Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Rui Zhang and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
Enantioselective gold catalysis has flourished due to its distinct performance. In particular, a series of valuable chiral ligands have been identified, including aryl phosphine ligands bearing the proximal chiral sulfinamide motif, phosphoramidite and phosphonite ligands, phosphine ligands comprising the ferrocene scaffold, bifunctional phosphine ligands, biphosphine ligands, chiral counterion-based ligands derived from chiral phosphoric acids and chiral carbene ligands for gold(I) catalysis, along with unique ligand frameworks for cyclometalated gold(III) catalysis.
- chiral ligand
- asymmetric
- gold catalysis
- π-acidic activation
1. Introduction
Catalysis is an advanced technology in both the chemical industry and academic research [1][2][3][1,2,3]. Transition-metal catalyzed organic transformations have attracted a great deal of attention for the efficient crack and formations of chemical bonds [4][5][6][7][4,5,6,7]; therefore, they have been widely applied in the research and development of drugs, pesticides, fine chemicals and other functional materials [8][9][10][8,9,10]. Compared to other transition metals, the d10 electron configuration of gold(I) results in superior π affinity for multiple carbon–carbon bonds (Figure 1a) [11][12][13][14][15][11,12,13,14,15]. In addition, the gold center adopted by linear coordination places the ancillary ligand and substrate in opposite positions (Figure 1b). Thus, the conventional chelating mode of the ligands used in catalytic reactions involving other transition metals could not be employed for the design of ligand-modified gold catalysts. Furthermore, the gold(I)-catalyzed carbophilic addition of nucleophiles to carbon–carbon triple bonds proceeds through outer-sphere activation [16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. These factors make asymmetric modulation in gold(I) catalysis challenging. On the other hand, several gold(III) catalysts have also been reported to be active for such transformations because of their inherent square-planar geometry that promotes the formation of chiral centers.
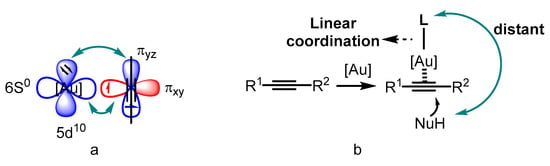
Figure 1.
The superior π affinity mode (
a
) and the linear coordination format (
b
).
The practical atom economy and step economy of enantioselective gold catalysis are attributed to its unique catalytic mode for constructing sets of complex molecules and efficient tandem processes, even when dealing with remote substrates and chiral ligand fragments [25][26][27][28][29][30][25,26,27,28,29,30]. Enantioselective gold catalysis has flourished due to its distinct performance. In particular, a series of valuable chiral ligands have been identified, including aryl phosphine ligands bearing the proximal chiral sulfinamide motif, phosphoramidite and phosphonite ligands, phosphine ligands comprising the ferrocene scaffold, bifunctional phosphine ligands, biphosphine ligands, chiral counterion-based ligands derived from chiral phosphoric acids and chiral carbene ligands for gold(I) catalysis, along with unique ligand frameworks for cyclometalated gold(III) catalysis. Notably, these types of chiral ligands and structural modifications are of crucial significance.
2. Classification of Various Ligands
2.1. Phosphoramidite and Phosphonite Ligands
In the gold(I)-catalyzed [4 + 3] or [4 + 2] cyclization, electron-withdrawing phosphite ligands are believed to fit the excellent activation of the corresponding gold(I) catalysts [31][32][34,35]. To construct better chiral modulation for the challenging asymmetric gold(I) catalysis, phosphoramidite ligands have also been incorporated into the catalytic systems owing to their similar electronic properties with phosphites and π–π interactions with substrates resulting from the attenuated flexibility around the gold center as well as the closer chiral information to the new carbon stereocenters. For the enantioselective intramolecular cycloaddition of allene-tethered 1,3-dienes 1, the bicyclic products 2 and 3 can be furnished smoothly, and phosphoramidite ligand L1-ligated gold(I) catalyst displayed superior chemoselectivity (16:1.2) and enantioselectivity (91% enantiomeric excess (ee)) over the chiral bisphophine (S)-(−)-2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthalene (S-BINAP)-coordinated gold(I) analogue (Scheme 1) [33][36]. The proposed mechanism begins with the activation of an allene through the coordination of a gold complex. This activation leads to a concerted [4 + 3] cycloaddition, resulting in the formation of gold carbene intermediate III. The selectivity between [1][2][1,2]-R migration and ring contraction was demonstrated with density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The calculation results indicate that the ring contraction pathway possesses a lower energy barrier than that of the [1,2]-R migration pathway.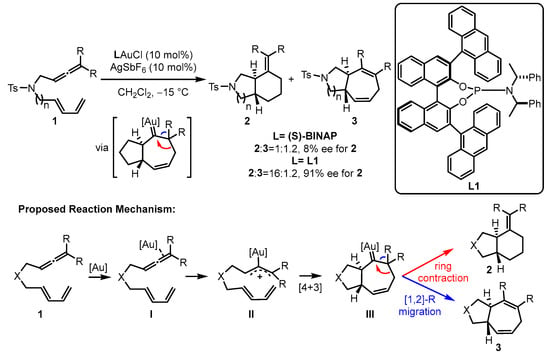
Scheme 1.
The chiral phosphoramidite-tethered gold(I)-catalyzed asymmetric cycloaddition.
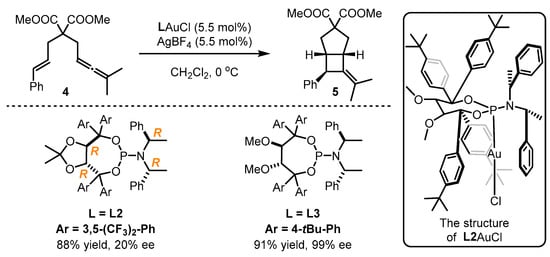
Scheme 2.
The application of TADDOL-containing ligands
L2
and
L3
in asymmetric gold catalysis.
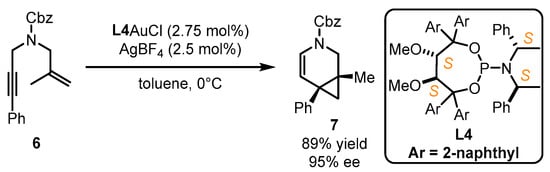
Scheme 3.
The application of TADDOL-containing ligand
L4
in asymmetric gold catalysis.
Scheme 4.
Chiral cationic ancillary phosphonites applied in gold(I) catalysis.
Scheme 5.
Chiral cationic ancillary phosphonites applied in gold(I) catalysis.
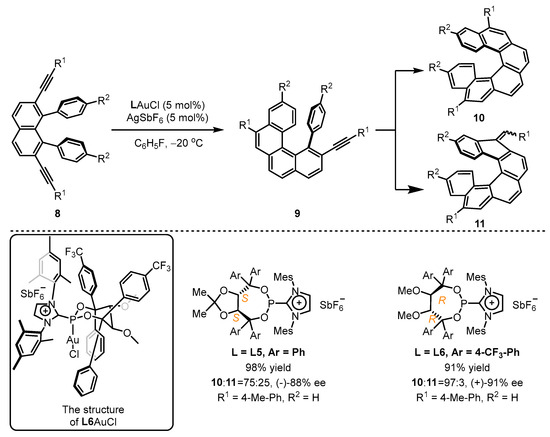
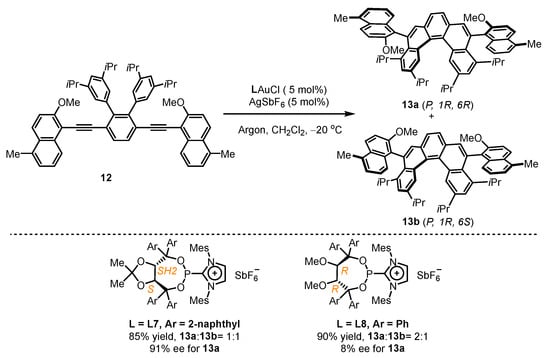
2.2. Aryl Phosphine Ligand with a Proximal Chiral Sulfinamide
Apart from the phosphoramidite and phosphonite ligands mentioned above, aryl phosphine ligands bearing one chiral sulfinamide motif have also been developed. As reported by Zhang and coworkers, the in situ formed monogold cationic catalyst generated from digold chloride [(AuCl)2] always showcased a better catalytic activation ability than the pre-prepared monogold cationic catalyst [39][40][42,43]. Zhang et al. provided an elaborate design of the MingPhos series (including L9 and L10), where the chiral sulfinamide moiety containing adjustable steric groups was located on the ortho-position of the aryl phosphines (Scheme 6) [41][44]. The L9/L10-tethered gold(I) complexes performed good activity for the intermolecular asymmetric cycloaddition of 2-(1-alkynyl)-2-alken-1-one 14 and nitrone 15 with the L10-based gold complex exhibiting higher performance than the L9-containing analogue in terms of enantioselectivity. Moreover, a proposed mechanism was presented.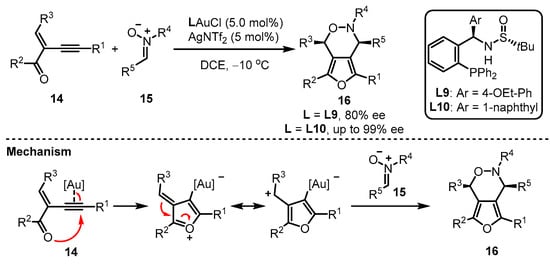
Scheme 6.
Asymmetric synthesis of chiral α-Allyl-α,β-butenolides.
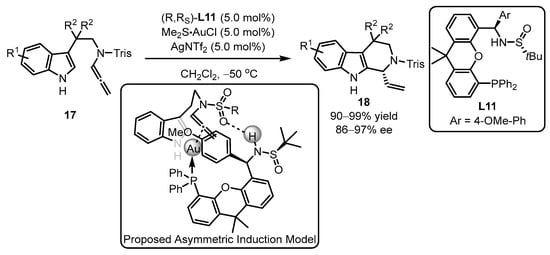
Scheme 7.
PC-Phos ligands ancillary to gold complex for the asymmetric arylation.
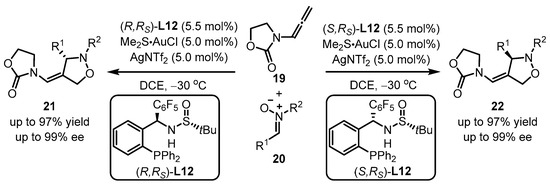
Scheme 8.
MingPhos ligands ancillary to gold complexes for asymmetric arylation.
2.3. Phosphine Ligands Comprising the Ferrocene Scaffold
Phosphine ligands bearing the ferrocene backbone are a typical class of chiral ligands used for enantioselective gold(I) catalysis due to their easy accessibility and possibility to modulate chiral formation. Hayashi and colleagues reported the successful cooperation between chiral bisphosphines with the ferrocene backbone decorated with an amino group and a gold complex, in situ generating an chiral gold species for the asymmetric aldol reaction of aldehyde 23 and isocyanoacetate 24 (Scheme 9) [44][47]. The diastereoselectivity and enantioselectivity depend on the selection of a bulky aldehyde and a suitable ligand. Furthermore, the L13-tethered gold template provided divergent chiral oxazoline derivative 25, while the similar ligand (L14) did not efficiently catalyze the process.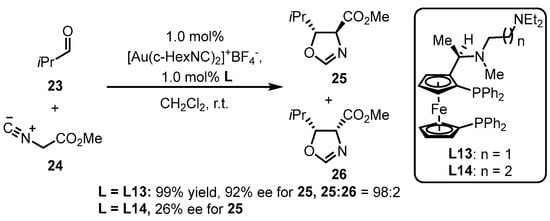
Scheme 9.
Phosphine ligands possessing the ferrocene backbone for asymmetric gold catalysis.
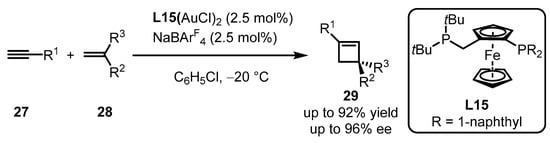
Scheme 10.
Ferrocenyl bisphosphine-ligated gold catalyzed asymmetric [2 + 2] cycloaddition.
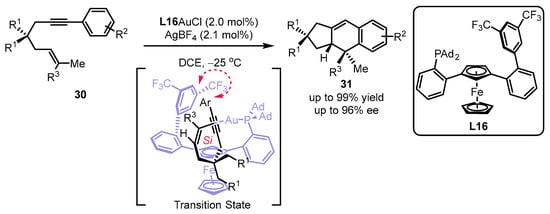
Scheme 11.
Design of planar chiral phosphines for the asymmetric [4 + 2] cyclization.
2.4. Bifunctional Phosphine Ligand
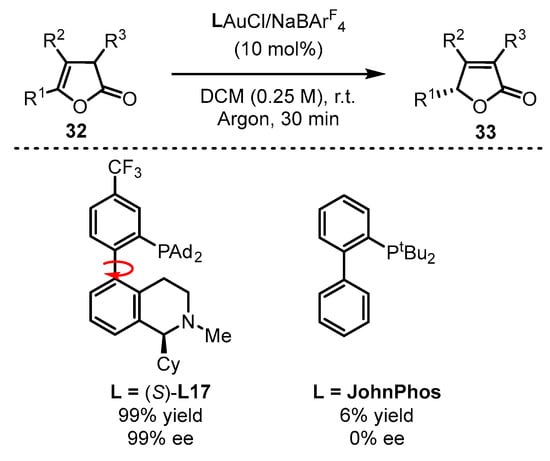
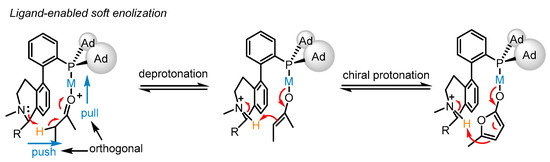
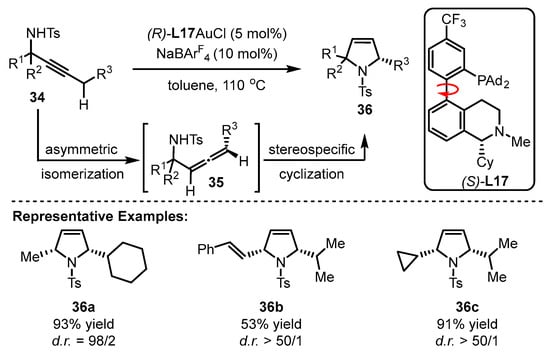
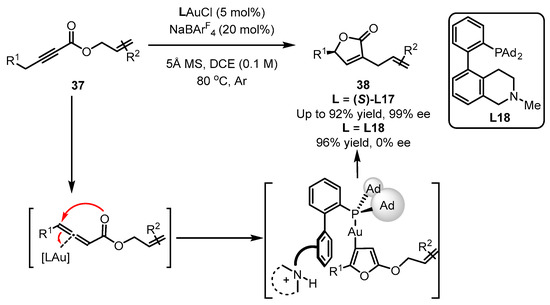
Benefitting from enol chemistry that the α-C−H bond of a carbonyl could be clearly attenuated by the activation from an acid (Lewis acid or protic acid) to the carbonyl group, the Zhang group developed bifunctional phosphine ligands for gold(I)-catalyzed asymmetric reactions [48][50]. In such reactions, a Lewis acid acts as a ‘pull’, and a weak base functions as a ‘push’. The weak base Et3N (pKa in DMSO, 9.0) can be employed to remove α-H of a carbonyl or an imine group (pKa in DMSO ∼16–30) [49][51]. Without the utilization of a strong base, the reactions could accommodate more base-sensitive substances (Scheme 12A) [50][51][52,53]. From the initial design, it is anticipated that the α-H of a C−C triple bond, i.e., a propargylic proton (estimated pKa in DMSO, >30) [52][53][54,55], could be removed by a weak base with the ‘pull’ of a gold(I) catalyst to an alkynyl group (Scheme 12B,C). As a typical example, biphenyl 2-ylphosphines with remote tertiary amino groups for gold(I) catalysis were conceived by Zhang and coworkers (Scheme 13) [50][52]. As expected, the ligated tertiary amino group could play the role of ‘push’ for the removal of the propargylic proton to initiate new allene reactions, conjugated alkene reactions and aldol-type reactions in alkyne chemistry. With the introduction of asymmetric elements into the ligand, chiral products could be effectively achieved. As per the principle, the authors successfully converted racemic β,γ-butenolides 32 into chiral α,β-butenolides 33 promoted by chiral bifunctional phosphine ligand (S-L17)-ligated gold(I) catalysts (Scheme 13) [54][56]. In contrast to the JohnPhos-tethered gold(I) catalyst exhibiting 6% product yield and no ee value, the (S)-L17-tethered gold(I) catalyst showed excellent asymmetric catalysis for the γ-protonation process (99% yield and 99% ee).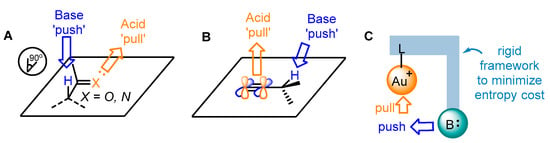
Scheme 12. The idea of enol chemistry (A) and the inspiration for the propargyl chemistry (B) and designed approach for bifunctional phosphine ligands in asymmetric gold catalysis (C).
Scheme 13.
Enantioselective isomerization of β,γ-butenolides to chiral α,β-butenolides.
Scheme 14.
Enantioselective isomerization of β,γ-butenolides to chiral α,β-butenolides.
Scheme 15.
Enantioselective isomerization of β,γ-butenolides to chiral α,β-butenolides.
Scheme 16.
Asymmetric synthesis of chiral α-Allyl-α,β-butenolides.
Scheme 17.
Asymmetric synthesis of chiral α-Allyl-α,β-butenolides.
2.5. Biphosphine Ligands
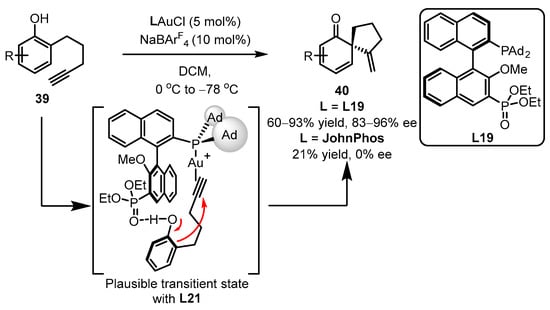
Apart from the above monophosphine ligands, biphosphine ligands have also been developed. Thus, this section intends to present the development of these biphosphine ligands and their applications in gold-catalyzed asymmetric reactions. Although the linear coordination of a ligand with the gold(I) complex generates a single coordination site from the metal center, the asymmetric bisphosphine ligands have been successfully applied to multiple carbon–carbon bond activation reactions. The arguable Au–Au interaction is believed to play a crucial role in modulating chiral transfer due to its subtle tortuosity for the linear coordination way. The Echavarren group first discovered the potential of a bisphosphine ligand (L20) in the gold(I)-catalyzed enantioselective tandem cycloisomerization and hydromethoxylation process (Scheme 18) [59][61]. Remarkably, the addition of a catalytic amount of a silver salt suggested that the monocationic Au species promoted the transformation. The reaction occurred as the electron-rich alkenyl part acted as a nucleophile to attack the chiral gold-activated alkynyl group. After the gold complex feedbacked one pair of electrons to the double bond, the alkenyl group combined with an unstable cation for the formation of a gold carbene species. Following the ring-opening and protodeauration process, the chiral alkoxylation product could be given.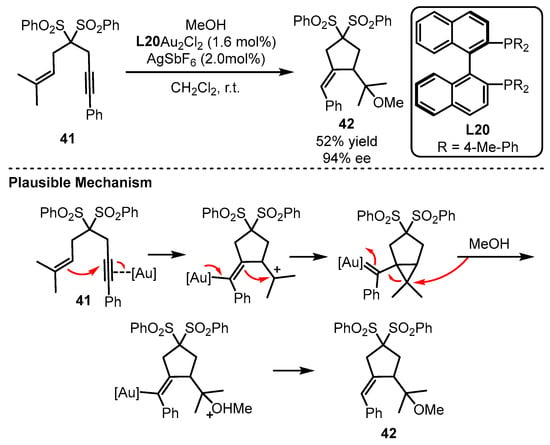
Scheme 18.
Enantioselective bisphosphine-tethered gold(I) catalysis.
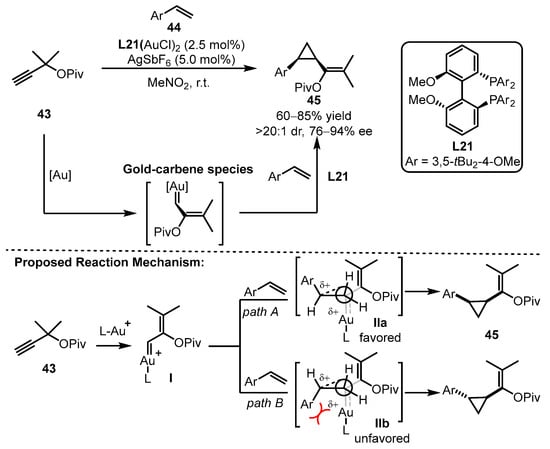
Scheme 19.
Asymmetric cyclopropanation of alkynes and aryl alkenes.
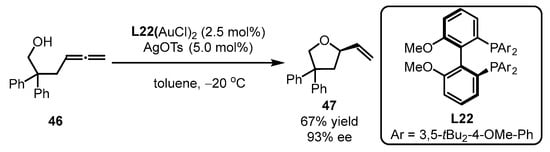
Scheme 20.
Gold(I)-catalyzed asymmetric alkoxylation of allenes.
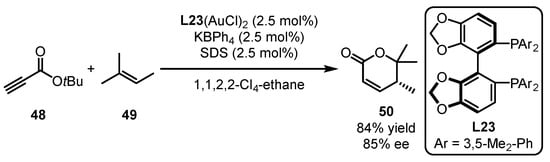
Scheme 21.
Dimeric gold catalyst-promoted enantioselective [4 + 2] cycloaddition.
2.6. Chiral Counterions Derived from Chiral Phosphoric Acids
The phosphine-containing organic ligands are summarized from Scetion 2.1.Section 2.1 to Section 2.5.. In this section, a unique type of phosphine ligand, referred to as chiral phosphoric acid-derived chiral counterion ligands, is discussed. The development of asymmetric gold catalysis via chiral ion pairs between cationic gold catalysts and chiral counterions is a successful strategy to confer to the enantioselectivity of gold-catalyzed reactions [63][65]. The Toste group explored the counterion strategy in gold catalysis for the intramolecular asymmetric hydroalkoxylation of allenes [64][66]. To achieve high enantioselectivity in the reactions, the “matched” effect of a phosphine-associated gold catalyst with a chiral silver salt should be considered (Scheme 22). Specifically, the cooperation of bis(chlorogold) bis(diphenylphosphino)methane [dppm(AuCl)2] with Ag-L24 prompted the asymmetric cyclization of allenol 51 to tetrahydrofuran 52 with excellent yield and enantioselectivity. On the contrary, inferior results were provided when Ph3PAuCl was utilized instead of dppm(AuCl)2.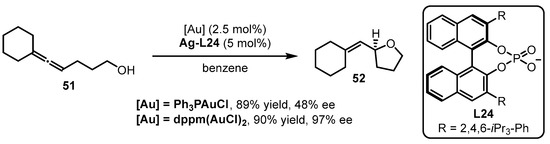
Scheme 22.
Chiral counterion-induced asymmetric cyclization of allenol
51
.
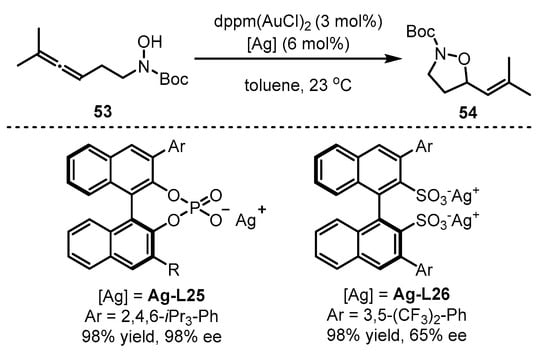
Scheme 23.
Gold(I)-catalyzed asymmetric formation of vinyl isoxazolidines.
2.7. Chiral Carbene Ligand
Apart from the above phosphine-containing organic ligands, chiral carbene ligands have also been developed for asymmetric gold catalysis. As the distinct performance of gold(I)-carbene complexes in terms of chemoselectivity and regioselectivity in carbophilic activation, chiral carbene ligand-involving gold(I) catalysts were also elaborately designed to conduct a set of asymmetric transformations [66][68]. Considering the repertoire of an electron-rich group in offering the stability of an allene intermediate, Toste and coworkers conceived that, compared to phosphite-tethered gold complexes, the more electron-donating carbene-coordinated gold(I) catalysts could facilitate 6-endo-trig cyclization of propargyl ester 55 in a more efficient manner (Scheme 24) [67][69]. Undoubtedly, incorporation of different substituents into the ligand skeleton is crucial for the effective enantioselectivity control. As observed, ligand L28 bearing a 4-CF3 group was identified as an excellent auxiliary for achieving 85% yield and 91% ee, while the unsubstituted ligand (L27) triggered an inferior result.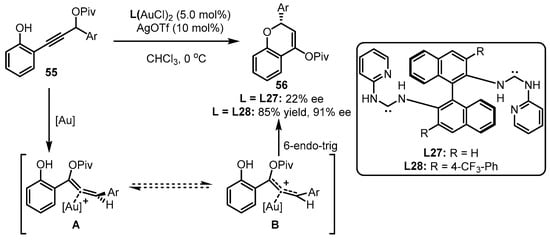
Scheme 24.
Asymmetric [3 + 3] reaction catalyzed by (acyclic diaminocarbene)-gold(I) complexes.
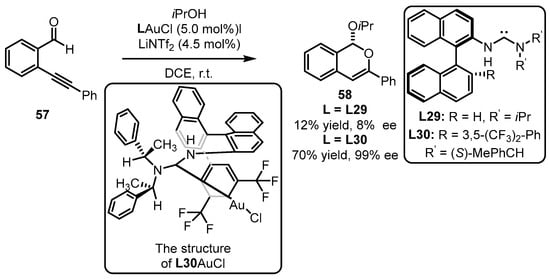
Scheme 25.
Tandem cyclization reaction catalyzed by (acyclic diaminocarbene)gold(I) complexes.
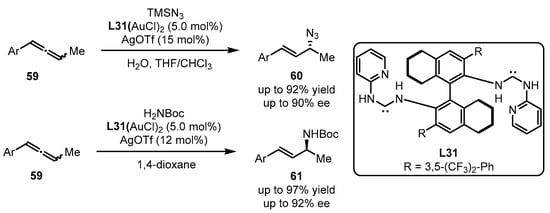
Scheme 26.
Chiral carbene-tethered gold catalyzed nucleophilic addition of allenes.
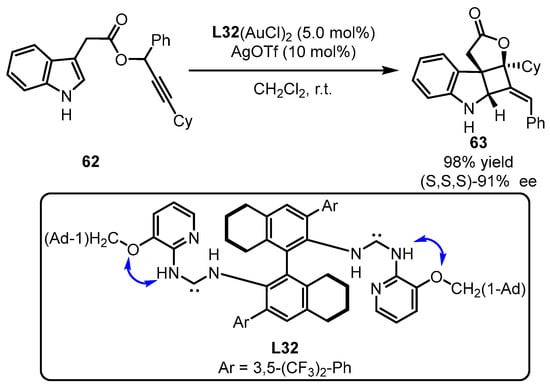
Scheme 27.
(Acyclic diaminocarbene)gold(I) complexes for challenging chirality formation.
2.8. Cyclometalated X-Y (X = C, O; Y = C, O) Ligand Frameworks
Enantioselective reactions with gold(I) catalysis have been extensively developed [71][72][73][73,74,75], as also illustrated in all the above examples. However, the linear geometry of gold(I) catalysts restricts its ability to modulate chirality formation (Scheme 28). On the other hand, the square-planar geometry of gold(III) catalysts introducing cyclometalated ligand frameworks is expected to avoid the restriction owing to the potential mediation from lithered chiral ligand proximal to the reactive center. However, the unstable risk of gold(III) complex 64 for reduction to gold(I) or unreactive state of traditional gold(III) catalyst 65 impeded its application in enantioenriched catalysis [74][75][76][76,77,78].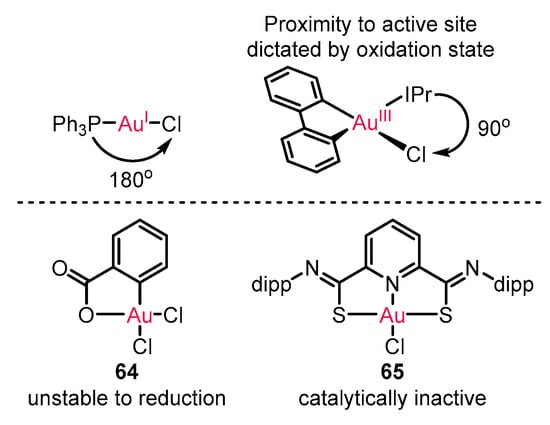
Scheme 28.
The innate difference of gold(I) and gold(III) catalytic mode.
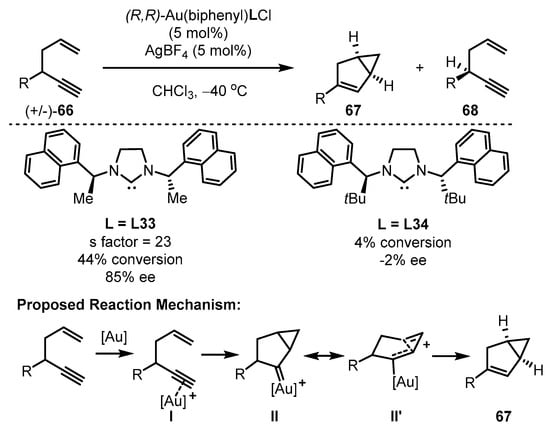
Scheme 29.
The chiral gold(III)-catalyzed asymmetric cycloisomerization of enynes.
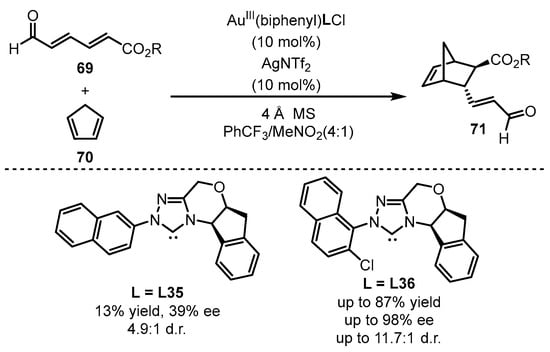
Scheme 30.
The chiral gold(III)-catalyzed enantioselective Diels–Alder reaction.
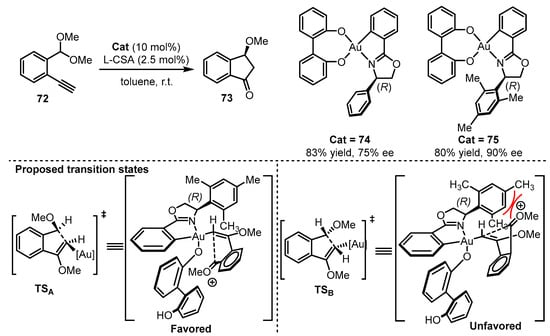
Scheme 31.
Asymmetric O,O-chelated cyclometalated oxazoline gold(III) catalysis.
