Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ivana Samarzija | + 4166 word(s) | 4166 | 2021-10-12 03:56:02 | | | |
| 2 | Bruce Ren | Meta information modification | 4166 | 2021-11-03 01:37:19 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Samarzija, I. Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Metastasis. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/15642 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Samarzija I. Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Metastasis. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/15642. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Samarzija, Ivana. "Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Metastasis" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/15642 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Samarzija, I. (2021, November 02). Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Metastasis. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/15642
Samarzija, Ivana. "Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Metastasis." Encyclopedia. Web. 02 November, 2021.
Copy Citation
Liver metastasis, originating either from a primary liver or other cancer types, represent a large cancer-related burden. Therefore, studies that add to better understanding of its molecular basis are needed. Herein, the role of the Wnt signaling pathway in liver metastasis is outlined. Its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), motility, migration, metastasis formation, and other steps of the metastatic cascade are presented. Additionally, the roles of the Wnt signaling pathway in the liver metastasis formation of colorectal, breast, gastric, lung, melanoma, pancreatic, and prostate cancer are explored.
Wnt signaling pathway
liver metastasis
hepatocellular carcinoma
colorectal cancer
breast cancer
gastric cancer
lung cancer
melanoma
pancreatic cancer
prostate cancer
1. Introduction
Malignant primary and secondary liver cancers account for the vast part of cancer-related negative burdens. The most common primary liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is among the top cancers according to the incidence and mortality. It represents approximately 90% of all liver cancers and has an incidence of 850,000 new cases per year [1]. HCC usually occurs in the setting of chronic liver inflammation and is often linked to chronic viral hepatitis infection (hepatitis B or C) or exposure to toxins (e.g., alcohol). Another type of common liver cancer is intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). ICC is an aggressive epithelial malignancy of the bile ducts within the liver that is often locally advanced to metastatic disease and has an extremely poor prognosis. The recurrence of liver cancer after hepatic resection remains a major complication with no adjuvant therapies able to prevent it. Recurrence rates are as high as 70% at 5 years and are divided into either early (<2 years) or late (>2 years) [2]. Recurrence that takes place earlier is usually due to micro-metastases that remained and progressed after resection, while the late onset recurrence results from de novo tumors arising in a microenvironment that is primed for their development. Although metastasis originating from HCC and ICC can be detected in other organs, the most common site of metastasis of the primary HCC and ICC is the liver itself, which contributes to the above-mentioned recurrence scenarios.
Another frequent cancer-related liver malignancy includes metastasis from the colorectal cancer (CRC) accounting for the most common primary cancer that metastasizes to the liver. The percentage of CRC that metastasize to the liver is 30–50% [3]. Liver metastasis is a leading cause of death for CRC patients and, given the fact that CRC is among the top five cancers by incidence and mortality [4], it is evident that this type of disease progression represents large cancer-related burden. Other common primary cancers that metastasize to the liver include lung, melanoma, breast, pancreatic, and gastric cancer, each with high incidences for this type of disease progression [3].
It is evident from these introductory lines that liver metastasis, originating either from primary liver or other cancer types (Figure 1), represents a significant cancer-related complication. Therefore, efforts are being made in understanding their biology and finding the targets for the effective treatment. In this paper, the role of the Wnt signaling pathway as a driving force in liver metastasis originating from primary liver cancer and from other cancer types is explored.
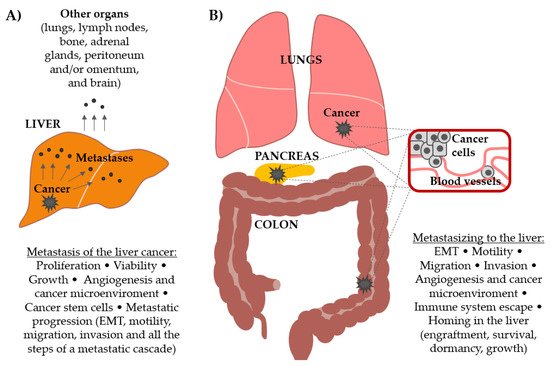
Figure 1. Involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway in (A) the progression and metastasis formation by primary liver cancer and in (B) the formation of secondary cancers in the liver (metastasis from other primary tumors, most commonly colorectal, pancreatic, melanoma, lung, breast, gastric, and prostate). Different processes that lead to metastatic outgrowth in both scenarios are delineated.
2. Wnt Signaling Pathways
Wnt signaling is initiated by Wnt-secreted glycoproteins that bind to the seven transmembrane spanning domains containing receptors from the Frizzled family. There are 19 Wnt and 10 Frizzled genes in humans. Specificity of the Wnt signaling is possibly achieved through cell-specific expression of Frizzled receptors, or additionally, through the association of Frizzled receptors with different co-receptors. Several different pathways downstream of Wnt binding to Frizzled could be initiated, like outlined below.
2.1. ‘Canonical’ Wnt Signaling Pathway
Among the Wnt signaling pathways, Wnt/β-catenin is the best studied and, therefore, denoted as the Wnt ‘canonical’ pathway. In the absence of Wnt ‘canonical’ pathway activation, cytoplasmic β-catenin is destined for a destruction in a so-called β-catenin destruction complex. This complex includes axin, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and diversin. In this complex, β-catenin becomes phosphorylated by the serine/threonine kinases casein kinase 1 (CK1) and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β). Subsequently, β-catenin is targeted for ubiquitination by the beta-transducin repeat-containing protein (β-TrCP) and is then degraded by the proteasome. Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway results in the recruitment of a cytoplasmic mediator Dishevelled (Dvl) which leads to the stabilization of a transcription co-factor β-catenin which accumulates in the cytoplasm and enters the nucleus. In the nucleus, β-catenin acts as a co-activator of the T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor-1 (TCF/LEF) transcription factors and contributes to the expression of different target genes. Among other genes with similar function, B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 protein (BCL9) has been shown to promote β-catenin’s transcriptional activity. The common Wnt/β-catenin target genes include c-Myc, cyclin D1 (CCND1), c-Jun, Axin-2, etc. In the absence of a Wnt signal, TCF/LEF family members interact with transcriptional inhibitors which serve to repress Wnt signaling. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is essential during development, cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and survival and is frequently deregulated in different pathological states [5].
2.2. ‘Non-Canonical’ Wnt Signaling Pathways
Several ‘non-canonical’ Wnt pathways have also been described. Among them, the Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) and Wnt/calcium pathways are the best understood. Common theme for both pathways is Dvl activation upon ligand binding to the receptor, but these pathways diverge further downstream. The PCP pathway is characterized by the activation of the Rho/Rac GTPases. When this pathway is activated, Wnt binding to Frizzled receptors mediates asymmetric cytoskeletal organization and the polarization of cells by influencing the actin cytoskeleton [6]. The Wnt/calcium pathway leads to the release of intracellular calcium and activates calcium-activated protein kinase C (PKC) and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CamKII). Frizzled co-receptors involved in this pathway include Knypek and receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor 2 (Ror2). The Wnt/calcium pathway is important for cell adhesion and cell movements during gastrulation [7].
For easier comprehension, Wnt signaling pathways are usually described as individual pathways, but reported crosstalk and shared components between the Wnt signaling branches suggest that Wnts act through a complex intracellular signaling network [8].
2.3. Proteins That Modulate Wnt Signaling Pathways
Some of the proteins that influence Wnt signaling include Wntless (Wls). Wls is a highly conserved transmembrane protein located in compartments of the secretory pathway that shuttles palmitoylated Wnt proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane and acts as a Wnt cargo receptor [9].
Wnt antagonists are divided into the secreted Frizzled related proteins (sFRP class) and the Dickkopf (DKK) class. sFRP class includes the sFRP family (sFRP1-5), Wnt inhibitory factor-1 (WIF-1), and Cerberus. These antagonists act by binding directly to Wnt, disturbing their ability to bind to the receptor. Members of the Dickkopf class (DKK1-4) inhibit Wnt signaling by binding to co-receptor LDL receptor related protein (LRP) 5/LRP6 of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Therefore, while sFRP class of the antagonists may inhibit both canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways, those of the DKK class specifically inhibit Wnt/β-catenin pathway [10].
3. Wnt Signaling Pathway Drives Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis
The role of Wnt signaling pathway in HCC primary growth and treatment is well described and has been reviewed elsewhere [11][12]. Briefly, most liver tumors have mutations in genes encoding key components of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This pathway has been suggested to have an important role in the pathogenesis of HCC and especially in the transition from chronic liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, to hepatocellular adenomas and further, from adenomas to HCC [12]. β-catenin activation has also been linked to immunotherapy resistance in HCC [13]. For these reasons, the Wnt/β-catenin pathway has been suggested to be a mechanism by which cells evade anti-tumor drugs and the immune system [14]. Consequently, the components of the Wnt pathway are considered to be the targets in HCC treatment [15][16].
This chapter explores another important role for Wnt signaling pathway in HCC and that is in their regional (intrahepatic) and systemic (other sites) metastatic progression.
3.1. Aberrant Expression of Wnt Signaling Pathway Components Correlates with the Ability of Liver Cancers to Metastasize
Early studies have noted that the expression of the genes that are implicated in the Wnt signaling pathway correlates with metastatic abilities of HCC. For example, nuclear accumulation combined with cytoplasmic accumulation of β-catenin tended to be associated with metastasis and vascular invasion in HCC [17]. High Wnt3a expression in HCC was related to poorly differentiated grade, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis B virus infection, higher tumor-node metastasis stage, and 5-year survival rate [18]. In addition, overexpression of Dvl2 correlated with histological grade, metastasis, and vein invasion in patients with HCC, and the knockdown of Dvl2 reduced cell migration and invasion in HepG2 cells. [19]. Further to this, the TCF4 gene expression was closely associated with intrahepatic metastasis of HCC [20] and BCL9 expression was significantly associated with microvascular invasion and intrahepatic metastasis [21]. Wls is highly expressed in advanced-stage ICC. The intensity of Wls expression was positively associated with tumor stage, tumor-node-metastasis stage, and lymphatic invasion in ICC [22]. These studies indicate that metastatic progression of HCC and ICC include higher expression of some of the components that positively regulate the Wnt signaling pathway.
3.2. Mechanisms of Action of the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Cancers Metastasis Process: The Roles in EMT, Migration, Invasion, and Metastasis Formation
Mechanistically, one of the first steps in metastatic cancer progression is epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by which epithelial cells gain migratory and invasive properties and become mesenchymal cells. It has been shown that crosstalk between β-catenin and Snail induces EMT in HCC [23]. Additionally, Wnt/β-catenin signaling enhances hypoxia-induced EMT in HCC by increasing the EMT-associated activity of HIF-1α [24]. Hypoxia, on the other hand, activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by inducing the expression of BCL9 in human HCC [25]. The importance of the Wnt pathway activation for EMT in HCC cells was further confirmed by the study that showed that TGFβ signaling in HCC EMT includes joint activation of the Sonic hedgehog and Wnt signaling pathways [26]. These studies have described that Wnt pathway is an important part of the network of signaling pathways that induce complex EMT process. To delineate components of the Wnt pathway that are involved in HCC EMT, it was shown, for example, by pharmacologic and genetic interventions, that Fzd2 expression induces EMT and enhances cell migration and invasiveness through a previously unknown, non-canonical pathway that includes Fyn and Stat3 [27][28].
Further mechanistic insights into Wnt pathways’ role in HCC metastasis came from the study that has shown that deletion of Wnt3a inhibits migration and invasion by downregulating matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) -2/-7/-9 expression via the MAPK pathway [29]. MMPs stimulate the degradation of extracellular matrix components and promote the migration of cancer cells into the surrounding tissue. The involvement of miRNAs downstream of Wnt signaling has been shown in the work that described that the β-catenin/TCF-4-LINC01278-miR-1258-Smad2/3 axis promotes HCC lung metastasis [30]. Taken together, these publications are delineating the events downstream of Wnt signaling pathway activation that induce HCC metastasis formation.
While the above studies interrogated mainly the role of Wnt/β-catenin pathway, a recent study has shown that downregulation of VANGL1 inhibits cellular invasion and only slightly affects motility in HCC cells. The VANGL1 protein is one of the core components of the Wnt/PCP pathway and this work suggests that the Wnt/PCP pathway may play a role in progression of HCC affecting cellular invasion but its role in cell motility is less prominent [31].
Since the discovery of the positive role of Wnt signaling in HCC metastasis formation, several studies have explored the expression and the ability of re-introduction of its antagonists into HCC cell lines and a consecutive role in metastasis formation. In this way, it has been shown that reconstitution of Wnt pathway antagonist, sFRP-1, suppresses tumor growth, angiogenesis, and lung metastasis in HCC cell line MHCC97-H xenografts [32]. Furthermore, the expression of another antagonist, WIF1, in HCC cell lines negatively correlated with their metastatic potential. The up-regulation of WIF1 expression inhibited the invasion of HepG2 and SMMC-7721 HCC cell lines possibly through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [33]. Although DKK1 is a well-described antagonist that suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling, studies have shown that it might promote HCC cell migration and invasion through the β-catenin/MMP7 signaling pathway [34][35][36]. However, DKK4 suppresses cell invasion in human hepatoma cells [37]. These studies remind of the complexity of the Wnt signaling pathways and multitude of players that are involved and whose specificity of action most probably depends on a cell type, as seen with DKK1 [38].
Proteins That Converge to Wnt Signaling Pathway to Influence Liver Cancer Metastasis Formation
The studies mentioned above clearly indicate a role for Wnt signaling in HCC metastasis formation. Numerous other studies that analyze the roles of single proteins in HCC metastasis formation have shown that many of these proteins converge to the Wnt signaling pathway. Such a network of proteins is briefly outlined in the Table 1, establishing firmly the role of the Wnt pathway in HCC EMT, motility, migration, invasion, and metastasis formation. Additionally, the involvement of several miRNAs and lncRNAs into signaling that leads to Wnt pathway activation has been shown. Those are either downstream of the Wnt signaling pathway like miR-25 [39] and miR-1258 [30] or converge to its activation or inhibition like, for example, miR-885-5p [40], miR-148b [41], miR-429 [42], miR-197 [43], miR-212 [44], miR-3194-3p [45], and miR-186 [46].
Table 1. Proteins that converge to the Wnt signaling pathway and in that way influence epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), motility, migration, invasion, and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The publications are listed in chronological order.
| Protein | Mechanism | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| HGF | Activates Wnt pathway by transcriptional activation of LEF1 | Facilitates in vitro tumor migration and invasion | [47] |
| CTHRC1 | Activates the PCP pathway of Wnt signaling | Promotes in vitro tumor migration and invasion and cell-matrix adhesion | [48] |
| CAV1 | Induces Wnt/β-catenin pathway through nuclear accumulation of β-catenin | Enhances EMT, invasiveness, and lung metastasis in vitro and in vivo | [49] |
| CLDN3 | Inactivates the Wnt/β-catenin-EMT axis through downregulation of GSK3B, CTNNB1, SNAI2, and CDH2 | Inhibits cell motility and invasiveness in vitro and in vivo | [50] |
| AEG-1 | Transcriptionally regulated by c-Myc and induces c-Myc by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Activates prosurvival and EMT–signaling pathways and induces in vivo lung metastasis | [51] |
| GAL1 | Promotes β-catenin nuclear translocation, TCF4/LEF1 transcriptional activity and CCND1 and c-Myc expression | Triggers EMT in vitro | [52] |
| TRIM37 | Activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Promotes in vitro and in vivo cell migration and metastasis by inducing EMT | [53] |
| HKDC1 | Downregulation represses β-catenin and c-Myc expression | Associated with aggressive phenotype | [54] |
| FRAT1 | Knockdown suppresses Wnt/β-catenin pathway by partially suppressing the expression levels of β-catenin, CCND1, and c-Myc | Knockdown inhibits in vitro hypoxia-induced EMT, migration, and invasion | [55] |
| NTR1 | NTS/NTR1 co-expression correlates with the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | NTS/NTR1 co-expression enhances EMT, invasion, and in vivo metastasis formation | [56] |
| CTNND1 | Acts, at least in part, by indirectly enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling | Promotes in vitro migration, invasion, and in vivo metastasis formation | [57] |
| PRC1 | Inhibits APC stability, and promotes β-catenin release from the APC complex | Promotes in vitro migration and invasion | [58] |
| CX32 | Its inhibition enhances Snail expression through activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling | Regulates EMT, migration, and invasion in vitro and inhibits tumor metastasis in vivo | [59] |
| FERMT2 | Activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and increases β-catenin expression (especially non-phosphorylated form) | Promotes in vitro invasion and metastasis | [60] |
| OCT4 | Upregulates LEF1, a key component of the WNT signaling pathway | Induces EMT in vitro | [61] |
| DDX39 | Activates Wnt/β-catenin pathway by increasing β-catenin levels in the nucleus | Promotes tumor growth, migration, invasion, and in vivo metastasis | [62] |
| PCL3 | Inhibits β-catenin degradation, and activates β-catenin/TCF signaling | Positively regulates the migration, invasion, and in vivo metastasis formation | [63] |
| ITGB5 | Directly interacts with β-catenin and inhibits its degradation, thus leading to Wnt/β-catenin activity | Elevated ITGB5 facilitates in vitro cell migration | [64] |
| JUB | Activates β-catenin in the nuclei | Induces in vitro EMT and migration | [65] |
| LRP16 | Its overexpression could prevent β-catenin from entering the nucleus | Attenuates cell migration, and invasion in vitro, and metastasis in vivo | [66] |
| ZIC5 | Increases the expression of β-catenin and CCND1 and promotes β-catenin to enter the nucleus | Promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo | [67] |
| SOX9 | SOX9-AS1/miR-5590-3p/SOX9 positive feedback acts through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Aggravates HCC progression and metastasis in vitro and in vivo | [68] |
| AKIP1 | Interacts with and sustains β-catenin in the nucleus by blocking its interaction with APC; enhances phosphorylation of β-catenin | Promotes invasion and increases intrahepatic and lung metastasis in vivo | [69] |
| FBXO17 | Its silencing might function through downregulating the expression of proteins in Wnt/β-catenin pathway | In vitro metastasis ability in the anti-FBXO17 group is decreased | [70] |
| FOXG1 | Activates Wnt signaling through forming TCF4/β-catenin/FOXG1 complex | Promotes EMT and aggressiveness in vitro and enhances metastasis in vivo | [71] |
| GATA5 | Co-localizes with β-catenin in the cytoplasm, preventing β-catenin from entering the nucleus | Inhibits in vitro cell growth, colony formation, migration, and invasion | [72] |
| GRP78 | Activates the Wnt/HOXB9 pathway by chaperoning LRP6 | Promotes in vitro and in vivo invasion and metastasis | [73] |
| HEG1 | Promotes β-catenin expression and maintains its stability, leading to its accumulation and nuclear translocation | Promotes EMT and in vitro and in vivo invasion and metastasis | [74] |
| NDRG3 | Promotes nuclear translocation of β-catenin | Enhances metastasis and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo | [75] |
| MSI1 | Activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (downregulation reduces the expression of phospho-β-catenin and CCND1 and elevates the protein expression of DKK1 and APC) | Affects in vitro cancer cell viability, migration, and invasiveness | [76] |
| p62/IMP2 | Activates Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Promotes in vitro EMT and migration | [77] |
| RICH2 | Overexpression positively correlates with the expression of WNT5a and inversely correlates with β-catenin | Inhibits formation of filopodia and invasion and proliferation in vitro | [78] |
| AQP9 | Overexpression reduces the levels of DVL2, GSK-3β, CCND1, and β-catenin | Overexpression suppresses in vitro migration, invasion, and EMT | [79] |
| ARHGEF11 | Induces β-catenin nuclear translocation and upregulates ZEB1 | Promotes EMT and migration in vitro | [80] |
| GAL3 | Activates the PI3K-Akt-GSK-3β-β-catenin signaling cascade | Regulates in vitro angiogenesis and EMT and favors tumor lung metastasis in vivo | [81] |
| KIF2C | Direct target of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway that mediates the crosstalk between Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling | Promotes migration, invasion, and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo | [82] |
| KIF18B | The knockdown downregulates the expression of c-Myc, CCND1, β-catenin, and p-GSK-3β | Knockdown might suppressproliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro | [83] |
| MTDH | Its overexpression induces PRMT5 translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and translocation of β-catenin from the cytoplasm to the nucleus which upregulates WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway | PRMT5 and β-catenin play a pivotal role in MTDH-mediated HCC in vivo metastasis | [84] |
| NRF1 | Enhances ubiquitination of β-catenin for targeting proteasomal degradation | Promotes invasion and metastasis to the lung and liver in in vivo models | [85] |
| FXR | Decreases expression of β-catenin target genes and reduces nuclear translocation of β-catenin proteins in vitro and in vivo | Suppresses migration and invasion in vitro and inhibits local invasion and lung metastasis in vivo | [86] |
| USP1 | Its knockout impairs expression of Wnt target genes | Frequently upregulated in liver circulating tumor cells and expression correlates with metastasis | [87] |
| ATE1 | Accelerates degradation of β-catenin and inhibits Wnt signaling by regulating turnover of RGS5 | Knockdown promotes cancer growth, migration, and disease progression in vitro and in vivo | [88] |
| PGC1α | Inhibits Warburg effect by PPARγ–dependent WNT/β-catenin/PDK1 axis | Suppresses in vitro and in vivo metastasis | [89] |
| RAD54B | Increases nuclear β-catenin and up-regulates Wnt/β-catenin downstream target genes (c-Myc, CCND1, MMP7, CD44, VEGF, c-Jun) | Increases in vitro cell viability and motility, and in vivo intrahepatic metastasis | [90] |
| ZEB1 | Could activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by upregulating the protein expression levels of β-catenin, c-Myc, and CCND1 | Promotes in vitro cell proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis | [91] |
3.3. Wnt Signaling Pathway in Liver Cancer Stem Cell and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Biology
Besides its roles in the above-mentioned processes that endow cancer cells with increased metastatic abilities, the Wnt signaling pathway is also active and contributes to the biology of other cells that are implicated in the metastatic outgrowth. For example, metastatic cancer spread is potentiated by cancer stem cells (CSC) which possess qualities that are characteristic of embryonic or adult stem cells. Those include self-renewal, differentiation, dormancy, and cellular plasticity which enables their adaptation to new environments. These abilities are needed for the successful establishment of metastasis [92]. The roles of Wnt signaling in CSCs biology is well described and has been a subject of several reviews [93][94]. In HCC, it was shown that deacetylation of β-catenin by SIRT1 increases its protein stability and regulates self-renewal and oncogenesis of liver CSCs through promoting the transcription of Nanog [95]. Additionally, a small molecule inhibitor that inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling targets and depletes CD133+/ALDH+ liver CSCs, which decreases their tumorigenicity in vitro and in vivo [96]. Sox9 is a member of the Sox proteins that are involved in human development by regulating lineage restriction, cell differentiation, and stem cell properties. It was shown that Sox9 confers stemness properties in HCC and suppresses HCC cell migration, invasion, and in vivo lung metastasis through Frizzled-7 mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling [97]. In the mentioned publication, Frizzled-7 was identified to be the direct transcriptional target of Sox9. A further paper confirmed the role of the above-mentioned signaling axis that includes Sox9 and Wnt/β-catenin in the self-renewal of liver CSCs [98]. Additionally, several miRNAs and lncRNAs have been shown to influence liver CSCs through the Wnt pathway [99]. These include miR-612 [100], miR-452 [101], miR-5188 [102], lncAPC [103], lncSAMMSON [104], and lncFZD6 [105].
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multipotent adult stem cells that are present in multiple tissues. MSCs promote hepatocarcinogenesis and metastasis formation via signaling that includes activated Wnt/β-catenin pathway and EMT [106]. Further to this, irradiated mesenchymal stem cells have been shown to increase the ratio of CD133+ HCC cells and support stemness maintenance of HCC stem cells through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This was reflected when liver CSCs were co-cultured with irradiated MSCs, which resulted in increased colony and tumor formation abilities via increased activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [107]. In another study, it was also shown that overexpression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4a) in human MSCs inhibits HCC progression by reducing hepatoma cell growth, migration, and invasion through downregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [108].
3.4. Wnt Signaling Pathway Affects the Communication between Different Components of the Liver Cancer Microenvironment That Promote Metastasis
The activation of Wnt signaling in other components of a liver cancer microenvironment that promote metastasis has been documented. These include crosstalk between hepatic tumor cells and macrophages, which takes place via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. This communication promotes M2-like macrophage polarization and tumor growth, migration, metastasis, and immunosuppression in HCC [109]. To confirm the role of Wnt signaling in this process, it was shown that lncRNA LINC00662 promotes M2 macrophage polarization and HCC progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [110]. Another component of a liver cancer microenvironment, hepatic stellate cells, have been shown to promote EMT, proliferation, invasiveness, and metastatic abilities of HCC in vitro and in vivo through microRNA-1246-RORα-Wnt/β-catenin axis [111].
Angiogenesis is another important prerequisite for cancer cells to grow and metastasize. Wnt signaling is involved in vasculature formation [112] and in endothelial cell proliferation and migration [113]. Recently, angiocrine Tie-Wnt signaling axis in the liver controlling hepatocyte function during liver regeneration was described [114]. Moreover, angiocrine Wnt signaling controls liver growth and development of metabolic liver zonation in mice [115]. In HCC, miR-1301 was shown to inhibit angiogenesis, cell migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo by decreasing Wnt/β-catenin signaling through downregulation of BCL9, β-catenin, and VEGF expression in tumor cells. [116]. These papers add to the evidence that show that Wnt signaling affects many of the processes required for metastatic expansion, including vasculature formation.
3.5. Wnt Signaling Pathway Is Activated in Residual HCC Cells after Incomplete Radiofrequency Ablation
Some therapeutic approaches in HCC, like incomplete radiofrequency ablation (RFA), leave residual cancer cells behind. It was shown that incomplete RFA enhances invasiveness and metastasis of residual HCC cells by stimulating EMT-like phenotype changes through activation of the β-catenin signaling in HCCLM3 cells [117]. Another study has shown that insufficient radiofrequency ablation promotes the metastasis of residual hepatocellular carcinoma cells via upregulating flotillin proteins which altered the EMT status and metastatic potential of heat-treated HCCLM3 cells by activating the Akt/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [118].
Taken together, the data presented in Section 3 confirm that the expression of the components of the Wnt pathway is de-regulated during HCC metastatic progression. Further, the Wnt pathway has been shown to strongly influence HCC EMT, motility, migration, invasion, and metastasis. It has a key role in CSCs, too, as well as in the biology of other components of the HCC microenvironment that potentiate the metastatic spread. Finally, after the treatment of HCC, the residual cancer cells, which are usually more aggressive and have higher metastatic abilities, show the activation of the Wnt pathway. Since the treatment options in advanced liver cancer are limited, the data presented here point to the possibility that targeting Wnt signaling pathways in liver cancers could alleviate metastasis related complications.
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 14, 16018.
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6.
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Brodt, P.; Clavien, P.A.; Muschel, R.J.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Endo, I.; Parks, R.W.; Doyle, M.; de Santibañes, E.; Pawlik, T.M. Liver metastases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 27.
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249.
- Clevers, H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006, 127, 469–480.
- Yang, Y.; Mlodzik, M. Wnt-frizzled/planar cell polarity signaling: Cellular orientation by facing the wind (Wnt). Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 13, 623–646.
- De, A. Wnt/Ca 2 signaling pathway: A brief overview. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2011, 43, 745–756.
- Kestler, H.A.; Kühl, M. From individual Wnt pathways towards a Wnt signalling network. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 1333–1347.
- Das, S.; Yu, S.; Sakamori, R.; Stypulkowski, E.; Gao, N. Wntless in Wnt secretion: Molecular, cellular and genetic aspects. Front. Biol. 2012, 7, 587–593.
- Malinauskas, T.; Jones, E.Y. Extracellular modulators of Wnt signalling. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 29, 77–84.
- He, S.; Tang, S. WNT/β-catenin signaling in the development of liver cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110851.
- Khalaf, A.M.; Fuentes, D.; Morshid, A.I.; Burke, M.R.; Kaseb, A.O.; Hassan, M.; Hazle, J.D.; Elsayes, K.M. Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma, pathogenesis, and clinical significance. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2018, 27, 61–73.
- Kwee, S.A.; Tiirikainen, M. Beta-catenin activation and immunotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms and biomarkers. Hepatoma Res. 2021, 7, 8.
- Martin-Orozco, E.; Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Ortiz-Parra, I.; Ayala-San Nicolas, M. WNT signaling in tumors: The way to evade drugs and immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2854.
- Vilchez, V.; Turcios, L.; Marti, F.; Gedaly, R. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 823–832.
- Chen, J.; Rajasekaran, M.; Hui, K.M. Atypical regulators of Wnt/β-catenin signaling as potential therapeutic targets in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1142–1149.
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, R.; Shen, J.; Liang, Y.; Ma, R.; Lin, H.; Liang, X.; Yu, H.; Cai, X. Cytoplasmic and/or nuclear expression of β-catenin correlate with poor prognosis and unfavorable clinicopathological factors in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111885.
- Pan, L.H.; Yao, M.; Cai, Y.; Gu, J.J.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, L.; Yao, D.F. Oncogenic Wnt3a expression as an estimable prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3829–3836.
- Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, B.; Ni, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Overexpression of dishevelled 2 is involved in tumor metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 19, 1507–1517.
- Jiang, Y.; Zhou, X.D.; Liu, Y.K.; Wu, X.; Huang, X.W. Association of hTcf-4 gene expression and mutation with clinicopathological characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 804–807.
- Hyeon, J.; Ahn, S.; Lee, J.J.; Song, D.H.; Park, C.K. Prognostic significance of bcl9 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J. Pathol. 2013, 47, 130–136.
- Shi, Y.; Bai, J.; Guo, S.; Wang, J. Wntless is highly expressed in advanced-stage intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2018, 244, 195–199.
- Zucchini-Pascal, N.; Peyre, L.; Rahmani, R. Crosstalk between beta-catenin and snail in the induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocarcinoma: Role of the ERK1/2 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20768–20792.
- Zhang, Q.; Bai, X.; Chen, W.; Ma, T.; Hu, Q.; Liang, C.; Xie, S.; Chen, C.; Hu, L.; Xu, S.; et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling enhances hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via crosstalk with hif-1α signaling. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 962–973.
- Xu, W.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, M.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; He, S.; Luo, X.; Huang, W.; Chen, T.; Yan, W.; et al. Hypoxia activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by regulating the expression of BCL9 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40446.
- Steinway, S.N.; Zanudo, J.G.T.; Ding, W.; Rountree, C.B.; Feith, D.J.; Loughran, T.P.; Albert, R. Network modeling of TGFβ signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition reveals joint sonic hedgehog and Wnt pathway activation. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5963–5977.
- Asano, T.; Yamada, S.; Fuchs, B.C.; Takami, H.; Hayashi, M.; Sugimoto, H.; Fujii, T.; Tanabe, K.K.; Kodera, Y. Clinical implication of Frizzled 2 expression and its association with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1647–1654.
- Gujral, T.S.; Chan, M.; Peshkin, L.; Sorger, P.K.; Kirschner, M.W.; Macbeath, G. A noncanonical frizzled2 pathway regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell 2014, 159, 844–856.
- Lu, C.; He, Y.; Duan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, J.; Liao, W.; Huang, X.; Zhu, R.; Li, M. Expression of Wnt3a in hepatocellular carcinoma and its effects on cell cycle and metastasis. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 159, 844–856.
- Huang, W.J.; Tian, X.P.; Bi, S.X.; Zhang, S.R.; He, T.S.; Song, L.Y.; Yun, J.P.; Zhou, Z.G.; Yu, R.M.; Li, M. The β-catenin/TCF-4-LINC01278-miR-1258-Smad2/3 axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4538–4550.
- Cetin, G.O.; Toylu, A.; Atabey, N.; Sercan, Z.; Sakizli, M. Downregulation of VANGL1 inhibits cellular invasion rather than cell motility in hepatocellular carcinoma cells without stimulation. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 2015, 19, 283–287.
- Jiang, G.X.; Liu, W.; Cui, Y.F.; Zhong, X.Y.; Tai, S.; Wang, Z.D.; Shi, Y.G.; Li, C.L.; Zhao, S.Y. Reconstitution of secreted frizzled-related protein 1 suppresses tumor growth and lung metastasis in an orthotopic model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 2838–2843.
- Song, G.; Cao, H.X.; Yao, S.X.; Li, C.T. Abnormal expression of WIF1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its regulating effect on invasion and metastasis factors of TIMP-3 and caveolin-1 of hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 958–963.
- Chen, L.; Li, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.J.; Xie, S.Q. DKK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through β-catenin/MMP7 signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 157.
- Fezza, M.; Moussa, M.; Aoun, R.; Haber, R.; Hilal, G. DKK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma inflammation, migration and invasion: Implication of TGF-β1. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223252.
- Tao, Y.M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.L. Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) promotes invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2013, 45, 251–257.
- Liao, C.H.; Yeh, C.T.; Huang, Y.H.; Wu, S.M.; Chi, H.C.; Tsai, M.M.; Tsai, C.Y.; Liao, C.J.; Tseng, Y.H.; Lin, Y.H.; et al. Dickkopf 4 positively regulated by the thyroid hormone receptor suppresses cell invasion in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology 2012, 55, 910–920.
- Li, J.; Gong, W.; Li, X.; Wan, R.; Mo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, P.; Hu, Z.; Lai, Z.; Lu, X.; et al. Recent Progress of Wnt Pathway Inhibitor Dickkopf-1 in Liver Cancer. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 5192–5206.
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Su, Z.; Fei, H.; Liu, X.; Pan, Q. miR-25 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth, migration and invasion by inhibiting RhoGDI1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 36231–36244.
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Shen, W.; Zhang, C.; Mou, W.; Luo, J.; Yan, H.; Sun, P.; Luo, Y.; et al. miR-885-5p suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75038–75051.
- Zhang, J.G.; Shi, Y.; Hong, D.F.; Song, M.; Huang, D.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhao, G. MiR-148b suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting WNT1/β-catenin pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8087.
- Tang, J.; Li, L.; Huang, W.; Sui, C.; Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; Hou, G.; Chen, X.; Fu, J.; Yuan, S.; et al. MiR-429 increases the metastatic capability of HCC via regulating classic Wnt pathway rather than epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2015, 364, 33–43.
- Hu, Z.; Wang, P.; Lin, J.; Zheng, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, G.; Chen, D.; Xie, J.; Gao, Z.; Peng, L.; et al. MicroRNA-197 promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 470–486.
- Jia, P.; Wei, G.; Zhou, C.; Gao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, X. Upregulation of MiR-212 inhibits migration and tumorigenicity and inactivates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 533034618765221.
- Yao, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-3194-3p inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by decreasing Wnt/β-catenin signaling through targeting BCL9. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3885–3895.
- Wang, H.; Ou, J.; Jian, Z.; Ou, Y. miR-186 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and mobility via targeting MCRS1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 23135–23145.
- Huang, F.I.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, C.N.; Yuan, R.H.; Jeng, Y.M. Hepatocyte growth factor activates Wnt pathway by transcriptional activation of LEF1 to facilitate tumor invasion. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1142–1148.
- Chen, Y.L.; Wang, T.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Yuan, R.H.; Jeng, Y.M. Overexpression of CTHRC1 in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes tumor invasion and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70324.
- Yu, H.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, F.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Yang, P. CAV1 promotes HCC cell progression and metastasis through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106451.
- Jiang, L.; Yang, Y.D.; Fu, L.; Xu, W.; Liu, D.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Guan, X.Y.; Wu, B.; et al. CLDN3 inhibits cancer aggressiveness via Wnt-EMT signaling and is a potential prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7663–7676.
- Srivastava, J.; Siddiq, A.; Gredler, R.; Shen, X.N.; Rajasekaran, D.; Robertson, C.L.; Subler, M.A.; Windle, J.J.; Dumur, C.I.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 and c-Myc cooperate to promote hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 915–929.
- Bacigalupo, M.L.; Manzi, M.; Espelt, M.V.; Gentilini, L.D.; Compagno, D.; Laderach, D.J.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Troncoso, M.F. Galectin-1 Triggers epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 1298–1309.
- Jiang, J.; Yu, C.; Chen, M.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. Over-expression of TRIM37 promotes cell migration and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 1120–1127.
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, D.; Peng, B.; Zhou, Q. High expression of hexokinase domain containing 1 is associated with poor prognosis and aggressive phenotype in hepatocarcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 673–679.
- Fan, W.H.; Du, F.J.; Liu, X.J.; Chen, N. Knockdown of FRAT1 inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelialto-mesenchymal transition via suppression of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2999–3004.
- Ye, Y.; Long, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Li, H.; Wei, F.; Yu, W.; Ren, X.; Yu, J. NTS/NTR1 co-expression enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor metastasis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 70303–70322.
- Tang, B.; Tang, F.; Wang, Z.; Qi, G.; Liang, X.; Li, B.; Yuan, S.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; He, S. Overexpression of CTNND1 in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes carcinous characters through activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 82.
- Chen, J.; Rajasekaran, M.; Xia, H.; Zhang, X.; Kong, S.N.; Sekar, K.; Seshachalam, V.P.; Deivasigamani, A.; Goh, B.K.P.; Ooi, L.L.; et al. The microtubule-associated protein PRC1 promotes early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Gut 2016, 65, 1522–1534.
- Yan, Y.; Na, Z.; Zhu, J.; Hong, X.T.; Liu, H.; Ou, Y.R.; Su, F.; Rui, W.; Li, Y.M.; Wu, Q. Downregulated connexin32 promotes EMT through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting Snail expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1977–1988.
- Lin, J.; Lin, W.; Ye, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Zang, S.; Huang, A. Kindlin-2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis by increasing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 134.
- Sun, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, S.; Guo, K.; Liu, Y. Oct4 induces EMT through LEF1/β-catenin dependent WNT signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2599–2606.
- Zhang, T.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, B.; Zou, Y.; Li, H. DDX39 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway article. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 675.
- Cai, Z.; Qian, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.; Ma, N.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Ren, X.X.; Shang, Y.R.; Wang, J.J.; Li, J.J.; et al. hPCL3s promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by activating b-catenin signaling. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2536–2549.
- Lin, Z.; He, R.; Luo, H.; Lu, C.; Ning, Z.; Wu, Y.; Han, C.; Tan, G.; Wang, Z. Integrin-β5, a MIR-185-targeted gene, promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis by regulating β-catenin stability. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 17.
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Ding, Y. JUB induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 1374–1382.
- Shao, L.; Jing, W.; Wang, L.; Pan, F.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Hu, M.; Fan, K. LRP16 prevents hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 96, 547–558.
- Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Sun, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z. ZIC5 facilitates the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma through activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2173–2179.
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; Hou, B.; Wang, Y.; Deng, D.; Fu, Z.; Xu, Z. A SOX9-AS1/miR-5590-3p/SOX9 positive feedback loop drives tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2194–2210.
- Cui, Y.; Wu, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L.; Ren, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; et al. AKIP1 promotes early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma through activating the Wnt/β-catenin/CBP signaling pathway. Oncogene 2019, 38, 5516–5529.
- Liu, F.H.; Cui, Y.P.; He, Y.K.; Shu, R.H. FBXO17 promotes malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8265–8273.
- Zheng, X.; Lin, J.; Wu, H.; Mo, Z.; Lian, Y.; Wang, P.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Peng, L.; Xie, C. Forkhead box (FOX) G1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating Wnt signal through forming T-cell factor-4/Beta-catenin/FOXG1 complex. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 475.
- Feng, H.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, K.; Lin, B.; et al. GATA5 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells malignant behaviours by blocking expression of reprogramming genes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2536–2548.
- Xiong, H.; Xiao, H.; Luo, C.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Zou, S.; Guan, J.; Yang, D.; Wang, K. GRP78 activates the Wnt/HOXB9 pathway to promote invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by chaperoning LRP6. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 383, 111493.
- Zhao, Y.R.; Wang, J.L.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.M.; Sun, B.; Yang, L.Y. HEG1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion, metastasis, and EMT by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1645–1662.
- Shi, J.K.; Zheng, H.Z.; Yuan, L.Y. High NDRG3 expression facilitates HCC metastasis by promoting nuclear translocation of β-catenin. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 451–456.
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, B. Upregulation of musashi1 increases malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and predicts a poor prognosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 230.
- Xing, M.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shi, J.; Qin, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Francia, G.; Zhang, J.Y. Overexpression of p62/IMP2 can promote cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma via activation of the wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancers 2020, 12, 7.
- Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Gong, L.; Zhu, S.; Tian, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, J.; Lan, M.; Li, Y.; et al. RICH2, a potential tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2019, 24, 1363–1376.
- Liao, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Gan, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Mei, Z. Aquaporin 9 inhibits growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 1527–1544.
- Du, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Lan, T.; Li, W.; Yuan, K.; Zeng, Y. ARHGEF11 promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma through activation of β-catenin pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 20235–20253.
- Song, M.; Pan, Q.; Yang, J.; He, J.; Zeng, J.; Cheng, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, C.; et al. Galectin-3 favours tumour metastasis via the activation of β-catenin signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1521–1534.
- Wei, S.; Dai, M.; Zhang, C.; Teng, K.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Feng, Z.; Kang, T.; Guan, X.; et al. KIF2C: A novel link between Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Protein Cell 2020, 12, 788–809.
- Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Rong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y. KIF18B promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through activating Wnt/β-catenin-signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6507–6514.
- Zhu, K.; Peng, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhan, H.; Yang, L.; Gao, Q.; Jia, H.; Luo, R.; Dai, Z.; Tang, Z.; et al. Metadherin-PRMT5 complex enhances the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the WNT-ß-catenin signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 130–138.
- Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Xiang, Y.; Ru, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y. Nrf1 is endowed with a dominant tumor-repressing effect onto the Wnt/β-catenin-dependent and Wnt/β-catenin-independent signaling networks in the human liver cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 5138539.
- Qianqian, L.I.; Ningbo, L.I.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, X.; Jie, L.I.; Hongying, S.U.; Meiqin, G.A.O.; Huang, X. Nuclear receptor FXR impairs SK-Hep-1 cell migration and invasion by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 161.
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, P.; Cheng, J.; Guo, W.; Ya, C.; Fan, J.; et al. USP1 Maintains the survival of liver circulating tumor cells by deubiquitinating and stabilizing TBLR1. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 554809.
- Xu, C.; Li, Y.-M.; Sun, B.; Zhong, F.-J.; Yang, L.-Y. ATE1 Inhibits liver cancer progression through rgs5-mediated suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 1441–1453.
- Zuo, Q.; He, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Jin, G.; Jin, H.; Cheng, Z.; Tao, X.; Yu, C.; Li, B.; et al. PPARγ coactivator-1α suppresses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting Warburg effect by PPARγ–dependent WNT/β-catenin/pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 1 axis. Hepatology 2021, 73, 644–660.
- Feng, S.; Liu, J.; Hailiang, L.; Wen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, G.; Gao, P.; Zeng, X. Amplification of RAD54B promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101124.
- Li, L.Y.; Yang, J.F.; Rong, F.; Luo, Z.P.; Hu, S.; Fang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yao, R.; Kong, W.H.; Feng, X.W.; et al. ZEB1 serves an oncogenic role in the tumourigenesis of HCC by promoting cell proliferation, migration, and inhibiting apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1676–1689.
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Savic, D.; Dudás, J.; Kvitsaridze, I.; Skvortsov, S.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I.I. Cancer stem cells and their unique role in metastatic spread. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 148–156.
- de Sousa e Melo, F.; Vermeulen, L. Wnt signaling in cancer stem cell biology. Cancers 2016, 8, 60.
- Kahn, M. Wnt signaling in stem cells and cancer stem cells: A tale of two coactivators. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 153, 209–244.
- Chen, X.; Huan, H.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, C. Deacetylation of β-catenin by SIRT1 regulates self-renewal and oncogenesis of liver cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2019, 463, 1–10.
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, K.K.; Choi, Y.K.; Nam, J.S.; Hong, I.S. CWP232228 targets liver cancer stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling: A novel therapeutic approach for liver cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20395–20409.
- Leung, C.O.N.; Mak, W.N.; Kai, A.K.L.; Chan, K.S.; Lee, T.K.W.; Ng, I.O.L.; Lo, R.C.L. Sox9 confers stemness properties in hepatocellular carcinoma through Frizzled-7 mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29371–29386.
- Deng, Y.; Li, M.; Zhuo, M.; Guo, P.; Chen, Q.; Mo, P.; Li, W.; Yu, C. Histone demethylase JMJD2D promotes the self-renewal of liver cancer stem-like cells by enhancing EpCAM and Sox9 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100121.
- Lou, W.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhong, G.; Ding, B.; Xu, L. MicroRNA regulation of liver cancer stem cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1126–1141.
- Tang, J.; Tao, Z.H.; Wen, D.; Wan, J.L.; Liu, D.L.; Zhang, S.; Cui, J.F.; Sun, H.C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; et al. MiR-612 suppresses the stemness of liver cancer via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 447, 210–215.
- Zheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xie, H.; Jiang, C.; Lin, B.; Chen, T.; Xing, C.; Liu, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-452 promotes stem-like cells of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting sox7 involving wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28000–28012.
- Lin, X.; Zuo, S.; Luo, R.; Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. HBX-induced miR-5188 impairs FOXO1 to stimulate β-catenin nuclear translocation and promotes tumor stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7583–7598.
- Fu, X.; Lin, J.; Qin, F.; Yang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q. LncAPC drives Wnt/β-catenin activation and liver TIC self-renewal through EZH2 mediated APC transcriptional inhibition. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 408–418.
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Dai, H.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. SAMMSON drives the self-renewal of liver tumor initiating cells through EZH2-dependent Wnt/β-catenin activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103785–103796.
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, P.; Weng, H. LncFZD6 initiates Wnt/β-catenin and liver TIC self-renewal through BRG1-mediated FZD6 transcriptional activation. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3098–3112.
- Yan, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Wu, S.; Qian, J.; Hao, Y.; Yan, F.; Zhu, P.; Wu, J.; Huang, G.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatocarcinogenesis via lncRNA–MUF interaction with ANXA2 and miR-34a. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6704–6716.
- Hou, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhu, P.; Chang, J.; Du, Y.; Shen, W. Irradiated mesenchymal stem cells support stemness maintenance of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 93.
- Wu, N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, H.T.; Li, D.W.; Dai, H.J.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Xia, Q.; Bian, J.M.; et al. Overexpression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α in human mesenchymal stem cells suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma development through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway downregulation. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 558–565.
- Yang, Y.; Ye, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.L.; Gao, C.C.; Han, H.; Liu, W.C.; Qin, H.Y. Crosstalk between hepatic tumor cells and macrophages via Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes M2-like macrophage polarization and reinforces tumor malignant behaviors. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 793.
- Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Niu, M.; Gao, S.; Qin, T.; Bao, D. Long noncoding RNA LINC00662 promotes M2 macrophage polarization and hepatocellular carcinoma progression via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 462–483.
- Huang, J.L.; Fu, Y.P.; Gan, W.; Liu, G.; Zhou, P.Y.; Zhou, C.; Sun, B.Y.; Guan, R.Y.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Hepatic stellate cells promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through microRNA-1246-RORα-Wnt/β-Catenin axis. Cancer Lett. 2020, 476, 140–151.
- Olsen, J.J.; Pohl, S.; Öther, G.; Deshmukh, A.; Visweswaran, M.; Ward, N.C.; Arfuso, F.; Agostino, M.; Dharmarajan, A. The role of Wnt signalling in angiogenesis. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2017, 38, 131–142.
- Samarzija, I.; Sini, P.; Schlange, T.; MacDonald, G.; Hynes, N.E. Wnt3a regulates proliferation and migration of HUVEC via canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 449–454.
- Inverso, D.; Shi, J.; Lee, K.H.; Jakab, M.; Ben-Moshe, S.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Schneider, M.; Wang, G.; Komeili, M.; Vélez, P.A.; et al. A spatial vascular transcriptomic, proteomic, and phosphoproteomic atlas unveils an angiocrine Tie–Wnt signaling axis in the liver. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1677–1693.
- Leibing, T.; Géraud, C.; Augustin, I.; Boutros, M.; Augustin, H.G.; Okun, J.G.; Langhans, C.D.; Zierow, J.; Wohlfeil, S.A.; Olsavszky, V.; et al. Angiocrine Wnt signaling controls liver growth and metabolic maturation in mice. Hepatology 2018, 68, 707–722.
- Yang, C.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, F.; Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; Rao, J.; Wang, X. Mir-1301 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis by decreasing wnt/β-catenin signaling through targeting bcl9. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2999.
- Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Chai, Z.T.; Zhu, Z.M.; Zhu, X.D.; Ma, D.N.; Zhang, Q.B.; Zhao, Y.M.; Wang, M.; Ao, J.Y.; et al. Incomplete radiofrequency ablation enhances invasiveness and metastasis of residual cancer of hepatocellular carcinoma cell HCCLM3 via activating β-catenin signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115949.
- Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Qin, C.; Ma, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wang, L. Insufficient radiofrequency ablation promotes the metastasis of residual hepatocellular carcinoma cells via upregulating flotillin proteins. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 895–907.
More
Information
Subjects:
Biochemistry & Molecular Biology
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
777
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
03 Nov 2021
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




