Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Sirius Huang and Version 1 by Hamed Taherdoost.
Blockchain is fundamentally a distributed, decentralized digital ledger that securely and permanently records transactions. The applications of blockchain technology in healthcare extend far beyond just patient records and include things like supply chain management and drug security, disease prediction, medicine traceability, insurance claims, and more.
- blockchain technology
- healthcare industry
- advancements
- data integrity
- patient privacy
1. Introduction
As our population ages, not only do we have a greater demand for healthcare, but also for increased productivity [1]. The aging population and the prevalence of chronic diseases have increased the focus on health and the quest for better medical care [2]. There is a shift in perspective away from traditional healthcare and toward patient-centered care. Recent years have seen a shift away from healthcare that focuses on the patient and the hospital, toward healthcare that is more mobile and electronic; this shift has resulted in universal healthcare [3].
The industry is at the forefront. Healthcare organizations, equipped with the necessary tools, are at the forefront of participating in the blockchain movement [4]. The health ecosystem’s primary focus is on patients, and its primary objective is to increase the security, confidentiality, and portability of health information. The healthcare sector generates copious amounts of data, including patient records, data from clinical trials, billing, and research findings [5]. Securing all internet-connected medical devices is the biggest obstacle to universal electronic healthcare [6].
Blockchain, a distributed, immutable, and powerful technology, is having profound effects on the healthcare industry [7]. The elimination of third-party middlemen is another useful feature of blockchain technology. These days, blockchain is used for more than only cryptocurrency transactions [8]. Since these problems are real ones, the healthcare management system has social relevance [9]. The overarching goal is to boost happiness by solving actual health problems [3]. Healthcare information technology emerged as a result of the incorporation of computer science into healthcare, leading to significant improvements in medical care [10]. There are significant problems and gaps in the healthcare system, notwithstanding its progress [11].
Since its start with cryptocurrencies and continuing with the latest blockchain-based application for industry 5.0 [12], blockchain technology has been deployed in a wide variety of areas as part of the infrastructure of some firms that require transparency, integrity, and reliability [13]. The applications of blockchain technology in healthcare extend far beyond just patient records and include things like supply chain management and drug security, disease prediction, medicine traceability, insurance claims, and more. By automating formerly laborious processes that relied on inefficient configurations and wasted time, blockchain technology has fundamentally altered how things are implemented [14]. Blockchain’s trustworthy environment and user-friendly network produce effective results that foster confidence among parties [14,15][14][15].
2. Core Features and Characteristics
The potential for blockchain technology to completely overhaul the healthcare sector has surfaced [16]. Blockchain is fundamentally a distributed, decentralized digital ledger that securely and permanently records transactions [17]. In the healthcare industry, where the confidentiality and security of patient data are crucial, this functionality is very useful [18]. Blockchain technology assures that no single party has complete control over the data by functioning on a peer-to-peer network [17,19][17][19]. This increases transparency and lowers the possibility of data modification or unauthorized access [18]. Healthcare data is protected by a crucial layer of security thanks to the immutability of blockchain records [17]. Since each transaction or item on the blockchain is cryptographically connected to the one before it, updating historical data would require changing every block after it [16]. This tamper-resistant quality protects medical data and critical information, greatly lowering the possibility of fraud, and boosting patient confidence [18]. All network users have access to a complete transaction history, allowing for the traceability of medical data, the authentication of products, and regulatory compliance [20]. Additionally, being able to audit and track data access improves accountability and fortifies security against data breaches. The long-standing issue of sharing medical data among various systems and stakeholders can be addressed with the help of blockchain’s interoperability features. Blockchain-based platforms can enable secure and seamless data transmission, improving care coordination and minimizing redundant procedures, by using standardized data formats and protocols. Blockchain’s special ability, smart contracts, automates healthcare procedures. Among other things, the processing of insurance claims, consent management, and supply chain tracking can all be automated using these self-executing agreements with specified rules. Smart contracts can streamline procedures, lower costs, and improve overall efficiency in the healthcare ecosystem by removing the need for middlemen and manual interventions. Despite its enormous promise, the implementation of blockchain in healthcare confronts difficulties. Significant obstacles still need to be solved in the areas of scalability, regulatory compliance, data protection, and interaction with current healthcare infrastructure [21]. However, continuous research and development in this field continue to look at novel approaches to deal with these difficulties as the fundamental traits and properties of blockchain drive the goal of a more secure, effective, and patient-centric healthcare environment.3. Employing Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology implementation in the healthcare industry has many benefits, including improved data security, interoperability, and simplified data management [22]. To do this, it is needed to first pinpoint the precise use cases where blockchain can provide value. These applications cover managing medical records, monitoring the medical supply chain, sharing data from clinical trials and research, processing healthcare payments, and integrating data from internet of things (IoT) devices. Once the use cases have been established, choosing the best blockchain platform is essential, taking into account elements like scalability, privacy needs, and consensus techniques. Strong data privacy and permission management methods are crucial due to the sensitivity of healthcare data and the requirement for compliance with tight standards. Implementations of blockchain need to follow privacy regulations and provide impenetrable consent management to guarantee that patient data is only accessible with the appropriate authorization. Smart contracts are extremely helpful in the healthcare industry for activities like processing insurance claims and managing data access rights [23] since they play a vital role in automating procedures and transactions based on specified rules [24]. Given that the majority of enterprises have legacy systems in place, integration with existing healthcare systems is essential. While challenging, a smooth integration is essential for a successful shift to blockchain technology [25]. Another crucial choice depends on the chosen blockchain platform and the healthcare use case [26], such as whether to employ proof of work (PoW) or proof of stake (PoS). Before implementing blockchain technology in a real-world healthcare setting, thorough testing and compliance checks are essential to guarantee data integrity, security, and adherence to legal standards. Finally, after implementation, it is crucial to maintain monitoring and improvement to address any problems that may emerge and enhance the functioning of the system. Figure 1 represents the step-by-step process of implementing blockchain technology in the healthcare industry.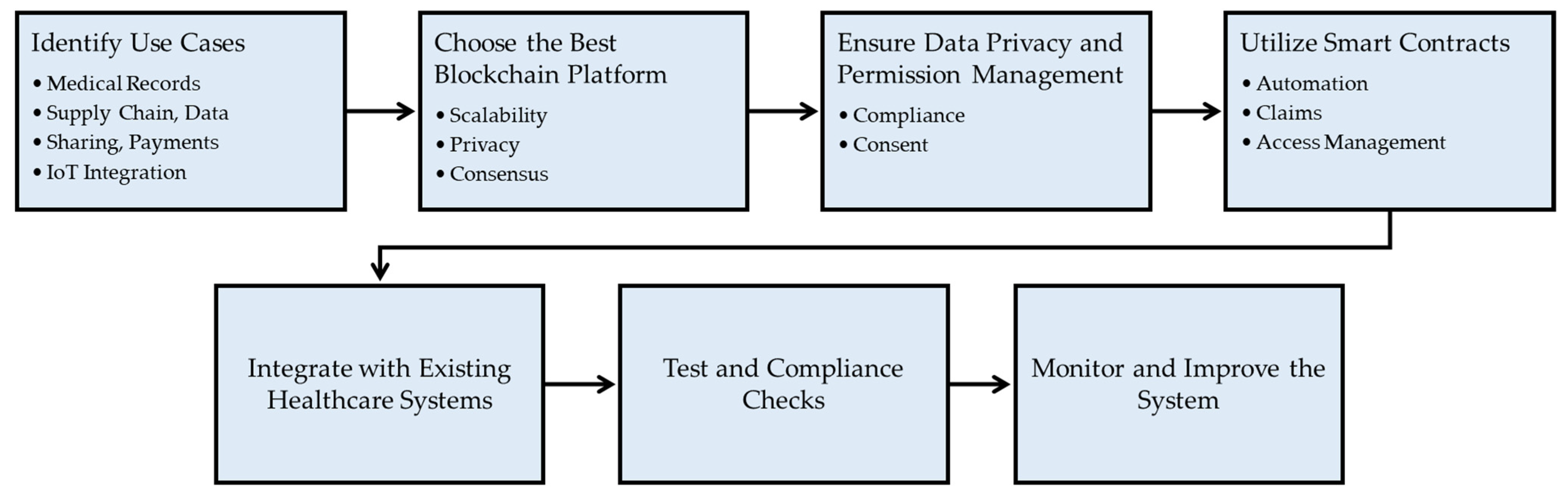
Figure 1.
Implementation of blockchain in the healthcare system.
4. Benefits and Potential Applications in Healthcare
Blockchain technology has numerous advantages and prospective uses that could completely transform the way healthcare is delivered and managed, and how patients fare. The unmatched data security and privacy capabilities of blockchain technology are among its most important benefits for the healthcare industry. Blockchain ensures that patient data is secure and tamper-resistant by using a decentralized and immutable ledger. This lowers the possibility of data breaches and illegal access, fostering more confidence in the healthcare system. Acheiving interoperability between various systems and stakeholders has been a major difficulty in the healthcare industry [27]. This problem is resolved by the open and standardized data exchange protocols offered by blockchain technology [28]. Healthcare organizations may safely exchange patient information in real time, allowing for seamless care coordination and a reduction in the number of tests and procedures that need to be repeated. Because of interoperability, healthcare professionals can make better judgments and provide patients with more thorough and effective care. The integration of blockchain technology has enormous potential benefits for electronic health records (EHRs). Blockchain technology can be used to make EHRs into a unified and impenetrable system. Authorized healthcare practitioners can quickly access medical records stored on the blockchain, assuring accurate and current patient information during medical treatment. A more accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment strategies, and ultimately better patient outcomes may result from this simplified access to patient data. The management of supply chains, notably in the pharmaceutical sector, is another prospective use of blockchain in healthcare [29]. Transparency and traceability are improved by blockchain’s capability to follow the distribution of medications and medical equipment from the maker to the final consumer. This supports patient safety and confidence in the healthcare system by ensuring the authenticity and integrity of medications while also assisting in the fight against the growth of counterfeit drugs. Blockchain technology can also have a big impact on managing research data and clinical trials. Researchers can use the transparent and auditable ledger of a blockchain to check the accuracy of trial outcomes and guarantee protocol adherence. Medical breakthroughs are ultimately accelerated by the immutability of data stored on the blockchain, which improves the reproducibility and legitimacy of study findings [30]. Blockchain-based smart contracts have the potential to transform other industries as well, including health insurance and claims processing [31]. Smart contract automation of claim settlements lowers administrative loads and avoids errors, resulting in a more effective and economical insurance system. Additionally, blockchain can give patients more control over their personal information by enabling them to manage their medical data and consent through smart contracts. Despite these promising uses, problems with scalability, legal compliance, and system integration continue. Blockchain technology is continuing to advance, overcoming these challenges and advancing the healthcare sector toward a more secure, effective, and patient-focused future. Blockchain technology is expected to have a revolutionary impact on healthcare as it develops, transforming how healthcare data is maintained, shared, and used to improve patient care and general public health.5. Evaluation of Improved Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Blockchain accelerates administrative procedures by utilizing its decentralized and tamper-proof ledger system, doing away with the need for middlemen and manual record reconciliation [32]. Smart contracts can automate processes like patient registration, billing, and insurance claim processing, which speeds up decision-making and improves collaboration among healthcare providers [33]. This improves patient care while simultaneously saving time. Blockchain’s interoperability features enable smooth data sharing between various healthcare organizations and systems [34,35][34][35]. Secure data exchange improves care coordination and lowers medical errors with patients, caregivers, and other authorized parties. Repetitive tests and treatments can be reduced with better patient access to their medical records, which lowers costs for both patients and healthcare providers. Moreover, efficiency and cost-effectiveness are further enhanced by blockchain’s ability to revolutionize supply chain management [36,37][36][37]. Counterfeit goods can be found and supply chain integrity ensured by tracking medications and medical equipment on the blockchain [38]. This openness not only increases patient safety but also lessens financial losses brought on by recalled goods and fake goods. Table 1 provides a comprehensive analysis of the potential impact of implementing blockchain technology in the healthcare industry. It examines various aspects of healthcare operations, comparing traditional systems to blockchain-based systems.Table 1.
Blockchain in healthcare: evaluating improved efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and challenges.
| Aspect | Traditional System | Blockchain System | Challenges/Limitations | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Security/Privacy | Limited security, data breaches possible. | High security via cryptographic algorithms. | Regulatory complexity, private key management | [16] |
| Interoperability | Data silos, incompatible formats. | Shared, standardized, transparent data access. | Integration challenges | [39] |
| Data Integrity | Centralized data, tampering risks. | Immutable ledger, reduced errors. | Scalability concerns | [40] |
| Claims Processing | Manual verification, time-consuming. | Efficient smart contract validation. | Transition challenges | [41] |
| Supply Chain Management | Lack of transparency in tracing. | Traceable supply chain data. | Onboarding difficulties. | [42] |
| Medical Research | Limited access to diverse datasets. | Decentralized data sharing with consent. | Data privacy, compliance challenges | [43] |
| Counterfeit Drugs Detection | Inadequate counterfeit drug identification. | Unique identifiers, history tracking. | Adoption hurdles | [44] |
| Auditability/Compliance | Manual audits, compliance issues. | Transparent, auditable blockchain records. | Privacy vs. transparency balance | [45] |
| Cost of Intermediaries | Increased costs due to intermediaries. | Direct peer-to-peer transactions. | Stakeholder trust transition | [46] |
References
- Hollander, M.J.; Chappell, N.L.; Prince, M.J.; Shapiro, E. Providing care and support for an aging population: Briefing notes on key policy issues. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 15, 34–45.
- Thilakarathne, N.N.; Kagita, M.K.; Gadekallu, T.R. The role of the internet of things in health care: A systematic and comprehensive study. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Res. 2020, 10, 145–159.
- Dash, S.P. The impact of IoT in healthcare: Global technological change & the roadmap to a networked architecture in India. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2020, 100, 773–785.
- Ivan, D. Moving toward a blockchain-based method for the secure storage of patient records. In ONC/NIST Use of Blockchain for Healthcare and Research Workshop; ONC/NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016; pp. 1–11.
- Bach, L.M.; Mihaljevic, B.; Zagar, M. Comparative analysis of blockchain consensus algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 1545–1550.
- Islam, A.; Shin, S.Y. A blockchain-based secure healthcare scheme with the assistance of unmanned aerial vehicle in Internet of Things. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 84, 106627.
- Taherdoost, H. Blockchain-Based Internet of Medical Things. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1287.
- Yaeger, K.; Martini, M.; Rasouli, J.; Costa, A. Emerging blockchain technology solutions for modern healthcare infrastructure. J. Sci. Innov. Med. 2019, 2, 1.
- Sadiku, M.N.; Eze, K.G.; Musa, S.M. Block chain technology in healthcare. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Res. Eng. 2018, 4, 154–159.
- Lewis, R.; McPartland, J.; Ranjan, R. Blockchain and financial market innovation. Econ. Perspect. 2017, 41, 1–17.
- Hathaliya, J.J.; Tanwar, S.; Tyagi, S.; Kumar, N. Securing electronics healthcare records in healthcare 4.0: A biometric-based approach. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 76, 398–410.
- Rupa, C.; Midhunchakkaravarthy, D.; Hasan, M.K.; Alhumyani, H.; Saeed, R.A. Industry 5.0: Ethereum blockchain technology based DApp smart contract. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 7010–7027.
- Jafar, U.; Ab Aziz, M.J.; Shukur, Z.; Hussain, H.A. A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis on Scalable Blockchain-Based Electronic Voting Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 7585.
- Dash, S.; Gantayat, P.K.; Das, R.K. Blockchain technology in healthcare: Opportunities and challenges. In Blockchain Technology: Applications and Challenges; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 97–111.
- Qian, C.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L. Green Supply Chain Circular Economy Evaluation System Based on Industrial Internet of Things and Blockchain Technology under ESG Concept. Processes 2023, 11, 1999.
- Saeed, H.; Malik, H.; Bashir, U.; Ahmad, A.; Riaz, S.; Ilyas, M.; Bukhari, W.A.; Khan, M.I.A. Blockchain technology in healthcare: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266462.
- Khezr, S.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Yassine, A.; Benlamri, R. Blockchain technology in healthcare: A comprehensive review and directions for future research. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1736.
- Azaria, A.; Ekblaw, A.; Vieira, T.; Lippman, A. Medrec: Using blockchain for medical data access and permission management. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Conference on Open and Big Data (OBD), Vienna, Austria, 22–24 August 2016; pp. 25–30.
- Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. Blockchain-Based New Business Models: A Systematic Review. Electronics 2023, 12, 1479.
- Musamih, A.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Arshad, J.; Debe, M.; Al-Hammadi, Y.; Ellahham, S. A blockchain-based approach for drug traceability in healthcare supply chain. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 9728–9743.
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.A.; Uddin, M.A.; Stea, G. A survey of blockchain-based IoT eHealthcare: Applications, research issues, and challenges. Internet Things 2022, 19, 100551.
- Wang, D.H. IoT based clinical sensor data management and transfer using blockchain technology. J. IoT Soc. Mob. Anal. Cloud 2020, 2, 154–159.
- Khatoon, A. A Blockchain-Based Smart Contract System for Healthcare Management. Electronics 2020, 9, 94.
- Dai, J.; Vasarhelyi, M.A. Toward blockchain-based accounting and assurance. J. Inf. Syst. 2017, 31, 5–21.
- Romashkova, I.; Komarov, M.; Ometov, A. Demystifying blockchain technology for resource-constrained IoT devices: Parameters, challenges and future perspective. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 129264–129277.
- Ray, P.P.; Dash, D.; Salah, K.; Kumar, N. Blockchain for IoT-based healthcare: Background, consensus, platforms, and use cases. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 15, 85–94.
- Reisman, M. EHRs: The challenge of making electronic data usable and interoperable. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 572.
- Zhang, P.; White, J.; Schmidt, D.C.; Lenz, G.; Rosenbloom, S.T. FHIRChain: Applying blockchain to securely and scalably share clinical data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 267–278.
- Haq, I.; Esuka, O.M. Blockchain technology in pharmaceutical industry to prevent counterfeit drugs. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2018, 180, 8–12.
- Bartling, S. Blockchain for science and knowledge creation. In Gesundheit Digital: Perspektiven zur Digitalisierung im Gesundheitswesen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 159–180.
- Taherdoost, H. Smart Contracts in Blockchain Technology: A Critical Review. Information 2023, 14, 117.
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Suman, R.; Khan, S. A review of Blockchain Technology applications for financial services. BenchCouncil Trans. Benchmarks Stand. Eval. 2022, 2, 100073.
- Zhang, P.; Schmidt, D.C.; White, J.; Lenz, G. Blockchain technology use cases in healthcare. In Advances in Computers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 111, pp. 1–41.
- Jabbar, R.; Fetais, N.; Krichen, M.; Barkaoui, K. Blockchain technology for healthcare: Enhancing shared electronic health record interoperability and integrity. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Informatics, IoT, and Enabling Technologies (ICIoT), Doha, Qatar, 2–5 February 2020; pp. 310–317.
- Gai, K.; She, Y.; Zhu, L.; Choo, K.-K.R.; Wan, Z. A blockchain-based access control scheme for zero trust cross-organizational data sharing. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2023, 23, 38.
- Taherdoost, H. The Role of Blockchain in Medical Data Sharing. Cryptography 2023, 7, 36.
- Gai, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, M.; Thuraisingham, B. Blockchain-enabled service optimizations in supply chain digital twin. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2022, 16, 1673–1685.
- Rawat, R. A Systematic Review of Blockchain Technology Use in E-Supply Chain in Internet of Medical Things (Iomt). Int. J. Comput. Inf. Manuf. (IJCIM) 2022, 2, 37–53.
- Miyachi, K.; Mackey, T.K. hOCBS: A privacy-preserving blockchain framework for healthcare data leveraging an on-chain and off-chain system design. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102535.
- Ali, A.; Al-Rimy, B.A.S.; Tin, T.T.; Altamimi, S.N.; Qasem, S.N.; Saeed, F. Empowering Precision Medicine: Unlocking Revolutionary Insights through Blockchain-Enabled Federated Learning and Electronic Medical Records. Sensors 2023, 23, 7476.
- Tursilli, A. How Blockchain Technology and Smart Contracts Could Revolutionize Health and Life Insurance Industry. Bachelor’s Thesis, Luiss Guido Carli, Roma, Italy, 2023.
- Khanna, A.; Jain, S.; Burgio, A.; Bolshev, V.; Panchenko, V. Blockchain-enabled supply chain platform for Indian dairy industry: Safety and traceability. Foods 2022, 11, 2716.
- Zheng, X.; Mukkamala, R.R.; Vatrapu, R.; Ordieres-Mere, J. Blockchain-based personal health data sharing system using cloud storage. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Ostrava, Czech Republic, 17–20 September 2018; pp. 1–6.
- Uddin, M.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Pesic, S.; Ellahham, S. Blockchain for drug traceability: Architectures and open challenges. Health Inform. J. 2021, 27, 14604582211011228.
- Fdhila, W.; Stifter, N.; Judmayer, A. Challenges and Opportunities of Blockchain for Auditable Processes in the Healthcare Sector. In International Conference on Business Process Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 68–83.
- Sun, S.; Du, R.; Chen, S.; Li, W. Blockchain-based IoT access control system: Towards security, lightweight, and cross-domain. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36868–36878.
More
