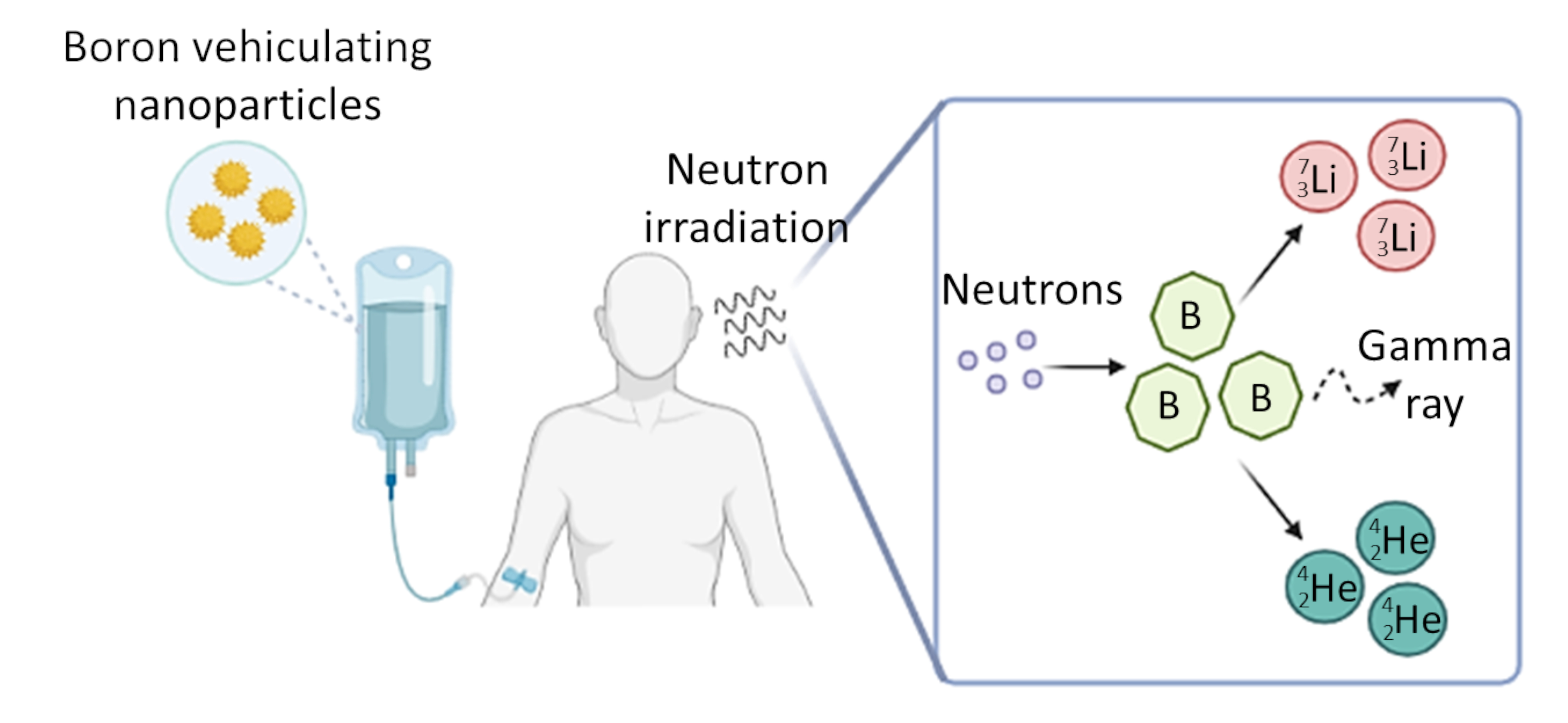
Boron neutron capture therapy is a low-invasive cancer therapy based on the neutron fission process that occurs upon thermal neutron irradiation of 10B-containing compounds; this process causes the release of alpha particles that selectively damage cancer cells. Although several clinical studies involving mercaptoundecahydro-closo-dodecaborate and the boronophenylalanine–fructose complex are currently ongoing, the success of this promising anticancer therapy is hampered by the lack of appropriate drug delivery systems to selectively carry therapeutic concentrations of boron atoms to cancer tissues, allowing prolonged boron retention therein and avoiding the damage of healthy tissues. To achieve these goals, numerous research groups have explored the possibility to formulate nanoparticulate systems for boron delivery. In this review we report the newest developments on boron vehiculating drug delivery systems based on nanoparticles, distinguished on the basis of the type of carrier used, with a specific focus on the formulation aspects.
- nanoparticles
- boron neutron capture therapy
- thermal neutron irradiation
- cancer
Graphical Abstract
1. Introduction
| Ref. | Functionalization for Targeting | B Derivative | Physical Features: Size/Drug Loading/Encapsulation Efficiency | Assays | BNCT Efficacy Assays |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [46] | Na2B10H10; Na2B12H11SH; Na2(n-B20H18); Na2(i-B20H18); K4B20H170H; Na3B20H19 | 43–70 nm/-/2–3% | Ex vivo: EMT6 mammary adenocarcinoma-bearing BALB/c mice | ||
| [47] | K[nido-7-CH3(CH2)15-7,8-C2B9Hll] | 42–114 nm/-/53–80% | Ex vivo: EMT6 mammary adenocarcinoma-bearing BALB/c mice | ||
| [48] | Na3[1-(2′-B10H9)-2-NH3B10H8] + K[nido-7-CH3(CH2)15-7,8-C2B9Hll] | 57–114 nm/-/- | Ex vivo: EMT6 mammary adenocarcinoma-bearing BALB/c mice | ||
| [49][50] | Na3[1-(2′-B10H9)-2-NH3B10H8] + K[nido-7-CH3(CH2)15-7,8-C2B9H11] | 109–134 nm/-/- | Ex vivo: EMT6 mammary adenocarcinoma-bearing BALB/c mice | ||
| [51] | O-closocarboranyl β-lactoside; 1-methyl-o-carboranyl-2-hexylthioporphyrazine | 140–450 nm/-/- | In vitro: DHD/K12/TRb rat colon carcinoma and B16-F10 murine melanoma cells | ||
| [52] | Internalizing-RGD | Doxorubicin conj. with 1-bromomethyl-o-carborane | 150–225 nm/-/- | In vitro: GL261 glioma cancer cells; in vivo: GL261-bearing C57BL/6 mice | In vivo and ex vivo on mice: survival curve and average weight change curve, histopathological analysis |
| [53] | BPA | -/-/- | |||
| [54] | BPA-fructose; BPA-fructose+BPA | 156–195 nm/-/52–82% | Ex vivo: liver metastases-induced BD-IX strain rats | ||
| [55] | BPA-fructose; 2-nitroimidazole derivative B-381 | 134–140 nm/1317–1801 ppb/4.5–5% | In vivo: bilateral D54 glioma-bearing athymic nude mice | ||
| [56] | BSH | 98–109 nm/-/2.5–3.4% | In vivo: male NIH-Swiss mice | ||
| [57] | Anti-human CEA monoclonal antibody | Cs210B12H11SH | -/-/- | In vivo: AsPC-1 human pancreatic carcinoma cells; in vivo: AsPC-1-bearing male BALB/c nu/nu mice | |
| [58] | Cs210B12H11SH | -/-/ - | In vivo: MRK nu/nu-1 human breast cancer cells | ||
| [59] | Transferrin | BSH | 107–123 nm/26–30 µg/µmol lipid/6–8% | In vivo: colon-26 mouse colon carcinoma cells; ex vivo: colon-26-bearing male BALB/c mice | In vivo on mice: survival and tumor growth rate |
| [60] | Rat or mouse anti-EGFR antibody | BSH | 130 nm/-/- | In vivo: U87 ΔEGFR, U87 WT and PAU87 human glioma cells; in vivo: U87 ΔEGFR-bearing BALB/c Slc-nu/nu mice | |
| [61] | Closo-dodecaborate lipids | 95–105 nm/-/- | In vivo: colon-26 mouse colorectal carcinoma cells; in vivo: colon-26-bearing female mice | In vivo on mice: tumor volume | |
| [62] | BSH-encapsulating 10% distearoyl boron lipid | 127 nm/-/- | In vivo: colon-26-bearing female Balb/c mice | In vivo on mice: tumor volume | |
| [63] | BSH sodium and spermidinium salts, Na2[B12H12], Na2[B12H11OH] and [B12H11NH3] sodium and spermidinium salts | 100 nm/2635–13970 ppm/- | In vivo: colon-26 cells mouse colon carcinoma cells; in vivo: colon-26-bearing female mice | ||
| [64] | BSH | 104–115 nm/-/2.5–46% |
| Ref. | Functionalization for Targeting | B Derivative | Physical Features: Size/Drug Loading/Encapsulation Efficiency | Assays | BNCT Efficacy Assays |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elemental Boron NPs | |||||
| [65] | B | 5–15 nm/100%/- | In vivo: T98G human glioma cells | In vivo on cells: cell viability | |
| [66] | B | 25–28 nm/-/- | In vivo: T98G, U87, and U251 human glioma cells | In vivo on cells: cell proliferation ability | |
| [67] | B | 37 nm/-/- | In vivo: HeLa cervical cancer cells | ||
| Iron Oxide NPs | |||||
| [68] | Boron nitride | 10 nm/-/- | In vivo: MCF-7, MCF-10, and HeLa cells | ||
| [69][70] | Carborane borate | 9–28 nm/11%/- | In vivo: mouse embryonic fibroblasts | ||
| [71][72] | Isopropyl-o-carborane | 60 nm/15%/- | In vivo: HeLa, PC-3 (prostate cancer cell), HT-29 (colon cancer cell), BxPC-3 (pancreatic cancer cell), L929 (mouse subcutaneous adipose tissue cells) | ||
| [73] | M-carboranylphosphinate and its acid form | 8–133 nm/-/- | In vivo: A172 glioblastoma and hCMEC/D3 endothelial cells; in vivo: mice | In vivo on cells: proliferation rate | |
| [74] | B | 64 nm/9%/- | In vivo: L929 mouse fibroblasts, 4T1 mammary carcinoma and B16 melanoma cells, human peripheral blood mononuclear cells; ex vivo, in vivo: Balb/c male mice | ||
| [75] | B | 15 nm/77%/- | In vivo: U87 human glioblastoma and SW-620 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells | ||
| [76] | GdBO3 | 20–150 nm/-/- | |||
| [77] | Folic acid | GdBO3 | 20–150 nm/2.5%/- | In vivo: MIA-Pa-Ca-2 human pancreatic cancer, HeLa human cervical carcinoma and A549 human lung carcinoma cells | |
| [78] | 3-(Isopropyl-o-carboranyl) hydrindone | 110 nm/0.077 mg/g/- | In vivo: PC-3 prostate cancer epithelial cells, BxPC3 pancreatic cancer cells, MCF7 breast cancer cells, HepG2 and L929 murine fibroblast cells, and human skin fibroblasts | ||
| [79] | Di(o-carborano-1,2-dimethyl)borate | 386 nm/15.4%/- | In vivo: HepG2 cancer cells and human skin fibroblasts | ||
| [80] | B | 180–280 nm/3.1 × 1017 atoms/mg/- | In vivo: T98G glioblastoma cells | ||
| Gold NPs | |||||
| [81] | 1,2-Dicarba-closo-dodecaborane(12)-9-thiol (9SHOCB) and 1,2-dicarba-closo-dodecaborane(12)-9,12-dithiol (9,12SH-OCB) | 35–74 nm/-/- | In vivo: UMR-106 rat osteogenic sarcoma cells | ||
| [82] | Carborane derivative (NH2NH3)+[7-NH2(CH2)3S-7,8-C2B9H11]− | 9 nm/-/- | In vivo: HeLa, U87cells and L02 cells; in vivo: HeLa-xenografted nude mice | ||
| [83] | 123I-labeled anti-HER2 | Boron cage-SH | 58 nm/-/28–36% | In vivo: N87 human gastric cancer cells; in vivo: male NOD/SCID mouse | |
| [84] | Thiol B cage, BPA, or BPA fructose | 158–395 nm/-/3–35% | In vivo: N87 human gastric cancer male immunodeficient mouse | ||
| [85] | Trastuzumab (pretargeting agent) | Cobalt bis(dicarbollide) anion [3,3′-Co(C2B9H11)2]− | 40 nm/195 µg/mg/- | In vivo: BT-474 breast cancer cells; in vivo: BT-474 breast cancer-bearing immunocompromised NOD/SCID mice | |
| [86] | Undecahydro-closo-dodecaborate (B12H12) | 29 nm/0.307 µg B/mg of gold/- | In vivo: MCF-7 human mammary adenocarcinoma cells; in vivo: U87 glioma-bearing male SCID mice | ||
| Silica NPs | |||||
| [87] | B | 64 nm/42%/- | |||
| [88] | RGD-K | B | 90 nm/-/- | In vivo: ALTS1C1 cells; in vivo: ALTS1C1-bearing mice | In vivo on cells: cell viability; ex vivo and in vivo on mice: tumor growth and mouse survival |
| [89] | Amino-galactoside ligands | O-carborane | -/445–539 µg/mg/- | In vivo: HepG2 liver cancer cells | In vivo on cells: colony formation |
| [90] | Activatable cell penetrating peptide | BSH | 200 nm/1.27%/- | In vivo: ALDH+ cancer stem cells sorted from CH-2879 chondrosarcoma cells; in vivo: BALB/c nu/nu male mice | In vivo on cells: DNA damage and clonogenic survival |
| [91] | cRGD targeting pancreatic tumor sites overexpressing integrin receptors | O-carborane | 136 nm/141.5 mg/g/- | In vivo: PANC-1 (human) and Panc-2 (mouse) cells; in vivo: female C57BL/6 mice | |
| [92] | BPA | 170 nm/2.5%/- | In vivo: OVCAR8 ovarian cancer cells, A549 lung cancer cells, FaDu head and neck cancer cells; animal model: CAM (chorioallantoic membrane) model transfected with human OVCAR8 ovarian cancer cells | ||
| [93] | pH-(low)-insertion peptide | Boric acid | -/190 μg/g/- | In vivo: B16−F10 mouse melanoma and WEHI 164 mouse fibrosarcoma cells; ex vivo, in vivo: WEHI 164 tumor-bearing mice | In vivo on cells: cell viability; ex vivo and in vivo on mice: tumor growth |
| Boron Carbide NPs and Quantum Dots | |||||
| [94][95] | TAT peptide | 284–459 nm/-/- | In vivo: B16 F10 mouse melanoma cells, B16-OVA cells; ex vivo, in vivo: B16-OVA-bearing C57BL/6J mice | ||
| [96] | Transferrin | 279 nm/-/- | In vivo: HeLa human cervical carcinoma and normal rat kidney epithelial cells; ex vivo: tumor-bearing mice | ||
| [97] | Human immunoglobulin G | 80 nm/-/- | In vivo: MC38 murine colon carcinoma and RAW 264.7 murine macrophages | ||
| [98] | 7 nm/-/- | In vivo: embryonic kidney HEK-293 cells, HeLa cervical cancer cells and human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells | |||
| [99] | Pretargeting with trans-cyclooctene modified trastuzumab | 7 nm/3.8%/- | In vivo: human BT-474 breast cancer cells; ex vivo, in vivo: BT-474 xenografted female NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid/J mice | ||
| Polymeric NPs and Micelles | |||||
| [100] | ACUPA (PSMA-targeting) | O-carborane | 150–165 nm/1.86%/- | In vivo: PC3-flu and PC3-pip prostatic adenocarcinoma cells; ex vivo, in vivo: PC3-flu and PC3-pip xenografted male athymic mice | |
| [101][102] | 1,2-bis(4-vinylbenzyl)-closo-carborane | 85 nm/0.26%/3.1% | In vivo: colon-26 cells; ex vivo, in vivo: colon-26 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice | ||
| [103] | Decaborane | 108 nm/9.9%/60.0% | Ex vivo: female Sprague−Dawley rats and U14 tumor-bearing female KM mice | Ex vivo and in vivo on U14 tumor-bearing female KM mice: tumor growth and mouse body weight | |
| [104] | Tumor penetrating RGD peptide | BSH | 25 nm/3.81%/- | In vivo: A549 human lung cancer cells, B16−F10 mouse melanoma cells, C6 rat glioma cells, 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells and HeLa cervical cancer cells; ex vivo: A549 tumor-bearing BALB/c nude mice and B16F10 tumor-bearing mice | |
| [105] | BSH | 36 nm/-/- | In vivo: C26 mouse colorectal carcinoma and human aortic endothelial cells; ex vivo: C26 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice | Ex vivo and in vivo on C26 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice: tumor growth and mouse body weight | |
| [106][107] | O-carborane | 100–150 nm/4.8–5.6%/- | In vivo: B16 melanoma cells; ex vivo: B16 melanoma-bearing mice | ||
| [108] | BPA | 145 nm/-/> 95% | In vivo: U87MG human glioblastoma cells | In vivo on CR-39 detectors | |
| [109] | Tetraboronated porphyrin | 100 nm/-/- | In vivo: mouse melanoma B16-F10 and 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells; ex vivo, in vivo: B16-F10 tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice and 4T1 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice | Ex vivo and in vivo on B16−F10 tumor-bearing mice | |
| [110] | Carborane | 110 nm/11.38%/- | In vivo: 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells; ex vivo, in vivo: 4T1 tumor-bearing mice | In vivo on 4T1 tumor-bearing mice | |
| [111] | Galactose | Carborane | 135 nm/3%/- | In vivo: CAL27 oral adenosquamous carcinoma, U251 glioma and HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells | In vivo on HepG2 cells: apoptosis rate |
| [112] | Carborane-containing arene ruthenium complex | 19 nm/-/- | In vivo: A2780 and A2780 cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells | In vivo on A2780 and A2780cisR cells: cell viability | |
| [113] | Dodecaborate | 13–15 nm/-/- | In vivo: U87 human glioblastoma, HeLa cervical cancer and Jurkat cells | ||
| Other NPs | |||||
| [114] | Folic acid | Boron oxide | 20–50 nm/8% mol B/NP/- | In vivo: HeLa cervical cancer cells | In vivo on HeLa cells: cell viability |
| [115] | Folic acid | 255 nm/9.8%/- | In vivo: erythrocytes and platelets from human plasma specimens, MO7e human megakaryoblastic leukemia cells, DHD colon carcinoma cells, UMR osteosarcoma cells | ||
| [116] | 5 nm/30% of boron atoms/NP/- | In vivo: on ALTS1C1 mouse astrocytes | In vivo on cells: cell viability | ||
| [117] | Phenyl-10B-boronic acid | 53–67 nm/2%/- | In vivo: CT26 murine colon tumor cells; ex vivo, in vivo: CT26 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice | In vivo on mice: tumor growth and body weight | |
| Exosomes and Biomimetic Vesicles | |||||
| [118] | Boron-containing carbon dots | 97 nm/17.90%/85.24% | In vivo: MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer, U251 glioma and HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells; ex vivo, in vivo: BALB/c nude mice, U-87 glioma-bearing mice | In vivo on mice: tumor growth and body weight | |
| [119] | 146 nm/-/- | In vivo: HEK 293 human embryonic kidney and HeLa cervical cancer cells; ex vivo: female Kunming mice | |||
2. Critical and Positive Aspects of the Nanosized Technologies
3. Conclusions
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cells11244029
References
- Barth, R.F.; Mi, P.; Yang, W.L. Boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy of cancer. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 1–15.
- Hu, K.; Yang, Z.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Xie, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Josephson, L.; Liang, S.H.; Zhang, M.R. Boron agents for neutron capture therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 405, 213139.
- Barth, R.F.; Coderre, J.A.; Vicente, M.G.H.; Blue, T.E. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: Current status and future prospects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3987–4002.
- Sumitani, S.; Nagasaki, Y. Boron neutron capture therapy assisted by boron-conjugated nanoparticles. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 522–530.
- Barth, R.F.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Liu, T. A realistic appraisal of boron neutron capture therapy as a cancer treatment modality. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 1–7.
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakai, K.; Matsumura, A. Boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2008, 262, 143–152.
- Barth, R.F.; Vicente, M.G.H.; Harling, O.K.; Kiger, W.S.; Riley, K.J.; Binns, P.J.; Wagner, F.M.; Suzuki, M.; Aihara, T.; Kato, I.; et al. Current status of boron neutron capture therapy of high grade gliomas and recurrent head and neck cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 146.
- Miyatake, S.I.; Kawabata, S.; Hiramatsu, R.; Kuroiwa, T.; Suzuki, M.; Kondo, N.; Ono, K. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for Malignant Brain Tumors. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 2016, 56, 361–371.
- Suzuki, M. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): A unique role in radiotherapy with a view to entering the accelerator-based BNCT era. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 43–50.
- Rossini, A.E.; Dagrosa, M.A.; Portu, A.; Saint Martin, G.; Thorp, S.; Casal, M.; Navarro, A.; Juvenal, G.J.; Pisarev, M.A. Assessment of biological effectiveness of boron neutron capture therapy in primary and metastatic melanoma cell lines. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 81–89.
- Hiratsuka, J.; Kamitani, N.; Tanaka, R.; Yoden, E.; Tokiya, R.; Suzuki, M.; Barth, R.F.; Ono, K. Boron neutron capture therapy for vulvar melanoma and genital extramammary Paget’s disease with curative responses. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 1–10.
- Matsuya, Y.; Fukunaga, H.; Omura, M.; Date, H. A Model for Estimating Dose-Rate Effects on Cell-Killing of Human Melanoma after Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Cells 2020, 9, 1117.
- Farr, L.E.; Sweet, W.H.; Locksley, H.B.; Robertson, J.S. Neutron capture therapy of gliomas using boron. Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium. Ther. Nucl. Med. 1954, 71, 279–293.
- Miller, H.C.; Miller, N.E.; Muetterties, E.L. Synthesis of Polyhedral Boranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 3885–3886.
- Hatanaka, H.; Nakagawa, Y. Clinical results of long-surviving brain-tumor patients who underwent boron neutron capture therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 28, 1061–1066.
- Wittig, A.; Hideghety, K.; Paquis, P.; Heimans, J.; Vos, M.; Goetz, C.; Haselsberger, K.; Grochulla, F.; Moss, R.; Morrissey, J.; et al. Current clinical results of the EORTC-Study 11961. In Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy; 10th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy; University Hospital of Essen: Esse, Germany, 2002; pp. 1117–1122.
- Vos, M.J.; Turowski, B.; Zanella, F.E.; Paquis, P.; Siefert, A.; Hideghety, K.; Haselsberger, K.; Grochulla, F.; Postma, T.J.; Wittig, A.; et al. Radiologic findings in patients treated with boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma multiforme within eortc trial 11961. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 61, 392–399.
- Burian, J.; Marek, M.; Rataj, J.; Flibor, S.; Rejchrt, J.; Vicrerbl, L.; Sus, F.; Honova, H.; Petruzelka, L.; Prokes, K.; et al. Report on the first patient group of the phase I BNCT trial at the LVR-15 reactor. Dev. Neurosci. 2004, 1259, 27–32.
- Yamamoto, T.; Matsumura, A.; Nakai, K.; Shibata, Y.; Endo, K.; Sakurai, F.; Kishi, T.; Kumada, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Torii, Y. Current clinical results of the Tsukuba BNCT trial. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 1089–1093.
- Miyatake, S.I.; Tamura, Y.; Kawabata, S.; Iida, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Ono, K. Boron neutron capture therapy for malignant tumors related to meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 82–90.
- Miyatake, S.I.; Kawabata, S.; Kajimoto, Y.; Aoki, A.H.; Yokoyama, K.; Yamada, M.; Kuroiwa, T.; Tsuji, M.; Imahori, Y.; Kirihata, M.; et al. Modified boron neutron capture therapy for malignant gliomas performed using epithermal neutron and two boron compounds with different accumulation mechanisms: An efficacy study based on findings on neuroimages. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 103, 1000–1009.
- Wittig, A.; Collette, L.; Appelman, K.; Buhrmann, S.; Jackel, M.C.; Jockel, K.H.; Schmid, K.W.; Ortmann, U.; Moss, R.; Sauerwein, W.A.G. EORTC trial 11001: Distribution of two 10B-compounds in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck, a translational research/phase 1 trial. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1653–1665.
- Wittig, A.; Malago, M.; Collette, L.; Huiskamp, R.; Buhrmann, S.; Nievaart, V.; Kaiser, G.M.; Jockel, K.H.; Schmid, K.W.; Ortmann, U.; et al. Uptake of two B-10-compounds in liver metastases of colorectal adenocarcinoma for extracorporeal irradiation with boron neutron capture therapy (EORTC trial 11001). Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1164–1171.
- Yanagie, H.; Higashi, S.; Seguchi, K.; Ikushima, I.; Fujihara, M.; Nonaka, Y.; Oyama, K.; Maruyama, S.; Hatae, R.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Pilot clinical study of boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent hepatic cancer involving the intra-arterial injection of a (BSH)-B-10-containing WOW emulsion. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 88, 32–37.
- Mishima, Y.; Honda, C.; Ichihashi, M.; Obara, H.; Hiratsuka, J.; Fukuda, H.; Karashima, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Kanda, K.; Yoshino, K. Treatment of malignant melanoma by single thermal neutron capture therapy with melanoma-seeking B-10-compound. Lancet 1989, 2, 388–389.
- Coderre, J.A.; Glass, J.D.; Fairchild, R.G.; Micca, P.L.; Fand, I.; Joel, D.D. Selective delivery of boron by the melanin precursor analog para-borophenylalanine to tumors other than melanoma. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 138–141.
- Yoshino, K.; Suzuki, A.; Mori, Y.; Kakihana, H.; Honda, C.; Mishima, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Kanda, K. Improvement of solubility of para-borophenylalanine by complex formation with monosaccharides. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 1989, 165, 127–129.
- Capala, J.; Stenstam, B.H.; Skold, K.S.; af Rosenschold, P.M.; Giusti, V.; Persson, C.; Wallin, E.; Brun, A.; Franzen, L.; Carlsson, J.O.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: Clinical studies in Sweden. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2003, 62, 135–144.
- Henriksson, R.; Capala, J.; Michanek, A.; Lindahl, S.A.; Satford, L.G.; Franzen, L.; Blomquist, E.; Westlin, J.E.; Bergenheim, A.T. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for glioblastoma multiforme: A phase II study evaluating a prolonged high-dose of boronophenylalanine (BPA). Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 88, 183–191.
- Skold, K.; H-Stenstam, B.; Diaz, A.Z.; Giusti, V.; Pellettieri, L.; Hopewell, J.W. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: Advantage of prolonged infusion of BPA-f. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2010, 122, 58–62.
- Kankaanranta, L.; Seppala, T.; Koivunoro, H.; Valimaki, P.; Beule, A.; Collan, J.; Kortesniemi, M.; Uusi-Simola, J.; Kotiluoto, P.; Auterinen, I.; et al. L-boronophenilalanine-mediated boron neutron capture therapy for malignant glioma progressing after external beam radiation therapy: A phase I study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 369–376.
- Miyatake, S.I.; Kawabata, S.; Yokoyama, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Michiue, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Kumada, H.; Suzuki, M.; Maruhashi, A.; Kirihata, M.; et al. Survival benefit of Boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent malignant gliomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2009, 91, 199–206.
- Miyatake, S.I.; Kawabata, S.; Nonoguchi, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Matsui, H.; Ono, K. Pseudoprogression in boron neutron capture therapy for malignant gliomas and meningiomas. Neuro-Oncology 2009, 11, 430–436.
- Joensuu, H.; Kankaanranta, L.; Seppala, T.; Auterinen, I.; Kallio, M.; Kulvik, M.; Laakso, J.; Vahatalo, J.; Kortesniemi, M.; Kotiluoto, P.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy of brain tumors: Clinical trials at the Finnish facility using boronophenylalanine. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2003, 62, 123–134.
- Kankaanranta, L.; Seppala, T.; Koivunoro, H.; Saarilahti, K.; Atula, T.; Collan, J.; Salli, E.; Kortesniemi, M.; Uusi-Simola, J.; Makitle, A.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy in the treatment of locally recurred head and neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 69, 475–482.
- Fuwa, N.; Suzuki, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Nagata, K.; Kinashi, Y.; Masunaga, S.; Maruhashi, A.; Imahori, Y.; Kodaira, T.; Tachibana, H.; et al. Treatment results of boron neutron capture therapy using intraarterial administration of boron compounds for recurrent head and neck cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2008, 81, 749–752.
- Wang, L.W.; Wang, S.J.; Chu, P.Y.; Ho, C.Y.; Jiang, S.H.; Liu, Y.W.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, H.M.; Peir, J.J.; Chou, F.I.; et al. BNCT for locally recurrent head and neck cancer: Preliminary clinical experience from a phase I/II trial at Tsing Hua Open-Pool Reactor. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1803–1806.
- Wang, L.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Ho, C.Y.; Liu, Y.W.H.; Chou, F.I.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, H.M.; Peir, J.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Chang, C.W.; et al. Fractionated Boron Neutron Capture Therapy in Locally Recurrent Head and Neck Cancer: A Prospective Phase I/II Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 396–403.
- Mishima, Y.; Ichihashi, M.; Hatta, S.; Honda, C.; Yamamura, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Obara, H.; Shirakawa, J.; Hiratsuka, J.; Taniyama, K.; et al. 1st human clinical trial of melanoma neutron capture—Diagnosis and therapy. Strahlenther. Und Onkol. 1989, 165, 251–254.
- Menendez, P.R.; Roth, B.M.C.; Pereira, M.D.; Casal, M.R.; Gonzalez, S.J.; Feld, D.B.; Cruz, G.A.S.; Kessler, J.; Longhino, J.; Blaumann, H.; et al. BNCT for skin melanoma in extremities: Updated Argentine clinical results. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S50–S53.
- Nuez-Martinez, M.; Pedrosa, L.; Martinez-Rovira, I.; Yousef, I.; Diao, D.; Teixidor, F.; Stanzani, E.; Martinez-Soler, F.; Tortosa, A.; Sierra, A.; et al. Synchrotron-Based Fourier-Transform Infrared Micro-Spectroscopy (SR-FTIRM) Fingerprint of the Small Anionic Molecule Cobaltabis(dicarbollide) Uptake in Glioma Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9937.
- Florio, T.; Barbieri, F. The status of the art of human malignant glioma management: The promising role of targeting tumor-initiating cells. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 1103–1110.
- Moss, R.L. Critical review, with an optimistic outlook, on Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 88, 2–11.
- Luderer, M.J.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, A.K. Advancements in Tumor Targeting Strategies for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 2824–2836.
- Dymova, M.A.; Taskaev, S.Y.; Richter, V.A.; Kuligina, E.V. Boron neutron capture therapy: Current status and future perspectives. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 406–421.
- Shelly, K.; Feakes, D.A.; Hawthorne, M.F.; Schmidt, P.G.; Krisch, T.A.; Bauer, W.F. Model studies directed toward the boron neutron capture therapy of cancer—Boron delivery to murine tumors with liposomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9039–9043.
- Feakes, D.A.; Shelly, K.; Hawthorne, M.F. Selective boron delivery to murine tumors by lipophilic species incorporated in the membranes of unilamellar liposomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1367–1370.
- Hawthorne, M.F.; Shelly, K. Liposomes as drug delivery vehicles for boron agents. J. Neuro-Oncol. 1997, 33, 53–58.
- Kueffer, P.J.; Maitz, C.A.; Khan, A.A.; Schuster, S.A.; Shlyakhtina, N.I.; Jalisatgi, S.S.; Brockman, J.D.; Nigg, D.W.; Hawthorne, M.F. Boron neutron capture therapy demonstrated in mice bearing EMT6 tumors following selective delivery of boron by rationally designed liposomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6512–6517.
- Khan, A.A.; Maitz, C.; Cai, Q.Y.; Hawthorne, F. BNCT induced immunomodulatory effects contribute to mammary tumor inhibition. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222022.
- Altieri, S.; Balzi, M.; Bortolussi, S.; Bruschi, P.; Ciani, L.; Clerici, A.M.; Faraoni, P.; Ferrari, C.; Gadan, M.A.; Panza, L.; et al. Carborane Derivatives Loaded into Liposomes as Efficient Delivery Systems for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7829–7835.
- Chen, J.J.; Dai, Q.; Yang, Q.Y.; Bao, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, H.Q.; Wu, L.J.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, Z.C.; Lu, Y.Y.; et al. Therapeutic nucleus-access BNCT drug combined CD47-targeting gene editing in glioblastoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 102.
- Martini, S.; Ristori, S.; Pucci, A.; Bonechi, C.; Becciolinic, A.; Martini, G.; Rossi, C. Boronphenylalanine insertion in cationic liposomes for boron neutron capture therapy. Biophys. Chem. 2004, 111, 27–34.
- Pavanetto, F.; Perugini, P.; Genta, I.; Minoia, C.; Ronchi, A.; Prati, U.; Roveda, L.; Nano, R. Boron-loaded liposomes in the treatment of hepatic metastases: Preliminary investigation by autoradiography analysis. Drug Deliv. 2000, 7, 97–103.
- Luderer, M.J.; Muz, B.; Alhallak, K.; Sun, J.; Wasden, K.; Guenthner, N.; de la Puente, P.; Federico, C.; Azab, A.K. Thermal Sensitive Liposomes Improve Delivery of Boronated Agents for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 144.
- Mehta, S.C.; Lai, J.C.K.; Lu, D.R. Liposomal formulations containing sodium mercaptoundecahydrododecaborate (BSH) for boron neutron capture therapy. J. Microencapsul. 1996, 13, 269–279.
- Yanagië, H.; Tomita, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Fujii, Y.; Nonaka, Y.; Saegusa, Y.; Hasumi, K.; Eriguchi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Ono, K. Inhibition of human pancreatic cancer growth in nude mice by boron neutron capture therapy. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 660–665.
- Yanagie, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Takeda, Y.; Yoshizaki, I.; Nonaka, Y.; Naka, S.; Nojiri, A.; Shinnkawa, H.; Furuya, Y.; Niwa, H.; et al. Inhibition of growth of human breast cancer cells in culture by neutron capture using liposomes containing B-10. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 93–99.
- Maruyama, K.; Ishida, O.; Kasaoka, S.; Takizawa, T.; Utoguchi, N.; Shinohara, A.; Chiba, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Eriguchi, M.; Yanagie, H. Intracellular targeting of sodium mercaptoundecahydrododecaborate (BSH) to solid tumors by transferrin-PEG liposomes, for boron neutron-capture therapy (BNCT). J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 195–207.
- Feng, B.; Tomizawa, K.; Michiue, H.; Miyatake, S.; Han, X.J.; Fujimura, A.; Seno, M.; Kirihata, M.; Matsui, H. Delivery of sodium borocaptate to glioma cells using immunoliposome conjugated with anti-EGFR antibodies by ZZ-His. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1746–1755.
- Ueno, M.; Ban, H.S.; Nakai, K.; Inomata, R.; Kaneda, Y.; Matsumura, A.; Nakamura, H. Dodecaborate lipid liposomes as new vehicles for boron delivery system of neutron capture therapy. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3059–3065.
- Koganei, H.; Ueno, M.; Tachikawa, S.; Tasaki, L.; Ban, H.S.; Suzuki, M.; Shiraishi, K.; Kawano, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Maitani, Y.; et al. Development of High Boron Content Liposomes and Their Promising Antitumor Effect for Neutron Capture Therapy of Cancers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2013, 24, 124–132.
- Tachikawa, S.; Miyoshi, T.; Koganei, H.; El-Zaria, M.E.; Vinas, C.; Suzuki, M.; Ono, K.; Nakamura, H. Spermidinium closo-dodecaborate-encapsulating liposomes as efficient boron delivery vehicles for neutron capture therapy. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12325–12328.
- Shirakawa, M.; Nakai, K.; Sato, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Harada, M.; Ishihara, K.; Yoshida, F.; Matsumura, A.; Tomida, H. Optimization of preparation methods for high loading content and high encapsulation efficiency of BSH into liposomes. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2021, 169, 109260.
- Uspenskii, S.A.; Khaptakhanova, P.A.; Zaboronok, A.A.; Kurkin, T.S.; Volkova, O.Y.; Mechetina, L.V.; Taranin, A.V.; Kanygin, V.V.; Akira, M.; Taskaev, S.Y. Elemental Boron Nanoparticles: Production by Ultrasonication in Aqueous Medium and Application in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Dokl. Chem. 2020, 491, 45–48.
- Zaboronok, A.; Khaptakhanova, P.; Uspenskii, S.; Bekarevich, R.; Mechetina, L.; Volkova, O.; Mathis, B.J.; Kanygin, V.; Ishikawa, E.; Kasatova, A.; et al. Polymer-Stabilized Elemental Boron Nanoparticles for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Initial Irradiation Experiments. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 761.
- Pastukhov, A.I.; Belyaev, I.B.; Bulmahn, J.C.; Zelepukin, I.V.; Popov, A.A.; Zavestovskaya, I.N.; Klimentov, S.M.; Deyev, S.M.; Prasad, P.N.; Kabashin, A.V. Laser-ablative aqueous synthesis and characterization of elemental boron nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9129.
- Wang, W.J.; Lin, J.; Xing, C.F.; Chai, R.; Abbas, S.; Song, T.; Tang, C.C.; Huang, Y. Fe3O4 nanoparticle-coated boron nitride nanospheres: Synthesis, magnetic property and biocompatibility study. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6371–6376.
- Tishkevich, D.I.; Korolkov, I.V.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Anisovich, M.; Vinnik, D.A.; Ermekova, A.E.; Vorobjova, A.I.; Shumskaya, E.E.; Zubar, T.I.; Trukhanov, S.V.; et al. Immobilization of boron-rich compound on Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Stability and cytotoxicity. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 797, 573–581.
- Dukenbayev, K.; Korolkov, I.V.; Tishkevich, D.I.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Trukhanov, S.V.; Gorin, Y.G.; Shumskaya, E.E.; Kaniukov, E.Y.; Vinnik, D.A.; Zdorovets, M.V.; et al. Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Complex Targeted Delivery and Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 494.
- Korolkov, I.V.; Ludzik, K.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Fadeev, M.S.; Shumskaya, A.E.; Gorin, Y.G.; Marciniak, B.; Jazdzewska, M.; Chudoba, D.; Kontek, R.; et al. Carboranes immobilization on Fe3O4 nanocomposites for targeted delivery. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101247.
- Korolkov, I.V.; Ludzik, K.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Fadeev, M.S.; Shumskaya, A.E.; Gorin, Y.G.; Jazdzewska, M.; Anisovich, M.; Rusakov, V.S.; Zdorovets, M.V. Immobilization of carboranes on Fe3O4-polymer nanocomposites for potential application in boron neutron cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 601, 125035.
- Oleshkevich, E.; Morancho, A.; Saha, A.; Galenkamp, K.M.O.; Grayston, A.; Crich, S.G.; Alberti, D.; Protti, N.; Comella, J.X.; Teixidor, F.; et al. Combining magnetic nanoparticles and icosahedral boron clusters in biocompatible inorganic nanohybrids for cancer therapy. Nanomed.-Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 20, 101986.
- Torresan, V.; Guadagnini, A.; Badocco, D.; Pastore, P.; Medina, G.A.M.; van Raap, M.B.F.; Postuma, I.; Bortolussi, S.; Bekic, M.; Colic, M.; et al. Biocompatible Iron-Boron Nanoparticles Designed for Neutron Capture Therapy Guided by Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001632.
- Aiyyzhy, K.O.; Barmina, E.V.; Zavestovskaya, I.N.; Kasatova, A.I.; Petrunya, D.S.; Uvarov, O.V.; Saraykin, V.V.; Zhilnikova, M.I.; Voronov, V.V.; Shafeev, G.A.; et al. Laser ablation of Fe2B target enriched in B-10 content for boron neutron capture therapy. Laser Phys. Lett. 2022, 19, 066002.
- Icten, O.; Kose, D.A.; Zumreoglu-Karan, B. Fabrication and characterization of magnetite-gadolinium borate nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 726, 437–444.
- Icten, O.; Kose, D.A.; Matissek, S.J.; Misurelli, J.A.; Elsawa, S.F.; Hosmane, N.S.; Zumreoglu-Karan, B. Gadolinium borate and iron oxide bioconjugates: Nanocomposites of next generation with multifunctional applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 92, 317–328.
- Korolkov, I.V.; Zibert, A.V.; Lissovskaya, L.I.; Ludzik, K.; Anisovich, M.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Shumskaya, A.E.; Vasilyeva, M.; Shlimas, D.I.; Marciniak, B.; et al. Boron and Gadolinium Loaded Fe3O4 Nanocarriers for Potential Application in Neutron Capture Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8687.
- Korolkov, I.V.; Zibert, A.V.; Lisovskaya, L.I.; Ludzik, K.; Anisovich, M.V.; Vasilyeva, M.M.; Shumskaya, A.E.; Usseinov, A.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Zdorovets, M.V. Simultaneous Immobilization of Gadolinium Ions and Di(o-carborano-1,2-dimethyl)borate on Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Bull. Univ. Karaganda-Chem. 2022, 106, 87–94.
- Icten, O.; Tuncdemir, B.E.; Mergen, H. Design and Development of Gold-Loaded and Boron-Attached Multicore Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles as a Potential Agent in Biomedical Applications. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20195–20203.
- Ciani, L.; Bortolussi, S.; Postuma, I.; Cansolino, L.; Ferrari, C.; Panza, L.; Altieri, S.; Ristori, S. Rational design of gold nanoparticles functionalized with carboranes for application in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 458, 340–346.
- Wang, J.L.; Chen, L.F.; Ye, J.; Li, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.; Yan, H.; Stogniy, M.Y.; Sivaev, I.B.; Bregadze, V.I.; Wang, X.M. Carborane Derivative Conjugated with Gold Nanoclusters for Targeted Cancer Cell Imaging. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1466–1472.
- Wu, C.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Chang, W.Y.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, H.S.; Hsu, H.J.; Yang, A.S.; Hsu, M.H.; Kuo, W.Y. Development of theranostic active-targeting boron-containing gold nanoparticles for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110387.
- Wu, C.Y.; Hsieh, H.H.; Chang, T.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Wu, C.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Lin, M.C.; Peng, S.L. Development of MRI-Detectable Boron-Containing Gold Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Biodegradable Polymeric Matrix for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8050.
- Feiner, I.V.J.; Pulagam, K.R.; Gomez-Vallejo, V.; Zamacola, K.; Baz, Z.; Caffarel, M.M.; Lawrie, C.H.; Ruiz-de-Angulo, A.; Carril, M.; Llop, J. Therapeutic Pretargeting with Gold Nanoparticles as Drug Candidates for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37, 2000200.
- Popova, T.V.; Pyshnaya, I.A.; Zakharova, O.D.; Akulov, A.E.; Shevelev, O.B.; Poletaeva, J.; Zavjalov, E.L.; Silnikov, V.N.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Godovikova, T.S. Rational Design of Albumin Theranostic Conjugates for Gold Nanoparticles Anticancer Drugs: Where the Seed Meets the Soil? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 74.
- Walton, N.I.; Gao, Z.; Eygeris, Y.; Ghandehari, H.; Zharov, I. Synthesis of water dispersible boron core silica shell (2) nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 112.
- Kuthala, N.; Vankayala, R.; Li, Y.N.; Chiang, C.S.; Hwang, K.C. Engineering Novel Targeted Boron-10-Enriched Theranostic Nanomedicine to Combat against Murine Brain Tumors via MR Imaging-Guided Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700850.
- Lai, C.H.; Lai, N.C.; Chuang, Y.J.; Chou, F.I.; Yang, C.M.; Lin, C.C. Trivalent galactosyl-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a target-specific delivery system for boron neutron capture therapy. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9412–9418.
- Vares, G.; Jallet, V.; Matsumoto, Y.; Rentier, C.; Takayama, K.; Sasaki, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Kumada, H.; Sugawara, H. Functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for innovative boron-neutron capture therapy of resistant cancers. Nanomed.-Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 27, 102195.
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Qiu, X.Y.; Li, N.; Zhu, Y.J.; Yan, L.J.; Li, W.P.; Huang, X.J.; Liang, K.Y.; et al. Carborane based mesoporous nanoparticles as a potential agent for BNCT. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 2771–2776.
- Tamanoi, F.; Chinnathambi, S.; Laird, M.; Komatsu, A.; Birault, A.; Takata, T.; Doan, T.L.H.; Mai, N.X.D.; Raitano, A.; Morrison, K.; et al. Construction of Boronophenylalanine-Loaded Biodegradable Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles for BNCT Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2251.
- Sharma, K.S.; Raju, M.S.; Phapale, S.; Valvi, S.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Goswami, D.; Ray, D.; De, A.B.J.; Phadnis, P.P.; Aswal, V.K.; et al. Multimodal Applications of Zinc Gallate-Based Persistent Luminescent Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment: Tumor Margining, Diagnosis, and Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3134–3145.
- Mortensen, M.W.; Sorensen, P.G.; Bjorkdahl, O.; Jensen, M.R.; Gundersen, H.J.G.; Bjornholm, T. Preparation and characterization of Boron carbide nanoparticles for use as a novel agent in T cell-guided boron neutron capture therapy. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2006, 64, 315–324.
- Petersen, M.S.; Petersen, C.C.; Agger, R.; Sutmuller, M.; Jensen, M.R.; Sorensen, P.G.; Mortensen, M.W.; Hansen, T.; Bjornholm, T.; Gundersen, H.J.; et al. Boron nanoparticles inhibit turnour growth by boron neutron capture therapy in the murine B16-OVA model. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 571–576.
- Tsuji, T.; Yoshitomi, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Koshizaki, N.; Suzuki, M.; Usukura, J. A method to selectively internalise submicrometer boron carbide particles into cancer cells using surface transferrin conjugation for developing a new boron neutron capture therapy agent. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2020, 15, 1–11.
- Kozien, D.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Rapak, A.; Szczygiel, A.; Anger-Gora, N.; Boratynski, J.; Pajtasz-Piasecka, E.; Bucko, M.M.; Pedzich, Z. Boron-Rich Boron Carbide Nanoparticles as a Carrier in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Their Influence on Tumor and Immune Phagocytic Cells. Materials 2021, 14, 3010.
- Singh, P.; Kaur, M.; Singh, K.; Meena, R.; Kumar, M.; Yun, J.H.; Thakur, A.; Nakagawa, F.; Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Fluorescent boron carbide quantum dots synthesized with a low-temperature solvothermal approach for boron neutron capture therapy. Phys. E-Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 132, 114766.
- Feiner, I.V.J.; Pulagam, K.R.; Uribe, K.B.; Passannante, R.; Simo, C.; Zamacola, K.; Gomez-Vallejo, V.; Herrero-Alvarez, N.; Cossio, U.; Baz, Z.; et al. Pre-targeting with ultra-small nanoparticles: Boron carbon dots as drug candidates for boron neutron capture therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 410–420.
- Meher, N.; Seo, K.; Wang, S.; Bidkar, A.P.; Fogarty, M.; Dhrona, S.; Huang, X.; Tang, R.; Blaha, C.; Evans, M.J.; et al. Synthesis and Preliminary Biological Assessment of Carborane-Loaded Theranostic Nanoparticles to Target Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 54739–54752.
- Sumitani, S.; Oishi, M.; Nagasaki, Y. Carborane confined nanoparticles for boron neutron capture therapy: Improved stability, blood circulation time and tumor accumulation. React. Funct. Polym. 2011, 71, 684–693.
- Sumitani, S.; Oishi, M.; Yaguchi, T.; Murotani, H.; Horiguchi, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ono, K.; Yanagie, H.; Nagasaki, Y. Pharmacokinetics of core-polymerized, boron-conjugated micelles designed for boron neutron capture therapy for cancer. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3568–3577.
- Xiong, H.J.; Zhou, D.F.; Qi, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xie, Z.G.; Chen, X.S.; Jing, X.B.; Meng, F.B.; Huang, Y.B. Doxorubicin-Loaded Carborane-Conjugated Polymeric Nanoparticles as Delivery System for Combination Cancer Therapy. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3980–3988.
- Chen, J.J.; Yang, Q.Y.; Liu, M.C.; Lin, M.T.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, Z.T.; Zhong, X.C.; Guo, N.N.; Lu, Y.Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Remarkable Boron Delivery Of iRGD-Modified Polymeric Nanoparticles for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8161–8177.
- Gao, Z.Y.; Horiguchi, Y.; Nakai, K.; Matsumura, A.; Suzuki, M.; Ono, K.; Nagasaki, Y. Use of boron cluster-containing redox nanoparticles with ROS scavenging ability in boron neutron capture therapy to achieve high therapeutic efficiency and low adverse effects. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 201–212.
- Takeuchi, I.; Nomura, K.; Makino, K. Hydrophobic boron compound-loaded poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for boron neutron capture therapy. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 360–365.
- Takeuchi, I.; Anyama, M.; Makino, K. Chitosan Coating Effect on Cellular Uptake of PLGA Nanoparticles for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 361–368.
- Soleimanbeigi, M.; Dousti, F.; Hassanzadeh, F.; Mirian, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Kasesaz, Y.; Rostami, M. Boron phenyl alanine targeted chitosan-PNIPAAm core-shell thermo-responsive nanoparticles: Boosting drug delivery to glioblastoma in BNCT. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 1607–1623.
- Shi, Y.X.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Duan, D.B.; Zhang, Z.C.; Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.B. Tracing Boron with Fluorescence and Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Boronated Porphyrin Nanocomplex for Imaging-Guided Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43387–43395.
- Shi, Y.X.; Fu, Q.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.B. Covalent Organic Polymer as a Carborane Carrier for Imaging-Facilitated Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55564–55573.
- Zhang, T.F.; Li, G.; Li, S.R.; Wang, Z.; He, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, J.L.; Bai, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.P.; et al. Asialoglycoprotein receptor targeted micelles containing carborane clusters for effective boron neutron capture therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2019, 182, 110397.
- Romero-Canelon, I.; Phoenix, B.; Pitto-Barry, A.; Tran, J.; Soldevila-Barreda, J.J.; Kirby, N.; Green, S.; Sadler, P.J.; Barry, N.P.E. Arene ruthenium dithiolato-carborane complexes for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 796, 17–25.
- Li, J.W.; Janouskov, O.; Fernandez-Alvarez, R.; Meskov, S.; Tosner, Z.; Kereche, S.; Uchman, M.; Matejcek, P. Designed Boron-Rich Polymeric Nanoparticles Based on Nano-ion Pairing for Boron Delivery. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14283–14289.
- Hwang, K.C.; Lai, P.D.; Chiang, C.S.; Wang, P.J.; Yuan, C.J. Neutron capture nuclei-containing carbon nanoparticles for destruction of cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8419–8425.
- Achilli, C.; Grandi, S.; Ciana, A.; Guidetti, G.F.; Malara, A.; Abbonante, V.; Cansolino, L.; Tomasi, C.; Balduini, A.; Fagnoni, M.; et al. Biocompatibility of functionalized boron phosphate (BPO4) nanoparticles for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) application. Nanomed.-Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 589–597.
- Chiang, C.W.; Chien, Y.C.; Yu, W.J.; Ho, C.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, T.W.; Chiang, C.S.; Keng, P.Y. Polymer-Coated Nanoparticles for Therapeutic and Diagnostic Non-B-10 Enriched Polymer-Coated Boron Carbon Oxynitride (BCNO) Nanoparticles as Potent BNCT Drug. Nanomaterials 2021, 1, 2936.
- Nishikawa, M.; Kang, H.G.; Zou, Y.J.; Takeuchi, H.; Matsuno, N.; Suzuki, M.; Komatsu, N. Conjugation of Phenylboronic Acid Moiety through Multistep Organic Transformations on Nanodiamond Surface for an Anticancer Nanodrug for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2021, 94, 2302–2312.
- Li, J.; Kong, J.L.; Ma, S.H.; Li, J.C.; Mao, M.R.; Chen, K.; Chen, Z.T.; Zhang, J.X.; Chang, Y.A.; Yuan, H.; et al. Exosome-Coated B-10 Carbon Dots for Precise Boron Neutron Capture Therapy in a Mouse Model of Glioma In Situ. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100969.
- Feng, S.N.; Li, H.; Ren, Y.J.; Zhi, C.Y.; Huang, Y.X.; Chen, F.X.; Zhang, H.J. RBC membrane camouflaged boron nitride nanospheres for enhanced biocompatible performance. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110964.
- Carlsson, J.; Bohl Kullberg, E.; Capala, J.; Sjöberg, S.; Edwards, K.; Gedda, L. Ligand liposomes and boron neutron capture therapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2003, 62, 47–59.