| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shingo Nakamura | + 695 word(s) | 695 | 2020-08-17 02:54:11 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 695 | 2020-10-29 03:43:19 | | |
Video Upload Options
Silver is easily available and known to have microbicidal effect with wide antibacterial spectrum due to its silver ions mainly; moreover, it does not impose any adverse effects on the human body. Furthermore, the development of multidrug-resistant bacteria, as in the case of antibiotics, is less likely. Recently, silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) have been synthesized and revealed its anti-viral activity. Because of their characteristics, Ag NPs are useful countermeasures against infectious diseases, which constitute a major issue in the medical field. Therefore, Ag NPs could expect to apply to materials preventing healthcare workers (HCWs), not only patient, from various infection.
1. Silver Nanoparticles (Ag NPs)
Silver is widely used in industrial applications because of its metallic properties, such as conductivity, and in the medical field due to its anti-microbial effect [1]. For a metallic particle to be considered as "nano", its size must be within 1–100 nm [2]. Metallic NPs exhibit specific properties, such as surface plasmon resonance [3], specific vivid color. In addition, NPs have a large specific surface area [4]. Metal NPs including Ag NPs are commonly synthesized via the reduction of metal salts in a solution [5], or the formation of metal atom aggregates by the heating or vaporization of a metal in inert gas or vacuum [6]. Size-controlled Ag NPs are also synthesized using new environment-friendly synthesis techniques [7]. Especially, in an aqueous environment, the surface of Ag NPs is oxidized in the presence of oxygen and protons and silver ions are released as the surface dissolves. As a result, the effective of silver ion concentration is maintained in the solution and the anti-microbial effect will last [4].
Various applications have been found in the medical field for Ag NPs; for example, they can be used for biosensors, drug delivery systems, and medical devices [8][9]. Because of their wide anti-bacterial and anti-viral spectrum, there are particularly high expectations for the suppression of multidrug-resistant bacteria. For example, Ag NPs are combined with a cationic polymer to produce a bactericidal material. Ag NPs have good applicability and are easily processed because of their low melting point [10].
2. Applications for Healthcare Workers (HCWs)
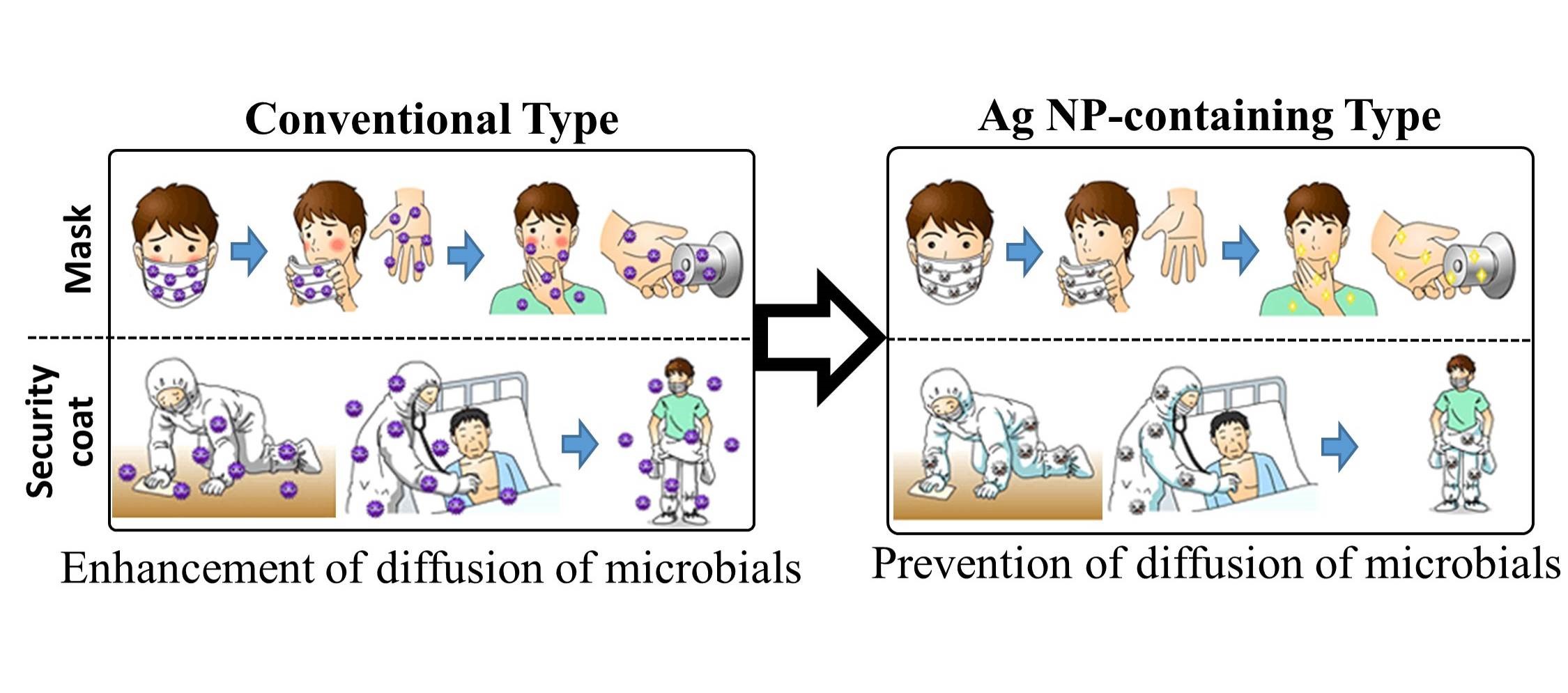
Ag NPs have a strong microbicidal activity with a broad spectrum. Furthermore, the mechanism that has been proposed is that Ag NPs yield reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to oxidative stress [11][12] in addition to the generation of free silver ions [13]. Therefore, Ag NPs will provide useful materials to protect HCWs from the risk of contact infection (Figure 1). To prevent contact infection, HCWs usually wear protective clothing. Pathogenic microbes, which are mainly generated by patients, stay alive on the surfaces of protective clothing. Therefore, especially, there is a risk of infection by incorrect contact when removing the clothing. To overcome that problem, the development of protective clothing and masks coated with Ag NPs is expected for instance.
Figure 1. The application of the Ag NPs/chitin nanofiber sheet (CNFS) complex to protect HCWs. To prevent contact infection of HCWs, we have proposed medical consumables (such as infection-protective coats, masks, and gloves) immobilized with Ag NPs.
3. Concluding Remarks
In this topic review, we briefly described the above contents extracted from our review article [14]. Applied research on Ag NPs in the biomedical field has been actively conducted. The application of Ag NPs in the medical field is fascinating, particularly concerning infectious diseases. Attempts have also been made to impart microbicidal properties to biocompatible medical devices, and Ag NPs are considered to be one of the materials that will contribute to the progress of medical science in the future. In addition, materials based on Ag NP technology are expected to contribute to research into protecting HCWs from various risks, such as contact infection during medical treatments on patients. As described, there are high expectations regarding nanoparticles’ use; however, the toxic effect of Ag NPs on living organisms and the related health problems are concerning when their concentration exceeds a certain level [15]. Current knowledge on the toxicity of Ag NPs to humans is based on in vitro tests and animal experiments, and there is no strict consensus about their toxicity. Therefore, the safety of Ag NPs when used for the human body needs further investigation.
References
- J Wesley Alexander; History of the Medical Use of Silver. Surgical Infections 2009, 10, 289-292, 10.1089/sur.2008.9941.
- Ping Gong; Huimin Li; Xiaoxiao He; Kemin Wang; Jianbing Hu; Weihong Tan; Shouchun Zhang; Xiaohai Yang; Preparation and antibacterial activity of Fe3O4@Ag nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 285604, 10.1088/0957-4484/18/28/285604.
- Sunari Peiris; John C. McMurtrie; Huai Yong Zhu; Metal nanoparticle photocatalysts: emerging processes for green organic synthesis. Catalysis Science & Technology 2016, 6, 320-338, 10.1039/c5cy02048d.
- I. Sondi; Branka Salopek-Sondi; Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2004, 275, 177-182, 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.02.012.
- Qiao Zhang; Na Li; James Goebl; Zhenda Lu; Yadong Yin; A Systematic Study of the Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates: Is Citrate a “Magic” Reagent?. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2011, 133, 18931-18939, 10.1021/ja2080345.
- Der-Chi Tien; Kuo-Hsiung Tseng; Chih-Yu Liao; Tsing-Tshih Tsung; Colloidal silver fabrication using the spark discharge system and its antimicrobial effect on Staphylococcus aureus. Medical Engineering & Physics 2008, 30, 948-952, 10.1016/j.medengphy.2007.10.007.
- Yasutaka Mori; Toshio Tagawa; Masanori Fujita; Toyohiko Kuno; Satoshi Suzuki; Takemi Matsui; Masayuki Ishihara; Simple and environmentally friendly preparation and size control of silver nanoparticles using an inhomogeneous system with silver-containing glass powder. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 2010, 13, 2799-2806, 10.1007/s11051-010-0168-z.
- Wittaya Ngeontae; Wanwisa Janrungroatsakul; Pattwat Maneewattanapinyo; Sanong Ekgasit; Wanlapa Aeungmaitrepirom; Thawatchai Tuntulani; Novel potentiometric approach in glucose biosensor using silver nanoparticles as redox marker. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2009, 137, 320-326, 10.1016/j.snb.2008.11.003.
- P. C. Lee; D. Meisel; Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. The Journal of Physical Chemistry 1982, 86, 3391-3395, 10.1021/j100214a025.
- Yong Son; Junyeob Yeo; Cheol Woo Ha; Jinhwan Lee; Sukjoon Hong; Koo Hyun Nam; Dong-Yol Yang; Seung Hwan Ko; Application of the specific thermal properties of Ag nanoparticles to high-resolution metal patterning. Thermochimica Acta 2012, 542, 52-56, 10.1016/j.tca.2012.03.004.
- Aruna Jyothi Kora; R.B. Sashidhar; Biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized with rhamnogalacturonan gum: Antibacterial activity, cytotoxicity and its mode of action. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2018, 11, 313-323, 10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.10.036.
- Jun Kinoda; Masayuki Ishihara; Hidemi Hattori; Shingo Nakamura; Koichi Fukuda; Hidetaka Yokoe; Cytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticle and Chitin-Nanofiber Sheet Composites Caused by Oxidative Stress. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 189, 10.3390/nano6100189.
- Masayuki Ishihara; Vinh Quang Nguyen; Yasutaka Mori; Shingo Nakamura; Hidemi Hattori; Adsorption of Silver Nanoparticles onto Different Surface Structures of Chitin/Chitosan and Correlations with Antimicrobial Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2015, 16, 13973-13988, 10.3390/ijms160613973.
- Shingo Nakamura; Masahiro Sato; Yoko Sato; Naoko Ando; Tomohiro Takayama; Masanori Fujita; Masayuki Ishihara; Synthesis and Application of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag NPs) for the Prevention of Infection in Healthcare Workers.. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 3620, 10.3390/ijms20153620.
- Malcolm M. Q. Xing; Liangpeng Ge; Meng Wang; Qingtao Li; Xiaojian Li; Jun Ouyang; Nanosilver particles in medical applications: synthesis, performance, and toxicity. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2399-2407, 10.2147/ijn.s55015.