Knowledge of the agricultural soil microbiota, of the microbial consortia that comprise it, and the promotion of agricultural practices that maintain and encourage them, is a promising way to improve soil quality for sustainable agriculture and to provide food security. Although numerous studies have demonstrated the positive effects of beneficial soil microorganisms on crop yields and quality, the use of microbial consortia in agriculture remains low. Microbial consortia have more properties than an individual microbial inoculum, due to the synergy of the microorganisms that populate them.
- Agricultural Soil Microbiota
- Microbial Consortia
- Sustainable Agriculture
1. Introduction
Currently, conventional agriculture and its practices are presented as a major threat to soil vitality [1], causing the alteration of microbial functional diversity and thus worldwide soil degradation, threatening the food chain and safety [2][3][4][2,3,4]. The intensification of agriculture through excessive and sometimes inappropriate use of chemical pesticides has led to land degradation and environmental pollution in several agroecosystems, which have contaminated water bodies and degraded soils, subsequently leading to the loss of biodiversity by killing beneficial plants, animals, insects, aquatic ecosystem, and other wildlife, and in some cases even poisoning the farm workers [5][6][7][5,6,7]. Another example is intensive agriculture under plastic covers, which profoundly affects soil quality because it greatly alters the water cycle as well as organic carbon (C) and other nutrient contents. On the one hand, natural rainfall is restricted under plastic tunnels, increasing the salinity of the soil in the upper layers. Likewise, soil acidification caused by the excessive application of minerals and nutrients, frequently used under plastic covers, increases the negative effect on soil quality over time, resulting in lower crop yields [8][9][8,9]. In addition, the intensive tillage changes the carbon–nitrogen (C/N) ratio due to loss of soil organic matter through erosion and leaching, causing soil degradation [10]. Nevertheless, there is still great potential in soils, which requires adopting strategies that protect them from harmful agricultural practices [6][11][6,11].
Although there are multiple strategies for addressing sustainable agriculture and feeding people by reducing environmental impacts, it has been widely reported that promoting agricultural practices that increase biodiversity and the composition of soil microorganisms, such as organic or agro-ecological agriculture, represents an important alternative for obtaining good quality food and improvements in environmental, economic, and social aspects [12][13][14][12,13,14].
Increased microbial biodiversity stabilizes the functioning of agro-ecosystems and increases the resilience to climate change [15]. Since ancient times, microorganisms have been present in association with plants and animals, giving them multiple benefits in a dynamic equilibrium, which has been attributed to multiple communication systems. Among them are chemical messages at the rhizosphere level [16][17][18][16,17,18]. These communication systems are fundamental in the agricultural ecosystem, since they regulate all biogeochemical processes in the soil, maintaining its fertility and health. These processes include the decomposition, nutrient cycling, and maintenance of organic matter, control of pathogens, degradation of contaminants, and reduction of greenhouse gases (GHG), which directly affect both crop productivity and the environmental quality [19][20][21][19,20,21].
In order to benefit from the enormous potential of the soil microbiome, it is necessary to know the distribution and composition of microbial communities in different territories and on different time scales, such as seasonal variations [22]. This information also allows predicting the changes that can be generated in a global climate change scenario. In addition, not knowing the effects of the loss of diversity in specific places and times, it can generate a great impact on ecosystem sustainability and therefore on human well-being [23][24][25][23,24,25]. The greater the diversity of microorganisms in the soil, the greater the functionality of that soil [26][27][26,27], which in turn means food with a higher nutraceutical quality proportional to the soil nutrition and health.
Recently, increasing attention has been given to crops rich in nutrients, minerals, antioxidants, or other metabolites, as they represent a higher food quality and reduce the risk of chronic diseases [28][29][30][28,29,30]. In this context, new crop practices have emerged that allow obtaining high yields of biomass with a high concentration of beneficial metabolites. The development of biofertilizers made up with beneficial microbial species has emerged [31], as well as the development of microbial consortia of different soil microorganisms [32].
Thus, it is necessary to understand the processes that determine the composition and abundance of soil microorganism communities in order to obtain their multiple benefits in agricultural systems and indirectly in human health.
2. The Microbial Consortia
Soil microbes are key ecosystem services provider and drive multifunctional processes, encompassing the interaction of different microbial communities, and the interaction of these with the other soil biota components, i.e., the micro- and mesofauna. Within this complex interconnected network, microorganisms are responsible for maintaining the energy fluxes supporting the entire ecosystem, through the recirculation of available resources [33][113]. However other organisms form ecological groups in the same environment and share a high multifunctionality in the ecosystem [22][34][22,114]. Soil microfauna are fundamental to the functionality of the ecosystem and any changes in these key organisms can produce changes at the vegetational, biome, and microbial level [26].
The most relevant groups of microorganisms in the soil are arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth-promoting bacteria. These microorganisms together increase N2 fixation and uptake, solubilize P, convert ammonium (which can be chemically bound to clay particles) into soluble, easily assimilable nitrate, protect from other pathogenic microorganisms, and even remediate contaminated soils [35][36][115,116] (Figure 1).
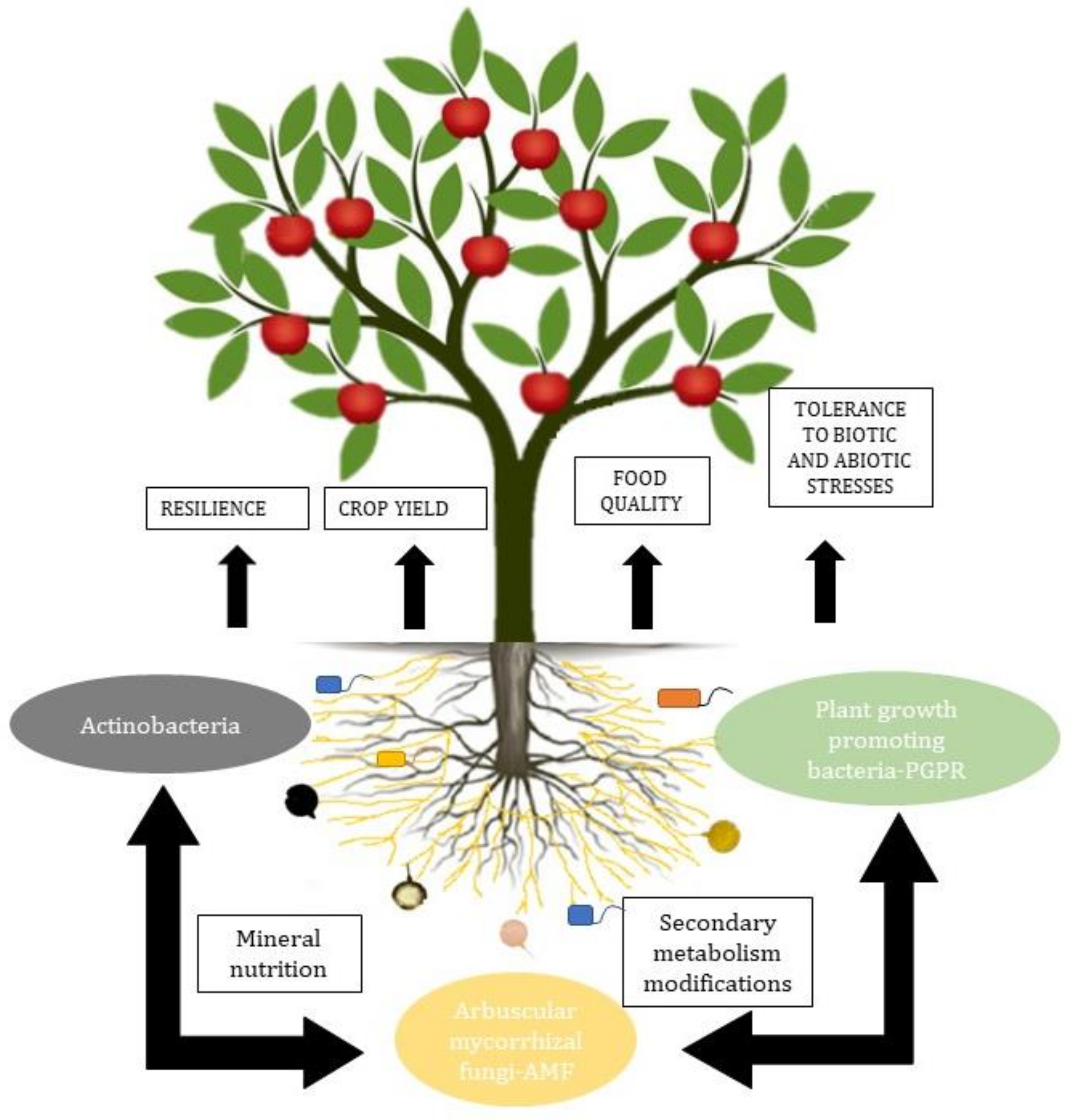
Arbuscular mycorrhizae, besides being related to plants, are also related to the PGPR in the rhizosphere and to the endobacteria, affecting their activity and generating a synergy in functionality [37][38][117,118]. The interactions between AMF and soil bacteria influence the expression of fungal genes. The interactions include the adhesion of bacteria to the surface of fungal spores, conidia, and hyphae, the injection of molecules into the fungal spores, the degradation of the fungal cell wall, and the production of volatile substances [39][119].
The consortia (fungi and bacteria) have multiple applications to sustainable agriculture that have been reported to allow greater nutrient uptake and biocontrol of pathogens, depending on agricultural practices that allow their maintenance [40][120], such as practices like null or scarce tillage; use of diverse and ideally native crops covers; use of organic amendments as compost; reduction or elimination of external inputs, such as fertilizers, herbicides, and control of pests and diseases; practices that promote agroecology; organic agriculture and smart agriculture to develop a regeneration of soil microbial consortiums; and an ecological intensification of crops [2][12][41][2,12,53]. Likewise, different communities of soil fungi have been detected that affect soil formation or stabilization at the macro- and microaggregate scale through different mechanisms within the physical, biochemical, and biological processes [42][43][121,122].
The biotechnological applications of consortia, such as the application of biofertilizers or biostimulants, is justified in agricultural soils of the Mediterranean climate that have less than 3.5% organic matter, where microorganisms can no longer perform their functions [44][123]. Considering that in these cases the soil microbiota must be restored with fundamental taxonomic groups or initiators, such as AMF [45][124], the application of microbial consortia is the preferred approach. These inoculants will have less ecological impact on the ecosystem and therefore on the environment and health [13]. Although further studies at the micro- and mesocosm level, followed by field research, will allow to assess the ability of selected AMF and bacteria to interact with native microorganisms and maintain their beneficial activities [46][125], the agricultural use of microbial consortia containing bacteria, fungi, and AMF is in its exponential phase [47][126], based on a range of evidence including wheat [48][49][127,128], Mediterranean vegetables [50][129], lettuce [51][130], vegetables [52][131], basil [53][132], tomato [54][133], and maize [55][134].
Despite the demonstrated benefits produced by soil microorganisms, there is ample space for gaining further insight, especially on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, which are crucial for many ecosystem services, such as nutrient cycling and food production. An example is the case of Latin America [56][135]. In Latin America [57][136] and Africa, there is a need to focus on soil health and biodiversity among farmers, major agribusinesses, and policy makers, complementing the current productivity paradigm with sustainability and conservation objectives. Therefore, it is vital to describe the development of the rhizosphere microbiome in all relevant crops, as microbial communities are deeply affected by agricultural management [58][59][137,138]. The databases of association between higher plants and mycorrhizal fungi are critical for addressing biogeographic and evolutionary issues [23]. In addition, soil biota is a key factor for the application of appropriate microbial inoculants in the field, but the genotype/genotype interactions between the microbial strain(s) and the crop cultivar(s), e.g., maize, often requires prior screening to obtain the desired results [57][136]; this is due to the lack of knowledge or neglect of the plant microbiome when selecting the germoplasm for higher productivity [1].
It has been observed that microbial communities are highly sensitive to changes in environmental properties, for example, the geographical location where the type of soil and its pH play a fundamental role in the distribution of species. In the same way, the climatic conditions and the type of vegetation determine in a dynamic interrelationship the biodiversity of the microbial communities in the different ecosystems [60][61][139,140].
Likewise, the specific inoculants of a single group of commercially produced microorganisms represent a small genetic group of fungi and/or bacteria selected to be both generalists and aggressive colonizers [13]. These traits have the potential to affect local communities of microorganisms, which may not be resistant to the introduction of other exogenous species [62][141]. The role of potentially invasive species in soil ecosystems has received little attention, despite knowledge of the role of soil biodiversity in ecosystem processes.
Currently, the knowledge of the identity of the species that make up a microbial community can be achieved through metagenomics. In order to be able to associate the functionality of certain taxa with the characteristics of crop productivity and resilience, it is necessary to carry on studies including the isolation and cultivation of the species [32]. In Latin America and Africa, there are still many knowledge gaps, where microbial communities are not known or are unidentified taxa [63][57][45,136]. This represents a problem when predicting changes at the ecosystem level that may be generated in the future, which is relevant in decision-making when designing public policies [23]. To protect the functionalities of terrestrial ecosystems in a productive eco-compatible modern agriculture, it is necessary to include soil microbiota and soil biota in environmental protection and impact assessment policies [22][26][22,26].
Climate change with its consequent events, such as droughts, temperature increases, and CO2 increases, generates environmental changes that affect the microbial community and therefore the whole ecosystem. In agriculture, this presents a great challenge since there will be a significant impact on the productivity and resilience of agricultural systems [12][13][12,13]. Currently, different strategies are being developed to abort this issue, one of them being the Climatic Smart Agriculture, which seeks to develop a sustainable food system; to increase crop productivity and quality; and to reduce the impacts of climate change, through the adaptation and building of crop resilience, as well as conserving and increasing carbon stocks in soils and reducing GHGs [27].
Some examples for smart agriculture are the reported associations of the bacteria Rahnella aquatilis, which improves organic phosphorus solubilization, with the mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis. The association between the rhizospheric yeast fungi Cryptococcus flavus or Candida railenensis and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis promotes root growth in corn plants [64][142]; in turn, the Brettanomyces naardensis yeast’s association with fungi reduces the incidence of the pathogen Macrophomina phaseolina in sunflower plants; in addition, this association significantly improves the plant’s growth parameters, such as plant height, dry weight, and number of leaves [65][143]. It has also been reported that consortia between filamentous fungi and PGPR stimulate the growth and yield of substances produced by plants, such as essential oils [66][144].
