Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Sirius Huang and Version 1 by Pingyang Zhu.
Plants and insects are engaged in a tight relationship, with phytophagous insects often utilizing volatile organic substances released by host plants to find food and egg-laying sites. Using plant volatiles as attractants for integrated pest management is vital due to its high efficacy and low environmental toxicity. Using naturally occurring plant volatiles combined with insect olfactory mechanisms to select volatile molecules for screening has proved an effective method for developing plant volatile-based attractant technologies.
- plant volatiles
- insect
- olfactory system
- attractant
- pest management
1. Introduction
Insects and plants have co-evolved for hundreds of millions of years [1]. During this evolutionary process, insects have developed a unique olfactory system that distinguishes plant volatiles from other environmental odors [2,3][2][3]. Plant volatile organic chemicals (PVOCs) are essential chemical information links for insect-searching host plants and locating habitat, and play critical roles in the interdependent relationship between plants and insects. Insects can use these volatile compounds to collect information about plants, such as assisting bark beetles in the location of stressed host trees [4]. Research on the olfactory sensory mechanism of insects on PVOCs can help reveal the coevolutionary relationship between insects and plants and provide a theoretical basis for developing ecological technologies for preventing and curing pests.
Plant volatiles meet several key prerequisites for modern pest management, including being species-specific and environmentally benign [5]. Methods that interfere with an insect’s normal sense of smell fulfill these conditions and have been implemented on a large scale in the field. For example, physicochemical trap technology utilizing insect pheromones and plant volatiles to attract pests is highly targeted and provides efficacious pest management, reducing the need for traditional chemical applications [6,7][6][7]. As modern molecular and behavioral biology techniques are applied to further study the interactions of plant volatiles on pest behavior, the capabilities of olfaction-based pest management will continue to advance. High-throughput screening methods are particularly promising and will enable the identification and testing of highly efficacious, natural plant volatiles to alter the behavior of or trap agronomic pests. This has the potential to continue to improve our pest management technology in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner in line with modern goals of ecological agriculture [8,9,10,11][8][9][10][11].
2. Plant Volatiles
PVOCs are a mixture of multiple volatile plant secondary metabolites. Plant volatiles can be divided into green leaf, floral, and fruit volatiles according to the different organs of the plant, in which straight-chain alcohols and aldehydes containing six carbon atoms as well as their esters are the primary source of green leaf odors. Terpenes such as monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and sesquiterpenes together with aromatic compounds are the main constituents of the floral odors of the plant. The short-chained acetic esters formed by the degradation pathway of carbohydrates are the main source of the fruit aroma (Table 1). The metabolic pathways of different plants can produce specific odors, such as the cystine and cysteine metabolic pathways of the lily family and the methionine metabolic pathway of the cruciferous family [12,13][12][13].| Plant Organs | Types of Volatiles |
|---|---|
| Green leaf | C6/C9 aldehydes, alcohols, and esters |
| Flower | Terpenoids, phenylpropanoids/benzenoids, and fatty acid derivatives |
| Root | Alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, esters, terpenes, furans, organic acids, aromatic compounds, and sulfur compounds |
3. Molecular Perception of PVOCs by Insects
3.1. The Role of Insect Antennal Olfactory Sensors in the Recognition of PVOCs
Insect antennae sensors have more than ten types based on the structural characteristics of the sensilla’s epidermis and its mode of attachment [24]. Different kinds of sensilla have their own roles, e.g., the sensilla squamiformia is a receptor that senses mechanical stimuli [25]; the sensilla trichodea is associated with plant volatile recognition [26]; the sensilla chaetica is associated with taste [27]; and most sensilla basiconca are a class of olfactory receptors which can function in capturing plant volatile molecules using a large number of pore structures on their surfaces which contain a large number of neuronal cells (Figure 1) [28].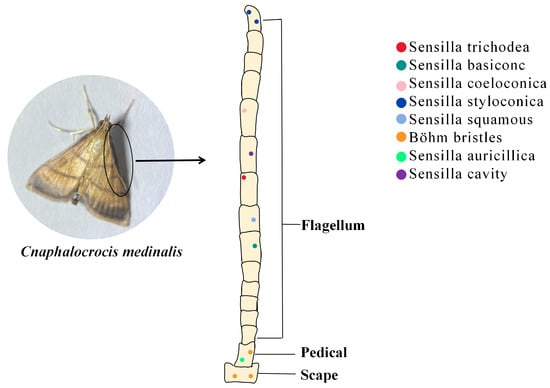
Figure 1. The role of insect antennal olfactory sensors in the recognition of PVOCs. Sensilla trichodea (red dot): mainly distributed in the center of the ventral surface of the antenna; Sensilla basiconc (dark green dot): distributed on the ventral and dorsal surface; Sensilla coeloconica (pink dot): distributed on the ventral surface; Sensilla styloconica (blue dot): distributed on the ventral surface and the end of the antennae; Sensilla squamous (light blue dot): distributed on the dorsal surface; Böhm bristles (orange dot): distributed on the scape and pedicel; Sensilla auricillica (green dot): distributed on the scape; Sensilla cavity (purple dot): distributed on all antenna surfaces.
3.2. The Role of Insect Antennal Olfaction-Related Proteins in the Recognition of PVOCs
Odor molecules enter the receptor lymphatic fluid through micropores in the olfactory sensory epidermis. However, hydrophobic odorants cannot cross the hydrophilic lymphatic fluid to reach the odorant receptor neuron (ORN) and must be carried by a transport protein. These odorant-transporting proteins fall into two categories known as odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) or chemosensory proteins (CSPs) [10]. After being wrapped by a transport protein in the lymphatic fluid to form a complex, the odorant is transported to the ORN and activates the odorant receptors (ORs), ionotropic receptors (IRs), or sensory neuron membrane proteins (SNMPs) on the dendritic membrane. Subsequent excitation of the olfactory neurons is induced, converting chemical signals into electrical signals, which are transmitted as action potentials to higher nerve centers (i.e., antennal lobes and mushroom bodies). Finally, the higher nerve centers integrate the electrical signals and release nerve impulses that direct the insect to produce specific physiological and behavioral responses (Figure 2) [10,42,43][10][42][43].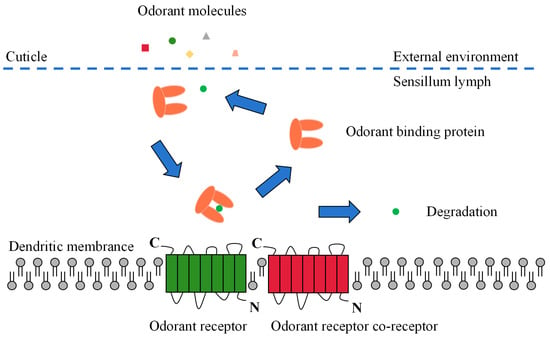
Figure 2.
Schematic view of the odorant perception process in insects.
References
- Wu, J.; Baldwin, I.T. New insights into plant responses to the attack from insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 1–24.
- Plettner, E. Insect pheromone olfaction: New targets for the design of species-selective pest control agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 1075–1085.
- Zu, P.; Zhang, D.Y.; Luo, Y.B. Chemical communication between plants and insects. J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 441–444.
- Fang, J.X.; Chen, D.F.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S.F.; Liu, F.; Shen, W.X.; Jia, C.Y.; Ma, S.C.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.B. Solid-phase microextraction and cuticular hydrocarbon differences related to reproductive activity in juniper bark borer Semanotus bifasciatus Motschulsky. J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 498–505.
- Rizvi, S.A.H.; George, J.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Zeng, X.; Guerrero, A. Latest developments in insect sex pheromone research and its application in agricultural pest management. Insects 2021, 12, 484.
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Cock, M.J.W.; Naranjo, S.E.; Fereti, A.; Williams, F.E.; Furlong, M.J. Ecological pest control fortifies agricultural growth in Asia–Pacific economies. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1522–1530.
- Zhao, J.; Cai, W.L.; Shen, Y.Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Pu, L.; Xie, M.Q.; Zou, Y.L.; Hua, H.X. Current situation and prospect of green rice pest control technology. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2022, 41, 92–104. (In Chinese)
- Beck, J.J.; Torto, B.; Vannette, R.L. Eavesdropping on plant-insect-microbe chemical communications in agricultural ecology: A virtual issue on semiochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5101–5103.
- Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Shi, Z.; An, X.; Khashaveh, A.; Li, Y.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Y. Identification and functional analysis of odorant-binding proteins provide new control strategies for Apolygus lucorum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 1129–1141.
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 184–200.
- Zeng, L.T.; Zhou, X.C.; Fu, X.M.; Hu, Y.L.; Gu, D.C.; Hou, X.L.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z.Y. Effect of the biosynthesis of the volatile compound phenylacetaldehyde on chloroplast modifications in tea (Camellia sinensis) plants. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad003.
- Dudareva, N.; Klempien, A.; Muhlemann, J.K.; Kaplan, I. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 16–32.
- Laothawornkitkul, J.; Taylor, J.E.; Paul, N.D.; Hewitt, C.N. Biogenic volatile organic compounds in the Earth system. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 27–51.
- Schiestl, F.; Ayasse, M. Post-pollination emission of a repellent compound in a sexually deceptive orchid: A new mechanism for maximising reproductive success? Oecologia 2001, 126, 531–534.
- Majetic, C.J.; Raguso, R.A.; Ashman, T.L. Sources of floral scent variation: Can environment define floral scent phenotype? Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 129–131.
- Martel, C.; Rakosy, D.; Romero, P.E.; Jersáková, J.; Ayasse, M. The evolution of tachinid pollination in Neotinea ustulata is related to floral cuticular composition and the combined high relative production of (Z)-11-C23/C25enes. J. Syst. Evol. 2021, 61, 487–497.
- Guo, M.; Du, L.; Chen, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, K.; Cao, S.; Huang, T.; Jacquin-Joly, E.; et al. Odorant receptors for detecting flowering plant cues are functionally conserved across moths and butterflies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 1413–1427.
- Feng, H.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Luo, Y.B.; Huang, S.Q. Floral scent emission is the highest at the second night of anthesis in Lonicera japonica (Caprifoliaceae). J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 530–537.
- Brevik, K.; Schoville, S.D.; Mota-Sanchez, D.; Chen, Y.H. Pesticide durability and the evolution of resistance: A novel application of survival analysis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1953–1963.
- Yan, X.Z.; Ma, L.; Li, X.F.; Chang, L.; Liu, Q.Z.; Song, C.F.; Zhao, J.Y.; Qie, X.T.; Deng, C.P.; Wang, C.Z.; et al. Identification and evaluation of cruciferous plant volatiles attractive to Plutella xylostella L. (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 5270–5282, Accepted Author Manuscript.
- Meagher, R.L.; Landolt, P.J. Binary floral lure attractive to velvetbean caterpillar adults (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Fla. Entomol. 2010, 93, 73–79.
- Desurmont, G.A.; Arx, M.V.; Turlings, T.C.J.; Schiestl, F.P. Floral odors can interfere with the foraging behavior of parasitoids searching for hosts. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 148.
- Wu, S.; Liu, F.; Zeng, W.; Xiao, Z.; Li, J.; Teng, K.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, J.; Du, Y. Evaluation of floral-derived volatile blend for attracting aphid parasitoids and lady beetles in the tobacco fields. Biol. Control 2022, 172, 104979.
- Schneider, D. Insect antennae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1964, 9, 103–122.
- Mclver, S.B. Structure of cuticular mechanoreceptors of arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1975, 20, 381–397.
- Roh, H.S.; Park, K.C.; Oh, H.W.; Park, C.G. Morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla of two tortricid moths, Cydia pomonella and C. succedana (Lepidoptera). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2016, 79, 1069–1081.
- Zacharuk, R.Y. Antennae and sensilla. Compr. Insect Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1985, 17, 1283–1284.
- Pophof, B.; Stange, G.; Abrell, L. Volatile organic compounds as signals in a plant-herbivore system: Electrophysiological responses in olfactory sensilla of the moth Cactoblastis cactorum. Chem. Senses 2005, 30, 51–68.
- Khallaf, A.; Knaden, M. Evolutionary neuroecology of olfactory-mediated sexual communication and host specialization in Drosophila—A review. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2022, 170, 289–302.
- Brilli, F.; Loreto, F.; Baccelli, I. Exploiting plant volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in agriculture to improve sustainable defense strategies and productivity of crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 264.
- Kwon, H.W.; Lu, T.; Rützler, M.; Zwiebel, L.J. Olfactory responses in a gustatory organ of the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13526–13531.
- Sun, X.; Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, G.A. Ultrastructural observations on antennal sensilla of Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 113–121.
- Piersanti, S.; Rebora, M. The antennae of damselfly larvae. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2018, 47, 36–44.
- Ma, R.Y.; Du, J.W. Antennal sensilla of insect. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 2000, 37, 179–183. (In Chinese)
- Li, C.D.; Yang, D.R.; Shen, F.R.; Yang, Y.X. Scanning electron microscopic observation on antennal sensilla of Hepialus yulongcnsis. Zool. Res. 1994, 11, 83–86. (In Chinese)
- Liébanas, G.; Sáez, Á.; Luna, Á.; Romero-Vidal, P.; Palma, A.; Pérez, J.M. The morphology of Colpocephalum pectinatum (Phthiraptera: Amblycera: Menoponidae) under scanning electron microscopy. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2021, 64, 101085.
- Dong, W.Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.R. Morphological and ultrastructural characterization of antennal sensilla and the detection of floral scent volatiles in Eupeodes corollae (Diptera: Syrphidae). Front. Neuroanat. 2021, 15, 791900.
- Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Cao, S.; Ma, B.; Guo, M.; Shen, J.; Wang, G. Fine structure and olfactory reception of the labial palps of Spodoptera frugiperda. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 680697.
- Liu, Y.Q.; Li, J.; Ban, L.P. Morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla in three species of Thripidae (Thysanoptera) infesting alfalfa Medicago sativa. Insects 2021, 12, 81.
- Shi, X.; Zhang, S.F.; Liu, F.; Xu, F.Y.; Zhang, F.B.; Guo, X.B.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.B. SEM analysis of sensilla on the mouthparts and antennae of Asian larch bark beetle Ips subelongatus. Micron 2021, 140, 102976.
- Du, Y.J.; Yan, F.S.; Tang, J. Structure and function of olfactory receptors in Aphis glycines antennae. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1995, 38, 1–7. (In Chinese)
- Brito, N.F.; Moreira, M.F.; Melo, A.C. A look inside odorant-binding proteins in insect chemoreception. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 95, 51–65.
- Krieger, J.; Breer, H. Olfactory reception in invertebrates. Science 1999, 286, 720–723.
- Fan, J.; Francis, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.L.; Cheng, D.F. An overview of odorant-binding protein functions in insect peripheral olfactory reception. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 3056–3069.
- Breer, H.; Krieger, J.; Raming, K. A novel class of binding proteins in the antennae of the silk moth Antheraea pernyi. Insect Biochem. 1990, 20, 735–740.
- Rihani, K.; Ferveur, J.F.; Briand, L. The 40-year mystery of insect odorant-binding proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 509.
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, G.R. Research progress of soluble proteins on chemosensationin insects. J. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 41, 229–240. (In Chinese)
- Wu, F.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y.L.; Li, H.L. Research progress of olfactory binding proteins in insects. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2021, 64, 523–535. (In Chinese)
- Sun, Y.L.; Dong, J.F.; Song, Y.Q.; Wang, S.L. GOBP1 from the variegated cutworm Peridroma saucia (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) displays high binding affinities to the behavioral attractant (Z)-3-Hexenyl acetate. Insects 2021, 12, 939.
- Zhou, J.J. Odorant-binding proteins in insects. Vitam. Horm. 2010, 83, 241–272.
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391.
- Venthur, H.; Zhou, J.J. Odorant receptors and odorant-binding proteins as insect pest control targets: A comparative analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1163.
- Li, T.T.; Liu, W.C.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.H.; Ma, C.; Lu, C.; Zhang, K.X. Crystal structure and ligand identification of odorant binding protein 4 in the natural predator Chrysopa pallens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 1004–1012.
- Northey, T.; Venthur, H.; De, B.F.; Chauviac, F.X.; Cole, A.; Ribeiro, K.A.J.; Grossi, G.; Falabella, P.; Field, L.M.; Keep, N.H.; et al. Crystal structures and binding dynamics of odorant-binging protein 3 form two aphid species Megoura viciae and Nasonovia ribisniari. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24739.
- Gonzalez, D.; Rihani, K.; Neiers, F.; Poirier, N.; Fraichard, S.; Gotthard, G.; Chertemps, T.; Maïbèche, M.; Ferveur, J.F.; Briand, L. The Drosophila odorant-binding protein 28a is involved in the detection of the floral odour ß-ionone. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2565–2577.
- Sandler, B.H.; Nikonova, L.; Leal, W.S.; Clardy, J. Sexual attraction in the silkworm moth: Structure of the pheromone-binding-protein-bombykol complex. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 143–151.
- Horst, R.; Damberger, F.; Luginbühl, P.; Güntert, P.; Peng, G.; Nikonova, L.; Leal, W.S.; Wüthrich, K. NMR structure reveals intramolecular regulation mechanism for pheromone binding and release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14374–14379.
- Li, G.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Binding properties of general odorant binding proteins from the oriental fruit moth, Grapholita molesta (Busck) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155096.
- Nagnan-Le, M.P.; Huet, J.C.; Maibeche, M.; Pernollet, J.C.; Descoins, C. Purification and characterization of multiple forms of odorant/pheromone binding proteins in the antennae of Mamestra brassicae (Noctuidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 26, 59–67.
- Ahmed, T.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, Z.Y.; He, K.L.; Bai, S.X. C-terminus methionene specifically involved in binding corn odorants to odorant binding protein 4 in Macrocentrus cingulum. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 62.
- Dong, K.; Duan, H.X.; Liu, J.T.; Sun, L.; Gu, S.H.; Yang, R.N.; Dhiloo, K.H.; Gao, X.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, Y.Y. Key site residues of pheromone-binding protein 1 involved in interacting with sex pheromone components of Helicoverpa armigera. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16859.
- del Mármol, J.; Yedlin, M.A.; Ruta, V. The structural basis of odorant recognition in insect olfactory receptors. Nature 2021, 597, 126–131.
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, B.X.; Rao, X.J.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, D.M.; Li, S.G. Transcriptome sequencing reveals abundant olfactory genes in the antennae of the rice leaffolder, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Entomol. Sci. 2017, 20, 177–188.
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Yu, J.; Pang, B.P.; Wang, G.R. Expression profiles and functional prediction of ionotropic receptors in Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 474–485.
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, S.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Francis, F.; Fan, J.; Chen, J. Functional analysis of odorant-binding proteins for the parasitic host location to implicate convergent evolution between the grain aphid and its parasitoid Aphidius gifuensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 510–524.
More
