Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Cardiac remodeling can cause ventricular dysfunction and progress to heart failure, a cardiovascular disease that claims many lives globally. Ivabradine, a funny channel (If) inhibitor, is used in patients with chronic heart failure as an adjunct to other heart failure medications.
- heart failure
- left ventricular dysfunction
- myocardial fibrosis
- cardiac function
1. Introduction
Heart failure is the leading cause of death worldwide. It is the costliest disease and has become a socioeconomic burden globally [1]. Its prevalence is estimated to be approximately 1–2% in developed countries [2], claiming nearly nine million lives in 2019 [3]. It causes repeated hospitalization [4]; it commonly arises from complications of other ailments, such as ischemic heart disease and uncontrolled hypertension [5].
A high resting heart rate increases the risk of adverse outcomes (morbidity and mortality) in patients with heart failure [6]. Thus, besides the reduction in excessive neurohumoral activation in patients with heart failure, slowing down the heart rate seems to be another therapeutic option [7][8]. This target is commonly achieved using β-blockers. However, clinically, uptitration of the drugs to the optimal dosage is complicated due to side effects [9]. Ivabradine (Figure 1), marketed as Procoralan®, Ivabid®, or Ivazine®, is a pure heart rate reducer [7]. The drug was originally approved for the treatment of angina pectoris; however, since 2005, it has been used as an adjunct therapy in patients with stable symptomatic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) with concomitant high resting heart rate (>70 beats per min), which is an independent predictor for cardiovascular disease [7][9].
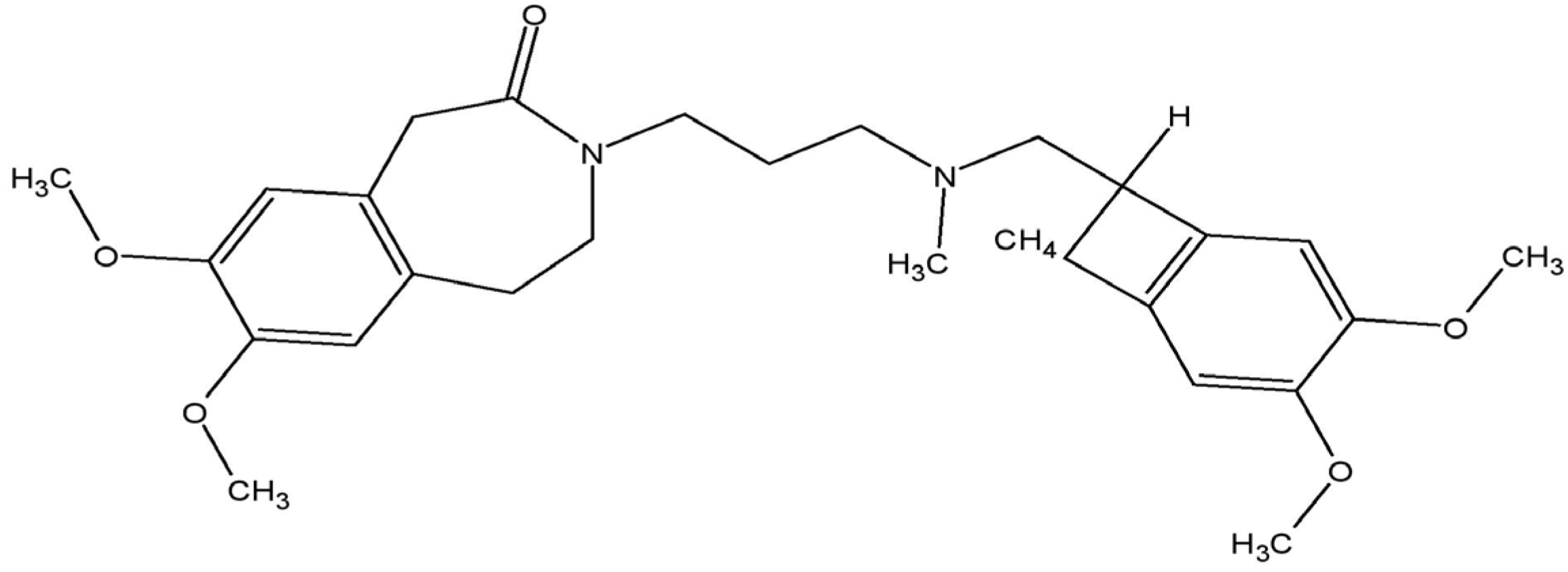
Figure 1. Molecular structure of ivabradine.
Cardiac remodeling is a process that involves structural changes affecting the size and shape of the myocardium, characterized by cardiac hypertrophy. Cellular and molecular changes can lead to cardiac dysfunction [10]. Animal studies demonstrated that ivabradine therapy reduced these changes, evidenced by a reduction in growth factors, collagen, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, the increase in which leads to myocardial fibrosis in animal models of heart failure [11][12]. It also ameliorated myocardial inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress as well as improved myocardial biogenesis in the remodeled hearts [12][13][14][15], all factors potentially contributing to the antiremodeling effects.
2. Clinical Outcomes of Ivabradine Therapy
Increased mortality due to cardiovascular events and frequent hospitalization are common in patients with heart failure. In addition, the progression of heart failure reduces the quality of life of these patients. Many clinical trials, such as the Systolic Heart Failure Treatment with the If Inhibitor Ivabradine Trial (SHIFT), Long-term Treatment with Ivabradine in Ambulatory Patients with Chronic Heart Failure (RELIf-CHF), Study Assessing the Morbidity-Mortality Benefits of the If Inhibitor Ivabradine in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease (SIGNIFY), and Morbidity-mortality Evaluation of the If Inhibitor Ivabradine in Patients with Coronary Disease and Left Ventricular Dysfunction (BEAUTIFUL), have been conducted to assess the outcomes. Heart failure patients taking ivabradine have a reduced risk, frequency, and length of hospitalization due to worsening heart failure, other cardiovascular disease, or other co-morbidities, compared with those who do not take ivabradine (Table 1) [16][17][18][19][20].
Table 1. Effects of ivabradine therapy on clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure.
| Subjects | Dose of Ivabradine | Type of Study | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with HF (LVEF < 40%, HR > 70 bpm) (n = 37) | 2.5–7.5 mg, b.i.d. for >12 months | Retrospective cohort study | ↓ risk of hospitalization ↓ number of hospitalizations ↔ length of hospitalization ↔ death rate |
[16] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients with HR > 70 bpm (n = 3241) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ event rates in patients with 0 or 3+ comorbidities ↓ HF hospitalization |
[17] |
| Hemodynamically stable acute HF patients (n = 63) | Started at 5 mg daily, followed by 10 mg daily for >90 days | Retrospective cohort | ↓ length of hospitalization ↓ rehospitalization ↓ high dose of β-blockers ↓ NYHA class |
[18] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients with HR > 77 bpm (n = 208) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 31–35 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ NYHA class ↑ Global self-assessment improvement ↑ Global assessment improvement (physician perspective) ↑ Health-related quality of life ↓ all-cause cardiovascular death ↓ all-cause hospitalization ↓ all-cause mortality |
[19] |
| Patients with chronic HF (n = 767) (RELIf-CHF study) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 12 months | Observational follow-up study | ↓ NYHA class ↓ decompensation ↓ HF hospitalizations ↑ general health ↑ QoL |
[20] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients with HR < 75 (n = 1188) and >75 bpm (n = 2052) (SHIFT study) | 5 mg b.i.d. titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. for a median follow-up of 22.5 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | In HR > 75 bpm group: ↓ cardiovascular death ↓ death from HF ↓ hospitalization In HR < 75 bpm group: ↔ cardiovascular death ↔ death from HF ↔ hospitalization |
[21] |
| Hospitalized HF patients in the SHIFT study (n = 514) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 3 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ all-cause hospitalization at 1, 2, and 3 months ↔ hospitalization due to cardiovascular causes at all time-points ↔ death rate |
[22] |
| Acute HF patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease (n = 12) | 2.5 mg/d b.i.d. titrated to 5 mg/d b.i.d. for 2 weeks | Retrospective observational study | ↓ NYHA class | [23] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients with HR > 70 bpm plus angina pectoris (n = 1085) (SHIFT and SIGNIFY studies) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 31-35 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | SHIFT study: ↔ Composite primary end point ↔ Cardiovascular death ↔ First hospitalization due to worsening HF SIGNIFY study: ↔ Composite primary end point ↔ Cardiovascular death ↔ non-fatal MI |
[24] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients (HR > 70 bpm) with prior mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) (n = 1981) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 31–35 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | Compared to the MRA group at baseline: ↔ Composite primary end point ↔ Cardiovascular death ↔ HF death |
[25] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients (HR > 70 bpm) with diabetes (n = 973) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 31–35 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↔ Outcomes of different treatments (ivabradine vs. placebo; insulin vs. non-insulin) In diabetic and non-diabetic patients: ↓ hospitalization for worsening HF ↓ cardiovascular hospitalization In non-diabetic patients: ↓ all-cause hospitalization |
[26] |
| Patients with HFpEF (n = 84) (EDIFY study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 8 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial | ↔ 6MWT | [27] |
| Acute decompensated HFrEF patients (n = 292) | Not given. Follow-up for 1 year after discharge | Retrospective study | ↓ cardiovascular death ↓ all-cause mortality ↓ rehospitalization ↓ NYHA class |
[28] |
| Patients with systolic chronic HF (n = 98) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 6 months | Open-label, blinded, parallel-group, interventional, prospective-cohort study | ↓ NYHA class | [29] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients (HR > 70 bpm) with left bundle branch block (n = 467) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 31-35 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↔ primary end point ↔ cardiovascular death ↔ HF hospitalization ↔ all-cause death |
[30] |
| Patients with chronic HF (n = 110) (APULIA study) | 5 mg b.i.d. for a month | Multicentric observational study | ↓ HR ↑ physical functioning ↑ physical role functioning ↑ emotional role functioning ↑ mental health scale |
[31] |
| Patients with cardiomyopathy (n = 33) | 5 mg b.i.d. for 3 months and 7.5 mg b.i.d. for 3 months | Observational study | ↓ NYHA class ↑ general health ↑ social activity ↑ physical health ↑ emotional health |
[32] |
| Hospitalized patients with acute decompensated systolic heart failure (n = 10) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. until discharged | Observational, open-label, longitudinal, and retrospective study | ↓ NYHA class | [33] |
| Patients with HF (n = 10) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. for 6 months | Randomized, double-blind study | ↓ NYHA class ↑ QoL |
[34] |
| Patients with chronic HF (n = 1873) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 4 months | Observational and longitudinal study | ↓ NYHA class ↓ decompensation |
[35] |
| Children with dilated cardiomyopathy (n = 74) | 0.02 mg/kg b.i.d. (6–12 months old) or 0.05 mg/kg b.i.d. (1–18 years old) or 2.5 mg b.i.d. (>40 kg bw) and titrated for 12 months. | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II/III clinical trial | ↑ PedQL ↔ NYHA class |
[36] |
b.i.d., twice daily; bw, body weight; HF, heart failure; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HR, heart rate; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; NYHA, New York Heart Association; PedQL, pediatric quality of life inventory; QoL, quality of life; 6MWT, 6 min walking test; ↔, no difference; ↓, reduced; ↑, increased.
However, the effects of ivabradine on mortality rate in these patients were inconsistent. Most studies including principal trials (SHIFT, BEAUTIFUL, and SIGNIFY) reported that ivabradine therapy failed to decrease the rate of death due to cardiovascular disease or other causes despite the reduction in hospitalization [16][22][24][25][30][37]. Nevertheless, three studies reported positive outcomes on mortality due to cardiovascular events or heart failure following ivabradine treatment [19][21][28] in patients with a resting heart rate higher than 75 beats per minute; however, these outcomes were not observed in patients with a lower resting heart rate [21]. An elevated resting heart rate predisposes a patient to developing left ventricular systolic dysfunction [38]. Therefore, a reduction in heart rate by ivabradine would potentiate systolic function, leading to a reduction in the severity of the disease, evidenced by a lower New York Heart Association class [18][19][20][23][28][29][32][33][34][36]. Furthermore, this would decrease hospital readmissions due to the worsening of heart failure.
In terms of quality of life, ivabradine therapy improved global assessment, either by patient self-assessment or assessment by their physician (Table 1) [19]. This translated to increased health-related quality of life evidenced by a reduction in heart-failure-associated symptoms and improvements in physical, social, and emotional functioning, well-being, vitality, and general health. Furthermore, these improvements led to increased mental health scores [20][31][32][34]. A clinical trial was conducted on children (aged 6 months to 18 years old) with dilated cardiomyopathy. It was reported that ivabradine improved the quality of life in these children [36]. In summary, ivabradine therapy improves heart-failure-associated symptoms, resulting in a better quality of life for patients, but with limited success in reducing mortality in these patients.
3. Effects on Cardiac Function
As previously mentioned, one of the primary targets in patients with chronic heart failure is a reduction in excessive neurohumoral activation, particularly in terms of the attenuation of the sympathetic system and renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system activation. The use of β-blockers not only decreases the heart rate but also decreases cardiac contractility and blood pressure in these patients. In addition, high doses of β-blockers result in reduced patient tolerance for the drug’s side effects, which include fatigue and hypotension [9]. Ivabradine is used as a second-line treatment in addition to β-blockers and other drugs used for heart failure treatment [9][39]. The heart-rate-lowering property of ivabradine at doses of 5–7.5 mg twice daily has been observed in many clinical studies in both acute and chronic heart failure patients (Table 2) [18][28][40][41]. However, the effect was not apparent in heart failure patients with a resting heart rate lower than 75 beats per minute [21], suggesting that it has the potential to not cause bradycardia.
Table 2. Effects of ivabradine on cardiac function in human studies.
| Subjects | Dose of Ivabradine | Type of Study | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitalized patients with severe CHF (n = 10) | Infusion at 0.1 mg/kg for 90 min, followed by 0.05–0.075 mg/kg for 90 min | Single-center open-label phase II clinical trial | At 4 h: ↓ HR, ↑ SV ↑ LV systolic work |
[40] |
| Hemodynamically stable acute HF patients (n = 63) | Started at 5 mg daily, followed by 10 mg daily for > 90 days | Retrospective cohort | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF ↔ SBP, ↔ DBP |
[18] |
| Patients with chronic HF (n = 1873) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 4 months | Observational and longitudinal study | ↑ LVEF | [35] |
| Acute decompensated HFrEF patients (n = 292) | Not given. Follow-up for 1 year after discharge | Retrospective study | ↓ HR ↔ SBP, ↔ LVEF |
[28] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients with HR < 75 (n = 1188) and >75 bpm (n = 2052) (SHIFT study) | 5 mg b.i.d. titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. for a median follow-up of 22.5 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | In HR > 75 bpm group: ↓ HR In HR < 75 bpm group: ↔ HR |
[21] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients with HR > 70 bpm (n = 298) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 8 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ office HR ↓ 24-HR ↓ HR awake ↓ HR asleep |
[42] |
| Patients with chronic HF (n = 30) | 5 mg b.i.d. for 4 months | Cross-sectional | ↓ LVEDV, ↓ LVESV ↑ LVEF, ↑ SV, ↑ Ees ↓ VAC |
[41] |
| Acute HF patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease (n = 12) |
2.5 mg/d b.i.d. titrated to 5 mg/d b.i.d. for 2 weeks | Retrospective observational study | ↓ HR ↑ LVEF |
[23] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients with HR > 77 bpm (n = 208) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 31–35 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ LVESVI, ↓ LVESV, ↓ LVEDVI, ↓ LVEDV, ↑ LVEF |
[19] |
| Patients with HFpEF (n = 84) (EDIFY study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 8 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ HR ↔ E/e′, ↔ E, ↔ Ea, ↔ Ees, ↔ Ea/Ees ↔ Total mitral flow duration ↔ Mitral flow integral time velocity ↔ Lateral e′, ↔ Septal e′ ↔ Mean of lateral and septal e′ ↔ LVEDV, ↔ SV, ↔ LAVI |
[27] |
| Male patients with chronic HF (n = 22) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg for 6 months | Longitudinal study | ↓ HR ↔ SBP, ↔ DBP, ↔ LVEF |
[43] |
| Patients with systolic chronic HF (n = 98) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 6 months | Open-label, blinded, parallel-group, interventional, prospective-cohort study | ↓ HR | [29] |
| Patients with systolic HF (n = 43) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 3 months | Longitudinal study | ↓ HR ↔ SBP, DBP ↔ LVEDV, LVESV, LVEF, ↔ E/A, ↓ E/E′ ↓ LA Vmax, ↓ LA Vp ↔ LA Vmin ↔ LA passive emptying volume and fraction ↓ LA active emptying volume and fraction ↓ PA lateral, septum, and tricuspid ↓ PA lateral–PA tricuspid ↔ PA lateral–PA septum ↓ PA septum–PA tricuspid ↓ interatrial conduction delay ↔ left intra-atrial conduction delay ↓ right intra-atrial conduction delay |
[44] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients (HR > 70 bpm) (n = 143) (SHIFT study) | Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 8 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ HR, ↔ LVESP, ↑ SV ↔ Pulse pressure, ↔ MAP ↑ Total arterial compliance ↓ Ea, ↔ TPR, ↔ CO, ↔ Ees ↑ LVEF, ↔ LVESV ↔ LVEDV, ↔ Ea/Ees |
[45] |
| Patients with cardiomyopathy (n = 33) |
5 mg b.i.d. for 3 months and 7.5 mg b.i.d. for 3 months | Observational study | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF | [32] |
| Hospitalized patients with acute decompensated systolic heart failure (n = 10) |
Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. until discharged | Observational, open-label, longitudinal, and retrospective study | ↓ HR, ↓ SBP ↔ DBP, ↔ MBP |
[33] |
| Moderate-to-severe HF patients (HR > 70 bpm) with left bundle branch block (n = 208) (SHIFT study) |
Started at 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 8 months | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter clinical trial | ↓ LVESVI, ↓ LVEDVI ↓ LVESV, ↓ LVEDV ↑ LVEF |
[46] |
| Patients with HF (n = 10) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg b.i.d. for 6 months | Randomized, double-blind, double-dummy study |
↑ VO2 | [34] |
| Patients with chronic HF (n = 1873) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 4 months | Observational and longitudinal study | ↑ LVEF | [35] |
| Patients with chronic HF (n = 767) (RELIf-CHF study) | 5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg or 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 12 months | Observational follow-up study | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF | [20] |
| Patients with stable symptomatic chronic HF (n = 52) |
5 mg b.i.d. and titrated to 7.5 mg 2.5 mg b.i.d. for 12 months | Observational follow-up study | ↓ LVEDV, ↓ LVESV, ↑ LVEF, ↓ DT ↔ TAPSE, ↔ PASP, ↔ RV FAC, ↔ E peak, ↔ A peak, ↔ myocardial performance index ↑ systolic velocity ↑ Early diastolic velocity ↓ Late diastolic velocity ↔ RV IVV, ↔ RV IVA ↑ RV GLS, ↑ RV LS ↑ RV LSRS, ↑ RV LSRE ↑ RV LSRA |
[47] |
| Children with dilated cardiomyopathy (n = 74) |
0.02 mg/kg b.i.d. (6–12 months old) or 0.05 mg/kg b.i.d. (1–18 years old) or 2.5 mg b.i.d. (>40 kg bw) and titrated for 12 months. | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II/III clinical trial | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF | [36] |
b.i.d., twice daily; bw, body weight; CHF, congestive heart failure; CO, cardiac output; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; DT, deceleration time; E, early diastolic mitral inflow velocity; E′, early diastolic mitral annular velocity; Ea, arterial elastance; E/A, early-to-late diastolic mitral inflow velocity; E/e′, ratio of peak early diastolic mitral flow velocity to the mean of annular lateral and septal velocities; Ees, left ventricular end-systolic elastance; FAC, fractional area change; GLS, global longitudinal strain; HF, heart failure; HR, heart rate; IVA, myocardial acceleration during isovolumic contraction; IVV, peak myocardial velocity during isovolumic contraction; LA, left atrium; LAVI, left atrial volume index; LS, longitudinal strain; LSRA, longitudinal strain rate diastolic late filling; LSRE, longitudinal strain rate diastolic early filling; LSRS, systolic longitudinal strain rate; LV, left ventricle; LVEDV, left ventricular end-diastolic volume; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVESP, left ventricular end-systolic pressure; LVESV, left ventricular end-systolic volume; LVESVI, left ventricular end-systolic volume index; MAP, mean arterial pressure; MBP, mean blood pressure; PA, the interval from the onset of P wave to appearance of the late diastolic wave in Doppler imaging; PASP, pulmonary artery systolic pressure; RV, right ventricle; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SV, stroke volume; TAPSE, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; TPR, total peripheral resistance; Vmax, maximum volume at the end-systolic phase; Vmin, minimum volume at the end-diastolic phase; VAC, ventricular-arterial coupling; VO2, peak oxygen consumption; Vp, volume before P wave; ↔, no difference; ↓, reduced; ↑, increased.
In contrast with β-blockers, ivabradine does not affect blood pressure [18][28][33][44] or myocardial contractility [9] in patients with heart failure. The reduction in heart rate observed in the patients taking ivabradine leads to a decrease in left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) [19][46] and the ratio of early diastolic mitral inflow velocity to early diastolic mitral annular velocity (E/E′) (Table 2) [44]. However, other parameters of diastolic function, such as ratios of early-to-late diastolic mitral inflow velocity (E/A) and early diastolic mitral inflow velocity to early diastolic velocity of the septal mitral annulus (E/e′), were not significantly altered by ivabradine [27][44]. Following the improvement in diastolic function, ivabradine indirectly ameliorates systolic work in patients, manifested by increased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), end-systolic elastance (Ees), and stroke volume and decreased end-systolic volume (LVESV) [18][19][23][35][40][41][46]. However, several studies demonstrated unaltered Ees [27][45] and LEVF [28][43][44] following ivabradine therapy.
Studies exploring the impact of ivabradine on right ventricular function in patients with heart failure are lacking. Only Gul et al. [47] reported that the drug therapy ameliorated right ventricular function based on the improvement of strain rate and global longitudinal strain parameters. However, it was a small non-randomized study involving only two centers. The improvement in the right ventricular function could arise from the improvement of the left ventricular performance, which decreases the right ventricular afterload.
Left ventricular dysfunction is closely related to prolonged atrial conduction time, with the latter increasing the risk of atrial fibrillation in patients with heart failure [48]. Only one study investigated the effects of ivabradine on atrial mechanical function. The delay in interatrial and right intra-atrial conduction was significantly reduced in patients with systolic heart failure after 3 months on ivabradine [44]. Furthermore, the drug improved atrial electromechanical function in these patients, indicated by decreased left atrial active emptying volume and fraction and decreased duration of onset of the P wave to the beginning of the late diastolic wave at the septal and lateral mitral annulus and right ventricular tricuspid annulus [44]. These observations suggest that ivabradine may exert beneficial effects on myocardial atrial performance, with the potential to reduce the risk of developing arrhythmia in patients with heart failure. However, a recent meta-analysis that included 13 clinical trials inferred that regardless of the dose, ivabradine increased the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients. However, the drug is effective in preventing post-operative atrial fibrillation [49]. Nonetheless, more clinical studies should be conducted to confirm these findings. Collectively, the findings obtained to date suggest that ivabradine may restore left ventricular, right ventricular, and left atrial function in failing hearts.
The cardioprotective effects of ivabradine were also demonstrated in animal studies. Ivabradine administered at 10 mg/kg/day in drinking water for 2–12 weeks produced improvements in cardiac function in various animal models of cardiac remodeling (Table 3).
Table 3. Effects of ivabradine on cardiac function in animal studies.
| Models | Dose and Duration of Ivabradine | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface ECG recordings and transesophageal electrophysiological study in female C57BL/10 mice |
Single dose of 10 mg/kg (i.p.) | ↓ HR ↑ QRS duration ↔ QR duration ↑ QT1 intervals ↑ QT2-P intervals ↑ S2Q2 intervals |
[50] |
| Chronic-hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy in pigs | 1 mg/kg/d infusion for 28 days | ↓ HR, ↑ SV, ↑ LVEDP ↑ LV twist, ↔ LV twisting rate ↑ LV untwisting rate ↑ LV untwisting velocity at MVO ↔ LV apical rotation ↑ LV basal rotation ↑ untwist during isovolumic relaxation time |
[51] |
| Experimental chronic- hypertension-induced cardiac remodeling in pigs |
1 mg/kg (i.v. bolus, single) | ↓ HR, ↔ CO ↔ dp/dtmax, ↔ LV pressure ↑ LV end-diastole internal diameter ↑ LV end-systole internal diameter ↑ LV relaxation filling ↑ LV early filling ↑ LV peak early filling rate |
[52] |
| Experimental hypertension- induced cardiac remodeling in SHR |
10 mg/kg/d in drinking water for 6 weeks | ↓ HR, ↔ SBP, ↑ LVEF ↑ LVFS, ↓ E/A, ↓ E/Em |
[53] |
| Isoproterenol-induced heart failure in rats | 10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 6 weeks | ↓ HR | [54] |
| Isoproterenol-induced heart failure in rats | 10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 14 days | ↓ HR | [55] |
| Diastolic-dysfunction-induced heart failure in diabetic mice | 20 mg/kg/d in drinking water for 4 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ E/A, ↓ EDT ↑ −dp/dtmin, ↓ Tau, ↓ IVRT |
[56] |
| Diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice | 20 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 12 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF | [13] |
| Myocardial I/R-induced cardiac remodeling in rats | 10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 28 days | ↓ HR, ↑ LVFS ↑ LVEF, ↑ delta LVEF |
[57] |
| Experimental HFpEF in mice | 10 mg/kg/d (low) and 20 mg/kg/d (high) (p.o.) for 4 weeks | High dose: ↓ HR, ↓ LVEDP, ↔ LVEF ↓ LV −dp/dtmax, ↔ LV +dp/dtmax, ↓ EDT, ↔ LVFS, ↓ IVRT Low dose: ↓ HR |
[58] |
| Experimental HFrEF in mice | 10 mg/kg/d and 20 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 8 weeks | High dose: ↓ HR, ↓ LVEDP, ↓ IVRT ↓ LV −dp/dtmax ↑ LV +dp/dtmax ↓ EDT, ↑ LVEF, ↑ LVFS Low dose: ↓ HR |
[58] |
| Post-MI-induced heart failure in rats | 10 mg/kg/min (via osmotic pump) for 2 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ CO, ↑ SV, ↔ LVEF ↔ LV +dp/dt ↔ LV −dp/dt ↔ LVEDP |
[59] |
| Myocardial I/R-induced cardiac remodeling in pigs | 0.3 mg/kg (i.v.) | ↓ HR, ↑ SV, ↓ CO, ↑ CVP ↔ MAP ↔ systemic arterial pressure ↔ pulmonary arterial pressure |
[60] |
| Hypertension-induced heart failure in rats | 10 mg/kg/d in drinking water for 10 weeks | ↓ HR, ↔ SBP, ↓ E/A, ↓ E/E′ ↑ LVFS, ↑ LVEF |
[11] |
| MI-induced cardiac remodeling in rats | 10 mg/kg/d in drinking water for 8 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF, ↓ LVEDP ↑ LVDP, ↑ LV +dp/dt ↑ LV −dp/dt ↓ LV diastolic wall stress |
[61] |
| Experimental hypertension- induced cardiac remodeling in rats |
10 mg/kg/d in drinking water for 4 weeks | ↓ HR, ↓ SBP, ↑ LVEF ↑ LVFS |
[62] |
| Severe post-MI chronic HF in rats | 10 mg/kg/d in drinking water for 3 months | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF, ↓ LVEDP ↓ LVEDV, ↓ LVESV ↑ SV, ↔ CO |
[63] |
| Abdominal-aorta- constriction-induced chronic heart failure in rats |
10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 12 weeks | ↓ LVEDP, ↑ LV +dp/dt ↓ L V −dp/dt |
[12] |
| Open chest with LV post- ischemia dysfunction in pigs |
Bolus infusion of 0.5 mg/kg | ↓ HR, ↑ SV, ↔ CO ↑ diastolic filling time ↔ MAP, cardiac efficiency |
[64] |
| Chronic ischemic heart failure in diabetic rats | 10 mg/kg/d (i.p.) for 7 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ LVFS, ↓ LVEDP | [65] |
| LAD coronary-artery- ligated-induced cardiac remodeling in rats |
10 mg/kg/d in drinking water for 90 days | ↓ HR, ↑ LVEF, ↔ LVEDV ↔ LVESV |
[14] |
| LAD coronary-artery- ligated-induced cardiac remodeling in rats |
6–8 mg/kg/d (i.p.) for 4 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ SV, ↔ LVEDV ↔ LVESV, ↓ LVEDV/LV mass ↑ LVEF, ↓ LVEDP ↑ LV coronary reserve ↔ coronary conductance |
[66] |
| LAD coronary-artery- ligated-induced cardiac remodeling in rats |
10 mg/kg/d (i.g.) for 7 days | ↑ LVSP, ↓ LVEDP ↑ +dp/dtmax, ↓ −dp/dtmax |
[67] |
| Doxorubicin-induced LV dysfunction in rats |
10 mg/kg (i.p.), alternate days for 2 weeks | ↓ HR, ↔ MAP, ↑ +dp/dtmax ↑ Tau, ↑ SDNN, ↓ LF ↔ HF, ↓ LF/HF, ↑ RMSSD ↑ Total power |
[68] |
| Pulmonary-arterial- hypertension-induced heart failure in rats |
10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 3 weeks | ↔ HR, ↑ RV S′, ↑ LV E’ ↓ RV fractional area ↓ RV IVCT, ↓ LV IVCT ↓ Time to mitral valve opening ↓ Time to RV peak radial motion ↓ Time to maximum LVSB ↓ Time to maximum TAPSE ↓ Time to tricuspid valve opening ↓ RV Tau (τ) |
[69] |
| Hypertension-induced cardiac remodeling in SHR | 1 mg/kg/d (i.p.) for 14 days | ↓ HR, ↓ SBP, ↓ DBP, ↓ MAP | [70] |
| Transverse-aortic- constriction-induced cardiac hypertrophy in mice |
10, 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg/d (i.g.) for 4 weeks | All doses: ↓ HR, ↓ LV Vols, ↑ LVEF ↑ LVFS 10 and 20 mg/kg/d: ↓ LV Vold |
[15] |
| Myocardial I/R-induced cardiac remodeling in pigs | 0.3 mg/kg for 7 days | ↑ LVEF | [71] |
| Pulmonary-hypertension- induced cardiac remodeling in rats |
10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 3 weeks | ↓ HR, ↓ RV longitudinal ↑ RV S′, ↓ RV S:D ratio ↓ RV TDI-MPI, ↓ TDI IVRT ↓ RDI IVRT/R-R, ↑ SV, ↑ CO ↑ RV +dp/dt, ↓ RV −dp/dt ↓ RV Tau |
[72] |
| RV pressure-loaded-induced cardiac remodeling in rats | 10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 3 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ FAC, ↑ TAPSE ↓ RV MPI, ↓ RV S:D ratio ↓ RV longitudinal ↓ RV TDI-MPI, ↓ TDI IVRT ↓ RDI IVRT/R-R, ↑ SV, ↑ CO ↓ RV EDP, ↑ RV +dp/dt ↓ RV −dp/dt, ↓ RV Ees ↓ RV Tau |
[72] |
| SU5416+Hypoxia-induced cardiac remodeling in rats |
10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 3 weeks | ↓ HR, ↑ FAC, ↑ TAPSE ↓ RV MPI, ↓ RV TDI-MPI ↓ TDI IVCT, ↓ TDI IVRT ↓ RDI IVRT/R-R, ↑ SV, ↑ CO ↓ RV EDP, ↓ RV Ees, ↓ RV EDPVR, ↓ RV Tau |
[72] |
| Hyperthyroid cardiomyopathy in rats | 10 mg/kg/d (p.o.) for 28 days | ↓ HR, ↓ EDT, ↑ Ea, ↓ E/Ea ↓ Scirc, ↓ SRcirc, ↓ Slong ↑ SRlong, ↑ Srad, ↑ SRrad |
[73] |
| Cardiogenic-shock-induced cardiac remodeling in pigs | 0.3 mg/kg (i.v. bolus) | ↓ HR, ↑ SV, ↑ LVEF | [74] |
A, late diastolic mitral inflow velocity; CO, cardiac output; CVP, central venous pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; ECG, electrocardiogram; +dp/dtmax, maximal rate of rise of left ventricular pressure; −dp/dtmax, maximal rate of fall of left ventricular pressure; E, early diastolic mitral inflow velocity; E′, early diastolic mitral annular velocity; Ea, peak early diastolic mitral annular velocity; E/A, early-to-late diastolic mitral inflow velocity; ECG, electrocardiogram; EDP, end-diastolic pressure; EDPVR, end-diastolic pressure–volume relation; EDT, E peak deceleration time; Ees, left ventricular end-systolic elastance; Em, the maximal velocity of early diastolic wall movement wave at the level of mitral annulus; FAC, fractional area change; HF, power in high-frequency range; HFpEF, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; HR, heart rate; i.p., intraperitoneum; I/R, ischemia/reperfusion; i.v., intravenous; IVCT, isovolumic contraction time; IVRT, isovolumetric relaxation time; LF, power in low-frequency range; LV, left ventricle; LAD, left anterior descending; LVEDP, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure; LVEDV, left ventricular end-diastolic volume; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LVESV, left ventricular end-systolic volume; LVFS, left ventricular fractional shortening; LVSB, early diastolic left ventricular septal bowing; LVSP, left ventricular systolic pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure; MI, myocardial infarction; MPI, myocardial performance index; MVO, mitral valve opening; p.o., per oral; RMSSD, square root of the mean squared differences of successive normal-to-normal intervals; RV, right ventricle; R-R, electrocardiogram R wave to R wave interval; S′, systolic tissue wave velocity; Scirc, circumferential strain; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SRcirc, circumferential strain rate; Slong, longitudinal strain; SRlong, longitudinal strain rate; Srad, radial strain; SRrad, radial strain rate; SBP, systolic blood pressure; S:D, ratio of systolic duration to diastolic duration; SDNN, standard deviation of all normal-to-normal intervals; SHR, spontaneous hypertensive rats; SU5416, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor; SV, stroke volume; TAPSE, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; Tau, relaxation time constant; TDI, tissue Doppler imaging; Vold, volume in diastole; Vols, volume in systole; ↔, no difference; ↓, reduced; ↑, increased.
It enhanced systolic function by increasing stroke volume, LVEF, left ventricular fractional shortening (LVFS), systolic pressure (LVSP) and developed pressure (LVDP), maximal rate of fall (−dp/dtmax) and rise (+dp/dtmax) of left ventricular pressure, and LVESV in these animal models [11][12][13][51][53][57][59][60][62][67].
Left ventricular dysfunction, commonly seen in heart failure, is characterized by impaired left ventricular filling capacity [75]. Ivabradine potentiates diastolic work by increasing the diastolic filling time [52][64] and decreasing left ventricular diastolic wall stress [61] in chronic-hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial-infarction-induced cardiac remodeling in animals. Reductions in left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), isovolumetric relaxation time (IVRT), Tau (early relaxation), LVEDV, and E/E′ were also noted (Table 3) [11][51][52][56][58][61][63][65][66][67].
The potential benefits of ivabradine were further investigated in right ventricular dysfunction. In a pulmonary-hypertension-induced heart failure rat model, oral administration of 10 mg/kg/day ivabradine for 3 weeks improved right ventricular systolic function evidenced by reduced maximum tricuspid systolic annular excursion (tTAPSE) and isovolumic contraction time (IVCT) and increased systolic tissue wave velocity (S’), stroke volume, and cardiac output (Table 3) [69][72]. Altered right ventricular +dp/dtmax and −dp/dtmax values were also reversed in the rats [72]. In addition, right ventricular diastolic function was preserved based on the improvement in IVRT, right ventricular end-diastolic pressure (RVEDP), and Tau [72]. Similar findings were noted in SU5416 (a tyrosine kinase inhibitor) plus hypoxia-induced cardiac remodeling and right-ventricular-pressure-overload-induced cardiac remodeling [72]. In primary right ventricular cardiomyocytes, ivabradine (0.01–1 μM) reduced beating frequency without affecting the beating amplitude [72], confirming its heart-rate-lowering effects with no direct impact on contractility.
Altered calcium uptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum hinders contractile performance [76]. Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2a (SERCA2a) and phosphorylated phospholamban are two proteins that regulate calcium uptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum [77][78]. Improved systolic work by ivabradine may partially be attributed to its influence on myocardial calcium regulation. The drug decreased the expression of SERCA2a and phosphorylated phospholamban in rats that were exposed to monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension to induce cardiac remodeling [72]. The transporting function of SERCA was increased following ivabradine treatment without affecting the function of sodium–calcium exchanger (NCX) and sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium storage. The net effect was an increase in calcium transient amplitude in the heart [61]. NCX mediates the exchange of Na+ and Ca2+ when the extracellular Na+ is high due to the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase, which transports Na+ out of cells in favor of transporting K+ into cells [79]. Calcium is also required for ATP generation in the mitochondria. Increased mitochondrial calcium uptake enhances ATP production, leading to improvements in energy metabolism and supply to contractile proteins during systolic and diastolic actions [80]. However, studies investigating the role of ivabradine in mitochondrial calcium uptake and release are lacking.
Based on the reported findings, it can be stipulated that ivabradine confers protection against left and right ventricular dysfunction in animal studies, which confirms the clinical observations. These findings may partially be attributable to the effects of ivabradine on myocardial calcium homeostasis. Other factors that should be investigated are the influence of the drug on other calcium regulators, such Na+/K+-ATPase, ryanodine receptor 2, which facilitates Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum [77], and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (Ca2+/CaMKII), which is involved in Ca2+ signal transduction [81]. Its effects on mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel 1, calcium uniporter, and calcium uptake proteins—mitochondrial calcium regulatory proteins [80]—should also be studied.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms24032801
References
- Afzal, M. Recent updates on novel therapeutic targets of cardiovascular diseases. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 145–155.
- Groenewegen, A.; Rutten, F.H.; Mosterd, A.; Hoes, A.W. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1342–1356.
- WHO. WHO Reveals Leading Causes of Death and Disability Worldwide: 2000–2019. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/09-12-2020-who-reveals-leading-causes-of-death-and-disability-worldwide-2000-2019 (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Van De Bruaene, A.; Meier, L.; Droogne, W.; De Meester, P.; Troost, E.; Gewillig, M.; Budts, W. Management of acute heart failure in adult patients with congenital heart disease. Hear. Fail. Rev. 2018, 23, 1–14.
- Maron, B.J.; Rowin, E.J.; Udelson, J.E.; Maron, M.S. Clinical Spectrum and Management of Heart Failure in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. JACC: Hear. Fail. 2018, 6, 353–363.
- Canet, E.; Lerebours, G.; Vilaine, J.-P. Innovation in coronary artery disease and heart failure: Clinical benefits of pure heart rate reduction with ivabradine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1222, 90–99.
- Thorup, L.; Simonsen, U.; Grimm, D.; Hedegaard, E.R. Ivabradine: Current and Future Treatment of Heart Failure. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 89–97.
- Sciatti, E.; Vizzardi, E.; Bonadei, I.; Dallapellegrina, L.; Carubelli, V. The role of heart rate and ivabradine in acute heart failure. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2019, 89, 1091.
- Chen, C.; Kaur, G.; Mehta, P.K.; Morrone, D.; Godoy, L.C.; Bangalore, S.; Sidhu, M.S. Ivabradine in Cardiovascular Disease Management Revisited: A Review. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2021, 35, 1045–1056.
- Nakamura, M.; Sadoshima, J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 387–407.
- Kakehi, K.; Iwanaga, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Sonobe, T.; Akiyama, T.; Shimizu, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Miyazaki, S. Modulation of Sympathetic Activity and Innervation with Chronic Ivabradine and β-Blocker Therapies: Analysis of Hypertensive Rats with Heart Failure. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 24, 387–396.
- Ma, D.; Xu, T.; Cai, G.; Wu, X.; Lei, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, N. Effects of ivabradine hydrochloride combined with trimetazidine on myocardial fibrosis in rats with chronic heart failure. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1639–1644.
- Zuo, G.; Ren, X.; Qian, X.; Ye, P.; Luo, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Inhibition of JNK and p38 MAPK-mediated inflammation and apoptosis by ivabradine improves cardiac function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 1925–1936.
- Ceconi, C.; Comini, L.; Suffredini, S.; Stillitano, F.; Bouly, M.; Cerbai, E.; Mugelli, A.; Ferrari, R. Heart rate reduction with ivabradine prevents the global phenotype of left ventricular remodeling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H366–H373.
- Yu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S. Ivabradine improved left ventricular function and pressure overload-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a transverse aortic constriction mouse model. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 450, 25–34.
- Al-Balushi, S.; Alam, M.F.; Abid, A.R.; Sharfi, A. The effect of ivabradine on hospitalization of heart failure patients: A retrospective cohort study. Hear. Views 2021, 22, 165–173.
- Böhm, M.; Robertson, M.; Ford, I.; Borer, J.S.; Komajda, M.; Kindermann, I.; Maack, C.; Lainscak, M.; Swedberg, K.; Tavazzi, L. Influence of Cardiovascular and Noncardiovascular Co-morbidities on Outcomes and Treatment Effect of Heart Rate Reduction with Ivabradine in Stable Heart Failure (from the SHIFT Trial). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 1890–1897.
- Liu, Y.X.; Chen, W.; Lin, X.; Zhu, Y.L.; Lai, J.Z.; Li, J.Y.; Guo, X.X.; Yang, J.; Qian, H.; Zhu, Y.Y.; et al. Initiating ivabradine during hospitalization in patients with acute heart failure: A real-world experience in China. Clin. Cardiol. 2022, 45, 928–935.
- Bouabdallaoui, N.; O’Meara, E.; Bernier, V.; Komajda, M.; Swedberg, K.; Tavazzi, L.; Borer, J.S.; Bohm, M.; Ford, I.; Tardif, J.C. Beneficial effects of ivabradine in patients with heart failure, low ejection fraction, and heart rate above 77 b.p.m. ESC Hear. Fail. 2019, 6, 1199–1207.
- Zugck, C.; Störk, S.; Stöckl, G.; RELIf-CHF Study Investigators. Long-term treatment with ivabradine over 12 months in patients with chronic heart failure in clinical practice: Effect on symptoms, quality of life and hospitalizations. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 240, 258–264.
- Böhm, M.; Borer, J.; Ford, I.; Juanatey, J.R.G.; Komajda, M.; Lopez-Sendon, J.; Reil, J.-C.; Swedberg, K.; Tavazzi, L. Heart rate at baseline influences the effect of ivabradine on cardiovascular outcomes in chronic heart failure: Analysis from the SHIFT study. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2013, 102, 11–22.
- Komajda, M.; Tavazzi, L.; Swedberg, K.; Böhm, M.; Borer, J.S.; Moyne, A.; Ford, I.; SHIFT Investigators. Chronic Exposure to Ivabradine Reduces Readmissions in The Vulnerable Phase After Hospitalization for Worsening Systolic Heart Failure: A Post-Hoc Analysis of SHIFT. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 1182–1189.
- Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, D.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lai, J.; Shen, Z. Early short-term ivabradine treatment in new-onset acute systolic heart failure and sinus tachycardia patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 305–311.
- Borer, J.S.; Swedberg, K.; Komajda, M.; Ford, I.; Tavazzi, L.; Böhm, M.; Depre, C.; Wu, Y.; Maya, J.; Dominjon, F. Efficacy Profile of Ivabradine in Patients with Heart Failure plus Angina Pectoris. Cardiology 2017, 136, 138–144.
- Komajda, M.; Böhm, M.; Borer, J.; Ford, I.; Krum, H.; Tase, A.; Tavazzi, L.; Swedberg, K. Influence of background treatment with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists on ivabradine’s effects in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2013, 15, 79–84.
- Komajda, M.; Tavazzi, L.; Francq, B.G.; Böhm, M.; Borer, J.S.; Ford, I.; Swedberg, K.; SHIFT Investigators. Efficacy and safety of ivabradine in patients with chronic systolic heart failure and diabetes: An analysis from the SHIFT trial. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2015, 17, 1294–1301.
- Komajda, M.; Isnard, R.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Metra, M.; Pieske, B.; Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Dominjon, F.; Henon-Goburdhun, C.; Pannaux, M.; et al. Effect of ivabradine in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The EDIFY randomized placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2017, 19, 1495–1503.
- Liao, C.T.; Huang, J.L.; Liang, H.W.; Chung, F.P.; Lee, Y.H.; Lin, P.L.; Chiou, W.R.; Lin, W.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chang, H.Y. The association between ivabradine and adverse cardiovascular events in acute decompensated HFrEF patients. ESC Hear. Fail. 2021, 8, 4199–4210.
- Ordu, S.; Yildiz, B.S.; Alihanoglu, Y.I.; Ozsoy, A.; Tosun, M.; Evrengul, H.; Kaftan, H.A.; Ozhan, H. Effects of ivabradine therapy on heart failure biomarkers. Cardiol. J. 2015, 22, 501–509.
- Reil, J.-C.; Robertson, M.; Ford, I.; Borer, J.; Komajda, M.; Swedberg, K.; Tavazzi, L.; Böhm, M. Impact of left bundle branch block on heart rate and its relationship to treatment with ivabradine in chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2013, 15, 1044–1052.
- Riccioni, G.; Masciocco, L.; Benvenuto, A.; Saracino, P.; De Viti, D.; Massari, F.; Meliota, G.; Buta, F.; Speziale, G. Ivabradine Improves Quality of Life in Subjects with Chronic Heart Failure Compared to Treatment with β-Blockers: Results of a Multicentric Observational APULIA Study. Pharmacology 2013, 92, 276–280.
- Rohm, I.; Kretzschmar, D.; Pistulli, R.; Franz, M.; Schulze, P.C.; Stumpf, C.; Yilmaz, A. Impact of Ivabradine on Inflammatory Markers in Chronic Heart Failure. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 6949320.
- Sargento, L.; Satendra, M.; Longo, S.; Lousada, N.; dos Reis, R.P. Heart Rate Reduction with Ivabradine in Patients with Acute Decompensated Systolic Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2014, 14, 229–235.
- Villacorta, A.S.; Villacorta, H.; Caldas, J.A.; Precht, B.C.; Porto, P.B.; Rodrigues, L.U.; Neves, M.; Xavier, A.R.; Kanaan, S.; Mesquita, C.T.; et al. Effects of Heart Rate Reduction with Either Pyridostigmine or Ivabradine in Patients with Heart Failure: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 24, 139–145.
- Zugck, C.; Martinka, P.; Stöckl, G. Ivabradine Treatment in a Chronic Heart Failure Patient Cohort: Symptom Reduction and Improvement in Quality of Life in Clinical Practice. Adv. Ther. 2014, 31, 961–974.
- Bonnet, D.; Berger, F.; Jokinen, E.; Kantor, P.; Daubeney, P.E. Ivabradine in Children with Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Symptomatic Chronic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1262–1272.
- Koruth, J.S.; Lala, A.; Pinney, S.; Reddy, V.Y.; Dukkipati, S.R. The Clinical Use of Ivabradine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1777–1784.
- Flannery, G.; Gehrig-Mills, R.; Billah, B.; Krum, H. Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials on the Effect of Magnitude of Heart Rate Reduction on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Systolic Chronic Heart Failure Receiving Beta-Blockers. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 865–869.
- Lee, W.-C.; Fang, H.-Y. Ivabradine for the Treatment of Acute Mitral-Regurgitation-Related Decompensated Heart Failure. Cardiology 2019, 144, 97–100.
- De Ferrari, G.M.; Mazzuero, A.; Agnesina, L.; Bertoletti, A.; Lettino, M.; Campana, C.; Schwartz, P.J.; Tavazzi, L. Favourable Effects of Heart Rate Reduction with Intravenous Administration of Ivabradine in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 550–555.
- Bonadei, I.; Sciatti, E.; Vizzardi, E.; Fabbricatore, D.; Pagnoni, M.; Rossi, L.; Carubelli, V.; Lombardi, C.M.; Metra, M. Effects of ivabradine on endothelial function, aortic properties and ventricular-arterial coupling in chronic systolic heart failure patients. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2018, 36, e12323.
- Böhm, M.; Borer, J.S.; Camm, J.; Ford, I.; Lloyd, S.M.; Komajda, M.; Tavazzi, L.; Talajic, M.; Lainscak, M.; Reil, J.-C.; et al. Twenty-four-hour heart rate lowering with ivabradine in chronic heart failure: Insights from the SHIFT Holter substudy. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2015, 17, 518–526.
- Mert, K.U.; Dural, M.; Mert, G.Ö.; Iskenderov, K.; Özen, A. Effects of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on the international ındex of erectile function (IIEF-5) in patients with heart failure. Aging Male 2017, 21, 93–98.
- Ozturk, S.; Öztürk, S.; Erdem, F.H.; Erdem, A.; Ayhan, S.; Dönmez, I.; Yazıcı, M. The effects of ivabradine on left atrial electromechanical function in patients with systolic heart failure. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2016, 46, 253–258.
- Reil, J.-C.; Tardif, J.-C.; Ford, I.; Lloyd, S.M.; O’Meara, E.; Komajda, M.; Borer, J.S.; Tavazzi, L.; Swedberg, K.; Böhm, M. Selective Heart Rate Reduction with Ivabradine Unloads the Left Ventricle in Heart Failure Patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1977–1985.
- Tardif, J.-C.; O’Meara, E.; Komajda, M.; Böhm, M.; Borer, J.S.; Ford, I.; Tavazzi, L.; Swedberg, K.; SHIFT Investi-gators. Effects of selective heart rate reduction with ivabradine on left ventricular remodelling and function: Results from the SHIFT echocardiography substudy. Eur. Hear. J. 2011, 32, 2507–2515.
- Gul, M.; Inci, S.; Aksan, G.; Sigirci, S.; Keskin, P. Using Tissue Doppler and Speckle Tracking Echocardiography to Assess if Ivabradine Improves Right Ventricular Function. Cureus 2021, 13, e12920.
- Fang, F.; Lee, A.P.; Yu, C.-M. Left atrial function in heart failure with impaired and preserved ejection fraction. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2014, 29, 430–436.
- Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, A.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Hou, Y. Ivabradine and Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, 549–557.
- Amstetter, D.; Badt, F.; Rubi, L.; Bittner, R.E.; Ebner, J.; Uhrin, P.; Hilber, K.; Koenig, X.; Todt, H. The bradycardic agent ivabradine decreases conduction velocity in the AV node and in the ventricles in-vivo. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 893, 173818.
- Jozwiak, M.; Melka, J.; Rienzo, M.; Bizé, A.; Sambin, L.; Hittinger, L.; Berdeaux, A.; Su, J.B.; Bouhemad, B.; Ghaleh, B. Ivabradine improves left ventricular twist and untwist during chronic hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 252, 175–180.
- Melka, J.; Rienzo, M.; Bizé, A.; Jozwiak, M.; Sambin, L.; Hittinger, L.; Su, J.B.; Berdeaux, A.; Ghaleh, B. Improvement of left ventricular filling by ivabradine during chronic hypertension: Involvement of contraction-relaxation coupling. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2016, 111, 30.
- Simko, F.; Baka, T.; Stanko, P.; Repova, K.; Krajcirovicova, K.; Aziriova, S.; Domenig, O.; Zorad, S.; Adamcova, M.; Paulis, L. Sacubitril/Valsartan and Ivabradine Attenuate Left Ventricular Remodelling and Dysfunction in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats: Different Interactions with the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1844.
- Simko, F.; Baka, T.; Repova, K.; Aziriova, S.; Krajcirovicova, K.; Paulis, L.; Adamcova, M. Ivabradine improves survival and attenuates cardiac remodeling in isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 744–748.
- Noel, R.; Ali, M.N.A.K. Effect of Ivabradine on Cardiac Remodeling in Experimentally Induced Heart Failure in Rats. Iraqi J. Commun. Med. 2019, 32, 1–7.
- Xie, H.; Shen, X.-Y.; Zhao, N.; Ye, P.; Ge, Z.; Hu, Z.-Y. Ivabradine Ameliorates Cardiac Diastolic Dysfunction in Diabetic Mice Independent of Heart Rate Reduction. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 696635.
- Kim, H.B.; Hong, Y.J.; Park, H.J.; Ahn, Y.; Jeong, M.H. Effects of Ivabradine on Left Ventricular Systolic Function and Cardiac Fibrosis in Rat Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Model. Chonnam Med. J. 2018, 54, 167–172.
- Shao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, M.; Yuan, M.; Suo, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Bao, Q.; et al. Ivabradine Ameliorates Cardiac Function in Heart Failure with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction via Upregulation of miR-133a. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1257283.
- Paterek, A.; Sochanowicz, B.; Oknińska, M.; Śmigielski, W.; Kruszewski, M.; Mackiewicz, U.; Mączewski, M.; Leszek, P. Ivabradine prevents deleterious effects of dopamine therapy in heart failure: No role for HCN4 overexpression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111250.
- Pascual Izco, M.; Ramírez-Carracedo, R.; Hernández Navarro, I.; Osorio Ruiz, Á.; Castejón Navarro, B.; Cuadrado Berrocal, I.; Largo Aramburu, C.; Alonso Salinas, G.L.; Díez, J.; Saura Redondo, M.; et al. Ivabradine in Acute Heart Failure: Effects on Heart Rate and Hemodynamic Parameters in a Randomized and Controlled Swine Trial. Cardiol. J. 2020, 27, 62–71.
- Mączewski, M.; Mackiewicz, U. Effect of metoprolol and ivabradine on left ventricular remodelling and Ca2+ handling in the post-infarction rat heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 42–51.
- Simko, F.; Baka, T.; Poglitsch, M.; Repova, K.; Aziriova, S.; Krajcirovicova, K.; Zorad, S.; Adamcova, M.; Paulis, L. Effect of Ivabradine on a Hypertensive Heart and the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in L-NAME-Induced Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3017.
- Milliez, P.; Messaoudi, S.; Nehme, J.; Rodriguez, C.; Samuel, J.-L.; Delcayre, C. Beneficial effects of delayed ivabradine treatment on cardiac anatomical and electrical remodeling in rat severe chronic heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 296, H435–H441.
- Bakkehaug, J.P.; Naesheim, T.; Torgersen Engstad, E.; Kildal, A.B.; Myrmel, T.; How, O.-J. Reversing dobutamine-induced tachycardia using ivabradine increases stroke volume with neutral effect on cardiac energetics in left ventricular post-ischaemia dysfunction. Acta Physiol. 2016, 218, 78–88.
- Cao, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Xia, H. The Effects of Ivabradine on Cardiac Function after Myocardial Infarction are Weaker in Diabetic Rats. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2055–2064.
- Christensen, L.P.; Zhang, R.-L.; Zheng, W.; Campanelli, J.J.; Dedkov, E.I.; Weiss, R.M.; Tomanek, R.J. Postmyocardial infarction remodeling and coronary reserve: Effects of ivabradine and beta blockade therapy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H322–H330.
- Dai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, G.; Zha, L.; Li, X. Ivabradine protects rats against myocardial infarction through reinforcing autophagy via inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K pathway. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 1826–1837.
- El-Naggar, A.E.; El-Gowilly, S.M.; Sharabi, F.M. Possible Ameliorative Effect of Ivabradine on the Autonomic and Left Ventricular Dysfunction Induced by Doxorubicin in Male Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 72, 22–31.
- Gómez, O.; Okumura, K.; Honjo, O.; Sun, M.; Ishii, R.; Bijnens, B.; Friedberg, M.K. Heart Rate Reduction Improves Biventricular Function and Interactions in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H542–H551.
- Gomes, F.A.; Noronha, S.I.; Silva, S.C.; Machado-Júnior, P.A.; Ostolin, T.L.; Chírico, M.T.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Reis, A.B.; Cangussú, S.D.; Montano, N.; et al. Ivabradine treatment lowers blood pressure and promotes cardiac and renal protection in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120919.
- Hernandez, I.; Tesoro, L.; Ramirez-Carracedo, R.; Diez-Mata, J.; Sanchez, S.; Saura, M.; Zamorano, J.; Zaragoza, C.; Botana, L. Ivabradine Induces Cardiac Protection against Myocardial Infarction by Preventing Cyclophilin-A Secretion in Pigs under Coronary Ischemia/Reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2902.
- Ishii, R.; Okumura, K.; Akazawa, Y.; Malhi, M.; Ebata, R.; Sun, M.; Fujioka, T.; Kato, H.; Honjo, O.; Kabir, G.; et al. Heart Rate Reduction Improves Right Ventricular Function and Fibrosis in Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 63, 843–855.
- Kim, B.H.; Cho, K.I.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, N.; Han, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, I.J. Heart rate reduction with ivabradine prevents thyroid hormone-induced cardiac remodeling in rat. Hear. Vessel. 2012, 28, 524–535.
- Tesoro, L.; Ramirez-Carracedo, R.; Hernandez, I.; Diez-Mata, J.; Pascual, M.; Saura, M.; Sanmartin, M.; Zamorano, J.L.; Zaragoza, C. Ivabradine induces cardiac protection by preventing cardiogenic shock-induced extracellular matrix degradation. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2021, 74, 1062–1071.
- Sadeghpour, A.; Alizadehasl, A. Echocardiography. In Practical Cardiology; Maleki, M., Alizadehasl, A., Haghjoo, M., Eds.; Elsevier: St Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 67–111.
- Kranias, E.G.; Hajjar, R.J. Modulation of Cardiac Contractility by the Phopholamban/SERCA2a Regulatome. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1646–1660.
- Ramli, F.F.; Hashim, S.A.S.; Raman, B.; Mahmod, M.; Kamisah, Y. Role of Trientine in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Review of Mechanistic Aspects. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1145.
- Frank, K.; Kranias, E.G. Phospholamban and cardiac contractility. Ann. Med. 2000, 32, 572–578.
- Salim, S.; Yunos, N.; Jauri, M.; Kamisah, Y. Cardiotonic Effects of Cardiac Glycosides from Plants of Apocynaceae Family. Chula. Med. J. 2020, 64, 449–456.
- Lai, L.; Qiu, H. The Physiological and Pathological Roles of Mitochondrial Calcium Uptake in Heart. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7689.
- Zhang, T. Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 476–486.
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
