Lonidamine (LND) is an indazole derivative that was first introduced in 1979 as an anti-spermatogenic agent. Later, LND was found to have antitumor activity by interfering with the energy metabolism, especially its action on tumor mitochondria. Furthermore, some studies also indicated that LND inhibited hexokinase II (HK-II), followed by the inhibition of glycolytic pathway, as well as pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), leading to the reduction of NADPH and GSH levels. Thus, it was usually used as a glycolytic inhibitor for antitumor research.
- hexokinase II
- glycolytic inhibitor
- mitochondria
1. Introduction
Lonidamine (LND) is an indazole derivative (Figure 1A) that was first introduced in 1979 as an anti-spermatogenic agent [1]. Later, LND was found to have antitumor activity by interfering with the energy metabolism, especially its action on tumor mitochondria. First, LND inhibits lactate export and the uptake of pyruvate into mitochondria by the inhibition of proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) and mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC), respectively. However, the IC50 of LND against MPC is an order of magnitude lower than the IC50 against MCT [2]. Therefore, LND-mediated inhibition of MPC is likely to play a key role. Second, LND inhibits complexes I and II of the mitochondrial electron transport chain [2]. By measuring the succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) activity in complex II and the succinate-ubiquinone reductase (SQR) activity (determined via the formation of ubiquinone by complex II), the inhibition of SQR activity was found to be much greater than that of SDH activity at all LND concentrations tested [3]. Therefore, LND is thought to inhibit complex II activity by interfering with the ubiquinone binding sites of succinate dehydrogenase C (SDHC) and succinate dehydrogenase D (SDHD) (Figure 2) [3]. The inhibition of mitochondrial complex II can induce reactive oxidative species (ROS) production to promote cell apoptosis. Third, LND disrupts the mitochondrial transmembrane potential by directly affecting the mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) pore which is under the control of the members of the Bcl-2 family [4]. After LND treatment, AKT phosphorylation also decreases, which promotes the transfer of p53 from cytoplasm to mitochondria, leading to cell apoptosis [5][6]. Furthermore, some studies also indicated that LND inhibited hexokinase II (HK-II), followed by the inhibition of glycolytic pathway, as well as pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), leading to the reduction of NADPH and GSH levels. Thus, it was usually used as a glycolytic inhibitor for antitumor research (Figure 2) [7][8]. By using 31P NMR technology, LND was shown to produce intracellular acidification and de-energization in vitro and in vivo, and it exhibited selectivity against tumors in vivo without obvious toxic effects on skeletal muscle and brain [9]. Indeed, Nath et al. further showed that LND selectively reduced tumor intracellular pH and ATP levels, and sensitized DB-1 melanoma xenografts to melphalan [10]. LND has also been demonstrated to induce a cytotoxic autophagic response in glioblastoma cells [6]. LND triggers late autophagy, which eventually leads to the transition from autophagy to apoptosis that occurred before phosphatidylinositol disappeared and p-AKT decreased [6]. Currently, LND has been explored for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [11], breast cancer [12], colon cancer [13], astrocytoma [14], squamous cell carcinoma, human glioma, and so on [15]. The research on LND’s derivative, adjudin (ADD), is also worthy of attention (Figure 1B). Similarly, ADD was also originally used as an anti-spermatogenic agent [16]. It was not until 2013 that Xie et al. determined, for the first time, that ADD also had anticancer properties, and consequently, revealed its potential clinical utility as a chemotherapeutic agent [17]. In this study, ADD was proved to be effective for at least fifteen cancer cell lines [17]. When in combination with other chemotherapeutics, ADD also showed a potent synergistic anticancer effect [18][19]. ADD also causes mitochondrial dysfunction to interfere with energy metabolism and induce mitochondrial apoptosis pathway, thus triggering cell apoptosis and autophagy [17]. As ADD, a simple LND derivative, also shows potential anticancer effects, we will briefly summarize the drug combinations related to ADD in recent years as well.
Figure 1. Molecular structures of (A) LND and (B) ADD. LND and ADD are indazole derivatives. Their chemical names are 1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxylic acid and 1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carbohydrazide, respectively.
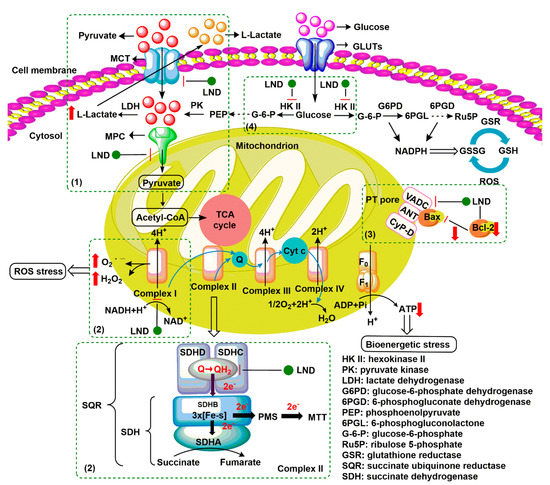
Figure 2. Underlying mechanisms of LND-mediated antitumor activity. (1) LND inhibits the lactate export and the uptake of pyruvate into mitochondria by the inhibition of proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) and mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC), respectively. (2) LND inhibits complexes I and II by interfering with ubiquinone reduction, leading to ATP depletion and ROS production. (3) LND affects the mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) pore which is under the control of the members of the Bcl-2 family. (4) LND inhibits glycolysis through the inhibition of hexokinase II (HK-II), thereby reducing the levels of NADPH and glutathione (GSH) in part by the inhibition of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) flux.
As a single chemotherapeutic agent, LND was found to be ineffective or only mildly effective in preventing the growth of cancer cells in vivo and in vitro, because its anticancer effects are transient and reversible [20]. In the phase II study of oral LND, the most common side effects were myalgia, weakness, and lethargy, testicular pain was also observed [21]. Myalgia displayed dose-limiting toxicity, occurring at a dose of 300–400 mg/m2 [22][23]. Severe vomiting and signs of acute hepatic and pancreatic toxicity were observed when the dose exceeded 400 mg/m2 during intravenous administration [24]. However, if receiving oral LND, it will face the problem of poor bioavailability.
Therefore, in order to reduce the toxic and side effects of LND by intravenous administration, it can be used in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents or physical therapies, or be loaded into a system with tumor targeting properties to reduce the damage to normal cells [24][25][26]. Interestingly, LND has no common side effects of traditional anticancer drugs, such as bone marrow suppression, alopecia, gastrointestinal mucosal necrosis, and does not cause somatic and germ cell mutations [21]. Moreover, because the association of energy metabolism of tumor cells with chemo- or radio-resistance [27], and LND-mediated inhibition of glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration [2], from the point of combination treatment, LND can potentiate the anticancer effects of chemotherapeutic drugs or enhance the therapeutic efficacy when in combination with physical therapies. In view of the tumor selectivity of LND, in this case, the dose of chemotherapeutic drugs may be decreased while avoiding or maximally decreasing the toxic and side effects. The most critical characteristic of LND is its selective activity against a wide range of tumors, with little effect on normal tissues at doses below 400 mg/m2 (oral or intravenous) [10]. Tumor selectivity and low toxicity to normal tissues are key features that make LND an attractive sensitizer to enhance the anticancer activity of chemotherapeutic drugs and physical therapies.
In addition to being a chemosensitizer, in the past five years, LND has often been coupled with targeted agents or other chemotherapeutics and encapsulated in a nanometer system to better improve its tumor targeting and the effectiveness of combined drugs [25][28][29]. For instance, in 2019, Cheng et al. developed the mitochondria-targeted LND (Mito-LND) by conjugating LND to triphenylphosphonium cation (TPP+) via a linker aliphatic chain with reference to other mitochondrial targeting agents such as Mito-Q and Mito-Metformin using Co-Q and metformin as bioactive molecules, respectively. Compared to free LND, Mito-LND not only had significantly higher cytotoxicity to lung cancer cells, but also showed inhibition of mice tumor xenografts and lung cancer brain metastasis in vivo by the inhibition of mitochondrial bioenergetics, induction of ROS and mitochondrial oxidative stress, downregulation of the AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway, and induction of cytotoxic autophagy [28]. Especially, Mito-LND caused cell death mainly by autophagy rather than caspase-dependent apoptosis, as indicated by the conversion of LC3-I to autophagic LC3-II, markedly increased autophagic vacuoles, and flow cytometric analysis. In tumor tissues from mice, Mito-LND-induced autophagy was also observed. Of note, Mito-LND showed no observable toxicity in mice even at doses up to 50 times (375 μmol/kg) the effective inhibitory dose (7.5 μmol/kg) when administered for eight weeks.
3. LND Sensitizes Tumor Cells to Physical Therapy
After exposure to chemotherapeutics, cell survival can be modified by the post-exposure environment. Therefore, oncologists and pharmacologists are trying to treat cancer using new therapies combining chemotherapeutics other than traditional chemotherapeutics alone. LND as a traditional anticancer candidate drug; it is capable of sensitizing tumors to physical therapy. The following section is a brief overview of LND in combination with radiotherapy (RT), hyperthermia (HT), and photodynamic therapy (PDT) (Table 2).
Table 2. Combination of LND with physical therapy.
| Therapy Method | Mechanism of Action | Tumor Type | Synergistic Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiotherapy (RT) | Cancer cells exhibit sensitivity to radiation, poor tolerance, while the normal cell population is opposite | BALB/c, C3H/He mice fibrosarcoma cells (in vivo); HeLa cells (in vivo) | LND interferes with the energy-dependent PLD repair process. | [30][31][32][33] |
| Hyperthermia (HT) | Cancer cells can easily store more heat than normal cells. When heated to 40–43 °C, cancer cells undergo membrane structure destruction, cytoskeleton deformation, DNA synthesis inhibition, and blood vessel damage, thus resulting in death. | BALB/c mice fibrosarcoma cells (in vivo); HeLa cells (in vivo); human glioma cells (in vivo); Head-neck squamous cells (in vivo); DB-1 melanoma xenografts (in vivo); R3327G rat prostatic adenocarcinoma (in vivo) | (1) HT can lead t78o the formation of condensed mitochondria, which LND targets more easily. (2) HT increases blow flow and drug delivery. (3) HT increases cell uptake of drugs. (4) LND inhibits the repair of HT-induced (sub)lethal damage as well as the proteins involved in cell survival. |
[34][35][36][37][38][39] |
| Photodynamic therapy (PDT) | PDT can cause mitochondrial damage, causing ATP consumption and ROS production. | MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells (in vitro) | LND and PDT synergistically destruct mitochondrial structure, decrease intracellular ATP level, and induce the generation of ROS. | [40][41][42][43] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cancers12113332
References
- Cioli, V.; Bellocci, B.; Putzolu, S.; Malorni, W.; Demartino, C. Anti-spermogenic activity of lonidamine (AF-1890) in rabbit. Ultramicroscopy 1980, 5, 418.
- Nath, K.; Guo, L.; Nancolas, B.; Nelson, D.S.; Shestov, A.A.; Lee, S.-C.; Roman, J.; Zhou, R.; Leeper, D.B.; Halestrap, A.P.; et al. Mechanism of antineoplastic activity of lonidamine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2016, 1866, 151–162.
- Guo, L.; Shestov, A.A.; Worth, A.J.; Nath, K.; Nelson, D.S.; Leeper, D.B.; Glickson, J.D.; Blair, I.A. Inhibition of mitochondrial complex II by the anticancer agent lonidamine. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 42–57.
- Ravagnan, L.; Marzo, I.; Costantini, P.; Susin, S.A.; Zamzami, N.; Petit, P.X.; Hirsch, F.; Goulbern, M.; Poupon, M.-F.; Miccoli, L.; et al. Lonidamine triggers apoptosis via a direct, Bcl-2-inhibited effect on the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2537–2546.
- Floridi, A.; Bellocci, M.; Paggi, M.G.; Marcante, M.L.; De Martino, C. Changes of energy metabolism in the germ cells and Ehrlich sscites tumor cells. Chemotherapy 1981, 27, 50–60.
- Davidescu, M.; Macchioni, L.; Scaramozzino, G.; Marchetti, M.C.; Migliorati, G.; Vitale, R.; Corcelli, A.; Roberti, R.; Castigli, E.; Corazzi, L. The energy blockers bromopyruvate and lonidamine lead GL15 glioblastoma cells to death by different p53-dependent routes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14343.
- Cervantes-Madrid, D.; Duenas-Gonzalez, A. Antitumor effects of a drug combination targeting glycolysis, glutaminolysis and de novo synthesis of fatty acids. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 1533–1542.
- Cervantes-Madrid, D.; Domínguez-Gómez, G.; Gonzalez-Fierro, A.; Pérez-Cárdenas, E.; Taja-Chayeb, L.; Trejo-Becerril, C.; Duenas-Gonzalez, A. Feasibility and antitumor efficacy in vivo, of simultaneously targeting glycolysis, glutaminolysis and fatty acid synthesis using lonidamine, 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine and orlistat in colon cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1905–1910.
- Ben-Yoseph, O.; Lyons, J.C.; Song, C.W.; Ross, B.D. Mechanism of action of lonidamine in the 9L brain tumor model involves inhibition of lactate efflux and intracellular acidification. J. Neurooncol. 1998, 36, 149–157.
- Nath, K.; Nelson, D.S.; Heitjan, D.F.; Zhou, R.; Leeper, D.B.; Glickson, J.D. Effects of hyperglycemia on lonidamine-induced acidification and de-energization of human melanoma xenografts and sensitization to melphalan. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 395–403.
- Scarantino, C.W.; Mccunniff, A.J.; Evans, G.; Young, C.W.; Paggiarino, D.A. A prospective randomized comparison of radiation therapy plus lonidamine versus radiation therapy plus placebo as initial treatment of clinically localized but nonresectable non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1994, 29, 999–1004.
- Pacini, P.; Rinaldini, M.; Algeri, R.; Guarneri, A.; Tucci, E.; Barsanti, G.; Neri, B.; Bastiani, P.; Marzano, S.; Fallai, C. FEC (5-fluorouracil, epidoxorubicin and cyclophosphamide) versus EM (epidoxorubicin and mitomycin-C) with or without lonidamine as first-line treatment for advanced breast cancer. A multicentric randomised study. Final results. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 966–975.
- Gourdier, I.; Del Rio, M.; Crabbé, L.; Candeil, L.; Copois, V.; Ychou, M.; Auffray, C.; Martineau, P.; Mechti, N.; Pommier, Y.; et al. Drug specific resistance to oxaliplatin is associated with apoptosis defect in a cellular model of colon carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2002, 529, 232–236.
- Paggi, M.G.; Zupi, G.; Fanciulli, M.; Del Carlo, C.; Giorno, S.; Laudonio, N.; Silvestrini, B.; Caputo, A.; Floridi, A. Effect of lonidamine on the utilization of 14C-labeled glucose by human astrocytoma cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1987, 47, 154–165.
- Raaphorst, G.P.; Feeley, M.M.; Martin, L.; Danjoux, C.E.; Maroun, J.; DeSanctis, A.J.; Ko, D. Enhancement of sensitivity to hyperthermia by Lonidamine in human cancer cells. Int. J. Hyperth. 1991, 7, 763–772.
- Cheng, C.Y.; Silvestrini, B.; Grima, J.; Mo, M.-Y.; Zhu, L.-J.; Johansson, E.; Saso, L.; Leone, M.-G.; Palmery, M.; Mruk, D. Two new male contraceptives exert their effects by depleting germ cells prematurely from the testis1. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 449–461.
- Xie, Q.R.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B.; Mruk, D.D.; Silvestrini, B.; Cheng, C.Y.; et al. Male contraceptive Adjudin is a potential anti-cancer drug. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 345–355.
- Yang, C.L.; Tu, K.; Gao, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, T.; Kong, L.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, Z.P. The novel platinum (IV) prodrug with self-assembly property and structure-transformable character against triple-negative breast cancer. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119751.
- Li, X.; Gao, C.X.; Wu, Y.P.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Xia, W.L.; Zhang, Z.P. Combination delivery of Adjudin and Doxorubicin via integrating drug conjugation and nanocarrier approaches for the treatment of drug-resistant cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1556–1564.
- Forster, R.; Campana, A.; D’Onofrio, E.; Henderson, L.; Mosesso, P.; Barcellona, P.S. Lonidamine: A non-mutagenic antitumor agent. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 1509–1515.
- Mansi, J.L.; De Graeff, A.; Newell, D.R.; Glaholm, J.; Button, D.; Leach, M.O.; Payne, G.; Smith, I.E. A phase II clinical and pharmacokinetic study of Lonidamine in patients with advanced breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1991, 64, 593–597.
- Band, P.R.; Deschamps, M.; Besner, J.-G.; LeClaire, R.; Gervais, P.; De Sanctis, A. Phase I toxicologic study of lonidamine in cancer patients. Oncology 1984, 41, 56–59.
- Band, P.R.; Maroun, J.; Pritchard, K.; Stewart, D.; Coppin, C.M.; Wilson, K.; Eisenhauer, E. Phase II study of lonidamine in patients with metastatic breast cancer: A National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1986, 70, 1305–1310.
- Price, G.S.; Page, R.L.; Riviere, J.E.; Cline, J.M.; Thrall, D.E. Pharmacokinetics and toxicity of oral and intravenous lonidamine in dogs. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1996, 38, 129–135.
- Li, N.; Zhang, C.-X.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Ju, R.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Lu, W.-L. Development of targeting lonidamine liposomes that circumvent drug-resistant cancer by acting on mitochondrial signaling pathways. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3366–3380.
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Tang, X.; Zhai, Z.; Xu, K.; Zhong, W. An enzyme-assisted self-delivery system of lonidamine–peptide conjugates for selectively killing cancer cells. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 14852–14855.
- Lin, J.; Xia, L.; Liang, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tan, S.; Tian, Y.; Rao, S.; Chen, X.; et al. The roles of glucose metabolic reprogramming in chemo- and radio-resistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–13.
- Cheng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Lee, Y.; Ouari, O.; Hardy, M.; Zielonka, M.; Myers, C.R.; Zielonka, J.; Weh, K.; et al. Targeting lonidamine to mitochondria mitigates lung tumorigenesis and brain metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–14.
- Milane, L.; Duan, Z.; Amiji, M. Development of EGFR-targeted polymer blend nanocarriers for combination paclitaxel/lonidamine delivery to treat multi-drug resistance in human breast and ovarian tumor cells. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 185–203.
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, L.B.; Zhan, Q.; Gong, S.L.; Dong, L.H. Research progress on the relationship between tumor microenvironment and radiosensitivity of tumor cells. J. Jilin. Univ. Med. Edit. 2016, 42, 1038–1044.
- Hahn, G.M.; Van Kersen, I.; Silvestrini, B. Inhibition of the recovery from potentially lethal damage by lonidamine. Br. J. Cancer 1984, 50, 657–660.
- Kim, J.H.; Alfieri, A.A.; Kim, S.H.; Young, C.W. The potentiation of radiation effects on two murine tumors by lonidamine. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 1120–1123.
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; He, S.; Alfieri, A.A.; Young, C.W. Potentiation of radiation effects on multicellular tumor spheroids (mts) of hela cells by lonidamine. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1989, 16, 1277–1280.
- Issels, R.D. Hyperthermia adds to chemotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 2546–2554.
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Alfieri, A.; Young, C.W.; Silvestrini, B. Lonidamine: A hyperthermic sensitizer of HeLa cells in culture and of the Meth-A tumor in vivo. Oncology 1984, 41, 30–35.
- Silvestrini, B.; Hahn, G.M.; Cioli, V.; De Martino, C. Effects of lonidamine alone or combined with hyperthermia in some experimental cell and tumour systems. Br. J. Cancer 1983, 47, 221–231.
- Coss, R.A.; Storck, C.W.; Wells, T.C.; Kulp, K.A.; Wahl, M.; Leeper, D.B. Thermal sensitisation by lonidamine of human melanoma cells grown at low extracellular pH. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 30, 75–78.
- Horowitz, M.; Robinson, S.D. Heat shock proteins and the heat shock response during hyperthermia and its modulation by altered physiological conditions. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 162, 433–446.
- Bloch, W.E.; Lokeshwar, B.L.; Ferrell, S.M.; Block, N.L. Enhancement of hyperthermic toxicity by lonidarnine in the dunning R3327G rat prostatic adenocarcinorna. Prostate 1994, 24, 131–138.
- Stanisaw, K.; Bartosz, K.; Dawid, P.; Jolanta, S.; Ewa, K.D.; Karolina, K.C.; Jolanta, K.; Olga, M.; Krzysztof, K.; Julita, K. Photodynamic therapy-mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1098–1107.
- Ji, H.-T.; Chien, L.-T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chien, H.-F.; Chen, C.-T. 5-ALA mediated photodynamic therapy induces autophagic cell death via AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 91.
- Shevchuk, I.; Chekulayev, V.; Moan, J.; Berg, K. Effects of the inhibitors of energy metabolism, lonidamine and levamisole, on 5-aminolevulinic-acidinduced photochemotherapy. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 67, 791–799.
- Golding, J.; Wardhaugh, T.; Patrick, L.; Turner, M.; Phillips, J.B.; Bruce, I.J.; Kimani, S.G. Targeting tumour energy metabolism potentiates the cytotoxicity of 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 976–982.
