Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.

Submitted Successfully!
Thank you for your contribution! You can also upload a video entry or images related to this topic.
For video creation, please contact our Academic Video Service.
| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Johan Wallin | + 2307 word(s) | 2307 | 2021-06-04 06:24:20 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 2307 | 2021-06-08 11:22:28 | | |
Video Upload Options
We provide professional Academic Video Service to translate complex research into visually appealing presentations. Would you like to try it?
Cite
If you have any further questions, please contact Encyclopedia Editorial Office.
Wallin, J. Leukotriene Signaling Pathway in PD. Encyclopedia. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10622 (accessed on 07 February 2026).
Wallin J. Leukotriene Signaling Pathway in PD. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10622. Accessed February 07, 2026.
Wallin, Johan. "Leukotriene Signaling Pathway in PD" Encyclopedia, https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10622 (accessed February 07, 2026).
Wallin, J. (2021, June 08). Leukotriene Signaling Pathway in PD. In Encyclopedia. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/10622
Wallin, Johan. "Leukotriene Signaling Pathway in PD." Encyclopedia. Web. 08 June, 2021.
Copy Citation
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder where misfolded alpha-synuclein-enriched aggregates called Lewy bodies are central in pathogenesis. Parkinson’s disease is considered a multifactorial disease and evidence from multiple patient studies and animal models has shown a significant immune component during the course of the disease, highlighting immunomodulation as a potential treatment strategy. The immune changes occur centrally, involving microglia and astrocytes but also peripherally with changes to the innate and adaptive immune system.
montelukast
alpha-synuclein
leukotriene
microglia
neuroinflammation
Parkinson’s disease
1. Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [1]. Clinical manifestations of PD can vary, but a formal diagnosis relies on the presence of bradykinesia with rigidity and/or rest tremor according to Movement Disorder Society (MDS) criteria for PD [2]. Non-motor symptoms, such as hyposmia, constipation, depression, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder, are common and can in many cases manifest before classical motor symptoms. In later years, more emphasis has been put on non-motor symptoms, especially in the early stages of PD and which is evident in the proposed prodromal PD criterion by MDS [3]. The cause of disease phenotype is principally a degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta, but other areas of the central and peripheral nervous system are also affected. The pathogenesis is multifactorial but protein aggregates called Lewy bodies, mainly composed of misfolded α-synuclein, are believed to be the main cause of disease progression [4]. There is however growing evidence that immune responses and in particular increased microglial activity is a significant contributor to neurodegeneration in PD [5]. Current treatment strategies are focused on symptom relief. Drugs that enhance intracerebral dopamine concentrations or stimulate dopamine receptors are efficient, at least in the early stages, against motor symptoms. However, no neuroprotective or disease-modifying treatments are available [6].
2. Neuroinflammation in PD
As in other parts of the body, inflammation plays a fundamental role in the central nervous system (CNS) to protect from damage and pathogens. During recent years, more evidence has been found to suggest that hyperactivation of innate and adaptive immune responses plays an important role in the progression of neurodegeneration [7]. There are still many areas of uncertainty such as which parts of the innate and immune system play prominent roles in pathology, what triggers neuroinflammation, and if it is possible to analyze the evolution of various forms of inflammation during the course of the disease [8].
3. Immunomodulatory Treatment Studies
There is no current consensus on an anti-inflammatory treatment of PD, but many candidates have been studied in the past. A 2011 Cochrane review analyzed non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) as a preventive treatment for PD. Only observational studies regarding primary prevention were found at the time and the combined data showed a small reduction in risk of PD by regular use of ibuprofen [9]. Other NSAIDs were not shown to have any statistical effect on the risk of developing PD. In conclusion, there was not enough evidence to recommend any NSAID as a preventive measure, but it highlights the possible role of anti-inflammatory drugs as future treatments.
Some epidemiological studies have shown a lower risk of PD in patients who are taking other forms of immunosuppressive drugs. A population-based case-control study with around 50,000 patients and controls in the US showed a lower risk of PD in patients taking monophosphate dehydrogenase inhibitors or corticosteroids [10]. A retrospective cohort study analyzing the incidence of PD among patients with inflammatory bowel disease showed a higher incidence of PD among patients with IBD than without but also that early exposure to anti-TNF-α therapy was associated with a reduced PD incidence. This can be seen as evidence for the role of autoimmunity and also the possible role of immunosuppressive treatment in preventing or treating PD [11].
Drugs affecting microglia in PD have been studied by Jucaite and colleagues, who showed the drug candidate AZD3241 to reduce microglial activity by inhibiting the enzyme myeloperoxidase [12]. The trial was limited to 8 weeks and thus the study had no clinical rating reflecting progression as a primary endpoint. AZD3241 has not been further studied on PD patients but there is an ongoing trial (NCT04616456) studying the effects on patients suffering from multiple system atrophy (MSA) with the drug Verdiperstat, which is another name for AZD3241.
Vinpocetine has been suggested as a neuroprotective agent due to its effects on inflammatory signaling and cerebral blood flow [13]. In a randomized controlled trial on PD patients, vinpocetine reduced circulating mRNA levels of TLR2/4 and downstream inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α. A small improvement in cognitive function was noted but no change in motor symptoms was seen [14]. The study was limited by only 14 days of treatment which in part explains the lack of change in motor symptoms.
Niacin (vitamin B3) has been proposed as a neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory treatment for PD because of its interaction with the G-protein-coupled receptor GPR109A. The receptor is expressed in monocytes, leukocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages and becomes upregulated in a pro-inflammatory environment [15]. Inhibition of GPR109A by niacin leads to decreased translocation of NF-κB and reduction of inflammatory cytokines in an in vitro study [16]. A case report with low-dose niacin treatment showed promising effects on PD symptoms and a randomized controlled trial (NCT03462680) has been completed although no data have been published as of yet [17].
Another ongoing trial by Greenland and colleagues (EudraCT-2018-003089-14) is studying the efficacy of the immunosuppressive drug azathioprine in a phase II randomized controlled trial with clinical progression as the primary endpoint [18].
4. Leukotriene Signaling Pathway
4.1. Leukotrienes
Leukotrienes are along with prostaglandins, lipoxins, and thromboxanes included in a group of long-chain fatty acids known as eicosanoids. They are known to play important parts in the inflammatory response such as leukocyte chemotaxis, vascular leakage, and astrocyte proliferation, and were first described by Bengt Samuelsson and colleagues in 1983 [19]. Leukotrienes (LT) are synthesized from free arachidonic acid (AA) by the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) into LTA4, which is then further metabolized into LTB4, C4, D4, and E4 [20]. LTC4, D4, and E4 are grouped by their molecule structure to form the cysteinyl leukotrienes and they mainly activate two receptors, CysLT1 and CysLT2. CysLT1 is a Gq/11 family G-protein-coupled receptor with signaling through phospholipase C and Ca2+ mobilization [21]. The abundance of research on CysLTs has been done in the context of asthma where CysLT1 has been repeatedly shown to damage lung tissue through smooth muscle contraction and eosinophil migration [21][22]. CysLT receptors have also been implicated in cardiovascular disease, where CysLT signaling has been shown to induce vasoconstriction and chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is believed to play a main role in atherosclerosis [23].
4.2. Leukotrienes in CNS Disorders
In the CNS, evidence for CysLT1 expression has been seen in multiple cell types including neurons, endothelial cells, astrocytes, and microglia in several brain regions including cortex, hippocampus, striatum, and substantia nigra [24]. In the healthy brain, expression of CysLT receptors is low but several studies have shown that cerebral insult such as stroke or trauma increases the expression significantly [25][26][27]. In the context of brain injury, CysLTs have also been shown to increase blood-brain barrier permeability [28].
Expression of CysLT receptors has also been shown to be elevated in an MPTP-induced PD mouse model [29]. Specific upregulation of CysLT1 on microglia has been seen after rotenone stimulation in a BV2 microglial cell model suggesting an increased receptor expression in activated microglia [30]. The binding of CysLTs to microglial CysLT1 leads to an increased inflammatory response by upregulation of NF-κB through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), which ultimately leads to increased secretion of cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α. CysLTs also affect the phagocytosis of microglia and the production of free radicals through the regulation of nitric oxide synthase [31].
In AD, both in vivo and in vitro studies have shown that LTD4-induced upregulation of the CysLT1 receptor is correlated with increased β-amyloid and cognitive dysfunction in mice [32]. LTD4 directly upregulates beta-secretase (BACE)1, the enzyme responsible for β-amyloid production in neurons [33]. Similar expression of CysLT receptors on astrocytes and microglia is observed in AD as in PD mouse models, but upregulation of these cells is observed in the hippocampus and cortex where AD pathology is most abundant [34].
4.3. 5-Lipoxygenase
5-LOX is a key enzyme in the leukotriene pathway since it catalyzes the formation of LTA4 from AA [35]. 5-lipoxygenase is expressed in neuronal and glial cells providing a supply of LTA4 but evidence shows that LTA4 can also be supplied by peripheral neutrophils for further metabolization in brain resident cells [36].
In PD, 5-LOX has been shown to be involved in DA cell death in mice after MPTP injection. Knockout of 5-LOX showed a protective effect with no significant reduction in DA neurons after MPTP injection [37]. Similar results were seen in another study where the use of a 5-LOX inhibitor protected against neuronal cell death in both a human DA cell line and mouse model [38].
In AD, 5-LOX is upregulated in postmortem brains, and in vitro studies have shown 5-LOX overexpression to be linked with β-amyloid formation and tau hyperphosphorylation [39]. Studies on 5-LOX inhibitors such as zileuton have shown promising results in ameliorating neuroinflammation and improving neurogenesis in the hippocampus, which makes it a promising candidate for studies on other CNS disorders [40].
5. Montelukast
5.1. Discovery and Current Use
Pre-clinical research on CysLT receptors and their role in asthma pathology led to the development of the CysLT1 antagonist montelukast in the late 1990s [41][42]. Montelukast and other CysLT1 antagonists are currently used as an adjuvant therapy for children and adults suffering from asthma [43]. Other indications have been proposed and most evidence exists for the use of montelukast to treat allergic rhinitis, but its use in other inflammatory conditions, such as atherosclerosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, have also been suggested [21][23]. Because of montelukast’s effect on inflammation and vascular damage in the lung, it has also been proposed as a treatment for COVID-19 associated pneumonitis [44].
5.2. Montelukast as a Treatment for PD
In a study from 2017, Jang and colleagues showed that montelukast protected DA neurons against microglial activation and attenuated the production of neurotoxic cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1β in a mouse model of PD [45]. Similar results were seen in a study by Nagarajan and colleagues in 2018 where montelukast attenuated rotenone-induced microglial activation and had a protective effect on motor function deterioration [46]. A more detailed study on the diverse effects of montelukast in a PD mouse model by Mansour and colleagues showed similar results regarding reduced microglial activation and improved motor symptoms. Furthermore, a positive effect on neuronal survival was seen due to a downregulation of pro-apoptotic p53 expression and attenuated oxidative stress due to the ROS scavenging properties of montelukast (Figure 1) [47].
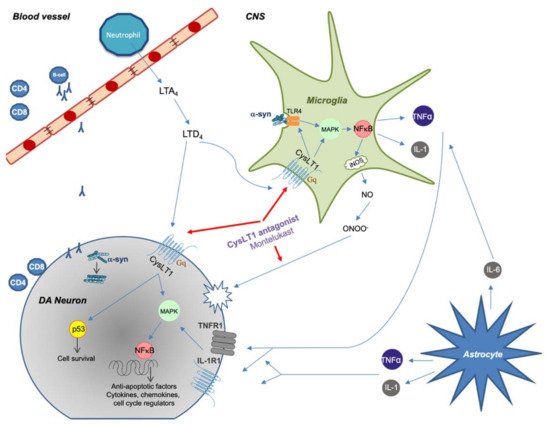
Figure 1. Summary of proposed immune system involvement in Parkinson’s disease (PD) with an emphasis on CysLT signaling. Peripheral immune cells are activated and can enter the CNS during pathological conditions. Misfolded α-synuclein in the CNS or periphery can trigger CD4 and CD8 T-cell recruitment with direct neuronal cell death as a consequence. α-synuclein can also activate microglia through TLR4-mediated phagocytosis, which causes an increased inflammatory response through NF-κB signaling. Astrocytes react to tissue damage and further enhance inflammatory response through production of cytokines. CysLTs increases inflammatory response by binding to CysLT1 receptor, thus further increasing microglial activity. CysLT1 on DA neurons can trigger apoptosis by upregulating p53 gene. Montelukast decreases inflammation by inhibiting CysLT1 signaling but can also act as an antioxidant by binding directly to reactive nitrogen species.
The authors of this review are currently recruiting patients for a phase II unblinded study on the safety and tolerability of montelukast in PD patients (EudraCT: 2020-000148-76). All participants will receive 40 mg of montelukast daily and microglial activity will be measured with PET imaging before and after 12-week treatment. Inflammatory biomarkers will be collected along with clinical rating scales.
5.3. Montelukast as a Treatment for other CNS Disorders
Montelukast treatment has been studied in AD animal models where it has been shown to have a rescuing effect of β-amyloid induced neurotoxicity and reversal of CysLT1R expression with a reduction of pro-inflammatory factors and apoptosis-related proteins as a result [48].
Montelukast has also been studied in the context of aging where its positive effect on microglial activation was again seen, but more interestingly, hippocampal neurogenesis was increased, which suggests that the drug could restore neuronal circuitries [49]. In a more recent study by the same authors, montelukast treatment was shown to reduce α-synuclein load and restore memory in an α-synuclein-based mouse model of Lewy-body dementia [50].
Building on the idea of montelukast as a treatment for cognitive impairment, a case study with 17 patients in 2017 showed promising subjective improvements in memory and other symptoms relating to dementia [51]. This hypothesis was tested in a register-based study in Norway where the possible effects of montelukast on neurological aging were analyzed. Data from the Norwegian prescription database and a prospective cohort study with health data from 45,000 people between 1974‒2016 was used. Results showed a correlation between the previous use of montelukast and improved scores on cognitive and neurological function tests [52].
There are also two ongoing phase II placebo-controlled trials on montelukast in Alzheimer’s disease (NCT03991988) and (NCT03402503). In the former, 15 participants are being recruited for a one-year study with 40 mg of montelukast or placebo and in the latter, a new buccal film formulation of the drug is being tested on 70 participants for 26 weeks.
An increase in CysLTs and CysLT receptors has been studied in the context of traumatic brain injury (TBI) where inflammation and disruption of the blood-brain barrier occur after a traumatic event [32]. The use of montelukast has been proposed as a treatment of TBI to attenuate chronic neurological damage caused by neuroinflammation [53].
In summary, the effects of montelukast on neuroinflammation in multiple neurodegenerative disorders are promising in animal models, where effects on both symptoms and disease biomarkers have been seen. Results from ongoing human trials will determine the possible role of montelukast as a treatment for inflammation in CNS disorders.
References
- Calabrese, V.P.; Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; et al. Projected Number of People With Parkinson Disease in the Most Populous Nations, 2005 Through 2030. Neurology 2007, 69, 223–224.
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601.
- Berg, D.; Postuma, R.B.; Adler, C.H.; Bloem, B.R.; Chan, P.; Dubois, B.; Gasser, T.; Goetz, C.G.; Halliday, G.; Joseph, L.; et al. MDS Research Criteria for Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1600–1611.
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912.
- Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Chang, S.C.; Lee, J. Significant Roles of Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Therapeutic Targets for PD Prevention. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 416–425.
- Fox, S.H.; Katzenschlager, R.; Lim, S.Y.; Barton, B.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Seppi, K.; Coelho, M.; Sampaio, C. International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society Evidence-Based Medicine Review: Update on Treatments for the Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1248–1266.
- Kaur, K.; Gill, J.S.; Bansal, P.K.; Deshmukh, R. Neuroinflammation—A Major Cause for Striatal Dopaminergic Degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 381, 308–314.
- Hirsch, E.C.; Standaert, D.G. Ten Unsolved Questions About Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 36, 16–24.
- Rees, K.; Stowe, R.; Patel, S.; Ives, N.; Breen, K.; Clarke, C.E.; Ben-Shlomo, Y. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs as Disease-Modifying Agents for Parkinson’s Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 11.
- Racette, B.A.; Gross, A.; Vouri, S.M.; Camacho-Soto, A.; Willis, A.W.; Searles Nielsen, S. Immunosuppressants and Risk of Parkinson Disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 870–875.
- Peter, I.; Dubinsky, M.; Bressman, S.; Park, A.; Lu, C.; Chen, N.; Wang, A. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy and Incidence of Parkinson Disease among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 939–946.
- Jucaite, A.; Svenningsson, P.; Rinne, J.O.; Cselényi, Z.; Varnäs, K.; Johnström, P.; Amini, N.; Kirjavainen, A.; Helin, S.; Minkwitz, M.; et al. Effect of the Myeloperoxidase Inhibitor AZD3241 on Microglia: A PET Study in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2015, 138, 2687–2700.
- Zhang, Y.-S.; Li, J.-D.; Yan, C. An Update on Vinpocetine: New Discoveries and Clinical Implications. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 819, 30–34.
- Ping, Z.; Xiaomu, W.; Xufang, X.; Liang, S. Vinpocetine Regulates Levels of Circulating TLRs in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 113–120.
- Offermanns, S. The Nicotinic Acid Receptor GPR109A (HM74A or PUMA-G) as a New Therapeutic Target. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 384–390.
- Giri, B.; Belanger, K.; Seamon, M.; Bradley, E.; Purohit, S.; Chong, R.; Morgan, J.C.; Baban, B.; Wakade, C. Niacin Ameliorates Neuro-Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease via GPR109A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4559.
- Wakade, C.; Chong, R.; Bradley, E.; Morgan, J.C. Low-dose Niacin Supplementation Modulates GPR109A, Niacin Index and Ameliorates Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms without Side Effects. Clin. Case Reports 2015, 3, 635–637.
- Greenland, J.C.; Cutting, E.; Kadyan, S.; Bond, S.; Chhabra, A.; Williams-Gray, C.H. Azathioprine Immunosuppression and Disease Modification in Parkinson’s Disease (AZA-PD): A Randomised Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Phase II Trial Protocol. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040527.
- Samuelsson, B. Leukotrienes: Mediators of Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions and Inflammation. Science 1983, 220, 568–575.
- Haeggström, J.Z.; Funk, C.D. Lipoxygenase and Leukotriene Pathways: Biochemistry, Biology, and Roles in Disease. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5866–5896.
- Bäck, M.; Powell, W.S.; Dahlén, S.E.; Drazen, J.M.; Evans, J.F.; Serhan, C.N.; Shimizu, T.; Yokomizo, T.; Rovati, G.E. Update on Leukotriene, Lipoxin and Oxoeicosanoid Receptors: IUPHAR Review 7. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3551–3574.
- Lynch, K.R.; O’Neill, G.P.; Liu, Q.; Im, D.S.; Sawyer, N.; Metters, K.M.; Coulombe, N.; Abramovitz, M.; Figueroa, D.J.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Characterization of the Human Cysteinyl Leukotriene CysLT1 Receptor. Nature 1999, 399, 789–793.
- Sasaki, F.; Yokomizo, T. The Leukotriene Receptors as Therapeutic Targets of Inflammatory Diseases. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 607–615.
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, L. Modulation of Neuroinflammation by Cysteinyl Leukotriene 1 and 2 Receptors: Implications for Cerebral Ischemia and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 87, 1–10.
- Zhao, C.Z.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, X.Q.; Shi, W.Z.; Liu, H.L.; Fang, S.H.; Lu, Y.B.; Zhang, W.P.; Tang, F.D.; et al. Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor 2 Is Spatiotemporally Involved in Neuron Injury, Astrocytosis and Microgliosis after Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Neuroscience 2011, 189, 1–11.
- Fang, S.H.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, L.S.; Zhang, W.P.; Wang, M.L.; Yu, G.L.; Peng, F.; Wei, E.Q. Spatio-Temporal Expression of Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor-2 MRNA in Rat Brain after Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 412, 78–83.
- Fang, S.H.; Wei, E.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.L.; Zhang, W.P.; Yu, G.L.; Chu, L.S.; Chen, Z. Increased Expression of Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor-1 in the Brain Mediates Neuronal Damage and Astrogliosis after Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Neuroscience 2006, 140, 969–979.
- Michael, J.; Marschallinger, J.; Aigner, L. The Leukotriene Signaling Pathway: A Druggable Target in Alzheimer’s Disease. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 505–516.
- Wang, H.; Shi, Q.; Shi, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Fang, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wei, E. Expression and Distribution of Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptors CysLT1R and CysLT2R, and GPR17 in Brain of Parkinson Disease Model Mice. J. Zhejiang Univ. Med. Sci. 2013, 42, 52–60.
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, D.M.; Zhang, S.R.; Li, C.T.; Zheng, W.; Yu, S.Y.; Wei, E.Q.; Zhang, L.H. Regulation of Rotenone-Induced Microglial Activation by 5-Lipoxygenase and Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor 1. Brain Res. 2014, 1572, 59–71.
- Gelosa, P.; Colazzo, F.; Tremoli, E.; Sironi, L.; Castiglioni, L. Cysteinyl Leukotrienes as Potential Pharmacological Targets for Cerebral Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017.
- Ghosh, A.; Chen, F.; Thakur, A.; Hong, H. Cysteinyl Leukotrienes and Their Receptors: Emerging Therapeutic Targets in Central Nervous System Disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 943–951.
- Rahman, S.O.; Singh, R.K.; Hussain, S.; Akhtar, M.; Najmi, A.K. A Novel Therapeutic Potential of Cysteinyl Leukotrienes and Their Receptors Modulation in the Neurological Complications Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 842, 208–220.
- Chen, F.; Ghosh, A.; Lin, J.; Zhang, C.; Pan, Y.; Thakur, A.; Singh, K.; Hong, H.; Tang, S. 5-Lipoxygenase Pathway and Its Downstream Cysteinyl Leukotrienes as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 844–855.
- Sinha, S.; Doble, M.; Manju, S.L. 5-Lipoxygenase as a Drug Target: A Review on Trends in Inhibitors Structural Design, SAR and Mechanism Based Approach. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3745–3759.
- Farias, S.E.; Zarini, S.; Precht, T.; Murphy, R.C.; Heidenreich, K.A. Transcellular Biosynthesis of Cysteinyl Leukotrienes in Rat Neuronal and Glial Cells. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 1310–1318.
- Chou, V.P.; Holman, T.R.; Manning-Bog, A.B. Differential Contribution of Lipoxygenase Isozymes to Nigrostriatal Vulnerability. Neuroscience 2013, 228, 73–82.
- Kang, K.H.; Liou, H.H.; Hour, M.J.; Liou, H.C.; Fu, W.M. Protection of Dopaminergic Neurons by 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor. Neuropharmacology 2013, 73, 380–387.
- Di Meco, A.; Li, J.G.; Praticò, D. Dissecting the Role of 5-Lipoxygenase in the Homocysteine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 1337–1344.
- Liu, C.H.; Tan, Y.Z.; Li, D.D.; Tang, S.S.; Wen, X.A.; Long, Y.; Sun, H.-B.; Hong, H.; Hu, M. Zileuton Ameliorates Depressive-like Behaviors, Hippocampal Neuroinflammation, Apoptosis and Synapse Dysfunction in Mice Exposed to Chronic Mild Stress. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 78, 105947.
- Reiss, T.F.; Altman, L.C.; Chervinsky, P.; Bewtra, A.; Stricker, W.E.; Noonan, G.P.; Kundu, S.; Zhang, J. Effects of Montelukast (MK-0476), a New Potent Cysteinyl Leukotriene (LTD4) Receptor Antagonist, in Patients with Chronic Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 528–534.
- Malmstrom, K.; Schwartz, J.; Reiss, T.F.; Sullivan, T.J.; Reese, J.H.; Jauregui, L.; Miller, K.; Scott, M.; Shingo, S.; Peszek, I.; et al. Effect of Montelukast on Single-Dose Theophylline Pharmacokinetics. Am. J. Ther. 1998, 5, 189–195.
- Trinh, H.K.T.; Lee, S.H.; Cao, T.B.T.; Park, H.S. Asthma Pharmacotherapy: An Update on Leukotriene Treatments. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 1169–1178.
- Aigner, L.; Pietrantonio, F.; Bessa de Sousa, D.M.; Michael, J.; Schuster, D.; Reitsamer, H.A.; Zerbe, H.; Studnicka, M. The Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist Montelukast as a Potential COVID-19 Therapeutic. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 610132.
- Jang, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.M.; Oh, Y.-S.; Park, S.M.; Kim, S.R. Montelukast Treatment Protects Nigral Dopaminergic Neurons against Microglial Activation in the 6-Hydroxydopamine Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 242–249.
- Nagarajan, V.B.; Marathe, P.A. Effect of Montelukast in Experimental Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 682, 100–105.
- Mansour, R.M.; Ahmed, M.A.E.; El-Sahar, A.E.; El Sayed, N.S. Montelukast Attenuates Rotenone-Induced Microglial Activation/P38 MAPK Expression in Rats: Possible Role of Its Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Antiapoptotic Effects. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 358, 76–85.
- Lai, J.; Mei, Z.L.; Wang, H.; Hu, M.; Long, Y.; Miao, M.X.; Li, N.; Hong, H. Montelukast Rescues Primary Neurons against Aβ1-42-Induced Toxicity through Inhibiting CysLT1R-Mediated NF-ΚB Signaling. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 75, 26–31.
- Marschallinger, J.; Schäffner, I.; Klein, B.; Gelfert, R.; Rivera, F.J.; Illes, S.; Grassner, L.; Janssen, M.; Rotheneichner, P.; Schmuckermair, C.; et al. Structural and Functional Rejuvenation of the Aged Brain by an Approved Anti-Asthmatic Drug. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8466.
- Marschallinger, J.; Altendorfer, B.; Rockenstein, E.; Holztrattner, M.; Garnweidner-Raith, J.; Pillichshammer, N.; Leister, I.; Hutter-Paier, B.; Strempfl, K.; Unger, M.S.; et al. The Leukotriene Receptor Antagonist Montelukast Reduces Alpha-Synuclein Load and Restores Memory in an Animal Model of Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurotherapeutics 2020, 17, 1061–1074.
- Rozin, S.I. Case Series Using Montelukast in Patients with Memory Loss and Dementia. Open Neurol. J. 2017, 11, 7–10.
- Grinde, B.; Schirmer, H.; Eggen, A.E.; Aigner, L.; Engdahl, B. A Possible Effect of Montelukast on Neurological Aging Examined by the Use of Register Data. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2020.
- Fatima, N.; Shuaib, A. The Role of Montelukast in Traumatic Brain Injury and Brain Ischemia. Neurosurgery 2020, 67.
More
Information
Subjects:
Pathology
Contributor
MDPI registered users' name will be linked to their SciProfiles pages. To register with us, please refer to https://encyclopedia.pub/register
:
View Times:
1.0K
Revisions:
2 times
(View History)
Update Date:
08 Jun 2021
Notice
You are not a member of the advisory board for this topic. If you want to update advisory board member profile, please contact office@encyclopedia.pub.
OK
Confirm
Only members of the Encyclopedia advisory board for this topic are allowed to note entries. Would you like to become an advisory board member of the Encyclopedia?
Yes
No
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Back
Comments
${ item }
|
More
No more~
There is no comment~
${ textCharacter }/${ maxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
${ selectedItem.replyTextCharacter }/${ selectedItem.replyMaxCharacter }
Submit
Cancel
Confirm
Are you sure to Delete?
Yes
No




