The use of CO2 as C1 building block for chemical synthesis is receiving growing attention, due to the potential of this simple molecule as abundant and cheap renewable feedstock. Among the possible reductants used in the literature to bring about CO2 reduction to C1 derivatives, hydroboranes have found various applications, in the presence of suitable homogenous catalysts. The main results obtained since 2016 in the synthetic design of main group, first and second row transition metals for use as catalysts for CO2 hydroboration are summarized.
- carbon dioxide conversion
- hydroboration
- metal complexes
- selectivity
1. Introduction
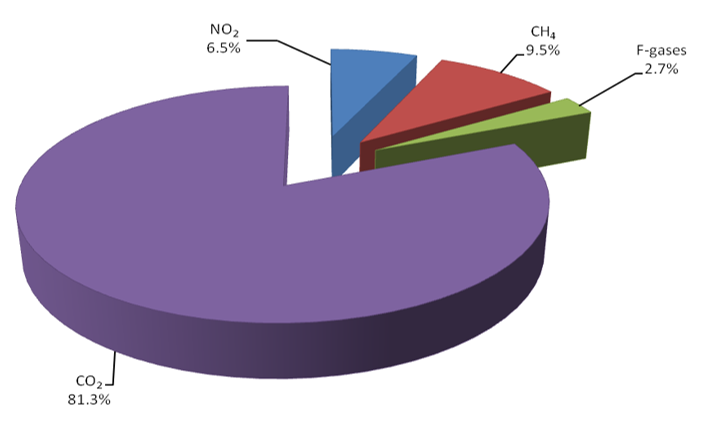
In recent years, the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has steadily increased due to human activity [1]. The combustion of fossil fuels for the production of energy is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions [2]. CO2 is a by-product of fuel combustion, representing the most abundant greenhouse gas (81.3%) of the global anthropogenic emissions (Figure 1). A significant increase of CO2 in the atmosphere is expected in view of growing demand for energy [3]. These reasons, combined with the need for sustainable, fossil-free routes to chemicals and fuels, fostered a new impetus in the use of CO2 as a C1 building block for chemical synthesis [1].
Figure 1. Global greenhouse gas emission per type of gas in 2018 [1].
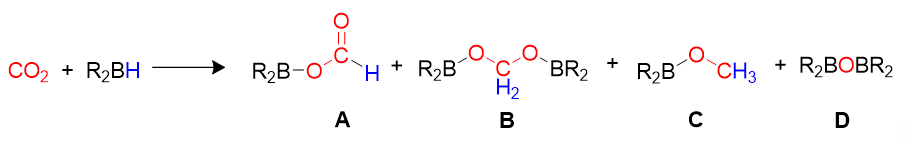
Carbon dioxide can be used to make added value products, by reactions such as copolymerization [4], hydrogenation [5][6][5,6], biochemical approaches [7], and electrochemical reduction [7][8][7,8]. Recently, there has been an increase in interest in the homogeneous reduction of CO2 using hydrogen [9][10][11][9–11], hydrosilanes [12][13][14][15][12–15] and hydroborates [16][17][16,17]. Reductive approaches allow to obtain simple C1 molecules such as formic acid (HCO2H), formaldehyde (HCHO), methanol (CH3OH), dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3), methane (CH4) or higher hydrocarbons, that find many applications in chemistry, manufacturing and industry [18][19][20][21][22][23][18–23]. CO2 hydrogenation (i.e., reduction under a pressure of hydrogen gas) is, in principle, the most atom-efficient method, but has safety risks connected with the use of flammable, pressurized gas. Alternative reductants such as hydrosilanes and hydroboranes have been successfully applied to replace H2, as they are liquid at room temperature, hence easier and safer to handle and store. They can bring about CO2 reduction to different products under mild reaction conditions, due to the fact that E–H bonds (E = Si, B) are weaker than the H–H bond, and that the formation of stronger E–O bonds constitutes a driving force for the reaction. It has been demonstrated that CO2 can be reduced by a hydroborane (Scheme 1) to give formoxyborane (A), bis(boryl)acetal (B), methoxyborane (C) and bis(boryl)ether (D), and that the choice of appropriate homogeneous catalysts can drive the selectivity of the process to the desired products, further than promoting the overall reaction rate [16]. Although precious transition metals play a dominant role as catalysts for CO2 reduction, various studies demonstrated the possible use of earth-abundant metals and p-block elements [24][25][24,25]. An excellent, comprehensive review on this chemistry was published by Bontemps in 2016 [16].
Scheme 1.
General reaction and product distribution for CO
2
hydroboration.
2. Main Group Metal Catalysts for CO2 Hydroboration
Main group metal (Li, Na, K, Mg) and non-metal (Si) compounds and adducts showed a modest degree of activity for CO2 hydroboration, using hydroboranes such as pinacolborane (HBpin), catecholborane (HBcat) and 9-BBN, under mild reaction conditions. Whereas alkali metals did not play a role in either borane or CO2 activation, the role of the Mg(II) centers in the activation mechanism likely depended on the nature of the complex, and in some cases, borane activation seems to take place first. On the other hand, Si(II)-NHC hydrido adducts were proposed to activate preferentially CO2, which then reacts with HBpin in an outer-sphere fashion, to give formoxyborane as product. The process selectivity varied from formoxy- to methoxyborane products, and the latter are generally obtained at higher temperature (90–100 °C, Table 1).
3. First-row transition metal catalysts for CO2 hydroboration
Different first-row transition metal (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) complexes showed to be competent catalysts for CO2 hydroboration at different reductions levels. A wide variety of stabilizing ligands, ranging from simple bidentate bis(phosphines) such as dmpe, to tripodal triphos-type phosphine and phosphinite ligands forcing facial coordination to metal, to PNP, PCP, POCOP pincer-type, meridional ligands were applied, together with ancillary ligand-free catalytic protocols, as in the case of Co(acac)3 [26]. Moderate to very good conversions, yields, TONs and TOFs were obtained in the different cases, with remarkable selectivities to multi-electron reductions up to the methoxy level [27, [27][28]28] and to the challenging acetal level [29, [29][30]30]. Although not all studies have reported mechanistic details, the presence of metal-hydrido bonds in the active catalysts were often invoked to explain three-step reduction pathways, starting with insertion of CO2 into the M-H bond. The major effects in driving the selectivity of the process to a specific product were demonstrated to be more due to the steric and electronic properties of the hydroborane and to the choice of temperature and solvent rather than on the nature of the catalyst.
4. Second-row transition metal catalysts for CO2 hydroboration
The recent contributions describing second-row transition metal (Ru, Pd, Ir) catalyzed CO2 hydroboration are focused mainly on the application of pincer-type complexes. Mechanistic details were achieved in various cases, showing for example [31] that it is possible to drive the process selectivity by tuning the reaction conditions, such as solvent, temperature and use of additivies, to bring about selectivity switch from 2-electrons to 6-electrons reduction of CO2.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, remarkable results have been described in the period 2016-2020 both with first-row and second-row transition metals, in particular Mn, Fe, Ni and Pd, setting a new state-of-the-art for the conversion of CO2 to added value products such as HCOOH, HCHO and MeOH by hydroboration processes. The advantage of such an approach was confirmed as the possibility to use very mild conditions of temperature (in general favoring 2-electrons reduction), small amounts of catalysts and different hydroboranes. Under this point of view, the recent studies confirmed that the less sterically hindered HBcat favors in general 6-electron reduction to methoxyboranes. Noteworthy, recent results showed that also the challenging 4-electrons reduction to bis(boryl)acetals can be achieved with high selectivity. In our view, this can be considered as one of the most likely targets for future research in the field of CO2 hydroboration, due to the possible synthetic applications of such molecules as efficient methylene transfer reagents in organic synthesis.
References
- Data from United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Overview of Greenhouse Gases | Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions | US EPA, 2018.
- International Energy Agency Editions, Imprimerie Centrale, Luxembourg, 2012.
- Mleczko, L.; Wolf, A.; and Lolli, G. New Feedstocks and Chemistry for Lower CO2‐Footprint: Today, Tomorrow, and in the Future. Rev. 2016, 3, 204-218.
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wu, G.-P.; Darensbourg, D. J. CO2-Based Block Copolymers: Present and Future Designs. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 8, 750-763.
- Jiang, X.; Nie, X.; Guo, X.; Song, C.; Chen, J. G. Recent Advances in Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation to Methanol via Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 15, 7984-8034.
- Onishi, N.; Laurenczy, G.; Beller, M.; Himeda, Y. Recent progress for reversible homogeneous catalytic hydrogen storage in formic acid and in methanol. Chem. Rev. 2018, 373, 317–332.
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Varjani, S.J.; Saravanan, A. A review on photochemical, biochemical and electrochemical transformation of CO2 into value-added products. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 131-147.
- Daiyan, R.; Saputera, W. H.; Masood, H.; Leverett, J.; Lu, X.; Amal, R. A Disquisition on the Active Sites of Heterogeneous Catalysts for Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to Value‐Added Chemicals and Fuel. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 11, art. no. 1902106.
- Modak, A.; Bhanja, P.; Dutta, S.; Chowdhury, B.; Bhaumik A. Catalytic reduction of CO2 into fuels and fine chemicals. Green Chem., 2020, 22, 4002-4033.
- Singh, A. K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A. Hydrogen energy future with formic acid: a renewable chemical hydrogen storage system. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 12-40.
- Sordakis, K.; Tang, C.; Vogt, L. K.; Junge, H.; Dyson, P. J.; Beller, M.; Laurenczy, G. Homogeneous Catalysis for Sustainable Hydrogen Storage in Formic Acid and Alcohols. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 372-433.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Das, S. Catalytic transformation of CO2 into C1 chemicals using hydrosilanes as a reducing agent. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1800-1820.
- Fernández-Alvarez, L. A.; Oro, L. O. Homogeneous Catalytic Reduction of CO2 with Silicon‐Hydrides, State of the Art ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 4783–4796.
- Fernández-Alvarez, F. J.; Aitani, A. M.; Oro, L. A. Homogeneous catalytic reduction of CO2 with hydrosilanes. Sci.Technol. 2014, 4, 611–624.
- Tlili, A.; Blondiaux, E.; Frogneux, X.; Cantat, T. Reductive functionalization of CO2 with amines: an entry to formamide, formamidine and methylamine derivatives. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 157–168.
- Bontemps, S. Boron-mediated activation of carbon dioxide. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 308, 117–130.
- Geier, S. J.; Vogels, C. M.; Westcott, S. A. in Boron Reagents in Synthesis (Coca, A., ed.) ACS Symposium Series 2016, Chapter 6, pages 209-225, ISBN13: 9780841231832.
- Wu, X.-F.; Beller, M. (eds), Chemical Transformations of Carbon Dioxide. Topics in Current Chemistry Collections, 1st Edition, Springer International Publishing 2018.
- Aresta, M.; Dibenedetto, A.; Angelini, A. Catalysis for the Valorization of Exhaust Carbon: from CO2 to Chemicals, Materials, and Fuels. Technological Use of CO2. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1709– 1742.
- Peters, M.; Koehler, B.; Kuckshinrichs, W.; Leitner, W.; Markewitz, P.; Mueller, T. E. Chemical Technologies for Exploiting and Recycling Carbon Dioxide into the Value Chain. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1216– 1240.
- Aresta, M.; Dibenedetto, A. Utilisation of CO2 as a Chemical Feedstock: Opportunities and Challenges. Dalton Trans. 2007, 2975-2992.
- Pinaka, A.; Vougioukalakis, G. C. Using Sustainable Metals to Carry out "Green" Transformations: Fe- and Cu-Catalyzed CO2 Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 288, 69–97.
- Grice, K. A. Carbon dioxide reduction with homogenous early transition metal complexes: Opportunities and challenges for developing CO2 Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 336, 78–95.
- Dagorne, S.; Wehmschulte, W. Recent Developments on the Use of Group 13 Metal Complexes in Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2509–2520.
- Wang, X.; Xia, C.; Wu, L. Homogeneous carbon dioxide reduction with p-block element-containing reductants. Green Chem., 2018, 20, 5415-5426.
- Tamang, S. R.; Findlater, M. Cobalt catalysed reduction of CO2 via hydroboration. Dalton Trans., 2018, 47, 8199–8203.
- Erken, C.; Kaithal, A.; Sen, S.; Weyhermüller, T., Hölscher, M.; Werlé, C.; Leitner W. Manganese-catalyzed hydroboration of carbon dioxide and other challenging carbonyl groups. Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, art. no. 4521.
- Kostera, S.; Peruzzini, M.; Kirchner, K.; Gonsalvi, L. Mild and Selective Carbon Dioxide Hydroboration to Methoxyboranes Catalyzed by Mn(I) PNP Pincer Complexes. ChemCatChem, 2020, 12, 4625-4631.
- Aloisi, A.; Berthet, J.-C.; Genre, C.; Thuéry P.; Cantat, T. Complexes of the tripodal phosphine ligands PhSi(XPPh2)3 (X = CH2, O): synthesis, structure and catalytic activity in the hydroboration of CO2. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 14774-14788.
- Desmons, S.; Zhang, D.; Fajardo, A. M.; Bontemps, S. Versatile CO2 Transformations into Complex Products: A One-pot Two-step Strategy. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 153, art. no. 60348.
- Espinosa, M. R., Charboneau, D. J.; de Oliveira, A. G.; Hazari, N. Controlling Selectivity in the Hydroboration of Carbon Dioxide to the Formic Acid, Formaldehyde, and Methanol Oxidation Levels. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1, 301−314.