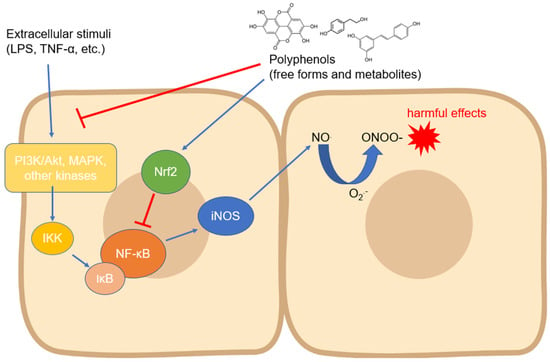
1. Activity and Expression of Inducible NOS
The iNOS isoform is probably the most studied with regard to its modulation by compounds of natural origin. Regarding polyphenols, its expression has been measured in countless cell types and in different experimental systems, even with contrasting results depending on the cell type and the compound tested. In most cases, the modulation of iNOS expression has been studied as a function of some anti-inflammatory activity of the tested compounds, but the related countless studies are not reported in this review. Instead, we focused on the research reporting the mechanisms involved in the biological action of polyphenols on iNOS expression and activity. Almost all the signaling pathways studied in this context converge on the modulation of the activity of NF-ĸB, a transcription factor which, once translocated into the nucleus, activates the processes that lead to the expression of iNOS in manifold cell types [
27] (
Figure 1). The translocation occurs through an important step, which is the degradation of the inhibitor of NF-ĸB, i.e., IĸB (mainly its α isoform), which occurs via phosphorylation induced by kinases such as IKK, which are in turn activated by other upstream kinases [
58]. Numerous studies have, therefore, focused on the regulation of these kinases by polyphenols of various origins and chemical structures. The regulation of iNOS activity by dietary phenols has been studied mainly at the intestinal level, where this enzyme plays a key role in acute and chronic inflammatory diseases and where polyphenols may accumulate in physiologically relevant concentrations [
59], thus representing an important tool to prevent the onset and progression of intestinal and systemic diseases [
60].
Figure 1. Modulation of iNOS expression by polyphenols involving the downregulation of upstream kinases and NF-κB. Abbreviations: IKK—IĸB kinase; iNOS—inducible nitric oxide synthase; IκB—inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B; LPS—lipopolysaccharide; MAPK—mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB—nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NO—nitric oxide; O2●−—superoxide anion; ONOO−—peroxynitrite; PI3K—inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate kinase; and TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor-α.
Ellagic acid was tested in an experimental murine model of Crohn’s disease by intra-colonic administration of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS) in rats. This polyphenol could reduce the activation of p38, JNK, and ERK1/2 MAPKs, thus preventing the degradation of inhibitory protein IĸB and inducing an inhibition of the p65-NF-κB level in colonic mucosa [
61]. In an identical experimental model, the upstream inhibition of cytosolic IKK and the consequent preservation of IĸBα in colon tissue was instead observed regarding treatments with theaflavin-3,3′-digallate (TFDG) [
62]. In the case of curcumin, the inhibitory effects occurred on p38 but not on JNK, however, leading to the downregulation of iNOS and COX-2 expression [
63]. In an acute injury model obtained by intra-colonic administration of acetic acid in rats, curcumin showed instead an inhibitory action on JNK as well as on p38 [
64]. Gallic acid, a low-molecular-weight trihydroxybenzoic acid, was tested in an experimental murine model of ulcerative colitis. It was observed that gallic acid reduced the activation and nuclear accumulation of hosphor-STAT3Y705, preventing the degradation of IκB and inhibiting the nuclear translocation of p65-NF-κB in colonic mucosa, thus decreasing the expression of iNOS and COX-2 [
65]. Furthermore, in BALB/c mice subjected to ischemia/reperfusion, resveratrol significantly ameliorated subacute intestinal injury through the decrease of NO production as well as iNOS expression, upregulating the expression of the deacetylase Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) and, consequently, inhibiting the activity of NF-κB [
66]. In vitro, in an intestinal model of HT-29 cells, cyanidin-3-glucoside reduced cytokine-induced inflammation in terms of NO, PGE2, and IL-8 production and of iNOS and COX-2 expressions. The phenolic compound did not act to prevent IκB-α degradation but significantly reduced levels of activated STAT1 accumulated in the cell nucleus. Moreover, it was established that the phosphorylation of p38 was not involved in this protective effect [
67]. In the same cell model stimulated with cytokines, luteolin significantly inhibited IL-8 production, COX-2 and iNOS expression, and NO overproduction. Mechanistically, the inhibition of the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) pathway was identified as a major event in the observed anti-inflammatory effects [
68]. iNOS activation induced by a combination of cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ) in HT-29 cells was also counteracted by resveratrol, following the downregulation of the JAK-STAT pathway, decreasing the levels of activated STAT1 in the nucleus and the cytokine-stimulated activation of SAPK/JNK pathway, whereas no effects were exerted on p38 [
69]. It has been observed that in Caco-2 cells stimulated with LPS, resveratrol was able to inhibit the phosphorylation of IĸB and prevent the expression of iNOS downstream through the downregulation of the TRL-4 receptors, which are implicated in the proinflammatory effects of LPS [
70]. In the same experimental model, our research group has recently described how the main polyphenols of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) and ferulic acid derivatives, as well as their phase II metabolites formed in vivo following their ingestion, have been able to inhibit the degradation of IĸBα by acting on the p38, ERK1/2, and JNK MAPKs, consequently preventing the activation of iNOS and the release of NO [
71,
72,
73]. In the same investigations, it was also shown that EVOO polyphenols such as hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and their metabolites did not act through the downregulation of the Akt kinase, whereas ferulic acid and its metabolites and derivatives were able to inhibit both MAPK and Akt kinases phosphorylation and to activate the Nrf-2 pathway, which is known to be involved in the inhibition of NF-ĸB activity.
The mechanisms to control iNOS expression have also been studied in other tissues, although less thoroughly than in the gastrointestinal system and macrophages. In chondrocytes, for example, the release of NO has been studied in the context of chronic inflammatory diseases such as osteoarthritis, and it has been shown that compounds such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), fisetin, and resveratrol are able to modulate the inflammatory response switching off the expression of iNOS through different signaling pathways: activation of the Sirt1 pathway and subsequent inactivation of NF-ĸB translocation and inhibition of p65 acetylation [
86,
87,
88]. Some studies have been conducted on microglia because activated microglial cells play an important role in the proinflammatory status that characterizes neurodegenerative diseases in the central nervous system. Compounds belonging to the lignans family, such as sauquinone, have been shown in LPS-treated BV2 microglial cells to limit iNOS expression by acting on the downregulation of the Akt pathway but not on MAPKs [
89]. Resveratrol, on the other hand, activated Akt via phosphorylation together with PTEN and mTOR, with the latter appearing to be the key to the anti-inflammatory activity ascertained in this study against MAPKs and NF-ĸB activation [
90]. A quinolyl-substituted analogue of resveratrol, in addition to acting on MAPKs, has been shown to be able to act upstream by limiting the expression of TLR4 in microglia cells incubated with LPS [
91]. Quercetin has been shown to suppress LPS-induced IKK, NF-κB, and AP-1 activation as well as the IFN-γ- induced NF-κB, STAT1, and interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1) activation in BV2 cells. Almost all these factors are upstream of the NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways, and they downregulate iNOS expression [
92]. Still in microglia but in EOC13.31 cells, EGCG acted by promoting Nrf2 expression through the inhibition of the NF-ĸB pathway activated by amyloid β (Aβ) [
93]. At the hepatic level, a study in vitro by Kimbrough et al. [
94] demonstrated that resveratrol was able to activate JNK phosphorylation and NF-ĸB translocation in isolated rat hepatocytes, but at the same time, iNOS mRNA expression was inhibited as well as the activation of Akt. In male Sprague-Dawley rats administrated with CCl4, chlorogenic acid proved to be able of efficiently inhibit liver fibrosis, and the protective effect was associated with the inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-ĸB/iNOS signaling pathway [
95]. In the same experimental model, oligonol suppressed p65 activation, phosphorylation of MAPKs ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 as well as Akt, thus inhibiting iNOS expression and NO release [
96]. In other tissues and organs, resveratrol was the most studied, showing an effect on several signaling pathways. In hypoxia-induced cardiomyocytes, resveratrol showed inhibitory effects on iNOS proteins and mRNA expression, and the suggested mechanism might be associated with HIF-1α inhibition [
97]. In a spinal cord ischemia–reperfusion injury (IRI) rat model, it significantly decreased the levels of plasma nitrite/nitrate, iNOS mRNA and protein expressions, and phosphorylation of p38 [
98]. Furthermore, resveratrol has been demonstrated to be able to specifically inhibit iNOS induction in muscle through a mechanism involving 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) but not Sirt1 activation in mice myocites and adipocites challenged with LPS [
99]. In the context of vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation, which is linked to progression of hypertension and atherosclerosis, resveratrol did not alter iNOS protein level, but it dose-dependently increased the level of iNOS activity, of iNOS cofactor BH4, and of guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I protein, the rate-limiting enzyme in BH4 biosynthesis [
100].
2. Activity and Expression of Endothelial NOS
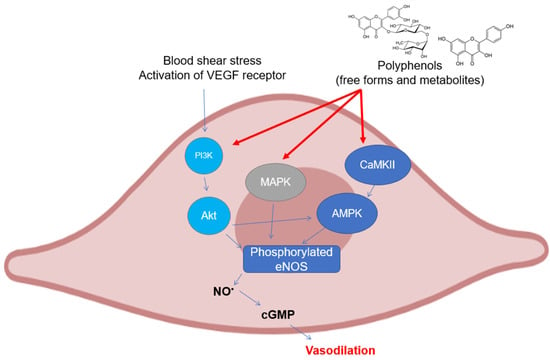
As can be easily understood, most of the studies on the modulation of eNOS by polyphenols have been assessed on endothelial cell cultures and ex vivo cardiovascular tissues. There are several mechanisms that have been investigated in the last twenty years, all of which are related to the maintenance of the basic functionality of eNOS or its recovery following pathological events (
Figure 2). The most studied polyphenol is undoubtedly resveratrol, to which dozens of investigations on the subject have been dedicated. The activation of eNOS following phosphorylation is the major event that causes the release of moderate doses of NO useful for maintaining vascular tone and for its antiplatelet properties. As already described above, phosphorylation can occur in different sites and is caused upstream by the activation of signals such as PI3K/Akt, widely studied because it is modulated by polyphenols from different subclasses. In mice with artificial diabetes, the flavonoid morin increased NO levels and endothelial-dependent relaxation responses via Akt signaling, upregulating hosphor-Akt (at Ser473 and Thr308) and consequently hosphor-eNOS (at Ser1177) in aortas [
101], as was also seen for protocatechuic acid in the aorta of male hypertensive rats [
102]. The increase in the phosphorylation of Akt and eNOS was also observed in rats treated with tyrosol in an in vivo model of myocardial infarction [
103]. The activation of Akt/eNOS was also evaluated as a measure of the restoration of endothelial function in diabetic rabbits with carotid damage, where EGCG was able to reactivate this molecular signaling pathway and improve cardiovascular functions [
104]. The xanthonoid mangiferin markedly decreased plasma lipids and inflammatory levels in HFD-induced vascular injury in mice, probably via the PTEN/Akt/eNOS pathway, which was activated by mangiferin itself in HUVEC cells that had been previously treated with oxLDL [
105]. Other polyphenols such as EGCG, ellagic acid, procyanidins, and some stilbenes have been tested in cell lines of different origins (HAEC, BAEC, HUVEC, and EA.hy926) obtaining similar results in terms of activation of the PI3K/Akt /eNOS pathway [
106,
107,
108,
109,
110,
111]. In addition to the free forms of polyphenols, their phase-II metabolites have also been recently studied by our research group, which has demonstrated how some of the modulatory properties remain intact on the Akt/eNOS phosphorylation pathway, as shown by their precursors, such as hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, ferulic acid, and some derivatives in HUVEC and HAEC cells [
73,
112,
113]. Phosphorylation of eNOS can also occur at Ser633 site other than at Ser1177, in addition to dephosphorylation at Thr495, which displays the same physiological functions. The activation of these mechanisms has also been observed in human coronary endothelial cells by epicatechin, where the proposed upstream mechanism is the one related to the modulation of the CaMKII pathway, which induces eNOS uncoupling from caveolin-1 [
114]. Another signaling pathway involved in eNOS activation and regulated by polyphenols is that of AMPK, which has been shown to be modulated in particular by resveratrol. It led to a significant increase in the phosphorylation of eNOS in vivo in mesenteric arteries from SHRs and Angiotensin-II infused mice [
115], whereas in vitro in human endothelial cells, no change regarding its activity was observed [
116]. In HAEC cells, the activation of the AMPK/eNOS pathway was instead verified after treatment with rosmarinic acid, which reverted the effects caused by H
2O
2 incubation [
117].
Figure 2. Polyphenols elicit eNOS phosphorylation in endothelial cells through the activation of different upstream kinases. Abbreviations: AMPK—5′ AMP-activated protein kinase; CaMKII—Ca2+/calmodulin dependent kinase II; cGMP—guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate; eNOS—endothelial nitric oxide synthase; MAPK—mitogen activated protein kinase; NO—nitric oxide; and PI3K, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate kinase.
In HAEC and HUVEC, the efficacy of different polyphenols was also evaluated in modulation of the activation of eNOS by regulating the p38 and ERK1/2 MAPKs pathways. This was especially seen for resveratrol, which activated both p38 and ERK1/2 MAPKs in HUVEC in two different experiments [
118,
119], causing the phosphorylation of Ser1177; whereas in HUVEC and in platelets in vitro, the exact opposite effect was still seen in the context of contrasting the action of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis and oxidative stress [
120,
121]. The same outcome was observed for the resveratrol derivative piceatannol, which was proposed to bind with VEGF in HUVEC cells, thus attenuating VEGF receptor response and blocking VEGF-mediated downstream signaling pathways, including expressions of ERK1/2 and, consequently, of phosphorylated eNOS [
122]. Malvidin was also tested in HUVEC, and it was proven to be effective in the promotion of the release of cGMP starting from the activation of PI3K/Akt/eNOS/NO/cGMP and that of ERK1/2/eNOS/NO/cGMP [
123]. The enzymatic activity of eNOS is also regulated by acetylation/deacetylation processes. Short-term treatments of endothelial cells with resveratrol are known to lead to eNOS deacetylation at Lys496 and Lys506 in the CaM-binding domain, leading to an increase in eNOS activity. The mechanisms by which resveratrol is able to induce eNOS deacetylation are through the upregulation of Sirt1, which is usually downregulated by oxidative stress [
124]. For this reason, the Sirt1 pathway has been studied in the context of deacetylation and, therefore, activation of eNOS by polyphenols. Frombaum et al. [
119] reported, for example, that resveratrol acts on the release of NO also by modulating Sirt1 in HUVEC, as has been observed for salvianolic acid (in HUVEC as well) and for a nitrated derivative of hydroxytyrosol in vivo in diabetic mice [
125,
126]. In addition to the already mentioned eNOS phosphorylation, consequent to the activation of different signaling pathways, the increase of its expression induced by treatment with different phenolic compounds has been studied. For example, resveratrol was found to be active in increasing eNOS gene expression in a dose-dependent manner in 2T3 and MC3T3 osteoblasts, whereas it did not promote any significant enzyme activation via phosphorylation in the same cells [
127]. Similarly, the same compound has improved coronary flow during reperfusion associated with increased eNOS, Sirt1, and hosphor-Akt protein expression in rat hearts [
128]. Conversely, resveratrol in HAEC and HPAEC endothelial cells showed instead a suppression of eNOS, measured by RT-PCR [
129]. Again, in HAEC, different results were observed after treatment with chlorogenic acid and with the oat derivative avenanthramide-2c, which promoted the expression of eNOS and, in the first case, also its dimerization necessary for NO release [
130,
131]. In a model of 2K-1C (two kidneys, one clip) rat renovascular hypertension, eNOS expression was restored by curcumin treatment, which simultaneously reduced oxidative stress and hypertension [
132].
In addition to its expression at physiologically relevant levels, it is essential that eNOS works correctly by releasing NO. Under certain circumstances, indeed, eNOS itself can release O
2●− instead of NO. This phenomenon, eNOS uncoupling, is closely linked to the availability of the crucial eNOS cofactor BH4. ONOO
− mediated oxidation of BH4 compromises eNOS function and leads to a vicious circle of BH4 destruction, further eNOS uncoupling, and increasing vascular ROS production [
133]. In this regard, it was observed that resveratrol, well known as a powerful antioxidant, was able to prevent the uncoupling of eNOS induced by O
2●− in hypertensive rats [
134].
3. Activity and Expression of Neuronal NOS
The neuronal isoform of NOS and its modulation by dietary polyphenols is still a little-explored field, despite its pharmacological relevance. There are very few investigations, and most of them are in vivo studies that show different pathological aspects related to the activity of nNOS. NO at the neuronal level is known to be implicated in many processes related to memory and learning, but above all, it is implicated in the etiopathogenesis of various neurological diseases. For instance, the implication of NO in Parkinson disease (PD) has been firstly proposed when high levels of nNOS and iNOS were found in the nigrostriatal region and basal ganglia of postmortem PD brains. In PD, the increase of NO levels is caused either by the overexpression of nNOS or by other mechanisms, including glutamate excitotoxicity. NO rapidly reacts with O
2●− Anions formed during dopamine metabolism, thus generating ONOO
−, which is considered one of the main damaging substances in dopaminergic neuronal cells [
135]. Therefore, given the growing incidence and mortality of these diseases, the main goal would be to find phenolic compounds which act selectively on this isoform. This would limit its functionality, especially in patients with full-blown pathology, without affecting the activity of other isoforms such as eNOS in the other tissues. In this regard, a polyphenolic extract of green tea that includes EGCG downregulated nNOS expression induced by 6-OHDA exposure to simulate PD conditions in SH-SY5Y cells [
136]. An interesting in vivo study in mice, although not focused on the mechanism involved, showed that intervention with EGCG was able to limit the expression of nNOS in brain tissues in the context of memory deficits, characterized by high levels of enzyme expression [
137]. The EGCG was also tested in rats, where it showed a dose-dependent suppressive effect on the nNOS expression in the nodose neurons of adult rats after severe hypoxic insult [
138]. The same treatment was also carried out in rats prior to crushing their hypoglossal and vagus nerves, which showed elevated levels of nNOS compared to untreated rats. Even in this case, EGCG treatment was effective in restoring the expression levels of nNOS to values similar to those of the control [
139]. A significant downregulation of nNOS protein expression along with reduced lipofuscin content was observed in middle-aged and aged rats treated with curcuminoids, suggesting that these compounds may act as a drug candidate for the prevention of deleterious effects of aging and age-associated neurodegenerative disorders [
140]. Regarding seizure, it has been noted to some extent how the activity of nNOS can somehow diminish its deleterious effects. Oleuropein, a polyphenol from olives and EVOO, has been studied in this regard for its anticonvulsant properties in mice, and it has been seen that its effectiveness is derived in part from its ability to positively modulate the expression of nNOS. Its anticonvulsant effect was in fact completely reversed by acute pretreatment with L-NAME (a nonselective NOS inhibitor) and 7-NI (a selective inhibitor of nNOS) [
141]. Being also found in other tissues, nNOS has been shown to be implicated in various physiological mechanisms outside the central and/or peripheral nervous system. For example, it has been observed how the localization of nNOS in the sarcolemma is essential for maintaining muscle activity and mass, and delocalization of nNOS from sarcolemma represents one major initiating event leading to disuse muscle atrophy. Delocalization of nNOS active molecules from sarcolemma to sarcoplasm has been recognized as a major event favoring increased NO availability at this site and improving activation by nitrosylation of atrophy regulators [
142]. In this regard, Vitadello et al. [
143] showed that curcumin administration to female Wistar rats counteracted the loss of mass and force by involving the Grp94 chaperone and mechanistically preserving the sarcolemmal localization of nNOS. In rats with fructose-induced hypertension, resveratrol activated nNOS to release NO to dilate large caliber vessels. Resveratrol effect was exerted through the modulation of ERK1/2-RSK-nNOS pathway by activating AMPK to negatively regulate Rac1-induced NADPH oxidase levels [
144].
4. Simultaneous Activity of Dietary Polyphenols on Different NOS Isoforms
The modulatory action on the mechanisms leading to the expression and/or activation/deactivation of the three NOS isoforms indicates that polyphenols can simultaneously perform different functions based on the tissue and the NOS isoform involved. Several studies have shown interesting implications from the perspective of the selectivity of polyphenols towards a specific NOS isoform, thus leading to relevant biological effects [
Table 1]. As already mentioned above, resveratrol has been the main object of studies regarding the interaction between polyphenols and the biological activity of NOS isoforms. It has been shown to be able to inhibit cell growth and to promote apoptosis by the elevation of NO in human melanoma A375 cells, and Western blot analysis showed the expression of all the three NOS isoforms, all of which were increased [
145]. Resveratrol showed concentration-related increases in eNOS and a simultaneous reduction in iNOS expression in human glaucomatous trabecular meshwork (TM) cells [
146]. At the physiological level, it was also tested over the long term to evaluate its impact on endothelial function and on the activity of eNOS and iNOS. Overall, it was seen that it was able to increase the expression of eNOS in endothelial HUVEC but not its activation by phosphorylation, and at the same time, no significant effect occurred with regard to the expression of iNOS [
147]. At the endothelial level, a hydroxylated analogue of resveratrol, i.e., piceatannol, was tested against the deleterious action of H
2O
2 in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Piceatannol pretreatment was able to regulate PI3K-Akt-eNOS signaling pathway to alleviate peroxidative injury, and in parallel, it decreased iNOS expression [
148].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/antiox12010147