Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by LIU JIAYUE and Version 2 by Peter Tang.
Dried salted fish is a traditional dry-cured fish that is sprinkled with salt before the curing process. With a unique flavor as well as diverse varieties, dry-cured fish is popular among consumers worldwide. The presence of various microbial communities during the curing process leads to numerous metabolic reactions, especially lipid oxidation and protein degradation, which influence the formation of flavor substances.
- dry-cured fish
- microbial community
- flavor formation mechanism of dried salted fish
- volatile flavor substances
- endogenous enzymes
1. Introduction
Dry-cured fish is a traditional processed fish product. Dry salting involves the direct application of salt to fresh fish meat; the fish is dehydrated under the high osmotic pressure of salt, which dissolves into salt water and gradually seeps into the raw materials. Dry curing was originally used for the improved storage and preservation of fresh fish but is now popular among consumers because of the use of solid-state fermentation, which improves the flavor and nutritional value of the products. The unique flavor of salted and dried fish is mainly produced by the microbial metabolism of carbohydrates, the interaction of endogenous proteases, and the decomposition of fat. These salted and dried fish products are mostly regional.
The basic phases of dry salted fish preparation (Figure 1) are raw material selection (the descaling and gutting of fresh fish) and washing them in freshwater. Then, the fish are treated in a salt brine for hours and are dried for days. Finally, the dry-cured fish is packaged and ready for consumption. The principal steps influencing the flavor composition are drying and curing [1].

Figure 1.
Process flow diagram of dry-cured fish.
For a long time, traditional dried salted and dried fish mainly used natural fermentation, which is restricted by the natural external conditions. For instance, unstable weather makes it more difficult to maintain a consistent temperature and humidity level. This process can result in poor food safety and has difficulty meeting the huge market demand. To increase the production of dried fish and to satisfy consumers’ new demands for product taste and quality, traditional salted and dried fish products must undergo industrialization development [2]. Fresh fish are rich in protein, low in fat, and nutritious. The flavor of dried salted fish products is also vital for better edibility. Research has shown that the unique flavor of dried salted fish is created by volatile flavor precursors, which are mainly free fatty acids produced by lipolysis and free amino groups produced by protein hydrolysis [3][4][3,4]; biochemical reactions involving endogenous enzymes; and a range of microorganisms.
The main aroma substances in dried salted fish products include aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, and other small molecular flavor substances, and most of the aldehydes are derived from the oxidation and decomposition of fatty acids [5]. Lipase hydrolyzes lipids to generate flavor precursors like free fatty acids, which are then oxidized to form volatile taste molecules. The endogenous lipases in dried salted fish are mainly divided into lipohydrolase and lipoxygenase, which are closely related to the degradation and oxidation of fat and the formation of volatile flavor substances. The effects of lipid oxidation and microbial metabolism promote the formation of a unique salty flavor in dried salted fish products. The impacts of microorganisms and enzymes on flavor were summarized by combining the metabolic process with the dominating strains in the curing process of dried salted fish at home and abroad. From the perspectives of lipid hydrolysis, oxidation, and flavor formation, the relative roles of microorganisms and endogenous enzymes in lipid and flavor changes were investigated. For instance, 3-methylbutyral and phenylacetaldehyde were produced from amino acid degradation, which was related to microbial activities [6].
2. Formation Pathway of Flavor Substances Derived from Lipid Oxidization or Protein Hydrolysis and Strecker Degradation in Dried Salted Fish
Protein degradation, lipid hydrolysis, and fat oxidation are crucial to the formation of the unique flavor of salted and dried fish, and endogenous and microbial enzymes play an important role [7][8][7,8]. The relative roles of microbial flora and endogenous enzymes in lipid and protein degradation and flavor formation in salted and dried fish products have been studied. Compared with microbial flora, fish lipase plays a major role in lipid hydrolysis, whereas microorganisms play a dominant role in lipid oxidation and flavor formation [9][10][9,10]. Microorganisms play a major role in protein degradation and amino acid metabolism, which is a key step in the formation of protein-derived flavor substances. The typical components detected in salted and dried fish can be divided into nine categories: aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, esters, alkanes, alkenes, aromatic compounds, amines, and other volatile substances [11]. Common flavor substances in salted and dried fish include aldehydes (e.g., hexyl aldehyde, nonal, octyl aldehyde, 3-methyl-butyral, and phenylacetaldehyde), ketones (e.g., 6-methyl-5-heptene-2-ketone; 2, 3-heptene-2-ketone; 3-heptene-2-ketone; 2-heptene-ketone; 2-nonone; 3-octyl ketone; 1-octene-3-ol; hexol; and 1-hexanol), esters (e.g., 2-methyl-butyl butyrate, methyl phthalate, ethyl acetate, and 3-methyl-1-butanol propionate), and olefins (e.g., terpenes). Common key flavor substances such as aldehydes usually have a low sensory threshold and a relatively high content in volatile flavor substances and mainly affect the flavor of dried salted fish (Figure 2) [12].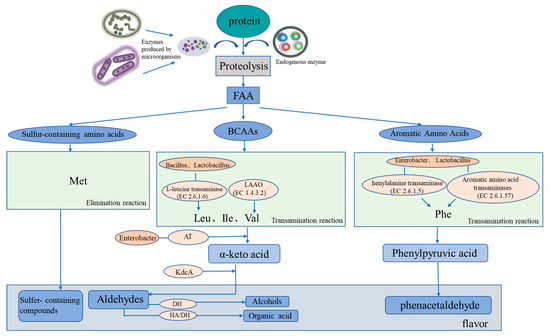
Figure 2. Mechanism of protein-derived flavor formation by microorganisms and endogenous enzymes in dry-cured fish. FAA represents free amino acids, BCAAs represents branched-chain amino acids, LAAO represents L-amino acid oxidase, and AT represents amine transaminase.
3. The Role of Microorganisms
Microbial succession plays an important role in the formation of flavor during fermentation and is closely related to food safety. Currently, changes in the microbial community composition of salted and dried fish can be analyzed through amplicon sequencing and other methods. Changes in microbial communities have been attributed to changes in substrate composition and fermentation parameters, such as the salt concentration and fermentation temperature [13][27]. Proteobacteria and Firmicutes have been shown to dominate in salted and dried fish products [14][28]. Carbohydrate metabolism is reported to be closely related to the presence of Firmicutes, whereas amino acid and lipid metabolism is closely related to the presence of Proteus. Halophilic or halophobic microorganisms are more likely to exist in traditional fermented fish, such as halophilic o-omonas [15][29]. Cytoscape is used for bacterial correlation visualization, with more than four key flavor substances (ROAV ≥ 1), to identify key microorganisms by analyzing the correlation between bacteria and a volatile flavor via the Pearson correlation coefficient [16][30]. The complex microbial community plays an important role in flavor formation in traditional dry-cured fish. Based on the summary of the core microorganisms in the main salted and dried fish products (Figure 2), Halomonas and particularly Staphylococcus have been shown to be the most abundant genera detected in high-salt dried salted fish products. Specifically, to some extent, Staphylococcus species are the dominant microorganisms in these fish products. One study found Staphylococcus, with a relative abundance of 34.46%, to be the dominant bacterial genus [17][31]. Staphylococcus can affect the flavor and quality of dried salted and dried fish. When used as a starter culture, Staphylococcus promotes the rapid formation of flavor and delays the formation of fat oxidation [18][32]. Similar to LAB, Staphylococcus species have lipolytic and proteolytic activities and can slowly utilize carbohydrates and convert them into organic acids and aromatic substances, such as 2, 3-butanedione; acetaldehyde; and acetoin [19][33]. In the curing process of salted and dried fish, several metabolites produced by LAB and yeast are flavor substances. LAB can produce lactic, acetic, and propionic acids and can interact with alcohols and aldehydes in the fermentation process to form more complex flavor compounds and to promote the formation of flavor substances. LAB are used as starter cultures in most salted and dried fish products and degrade lipids and carbohydrates and act as biological preservatives [20][34]. A summary of the microbial community succession in salted and dried fish (Figure 2) shows that Lactobacillus strains (LAB) and Saccharomyces predominate. LAB includes Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Connostrea, Enterococcus, Pediococcus, and Lactococcus among which Lactobacillus occupies a dominant position in the late curing process and is the dominant bacteria group. During salting, the organic acids (such as acetic and lactic acid) produced by LAB act as the main producers of acids and decrease the pH of the dried salted and dried fish system through glycolysis. Similar to Staphylococcus species, some LAB species have lipase and protease activities, contributing to the formation of dried salted and dried fish’s flavor compounds [21][35]. Yeast can not only hydrolyze lipids but also can use fatty acids to synthesize esters and therefore has an important role in the formation of salted and dried fish’s flavor. Fungal communities are often dominated by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Kazachstania exigua, Torulaspora delbrueckii, Wickerhamomyces anomalus, and Pichia kudriavzevii. Demaria and Candida albicans are common yeasts in fermented fish products. They can reproduce in an acidic environment and have a strong perfuming ability [22][23][38,39]. The metabolic activities of numerous bacteria are directly related to the flavor of dried salted fish, and the metabolic pathway of flavor compound breakdown is intimately tied to microbial enzymes. Lipid decomposition and oxidation and protein degradation are considered to be the key processes in the formation of dried salted fish’s flavor [24][25][40,41]. Through fat decomposition and oxidation, fats become flavor compounds or flavor precursors [26][42]. However, the excessive oxidation of fat can also lead to undesirable odors in dried fish products. The interaction of endogenous proteases and microbial enzymes cause protein degradation [27][43]. According to a study on lipid oxidation in black carp during storage, Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria were the most common bacterial phyla, with several being strongly linked to meat rotting [22][38]. During the process of protein degradation, for example, Belleggia et al. demonstrated that flesh-eating Bacillus can decarboxylate amino acids and degrade proline, leucine, and phenylalanine into methylpropanal, 3-methylbutanal, and phenylacetyl, respectively [28][44]. The KEGG (the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database can also be used to investigate the relationship between microorganisms and flavor. Molecular technologies, such as proteomics, macrotranscriptomics, and metagenomes, are combined with a KEGG analysis to construct the relationship networks between microorganisms and flavor compounds. A genomic analysis has been combined with the KEGG metabolic pathway, metabolic pathways and microbial correlations of key enzymes, and microorganisms to analyze the protein-derived flavor substances and fat-derived flavor substances in dried salted and dried fish [29][45]. Salted and dried fish products are rich in protein, and protein degradation and amino acid metabolism are consequently important for flavor formation (Figure 2). Microbial metabolism can form flavor substances in products in two main ways. One is through transamination, whereby flavor precursors are formed from amino acids, such as aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan), branched amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine), and sulfur-containing amino acids (cysteine and methionine) [30][46]. Branched amino acids are first converted into alpha-ketoacids under the action of aminotransferases; these compounds are then converted into aldehydes through the catalytic action of ketoacid decarboxylate (KdcA) and are further converted into alcohols (Alchol) with the aid of dehydrogenase. Aldehydes can also be converted from hydroxyacid dehydrogenase to organic acids [31][47]. The second pathway is the elimination reaction, whereby methionine generates sulfur-containing compounds. The associated microorganisms involved in the reactions include Bacillus with amino acid transaminase, Enterobacter with branched-chain amino acid transaminase and with aromatic amino acid transaminase, Macrococcus with alpha-ketoacid decarboxylase, and Lactococcus with phenylpyruvate decarboxylase. Further studies have demonstrated that the protein flavoring substances are related to specific microorganisms during the processing of salted and dried fish. In salted and dried fish, the fat source is also one of the main sources of flavor (Figure 3). The initial reaction of flavor formation is the hydrolysis of fat into fatty acids by lipase and the release of free fatty acids (FFAs) for second-order fatty acid oxidation or reaction with proteins [32][50]. Lipoxygenases and lipoxygenases in adipose tissue or muscle fibers are the main endogenous lipases in adipose hydrolysis and oxidation. However, microorganisms have been shown to inhibit the activity of endogenous lipase through rapid fermentation to produce acid in the salting process. Therefore, in the process of fat oxidation, lipid lipoxygenase mainly oxidizes lipids, and automatic oxidation involving microorganisms also occurs. Although endogenous lipase is thought to be primarily responsible for lipolysis, the effect of microbial lipase on lipolysis cannot be ignored [33][51]. Microorganisms can also promote the release of FFA to a certain extent, and the relative action of endogenous and microbial enzymes can be studied by adding antibiotics to inhibit microbial growth [34][52].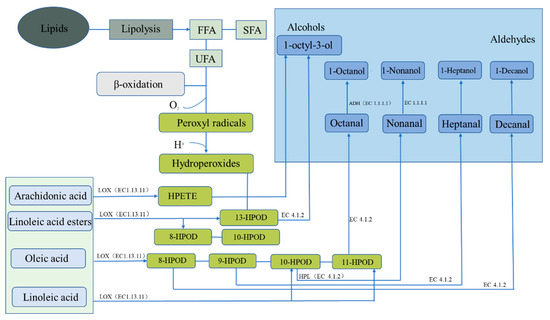
Figure 3. Fat metabolism pathway of endogenous enzymes forming flavor substances in dry-cured fish. ADH represents alcohol dehydrogenases, HPL represents hydroperoxide lyase, and LOX represents lipoxygenase.
