. Resin Curing
Resin 3D printing processes expose photosensitive monomers to controlled ultraviolet light or other high energy light sources [54]. Resin curing processes typically benefit from high resolutions and quality part finishing in comparison to other printing methods in comparable price ranges. Ultraviolet curing strategies include stereolithography with direct laser writing (SLA;
Resin 3D printing processes expose photosensitive monomers to controlled ultraviolet light or other high energy light sources [56]. Resin curing processes typically benefit from high resolutions and quality part finishing in comparison to other printing methods in comparable price ranges. Ultraviolet curing strategies include stereolithography with direct laser writing (SLA; B), digital light processing (DLP) [55][56], continuous liquid interface production (CLIP) [56], and continuous digital light manufacturing (CDLM) [57], which all have varied strategies of exposing a vat of resin to light to form a part. Stereolithography printing with direct laser writing includes a resin tank, a high energy light source, and a reflecting mirror to control the resin exposure to a laser. The resin in the tank is exposed to a computer-controlled laser that solidifies the resin to form a solid layer. After exposure to one layer, the printing platform moves vertically for printing the next layer [54]. After all the layers are printed, the part is washed and cured under ultraviolet light to strengthen the structure, which provides fine tuning for specific applications [58]. The duration of curing alters the printed part mechanics, for instance, when comparing parts that were post-cured for 30 h to those that had no post-curing, the post-curing with ultraviolet light was more time-efficient and improved mechanical properties, such as elastic modulus, and promoted material homogeneity through higher crosslinking [59]. Though stereolithography printing has a high resolution and printing speed, in general, it lacks multi-material printability.
B), digital light processing (DLP) [57,58], continuous liquid interface production (CLIP) [58], and continuous digital light manufacturing (CDLM) [59], which all have varied strategies of exposing a vat of resin to light to form a part. Stereolithography printing with direct laser writing includes a resin tank, a high energy light source, and a reflecting mirror to control the resin exposure to a laser. The resin in the tank is exposed to a computer-controlled laser that solidifies the resin to form a solid layer. After exposure to one layer, the printing platform moves vertically for printing the next layer [56]. After all the layers are printed, the part is washed and cured under ultraviolet light to strengthen the structure, which provides fine tuning for specific applications [60]. The duration of curing alters the printed part mechanics, for instance, when comparing parts that were post-cured for 30 h to those that had no post-curing, the post-curing with ultraviolet light was more time-efficient and improved mechanical properties, such as elastic modulus, and promoted material homogeneity through higher crosslinking [61]. Though stereolithography printing has a high resolution and printing speed, in general, it lacks multi-material printability.
Polyjet (also known as inkjet) printing is an alternate resin curing process that uses a nozzle to deposit droplets of material that are immediately cured by an ultraviolet beam upon deposition to form a layer [60]. Polyjet printing is advantageous for printing multimaterial models rapidly with multi-nozzle jetting, which also enables printing with support materials [61][62]. However, materials should generally still have shear thinning properties, which limits availability [56]. Inkjet printing has applications in fields ranging from prototyping to electronics to bio-printing [60][62], and has been demonstrated recently for use in biomedical devices using mechanically efficient lattice structures [9]. Lattices were printed using a network of beams with diameters of approximately 400µm, with fabrication defects depending on topology design and build direction. Further studies are required to determine whether polyjet printing is suitable for tissue engineering applications, with a need to further demonstrate its capabilities by producing structures with cell seeding and proliferation capabilities [30]. However, the technology provides a potential for the rapid fabrication of large sets of structures that are customizable for specific patients in applications such as safety equipment.
Polyjet (also known as inkjet) printing is an alternate resin curing process that uses a nozzle to deposit droplets of material that are immediately cured by an ultraviolet beam upon deposition to form a layer [62]. Polyjet printing is advantageous for printing multimaterial models rapidly with multi-nozzle jetting, which also enables printing with support materials [63,64]. However, materials should generally still have shear thinning properties, which limits availability [58]. Inkjet printing has applications in fields ranging from prototyping to electronics to bio-printing [62,64], and has been demonstrated recently for use in biomedical devices using mechanically efficient lattice structures [9]. Lattices were printed using a network of beams with diameters of approximately 400µm, with fabrication defects depending on topology design and build direction. Further studies are required to determine whether polyjet printing is suitable for tissue engineering applications, with a need to further demonstrate its capabilities by producing structures with cell seeding and proliferation capabilities [30]. However, the technology provides a potential for the rapid fabrication of large sets of structures that are customizable for specific patients in applications such as safety equipment.
3.3. Powder Fusion
Powder fusion processes rely on depositing powder layers that are either melted or bonded to additively fabricate parts. Two common powder fusion techniques for polymer printing are selective laser sintering and binder jetting [63].
Powder fusion processes rely on depositing powder layers that are either melted or bonded to additively fabricate parts. Two common powder fusion techniques for polymer printing are selective laser sintering and binder jetting [65]. C demonstrates the working principles of selective laser sintering, which relies on a powder stock leveled to enable fusion of one layer through exposure to a laser that follows a specified path. Once a layer is printed, the platform is lowered, and the process is repeated. One of the major advantages of selective laser sintering is the leftover powder in the platform acts as a support during part construction. Therefore the process does not require printing a separate support material and enables complex part and assembly fabrication [45].
C demonstrates the working principles of selective laser sintering, which relies on a powder stock leveled to enable fusion of one layer through exposure to a laser that follows a specified path. Once a layer is printed, the platform is lowered, and the process is repeated. One of the major advantages of selective laser sintering is the leftover powder in the platform acts as a support during part construction. Therefore the process does not require printing a separate support material and enables complex part and assembly fabrication [47].
In binder jetting printing, a jetted material binds powder as an alternative to laser melting [63]. The powder is spread on the printing platform within a predetermined thickness and then the binding material is injected to form a bonded layer. The binder jetting technique uses multiple nozzles to inject the binding material, which is potentially faster than laser melting. Binder jetting is generally an efficient process capable of printing multicolor, multi-material, and functionally graded materials [64]. Since the binding material acts as an adhesive to hold the powder together and form a printed geometry, the achieved properties of the printed parts depend on the binding material in addition to the shape and size of the powder [65][66].
In binder jetting printing, a jetted material binds powder as an alternative to laser melting [65]. The powder is spread on the printing platform within a predetermined thickness and then the binding material is injected to form a bonded layer. The binder jetting technique uses multiple nozzles to inject the binding material, which is potentially faster than laser melting. Binder jetting is generally an efficient process capable of printing multicolor, multi-material, and functionally graded materials [66]. Since the binding material acts as an adhesive to hold the powder together and form a printed geometry, the achieved properties of the printed parts depend on the binding material in addition to the shape and size of the powder [67,68].
4. Design Considerations
Based on the material and process capabilities of polymer 3D printing, it is possible to use computer aided softwares to design complex geometries that have specified properties based on process and material selection. Computational algorithms are often used to automate the design of 3D printed parts, such that every print can be a unique and optimized structure that is suitable particularly for wide-ranging applications in customized medical designs for patients.