细胞外囊泡分布的外泌体携带与细胞高度一致的各种信息,成为肿瘤筛查的新型生物标志物。然而,虽然传统的表征技术可以量化外泌体的大小和形态,但在功能追踪、单位点蛋白质定量和微观结构信息等相关领域受到限制。Exosomes distributed by extracellular vesicles carry various information highly consistent with cells, becoming a new type of biomarker for tumor screening. However, although conventional characterization technologies can quantify size and morphology for exosomes, they are limited in related fields such as function tracing, protein quantification at unit point, and microstructural information. In this paper, firstly, different exosome characterization methods are systematically reviewed, such as dynamic light scattering, nanoparticle tracking analysis, flow cytometry, electron microscope, and emerging super-resolution imaging technologies. Then, advances in applications are described one by one. Last but not least, we compare the features of different technologies for exosomes and propose that super-resolution imaging technology can not only take into account the advantages of conventional characterization techniques but also provide accurate, real-time, and super-resolution quantitative analysis for exosomes. It provides a fine guide for exosome-related biomedical research, as well as application in liquid biopsy and analysis techniques.
- exosome
- tumor diagnosis
- optical analysis technology
- super-resolution microscope
1. 引言Introduction
2. 常规表征技术Conventional Characterization Technologies
Due to the unique biological function of exosomes, an increasing amount of basic research is being concentrated on it [37,38,39,40,41]. Characterization technologies play important roles in the study of exosomes [30]. Generally speaking, various approaches for analysis are categorized into two primary types: biochemical analysis and physical analysis. Biochemical analysis mainly determines the source and composition of exosomes, including Western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), in which the specific binding of antibody antigens decides the effect qualitatively or quantitatively [42]. However, the disadvantage is that the morphological characteristics and concentration of exosomes cannot be obtained. We introduce electron technologies such as tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS) and electron microscope (EM) in the first section. Then, we compare optical analysis technologies including dynamic light scattering (DLS), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and flow cytometry (FCM). Last but not least, we discuss the main parameters of different technologies, providing technical guidance for the fundamental research on exosome characterization.2.1. 可调电阻脉冲检测Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing
可调电阻脉冲检测Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing (TRPS)(TRPS) is based on Coulter’s principle. The suspension was mixed in the electrolyte, which could go through the nanopore chip with a specific aperture. The resistance between the two electrodes inside and outside changes instantaneously at the moment of passing through the nanopore, the result of which is a pulse signal as shown in 基于库尔特原理。将悬浮液混合在电解液中,电解液可以通过具有特定孔径的纳米孔芯片。两个电极内外之间的电阻在通过纳米孔的那一刻瞬时发生变化,其结果是脉冲信号,如图Figure 2所示。信号的强度和频率与外泌体的大小和数量有关。通过脉冲信号计数外泌体的表达。a. The intensity and frequency of the signal are related to the size and number of exosomes. The expression of exosomes was counted by the pulse signal. In 2014, Maas proposed a method to characterize the concentration and size of EVs by the TRPS based on the qNano system [43]. In 2017, researchers pointed out that TRPS has promise in the quantitative and dimensional analysis of single-particle EV [44]. In 2018, Durak-Kozica analyzed EVs from endothelial cells for a short time and found that the diameter of EVs was 121.84 ± 0.08 and 115.82 ± 0.96 nm from microvascular and big vessels, respectively [45]. This technology enables the efficient quantification of size and number, which cannot be specifically analyzed for exosomes due to the principle of potential pulses.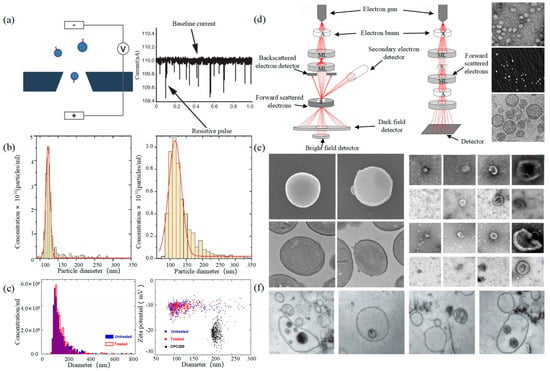
2.2. 电子显微镜
Electron Microscope
2.3. 动态光散射
动态光散射(Dynamic Light Scattering
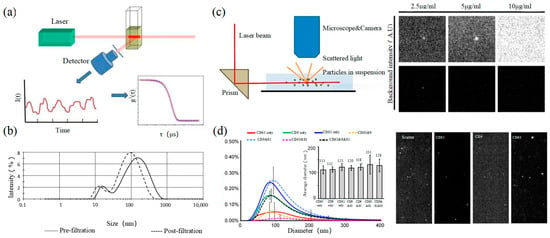
2.4. 纳米粒子跟踪分析Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
2.5. Flow Cytometry
Size and morphology are the basic parameters for the characterization of exosomes. The characterization of functional parameters such as surface protein quantitative expression and signal transduction mode is of paramount importance. Flow Cytometry (FCM) realizes the rapid multi-parameter quantitative analysis of cells or submicron particles based on light scattering changes, and its basic principle is shown in Figure 4. Scatters of light from particles suspended in a sheath stream reflect the size and density of the cells or particles, and they were acquired by a detector array. At the same time, the specific gene expression, protein expression, enzyme activity, ion concentration, and other biomolecular substances labeled by fluorescent dyes were specifically measured by different channels. The sensitivity of traditional flow cytometry is limited to 300 to 500 nm [76], so it is obviously difficult to measure exosomes. Yan Xiaomei’s team developed nFCM by combining Rayleigh scattering with sheath flow single-molecule fluorescence detection technology, which enables the high-throughput analysis of exosomes with a size of 40 nm, as shown in Figure 4 [77,78]. Compared with traditional flow cytometry, the scattered light detection sensitivity of nFCM is improved by four to six orders.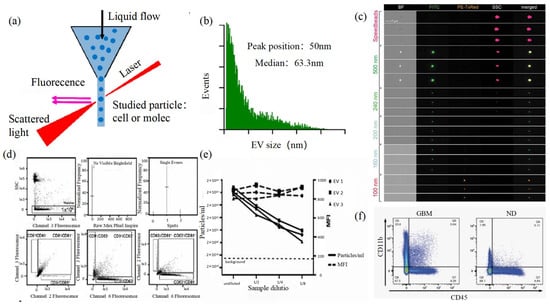
3. Super-Resolution Imaging Technology
3.1. Single Molecule Localization Imaging Technology
The basic principle of SMLM is based on the flicker of a single fluorescent molecule to locate a single molecule and then reconstruct super-resolution images. Compared with other technologies, SMLM has the advantages of low phototoxicity and low cell damage. It is more suitable for living cells, thus becoming a new super-resolution analysis method for exosomes in vivo observation. SMLM opens a new observation perspective for exosome-related studies.3.1.1. Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy and Photoactivated Localization Microscopy Technology
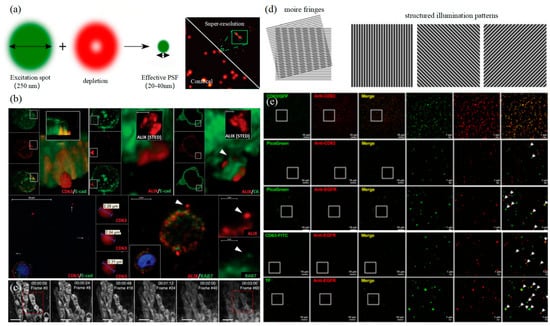
PALM and STORM technologies are classical technologies in SMLM. In 2006, Eric Betzig et al. proposed the PALM technology [82], and Xiaowei Zhuang et al. proposed the STORM technology [83] at the same time. Both of them are based on single-molecule localization technology to achieve the super-resolution imaging of subcellular structure molecules. One of the key elements is the switched fluorophores. For example, PALM uses photoactivated green fluorescent protein (PA-GFP) to label the protein and irradiate the cell surface with different lasers so as to cause the fluorescence molecule cycle to complete the excitation localization process. One of the key points is the spatial and temporal resolution for SMLM. That requires more than 10,000 frames of images during the process of reconstruction, which needs much more time. The rapid development of EMCCD cameras has greatly improved imaging speed. In 2011, Zhuang Xiaowei’s group pictured extracellular vesicles with a high-speed EMCCD. The temporal resolution was improved to 0.5 s, which means that STORM has the potential to monitor live cell imaging in real-time [85]. In 2011, Zhuang’s team used the stage-specific neurite-associated protein (SNAP) label to label the Alexa Flour 467 optical switching probe to clathrin in living BS-C-1 cells. STORM technology was successfully used to obtain a 30 nm horizontal resolution and a 50 nm vertical resolution [85]. In 2012, Shim et al. determined the STORM membrane probe for live cell imaging through a large number of experiments and performed the super-resolution imaging of organelle membranes in live cells, reaching a spatial resolution of 20~60 nm [92]. In 2018, Zong Shenfei et al. discovered that silicon quantum dots (Si QD) have fluorescent scintillation behavior and applied them as SMLM imaging nanoprobes to stain CD63 of breast cancer cell (SKBR3)-derived EVs using CD63 aptamers fused with Si QD, achieving an imaging accuracy of about 30 nm. They demonstrated that Si QD can be used for the SMLM imaging of small objects such as exosomes. Moreover, Si QD has the characteristics of high biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity, which makes it a better choice of fluorophores for SMLM live cell imaging [93].3.1.2. DNA-PAINT Technology
Similar to the STORM/PALM technology, DNA-PAINT also achieves super-resolution imaging by controlling the flicker of individual fluorophores. In 2014, Ralf Jungmann et al. proposed the DNA-PAINT technology, which uses reversible binding between complementary DNA sequences to produce an effect similar to the “flicker” of fluorescent molecules [101]. In double-strand DNA, one strand is connected to the fluorophores, called the imager strand, and the other is connected to the target molecule, called the docking strand. Due to the highly specific binding of the double-strand DNA, the imaging strand and the docking strand are bound spontaneously, producing single-molecule fluorescence in the focal plane [102] as shown in Figure 6. In addition, multi-channel fluorescence imaging can be realized by different proteins labeled with various docking strands.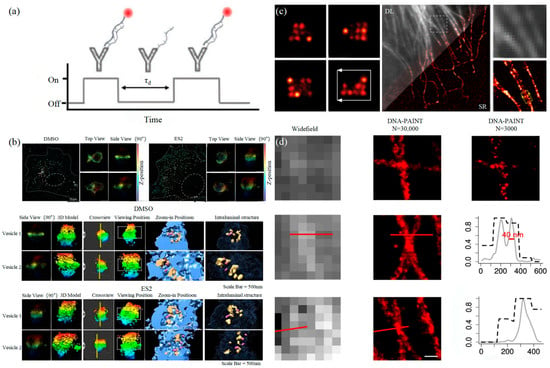
3.2. Stimulated Emission Depletion Technology