Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Marcelo Tavares Lima and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
In pre-combustion CO2 capture, the fuel (e.g., biomass, coal, natural gas) is firstly converted into syngas and then subjected to shift conversion to react CO and increase H2 content.
- glycolic acid
- CO2 capture
- green hydrogen
- CO2 hydrogenation
1. Introduction
To achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement, global anthropogenic CO2 emissions should be zero by 2050, and although major CO2 sources come from power, steel, and cement industries [1][2][1,2], efforts from all areas of society will be needed. However, the challenge involves unequal abatement costs across sectors. For example, chemical and steel companies may face higher costs for decarbonization in comparison with electricity generation plants [3]. In this scenario, carbon capture and storage (CCS) and carbon capture and utilization (CCU) are solutions for CO2 abatement that are widely discussed in the literature [4][5][6][4,5,6]. Both involve separation processes to avoid the release of CO2 to the atmosphere, generated by conversion of fossil or biomass resources, differing mainly by fate of the CO2 stream and whether it contributes to revenues of the project.
CCS prescribes sending captured CO2 (e.g., from combustion, industrial separation, or direct air capture) to geological storage, returning carbon to underground locations if it comes from a fossil resource. Power plants with CCS have been extensively studied in the literature [7] regarding challenges in the efficient capture and safe storage of CO2 [8]. CCS can provide considerable reduction of global CO2 emissions by 2050 [9][10][9,10], but the deployment of projects depends on a combination of favorable local aspects and leverages, like regulatory requirements and proper economic incentives [11].
In turn, CCU encompasses all routes where CO2 is used commercially to add revenues, either chemically as a raw material or physically as in enhanced oil recovery (EOR), among other uses. The concept may be regarded as a current “hot topic”, but it is not new. Back in 1972, a plant was launched in Texas for the purpose of improving productivity of old wells by EOR using CO2 captured from natural gas. Most early projects addressed EOR and utilized CO2 that had to be captured for other reasons (e.g., natural gas conditioning), but even in the 1970s there were studies considering the capture of CO2 from flue gases, which is believed by some as the origin of the CCS/CCU concept [8]. The chemical conversion of CO2 has also been studied for many decades [11], as a possible low-cost raw material, with possible uses in the production of methanol and methane by hydrogenation, as well as in carboxylation reactions to produce carbonates, acrylates, and polymers [12][13][12,13]. However, since CO2 is a relatively stable molecule, the processes are usually energy-intensive. Also, the reaction kinetics for CO2 conversion require special catalysts [14].
Beyond global warming concerns related to energy use and direct CO2 emissions, other significant environmental problems are caused by non-biodegradable plastic waste. It is well known to impact ecosystems but may also indirectly lead to the emission of greenhouse gases (e.g., from landfilling and incineration) [14][15][16][14,15,16]. This kind of waste mostly consists of common synthetic polymers like polyolefins (polyethylene, polypropylene), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and nylon, as well as their combinations and composites. In this scenario, one sustainable alternative is to invest in the production of biodegradable polymers like polyglycolic acid (PGA), whose monomer (glycolic acid) can be produced from renewable feedstocks (Figure 1), showing reduced lifetime (i.e., better biodegradability) when compared to other sustainable polymers (e.g., polycaprolactone and polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate) [15].
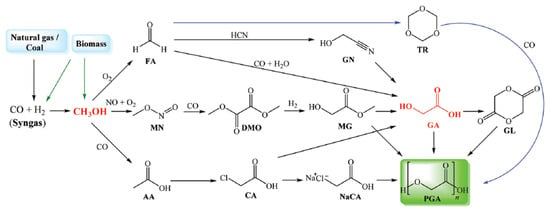
Figure 1.
Reaction pathways from syngas to polyglycolic acid polymers.
Glycolic acid also has other applications, and its global demand has increased, with possible use in food, cosmetic, textile, and cleaning chemical industries [17][18][19][17,18,19]. The production of glycolic acid from CO2 involves the following sequence of steps: syngas generation (e.g., by gasification), CO2 and/or CO separation (excess CO2 can be geologically stored), methanol synthesis, methanol partial oxidation, and formaldehyde reaction with CO (carbonylation).
2. CO2 Capture
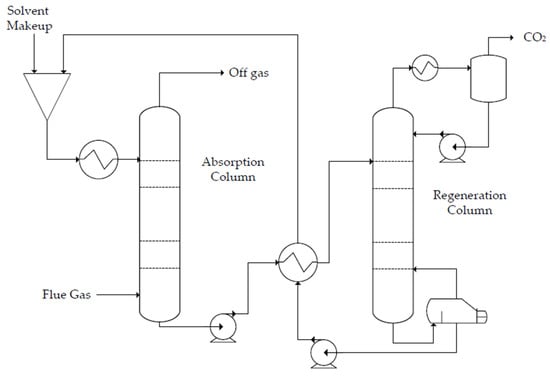
The production of polyglycolic acid can be carried out through different reaction pathways, shown in Figure 1. The routes have in common the need for methanol synthesis, where hydrogen reacts with CO and CO2. In this case, a CCU concept could be employed to replace syngas production, with CO2 hydrogenation to methanol addressed by use of renewable H2 from electrolysis. The CO2 could be obtained through different capture technologies, with the choice being mainly a function of the characteristics of the gas carrying the CO2 to be captured and the energy resource of the process; in a general way, the lower the CO2 partial pressure and the carbon content of the resource gas, the more expensive the capture process. The capture strategies are generally classified into three main groups when applied to power generation processes: pre-combustion, post-combustion, and oxy-combustion [20][21][20,21]. They are briefly described below. In pre-combustion CO2 capture, the fuel (e.g., biomass, coal, natural gas) is firstly converted into syngas and then subjected to shift conversion to react CO and increase H2 content, as illustrated in Figure 2. Syngas generation occurs between 700 and 1000 °C, and the required heat is usually supplied in situ by partial oxidation or indirectly by combustion. Then, H2/CO2 fractionation takes place, usually by chemical or physical absorption, and the H2 stream experiences combustion. The advantage of the strategy relies mainly in performing separation with relatively high CO2 fugacity, in comparison with typical flue gases of the post-combustion route. The major drawback is the high capital investment, which is a consequence of the much greater plant complexity [22][23][22,23].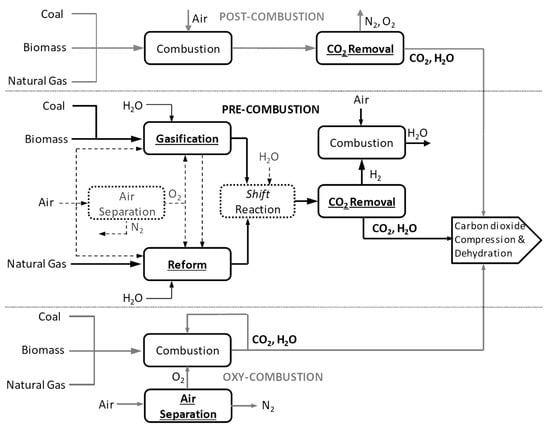
Figure 2.
Overview of main conceptual routes for CO
2
capture in power generation processes.
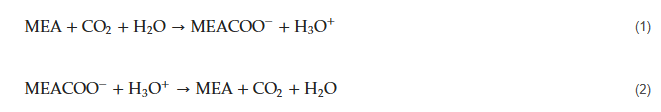 Separation by adsorption can occur through physical (e.g., using zeolites, activated carbon, or metal-organic frameworks) or chemical mechanisms (e.g., metal oxides, hydrotalcites, lithium zirconate) [33], among which physical adsorption has been more frequently used for CO2 capture. It involves a selective interaction between the target adsorbate CO2 and a solid material, which retains the CO2 in its surface, to later be regenerated, usually by pressure or temperature variation. At least two vessels installed in parallel are required for continuous cyclic operation: while one tower is regenerated, another one is active in the process. The cycle duration depends on adsorbent capacity and regeneration method (it usually operates for a few hours without regeneration if it is temperature-swing, but only a few minutes if it is pressure-swing) [34].
A relatively new concept is the use of selective membranes to separate CO2 from a gas stream. Membranes are semipermeable barriers that can be manufactured using different materials, which can be an organic (e.g., polymer) or inorganic type (e.g., ceramic, metallic). Separation by polymeric membranes has been more relevant in the field, and it is already utilized commercially for natural gas processing, since the stream is already found at high pressure, where it offers significant advantages of operational flexibility. The following two perspectives are important in the evaluation of membrane performance: permeability (for certain pressure drop) and selectivity (permeability ratio) of desired components. These determine component recoveries and stream purities after the separation process. The main drawbacks of gas permeation are low scalability (it is manufactured in modules), low product purity, and the need to compress the feed stream to generate separation driving-force if it is received at low pressure, which generally makes the option economically unattractive when compared to other separation methods [25]. In addition, the material may be sensitive to the presence of certain contaminants in the gas (e.g., sulfur compounds). However, membranes can be advantageous to promote process intensification in reactors and to improve reaction performance by in situ separation, as discussed in later sections [25].
Another separation method is cryogenic distillation, which is capable of producing high-purity streams and CO2 already pressurized and liquefied, ready to be pumped for transportation. The process involves high capital investment (due to feed gas pre-treatment, large amount of involved equipment, and requirement of resistant material for low-temperature operation) and high operating costs (linked to refrigeration), being economically competitive in large-scale applications where the feed stream has high CO2 content (usually above 50%) [22]. Some further advantages of this process—besides the production of pure liquid CO2—are the absence of solvents and good scalability (economic performance is substantially improved by process scale-up). Some of the existing process designs differ in how CO2 freeze-out is avoided or managed (CO2 solidification may be allowed at certain conditions, depending on the process) [22][35][22,35].
Chemical-looping combustion (CLC) uses metal oxides as oxygen carriers to convert the fuel and generate heat, in order to produce CO2 + H2O flue gas as in oxy-combustion (it is often classified in this category). A cyclic process of oxidation with air and reduction with fuel takes place to avoid the direct contact of air and fuel. The concept efficiently promotes CO2 capture with low energy requirements, while avoiding the presence of N2 in the flue gas, which not only increases the CO2 content but also has the further advantage of avoiding the formation of NOx. Besides high oxidation/reduction activity, the material should present long-term stability, with good mechanical resistance and minimum agglomeration. Additionally, the material should enable complete oxidation of the fuel for maximum system efficiency. Oxygen carriers meeting these requirements are under development [36].
Separation by adsorption can occur through physical (e.g., using zeolites, activated carbon, or metal-organic frameworks) or chemical mechanisms (e.g., metal oxides, hydrotalcites, lithium zirconate) [33], among which physical adsorption has been more frequently used for CO2 capture. It involves a selective interaction between the target adsorbate CO2 and a solid material, which retains the CO2 in its surface, to later be regenerated, usually by pressure or temperature variation. At least two vessels installed in parallel are required for continuous cyclic operation: while one tower is regenerated, another one is active in the process. The cycle duration depends on adsorbent capacity and regeneration method (it usually operates for a few hours without regeneration if it is temperature-swing, but only a few minutes if it is pressure-swing) [34].
A relatively new concept is the use of selective membranes to separate CO2 from a gas stream. Membranes are semipermeable barriers that can be manufactured using different materials, which can be an organic (e.g., polymer) or inorganic type (e.g., ceramic, metallic). Separation by polymeric membranes has been more relevant in the field, and it is already utilized commercially for natural gas processing, since the stream is already found at high pressure, where it offers significant advantages of operational flexibility. The following two perspectives are important in the evaluation of membrane performance: permeability (for certain pressure drop) and selectivity (permeability ratio) of desired components. These determine component recoveries and stream purities after the separation process. The main drawbacks of gas permeation are low scalability (it is manufactured in modules), low product purity, and the need to compress the feed stream to generate separation driving-force if it is received at low pressure, which generally makes the option economically unattractive when compared to other separation methods [25]. In addition, the material may be sensitive to the presence of certain contaminants in the gas (e.g., sulfur compounds). However, membranes can be advantageous to promote process intensification in reactors and to improve reaction performance by in situ separation, as discussed in later sections [25].
Another separation method is cryogenic distillation, which is capable of producing high-purity streams and CO2 already pressurized and liquefied, ready to be pumped for transportation. The process involves high capital investment (due to feed gas pre-treatment, large amount of involved equipment, and requirement of resistant material for low-temperature operation) and high operating costs (linked to refrigeration), being economically competitive in large-scale applications where the feed stream has high CO2 content (usually above 50%) [22]. Some further advantages of this process—besides the production of pure liquid CO2—are the absence of solvents and good scalability (economic performance is substantially improved by process scale-up). Some of the existing process designs differ in how CO2 freeze-out is avoided or managed (CO2 solidification may be allowed at certain conditions, depending on the process) [22][35][22,35].
Chemical-looping combustion (CLC) uses metal oxides as oxygen carriers to convert the fuel and generate heat, in order to produce CO2 + H2O flue gas as in oxy-combustion (it is often classified in this category). A cyclic process of oxidation with air and reduction with fuel takes place to avoid the direct contact of air and fuel. The concept efficiently promotes CO2 capture with low energy requirements, while avoiding the presence of N2 in the flue gas, which not only increases the CO2 content but also has the further advantage of avoiding the formation of NOx. Besides high oxidation/reduction activity, the material should present long-term stability, with good mechanical resistance and minimum agglomeration. Additionally, the material should enable complete oxidation of the fuel for maximum system efficiency. Oxygen carriers meeting these requirements are under development [36].