Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Anatomy & Morphology
The plasma-membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCXs) mediate Ca2+ extrusion/entry to dynamically shape Ca2+ signaling in biological systems ranging from bacteria to humans. The NCX gene orthologs, isoforms, and their splice variants are expressed in a tissue-specific manner and exhibit nearly 104-fold differences in the transport rates and diverse regulatory specificities to match the cell-specific requirements. About 280 residues are directly involved in the folding of Ca2+ binding CBD1 and CBD2 domains that form a two-domain regulatory tandem (CBD12). The X-ray and NMR structures of the CBD1, CBD2, and CBD12 domains reveal a β-immunoglobulin (Ig)-like folding, where two antiparallel β-sheets (with A-B-E and D-C-F-G strands) form a seven-strand β-sandwich motif. The remarkable similarity between the folding structures of CBD1 and CBD2 is evident since the overlay of the CBD1 and CBD2 crystal structures display nearly identical folding with RMSD = 1.3 Å, although all the Ca2+ binding sites in both CBDs reside at the C-terminal ends of distal loops. However, the striking difference between the CBDs is that the CBD1 domain contains four Ca2+ binding sites in all known variants, whereas in the CBD2 domain, the splicing segment varies the number of Ca2+ binding sites from zero to three. The challenge is to resolve the underlying structure-dynamic mechanisms that can explain how the Ca2+ interactions with different variants of eukaryotic NCXs can result in positive, negative, and neutral responses.
- sodium-calcium exchange
- NCX
- NCKX
- NCLX
- CAX
- Ca2+/CA
- alternating splicing
- calcium binding sites
- allosteric regulation
- regulatory diversity
1. Structure-Functional Specificities of High-Affinity Ca2+ Binding Sites at CBD1
Structural studies and Ca2+-binding assays revealed that the CBD1 of eukaryotic NCX and CALX orthologs, isoforms, and splice variants contain four Ca2+ binding sites (Ca1–Ca4). In contrast, the number of Ca2+ binding sites at CBD2 varies from zero to three (CaI–CaIII) due to the alternating splicing segment at CBD2 [39,40,41,42,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. The four Ca2+ binding sites of CBD1 are assembled in a parallelogram-like configuration. In contrast, pol coordination of Ca2+ ions by the D500 and E451 residues allows one to concomitantly ligate two and three Ca2+ ions, respectively [39,41,42]. This structural organization of closely located Ca2+ binding sites (~4 Å) allows the Ca2+ binding to CBD1 with high cooperativity, which is essential for activation of NCX under physiologically relevant conditions when cytosolic [Ca2+] undergoes relatively small changes [52,55,119,120]. Notably, the C3 and C4 sites of CBD1 possess a high affinity for Ca2+ binding (Kd ≈ 0.2–0.5 µM) [119,170], thus representing a primary allosteric sensor for Ca2+-dependent activation of mammalian NCXs [116,117,118,119,120]. Based on the sequence similarities, the CBD1 folding might be very similar in NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3. Notably, the CBD1 crystal structure of CALX1.1 [41] shows striking similarities to the CBD1 structure of NCX1 [39,42]. The common structural features of CBD1 are remarkable since, in contrast with full-size NCXs (which undergo activation upon Ca2+ binding to CBD1), the Ca2+ binding to CBD1 of full-size CALX1.1 results in inhibition [167,168,169,171,172,173].
Although the Kd values of Ca2+ binding to the high-affinity sites of CBD12 are comparable among the cardiac (ACDEF), brain (AD), and kidney (BD) splice variants of NCX1, the Ca2+ dissociation rates from the high-affinity sites differ up to 200-fold [24,25,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. More specifically, the stopped-flow measurements have identified slow rates (0.02–3 s−1) for the occluded Ca2+ dissociation from the high-affinity regulatory sites of CBD12 obtained from the different isoform/splice variants of NCX and CALX. These slow Ca2+ off-rates correlate remarkably with slow inactivation kinetics of full-size NCX variants, which were measured using patch-clamp techniques upon removal of the cytosolic Ca2+ [77,80,105,167,168,169,171]. Strikingly, the slow dissociation of regulatory Ca2+ can be observed only in the CBD12 constructs (the two-domain tandem) but not in the isolated CBD1 or CBD2 ones—this means that specific synergistic interactions between the two regulatory domains generate a slow dissociation of occluded Ca2+ [119,120,121,122,123,124]. The structure-based mutational analyses of CBD12-NCX1.4, CBD12-CALX1.1, and CBD12-CALX1.2 have shown that Ca2+ occlusion at the high-affinity C3 and C4 sites of CBD1 results in the Ca2+-dependent tethering of CBDs through a hydrogen-bonding network [41,42,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. Thus, slow dissociation of occluded Ca2+ (due to the Ca2+-driven driven tethering of CBDs) can couple diverse regulatory phenotypes in NCX and CALX.
2. Varying Compositions of Exons Control the Affinity and Number of Ca2+ Sites at CBD2
In contrast with CBD1, the Ca2+ binding sites of CBD2 are ~5.5 Å apart, where K585 (a homolog to E454 in CBD1) forms a salt bridge with D552 and E648 (in the absence of Ca2+), thereby yielding a relatively more stable apo-CBD2 structure [40,42]. Cumulative data revealed that the mutually exclusive exons (A and B) control three positions (522, 578, and 585) in CBD2 that predefine the number of Ca2+ binding sites at CBD2 [37,38,39,40,41,42,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124] (Figure 1B). The addition of cassette exons (CDEF) to the splicing segment shapes the Ca2+ binding affinities at both the CBD1 and CBD2 domains and modulates the Ca2+ dissociation rates from high-affinity regulatory sites to control NCX responses to cell-specific Ca2+ signaling/homeostasis [117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. Notably, in NCX1, the B-exon variants contain Arg (instead of Asp or Glu) and Cys (instead of Lys) at positions 578 and 585, respectively (Figure 1A,B); this prevents Ca2+ binding to CBD2 (e.g., in the kidney NCX1.3 variant). These structure-controlled arrangements significantly impact the regulatory capacity since the B-exon-dependent prevention of Ca2+ binding to CBD2 aborts the Ca2+-dependent alleviation of Na+-induced inactivation. In the CBD2 of NCX2 (no splice variants), the replacement of D552 by histidine eliminates the CaII site while dramatically reducing the Ca2+ affinity at the CaI site (Kd ≈ 100 µM) [124]. However, in the absence of Na+-induced inactivation of NCX2, the effect of potential Ca2+ binding to CBD2 cannot be tested. In NCX3, B-exon replaces K585 with Glu to generate three Ca2+ binding sites at CBD2, whereas K585 in the A-exon of NCX3 prevents Ca2+ binding to CBD2 (since K585 interactions with E516, D522, D578, and D578 preclude Ca2+ binding) (Figure 1B).
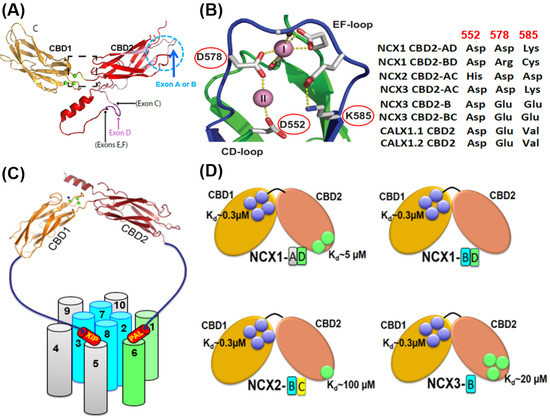
Figure 1. Structural basis of exon-dependent regulatory diversity in eukaryotic NCX variants. (A) Experimentally obtained NMR structures of CBD1 (2FWS), CBD2-AD (2FWU), and CBD2-BD (2KLT) of NCX1 were superimposed on the template of NCX1-CBD12 crystal structure (PBD 3US9) to demonstrate the structural positions of mutually exclusive (A or B) and cassette (CDEF) exons at CBD2. (B) The crystal structure of NCX1-CBD2-AD (PDB 2QVM) shows that K585 forms a salt bridge with D552 and E648 in the absence of Ca2+ (thereby stabilizing apo-CBD2), whereas in the presence of Ca2+, two Ca2+ binding sites (CaI and CaII) can be occupied by Ca2+. Different residues at the three key positions (522, 578, and 585) can predefine the number of Ca2+ binding sites at CBD2 in an exon-dependent manner. For example, in NCX1, exon B variants contain Arg (instead of Asp or Glu) and Cys (instead of Lys) at positions 578 and 585, respectively, which presents Ca2+ binding to CaI of NCX1-CBD2, thereby destabilizing the CBD2 folding. In contrast, the A-exon containing variants of NCX1 retain its structural integrity even in the absence of Ca2+ since K585 can form salt bridges with neighboring negatively charged residues (E516, D522, D578, and D578). In NCX2-CBD2 (which lacks splice variants), the substitution of D552 by histidine eliminates the CaII site while reducing the Ca2+ affinity at CaI. In NCX3, B-exon K585 is substituted by glutamate, generating three Ca2+ binding sites at CBD2. In contrast, the A-exon containing NCX3 variant has K585, which prevents Ca2+ binding to CBD2 (since K585 can form strong interactions with E516, D522, D578, and D578 in the absence of Ca2+). (C) Topological location of the regulatory CBD1 and CBD2 domains with regarding the autoinhibitory (XIP) and palmitoylation (PAL) domains. The ion-transporting helices (TM2, TM3, TM7, and TM8) are in blue. The sliding cluster (the TM1/TM6 bundle) is in green. The image of the regulatory two-domain tandem (CBD12) is presented according to the crystal structure of CBD12-NCX1.4 (PBD 3US9). (D) The Ca2+ binding sites of CBD1 (shown in blue circles) have a comparable affinity (Kd ≈ 0.3 µM) among NCX isoform/splice variants. In contrast, the Kd values of the Ca2+ binding sites of CBD2 (shown in green circles) vary from 5 µM to 100 µM. Thus, the exon-dependent structural variances control the number of Ca2+ binding sites (from zero to three) at CBD2 and the Ca2+ binding affinity.
Like mammalian NCXs, CALX1 also undergoes alternative splicing at CBD2, although the splicing segments of CALX1.1 and CALX1.2 are much shorter and differ from each other by only five residues [41,65]. Structural studies have shown that these five residues in CALX1-CBD2 are located within an FG-loop between the H1 α-helix and the β-strand, similar to the cassette exons’ (C, D, E, and F) positions that appear in mammalian NCXs [41,42]. Notably, the CBD2 domain of the CALX1 splice variants does not bind Ca2+.
3. The CBD1-CBD2 Linker and Dynamic Coupling of Ca2+-Dependent Tethering of CBDs
Comprehensive analysis of mutants using stopped-flow assays revealed that a short interdomain linker (501-HAGIFT-506) connecting the two CBDs is essential for structure-based regulatory coupling [42,116,117]. Notably, the interdomain CBD1-CBD2 linker is highly conserved among all known NCX and CALX variants. The CBD12 structural crystal structures of the NCX1.4, CALX1.1, and CALX1.2 underscore the crucial role of the CBD1-CBD2 linker in the Ca2+-dependent tethering of the CBD1 and CBD2 domains [41,42]. Genetically encoded elongation of the CBD1-CBD2 linker accelerates (up to 50-fold) the occluded Ca2+ off-rates and decreases the affinity of Ca2+ binding (up to 10-fold) at the high-affinity Ca3-Ca4 sites of CBD12, either in NCX or CALX [24,25,26,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. Mutational analysis revealed that G503 is the only residue in the linker whose mutation abolishes the slow dissociation of occluded Ca2+ and alters the interdomain movements of CBDs [42,116]. Moreover, the crystal structures of NCX1-CBD12 and CALX-CBD12 indicate that the dihedral φ/ψ angles at position 503 are only allowed for the glycine residue [41,42] (any other residue at this position in the linker would result in a steric clash of protein folding). Functional analyses of full-size NCX and CALX have shown that mutations of either G503 in NCX1.1 or analogous G555 in CALX1.1 abort the Ca2+-dependent regulation of NCX ion currents [167,168,169,171]. Thus, the highly conserved CBD1-CBD2 linker controls the Ca2+-dependent interdomain tethering/coupling of CBDs in NCX and CALX.
4. The Structure of the Two-Domain Interface Predefines the Dynamic Coupling of CBDs
The discovery of the two-domain tandem (CBD12) crystal structures [41,42] provided a basis for elucidating the structure-dynamic determinants that predefine positive, negative, and no response to regulatory Ca2+ in NCX and CALX variants. The X-ray structures of the brain NCX1-CBD12-AD, CALX1.1-CBD12, and CALX1.2-CBD12 variants depict a relatively small contact area (~360 Å2) between the CBD1 and CBD2. Notably, the Ca2+ coordination chemistry is very similar in isolated CBD1, CBD2, and CBD12 domains, derived from either NCX or CALX orthologs. However, a few structural differences have a primary mechanistic significance [41,42], as specified below. Namely, E385 only coordinates Ca3 in isolated CBD1, whereas this residue contributes to Ca2+ ligation at the Ca2, Ca3, and Ca4 sites in the CBD12 of NCX1-AD, CALX1.1, or CALX1.2. The most important structural difference between the isolated CBD1 and CBD12 is that D499 forms bidentate coordination with Ca4 in CBD12 in contrast with monodentate coordination in isolated CBD1. The significance of these structural arrangements is that they may predefine the structural stability of Ca2+-dependent tethering of CBDs in NCX and CALX [3,5,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124].
In general, the crystal structures of NCX1-CBD12 and CALX1-CBD12 revealed three regions (assigned as the hydrophilic, hydrophobic, and loop/α-helix arrays), which involve over 20 residues [41,42,172,173]. The hydrophilic region includes a pivotal electrostatic network centered at R532 in CBD2, where R532 forms a bifurcated network of salt bridges with D499 and D500 in CBD1 and D565 in CBD2 once Ca3-Ca4 become occupied by Ca2+ [42]. Notably, this Ca2+-related tethering (through D499 and D500) contributes to two Ca2+ coordination at Ca3-Ca4 while concomitantly stabilizing the CBD interface (Figure 2). Thus, this highly conserved network of salt bridges acts as a major linchpin that holds the two CBDs together upon Ca2+ occlusion at the two-domain interface. The Ca2+-dependent rigidification of the two-domain interface is further supported by SAXS and HDX-MS analyses of isolated CBD12 variants [42,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. Thus, the coupling of Ca2+ occlusion with CBD tethering represents a unifying mechanism for interdomain coupling, where the structure-dynamic stability (rigidity) of the interdomain realm can be gradually modulated by varying composition of exons [3,8,25,26,119,120,121,122,123,124].
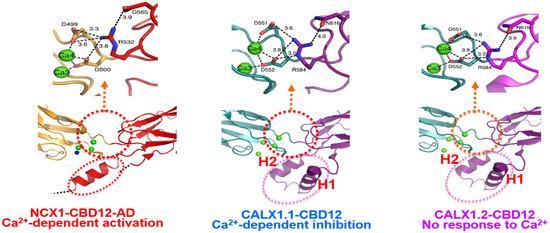
Figure 2. The interface structures of the two-domain CBD12 tandem in the NCX and CALX orthologs. Carton presentation of NCX1-CBD12-AD (PDB 3US9) and CALX1.1-CBD12 (PDB 3RB5) and CALX1.2 (PDB 3RB7) crystal structures depict highly conserved residues participating in the network of interdomain salt bridges. Green balls indicate the Ca2+ binding sites at the interface of NCX1-CBD12-AD, CALX1.1-CBD12, and CALX1.2-CBD12. The blue ball in NCX1-CBD12 refers to the Ca2+ binding site that cannot be resolved in the PDB 3US9 crystal structure, although the position of this Ca2+ binding site is nearly identical to the Ca2+ binding site of CALX1.1-CBD12 (PDB 3RB5) and CALX1.2 (PDB 3RB7) as revealed by these crystal structures. The Ca2+ occlusion occurs at the high-affinity binding sites (Ca3-Ca4) of CBD1 in all three proteins (shown in the red-dotted cycle). Although the interdomain salt-bridge structures are highly conserved among NCX and CALX variants, a striking difference between the NCX and CALX variants occurs in the structural organization of the FG-loop α-helix at CBD2. More specifically, the CALX1.1-CBD12 and CALX1.2-CBD12 variants have a two-headed (H1 and H2) short-helix structure, which situates nearly perpendicularly to the β-sheet plane of CBD2. In contrast, the α-helix of NCX1-CBD12 is longer, while adopting a straight configuration. These structural disparities in the α-helix folding (in conjunction with variations in exon composition) can predefine the dynamic features of CBDs movements and, thus, the regulatory specificities of a given ortholog/isoform/splice variant. Thus, the structure-encoded dynamic distinctions of relevant structural elements may predefine (at least partially) the characteristic responses of full-size NCX and CALX variants to regulatory Ca2+.
The hydrophobic region at the two-domain interface contains residues that locate on the Ca2+-binding EF loop of CBD1, the interdomain linker, and the FG loop of CBD2. The crucial point is that F450 interacts with H501, I628, A629, M631, and G632 (through van der Waals interactions) to form a tightly packed hydrophobic core [42]. Notably, these residues are inaccessible to the bulk phase, so even minute structural changes within this tightly packed hydrophobic core can significantly affect the dynamic features of interdomain motions. For example, the Ca2+-dependent interaction of F450 with H501 may limit the flexibility of the interdomain linker. Moreover, neighboring interactions between the CD and EF loops of CBD1 and the FG-loop of CBD2 (including the splicing segment) can modulate the Ca2+ binding affinity to the Ca3-Ca4 sites of CBD1. Since the FG-loop of CBD2 is unstructured (except for a short α-helix region at the C-terminus of the FG-loop), it is reasonable to assume that the side chains of a canonical α-helix impact the structure-dynamic features of the two-domain interface [42]. Notably, the FG-loop of CALX1-CBD12 forms a two-headed short helix structure (H1 and H2), upright to the β-sheets [41]. This structural organization of CALX-CBD12 is strikingly different from the matching helix structure of NCX1-CBD12-AD [42] (Figure 2).
The α-helix region (belonging to the FG-loop of CBD2) is very close to the CBD1-CBD2 linker and the Ca3-Ca4 sites of CBD1 (either in NCX or CALX), thereby suggesting that the relevant interactions may affect the Ca2+ access to high-affinity binding sites of CBD1. The two-headed short helices (H1 and H2) of CALX can more effectively stabilize the interdomain linker and CBD2 folding as compared with mammalian NCX variants, having a straight and longer α-helix at the matching position. These “minute” differences between NCX1 and CALX1 in the structural organization of the FG-loop α-helix can differently affect the rigidity of the interdomain linker and CBD2 folding [119,120,121,122,123,124].
5. Dynamic Features Might Predefine the Opposing Responses of NCX and CALX to Regulatory Ca2+
Based on the crystal structures of Ca2+-bound CALX1.1-CBD12 and CALX1.2-CBD12, it was suggested that slight differences in the interdomain angle (~8º) between the CBD1 and CBD2 domains determine different responses to regulatory Ca2+ in full-size CALX1.1 and CALX1.2 variants [41]. However, the crystal structure of NCX1-CBD12 demonstrated that the interdomain angle of Ca2+-bound CBD12 is nearly identical for NCX1-CBD12-AD (117.4°) and CALX1.1-CBD12 (117.7°), which means that the fixed-angle alignment of CBDs cannot account for Ca2+-dependent activation (NCXs) and inhibition (CALX1.1) [42]. Cumulative data obtained by NMR [125,179,180,181], SAXS [117,118,119,120,121], and HDX-MS [120,121,122,123,124] reveal a common model for Ca2+-dependent activation of mammalian NCXs. According to this unifying mechanism, the Ca2+-dependent activation of mammalian NCXs involves the Ca2+-dependent tethering of two CBDs (due to the Ca2+ occlusion), which restricts the interdomain movements of CBDs to keep mammalian NCX active. Subsequently, a slow dissociation of occluded Ca2+ leads to NCX inactivation, where the time scale of NCX activation depends on the kinetics of the occluded Ca2+ dissociation. Even though the interdomain network of R532, D499, and D500 residues is a common structural module for the Ca2+ occlusion and subsequent tethering of CBDs either in NCX or CALX (Figure 2), the structure-dynamic stability of the two-domain tethering may predefine the regulatory outcomes of the Ca2+-dependent regulation in distinct variants. The emerging working hypothesis is that the structure-dynamic stability of the two-domain tethering might differ among NCX and CALX variants since effects of the two-domain interface, the CBD1-CBD2 linker, and varying compositions of exons characteristically differ among NCX and CALX variants [42,119,120,121,122,123,124]. For example, it is reasonable to assume that the two-domain tethering is less stable in CALX than in NCX since the off-rates of the occluded Ca2+ are much faster in CALXs (3–12 s−1) than in NCXs (0.03–0.5 s−1) [42,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. How these dynamic differences in the Ca2+ tethering could be related to translational and rotational movements of CBDs, remains to be resolved (see below).
6. Population Shift Mechanism Can Account for Opposite Responses to Regulatory Ca2+
The analyses of CALX1.1-CBD12, CALX1.2-CBD12, NCX1-CBD12, NCX2-CBD12, and NCX3-CBD12 by SAXS have shown that the occupation of the Ca3-Ca4 sites by Ca2+ shifts the fractional distribution of conformational states toward a more constrained population [42,117,118,119,120,121]. These findings revealed that the Ca2+ binding rigidifies the interdomain movements of CBDs, where the average distance between the CBD1 and CBD2 (as well as their alignment) remains unaffected. These findings are consistent with the population shift mechanism, according to which the ligand (Ca2+) binding to a given protein does not generate new conformational states; instead, the ion binding shifts a predominant population of unstable conformational states to a new population of more stable conformational states [118,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190]. Thus, upon Ca2+ binding, the fraction of more rigid (constrained) conformational states becomes dominant at dynamic equilibrium. The unique feature of the population shift mechanism is that it avoids large conformational transitions requiring sizable free energy changes [182,185,190]. The advantage of the population shift mechanism versus the induced fit mechanism (an alternative mechanism to the population shift mechanism) is that the induced fit can operate under one of two scenarios: when ligand (ion) concentrations are very high or when the protein has a very high affinity for ligand binding [115,116,117,118,182,183,184,185]. Neither of these conditions fits the Ca2+-dependent regulation of NCXs since the quick and effective response of tissue-specific NCX variants is required to match the Ca2+-dependent events that occur from the millisecond time range to minutes and hours [182,183,184,185,186,189].
Consistent with the population shift mechanism, NMR analysis revealed that Ca2+ binding to the Ca3–Ca4 sites of NCX1-CBD12 or CALX-CBD12 restricts the linkers’ flexibility and interdomain movements of CBDs [125,179,180,181]. These data are consistent with the SAXS and HDX-MS findings, revealing that Ca2+ occlusion at Ca3-Ca4 of NCX and CALX rigidifies the backbone dynamics of the two-domain interface, which is coupled with CBD tethering through Ca2+ occlusion [41,42,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. Interestingly, the global structural parameters of CBDs (e.g., the maximal interdomain distance and the radius of gyration) are similar in the apo- and the Ca2+-bound forms in all tested variants (the NCX1.4-CBD12, CALX1.1-CBD12, and CALX 1.2-CBD12 variants), although the Ca2+ binding narrows and shifts the population of conformational states under a dynamic equilibrium [42,118]. Although NCX1.4-CBD12, CALX1.1-CBD12, and CALX 1.2-CBD12 show striking similarities in Ca2+-dependent tethering [41,42], the stability of this network is diverged by the two-domain interphase and varying exon compositions [116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124].
7. Allosteric Signal Transfer from CBD1 to CBD2 May Modulate the TM1/TM6 Sliding
The HDX-MS analyses of CBD12 preparations revealed that the Ca2+-dependent tethering of CBDs rigidifies the CBD interface in NCX and CALX [42,120,121,122,123,124]. However, the strength and spread of the Ca2+-dependent rigidification characteristically differs in NCX1-CBD12 (AD), NCX2-CBD12, NCX3-CBD12 (BC), and CALX1.1. These differences in the backbone rigidification are especially prominent when comparing NCX and CALX variants. In NCX1-CBD12-AD, the Ca2+ binding to CBD1 rigidifies the backbone from the Ca3–Ca4 sites of CBD1 up to the C-terminal tip of CBD2 (Figure 3). This allosteric pathway covers a distance of ~50 Å, which also embraces the CBD2 α-helix, including the splicing segment. Notably, the mutation of F450 (a central residue with the hydrophobic core of the two-domain interface) aborts the propagation of the Ca2+-dependent rigidification of CBD2. Thus, the F450-dependent stabilization of the CBD1-CBD2 linker is essential for transferring the allosteric massage from CBD1 to CBD2. In CALX1.1-CBD12 the propagation of the Ca2+-dependent rigidification of the backbone also begins from the Ca3-Ca4 sites. However, the rigidification occurs in a very short distance that stops at the CBD2 α-helix [122,123,124]. The NMR [125,179,180,181] analyses [125,179,180,181] provided consistent and complementary information on the relevant issues. According to a fundamental paradigm, two domains connected through a short interdomain linker (as occurs in CBD12) might undergo transitional and rotational movements (Figure 3C,D). The output of transitional and rotational movements could be characteristically different among NCX and CALX variants. In mammalian NCXs, the allosteric signal propagates from the C-terminal tip of CBD1 to the C-terminal CBD2 tip. The splicing segment can specifically shape a relationship between the translational and rotational movements in a given isoform/splice variant, thereby yielding distinct regulatory profiles. In CALX, the unstable tethering of CBDs and folding stability of CBD2 modulate the translational and rotational movements in such a way that this leads either to inhibition or no response to regulatory Ca2+. The resolution of the underlying mechanisms is essential since the C-terminal of CBD2 links to TM6, meaning that the different allosteric pathways may affect the sliding of the TM1/TM6 bundle (Figure 3A,B). These structural arrangements may provide a basis for a cross-talk between the CBDs and transport domains either in NCX or CALX proteins. The analyses of nanodisc-reconstituted NCX and CALX using the Cryo-EM and HDX-MS techniques may provide crucial information on the positive, negative, and no responses to Ca2+.
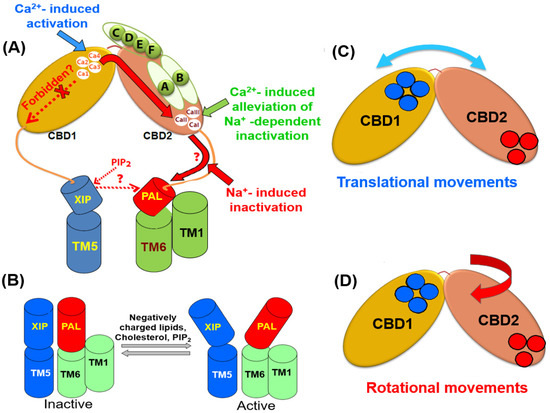
Figure 3. Structural elements that contribute to the propagation and integration of allosteric signals. (A) The occupation of the Ca3-Ca4 sites by Ca2+ rigidifies the backbone dynamics at the two-domain interface of CBDs. The allosteric signal propagation from the C-terminal tip of CBD1 to the C-terminal end of CBD2 (shown in a solid red arrow) is under the control of the splicing segment at CBD2 and the two-domain interface. (B) The positively charged XIP (autoinhibitory) domain can anchor the negatively charged helix (PAL) at the palmitoylation site. Since the PAL domain links to TM6, the XIP/PAL unit may affect the sliding of the TM1/TM6 bundle, thereby modulating the transport rates. The interactions of inhibitory (e.g., Na+) and activating (e.g., PIP2) ligands with respective sites (located of the XIP/PAL unit) can shift a steady-state equilibrium between the active and inactive states. Blue and red cylinders represent the XIP and PAL domains, respectively. The interdomain movements of the CBD1 and CBD2 domains might involve translational (C) and rotational (D) movements. Specific structural elements (e.g., the two-domain interface, XIP/PAL unit, and varying exon compositions) may characteristically shape the outcomes of regulatory specificity in a given NCX variant by controlling a relationship between the translational and rotational movements. The blue and red cycles represent the Ca2+ binding sites of CBD1 and CBD2, respectively.
8. Mutually Exclusive and Cassette Exons Operate through Different Regulatory Modules
Conceptually, the splicing segments of proteins contain intrinsically disordered regions, which avoids the formation of stable tertiary structures [185,186,187]. Instead, the splicing segments can embrace more stable conformational states upon ligand binding, which allows dynamic functional transitions in a given protein [186,187,188,189,190,191]. Consistent with this general concept, the Ca2+ binding to CBDs results in a population shift of numerous pre-existing conformational states through incremental (low energy) conformational transitions. The mutually exclusive exons, A and B, are located at the C-terminus tip of CBD2 (on the loops that are directly involved in Ca2+ coordination) [37,38,39,40,41,42]. Exons A and B play opposite roles in NCX1 and NCX3 [3,38,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. In NCX1, exon B increases the Ca2+ affinity at the Ca3-Ca4 sites of CBD1 (while decelerating the off-rates of occluded Ca2+ dissociation from Ca3-Ca4), whereas exon B structurally prevents Ca2+ binding to CBD2 (Figure 1A–C). In NCX1, exon A forms two Ca2+ binding sites at CBD2, while decreasing Ca2+ affinity at CBD1. The roles of exons A and B exon become inverted in NCX3 as compared with NCX1—namely, in NCX3, exon A prevents Ca2+ binding to CBD2 while increasing the Ca2+ binding affinity at CBD1 (Figure 1B,C). In NCX3, exon B generates three Ca2+ sites at CBD2 (due to K585 replacement by glutamate, which also decreases the Ca2+ affinity at CBD1 (106–110). Thus, the mutually exclusive exons (A and B) not only condition the Ca2+ binding stoichiometry to CBD2 but also shape the Ca2+ affinity to CBD1 and CBD2 domains [117,120,121,122].
The cassette exons (C, D, E, and F) are located at the unfolded segment of the FG-loop while being in proximity with the high-affinity sites (Ca3-Ca4) of CBD1 and the interdomain CBD1-CBD2 linker [37,38,39,40,41,42] (Figure 1A). As a complementary unit for modulating the dynamic features of interdomain coupling, the cassette exons (C, D, E, and F) can effectively rigidify the interdomain linker thereby stabilizing the CBD2 folding [3,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124]. Notably, the gradual additions of the cassette exons (C, D, E, and F) to exon A incrementally enhances the affinity of the Ca2+ binding sites at CBD1 as well as slows down the dissociation of occluded Ca2+ from the Ca3-Ca4 sites [119,120,121,122,123]. Notably, the gradual additions of the cassette exons compensate for the destabilizing effect caused by exon A on the high-affinity Ca2+ binding sites of CBD1. Most probably, the exon-dependent rigidification of the CBD2 BC-loop and interdomain linker (upon Ca2+ binding to the Ca3-Ca4 sites of CBD1) reduces the translational movement of CBD12. In contrast, the exon-dependent rigidification of the neighboring β-strands in CBD2 might restrict the rotational motion of CBD2. Besides the exons’ compositions, the intrinsic folding energy of CBD2 may affect the integration of transitional and rotational movements. For example, the intrinsic structure of CBD2 might be more rigid in CALX than in NCXs, which may limit the rotational movements of CBD2, thereby causing a negative or no response to Ca2+ in CALX1.1 or CALX1.2, respectively
References:
- Philipson, K.D.; Nicoll, D.A. Sodium-calcium exchange: A molecular perspective. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000, 62, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaustein, M.P.; Lederer, W.J. Sodium/calcium exchange: Its physiological implications. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 763–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khananshvili, D. Basic and editing mechanisms underlying ion transport and regulation in NCX variants. Cell Calcium 2019, 85, 102131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khananshvili, D. The Archaeal Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger (NCX_Mj) as a Model of Ion Transport for the Superfamily of Ca2+/CA Antiporters. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 722336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytton, J. Na+/Ca2+ exchangers: Three mammalian gene families control Ca2+-transport. Biochem. J. 2007, 406, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottolia, M.; John, S.; Hazan, A.; Goldhaber, J.I. The Cardiac Na+-Ca2+ Exchanger: From Structure to Function. Compr. Physiol. 2021, 12, 2681–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khananshvili, D. The SLC8 gene family of sodium-calcium exchangers (NCX)—Structure, function, and regulation in health and disease. Mol. Aspects Med. 2013, 34, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khananshvili, D. Sodium-Calcium Exchangers (NCX): Molecular Hallmarks Underlying the Tissue-Specific and Systemic Functions. Plügers Arch. 2014, 466, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Luo, L.; Sun, B.; Sun, D. Roles of glial ion transporters in brain diseases. Glia 2019, 68, 472–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, P.; Natale, S.; Serani, A.; Calabrese, L.; Secondo, A.; Tedeschi, V.; Valsecchi, V.; Pannaccione, A.; Scorziello, A.; Annunziato, L. Genetically modified mice to unravel physiological and pathophysiological roles played by NCX isoforms. Cell Calcium 2020, 87, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Song, S.; Ezenwukwa, C.C.; Jalali, S.; Sun, B.; Sun, D. Ion channels and transporters in microglial function in physiology and brain diseases. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 142, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.R.; Ziemens, D.; Verkhratsky, A. On the special role of NCX in astrocytes: Translating Na+-transients into intracellular Ca2+ signals. Cell Calcium 2019, 86, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscia, F.; de Rosa, V.; Cammarota, M.; Secondo, A.; Pannaccione, A.; Annunziato, L. The Na+/Ca2+ exchangers in demyelinating diseases. Cell Calcium 2019, 85, 102130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, C.R.; Verkhratsky, A. Principles of sodium homeostasis and sodium signaling in astroglia. Glia 2016, 64, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, T.; Piccirillo, S.; Magi, S.; Preziuso, A.; Ramos, V.d.S.; Serfilippi, T.; Orciani, M.; Alvarez, M.M.P.; Tersariol, I.L.D.S.; Amoroso, S.; et al. Control of Ca2+ and metabolic homeostasis by the Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCXs) in health and disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 203, 115163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Ma, X.; Song, M. Suppressing Effect of Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger (NCX) Inhibitors on the Growth of Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magli, E.; Fattorusso, C.; Persico, M.; Corvino, A.; Esposito, G.; Fiorino, F.; Luciano, P.; Perissutti, E.; Santagada, V.; Severino, B.; et al. New Insights into the Structure–Activity Relationship and Neuroprotective Profile of Benzodiazepinone Derivatives of Neurounina-1 as Modulators of the Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger Isoforms. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 17901–17919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.A.; Fattahi, F. New strategies for treatment of infectious sepsis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlovák, J.; Tomek, J.; Zhou, X.; Tóth, N.; Veress, R.; Horváth, B.; Szentandrássy, N.; Levijoki, J.; Papp, J.G.; Herring, N.; et al. Blockade of sodium-calcium exchanger via ORM-10962 attenuates cardiac alternans. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 153, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Kiss, L.; Varró, A.; Nánási, P.P. Potential therapeutic effects of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger inhibition in cardiac diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3294–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignataro, G.; Sirabella, R.; Anzilotti, S.; Di Renzo, G.; Annunziato, L. Does Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger, NCX, Represent a New Druggable Target in Stroke Intervention? Transl. Stroke Res. 2013, 5, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chovancova, B.; Liskova, V.; Babula, P.; Krizanova, O. Role of Sodium/Calcium Exchangers in Tumors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziato, L.; Secondo, A.; Pignataro, G.; Scorziello, A.; Molinaro, P. New perspectives for selective NCX activators in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Calcium 2020, 87, 102170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giladi, M.; Shor, R.; Lisnyansky, M.; Khananshvili, D. Structure-Functional Basis of Ion Transport in Sodium–Calcium Exchanger (NCX) Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Tal, I.; Khananshvili, D. Structural Features of Ion Transport and Allosteric Regulation in Sodium-Calcium Exchanger (NCX) Proteins. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khananshvili, D. Structure-Dynamic and Regulatory Specificities of Epithelial Na+/Ca2+ Exchangers (NCX). In Ion Channels and Transporters of Epithelia in Heatllh and Disease; Hamilton, K., Devor, C.D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Chapter 8; pp. 325–381. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Li, H.; Zeng, W.; Sauer, D.B.; Belmares, R.; Jiang, Y. Structural Insight into the Ion-Exchange Mechanism of the Sodium/Calcium Exchanger. Science 2012, 335, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Marinelli, F.; Lee, C.; Huang, Y.; Faraldo-Gómez, J.D.; Jiang, Y. Mechanism of extracellular ion exchange and binding-site occlusion in a sodium/calcium exchanger. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPolo, R.; Beaugé, L. Sodium/calcium exchanger: Influence of metabolic regulation on ion carrier interactions. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 155–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaback, H.R.; Smirnova, I.; Kasho, V.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, Y. The Alternating Access Transport Mechanism in LacY. J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 239, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, L.R.; Krämer, R.; Ziegler, C. The structural basis of secondary active transport mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1807, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.; Boudker, O. Shared molecular mechanisms of membrane transporters. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 543–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, B.; Bernèche, S.; Egwolf, B.; Lev, B.; Noskov, S.; Rowley, C.; Yu, H. Ion selectivity in channels and transporters. J. Gen. Physiol. 2011, 137, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waight, A.B.; Pedersen, B.P.; Schlessinger, A.; Bonomi, M.; Chau, B.H.; Roe-Zurz, Z.; Risenmay, A.J.; Sali, A.; Stroud, R.M. Structural basis for alternating access of a eukaryotic calcium/proton exchanger. Nature 2013, 499, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Kita, S.; Maturana, A.D.; Furuya, N.; Hirata, K.; Kasuya, G.; Ogasawara, S.; Dohmae, N.; Iwamoto, T.; Ishitani, R.; et al. Structural Basis for the Counter-Transport Mechanism of a H+/Ca2+ Exchanger. Science 2013, 341, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Tong, S.; Waltersperger, S.; Diederichs, K.; Wang, M.; Zheng, L. Crystal structure of Ca2+/H+ antiporter protein YfkE reveals the mechanisms of Ca2+ efflux and its pH regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11367–11372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilge, M.; Aelen, J.; Vuister, G.W. Ca2+ regulation in the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger involves two markedly different Ca2+ sensors. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilge, M.; Aelen, J.; Foarce, A.; Perrakis, A.; Vuister, G.W. Ca2+ regulation in the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger features a dual electrostatic switch mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14333–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, D.A.; Sawaya, M.R.; Kwon, S.; Cascio, D.; Philipson, K.D.; Abramson, J. The crystal structure of the primary Ca2+ sensor of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger reveals a novel Ca2+ binding motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21577–21581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besserer, G.M.; Ottolia, M.; Nicoll, D.A.; Chaptal, V.; Cascio, D.; Philipson, K.D.; Abramson, J. The second Ca2+-binding domain of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger is essential for regulation: Crystal structures and mutational analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18467–18472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tong, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Jayaraman, V.; Spudich, J.L.; Zheng, L. Structural Basis of the Ca2+ Inhibitory Mechanism of Drosophila Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger CALX and Its Modification by Alternative Splicing. Structure 2011, 19, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Sasson, Y.; Fang, X.; Hiller, R.; Buki, T.; Wang, Y.-X.; Hirsch, J.A.; Khananshvili, D. Ca2+-Driven Interdomain Switch of NCX: Structural and Biochemical Studies of the Two-Domain Ca2+ Sensor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39985. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, L.; Whelan, S.; Hirschi, K.D.; Pittman, J.K. Protein Phylogenetic analysis of Ca2+/CA antiporters and insights into their evolution in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittman, J.K.; Hirschi, K.D. CAX-ing a wide net: Cation/H+ transporters in metal remediation and abiotic stress signalling. Plant Biol. 2016, 18, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnetkamp, P.P. The SLC24 gene family of Na+/Ca2+–K+ exchangers: From sight and smell to memory consolidation and skin pigmentation. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalloul, A.H.; Szerencsei, R.T.; Rogasevskaia, T.P.; Schnetkamp, P.P.M. Structure-function relationships of K+-dependent Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCKX). Cell Calcium 2020, 86, 102153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhekova, H.; Zhao, C.; Schnetkamp, P.P.M.; Noskov, S.Y. Characterization of the Cation Binding Sites in the NCKX2 Na+/Ca2+-K+ Exchanger. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 6445–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assali, E.A.; Sekler, I. Sprinkling salt on mitochondria: The metabolic and pathophysiological roles of mitochondrial Na+ signaling mediated by NCLX. Cell Calcium 2021, 97, 102416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, L.R. Structural Symmetry in Membrane Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2015, 44, 311–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, A.M.; Meiler, J. Inverted Topologies in Membrane Proteins: A Mini-Review. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, e201308004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.P.; Hale, C.C. The stoichiometry of the cardiac sodium-calcium exchange system. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 7733–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, N.M.; Ginsburg, K.S. Na:Ca stoichiometry and cytosolic Ca-dependent activation of NCX in intact cardiomyocytes. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Blackwell Publishing Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlosman, I.; Marinelli, F.; Faraldo-Gómez, J.D.; Mindell, J.A. The prokaryotic Na+/Ca2+ exchanger NCX_Mj transports Na+ and Ca2+ in a 3:1 stoichiometry. J. Gen. Physiol. 2017, 150, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khananshvili, D. Distinction between the two basic mechanisms of cation transport in the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange system. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 2437–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgemann, D.W.; Nicoll, D.A.; Philipson, K.D. Charge movement during Na+ translocation by native and cloned cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Nature 1991, 352, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niggli, E.; Lederer, W. Molecular operations of the sodium–calcium exchanger revealed by conformation currents. Nature 1991, 349, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, D.M. (2002) Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature 2002, 415, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgemann, D. Unitary cardiac Na+, Ca2+ exchange current magnitudes determined from channel-like noise and charge movements of ion transport. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baazov, D.; Wang, X.; Khananshvili, D. Time-resolved monitoring of electrogenic Na+-Ca2+ exchange in the isolated cardiac sarcolemma vesicles by using a rapid-response fluorescent probe. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagor, L.; Giladi, M.; van Dijk, L.; Buki, T.; Hiller, R.; Khananshvili, D. Functional asymmetry of bidirectional Ca2+-movements in an archaeal sodium–calcium exchanger (NCX_Mj). Cell Calcium 2014, 56, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.; Reeves, J.P. Site density of the sodium-calcium exchange carrier in reconstituted vesicles from bovine cardiac sarcolemma. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkin, J.T.; Ahrens, D.C.; Aceto, J.F.; Condrescu, M.; Reeves, J.P. Molecular and Functional Studies of the Cardiac Sodium-Calcium Exchanger. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 639, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doering, A.E.; Eisner, D.A.; Lederer, W.J. Cardiac Na-Ca exchange and pH. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Blackwell Publishing Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipolo, R. Calcium influx in internally dialyzed squid giant axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 1979, 73, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Benzer, S. Calx, a Na-Ca exchanger gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10249–10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Husovic, A.; Ali, L.; Weddle, E.; Nagle, L.; Ahearn, G.A. Ocean acidification: Synergistic inhibitory effects of protons and heavy metals on 45Ca uptake by lobster branchiostegite membrane vesicles. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2019, 189, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaeli, B.; Hiller, R.; Khananshvili, D. Characteristic attributes limiting the transport rates in NCX orthologs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2021, 1864, 183792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Almagor, L.; van Dijk, L.; Hiller, R.; Man, P.; Forest, E.; Khananshvili, D. Asymmetric Preorganization of Inverted Pair Residues in the Sodium-Calcium Exchanger. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; van Dijk, L.; Refaeli, B.; Almagor, L.; Hiller, R.; Man, P.; Forest, E.; Khananshvili, D. Dynamic distinctions in the sodium-calcium exchanger adopting the inward- and outward-facing conformational states. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12311–12323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, M.; Refaeli, B.; van Dijk, L.; Hiller, R.; Giladi, M.; Kandori, H.; Khananshvili, D. Structure-affinity insights into the Na+ and Ca2+ interactions with multiple sites of a sodium-calcium exchanger. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 4678–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaeli, B.; Liu, S.; Hiller, R.; Giladi, M.; Baiz, C.R.; Khananshvili, D. Proton-modulated interactions of ions with transport sites of prokaryotic and eukaryotic NCX prototypes. Cell Calcium 2021, 99, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, L.; Giladi, M.; Refaeli, B.; Hiller, R.; Cheng, M.H.; Bahar, I.; Khananshvili, D. Key residues controlling bidirectional ion movements in Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. Cell Calcium 2018, 76, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoll, D.A.; Longoni, S.; Philipson, K.D. Molecular cloning and functional expression of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Science 1990, 250, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Matsuoka, S.; Hryshko, L.V.; Nicoll, D.A.; Bersohn, M.M.; Burke, E.P.; Lifton, R.P.; Philipson, K.D. Cloning of the NCX2 isoform of the plasma membrane Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17434–17439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.L.; Yu, A.S.; Lytton, J. Tissue-specific expression of Na+-Ca2+ exchanger isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14849–14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofuji, P.; Lederer, W.J.; Schulze, D.H. Mutually exclusive and cassette exons underlie alternatively spliced isoforms of the Na/Ca exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 5145–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linck, B.; Qiu, Z.; He, Z.; Tong, Q.; Hilgemann, D.W.; Philipson, K.D. Functional comparison of the three isoforms of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1, NCX2, NCX3). Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1998, 274, C415–C423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.Y.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Towards Understanding the Role of the Na⁺-Ca²⁺ Exchanger Isoform 3. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 168, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosnoski, D.M.; Gay, C.V. NCX3 is a major functional isoform of the sodium–calcium exchanger in osteoblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 103, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Lachuer, J.; Bilbaut, A.; Georges, B.; Andrieu, J.-L.; Diez, J.; Ojeda, C. Characterization of a Na+-Ca2+ exchanger NCX1 isoform in bovine fasciculata cells of adrenal gland. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 218, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lariccia, V.; Amoroso, S. Calcium- and ATP-dependent regulation of Na/Ca exchange function in BHK cells: Comparison of NCX1 and NCX3 exchangers. Cell Calcium 2018, 73, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, F.; Almagor, L.; Hiller, R.; Giladi, M.; Khananshvili, D.; Faraldo-Gómez, J.D. Sodium recognition by the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in the outward-facing conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5354–E5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Khananshvili, D. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass-spectrometry (HDX-MS) of transporters: From structural dynamics to molecular mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Mitra, S.; Simhaev, L.; Hiller, R.; Refaeli, B.; Strauss, T.; Baiz, C.R.; Khananshvili, D. Exploring the Li+ transporting mutant of NCX_Mj for assigning ion binding sites of mitochondrial NCLX. Cell Calcium 2022, 107, 102651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carafoli, E. The release of calcium from heart mitochondria by sodium. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1974, 6, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palty, R.; Silverman, W.F.; Hershfinkel, M.; Caporale, T.; Sensi, S.L.; Parnis, J.; Nolte, C.; Fishman, D.; Shoshan-Barmatz, V.; Herrmann, S.; et al. NCLX is an essential component of mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 107, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, L.; Williams, G.S.; Khananshvili, D.; Sekler, I.; Lederer, W. NCLX: The mitochondrial sodium calcium exchanger. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 59, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbincius, J.F.; Elrod, J.W. Mitochondrial calcium exchange in physiology and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2022, 102, 893–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaeli, B.; Giladi, M.; Hiller, R.; Khananshvili, D. Structure-Based Engineering of Lithium-Transport Capacity in an Archaeal Sodium–Calcium Exchanger. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Refaeli, B.; Hiller, R.; Chung, K.Y.; Khananshvili, D. Structure-dynamic and functional relationships in a Li+-transporting sodium-calcium exchanger mutant. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2018, 1860, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, S.; Deredge, D.J.; Nagarajan, A.; Forrest, L.R.; Wintrode, P.L.; Singh, S.K. Conformational dynamics of a neurotransmitter:sodium symporter in a lipid bilayer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1786–E1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallant, K.C.T.; Martens, C. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange coupled to mass spectrometry: A multifaceted tool to decipher the molecular mechanism of transporters. Biochimie 2022, S0300-9084(22)00218-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stariha, J.T.B.; Hoffmann, R.M.; Hamelin, D.J.; Burke, J.E. Probing Protein–Membrane Interactions and Dynamics Using Hydrogen–Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry (HDX-MS). Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2263, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lv, G.; Razavi, A.M.; Huysmans, G.H.M.; Weinstein, H.; Bracken, C.; Eliezer, D.; Boudker, O. Use of paramagnetic 19F NMR to monitor domain movement in a glutamate transporter homolog. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.K.; Pandey, A.; Tran, D.P.; Villanueva, N.L.; Kitao, A.; Sunahara, R.K.; Sljoka, A.; Prosser, R.S. Delineating the conformational landscape of the adenosine A2A receptor during G protein coupling. Cell 2021, 184, 1884–1894.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthenveetil, R.; Christenson, E.T.; Vinogradova, O. New Horizons in Structural Biology of Membrane Proteins: Experimental Evaluation of the Role of Conformational Dynamics and Intrinsic Flexibility. Membranes 2022, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khananshvili, D. Voltage-dependent modulation of ion-binding and translocation in the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 13764–13769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khananshvili, D.; Weil-Maslansky, E. The Cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger: Relative rates of calcium and sodium movements and their modulation by protonation-deprotonation of the carrier. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khananshvili, D.; Shaulov, G.; Weil-Maslansky, E. Rate-limiting mechanisms of exchange reactions in the cardiac sarcolemma Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. Biochemistry 1995, 33, 10290–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, R.; Philipson, K.D. Phospholipid composition modulates the Na+-Ca2+ exchange activity of cardiac sarcolemma in reconstituted vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 937, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, R.; Philipson, K.D. Influence of sterols and phospholipids on sarcolemmal and sarcoplasmic reticular cation transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 8680–8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeck, M.; Kapri-Pardes, E.; Sharon, M.; Karlish, S.J.D. Specific phospholipid binding to Na, K-ATPase at two distinct sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2904–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ander, B.P.; Hurtado, C.; Raposo, C.S.; Maddaford, T.G.; Deniset, J.F.; Hryshko, L.V.; Pierce, G.N.; Lukas, A. Differential sensitivities of the NCX1.1 and NCX1.3 isoforms of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger to alpha-linolenic acid. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läuger, P. Voltage dependence of sodium-calcium exchange: Predictions from kinetic models. J. Membr. Biol. 1987, 99, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgemann, D.W. Regulation of ion transport from within ion transit pathways. J. Gen. Physiol. 2019, 152, e201912455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgemann, D.W. Control of cardiac contraction by sodium: Promises, reckonings, and new beginnings. Cell Calcium 2019, 85, 102129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgemann, D.W.; Matsuoka, S.; Nagel, G.; Collins, A. Steady-state and dynamic properties of cardiac sodium-calcium exchange. Sodium-dependent inactivation. J. Gen. Physiol. 1992, 100, 905–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgemann, D.W. Regulation and deregulation of cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange in giant excised sarcolemmal membrane patches. Nature 1990, 344, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgemann, D.W.; Ball, R. Regulation of cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchange and MgATP potassium channels by PIP2. Science 1996, 273, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgemann, D.W. Local PIP2 signals: When, where, and how? Pflugers. Arch. 2007, 455, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgemann, D.W.; Feng, S.; Nasuhoglu, C. The Complex and Intriguing Lives of PIP2 with Ion Channels and Transporters. Sci. Signal. 2001, 2001, re19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lariccia, V.; Piccirillo, S.; Preziuso, A.; Amoroso, S.; Magi, S. Cracking the code of sodium/calcium exchanger (NCX) gating: Old and new complexities surfacing from the deep web of secondary regulations. Cell Calcium 2020, 87, 102169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Lin, M.J.; Yaradanakul, A.; Lariccia, V.; Hill, J.A.; Hilgemann, D.W. Dual control of cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange by PIP2: Analysis of the surface membrane fraction by extracellular cysteine PEGylation. J. Physiol. 2007, 582, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.A.; Ribalet, B.; Weiss, J.N.; Philipson, K.D.; Ottolia, M. Ca2+-dependent structural rearrangements within Na+-Ca2+ exchanger dimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Ottolia, M.; John, S.A.; Chen, J.-N.; Philipson, K.D. Conformational changes of a Ca2+-binding domain of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger monitored by FRET in transgenic zebrafish heart. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C388–C393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Boyman, L.; Mikhasenko, H.; Hiller, R.; Khananshvili, D. Essential Role of the CBD1-CBD2 Linker in Slow Dissociation of Ca2+ from the Regulatory Two-domain Tandem of NCX1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28117–28125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giladi, M.; Bohbot, H.; Buki, T.; Schulze, D.H.; Hiller, R.; Khananshvili, D. Dynamic features of allosteric Ca2+ sensor in tissue-specific NCX variants. Cell Calcium 2012, 51, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giladi, M.; Hiller, R.; Hirsch, J.A.; Khananshvili, D. Population Shift Underlies Ca2+-induced Regulatory Transitions in the Sodium-Calcium Exchanger (NCX). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23141–23149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, L.; Mikhasenko, H.; Hiller, R.; Khananshvili, D. Kinetic and equilibrium properties of regulatory calcium sensors of NCX1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6185–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, L.; Hagen, B.M.; Giladi, M.; Hiller, R.; Lederer, W.J.; Khananshvili, D. Proton-Sensing Ca2+ Binding Domains Regulate the Cardiac Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 28811–28820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Khananshvili, D. Molecular Determinants of Allosteric Regulation in NCX Proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 961, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Hiller, R.; Chung, K.Y.; Khananshvili, D. Structure-dynamic determinants governing a mode of regulatory response and propagation of allosteric signal in splice variants of Na+/Ca2+ exchange (NCX) proteins. Biochem. J. 2015, 465, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Giladi, M.; Bohbot, H.; Hiller, R.; Chung, K.Y.; Khananshvili, D. Structure-dynamic basis of splicing dependent regulation in tissue-specific variants of the sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX1). FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1356–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Ariely, Y.; Teldan, Y.; Granit, R.; Strulevich, R.; Haitin, Y.; Chung, K.Y.; Khananshvili, D. Structure-based dynamic arrays in regulatory domains of sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX) isoforms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, R.K.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Johnson, E.; Brüschweiler, R. Ca2+ Binding Alters the Interdomain Flexibility between the Two Cytoplasmic Calcium-binding Domains in the Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32123–32131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottolia, M.; Nicoll, D.A.; John, S.; Philipson, K. Interactions between Ca2+ binding domains of the Na+-Ca2+ exchanger and secondary regulation. Channels 2010, 4, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenrauch, A.; Juhaszova, M.; Blaustein, M. Regulatory Processes on the Cytoplasmic Surface of the Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger from Lobster Exoskeletal Muscle. J. Membr. Biol. 2000, 174, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, V.; Sisalli, M.J.; Pannaccione, A.; Piccialli, I.; Molinaro, P.; Annunziato, L.; Secondo, A. Na+/Ca2+ exchanger isoform 1 (NCX1) and canonical transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6) are recruited by STIM1 to mediate Store-Operated Calcium Entry in primary cortical neurons. Cell Calcium 2021, 101, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pobarko, D.; Fameli, N.; Kuo, K.H.; van Breemen, C. Ca2+ signaling in smooth muscle: TRPC6, NCX, and Na+ in nanodomains. Channels 2008, 2, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantero-Recasens, G.; Butnaru, C.M.; Brouwers, N.; Mitrovic, S.; Valverde, M.A.; Malhotra, V. Sodium channel TRPM4 and sodium/calcium exchangers (NCX) cooperate in the control of Ca2+-induced mucin secretion from goblet cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, V.S.; Poburko, D.; Liao, C.-H.; Cole, W.C.; van Breemen, C. Na+ entry via TRPC6 causes Ca2+ entry via NCX reversal in ATP stimulated smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 352, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrikopoulos, P.; Eccles, S.A.; Yaqoob, M.M. Coupling between the TRPC3 ion channel and the NCX1 transporter contributed to VEGF-induced ERK1/2 activation and angiogenesis in human primary endothelial cells. Cell. Signal. 2017, 37, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, A.G.S.; Sage, S.O. TRP-Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger Coupling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 898, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Doleschal, B.; Primessnig, U.; Wolkart, G.; Wolf, S.; Schernthaner, M.; Lichtenegger, M.; Glasnov, T.N.; Kappe, C.O.; Mayer, B.; Antoons, G.; et al. TRPC3 contributes to regulation of cardiac contractility and arrhythmogenesis by dynamic interaction with NCX1. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 106, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. New Insights into the Contribution of Arterial NCX to the Regulation of Myogenic Tone and Blood Pressure. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 961, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Kita, S.; Zhang, J.; Blaustein, M.P.; Arai, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Wakimoto, K.; Komuro, I.; Katsuragi, T. Salt-sensitive hypertension is triggered by Ca2+ entry via Na+/Ca2+ exchanger type-1 in vascular smooth muscle. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulina, M.V.; Zulian, A.; Baryshnikov, S.G.; Linde, C.I.; Karashima, E.; Hamlyn, J.M.; Ferrari, P.; Blaustein, M.P.; Golovina, V.A. Cross Talk between Plasma Membrane Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger-1 and TRPC/Orai-Containing Channels: Key Players in Arterial Hypertension. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 961, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.Y.; Song, H.; Nakai, J.; Ohkura, M.; Kotlikoff, M.I.; Kinsey, S.P.; Golovina, V.A.; Blaustein, M.P. Local subplasma membrane Ca2+ signals detected by a tethered Ca2+ sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13232–13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Zhao, L.; Clapham, D.E. Genome-wide RNAi screen identifies Letm1 as a mitochondrial Ca2+/H+ antiporter. Science. 2009, 326, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.F.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, L.; Clapham, D.; Miller, C. Functional reconstitution of the mitochondrial Ca2+/H+ antiporter Letm1. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 143, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.; Mekis, R.; Mohammed, S.E.M.; Scalise, M.; Wang, W.A.; Galluccio, M.; Pfeiffer, C.; Borovec, T.; Parapatics, K.; Vitko, D.; et al. TMBIM5 is the Ca2+/H+ antiporter of mammalian mitochondria. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patron, M.; Tarasenko, D.; Nolte, H.; Kroczek, L.; Ghosh, M.; Ohba, Y.; Lasarzewski, Y.; Ahmadi, Z.A.; Cabrera-Orefice, A.; Eyiama, A.; et al. Regulation of mitochondrial proteostasis by the proton gradient. EMBO J. 2022, 2022 41, e110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Schlame, M. The mystery of mitochondrial plasticity: TMBIM5 integrates metabolic state and proteostasis. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e111834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, J.; Singh, J.B.; Motiani, R.K. Molecular machinery regulating mitochondrial calcium levels: The nuts and bolts of mitochondrial calcium dynamics. Mitochondrion 2021, 57, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, G.K.; Mishra, J.; Camara, A.K.S.; Kwok, W.M. LETM1: A Single Entity With Diverse Impact on Mitochondrial Metabolism and Cellular Signaling. Front Physiol. 2021, 12, 637852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Matsuoka, S. Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles of Mitochondrial Na+-Ca2+ Exchanger, NCLX, in Hearts. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, T.; Trebak, M. Mitochondrial Ca2+ signaling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 192, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoshevski, T.; Ben-Kasus Nissim, T.; Sekler, I. Recent studies on NCLX in health and diseases. Cell Calcium. 2021, 94, 102345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbi, P.; Castaldo, P.; Minelli, A.; Salucci, S.; Magi, S.; Corcione, E.; Amoroso, S. Mitochondrial localization of Na+/Ca2+ exchangers NCX1-3 in neurons and astrocytes of adult rat brain in situ. Pharmacol Res. 2007, 56, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannaccione, A.; Piccialli, I.; Secondo, A.; Ciccone, R.; Molinaro, P.; Boscia, F.; Annunziato, L. The Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Calcium. 2020, 87, 102190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorziello, A.; Savoia, C.; Sisalli, M.J.; Adornetto, A.; Secondo, A.; Boscia, F.; Esposito, A.; Polishchuk, E.V.; Polishchuk, R.S.; Molinaro, P.; et al. NCX3 regulates mitochondrial Ca2+ handling through the AKAP121-anchored signaling complex and prevents hypoxia-induced neuronal death. J. Cell. Sci. 2013, 126, 5566–5577. [Google Scholar]
- Wood-Kaczmar, A.; Deas, E.; Wood, N.W.; Abramov, A.Y. The role of the mitochondrial NCX in the mechanism of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Adv. Exp. Med Biol. 2013, 961, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisalli, M.J.; Ianniello, G.; Savoia, C.; Cuomo, O.; Annunziato, L.; Scorziello, A. Knocking-out the Siah2 E3 ubiquitin ligase prevents mitochondrial NCX3 degradation, regulates mitochondrial fission and fusion, and restores mitochondrial function in hypoxic neurons. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plain, F.; Congreve, S.D.; Yee, R.S.Z.; Kennedy, J.; Howie, J.; Kuo, C.-W.; Fraser, N.J.; Fuller, W. An amphipathic α-helix directs palmitoylation of the large intracellular loop of the sodium/calcium exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10745–10752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, L.; Howie, J.; Wypijewski, K.; Ashford, M.L.; Hilgemann, D.W.; Fuller, W. Palmitoylation of the Na/Ca exchanger cytoplasmic loop controls its inactivation and internalization during stress signaling. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4532–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, W.; Reilly, L.; Hilgemann, D.W. S-palmitoylation and the regulation of NCX1. Channels 2015, 10, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gök, C.; Main, A.; Gao, X.; Kerekes, Z.; Plain, F.; Kuo, C.-W.; Robertson, A.D.; Fraser, N.J.; Fuller, W. Insights into the molecular basis of the palmitoylation and depalmitoylation of NCX1. Cell Calcium 2021, 97, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, A.; Fuller, W. Protein S-Palmitoylation: Advances and challenges in studying a therapeutically important lipid modification. FEBS J. 2021, 289, 861–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Lipid-induced S-palmitoylation as a Vital Regulator of Cell Signaling and Disease Development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4223–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, A.; Dewangan, N.; Panda, B.; Bhowmick, D.; Tarafdar, P.K. Lipid and Lipidation in Membrane Fusion. J. Membr. Biol. 2022, 255, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassinelli, S.; Viñola-Renart, C.; Benavente-Garcia, A.; Navarro-Pérez, M.; Capera, J.; Felipe, A. Palmitoylation of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, C.; Fuller, W. Regulation of NCX1 by palmitoylation. Cell Calcium 2020, 86, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Dematteis, G.; Tapella, L.; Genazzani, A.A.; Calì, T.; Brini, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Ca2+ handling at the mitochondria-ER contact sites in neurodegeneration. Cell Calcium 2021, 98, 102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csordás, G.; Weaver, D.; Hajnóczky, G. Endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondrial contactology: Structure and signaling functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorrano, L.; De Matteis, M.A.; Emr, S.; Giordano, F.; Hajnóczky, G.; Kornmann, B.; Lackner, L.L.; Levine, T.P.; Pellegrini, L.; Reinisch, K.; et al. Coming together to define membrane contact sites. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, W.A.; Toulmay, A.; Balla, T. The functional universe of membrane contact sites. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.; Elias, C.L.; Le, H.D.; Omelchenko, A.; Hryshko, L.V.; Lytton, J. The molecular determinants of ionic regulatory differences between brain and kidney Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1) isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33957–33962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, C.; Omelchenko, A.; Elias, C.L.; Quednau, B.D.; Philipson, K.D.; Hnatowich, M.; Hryshko, L.V. Ionic Regulatory Properties of Brain and Kidney Splice Variants of the Ncx1 Na+-Ca2+ Exchanger. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999, 114, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hryshko, L. What regulates Na+/Ca2+ exchange? Focus on “Sodium-dependent inactivation of sodium/calcium exchange in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells”. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C869–C871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitsky, D.O.; Nicoll, D.A.; Philipson, K.D. Identification of the high affinity Ca2+-binding domain of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22847–22852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hryshko, L.V.; Matsuoka, S.; Nicoll, D.A.; Weiss, J.N.; Schwarz, E.M.; Benzer, S.; Philipson, K.D. Anomalous regulation of the Drosophila Na+-Ca2+ exchanger by Ca2+. J. Gen. Physiol. 1996, 108, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, M.; Nix, J.; Hryshko, L.V.; Zheng, L. Crystal structure of CBD2 from the Drosophila Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: Diversity of Ca2+ regulation and its alternative splicing modification. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 387, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Le, H.D.; Wang, M.; Yurkov, V.; Omelchenko, A.; Hnatowich, M.; Nix, J.; Hryshko, L.V.; Zheng, L. Crystal structures of progressive Ca2+ binding states of the Ca2+ sensor Ca2+ binding domain 1 (CBD1) from the CALX Na+/Ca2+ exchanger reveal incremental conformational transitions. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 285, 2554–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, J.P.; Condrescu, M. Ionic regulation of the cardiac sodium-calcium exchanger. Channels 2008, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scranton, K.; John, S.; Escobar, A.; Goldhaber, J.I.; Ottolia, M. Modulation of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger by cytoplasmic protons: Molecular mechanisms and physiological implications. Cell Calcium 2019, 87, 102140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, S.; Kim, B.; Olcese, R.; Goldhaber, J.I.; Ottolia, M. Molecular determinants of pH regulation in the cardiac Na+–Ca2+ exchanger. J. Gen. Physiol. 2018, 150, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipson, K.D.; Bersohn, M.M.; Nishimoto, A.Y. Effects of pH on Na+-Ca2+ exchange in canine cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Circ. Res. 1982, 50, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipson, K.D.; Nishimoto, A.Y. Stimulation of Na+-Ca2+ exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles by phospholipase D. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiko, L.A.; Vitale, P.M.; Favaro, D.C.; Hauk, P.; Li, D.-W.; Yuan, J.; Bruschweiler-Li, L.; Salinas, R.K.; Brüschweiler, R. Model for the allosteric regulation of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger NCX. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2016, 84, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, M.F.d.S.; Vitale, P.A.; Abiko, L.A.; Zacharias, M.; Sattler, M.; Oliveira, C.L.; Salinas, R.K. Molecular insights on CALX-CBD12 interdomain dynamics from MD simulations, RDCs, and SAXS. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 3664–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.V.; Rivera, J.D.; Vitale, P.A.; Degenhardt, M.F.; Abiko, L.A.; Oliveira, C.L.; Salinas, R.K. CALX-CBD1 Ca2+-Binding Cooperativity Studied by NMR Spectroscopy and ITC with Bayesian Statistics. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Enzyme dynamics point to stepwise conformational selection in catalysis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Tsai, C.-J.; Haliloğlu, T.; Nussinov, R. Dynamic Allostery: Linkers are not merely flexible. Structure 2011, 19, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiso, D.S. Identifying and Quantitating Conformational Exchange in Membrane Proteins Using Site-Directed Spin Labeling. Accounts Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3102–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, F.; Vallée-Bélisle, A.; Simon, A.J.; Porchetta, A.; Plaxco, K.W. Using Nature’s “Tricks” To Rationally Tune the Binding Properties of Biomolecular Receptors. Accounts Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, M.M.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Pappu, R.V. Versatility from protein disorder. Science 2012, 337, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussinov, R.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Jang, H. AlphaFold, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Allostery. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 6372–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Protein intrinsic disorder and structure-function continuum. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 166, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Raduly, Z.; Miskei, M.; Fuxreiter, M. Fuzzy complexes: Specific binding without complete folding. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589 Pt 19, 2533–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.M. The contribution of intrinsically disordered regions to protein function, cellular complexity, and human disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1185–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buljan, M.; Chalancon, G.; Dunker, A.K.; Bateman, A.; Balaji, S.; Fuxreiter, M.; Babu, M.M. Alternative splicing of intrinsically disordered regions and rewiring of protein interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipson, K.D.; Nishimoto, A.Y. Na+-Ca2+ exchange in inside-out cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 5111–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veseli, E.; Soboloff, J. Palmitoylation: A new mechanism for control of NCX1 function. Cell Calcium 2020, 91, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipson, K.D. Interaction of charged amphiphiles with Na+-Ca2+ exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 13999–14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilgemann, D.W.; Collins, A. Mechanism of cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange current stimulation by MgATP: Possible involvement of aminophospholipid translocase. J. Physiol. 1992, 454, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipson, K.D.; Ward, R. Effects of fatty acids on Na+-Ca2+ exchange and Ca2+ permeability of cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 9666–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, M.J.; Baczko, I.; Searle, G.J.; Webster, N.; Fercho, M.; Jones, L.; Lang, J.; Lytton, J.; Dyck, J.R.; Light, P.E. Metabolic regulation of sodium-calcium exchange by intracellular acyl CoAs. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4605–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Feng, S.; Tong, Q.; Hilgemann, D.W.; Philipson, K.D. Interaction of PIP2 with the XIP region of the cardiac Na/Ca exchanger. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000, 278, C661–C666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaradanakul, A.; Feng, S.; Shen, C.; Lariccia, V.; Lin, M.J.; Yang, J.; Kang, T.M.; Dong, P.; Yin, H.L.; Albanesi, J.P.; et al. Dual control of cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange by PIP2: Electrophysiological analysis of direct and indirect mechanisms. J. Physiol. 2007, 582, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khananshvili, D. How a helix imposes palmitoylation of membrane protein?—What one can learn from NCX. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10753–10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedger, G.; Sansom, M.S. Lipid interaction sites on channels, transporters and receptors: Recent insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 2390–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms24010061
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
