Prunus spinosa L. is a perennial, thorny shrub, highly decorative for landscape and forest edges, belonging to the Rosaceae family, genus Prunus, representing one of the ancestors of P. domestica. Modern phytotherapeutics emphasizes the benefits of consuming parts or products based on the Prunus spinosa L. shrub, as it is considered a plant with functional nutritional and therapeutic properties, remarkable in various pathologies with increasing incidence. Up to now, research has shown that the polyphenols found in large amounts in the fruits of P. spinosa L. are biofunctional compounds. These include anthocyanins, phenolic acids, flavonoids, and coumarin derivatives.
- Prunus spinosa L.
- phenol compounds
- oxidative stress
1. Introduction
2. The Bioecology of the P. spinosa L. Shrub
Prunus spinosa L. is a perennial, thorny shrub, highly decorative for landscape and forest edges, belonging to the Rosaceae family, genus Prunus, representing one of the ancestors of P. domestica [6][17][18][6,23,26]. It is native to Europe (Figure 1), mainly central and southern Europe, except the lower half of the Iberian Peninsula, extending northwards to the southern part of the Scandinavian Peninsula [18][19][26,27]. P. spinosa L. is also widespread in western Asia and northwest Africa and is locally present in New Zealand, Tasmania, and eastern North America (USDA NRCS, The PLANTS database, 2015) [20][28], the Pacific Northwest and New England in the U.S. (Figure 1). Some authors believe that it originates in the northernmost tip of the European continent, in Scotland [21][29], and is commonly found in Europe, around deciduous forests, and in the temperate areas of Asia, especially in central, northern, western, and southern Anatolia. Towards the east, it reaches Asia Minor, the Caucasus, and the Caspian Sea [22][30]. Isolated populations have been found in Tunisia and Algeria. It is widespread in the Southern Alps, Switzerland, at altitudes up to 1600 m [23][31]. Species of P. spinosa L. are also found on the slopes of wild, uncultivated areas in several regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina [24][32]. It is commonly found at forest edges and openings, on sunny, rocky slopes, in ravines and river valleys, and meadows and pastures from low plains to mountains [25][26][33,34]. In Romania, P. spinosa L., can be found in lowland, plain areas but is more abundant in hilly areas, extending to mountainous areas with altitudes of 900–1000 m, being present at the edge of agricultural lands, decorating the landscape or on abandoned pastures, as well as on the edge of oak and beech forests [18][27][28][29][26,35,36,37].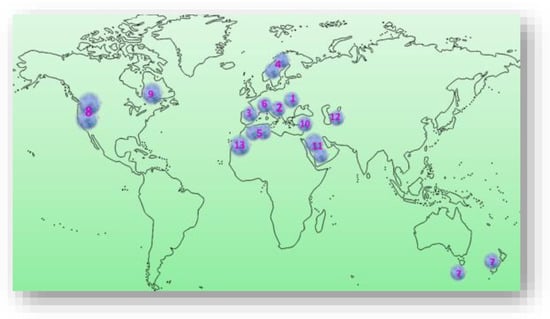
3. Nutritional composition of P. spinosa L.
The nutritional composition and estimated energy value of the blackthorn fruits are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Nutritional value of blackthorn fruits based on literature.
6.65 ± 2.03 | |||||
nd | 0.69 ± 0.04 |
2.72 |
1.18 ± 0.56 |
||
|
Fiber (g/100 g) |
nd |
9 |
5.79 ± 0.1 |
4.6 |
0.67 ± 0.26 |
The observed variations in the nutrient content of P. spinosa L. fruits (as shown in Table 1) can primarily be attributed to climatic conditions. Fruits grown in hot, dry climates are distinguishable by a lower level of moisture.
Differences were noted in the sugar content values (Table 1), ranging from 8.64 to 88.51 g/100 g. The variation in sugar content may be attributed to the intrinsic physicochemical properties and ripeness of blackthorn, as well as the environmental conditions [45][54].
An analysis of the amino acid composition of P. spinosa L. fruits [46][58] revealed that leucine, was found in a concentration of 122.6 mg/100 g. This amount is equivalent to 7.66% of the FAO (Food and Drug Administration) and WHO/DRIs (World Health Organization/Dietary Reference Intakes) recommended daily allowances (RDAs).Additional essential amino acids detected in P. spinosa L. were Valine (87.8 mg/100 g), Phenylalanine (84.7 mg/100 g), Lysine (50.6 mg/100 g), and Threonine (47.6 mg/100 g) [46][58].
Fatty acids found in P. spinosa L. fruits include oleic acid, linoleic acid, arachidonic acid, linolenic acid, EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DPA (docosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) [47][57]. Fatty acid content was dominated by monounsaturated fatty acids [47][57], followed by polyunsaturated fatty acids. According to the study conducted by Babalau-Fuss (2021) [47][57] on the analysis of fatty acid content in P. spinosa L. fruits, it was found that monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) were the most abundant, accounting for 46.20% of the total fat content. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) were identified in a proportion of 34.54%.
Among the mineral elements identified in P. spinosa L., potassium had the highest amount, followed by phosphorus, calcium, and sodium. The potassium levels varied between 1035.826 and 2014.23 mg/kg, the calcium levels ranged from 19.86 to 1504.41 mg/kg, and the sodium levels varied between 2.56 and 534.81 mg/kg [24][48][47][32,54,57].
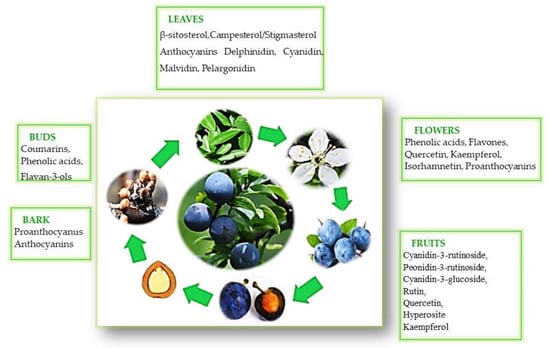
4. The Polyphenol Composition in Various Parts of the P. spinosa L. Shrub
|
Organs of P. spinosa |
Type of Sample/ Technique |
Phenols |
References |
|
Fruits |
Cold solution (1% BHT [w/v], 3% formic acid [v/v] in methanol) HPLC–DAD–MS |
Phenolic acids Cinnamic acid derivatives: · 3-p-Coumaroylquinic acid; · 4-p-Coumaroylquinic acid 1; · Caffeic acid hexoside 1; · Caffeic acid hexoside 3; · p-Coumaric acid hexoside 1; · 3-Caffeoylquinic acid; · 4-Caffeoylquinic acid; · 5-Caffeoylquinic acid 1; · 3-Feruloylquinic acid; Flavanols · Catechin; · Epicatechin; · Procyanidin dimer 1; · Procyanidin dimer 2; · Procyanidin dimer 3; · Procyanidin trimer 2; Flavonols · Quercetin triglycoside; · Quercetin acetyl hexoside; · Quercetin acetyl rutinoside; · Quercetin hexosyl pentoside 2; · Quercetin hexosyl rhamnoside; · Quercetin-3-xyloside; · Quercetin pentoside 2; · Quercetin pentoside 3; · Quercetin rhamnosyl hexoside; · Querectin-3-galactoside; · Quercetin-3-glucoside; · Quercetin-3-rhamnoside; · Quercetin-3-rutinoside; · Isorhamnetin hexoside; · Kaempferol pentoside hexoside; · Kaempferol rhamnosyl hexoside 1; · Kaempferol rhamnosyl hexoside 2; · Kaempferol pentoside; Flavones · Apigenin pentoside; Anthocyanins · Cyanidin pentoside; · Cyanidin 3-acetylglucoside; · Cyanidin-3-glucoside; · Cyanidin-3-rutinoside; · Pelargonidin-3-glucoside; · Peonidin-3-acetylglucoside; · Peonidin-3-glucoside; · Peonidin-3-rutinoside; · Petunidin-3-rhamnoside. |
[65] |
|
|
|||
|
Ethyl acetate fraction of methanol-water extract (75:25, v/v) in dried fruit UHPLC-PDA-ESI-MS |
Phenolic acids · Protocatechuic acid 4-O-hexoside; · Protocatechuic acida; · 3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid; · p-Hydroxybenzoic acida; · Caffeoylshikimic acid derivative; · Vanilloyl malate hexoside; · 3-O-p-Coumaroylquinic acid; · p-Coumaric acid O-hexoside; · 5-O-Caffeoylquinic acid; · cis-3-O-Feruloylquinic acid; · 4-O-Caffeoylquinic acid; · Caffeic acid 3/4-O-hexoside; · 3-O-Feruloylquinic acid; · Vanillina; · 4-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid; · 4-O-Feruloylquinic acid; · Caffeoylshikimic acid; · Caffeoylshikimic acid; · p-Coumaroylshikimic acid; · Aromadendrin hexoside; · p-Coumaroylshikimic acid; Flavonols · Quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactoside; · Quercetin 3-O-(6′′-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside; · Quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside; · Quercetin 3-O-α-D-xylopyranoside; · Quercetin 3-O-α-L-arabinopyranoside; · Quercetin 3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside; · Quercetin 3-O-(4′′-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside; · Quercetin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside; · Quercetin malyl-pentoside; · Quercetin acetyl-hexoside-rhamoside. |
[24] |
|
|
Flowers |
Defatted methanol-water extract RP-HPLC-PDA |
Phenolic acids · 3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid (neochlorogenic acid); · 5-O-Caffeoylquinic acid (chlorogenic acid); · 4-O-Caffeoylquinic acid (cryptochlorogenic acid); · Caffeic acid; · p-Coumaric acid; Flavanols · (+)-Catechin; · (–)-Epicatechin; Flavonols · Kaempferol 3-O-α-L-arabinopyranoside-7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside; · Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-xylopyranoside-7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (lepidoside); · Kaempferol 3,7-di-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (kaempferitrin); · Kaempferol 3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside-7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside; · Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-xylopyranoside; · Kaempferol 3-O-(4’’-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (multiflorin B); · Kaempferol 3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside (juglanin); · Kaempferol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (afzelin); · Kaempferol 7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside; · Kaempferol 3-O-(2’’-O-E-p-coumaroyl)-α-L-arabinofuranoside-7-O-α-Lrhamnopyranoside; · Kaempferol 3-O-(6’’-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside; · Kaempferol 3-O-(2’’-O-E-p-coumaroyl)-α-L-arabinofuranoside. · Kaempferol; · Quercetin 3-O-(6’’-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside (rutin); · Quercetin 3-O-(2’’-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-α-L-arabinofuranoside; · Quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (isoquercitrin); · Quercetin 3-O-β-D-galactopyranoside (hyperoside); · Quercetin 3-O-α-D-xylopyranoside (reinutrin); · Quercetin 3-O-α-L-arabinopyranoside (guaiaverin); · Quercetin 3-O-(4’’-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (multinoside A); · Quercetin 3-O-α-L-arabinofuranoside (avicularin); · Quercetin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (quercitrin); · Quercetin; |
[66] |
|
Leaves |
70% (v/v) aqueous-methanolic extract UHPLC-PDA-ESI–MS |
Phenolic acids · 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid (neochlorogenic acid); · 3-O-p-coumaroylquinic acid; · 3-O-feruloylquinic acid; · 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid (cryptochlorogenic acid); Flavanols · procyanidin type-B dimer; · procyanidin type-B dimer; · (+)-catechina; Flavonoids · kaempferol 3-O-a-L-arabinopyranoside-7-O-a-L-rhamnopyranosidea; · kaempferol 3-O-b-D-xylopyranoside-7-O-a-L-rhamnopyranoside (lepidoside); · quercetin 3-O-(200-O-b-D-glucopyranoside)-a-L-arabinofuranosidea; · kaempferol 3,7-di-O-a-L-rhamnopyranoside (kaempferitrin); · kaempferol 3-O-a-L-arabinofuranoside-7-O-a-L-rhamnopyranosidea; · quercetin 3-O-a-L-arabinofuranoside (avicularin); · kaempferol hexoside-pentoside; · kaempferol 3-O-a-L-arabinofuranoside (juglanin); · kaempferol 3-O-a-L-rhamnopyranoside (afzelin); · quercetin acetyl-hexoside-rhamnoside; · kaempferol acetyl-hexoside-rhamnoside; · kaempferol 7-O-a-L-rhamnopyranosidea; · kaempferola; · kaempferol 3-O-(2”-E-p-coumaroyl)-a-L-arabinofuranoside-7-O-a-L-rhamnopyranoside. |
[67] |
|
Branches |
Lyophilized extract HPLC/MS |
Phenolic acids · Protocatechuic acid; · Gallic acid; · Caffeic acid; Proanthocyanidins or flavan-3-ols · Ent-(epi)-catechin-(2α→O→7,4α→8)-(epi)-catechin-3′-O-gallate; · Ent-(epi)-afzelechin-(2α→O→7,4α→8)-(epi)-catechin-3′-O-gallate; · Ent-(epi)-gallocatechin (2α→O→7, 4α→8)(epi)-catechin; · Ent-(epi)-catechin (2α→O→7, 4 α→8)-catechin; · Ent-(epi)-gallocatechin (2α→O→7, 4α→8)-(epi)-catechin; · Ent-(epi)-catechin (2α→O→7, 4 α→8)-(epi)-catechin; · Ent-(epi)-afzalechin (2α→O→7, 4α→8) catechin; · Epigallocatechin; ·Ent-(epi)-afzalechin (2α→O→7, 4α→8)-(epi)-catechin; · Gallocatechin; · Epicatechin; · Catechin; · Epiafzelechin; · Afzelechin; Coumarins · 5-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-O-β-D-glucosyl coumarin; · 5-hydroxy-6-methoxy-7-O-β-D-rhamnosyl coumarin; Flavonols · Quercetin 3-O-rutinoside; · Kaempferol 3,7-O-dirhamnoside; ·Kaempferol 3-O-arabinoside-7-O-rhamnoside; kaempferol 3-O-arabinoside; · Quercetin; · Kaempferol |
[6] |
5. The Effect of Bioactive Compounds Found in the Blackthorn Fruits in the Treatment of Various Diseases
| Bioactive Compounds | Health Effect | Main Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids (Quercitin, Rutin) |
Neurogenerative effect | -acetylcholinesterase inhibition -monoamine oxidase inhibition -↓ peroxyl radical capture and oxidation -neurotrophic action -maintenance of physiological functions of vital organs |
[61][62][88,89] |
| Flavonoids | Cardiovascular effect | -inhibition of pro-inflammatory enzymes -anti-atherosclerotic effects -anti-atherothrombotic effects -modulation of lipid metabolism, -normalization of the LDL/HDL ratio, -improving capillary permeability -improved endothelial function, vasodilatory effects -↑ release of nitric oxide and uncoupling of endothelial nitric oxide synthesis -↓ oxidative DNA damage |
[41][63][64][65][66][67][68][48,62,90,91,92,93,94] |
| Proantocianidine | -modulates lipid metabolism, -↑ anti-oxidant capacity of plasma, - improve vascular functions -↓ platelet activity |
[41][69][48,95] | |
| Cianidin-3-rutinoside | -improve lipid ↓ mechanisms, -inhibition of lipolytic digestive enzymes -inhibition of lipid absorption processes -anti-oxidant activity on ROS, -antiglycating activity -cardioprotective activity mixed competitive inhibition of pancreatic lipase and pancreatic cholesterol esterase -inhibition of cholesterol mycelial formation linked to primary and secondary bile acid -inhibition of cholesterol mycelial absorption in the proximal jejunum. |
[41][70][71][48,96,97] | |
| Cianidin-3-glucoside | -↑ tissue tolerance to ischemic injury -↓ risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, -capacity to scavenge ROS -↓ oxidative stress, enhancing inflammatory responses |
[70][72][96,98] | |
| Cianidin-3-glucoside Cianidin 3-rutinoside |
Diabetes and associated metabolic diseases | ↓ risk of diabetes and obesity ↓ postprandial glucose by inhibition of pancreatic α-amylase and intestinal α-glucosidase -modulates postprandial blood glucose by inhibiting carbohydrate digestive enzymes -↓ glucose transport in the small intestine. -inhibit glucose uptake in colorectal adenocarcinoma epithelial cells |
[72][73][98,99] |
| Phenolic acids | Anticancer effect | -cytotoxic activity on some cancer cell lines -induction in vitro of endogenous anti-oxidant mechanisms -modulation of Nrf2 transcription factors, a regulator of cellular resistance to oxidative damage, -↓ disruption of the pro-oxidant/anti-oxidant balance with a key role in some cancers |
[16][17][74][75][16,20,23,100] |
| Anthocyanins | -unchanged dietary absorption and incorporation into cells, -major contribution to establishing anti-oxidant activity, reducing cancer risk |
[2][52][64][76][77][78][2,15,67,90,101,102] | |
| Phytosterols | -anticancer activity on prostate cancer | [76][15] | |
| Cianidin-3-glucozide | ↓ cancer risk due to the ability to scavenge ROS | [75][100] |
Reference |
|
[52][1] |
[37][1] |
[15][1] |
[53][1] |
[54] |
|
|
Energy (kcal/100 g) |
383.27 ± 7.09 |
57 |
154.93 |
249 |
nd |
|
Moisture (%) |
60.86 ± 1.69 |
54.85 ± 2.11 |
nd |
69.37 |
nd |
|
Carbohydrates (g/100 g dw) |
88.51 ± 2.24 |
8.64 |
31.07 ± 0.62 |
nd |
15.17 ± 25.83 |
|
Proteins (g/100 g dw) |
2.86 ± 0.03 |
0.75 |
2.07 ± 0.04 |
3.4 |
0.99 ± 0.25 |
|
Fat (g/100 g dw) |
1.98 ± 0.32 |
1 |
2.05 ± 0.12 |
2.06 |
nd |
|
Ash |
