Forensic entomology is a branch of forensic science that incorporates insects as a part of solving crime. Insect-based evidence recovered at a crime scene can be used to estimate the minimum postmortem interval, determine if a carcass/corpse has been relocated, and contribute to the cause and manner of death. Sampling and preservation of insect material is paramount if this evidence is presented in court. To this end, a qualified forensic entomologist should attend the crime scene, however this is not always the case and such evidence is collected and preserved by a proxy. After reading this paper and fFollowing a number of essential protocols, a proxy should be able to submit insect evidence that a forensic entomologist may be able to use and present a best estimate of the time since death.
- casework
- crime scene
- skill base
- entomology procedures
1. Introduction
2. Forensic Entomology for Crime Scene Investigations
What is forensic entomology? It is known for using insects and other arthropods to aid in solving criminal and civil crimes [7][8]. Generally, forensic entomology involves three main subcategories: urban, stored product, and medicolegal entomology [6]. Urban entomology investigates the insect-related structural defects of buildings and medical myiasis [9][10]. Stored product entomology is used to assess biosecurity risks associated with food contamination and environmental pollution [11]. The last category, medicolegal entomology, uses insect-based evidence to investigate numerous criminal activities associated with homicides, suspicious fatalities, abuse of vulnerable people, hospital neglect, animal cruelty, contraband trafficking, and wildlife poaching [7][8][12]. The primary function of insects in crime solving is as biological indicators to estimate the time elapsed since death or the minimum postmortem interval (minPMI) [13]. Furthermore, the colonisation time of dipteran larvae in myiasis wounds can provide an indication of the time of neglect for humans, pets, and livestock [14]. The two fundamental principles of utilising insects are determining the minPMI based on their predictable temperature-based development and the sequential colonizing patterns on carcasses [7]. Flies (Order Diptera) are the main protagonists of all the carrion arthropods that are predominantly considered for use in determining the postmortem interval due to their involvement in carcass decomposition as both early and enduring colonisers [15][16]. The role of flies in carcass decomposition interchanges between scavengers of decaying tissues and prey to other predacious invertebrates (e.g., beetles and ants) and vertebrates (e.g., hyenas and vultures) [16][17] (Figure 1a–d).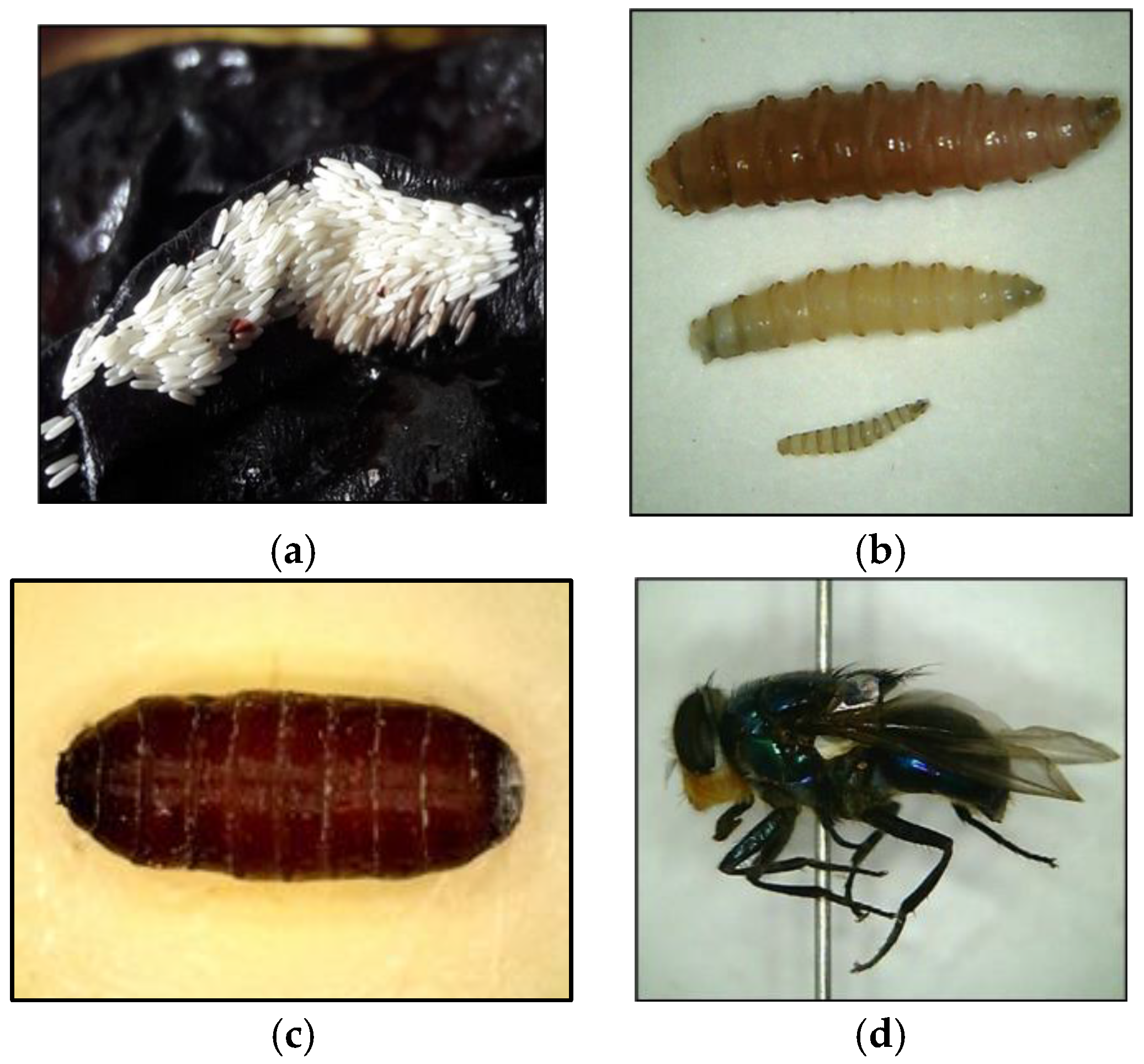
2.1. Forensic Entomologist: An Apprentice to an Expert
The analyses of entomofauna at a crime scene is complex, involving sampling and identifying insects, determining species–habitat relationships, evaluating the development stages and successional patterns, and assessing insect ethology concerning variations in climatic parameters [37]. Becoming a practitioner in forensic entomology requires training in the fundamentals of entomology and ecology. To conduct these tasks, an FE must understand concepts such as insect physiology, taxonomic and phylogenetic relationships, the behavioural adaptation of insects for different ecological setups, and their impacts on human affairs [38][39]. This training should then be narrowed down to specific topics that directly address the diagnostic characteristics and interrelationships of forensically important insect groups. This subset of knowledge related to forensic entomology can be acquired by following an undergraduate or postgraduate level specialised course or a degree program [40].2.2. Forensic Entomology in Crime Investigation: Complexity and Constraints
Insects play a pivotal role in carcass decomposition [41]. Flies and other arthropods visit a carcass if there are no physical barriers to block their access. When the food source (carcass) is exhausted, the insects leave [42]. The insect colonisation of a carcass primarily relies on the seasonal- and regional-based climate, including temperature, humidity, and photoperiod. It also relies on the intra and interspecies dynamics, including feeding preferences and competition and various habitat scenarios such as terrestrial and aquatic, urban and rural, indoor and outdoor, and burial and exposed [24]. In addition, secondary factors such as the method of death, including burning, poisoning, drowning, dismemberment, concealment, and hanging, as well as carcass features such as age, size, clothing, and trauma also influence the patterns of insect colonisation while impacting on the decomposition process. Besides these carcass insect complexities, an FE must also deal with many regulatory challenges such as interdisciplinary cooperation with other investigators at crime scenes, including other scientists and forensic field agents, strict deadlines to submit expert witness statements, and courtroom conflicts [43][44].2.3. Progression and Standardisation in Forensic Entomology
Several early classic works by Mégnin (1894) [45] and Payne (1965) [46] highlighted the importance of insects in contributing to the carrion decomposition process. These studies laid the conceptual framework to utilise insects in solving crime. Mégnin (1894) [45] proposed the first formal definition and testable mechanism of insect succession in carrion, and Payne (1965) [46] emphasised the significant involvement of insects in reducing carrion biomass in the early stages of decomposition. Following these formative works, many studies have been conducted in different regions of the world to introduce identification keys for carrion insects, document carrion-associated insect succession under different temporal and spatial conditions, record fly development periods under field and laboratory conditions, and unite forensic entomology with other related fields such as genetics, toxicology, and microbiology [13][47]. These findings have been incorporated into many crime investigations, published as casework in books and scientific journals, presented in conference proceedings, and sometimes proffered by popular media. The standardisation of entomological methods developed for solving crime has strengthened the science of forensic entomology and has allowed this science to gain more visibility and acceptability among law enforcement agencies. Several crucial studies have been published recently that critically evaluate many successional and development studies, bridging the gap between research and casework. This has led to the improvement of standards and protocols for the FE to use in real crime situations [21][48][49][50]. Numerous attempts have been made to propose global standards to assist an FE in performing their work logically and systematically under field and laboratory conditions [7][49][51][52]. These standards outline the basic procedures and the equipment required to conduct entomology-associated tasks by an FE at a crime scene and in a laboratory to generate accurate estimates of the minPMI [7][52]. However, these standards are not rigid and can be modified based on the degree of training and experience of the practitioner, availability of resources, and the circumstances of the crime scene. The three standards presented here (Gold, Silver, and Bronze) do not substantially change the basic procedures but provide some alternative ways to limit any misinterpretations [7][53].3. Crime Scene and Health Pathology Facility
The following procedures fall into two major categories based on the location where specific entomological interpretations are undertaken: crime scene/pathology facility and the entomology laboratory [7][54]. Generally, FEs or proxies collect insect evidence at a crime scene, or later at a health pathology facility, where autopsies are usually conducted. The remains are assigned to these facilities by police, pathologists, and medical examiners/coroners. A request then follows if insect material is evident to determine the minPMI and/or provide a general statement about the entomological context of the crime scene [8][53]. At any of these sites, an FE or proxy must perform several standard tasks, namely, the collection of the crime scene parameters (being present or via video and photos), including climatic parameters, insects, and their remnants (e.g., mouth parts, appendages, wings, empty puparia). Following collection, some insects may be preserved and stored, and some placed (40% of eggs larvae and full puparia) on a medium to be reared, followed by transporting these live and dead specimens to an entomology laboratory for further analysis [7][51][54]. An FE or proxy should adhere to the general guidelines set by the law enforcement agency controlling the crime scene [53]. An FE or proxy, similar to all other investigators at a crime scene, must wear the appropriate clothing and personal protection equipment (e.g., closed-toed shoes, long pants, scrubs, (disposable overalls) and masks) to avoid any possible contamination and biohazard risks [7][53]. They must visit the scenes with the necessary equipment and documentation to fulfil three major purposes. Firstly, collecting insects (live and/or dead): labelled plastic containers and vials, a handheld lens, hot water (insulated bottle), forceps, fined tipped artist paint brushes, an insect net, bedding materials (e.g., dry sand, sawdust, vermiculite), and food sources (e.g., beef, pork pieces) for rearing purposes, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) for killing and preserving insects. Secondly, gather the microclimatic data: a portable weather gauge, an infrared thermometer, and a temperature data lodging device. Thirdly, document necessary information via prepared data entry sheets. An FE should have an a priori knowledge of the standard operating procedures of law enforcement at a particular location and this should determine if other devices such as a camera and a video recorder should be included equipment [7][53].3.1. Collection of Onsite Data
The collection and preservation of entomological evidence at a crime scene should be carried out as soon as possible after a body is discovered [55]. The delayed recording and sampling of entomofauna could potentially generate misleading information. This is due to the development, succession, and orientation patterns of carrion insects, which continuously alter with climatic changes and other interruptions caused by inadvertent destruction by investigator activities and scavenging of the remains by other vertebrates and invertebrates [56]. Due to a possible high risk of damage and contamination, the insect evidence should be safeguarded by the law enforcement agency protocols at a crime scene. When law enforcement establishes a crime scene perimeter, it is essential to consider the area where insect activity may be evident in and around a carcass [57]. This is dependent on the decomposition stage and the age of the immature insects on the remains [53]. Specifically, eggs and feeding larval stages of flies are restricted to the carcass; however, post-feeding larval and pupal stages can be dispersed underneath the carcass, within the surrounding cadaveric soil, some distance from the remains and buried in the soil. In dwellings, these stages maybe located near physical objectives present in the vicinity of the carcass (e.g., under carpets, cupboards, and other household items) [7][54]. It is essential to request from the forensic investigator in charge any related information concerning the management of the scene. This should include photographs and video footage from any initial visits of investigators to the scene, and any evidence of physical alterations made to the immediate environment after the remains were discovered (e.g., opening windows, switching on/off heaters or air conditioners, and placing light sources to conduct investigations at night). A potential bias associated with a crime scene is informing the FE or proxy about the date of the last sighting of the deceased. Such information should ideally only be obtained after estimations of the minPMI have been ascertained by the FE [44]. Following the arrival at a crime scene and consulting with law enforcement, the FE or proxy should be able to view the remains and observe the patterns of insects on and around the carcass. Following this assessment, the FE or proxy can realise what tools are required to work the scene. Sometimes, large larval aggregations may be present in and around the natural orifices of carcasses, such as in and around the mouth, nostrils, ears, and the genital region [58]. These body regions provide protection and suitable soft tissues for larval feeding in the early stages of development [58][59]. These early colonizing sites can also occur on other parts of the body based on factors such as surface humidity, insulation, body orientation, clothing, and the wrapping of bodies and wounds [59].3.2. Collection of Microclimatic Data at a Crime Scene
Insects are poikilothermic, their body temperatures fluctuate along with the ambient temperatures to be in homeostasis [60]. Therefore, entomological assessments at crime scenes should be conducted concerning ambient temperatures, as it affects the development and succession patterns of carrion insects [61][62]. Specifically, temperature impacts insect development by regulating their movement, metamorphosis, reproduction, and diapause [63]. In contrast, succession patterns change with temperature fluctuations as it affects the microbial activities associated with the carcass decomposition [64]. The best available source to obtain environmental temperature readings at a crime location is the crime scene itself matched to the temperatures from the nearest meteorological station [51]. Investigators can request daily or hourly temperature data for as many days as required prior to discovering the remains [7][51][65]. However, when cadavers are inside a dwelling, these meteorological station data are only helpful if the indoor space is open to the outdoor by windows, doors, and vents. In such situations, the outside temperature data must be paired with the indoor temperatures when constructing the thermal simulation model for the crime scene environment [66]. Apart from the environmental temperatures, body, water, soil, and larval mass temperatures should also be recorded based on the context of the crime. A contactless infrared thermometer can measure the body, and larval mass temperatures, and the soil and water body temperatures can be recorded by a temperature probe [7][53]. The decision of the temperature data most relevant for minPMI estimations must be made based on their degree of heat transfer for larval development.3.3. Recovery of Insects for Storage or Rearing Purposes
The specimens collected at a crime scene should be a clear cross-section of the different development stages (eggs, larvae, full and empty puparia, and adults) of various insect successional groups (flies, beetles, mites, and moths) wherever located on the carcass and its surrounding environment [51]. The number of individuals recovered at each stage of development must be adequate for conducting a range of entomological assessments in the laboratory (i.e., species identification, PMI estimation, and xenobiotic determination). However, these sampling numbers depend on their availability and could range from a single egg or larva to several egg rafts and larval masses [67]. Insects collected at a crime scene should be divided into two batches, one batch preserved and the other reared to adult. This is generally performed at the scene, but if appropriate equipment is unavailable, then they must be cooled (not frozen) to slow down development and dispatched rapidly to a laboratory [7]. Preserved specimens are used for identifying the species, determining their age at the time of sampling based on their instar stage, the larval length and width measurement, and extracting gut contents for genetic and toxicological analysis [68].3.3.1. Preservation of Insects
As mentioned above, insects recovered from a carcass should be preserved at their collection point [7]. When kept alive in containers to preserve for a later time and not cooled, their age status will alter, may exacerbate some cannibalistic behaviour, and reduce the number of collected larvae for further analyses [69]. In such circumstances, the development rate is compromised, and such samples should not be used to estimate the minPMI [69]. However, if a complete record of the thermal history of a sample is provided, an FE should be able to backtrack the age of the insects at the collection time and extrapolate useful information concerning the minPMI for the investigators. Fly eggs and adult stages can be difficult for estimating the PMI, as limited knowledge is available pertaining to only a few species [7][70]. However, sometimes, the only samples collected are these life history stages, and a practiced FE may be able to identify the morphological changes that occur during egg embryogenesis [71], as well as using some of the methods described by Tyndale-Biscoe (1984) [72] with regard to the age of adults, especially those captured inside a dwelling. Once eggs are located, they can be collected after differentiating them from soil and litter particles using a handheld lens and a fined-tipped artist paint brush [73]. In contrast, the adult flies at the scene can be trapped using an insect net. Following capture, they can simply be removed by dipping or spraying the fly with 70% alcohol and then transferring the dead specimen to a vial. If alcohol is unavailable, then the adult fly can be captured in the net and carefully placed into an insect killing jar prior to preservation [7]. Beetles collected at a crime scene should be handpicked using forceps and hot water, dipped to kill them before being placed in vials containing 70% ethanol. Beetles may be observed by thoroughly examining the litter surrounding the carcass as well as sieving the soil under the carcass to a depth of approximately 20 cm [74]. It is worthwhile to mention here that Silver and Bronze personnel should collect all insects associated with the corpse and allow the FE to make the necessary decisions on their relevance. When dealing with a crime scene located in an aquatic environment, the larval stages of freshwater insects such as mayflies (Order: Ephemeroptera), stone flies (Order: Plecoptera), and caddis flies (Order: Trichoptera) should be collected from submerged and floating bodies into plastic vials (70% ethanol) using forceps. Once again, it is recommended that Silver and Bronze personnel collect all aquatic fauna that they observe associated with the corpse.3.3.2. Preparation of Insects at the Crime Scene for Rearing Purposes
The live insects for rearing purposes collected at the crime scene should be placed on a dish (Petri dish, foil) with a suitable food source (e.g., meat). This dish is then placed on 2–3 cm of bedding material (sawdust, vermiculite, builders’ sand) inside a container with a mesh lid [7]. When preparing full puparia for transporting to the laboratory, they can be directly transferred into containers half filled with bedding material with a standard lid. No feeding source or ventilation is required if all insect material is transported inside a cooler or kept refrigerated.3.4. Laboratory
The following sections pertain to the work that an FE must conduct on either the material collected by themselves, or the material collected by their proxy. To identify, measure larval, pupal, and adult external body characters and rear immatures to adult stage. An entomology laboratory should be equipped with the following basic apparatus: stereo microscopes, vernier callipers, growth chambers or temperature-regulated rooms, preservative chemicals (ethanol), gloves, forceps, scalpels, and Petri dishes.3.5. Identification
The identification of specimens to species level should be completed first. Without this knowledge, other analyses will be compromised [75]. Generally, insect identifications are made using morphological and/or molecular methods. Other techniques such as hyperspectral or CT imaging, tomography, and chemical techniques may also be used; however, each has associated pros and cons according to expense and availability [76][77]. Nonetheless, whichever technique is used, it should provide the best identification outcome. In fact, the most informative and best identification is to send the collected specimens relevant to the minPMI to a dipteran taxonomist. The following sections discuss the two main techniques used to identify insects: the morphological identification and molecular identification. The morphological identification of carrion insects to species level can be achieved using taxonomic keys and standard or electron microscopic images [78][79]. Dichotomous taxonomic keys provide a stepwise assessment using morphological characters that guide the user to identify the species [75]. The level of accuracy and confidence in using taxonomic keys for species determination develops with a skill base in entomology a Ultrastructure studies of eggs, larvae, full and empty puparia, and adult stages of different fly species by scanning electron microscopes (SEM) aid in precise species identification. Typical egg-associated ultrastructures are micropylar plate, median area, respiratory plastron, hatching lines, and chorion sculpturing [80][81]. The suite of larval characters includes the posterior spiracles, respiratory slits, peritreme ornamentation, anterior spiracles, cephaloskeleton, and spine arrangement [81][82]. When identifying full puparia, characteristics such as bubble membranes and respiratory horns are used, along with spine arrangements and posterior spiracles that are correlated with their preceding larval structures [77][80][81][83].3.6. Examining Larvae and Full Puparia for Age Determination
Development studies provide time frames required for immature flies that can be used as indications to estimate the minPMI [21]. The instar of fly larvae can be determined by a microscopic observation of the number of respiratory slits available at their posterior spiracles [84]. Typically, a first instar blow fly larva has a single slit, whereas second and third instar larvae have two and three slits, respectively. In contrast, pre- and post-feeding stages of third instar larvae are discriminated by their body colour change (translucent to opaque), a food distended crop, body compaction, and wandering behaviour away from the carcass [21]. In addition, the length and width of larvae can also be considered as an indication of age [85]. The length and width of larvae can be measured by a stage micrometre and a vernier calliper. The correlation of actual length and width data of a sampled individual with reference values given in previous publications aid in determining the age of the specimen, hence the PMI. However, temperature variations, the type of food substrates, and the presence of xenobiotics in it reflect on any of these age determinations. Furthermore, in previous studies, length and instar stage variation of larvae under different constant temperature regimes were demonstrated using isomegalen and isomorphen curves, respectively. These curves are available for species such as, Calliphora vicina (Robineae-Desvoidy), L. sericata, Ch. albiceps, Protophormia terraenovae (Robineae-Desvoidy), Ch. megacephala, and Liopygia argyrostoma (Robineae-Desvoidy) [86][87][88]. Pupal morphogenesis can be considered for minPMI estimations as the full puparia coexist with carcasses over a prolonged period [89][90]. The extent of the external organ development of pupae can be examined via a stereo microscope after removing the puparium using a surgical knife and forceps. A photograph showing the status of the external organ development of a sampled pupa can be coupled with a reference photograph series given for the same species in a previous publication for the age determination. However, it is essential to consider the temperature variations of the environment that the full puparia were exposed to prior to sampling, as low temperatures can delay pupal morphogenesis [91].3.7. Rearing
The rearing of eggs, larval, and pupal specimens until the adult stage can often facilitate a more accurate species identification [92]. Adult-level identification has a greater certainty in correct species determination, and they are well-described in taxonomic keys [93]. When rearing dipteran species in an insectary, they should be confined in insect cages and provided ad libitum with food, water, and oviposition substrates [15][21]. Immature stages are best reared in growth chambers whereby temperature, humidity, and photoperiod can be controlled. Such development studies are used to determine the time duration required to ascertain the development stage of the sampled species and their larval length and width changes. It is recommended to use swine muscle as larval food for these growth chamber studies as the domestic pig (Sus scrofa L.) is primarily considered as the proxy of humans when conducting development studies [94].3.8. Xenobiotic Detection
The utilisation of insects for xenobiotic detection relies on the prolonged tissue retention of drugs, pesticides, and metals, leading to high sensitivity for analytical detection techniques [95][96]. The fly larval, pupal, and adult stages collected at a crime scene can be used as a source to extract and detect chemicals. Previous studies showed that larvae collected from internal organs such as liver, or from the head and muscles of a carcass retain high concentrations of chemicals [97]. The larvae sourced from these regions should be kept alive and starved for several hours prior to analysis to ensure the absorption of any chemicals into their metabolic system. It is recommended to store killed larvae under dry conditions at −20 °C. Such steps will ensure a higher retention and concentration of chemicals because storing in ethanol may diminish trace volumes of drugs in larvae [97][98].4. Documentation
4.1. Referring to the Literature
The accuracy of establishing a successful entomological interpretation of the circumstances at a crime scene depends on the empirical analysis developed by an FE throughout their career [40]. One of the best ways of acquiring and upgrading the knowledge and skills associated with insects for solving crime is referring to previously published research and casework [99]. These publications essentially guide a practitioner to incorporate the available knowledge into procedures and provide a comprehensive guideline for researchers and academics to develop training models and conduct future research [99].4.2. Fly Development Studies
Development studies outline the variations in the fly life history [21]. The data from these development studies can be directly incorporated to estimate the minPMI, as these publications essentially contain life history tables and isomegalen/isomorphen curves. The timeline data given in life history tables and the lower development threshold temperatures can be used to calculate the ADD/ADH [23][100], and hence, the minPMI. However, when selecting a previous development study to corroborate a minPMI estimation of a particular fly species, the FE should determine if the temperature regimes, photoperiod and humidity, and larval feeding tissue type, along with the location where the source colonies originated, are appropriate to use [101].4.3. Insect Successional Studies
Insect successional studies provide a descriptive account of insect colonisation patterns concerning the decomposition changes in carcasses. These studies are either observational or experimental, and both are directed to gather information such as insect checklists, environment temperature, and rainfall data of the study period, and the characteristics and duration of the decomposition stage [102].4.4. Casework
Occasionally, a case is published which is the combination of facts and opinions of an FE who investigated a particular crime scene and may be relevant to the current case under investigation. Reference to casework can provide guidance to produce a robust witness statement but can also provide insight into areas where further research may benefit better interpretations.References
- James, S.H.; Nordby, J.J. Forensic Science: An Introduction to Scientific and Investigative Techniques, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 0-8493-1246-9.
- Saks, M.J.; Koehler, J.J. The coming paradigm shift in forensic identification science. Science 2005, 309, 892–895.
- Saferstein, R. Criminalistics: An Introduction to Forensic Science, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001.
- Brettell, T.A.; Butler, J.M.; Saferstein, R. Forensic science. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3839–3860.
- Horswell, J. Crime Scene Investigation. In The Practice of Crime Scene Investigation, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004.
- Katz, E.; Halámek, J. Forensic science: A multidisciplinary approach. J. Forensic Leg. Investig. Sci. 2016, 1, 1–4.
- Byrd, J.H.; Tomberlin, J.K. Forensic Entomology: The Utility of Arthropods in Legal Investigations, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-8153-5020-0.
- Dadour, I.R.; Morris, B. Forensic Entomology: A Synopsis, Guide, and Update. In Essentials of Autopsy Practice, 1st ed.; Rutty, G.N., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 105–130.
- Robinson, W.H. Urban Insects and Arachnids: A Handbook of Urban Entomology, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 9780521812535.
- Bugelli, V.; Tarozzic, I.; Galante, N.; Bortolini, S.; Franceschetti, L. Review on forensic importance of myiasis: Focus on medicolegal issues on post-mortem interval estimation and neglect evaluation. Legal Med. 2023, 63, 102263.
- Hagstrum, D.W.; Athanassiou, C.G. Improving stored product insect pest management: From theory to practice. Insects 2019, 10, 332.
- Haines, A.M.; Webb, S.L.; Wallace, J.R. Conservation Forensics: The Intersection of Wildlife Crime, Forensics, and Conservation. In Wildlife Biodiversity Conservation, 1st ed.; Underkoffler, S.C., Adams, H.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 125–146.
- Matuszewski, S. Post-mortem interval estimation based on insect evidence: Current challenges. Insects 2021, 12, 314.
- Bambaradeniya, Y.T.B.; Karunaratne, W.A.I.P.; Rakinawasam, S.V.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Goonerathne, I.; Kotakadeniya, R.B. Myiasis incidences reported in and around central province of Sri Lanka. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 336–342.
- Catts, E.P.; Goff, M.L. Forensic entomology in criminal investigations. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 253–272.
- Forbes, S.L.; Carter, D.O. Processes and Mechanisms of Death and Decomposition of Vertebrate Carrion. In Carrion Ecology, Evolution, and Their Applications, 1st ed.; Benbow, M.E., Tomberlin, J.K., Torone, A.M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 13–30.
- Payne, J.A.; King, E.W.; Beinhart, G. Arthropod succession and decomposition of buried pigs. Nature 1968, 219, 1180–1181.
- Noriki, S.; Iino, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Fukazawa, Y.; Inai, K.; Sakai, T.; Kimura, H. Pathological analysis of cadavers for educational dissection by using postmortem imaging. Pathol. Int. 2019, 69, 580–600.
- Bajerlein, D.; Taberski, D.; Matuszewski, S. Estimation of postmortem interval (PMI) based on empty puparia of Phormia regina (Meigen) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) and third larval stage of Necrodes littoralis (L.) (Coleoptera: Silphidae)–Advantages of using different PMI indicators. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2018, 55, 95–98.
- Pittner, S.; Bugelli, V.; Weitgasser, K.; Zissler, A.; Sanit, S.; Lutz, L.; Amendt, J. A field study to evaluate PMI estimation methods for advanced decomposition stages. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 1361–1373.
- Bambaradeniya, Y.T.B.; Magni, P.A.; Dadour, I.R. Current Status of Five Warm Season Diptera Species in Estimating the Post-Mortem Interval. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2023, 116, 19–50.
- Kreitlow, K.L.T. Insect Succession in a Natural Environment. In Forensic Entomology, 2nd ed.; Byrd, J.H., Castner, J.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 251–269.
- Amendt, J.; Richards, C.S.; Campobasso, C.P.; Zehner, R.; Hall, M.J. Forensic entomology: Applications and limitations. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2011, 7, 379–392.
- Campobasso, C.P.; Di Vella, G.; Introna, F. Factors affecting decomposition and Diptera colonization. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 18–27.
- Kulshrestha, P.; Satpathy, D.K. Use of beetles in forensic entomology. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 15–17.
- Frost, C.L.; Braig, H.R.; Amendt, J.; Perotti, M.A. Indoor Arthropods of Forensic Importance: Insects Associated with Indoor Decomposition and Mites as Indoor Markers. In Current Concepts in Forensic Entomology, 1st ed.; Amendt, J., Goff, M.L., Campobasso, C.P., Grassberger, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 93–108.
- Vanin, S. Advances in Forensic Entomology in Missing Persons Investigations. In Handbook of Missing Persons, 1st ed.; Morewitz, S.J., Colls, C.S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 309–317.
- Prasad, S.; Aneesh, E.M. Tools and techniques in forensic entomology—A critical review. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2020, 42, 2785–2794.
- Charabidze, D.; Gosselin, M.; Hedouin, V. Use of necrophagous insects as evidence of cadaver relocation: Myth or reality? Peer J. 2017, 5, e3506.
- Weatherbee, C.R.; Pechal, J.L.; Eric Benbow, M. The dynamic maggot mass microbiome. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2017, 110, 45–53.
- Di Luise, E.; Magni, P.; Staiti, N.; Spitaleri, S.; Romano, C. Genotyping of human nuclear DNA recovered from the gut of fly larvae. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 1, 591–592.
- Wells, J.D.; Stevens, J.R. Application of DNA-based methods in forensic entomology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 103–120.
- Garrido-Cardenas, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. The metagenomics worldwide research. Curr. Genet. 2017, 63, 819–829.
- Roumpeka, D.D.; Wallace, R.J.; Escalettes, F.; Fotheringham, I.; Watson, M. A review of bioinformatics tools for bioprospecting from metagenomic sequence data. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 23.
- Carvalho, F.; Dadour, I.R.; Groth, D.M.; Harvey, M.L. Isolation and detection of ingested DNA from the immature stages of Calliphora dubia (Diptera: Calliphoridae) A forensically important blowfly. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2005, 1, 261–265.
- Baqué, M.; Amendt, J.; Verhoff, M.A.; Zehner, R. Descriptive analyses of differentially expressed genes during larval development of Calliphora vicina (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Int. J. Legal Med. 2015, 129, 891–902.
- Stewart, M.A. The teaching of entomology. J. Econ. Entomol. 1929, 22, 777–781.
- Morris, B.; Harvey, M.L.; Dadour, I.R. International Collaborations and Training. In International Dimensions & Frontiers in Forensic Entomology, 1st ed.; Tomberlin, J., Benbow, E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; Volume 30, pp. 399–416.
- Schoenly, K.G.; Haskell, N.H.; Mills, D.K.; Bieme-Ndi, C.; Larsen, K.; Lee, Y. Recreating death’s acre in the school yard: Using pig carcasses as model corpses to teach concepts of forensic entomology & ecological succession. Am. Biol. Teach. 2006, 68, 402–410.
- Magni, P.; Guercini, S.; Leighton, A.; Dadour, I. Forensic entomologists: An evaluation of their status. J. Insect Sci. 2013, 13, 78.
- Michaud, J.P.; Schoenly, K.G.; Moreau, G. Rewriting ecological succession history: Did carrion ecologists get there first? Q. Rev. Biol. 2015, 90, 45–66.
- Benecke, M.; Barksdale, L. Distinction of bloodstain patterns from fly artifacts. Forensic Sci. Int. 2003, 137, 152–159.
- Archer, M.S.; Wallman, J.F. The development of forensic entomology in Australia and New Zealand: An overview of casework practice, quality control and standards. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2017, 49, 125–133.
- Lutz, L.; Zehner, R.; Verhoff, M.A.; Bratzke, H.; Amendt, J. It is all about the insects: A retrospective on 20 years of forensic entomology highlights the importance of insects in legal investigations. Int. J. Legal Med. 2021, 135, 2637–2651.
- Mégnin, P. La faune des Cadavres. Application de l’entomologie a la Médicine Légal (Fauna of Cadavers. Application of Enomology in Legal Medicine); Encyclopdie scientifique des Aides-Mémoire; Les Belles Lettres: Paris, France, 1894; p. 214.
- Payne, J.A. A summer carrion study of the baby pig Sus scrofa Linnaeus. Ecology 1965, 46, 592–602.
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Mohr, R.; Benbow, M.E.; Tarone, A.M.; Vanlaerhoven, S. A roadmap for bridging basic and applied research in forensic entomology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 401–421.
- Keh, B. Scope and applications of forensic entomology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1985, 30, 137–154.
- Tomberlin, J.K.; Byrd, J.H.; Wallace, J.R.; Benbow, M.E. Assessment of decomposition studies indicates need for standardized and repeatable research methods in forensic entomology. J. Forensic Res. 2012, 3, 1000147.
- Moreau, G. The pitfalls in the path of probabilistic inference in forensic entomology: A review. Insects 2021, 12, 240.
- Amendt, J.; Campobasso, C.P.; Gaudry, E.; Reiter, C.; LeBlanc, H.N.; Hall, M. Best practice in forensic entomology—Standards and guidelines. Int. J. Legal Med. 2007, 121, 90–104.
- Gaudry, E.; Dourel, L. Forensic entomology: Implementing quality assurance for expertise work. Int. J. legal Med. 2013, 127, 1031–1037.
- Dadour, I.R.; Cook, D.F.; Fissioli, J.N.; Bailey, W.J. Forensic entomology: Application, education and research in Western Australia. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 48–52.
- Hall, M.; Whitaker, A.; Richards, C. Forensic Entomology. In The Forensic Ecology Handbook: From Crime Scene to Court, 1st ed.; Marques-Grant, N., Roberts, J., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012; pp. 111–140. ISBN 978-1-119-97419-2.
- Campobasso, C.P.; Introna, F. The forensic entomologist in the context of the forensic pathologist’s role. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 132–139.
- Amendt, J.; Krettek, R.; Niess, C.; Zehner, R.; Bratzke, H. Forensic entomology in Germany. Forensic Sci. Int. 2000, 113, 309–314.
- Dolinski, C.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.; Lewis, E.E. Insect Cadaver Applications: Pros and Cons. In Nematode Pathogenesis of Insects and Other Pests, 1st ed.; Campos-Herrera, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 207–229.
- LeBlanc, H.N.; Logan, J.G. Exploiting Insect Olfaction in Forensic Entomology. In Current Concepts in Forensic Entomology, 1st ed.; Amendt, J., Goff, M.L., Campobasso, C.P., Grassberger, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 205–221.
- Charabidze, D.; Depeme, A.; Devigne, C.; Hedouin, V. Do necrophagous blowflies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) lay their eggs in wounds?: Experimental data and implications for forensic entomology. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 253, 71–75.
- Neven, L.G. Physiological responses of insects to heat. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2000, 21, 103–111.
- Sharanowski, B.J.; Walker, E.G.; Anderson, G.S. Insect succession and decomposition patterns on shaded and sunlit carrion in Saskatchewan in three different seasons. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 179, 219–240.
- Bambaradeniya, Y.T.B.; Karunarathne, W.A.I.P.; Goonerathne, I.; Kotakadeniya, R.B.; Tomberlin, J.K. Use of development data to estimate colonization time of the myiasis-causing fly, Chrysomya bezziana (Diptera: Calliphoridae) collected from human wounds. Sri Lanka J. Forensic Med. Sci. Law 2016, 7, 19–26.
- Iancu, L.; Dean, D.E.; Purcarea, C. Temperature influence on prevailing necrophagous Diptera and bacterial taxa with forensic implications for postmortem interval estimation: A review. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1369–1379.
- Guo, J.; Fu, X.; Liao, H.; Hu, Z.; Long, L.; Yan, W.; Cai, J. Potential use of bacterial community succession for estimating post-mortem interval as revealed by high-throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24197.
- Hofer, I.M.; Hart, A.J.; Martín-Vega, D.; Hall, M.J. Estimating crime scene temperatures from nearby meteorological station data. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 306, 110028.
- Charabidze, D.; Hedouin, V. Temperature: The weak point of forensic entomology. Int. J. Legal Med. 2019, 133, 633–639.
- Anderson, G.S.; Cervenka, V.J.; Haglund, W.; Sorg, M. Insects Associated with the Body: Their Use and Analyses. In Advances in Forensic Taphonomy: Method, Theory, and Archaeological Perspectives, 1st ed.; Haglund, W.D., Sorg, M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; p. 173200. ISBN 13: 978-14200-5835-2.
- Touroo, R.; Fitch, A. Crime Scene Findings and the Identification, Collection, and Preservation of Evidence. In Veterinary Forensic Pathology, 1st ed.; Brooks, J.S., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 9–25.
- Mohr, R.M.; Tomberlin, J.K. Development and validation of a new technique for estimating a minimum postmortem interval using adult blow fly (Diptera: Calliphoridae) carcass attendance. Int. J. Legal Med. 2015, 129, 851–859.
- Martín-Vega, D.; Hall, M.J.R. Estimating the age of Calliphora vicina eggs (Diptera: Calliphoridae): Determination of embryonic morphological landmarks and preservation of egg samples. Int. J. Legal Med. 2016, 130, 845–854.
- Hofer, I.M.; Hart, A.J.; Martín-Vega, D.; Hall, M.J. Optimising crime scene temperature collection for forensic entomology casework. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 270, 129–138.
- Tyndale-Biscoe, M. Age-grading methods in adult insects: A review. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1984, 74, 341–377.
- Firoozfar, F.; Moosa-Kazemi, H.; Baniardalani, M.; Abolhassani, M.; Khoobdel, M.; Rafinejd, J. Mass rearing of Lucilia sericata Meigen (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 54–56.
- Weithmann, S.; von Hoermann, C.; Degasperi, G.; Brandt, K.; Steiger, S.; Ayasse, M. Temporal variability of the rove beetle (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) community on small vertebrate carrion and its potential use for forensic entomology. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 323, 110792.
- Stamper, T.; Weidner, L.; Nigoghosian, G.; Johnson, N.; Wang, C.; Levesque-Bristol, C. Towards understanding how to instruct students in dichotomous identification keys in a mixed STEM forensic science education environment. JFSE 2020, 2, 1.
- Drijfhout, F.P. Cuticular Hydrocarbons: A New Tool in Forensic Entomology? In Current Concepts in Forensic Entomology, 1st ed.; Amendt, J., Goff, M.L., Campobasso, C.P., Grassberger, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009.
- Pechal, J.L.; Moore, H.; Drijfhout, F.; Benbow, M.E. Hydrocarbon profiles throughout adult Calliphoridae aging: A promising tool for forensic entomology. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 245, 65–71.
- Sukontason, K.; Sukontason, K.L.; Boonchu, N.; Chaiwong, T.; Piangjai, S. Ultrastructure of eggshell of Chrysomya nigripes Aubertin (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Parasitol. Res. 2004, 93, 151–154.
- Velásquez, Y.; Magaña, C.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Rojo, S. Diptera of forensic importance in the Iberian Peninsula: Larval identification key. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2010, 24, 293–308.
- Mendonça, P.M.; dos Santos-Mallet, J.R.; de Mello, R.P.; Gomes, L.; de Carvalho Queiroz, M.M. Identification of fly eggs using scanning electron microscopy for forensic investigations. Micron 2008, 39, 802–807.
- Ubero-Pascal, N.; Arnaldos, I.; López-Esclapez, R.; García, M.D. Microscopy and forensic entomology. Microsc. Sci. Technol. Appl. Educ. Microsc. Book Ser. 2010, 4, 1548–1556.
- Grzywacz, A. Third instar larva morphology of Hydrotaea cyrtoneurina (Zetterstedt, 1845) (Diptera: Muscidae)-a species of forensic interest. Pol. J. Entomol. 2013, 82, 303–315.
- Brunke, A.; Newton, A.; Klimaszewski, J.; Majka, C.; Marshall, S. Staphylinidae of eastern Canada and adjacent United States. Key to subfamilies: Staphylininae: Tribes and subtribes, and species of Staphylinina. Can. J. Arthropod Identif. 2011, 12, 1–110.
- Zumpt, F. Myiasis in Man and Animals in the Old World: A Textbook for Physicians, Veterinarians and Zoologists; Butterworth & Co., Ltd.: London, UK, 1965.
- Day, D.M.; Wallman, J.F. Width as an alternative measurement to length for post-mortem interval estimations using Calliphora augur (Diptera: Calliphoridae) larvae. Forensic Sci. Int. 2006, 159, 158–167.
- Bambaradeniya, Y.T.B.; Karunaratne, W.I.P.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Goonerathne, I.; Kotakadeniya, R.B.; Magni, P.A. Effect of temperature and tissue type on the development of the forensic fly Chrysomya megacephala (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1571–1581.
- Grassberger, M.; Reiter, C. Effect of temperature on Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae) development with special reference to the isomegalen-and isomorphen-diagram. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 32–36.
- Bambaradeniya, Y.T.B.; Karunaratne, W.I.P.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Goonerathne, I.; Kotakadeniya, R.B. Temperature and tissue type impact development of Lucilia cuprina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Sri Lanka. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 285–291.
- Davies, K.; Harvey, M.L. Internal morphological analysis for age estimation of blow fly pupae (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in postmortem interval estimation. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 79–84.
- Ma, T.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.F. Study on the pupal morphogenesis of Chrysomya rufifacies (Macquart) (Diptera: Calliphoridae) for postmortem interval estimation. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 253, 88–93.
- Bambaradeniya, Y.T.B.; Karunaratne, W.A.I.P.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Magni, P.A. Effect of type of tissue on the development of Chrysomya rufifacies (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in Sri Lanka. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1673–1679.
- Yanmanee, S.; Husemann, M.; Benbow, M.E.; Suwannapong, G. Larval development rates of Chrysomya rufifacies Macquart, 1842 (Diptera: Calliphoridae) within its native range in South-East Asia. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 266, 63–67.
- Van der Merwe, S.S. The Identification of Diptera of the Grave and Their Succession Patterns during Winter and Summer in Central South Africa, with Reference to Forensic Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2016. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11660/4033 (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Swiger, S.L.; Hogsette, J.A.; Butler, J.F. Laboratory colonization of the blow flies, Chrysomya megacephala (Diptera: Calliphoridae) and Chrysomya rufifacies (Diptera: Calliphoridae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1780–1784.
- Kintz, P.; Tracqui, A.; Ludes, B.; Waller, J.; Boukhabza, A.; Mangin, P.; Chaumont, A.J. Fly larvae and their relevance in forensic toxicology. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 1990, 11, 63–65.
- Pounder, D.J. Forensic entomo-toxicology. J. Forensic Sci. Soc. 1991, 31, 469–472.
- Gosselin, M.; Wille, S.M.; Fernandez, M.D.M.R.; Di Fazio, V.; Samyn, N.; De Boeck, G.; Bourel, B. Entomotoxicology, experimental set-up and interpretation for forensic toxicologists. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 208, 1–9.
- Introna, F.; Campobasso, C.P.; Goff, M.L. Entomotoxicology. Forensic Sci. Int. 2001, 120, 42–47.
- Hall, M.J.R. The relationship between research and casework in forensic entomology. Insects 2021, 12, 174.
- Krinsky, W.L. Forensic Entomology. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2019, 5, 51–60.
- Weidner, L.M.; Meeds, A.W.; Noblesse, A.P.; Hans, K.R. A review of Forensic Entomology literature in the southwestern United States. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Forensic Sci. 2021, 3, e1421.
- Matuszewski, S.; Hall, M.J.; Moreau, G.; Schoenly, K.G.; Tarone, A.M.; Villet, M.H. Pigs vs people: The use of pigs as analogues for humans in forensic entomology and taphonomy research. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 793–810.
