
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Edward Quadros | + 2878 word(s) | 2878 | 2021-07-26 03:34:13 | | | |
| 2 | Bruce Ren | -21 word(s) | 2857 | 2021-08-05 03:06:38 | | |
Video Upload Options
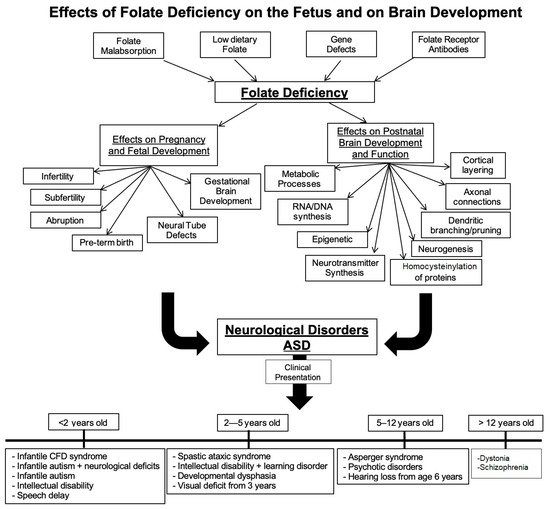
Folate deficiency and folate receptor autoimmune disorder are major contributors to infertility, pregnancy related complications and abnormal fetal development including structural and functional abnormalities of the brain. Food fortification and prenatal folic acid supplementation has reduced the incidence of neural tube defect (NTD) pregnancies but is unlikely to prevent pregnancy-related complications in the presence of folate receptor autoantibodies (FRAb). In pregnancy, these autoantibodies can block folate transport to the fetus and in young children, folate transport to the brain. These antibodies are prevalent in neural tube defect pregnancies and in developmental disorders such as cerebral folate deficiency (CFD) syndrome and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). In the latter conditions, folinic acid treatment has shown clinical improvement in some of the core ASD deficits. Early testing for folate receptor autoantibodies and intervention is likely to result in a positive outcome
1. Background
2. Folate Requirements during Pregnancy
3. Folate and Fetal Brain Development
4. Folate and Neonatal Brain Development
5. Folate Receptors: Expression and Function
| Protein | Gene | Chromosome | GPI Anchor? | Localization | Cofactors? | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRα | FOLR1 | 11q13.3 | Yes | Liver, kidney, uterus, placenta, choroid plexus, retinal pigment epithelium | LRP2 | [33][35][36][37][38] |
| FRβ | FOLR2 | 11q13.4 | Yes | Placenta, spleen, bone marrow, thymus, macrophages | NA | [33][35][36][37][38][39] |
| FRγ | FOLR3 | 11q13.4 | NA | Secretory granules of neutrophil granulocytes | NA | [33][35][36][37][38][39] |
| FRδ | FOLR4 | 11q14 | Yes | Oocytes | NA | [33][35][36][37][38][39] |
| RFC | SLC19A1 | 21q22.3 | No | Liver, kidney, placenta, choroid plexus, intestinal tract | Vitamin D, thiamine pyrophosphate | [34][40] |
| PCFT | SLC46A1 | 17q11.2 | No | Liver, kidney, choroid plexus, placenta, intestinal epithelium, human tumors | Proton gradient | [34][40] |
6. FRα Role in Maternofetal Transport of Folate
7. FRα Role in Folate Transport to the Brain
8. Folate Receptor Autoantibodies: Their Role in Disrupting Folate Transport
9. Pathologic Consequences of Folate Receptor Antibodies
10. Diagnosis of Folate Receptor Autoimmune Disorder
11. Assay for Blocking Antibodies
12. Assay for Binding Antibody
References
- Rucker, R.B.; Zempleni, J.; Suttie, J.W.; McCormick, D.B. Handbook of Vitamins, 4th ed.; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; Available online: https://books.google.com/books?id=AasGngEACAAJ (accessed on 4 November 2019).
- Mikkelsen, K.; Apostolopoulos, V. Vitamin B12, Folic Acid, and the Immune System. In Nutrition and Immunity; Mahmoudi, M., Rezaei, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019.
- Scott, J.M. Folate and vitamin B12. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1999, 58, 441–448.
- Ramaekers, V.T.; Blau, N. Cerebral folate deficiency. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2004, 46, 843–851.
- Cario, H.; Bode, H.; Debatin, K.M.; Opladen, T.; Schwarz, K. Congenital null mutations of the FOLR1 gene: A progressive neurologic disease and its treatment. Neurology 2009, 73, 2127–2129.
- Pérez-Dueñas, B.; Toma, C.; Ormazábal, A.; Muchart, J.; Sanmartí, F.; Bombau, G.; Serrano, M.; García-Cazorla, A.; Cormand, B.; Artuch, R. Progressive ataxia and myoclonic epilepsy in a patient with a homozygous mutation in the FOLR1 gene. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 795–802.
- Delmelle, F.; Thöny, B.; Clapuyt, P.; Blau, N.; Nassogne, M.C. Neurological improvement following intravenous high-dose folinic acid for cerebral folate transporter deficiency caused by FOLR-1 mutation. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 709–713.
- Ramaekers, V.T.; Rothenberg, S.P.; Sequeira, J.M.; Opladen, T.; Blau, N.; Quadros, E.V.; Selhub, J. Autoantibodies to folate receptors in the cerebral folate deficiency syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1985–1991.
- Ramaekers, V.T.; Segers, K.; Sequeira, J.M.; Koenig, M.; Van Maldergem, L.; Bours, V.; Kornak, U.; Quadros, E.V. Genetic assessment and folate receptor autoantibodies in infantile-onset cerebral folate deficiency (CFD) syndrome. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 124, 87–93.
- Cao, X.; Wolf, A.; Kim, S.E.; Cabrera, R.M.; Wlodarczyk, B.J.; Zhu, H.; Parker, M.; Lin, Y.; Steele, J.W.; Han, X.; et al. CIC de novo loss of function variants contribute to cerebral folate deficiency by downregulating FOLR1 expression. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 1–11.
- Ramaekers, V.T.; Blau, N.; Sequeira, J.M.; Nassogne, M.C.; Quadros, E.V. Folate receptor autoimmunity and cerebral folate deficiency in low-functioning autism with neurological deficits. Neuropediatrics 2007, 38, 276–281.
- Ramaekers, V.T.; Sequeira, J.M.; Thöny, B.; Quadros, E.V. Oxidative Stress, Folate Receptor Autoimmunity, and CSF Findings in Severe Infantile Autism. Autism Res. Treat. 2020, 2020, 9095284.
- Fekete, K.; Berti, C.; Trovato, M.; Lohner, S.; Dullmeijer, C.; Souverein, O.W.; Cetin, I.; Decsi, T. Effect of folate intake on health outcomes in pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis on birth weight, placental weight and length of gestation. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 1–8.
- Greenberg, J.A.; Bell, S.J.; Guan, Y.; Yu, Y. Folic acid supplementation and pregnancy—More than just neural tube defect prevention. Rev. Obs. Gynecol. 2011, 4, 52–59.
- Bailey, L.B.; Stover, P.J.; McNulty, H.; Fenech, M.F.; Gregory, J.F., 3rd; Mills, J.L.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Fazili, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ueland, P.M.; et al. Biomarkers of nutrition for development-Folate Review. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1636S–1680S.
- Rothenberg, S.P.; da Costa, M.P.; Sequeira, J.M.; Cracco, J.; Roberts, J.L.; Weedon, J.; Quadros, E.V. Autoantibodies against folate receptors in women with a pregnancy complicated by a neural-tube defect. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 134–142.
- Shapira, I.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V. Folate receptor autoantibodies in pregnancy related complications. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2015, 103, 1028–1030.
- Peng, L.; Dreumont, N.; Coelho, D.; Guéant, J.L.; Arnold, C. Genetic animal models to decipher the pathogenic effects of vitamin B12 and folate deficiency. Biochimie 2016, 126, 43–51.
- Kappen, C. Folate supplementation in three genetic models: Implications for understanding folate-dependent developmental pathways. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin Med. Genet. 2005, 135C, 24–30.
- Piedrahita, J.A.; Oetama, B.; Bennett, G.D.; van Waes, J.; Kamen, B.A.; Richardson, J.; Lacey, S.W.; Anderson, R.G.; Finnell, R.H. Mice lacking the folic acid-binding protein Folbp1 are defective in early embryonic development. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 228–232.
- Tang, L.S.; Santillano, D.R.; Wlodarczyk, B.J.; Miranda, R.C.; Finnell, R.H. Role of Folbp1 in the regional regulation of apoptosis and cell proliferation in the developing neural tube and craniofacies. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2005, 135C, 48–58.
- Craciunescu, C.N.; Brown, E.C.; Mar, M.H.; Albright, C.D.; Nadeau, M.R.; Zeisel, S.H. Folic acid deficiency during late gestation decreases progenitor cell proliferation and increases apoptosis in fetal mouse brain. J Nutr. 2004, 134, 162–166.
- Berrocal-Zaragoza, M.I.; Sequeira, J.M.; Murphy, M.M.; Fernandez-Ballart, J.D.; Abdel Baki, S.G.; Bergold, P.J.; Quadros, E.V. Folate deficiency in rat pups during weaning causes learning and memory deficits. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 1323–1332.
- Blaise, S.A.; Nédélec, E.; Schroeder, H.; Alberto, J.M.; Bossenmeyer-Pourié, C.; Guéant, J.L.; Daval, J.L. Gestational vitamin B deficiency leads to homocysteine-associated brain apoptosis and alters neurobehavioral development in rats. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 667–679.
- da Costa, M.; Sequeira, J.M.; Rothenberg, S.P.; Weedon, J. Antibodies to Folate Receptors Impair Embryogenesis and Fetal Development in the Rat. Birth Defects Res. Part A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2003, 67, 837–847.
- Sequeira, J.M.; Desai, A.; Berrocal-Zaragoza, M.I.; Murphy, M.M.; Fernandez-Ballart, J.D.; Quadros, E.V. Exposure to folate receptor alpha antibodies during gestation and weaning leads to severe behavioral deficits in rats: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152249.
- Desai, A.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V. Prevention of behavioral deficits in rats exposed to folate receptor antibodies: Implication in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1291–1297.
- Balashova, O.A.; Visina, O.; Borodinsky, L.N. Folate action in nervous system development and disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 391–402.
- Mann, A.; Portnoy, E.; Han, H.; Inbar, D.; Blatch, D.; Shmuel, M.; Ben-Hur, T.; Eyal, S.; Ekstein, D. Folate homeostasis in epileptic rats. Epilepsy Res. 2018, 142, 64–72.
- Kruman, I.I.; Mouton, P.R.; Emokpae, R., Jr.; Cutler, R.G.; Mattson, M.P. Folate deficiency inhibits proliferation of adult hippocampal progenitors. NeuroReport. 2005, 16, 1055–1059.
- Weng, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Tan, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, T.; Lu, Q.R.; Yang, B.; He, Q. Folate Metabolism Regulates Oligodendrocyte Survival and Differentiation by Modulating AMPKα Activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1705.
- Kim, G.B.; Chen, Y.; Kang, W.; Guo, J.; Payne, R.; Li, H.; Wei, Q.; Baker, J.; Dong, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. The critical chemical and mechanical regulation of folic acid on neural engineering. Biomaterials. 2018, 178, 504–516.
- Mayanil, C.S.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tomita, T. Novel functions of folate receptor alpha in CNS development and diseases. Neurosci. Discov. 2014, 2, 5.
- Hou, Z.; Matherly, L.H. Biology of the major facilitative folate transporters SLC19A1 and SLC46A1. Curr. Top. Membr. 2014, 73, 175–204.
- Antony, A.C. Folate receptors. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1996, 16, 501–521.
- Machacek, C.; Supper, V.; Leksa, V.; Mitulovic, G.; Spittler, A.; Drbal, K.; Suchanek, M.; Ohradanova-Repic, A.; Stockinger, H. Folate Receptor β Regulates Integrin CD11b/CD18 Adhesion of a Macrophage Subset to Collagen. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2229–2238.
- Kelemen, L.E. The role of folate receptor alpha in cancer development, progression and treatment: Cause, consequence or innocent bystander? Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 243–250.
- Spiegelstein, O.; Eudy, J.D.; Finnell, R.H. Identification of two putative novel folate receptor genes in humans and mouse. Gene 2000, 258, 117–125.
- Holm, J.; Hansen, S.I. Characterization of soluble folate receptors (folate binding proteins) in humans. Biological roles and clinical potentials in infection and malignancy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140466.
- Alam, C.; Hoque, M.T.; Finnell, R.H.; Goldman, I.D.; Bendayan, R. Regulation of Reduced Folate Carrier (RFC) by Vitamin D Receptor at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3848–3858.
- Yasuda, S.; Hasui, S.; Yamamoto, C.; Yoshioka, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Itagaki, S.; Hirano, T.; Iseki, K. Placental folate transport during pregnancy. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 2277–2284.
- Grapp, M.; Wrede, A.; Schweizer, M.; Hüwel, S.; Galla, H.J.; Snaidero, N.; Simons, M.; Bückers, J.; Low, P.S.; Urlaub, H.; et al. Choroid plexus transcytosis and exosome shuttling deliver folate into brain parenchyma. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2123.
- Alam, C.; Kondo, M.; O’Connor, D.L.; Bendayan, R. Clinical Implications of Folate Transport in the Central Nervous System. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 349–361.
- Desai, A.; Sequeira, J.M.; and Quadros, E.V. The metabolic basis for developmental disorders due to defective folate transport. Biochimie 2016, 126, 31–42.
- Berrocal-Zaragoza, M.I.; Fernandez-Ballart, J.D.; Murphy, M.M.; Cavallé-Busquets, P.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V. Association between blocking folate receptor autoantibodies and subfertility. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91 (Suppl. 4), 1518–1521.
- Vo, H.D.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V.; Schwarz, S.M.; Perenyi, A.R. The role of folate receptor autoantibodies in preterm birth. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1224–1227.
- Ramaekers, V.; Sequeira, J.M.; Quadros, E.V. Clinical recognition and aspects of the cerebral folate deficiency syndromes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 497–511.
- Frye, R.E.; Slattery, J.; Delhey, L.; Furgerson, B.; Strickland, T.; Tippett, M.; Sailey, A.; Wynne, R.; Rose, S.; Melnyk, S.; et al. Folinic acid improves verbal communication in children with autism and language impairment: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 247–256.
- Frye, R.E.; Delhey, L.; Slattery, J.; Tippett, M.; Wynne, R.; Rose, S.; Kahler, S.G.; Bennuri, S.C.; Stepan, M.; Sequeira, J.M.; et al. Blocking and binding folate receptor alpha autoantibodies identify novel autism spectrum disorder subgroups. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 80.
- Sequeira, J.M.; Ramaekers, V.T.; Quadros, E.V. The diagnostic utility of folate receptor autoantibodies in blood. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 545–554.
- Ramaekers, V.T.; Sequeira, J.M.; DiDuca, M.; Vrancken, G.; Thomas, A.; Philippe, C.; Peters, M.; Jadot, A.; Quadros, E.V. Improving Outcome in Infantile Autism with Folate Receptor Autoimmunity and Nutritional Derangements: A Self-Controlled Trial. Autism Res. Treat. 2019, 2019, 7486431.
- Zhou, J.; Liu, A.; He, F.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xu, R.; Guo, H.; Zhou, W.; Wei, Q.; Wang, M. High prevalence of serum folate receptor autoantibodies in children with autism spectrum disorders. Biomarkers 2018, 23, 622–624.




