Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Yuan Gong and Version 2 by Wendy Huang.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) represents a significant public health concern in modern society. Metabolic syndrome (MetS), which includes diabetes mellitus (DM) and obesity, represents a modifiable risk factor for AD. MetS and AD are interconnected through various mechanisms, such as mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, insulin resistance (IR), vascular impairment, inflammation, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Therefore, it is necessary to seek a multi-targeted and safer approach to intervention. Thus, 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10-HDA), a unique hydroxy fatty acid in royal jelly, has shown promising anti-neuroinflammatory, blood–brain barrier (BBB)-preserving, and neurogenesis-promoting properties.
- Alzheimer’s disease
- diabetes mellitus
- obesity
- 10-HDA
- molecular docking
- MetS
- royal jelly
1. Introduction
DM is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia that results from disturbed insulin secretion or insulin dysfunction, or both [1]. Reportedly, in 2018, a total of 440 million people worldwide were living with DM [2], and China and India were the countries with the highest rates [3]. It is estimated that this number will see a worldwide increase of 202 million by 2040 [3]. According to a nationwide population-based study, individuals recently diagnosed with DM have an increased risk of developing AD after an 11-year follow-up period [4]. Furthermore, an epidemiological study suggests that type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a critical independent risk factor for neuropsychological symptoms, inducing anxiety, depression, and appetite disturbance in early AD [5]. The strong association between AD and DM has led many researchers to refer to AD as “type 3 DM” [6].
Moreover, obesity is a risk factor of T2DM. Obesity is a global public health problem, the incidence of which has tripled since 1975 [7]. It is a health condition defined as excess body fat that endangers one’s health. In clinical practice, it is evaluated by the body mass index (BMI), calculated as weight (kg)/height2(m2), and is diagnosed at a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 according to the WHO [8].
AD is the primary cause of dementia, which is characterized by progressive memory loss and cognitive dysfunction. According to global data, it is estimated that 50 million people were living with dementia in 2018, and this is suggested to triple by 2050 [9]. According to current knowledge, AD is a neuron-jeopardizing disease, which brings about a gradual loss of capacity to carry out everyday functions such as walking and gripping. Furthermore, it can lead to coma and eventually, death [10]. All the above pose a considerable challenge to society. In addition, the risk of developing AD increases from 50% to 75% in people with DM [11], especially T2DM [12]. Moreover, the likelihood of a person having AD increases when their BMI is higher than average, especially if they have both obesity and poorly controlled DM [13][14][13,14]. Notably, T2DM and obesity originate from an unhealthy diet and lifestyle, which means that intervention through personal, clinical, and public health means is practical.
Through several interacting mechanisms, obesity and T2DM progressively cause tissue damage, particularly in the hippocampus, ultimately resulting in a decline in overall health [15][16][17][15,16,17]. Among the mechanisms linking MetS to AD, low-grade chronic inflammation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of AD. Importantly, low-grade inflammation disarms the BBB, making brain cells vulnerable to external stimuli [18][19][18,19].
Royal jelly (RJ), a white or yellowish gelatinous substance, is produced by the hypopharynx and mandibular salivary glands of honeybees [20]. It has a long history of use in traditional Chinese medicine due to its various benefits, including its antioxidative, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, neurotrophic, and MetS-preventing activities [21][22][21,22]. Regarded as a marker of RJ quality, 10-HDA is a distinctive, unsaturated fatty acid that is present in RJ [23], and it may be involved in the biological activities of RJ, such as antitumor and antimicrobial activities [24][25][24,25]. Moreover, recent research has found that 10-HDA exhibits various advantageous characteristics, such as anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antimicrobial, antitumor, antioxidative, and vessel-preserving properties [26]. These properties make 10-HDA a potentially valuable nutrient for addressing AD, particularly AD associated with MetS.
2. Anti-Neurodegeneration and Immunomodulation
The process of pyroptosis, a form of cell death associated with inflammation, has been implicated in the development of AD and MetS. The NLRP3 inflammasome is responsible for initiating pyroptosis. A study has shown that 10-HDA can enhance the function of the colonic barrier by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated apoptotic pathway [27][138]. Additionally, You et al. discovered that 10-HDA can alleviate neuroinflammation in microglia BV2 cells through the FOXO1-mediated autophagy pathway, indicating that it may be a promising agent for various neuroinflammation-associated diseases [28][139]. Damage to the BBB is considered a crucial factor in the pathogenesis of AD. You et al. demonstrated that 10-HDA can inhibit the degradation of tight-junction proteins, reduce BBB permeability, and protect the integrity of the BBB through the AMPK/PI3K/AKT pathway [29][140]. Furthermore, recent research has suggested that 10-HDA possesses immunomodulatory effects as it binds to pattern recognition receptors. One of these receptors is TLR4, which serves as a sensor for damage-associated molecular patterns [30][141]. Farshid et al. found that 10-HDA acts as an antagonist to inhibit immune cell activation induced by TLR4 [31][142]. These findings underscore the immunomodulatory properties of 10-HDA and its potential role in regulating immune responses.3. Antitumor
Zafer et al. found that 10-HDA elevates the expression of caspase 3, Bax, and miR-34a. Then, it increases necrotic and apoptotic human hepatoma cells [32][143]. Albalawi et al. found that 10-HDA, in combination with cyclophosphamide, showed antitumor effects against Ehrlich solid tumors [33][144]. Lin et al. suggested that 10-HDA induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells through the MAPK, STAT3, NF-κB, and TGF-β1 signaling pathways [34][145]. These studies highlight the potential antitumor properties of 10-HDA and its ability to induce cell death and inhibit cancer cell growth. Properties of 10-HDA are shown in Table 1.Table 1.
Mechanisms related to 10-HDA properties.
| Related Mechanisms | Results | Model | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apoptosis | Inhibits apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. | Human hepatoma cell line. | [32][143] |
| Inflammation Antioxidation |
Hypoglycemic effects on diabetic mice, through the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. | Diabetic C57BL/6J mice. | [35][146] |
) Details of the binding site be-tween PPAR-γ and 10-HDA. Here, 10-HDA is represented as orange sticks, while PPAR-γ is represented as a grey surface. And amino acid residues are represented as blue sticks, while hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed yellow sticks. Four hydrogen bonds are shown in the image, and 10-HDA is rooted in the binding pocket of PPAR-γ.
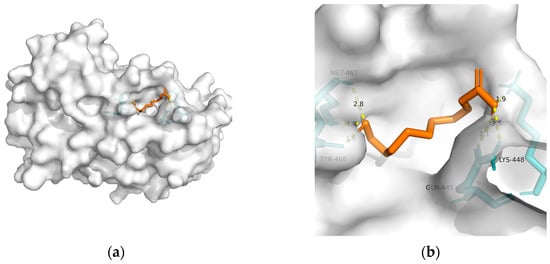
Figure 3. Docking results between 10-HDA and PPAR-α: (a) A gross view of the optimal conformation between PPAR-α and 10-HDA after molecular docking. (b) Details of the binding site be-tween PPAR-α and 10-HDA. Here, 10-HDA is represented as orange sticks, while PPAR-α is represented as a grey surface. And amino acid residues are represented as blue sticks, while hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed yellow sticks. Six hydrogen bonds are shown in the image, and 10-HDA is rooted in the binding pocket of PPAR-α.
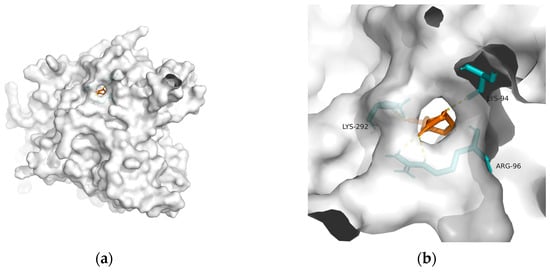
Figure 4. Docking results between 10-HDA and GSK-3: (a) A gross view of the optimal conformation between GSK-3 and 10-HDA after molecular docking. (b) Details of the binding site between GSK-3 and 10-HDA. Here, 10-HDA is represented as orange sticks, while GSK-3 is represented as a grey surface. And amino acid residues are represented as blue sticks, while hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed yellow sticks. Four hydrogen bonds are shown in the image, and 10-HDA is rooted in the binding pocket of GSK-3.
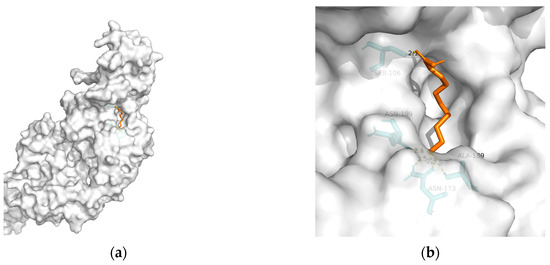
Figure 5. Docking results between 10-HDA and TREM2: (a) A gross view of the optimal conformation between TREM2 and 10-HDA after molecular docking. (b) Details of the binding site be-tween TREM2 and 10-HDA. Here, 10-HDA is represented as orange sticks, while TREM2 is represented as a grey surface. And amino acid residues are represented as blue sticks, while hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed yellow sticks. Five hydrogen bonds are shown in the image, and 10-HDA is rooted in the binding pocket of TREM2.
Table 2.
The results of molecular docking (optimal conformation).
| Macromolecule | PDB | DeltaG (KJ/mol) | RMSD (Å) | Binding Site (Number) |
Hydrogen Bonds | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1R | 3c5t | −24.27 | 2.193 | Ala28, Ser31, Thr35, and Pro90 | 4 | ||||
| PPAR-gamma | 2q59 | −20.59 | 0.956 | Asn375, Lys230, and Asp381(2) | 4 | ||||
| Inflammation | Blocks TLR4. | HEK293T cells with high TLR4 expression. | [31][142] | ||||||
| PPAR-alpha | 3vi8 | −22.47 | 1.598 | Tyr468(2), Met467, Gln445(2), and Lys448 | 6 | Inflammation Antioxidation |
Increases serum concentrations of immunoglobulin G at d 21, as well as IgM and interleukin-10 at d 42, while decreasing the levels of tumor necrosis factor-α. | Broiler Chickens. | [36] |
| GSK-3 | [ | 147 | ] | ||||||
| 1q5k | −23.81 | 1.556 | Lys | 292, Lys94, and Arg96 | 4 | Inflammation Antioxidation |
Inhibits inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis induced by LPS/ATP. | Male C57BL/6 mice. | [27] |
| TREM2 | [ | 138 | ] | ||||||
| 6yye | −12.38 | 1.212 | Ser | 106, Asn109, Asn173(2), and Ala189 | 5 | Antioxidation Energy metabolism Vascular function |
Maintains vascular health via scavenging •OH. | Vascular smooth-muscle cells. | [37][148] |
| Inflammation | Attenuates the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. | Macrophages (RAW264.7 cells) | [38][149] | ||||||
| Antimicrobial | Decreases biofilm viability and effectively eradicates mature biofilms. | Staphylococcus aureus. | [39][150] | ||||||
| Antitumor | Decreases tumor volume, tumor markers (AFP and CEA), and TNF-α level. | Female Swiss albino mice. | [33][144] | ||||||
| Immunomodulation | Blocks TLR4. | Dendritic cells | [30][141] | ||||||
| Antimicrobial Antioxidation |
Shows antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. | Statens Seruminstitut Rabbit Cornea cell culture line. | [40][151] | ||||||
| Apoptosis Antioxidation |
Induces apoptosis through ROS-mediated MAPK, STAT3, NF-κB, and TGF-β1 signaling pathways. | A549 human lung cancer cells. | [34][145] | ||||||
| Autophagy | Protects against neuroinflammation through FOXO1-mediated activation of autophagy. | Microglial BV-2 cells (LPS-induced). | [28][139] | ||||||
| Immunomodulation | Improves immunity in the thymus and spleen | BALB/c mice. | [41][152] | ||||||
| Vascular function | Improves blood–brain barrier dysfunction by activating the AMPK/PI3K/AKT pathway. | C57BL/6 mice (LPS-stimulated). | [29][140] | ||||||
| Insulin signaling Anti-adipogenesis |
Inhibits cAMP/PKA pathway and p-Akt- and MAPK-dependent insulin signaling pathway. | 3 T3-L1 adipocyte cell line. | [42][153] | ||||||
| Inflammation Antimicrobial |
Modulates interleukin-8, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. | WiDr cell. | [43][154] | ||||||
| Melanogenesis inhibitor | Inhibits the activity of tyrosinase and the expression of tyrosinase-related protein 1, TRP-2, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. | B16F1 melanoma cells. | [44][155] | ||||||
| Antioxidation | Decreases tumorigenic potential of various tumor cells. | Human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. | [45][156] | ||||||
| Insulin-like signaling | Extends lifespan through dietary restriction signaling. | Caenorhabditis elegans. | [46][157] | ||||||
| Antioxidation | Reduces the UVA-induced activation of the JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. | Human dermal fibroblasts. | [47][158] | ||||||
| Inflammation | Increases procollagen type I and TGF-β1 production. | Human dermal fibroblasts. | [48][159] |
4. Metabolic Adjusting Properties
As mentioned previously, IR plays a critical role in MetS-related AD. Hu et al. found that 10-HDA increases insulin sensitivity by upregulating the PI3K/Akt pathway in the liver [35][146]. In addition to adjusting glucose metabolism, Fan et al. found that 10-HDA may protect •OH-damaged vascular smooth-muscle cells by adjusting energy metabolism and protein metabolism [37][148]. Considering the above, T2DM and obesity are linked to AD through a spectrum of mechanisms, whereas no metabolic adjusting targets have been studied. Herein, several macromolecules that might be targets for MetS-related AD intervention are screened. Then, molecular docking between these macromolecules and 10-HDA is performed. The results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5.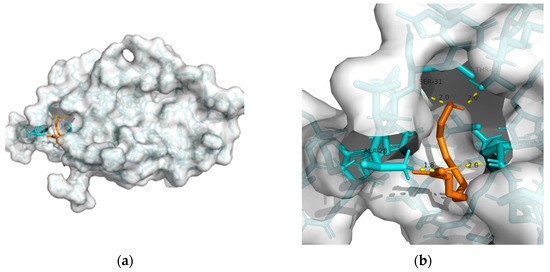
Figure 1. Docking results between 10-HDA and GLP-1R: (a) A gross view of the optimal conformation between GLP-1R and 10-HDA after molecular docking. (b) Details of the binding site be-tween GLP-1R and 10-HDA. Here, 10-HDA is represented as orange sticks, while GLP-1R is represented as a grey surface. And amino acid residues are represented as blue sticks, while hydrogen bonds are represented as dashed yellow sticks. Four hydrogen bonds are shown in the image, and 10-HDA is rooted in the binding pocket of GLP-1R.
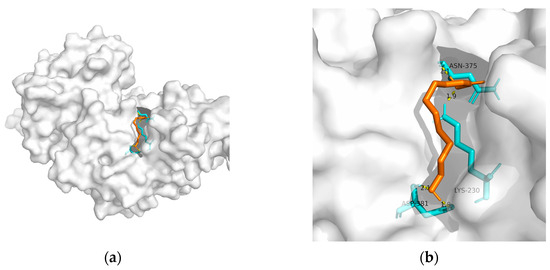
Figure 2. Docking results between 10-HDA and PPAR-γ: (a) A gross view of the optimal conformation between PPAR-γ and 10-HDA after molecular docking. (b
GLP-1 is an insulinotropic incretin hormone that plays a role in inhibiting beta cell death. It is also important to understand that GLP-1 mimetics can cross the BBB. Overall, this suggests that the GLP-1 pathway overlaps with the insulin pathway, and it could compensate for the DM, obesity, or AD damage to the insulin pathway. A review also suggests that GLP-1 serves as an ameliorator of ER stress, IR, CNS inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, etc., which sheds light on AD intervention [49][160]. A GLP-1R agonist, liraglutide, has been approved for obesity treatment [50][161]. Furthermore, GLP-1R agonists are currently used to treat T2DM [51][162].
PPARs are a family of type II nuclear receptors and transcription factors, which include PPAR-α, PPAR-δ, and PPAR-γ. They have been found to be involved in metabolic syndromes such as DM and obesity [52][163]. PPAR-γ is considered a general sensor for nutrients and lipids, residing in the nucleus, and playing a role in mediating responses to nutrients and hormones. It is also implicated in metabolic syndrome [53][164]. Lin et al. found that Aβ-induced ER stress can be alleviated through PPAR-γ signaling [54][165]. PPAR-α is another nuclear receptor belonging to PPARs. Many agonists, such as Gemfibrozil, are synthesized or found to tackle AD in clinical trials [55][166]. In the hippocampus, according to Avik Roy et al., PPAR-α resides in CA1, CA2, CA3, and the dentate gyrus in the brains of mice and monkeys, and the absence of PPAR-α in both wild-type mice and hippocampal neurons leads to an insufficient calcium influx and reduced hippocampal plasticity-related molecules, such as GluR1 and NR2A [56][167]. Moreover, PPAR-α participates in energy metabolism and fatty acid regulation in mitochondria. Furthermore, PPAR-α also plays a role in oxidative stress [57][168].
There are two isoenzymes in the GSK-3 family, called GSK-alpha and GSK-beta. GSK-beta, most importantly, acts as a blood glucose regulator in DM. It is also one of the vital factors that leads to IR and insulin deficiency [58][169]. Moreover, it is reported that GSK-3 plays an important role in energy metabolism and apoptosis. It is known as a negative regulator of inflammation in microglial cells, macrophages, and dendrite cells, and is also involved in osteoclast development. Furthermore, Min Park et al. suggested that TREM2 promotes IR and facilitates diet-induced obesity, which makes TREM2 a possible target in treating obesity and DM [59][170]. Zhang et al. used a DM rat model treated with a combination of HFD and a low dose of STZ. They found that TREM2 negatively regulates the p38 MAPK-mediated inflammation response and neuronal cell death in the hippocampus and cortex in cognitively impaired DM rats [60][171].
