This research assessed alternatives for air Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)AC systems to minimize Sick Building Syndrome and improve air quality while considering international programs/standards. For this purpose, an alternative technology known as desiccant wheels was studied by analyzing their principles and types when the existing selection software for these types of equipment was performed. In addition, energy-efficiency programs worldwide and in the Brazilian context were analyzed while aiming at implementing strategies in which desiccant wheels are appropriate. Finally, some examples of commercial software for desiccant wheels were compared to identify the different tools available in the air conditioning market.
- dehumidification
- desiccant wheels
- air quality
- air conditioning systems
1. Background
2. Types of Desiccant Dehumidification Systems
2.1. Spray Drying Tower
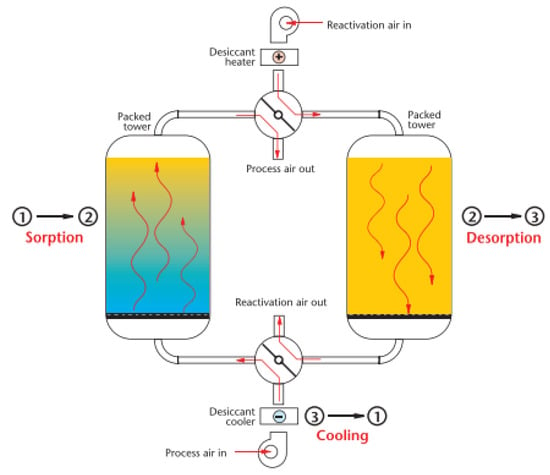
The spray drying tower has two tanks corresponding to the condenser and the regenerator. In this system, the humid air enters the segment of the condenser and passes through a saline fog that will capture the humidity of the air while the dry air is inflated for the process. At the bottom of the condenser tank, the saline solution is pumped to the second tank (regenerator), through which the second flow of high-temperature external air passes, causing the saline solution to lose moisture to the regeneration air. Thus, the hygroscopic material returns to the condenser tank [7][63].2.2. Dual-Tower Desiccant Dryers
2.3. Tray Dryer
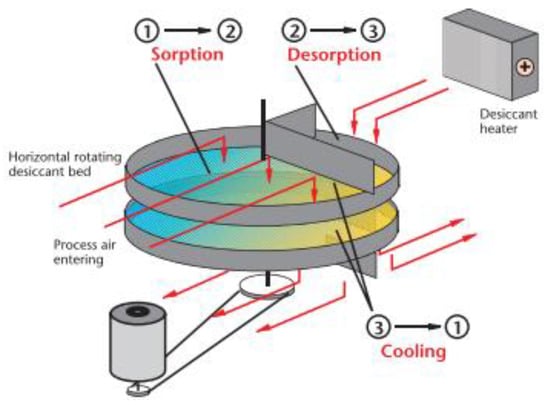
2.4. Multi-Belt Dryer
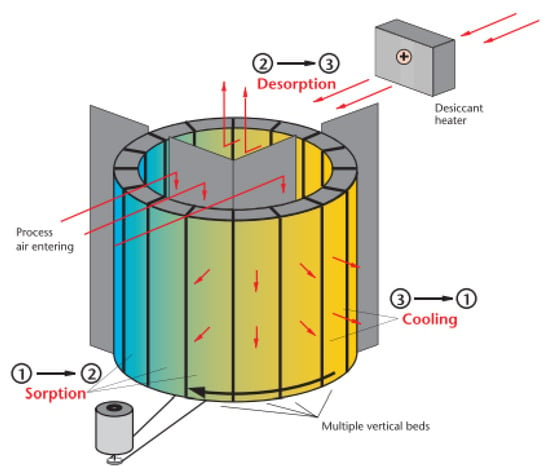
2.5. Desiccant Dehumidifier
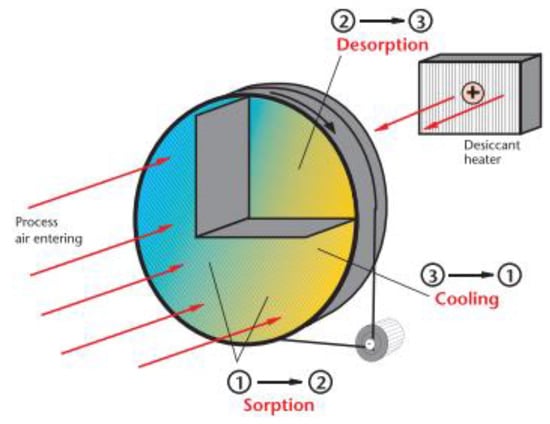
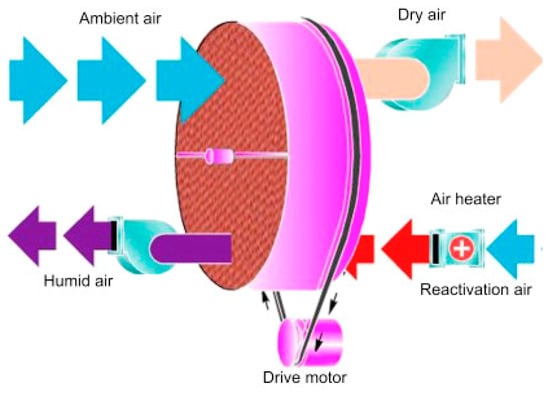
3. Desiccant Dehumidification by Heat-Recovery Wheel
3.1. Enthalpy Wheels
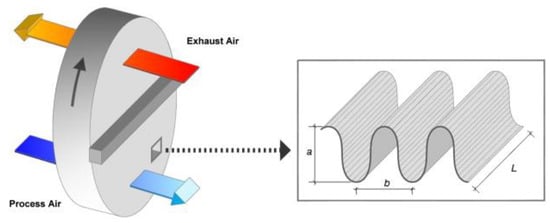
3.2. Cross-Flow Heat Exchangers
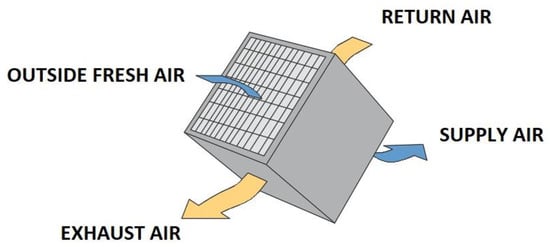
4. Software for Selecting Desiccant Wheels
| Novel Aire | Munters | Rotor Source | Puresci | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input data | ||||
| Process inlet dry bulb temperature | X | X | X | X |
| Absolute humidity entering the process | X | X | X | X |
| Regeneration inlet dry bulb temperature | X | X | X | X |
| Absolute inlet humidity in regeneration | X | X | X | X |
| Dry bulb temperature after heating in regeneration | X | X | X | X |
| Output data | ||||
| Output dry bulb temperature in the process | X | X | X | X |
| Output absolute humidity in the process | X | X | X | X |
| Dry bulb temperature after regeneration output | X | X | X | X |
| Output absolute humidity at regeneration output | X | X | X | X |
| Moisture removal charge | X | X | ||