| Version | Summary | Created by | Modification | Content Size | Created at | Operation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Carl E. Stafstrom | + 251 word(s) | 251 | 2020-09-16 12:05:37 | | | |
| 2 | Peter Tang | -1 word(s) | 250 | 2020-10-27 07:47:16 | | | | |
| 3 | Peter Tang | Meta information modification | 250 | 2020-11-06 15:04:11 | | |
Video Upload Options
The ongoing worldwide pandemic of the novel human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and the ensuing disease, COVID-19, has presented enormous and unprecedented challenges for all medical specialists. However, to date, children, especially neonates, have been relatively spared from the devastating consequences of this infection. Neurologic involvement is being increasingly recognized among adults with COVID-19, who can develop sensory deficits in smell and taste, delirium, encephalopathy, headaches, strokes, and peripheral nervous system disorders. Among neonates and children, COVID-19-associated neurological manifestations have been relatively rare, yet reports involving neurologic dysfunction in this age range are increasing.
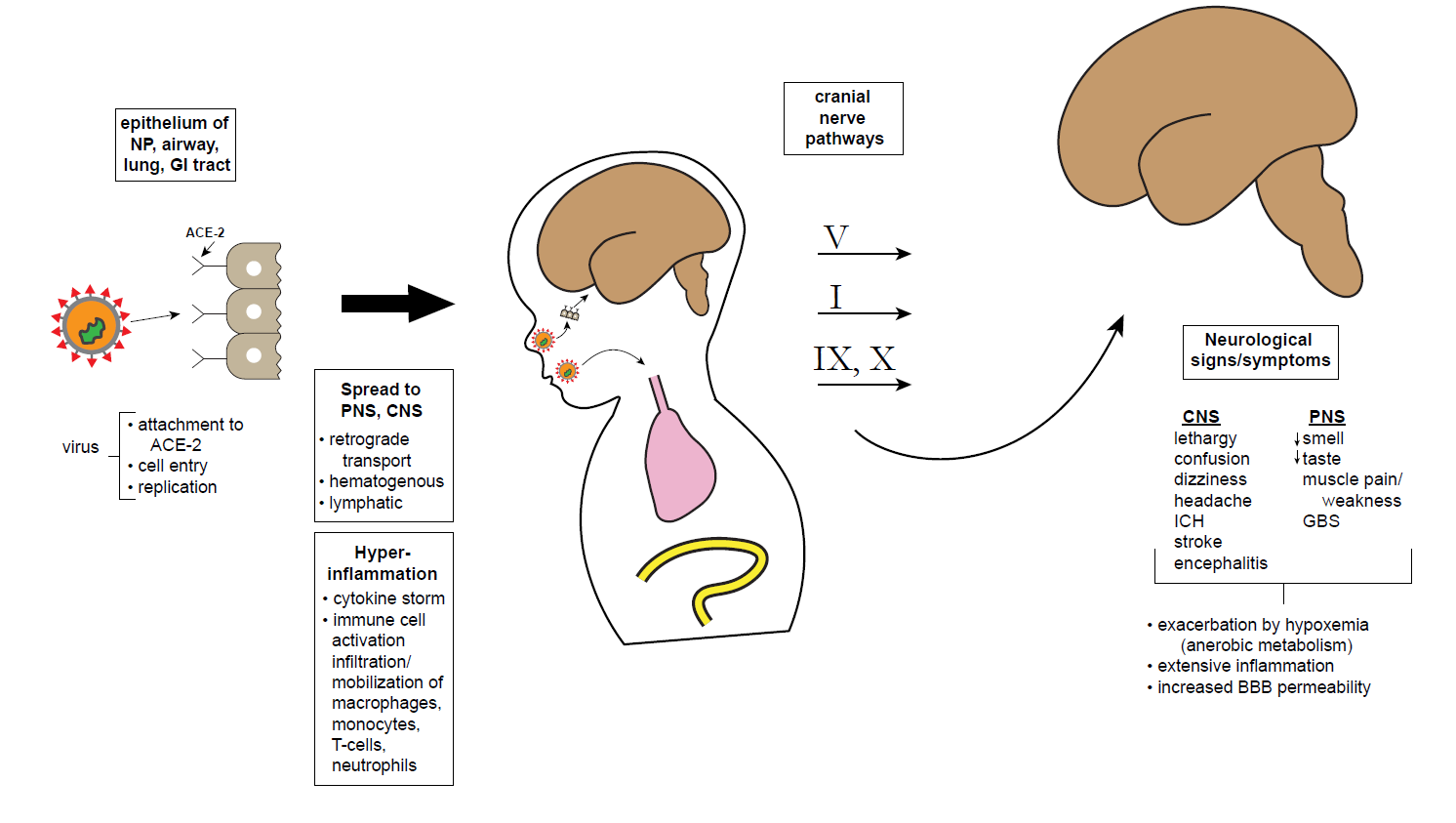
Schematic showing possible CNS entry points and effects of SARS-CoV-2. The SARS-CoV-2 virus attaches to olfactory epithelium using the ACE-2 receptor. After cell entry, the virus replicates and induces a massive immune response leading to excessive cytokine release, comprising a maladaptive immune response. Theoretically, virus particles may reach the CNS retrogradely via cranial nerve pathways: V from corneal epithelium or oropharyngeal cutaneous sensory receptors; I via the cribiform plate, infecting olfactory sensory neurons; VII and IX from tongue chemoreceptors; X via pulmonary mechanoreceptors. Once reaching CNS nuclei including brainstem and cortex, a variety of neurologic signs and symptoms are possible. However, it must be noted that the virus has not been recovered from CSF or brain tissue, making all of these pathways hypothetical at this point. Abbreviations: NP, nasopharynx; GI, gastrointestinal; ACE-2, angiotensin converting enzyme type 2 receptor; PNS, peripheral nervous system; CNS, central nervous system; ICH, intracranial hemorrhage; GBS, Guillain-Barre syndrome; BBB, blood-brain barrier.