2. HDL/apoA-I Kinetics
3. HDL Functions
3.1. Reverse Cholesterol Transport
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
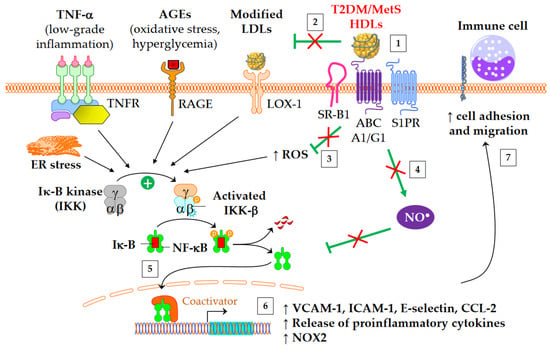
3.3. Antioxidative Properties
3.4. Nitric Oxide Production
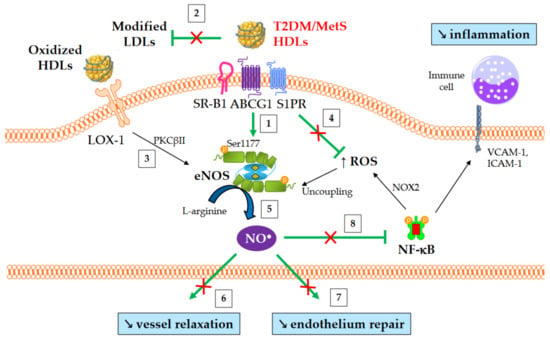
Alterations affecting high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) are one of the various abnormalities observed in dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. Kinetic studies have demonstrated that the catabolism of HDL particles is accelerated. Both the size and the lipidome and proteome of HDL particles are significantly modified, which likely contributes to some of the functional defects of HDLs. Studies on cholesterol efflux capacity have yielded heterogeneous results, ranging from a defect to an improvement. HDLs are less able to inhibit the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) proinflammatory pathway, and subsequently, the adhesion of monocytes on endothelium and their recruitment into the subendothelial space. In addition, the antioxidative function of HDL particles is diminished, thus facilitating the deleterious effects of oxidized low-density lipoproteins on vasculature. Lastly, the HDL-induced activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is less effective in T2DM and metabolic syndrome, contributing to several HDL functional defects, such as an impaired capacity to promote vasodilatation and endothelium repair, and difficulty counteracting the production of reactive oxygen species and inflammation
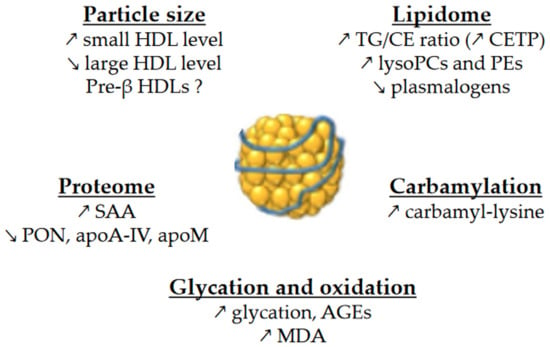
HDL particles are enriched in TGs in patients with T2DM [18,19,39,40,41], obesity [42], insulin resistance [40,43] or MetS [44]. The replacement of CE by TG molecules in HDLs affects the conformation of apoA-I [45], which could modulate binding to receptors and the functions of HDLs.
PLs and SPLs represent more than one third of the total mass of HDLs. They play a major role in HDL functions, either by binding to a specific receptor, such as sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors or by modulating the physicochemical properties of HDLs. Lipidomic studies have revealed several changes in the HDL phosphosphingolipidome, although the results are quite heterogeneous. The expression of results in relation to either total HDL mass, total HDL lipids, or apoA-I levels makes it challenging to compare between studies. The HDL content in total PLs has been found to be either decreased in T2DM when the results are expressed in relation to total lipids [40], or normal when the results are expressed in relation to total mass or total lipids [18,41].
Taken together, phosphatidylcholines (PCs, the main PL class) and sphingomyelins (SMs) represent more than 80% of PLs/SPLs in HDLs. When the results are expressed in relation to apoA-I, the HDL content in PCs and SMs in T2DM has been found to be either normal or decreased [19,41]. When the results are expressed in relation to total HDL lipids, PCs and SMs have been found decreased in T2DM HDLs [40].


This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/metabo13020253