The retina, a multi-layered nervous structure in the back of the eye, detects light stimuli via specialised primary sensory neurons, named after their morphologies as retinal rods and cones. Rods and cones in vitro may retain their ability to respond to light for several hours by generating an electrical response. However, their viability and long-term operation require the functional interaction with retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells and a vascular system with peculiar features, the choroidal capillaries (ChC), whose specific form and shape support its function.
- metabolism
- acid
- elovanoids
- DHA
- Elovl2
1. Photoreceptors’ Anatomy and Eye Structure Afford Protection from Oxidative Damage
In photoreceptors, the sustained oxidative metabolism in darkness may lead to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as the hydroxyl •OH− or superoxide O2•− radicals [1], and direct measurements in vivo with either newly-developed probes [2] or MRI [3] indicate the inner segment (IS) or the outer retina as the most active retinal site for ROS generation. The ROS may damage sensitive photoreceptor cell components, such as nucleic acids and OS lipids, threatening photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells’ viability.
The localisation of mitochondria at the IS, a cellular compartment distinct from the nuclear region, and the non-random distribution of mitochondria within the IS [4] may help attenuate the damage expected from highly reactive oxygen radicals, whose travel distance may fall short of the inner segment-nuclear distance. Indeed, the travelling distance of •OH− has been estimated as few Angstroms, while O2•− may travel several tenths of microns [5][6], although their charge may prevent these ROS from crossing both plasma and nuclear membranes. This analysis is consistent with the observation that high energy heavy ions (Z ≥ 6) interaction with water may generate •OH−, which may interact with lipids to generate peroxyl radicals. The annihilation of two peroxyl radicals leads to the emission of a visible photon (revised in [7]). Astronauts travelling in deep space report the perception of light flashes [8], indicating rhodopsin activation by photons triggered in response to •OH− generation by high energy heavy ions [9]. Consistent with the limited diffusion space of •OH−, people on the Earth do not usually report light flashes in darkness, suggesting •OH− generated by oxidative metabolism may not diffuse up to OS, consistent with its limited diffusion space.
Despite the protection afforded by photoreceptor morphology toward genetic material and OS components, photoreceptors need additional factors to protect these sensitive molecular components from the blue light-triggered mitochondrial generation of O2•− and lipid peroxidation of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA), whose travelling distance may extend over IS, OS and nuclear regions. The cornea has high transmittance (around 90%) at wavelengths ranging from 400 to 480 nm, and the energy of sunlight in this spectral region at midday is slightly lower than in the green region of the spectra. Despite the variability linked to daytime, latitude, season, and humidity, the blue/green light ratio stays close to 0.9 at midday [10]. The anatomical organisation of the eye and its optics provide additional protection against blue light-induced oxidant generation. Due to the chromatic aberration of eye optics, blue light is expected to focus at a different axial position from green-red light stimuli. Human eye chromatic aberration analysis indicates an axial focus shift of about one diopter (1D) between 450 and 550 nm light [11]. Considering a 60 D refracting power for the not accommodated emmetropic eye, the −1D axial chromatic aberration will cause blue light to focus about 280 µm in advance of the green/red light (550 nm) focus (Figure 1).
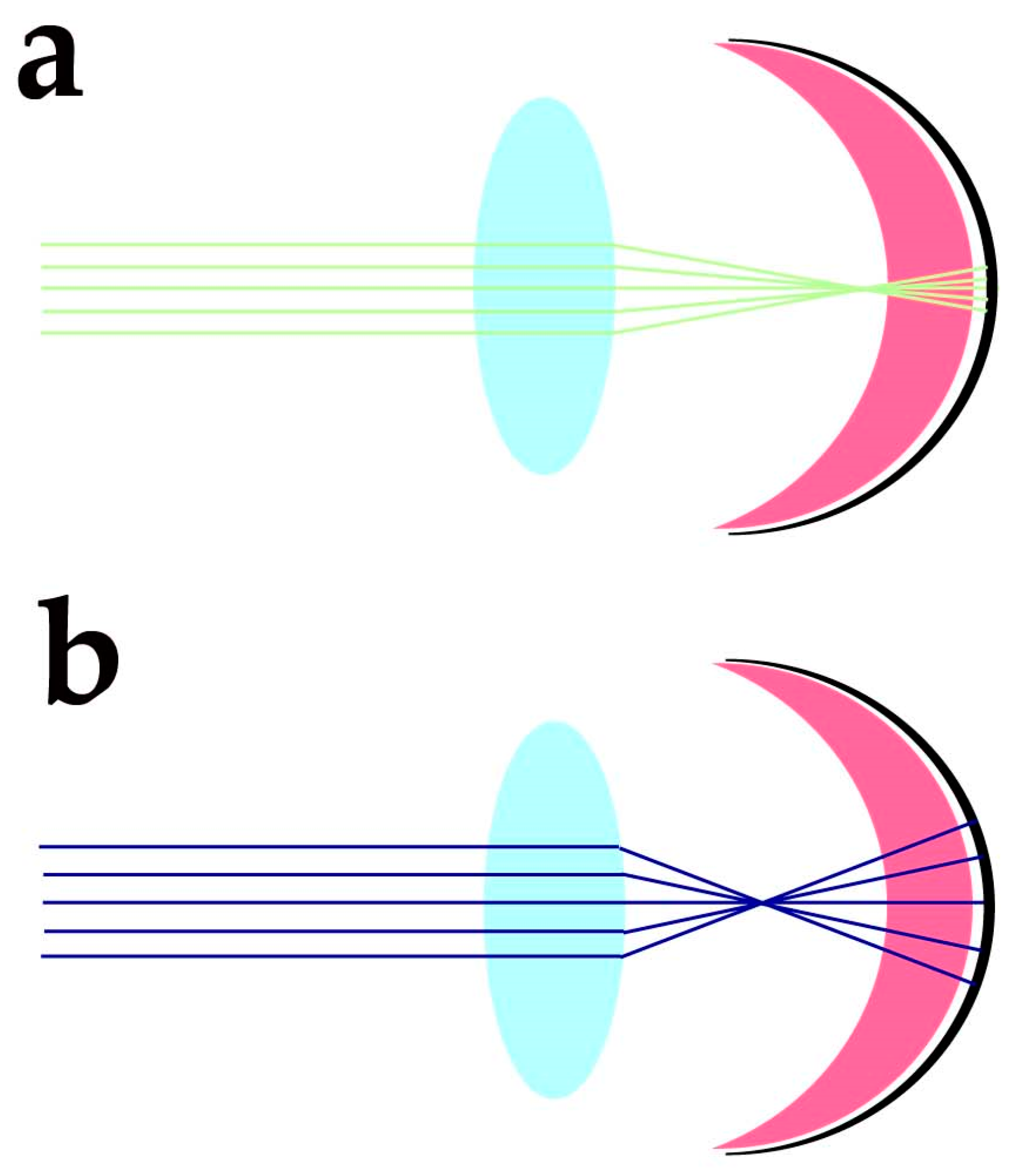
2. Protection against Oxidative Damage Requires Tight Control over Docosahexaenoic Acid Synthesis
The DHA and DHA-derived molecules provide a second protective mechanism against oxidative damage. Although OS PUFA may undergo peroxidation in response to blue light, emerging evidence indicates that DHA in the retina appears to operate as a double-edged sword, with damaging effects resulting from its oxidation and a protective role due to its metabolism in photoreceptors (reviewed in [13]) and RPE cells [14][15].
The balance between these opposing effects may depend on DHA levels. In the transgenic fat-1 mice expressing a Caenorhabditis elegans desaturase able to convert ω6 PUFA into ω3 [16] by introducing a double bond, retinal DHA levels increased two to five times in all phospholipid classes compared to WT mice, whereas ω6 fatty acid levels decrease [17]. The increase in DHA also associates with C32 and C34 ω-3 pentaenoic and hexaenoic VLCFA in phosphatidylcholine and depletion of ω-6 VLCFAs. From a functional perspective, fat-1 mice have scotopic and photopic ERGs a- (photoreceptor response) and b-wave (bipolar cell response) responses of unusually high amplitudes and lower thresholds, suggesting an increase in OS length [17] and an increased sensitivity to light. The latter effect may reflect an increased membrane fluidity and rhodopsin diffusion coefficient. The OS elongation may, however, increase the metabolic burden on photoreceptors due to increased Na+ and Ca2+ influx leading to increased O2 consumption and the development of hypoxic conditions at the IS, causing glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression in Müller cells and increased carboxyethylpyrrole (CEP, protein adducts produced from DHA oxidation) in photoreceptors [17]. In mice exposed to intense light, photoreceptors degeneration associated with enhanced lipid peroxidation increased with DHA levels [18], indicating a causal role for DHA in light-induced damage in photoreceptors. The observation of Müller glial cells activation, common during retinal degeneration, suggests that the increase in DHA leading to OS elongation may cause hypoxia and damage in photoreceptors and indicates the need for fine control over DHA levels in photoreceptors to prevent its adverse effects on retinal viability.
Photoreceptors may generate DHA from EPA [19] using the very long fatty acid elongase 2 (ELOVL2) (Figure 2a), which catalyses the conversion of EPA into docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) and then DPA conversion into tetracosapentaenoic acid, which is then converted into the DHA precursor tetracosahexaenoic acid by photoreceptor Δ6 desaturase [19] (reviewed in [20]).
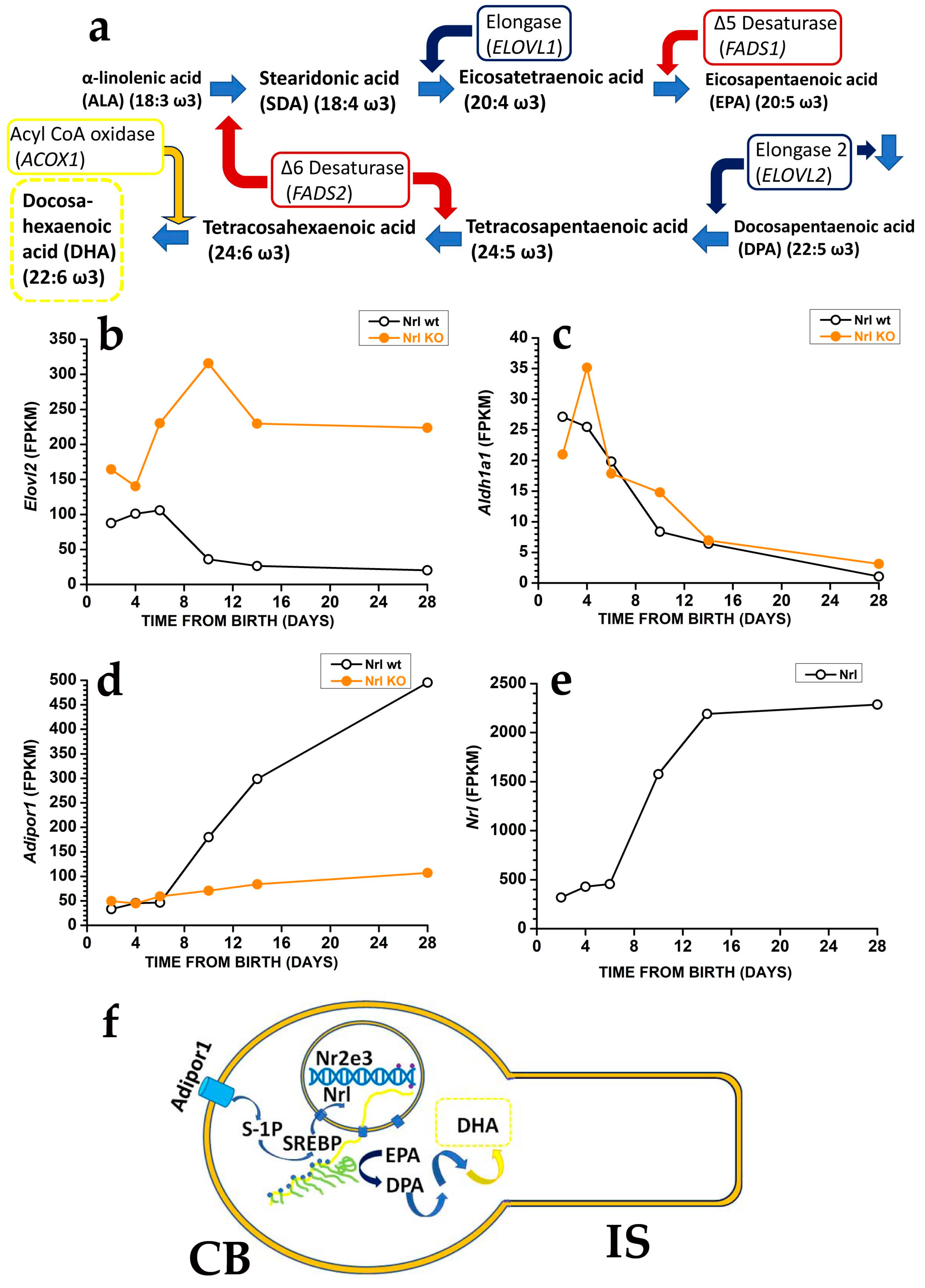
In mice, controlling DHA synthesis from EPA starts in rod precursors via the modulation of Elovl2 expression. The Elovl2 expression is already present two days after birth, i.e., before OS generation, but its levels decrease after postnatal days six, i.e., just before rods start developing an OS. As shown in Figure 2b, the reduction in Elovl2 expression may depend on the rod-specific transcription factor neural retina leucine zipper (Nrl), as Nrl-KO mice have an increased Elovl2 expression [21] (see also the RetSeq database at https://retseq.nei.nih.gov/ (accessed on 29 January 2023)). Vitamin A (all-trans-retinol) derivatives all-trans and 9-cis retinoic acid (RA) promote Nrl expression [22] in photoreceptors. There is evidence that during the early phase of mouse retinal development, both RPE cells and rod precursor express Aldh1a1, a gene coding for aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 subfamily a1 (Figure 2c) to generate at-RA from at-RAL [21] (see also the RetSeq database at https://retseq.nei.nih.gov/ (accessed on 29 January 2023)).
The orphan receptor transcription factor Nuclear receptor subfamily group E member 3, coded by Nr2e3 and whose expression is promoted by Nrl, may also contribute to Elovl2 downregulation [23]. These data may indicate that during the earlier retinal maturation, rods keep Elovl2 expression high to promote DHA synthesis and boost OS formation. However, rods reduce Elovl2 expression when OS appears, possibly to avoid their overgrowth that would translate into an increased at-RAL load for RPE cells. It is important to note that also Aldh1a1 expression drops at about the same time, which would translate into a reduced Nrl activation by at-RA. Reduced Nrl activation by RA would upregulate Elovl2 expression and DHA synthesis, thus promoting OS growth, and reduced Aldh1a1 expression may also prevent at-RAL detoxification in at-RA [24]. Recent evidence indicates that in the adult retina, at-RAL detoxification via its conversion into at-RA is carried out by two different enzymes, coded by Cyp26a1 expressed in Müller glial cells and by Cyp26b1 expressed in RPE cells [24]. It is relevant that Cyp26a1 expression in Müller cells starts after postnatal day 4 [25], i.e., when Aldha1 expression declines in rod precursors, indicating that the two enzymes operate over different temporal windows.The finding that rods have lower Elovl2 expression than cone-like cells of Nrl KO mice [26], while DHA levels are higher in rods than in cones, indicates a mismatch between the expression levels of the gene coding for a critical enzyme in DHA biosynthesis and DHA concentration in rods and cones OS. Although the mismatch cause is unclear, the different DHA turnover between rods and cones may be a possible reason. In rods, DHA is mainly used in phospholipids to increase disk membrane fluidity, increase rhodopsin diffusion coefficient, and amplify the first step in phototransduction, and its turnover is low. On the other hand, cones may have lower requirements for amplification in their phototransduction. They may instead mainly use DHA as a substrate for generating antioxidant molecules, whose increased turnover requires the higher synthetic rate provided by higher Elovl2 expression. Although this explanation sounds reasonable, it is important to stress that direct experimental support is lacking.
3. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid-Derived Very Long Chain Fatty Acids Exert Protective Effects toward Oxidative Stress by Turning on Specific Transduction Pathways
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/antiox12030617
References
- Du, Y.; Veenstra, A.; Palczewski, K.; Kern, T.S. Photoreceptor cells are major contributors to diabetes-induced oxidative stress and local inflammation in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 16586-16591, doi:10.1073/pnas.1314575110.
- Prunty, M.C.; Aung, M.H.; Hanif, A.M.; Allen, R.S.; Chrenek, M.A.; Boatright, J.H.; Thule, P.M.; Kundu, K.; Murthy, N.; Pardue, M.T. In Vivo Imaging of Retinal Oxidative Stress Using a Reactive Oxygen Species-Activated Fluorescent Probe. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2015, 56, 5862-5870, doi:10.1167/iovs.15-16810.
- Berkowitz, B.A.; Bredell, B.X.; Davis, C.; Samardzija, M.; Grimm, C.; Roberts, R. Measuring In Vivo Free Radical Production by the Outer Retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2015, 56, 7931-7938, doi:10.1167/iovs.15-18420.
- Meschede, I.P.; Ovenden, N.C.; Seabra, M.C.; Futter, C.E.; Votruba, M.; Cheetham, M.E.; Burgoyne, T. Symmetric arrangement of mitochondria:plasma membrane contacts between adjacent photoreceptor cells regulated by Opa1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 15684-15693, doi:10.1073/pnas.2000304117.
- Pryor, W.A. Oxy-radicals and related species: their formation, lifetimes, and reactions. Annu Rev Physiol 1986, 48, 657-667, doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.003301.
- Winterbourn, C.C. Reconciling the chemistry and biology of reactive oxygen species. Nat Chem Biol 2008, 4, 278-286, doi:10.1038/nchembio.85.
- Catala, A. An overview of lipid peroxidation with emphasis in outer segments of photoreceptors and the chemiluminescence assay. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2006, 38, 1482-1495, doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2006.02.010.
- Casolino, M.; Bidoli, V.; Morselli, A.; Narici, L.; De Pascale, M.P.; Picozza, P.; Reali, E.; Sparvoli, R.; Mazzenga, G.; Ricci, M.; et al. Space travel: Dual origins of light flashes seen in space. Nature 2003, 422, 680, doi:10.1038/422680a.
- Narici, L.; Paci, M.; Brunetti, V.; Rinaldi, A.; Sannita, W.G.; Carozzo, S.; Demartino, A. Bovine rod rhodopsin: 2. Bleaching in vitro upon 12C ions irradiation as source of effects as light flash for patients and for humans in space. Int J Radiat Biol 2013, 89, 765-769, doi:10.3109/09553002.2013.800245.
- Spitschan, M.; Aguirre, G.K.; Brainard, D.H.; Sweeney, A.M. Variation of outdoor illumination as a function of solar elevation and light pollution. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 26756, doi:10.1038/srep26756.
- Vinas, M.; Dorronsoro, C.; Cortes, D.; Pascual, D.; Marcos, S. Longitudinal chromatic aberration of the human eye in the visible and near infrared from wavefront sensing, double-pass and psychophysics. Biomed Opt Express 2015, 6, 948-962, doi:10.1364/BOE.6.000948.
- Marie, M.; Bigot, K.; Angebault, C.; Barrau, C.; Gondouin, P.; Pagan, D.; Fouquet, S.; Villette, T.; Sahel, J.A.; Lenaers, G.; et al. Light action spectrum on oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in A2E-loaded retinal pigment epithelium cells. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 287, doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0331-5.
- Bazan, N.G.; Calandria, J.M.; Serhan, C.N. Rescue and repair during photoreceptor cell renewal mediated by docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1. J Lipid Res 2010, 51, 2018-2031, doi:10.1194/jlr.R001131.
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Marcheselli, V.L.; Barreiro, S.; Hu, J.; Bok, D.; Bazan, N.G. Neurotrophins enhance retinal pigment epithelial cell survival through neuroprotectin D1 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 13152-13157, doi:10.1073/pnas.0705949104.
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Marcheselli, V.L.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.C.; Gordon, W.C.; Jackson, F.E.; Bazan, N.G. Photoreceptor outer segment phagocytosis attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis with concomitant neuroprotectin D1 synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 13158-13163, doi:10.1073/pnas.0705963104.
- Kang, J.X.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Kang, Z.B. Transgenic mice: fat-1 mice convert n-6 to n-3 fatty acids. Nature 2004, 427, 504, doi:10.1038/427504a.
- Suh, M.; Sauve, Y.; Merrells, K.J.; Kang, J.X.; Ma, D.W. Supranormal electroretinogram in fat-1 mice with retinas enriched in docosahexaenoic acid and n-3 very long chain fatty acids (C24-C36). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009, 50, 4394-4401, doi:10.1167/iovs.08-2565.
- Tanito, M.; Brush, R.S.; Elliott, M.H.; Wicker, L.D.; Henry, K.R.; Anderson, R.E. High levels of retinal membrane docosahexaenoic acid increase susceptibility to stress-induced degeneration. J Lipid Res 2009, 50, 807-819, doi:10.1194/jlr.M800170-JLR200.
- Simon, M.V.; Agnolazza, D.L.; German, O.L.; Garelli, A.; Politi, L.E.; Agbaga, M.P.; Anderson, R.E.; Rotstein, N.P. Synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid from eicosapentaenoic acid in retina neurons protects photoreceptors from oxidative stress. J Neurochem 2016, 136, 931-946, doi:10.1111/jnc.13487.
- Dyall, S.C. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Front Aging Neurosci 2015, 7, 52, doi:10.3389/fnagi.2015.00052.
- Kim, J.W.; Yang, H.J.; Brooks, M.J.; Zelinger, L.; Karakulah, G.; Gotoh, N.; Boleda, A.; Gieser, L.; Giuste, F.; Whitaker, D.T.; et al. NRL-Regulated Transcriptome Dynamics of Developing Rod Photoreceptors. Cell Rep 2016, 17, 2460-2473, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.074.
- Khanna, H.; Akimoto, M.; Siffroi-Fernandez, S.; Friedman, J.S.; Hicks, D.; Swaroop, A. Retinoic acid regulates the expression of photoreceptor transcription factor NRL. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 27327-27334, doi:10.1074/jbc.M605500200.
- Cheng, H.; Aleman, T.S.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Khanna, R.; Jacobson, S.G.; Swaroop, A. In vivo function of the orphan nuclear receptor NR2E3 in establishing photoreceptor identity during mammalian retinal development. Hum Mol Genet 2006, 15, 2588-2602, doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl185.
- Xia, Q.Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Li, J. All-trans-retinoic acid generation is an antidotal clearance pathway for all-trans-retinal in the retina. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2019, 20, 960-971, doi:10.1631/jzus.B1900271.
- Ueno, K.; Iwagawa, T.; Ochiai, G.; Koso, H.; Nakauchi, H.; Nagasaki, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, S. Analysis of Muller glia specific genes and their histone modification using Hes1-promoter driven EGFP expressing mouse. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 3578, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-03874-8.
- Nikonov, S.S.; Daniele, L.L.; Zhu, X.; Craft, C.M.; Swaroop, A.; Pugh, E.N., Jr. Photoreceptors of Nrl -/- mice coexpress functional S- and M-cone opsins having distinct inactivation mechanisms. J Gen Physiol 2005, 125, 287-304, doi:10.1085/jgp.200409208.
- Nguyen, T.M.D. Adiponectin: Role in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int J Prev Med 2020, 11, 136, doi:10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_193_20.
- Osada, H.; Toda, E.; Homma, K.; Guzman, N.A.; Nagai, N.; Ogawa, M.; Negishi, K.; Arita, M.; Tsubota, K.; Ozawa, Y. ADIPOR1 deficiency-induced suppression of retinal ELOVL2 and docosahexaenoic acid levels during photoreceptor degeneration and visual loss. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 458, doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03741-5.
- Rice, D.S.; Calandria, J.M.; Gordon, W.C.; Jun, B.; Zhou, Y.; Gelfman, C.M.; Li, S.; Jin, M.; Knott, E.J.; Chang, B.; et al. Adiponectin receptor 1 conserves docosahexaenoic acid and promotes photoreceptor cell survival. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 6228, doi:10.1038/ncomms7228.
- Sluch, V.M.; Banks, A.; Li, H.; Crowley, M.A.; Davis, V.; Xiang, C.; Yang, J.; Demirs, J.T.; Vrouvlianis, J.; Leehy, B.; et al. ADIPOR1 is essential for vision and its RPE expression is lost in the Mfrp(rd6) mouse. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 14339, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-32579-9.
- Ruiz, M.; Devkota, R.; Panagaki, D.; Bergh, P.O.; Kaper, D.; Henricsson, M.; Nik, A.; Petkevicius, K.; Hoog, J.L.; Bohlooly, Y.M.; et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate mediates adiponectin receptor signaling essential for lipid homeostasis and embryogenesis. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 7162, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-34931-0.
- Kita, S.; Fukuda, S.; Maeda, N.; Shimomura, I. Native adiponectin in serum binds to mammalian cells expressing T-cadherin, but not AdipoRs or calreticulin. Elife 2019, 8, doi:10.7554/eLife.48675.
- Pilon, M. Paradigm shift: the primary function of the "Adiponectin Receptors" is to regulate cell membrane composition. Lipids Health Dis 2021, 20, 43, doi:10.1186/s12944-021-01468-y.
- Chen, D.; Chao, D.L.; Rocha, L.; Kolar, M.; Nguyen Huu, V.A.; Krawczyk, M.; Dasyani, M.; Wang, T.; Jafari, M.; Jabari, M.; et al. The lipid elongation enzyme ELOVL2 is a molecular regulator of aging in the retina. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13100, doi:10.1111/acel.13100.
- Swinkels, D.; Das, Y.; Kocherlakota, S.; Vinckier, S.; Wever, E.; van Kampen, A.H.C.; Vaz, F.M.; Baes, M. Cell Type-Selective Loss of Peroxisomal beta-Oxidation Impairs Bipolar Cell but Not Photoreceptor Survival in the Retina. Cells 2022, 11, doi:10.3390/cells11010161.
- Das, Y.; Roose, N.; De Groef, L.; Fransen, M.; Moons, L.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Baes, M. Differential distribution of peroxisomal proteins points to specific roles of peroxisomes in the murine retina. Mol Cell Biochem 2019, 456, 53-62, doi:10.1007/s11010-018-3489-3.
- Lewandowski, D.; Sander, C.L.; Tworak, A.; Gao, F.; Xu, Q.; Skowronska-Krawczyk, D. Dynamic lipid turnover in photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelium throughout life. Prog Retin Eye Res 2022, 89, 101037, doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101037.
- German, O.L.; Insua, M.F.; Gentili, C.; Rotstein, N.P.; Politi, L.E. Docosahexaenoic acid prevents apoptosis of retina photoreceptors by activating the ERK/MAPK pathway. J Neurochem 2006, 98, 1507-1520, doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04061.x.
- German, O.L.; Monaco, S.; Agnolazza, D.L.; Rotstein, N.P.; Politi, L.E. Retinoid X receptor activation is essential for docosahexaenoic acid protection of retina photoreceptors. J Lipid Res 2013, 54, 2236-2246, doi:10.1194/jlr.M039040.
- Marcheselli, V.L.; Hong, S.; Lukiw, W.J.; Tian, X.H.; Gronert, K.; Musto, A.; Hardy, M.; Gimenez, J.M.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N.; et al. Novel docosanoids inhibit brain ischemia-reperfusion-mediated leukocyte infiltration and pro-inflammatory gene expression. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 43807-43817, doi:10.1074/jbc.M305841200.
- Bazan, N.G. Cell survival matters: docosahexaenoic acid signaling, neuroprotection and photoreceptors. Trends Neurosci 2006, 29, 263-271, doi:10.1016/j.tins.2006.03.005.
- Agbaga, M.P.; Brush, R.S.; Mandal, M.N.; Henry, K.; Elliott, M.H.; Anderson, R.E. Role of Stargardt-3 macular dystrophy protein (ELOVL4) in the biosynthesis of very long chain fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 12843-12848, doi:10.1073/pnas.0802607105.
- Yu, M.; Benham, A.; Logan, S.; Brush, R.S.; Mandal, M.N.A.; Anderson, R.E.; Agbaga, M.P. ELOVL4 protein preferentially elongates 20:5n3 to very long chain PUFAs over 20:4n6 and 22:6n3. J Lipid Res 2012, 53, 494-504, doi:10.1194/jlr.M021386.
- Yeboah, G.K.; Lobanova, E.S.; Brush, R.S.; Agbaga, M.P. Very long chain fatty acid-containing lipids: a decade of novel insights from the study of ELOVL4. J Lipid Res 2021, 62, 100030, doi:10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100030.
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Jun, B.; Belayev, L.; Heap, J.; Kautzmann, M.A.; Obenaus, A.; Menghani, H.; Marcell, S.J.; Khoutorova, L.; Yang, R.; et al. Elovanoids are a novel class of homeostatic lipid mediators that protect neural cell integrity upon injury. Sci Adv 2017, 3, e1700735, doi:10.1126/sciadv.1700735.
- Barabas, P.; Liu, A.; Xing, W.; Chen, C.K.; Tong, Z.; Watt, C.B.; Jones, B.W.; Bernstein, P.S.; Krizaj, D. Role of ELOVL4 and very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in mouse models of Stargardt type 3 retinal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 5181-5186, doi:10.1073/pnas.1214707110.
- Agbaga, M.P.; Tam, B.M.; Wong, J.S.; Yang, L.L.; Anderson, R.E.; Moritz, O.L. Mutant ELOVL4 that causes autosomal dominant stargardt-3 macular dystrophy is misrouted to rod outer segment disks. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014, 55, 3669-3680, doi:10.1167/iovs.13-13099.
- Jun, B.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Asatryan, A.; Kautzmann, M.A.; Heap, J.; Gordon, W.C.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Yang, R.; Petasis, N.A.; Bazan, N.G. Elovanoids are novel cell-specific lipid mediators necessary for neuroprotective signaling for photoreceptor cell integrity. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 5279, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-05433-7.
- Bazan, N.G. Overview of how N32 and N34 elovanoids sustain sight by protecting retinal pigment epithelial cells and photoreceptors. J Lipid Res 2021, 62, 100058, doi:10.1194/jlr.TR120001137.
