Pancreatic cancer is a highly lethal cancer and less than 10% of patients survive the 5-year mark. The molecular and biological underpinnings leading to this dismal prognosis are well-described, however, translation of these findings with subsequent improvement of the poor prognosis has been slow. The complex and dynamic accumulation of microbes, also called the microbiome, has recently attracted scientific interest in the pathogenesis of several diseases including pancreatic cancer. Since then, a limited number of significant findings were published pointing towards an important role of the microbiome in cancer, in particular pancreatic cancer.
- microbiome
- pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- biomarker
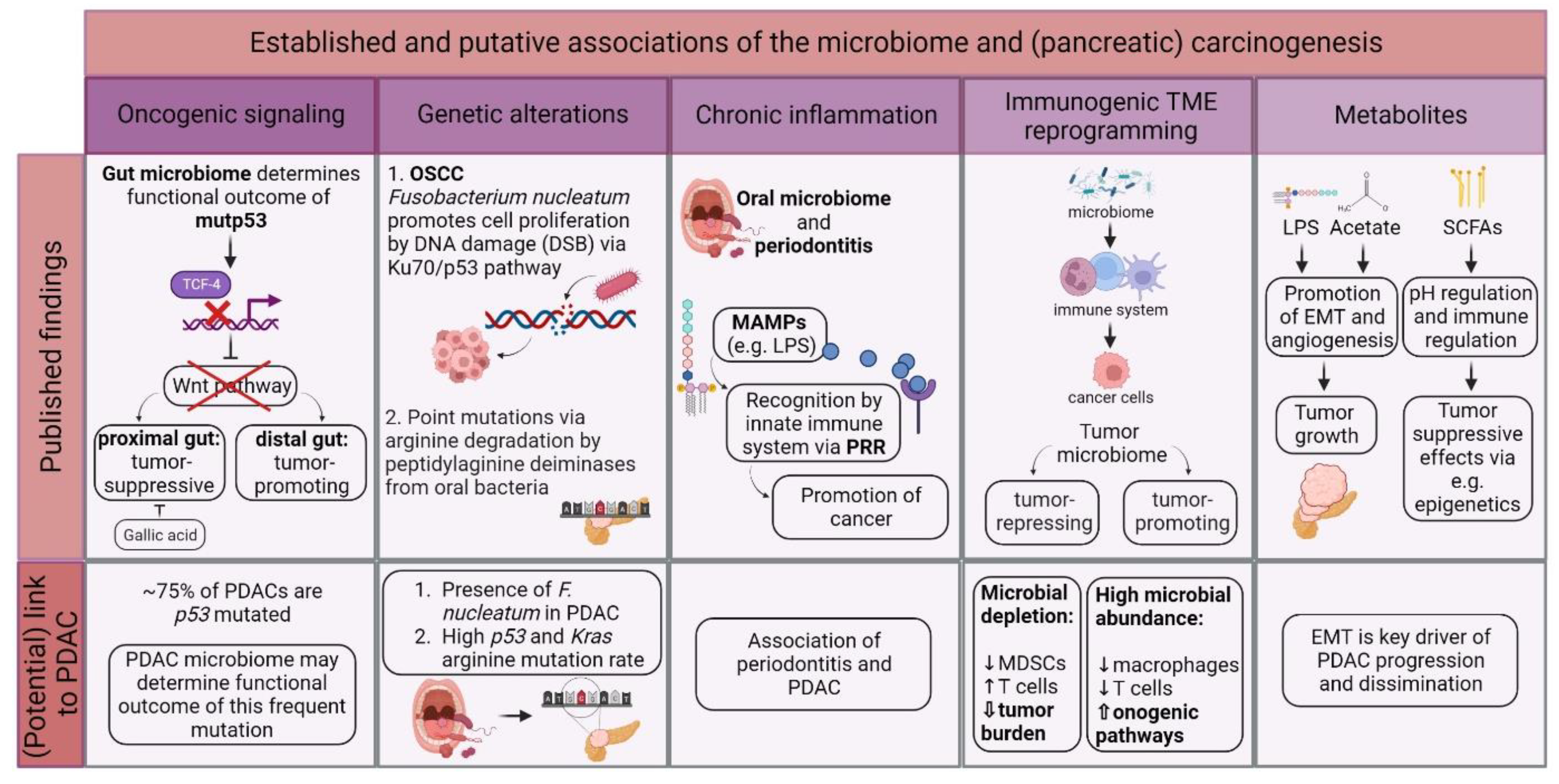
1. The Role of the Microbiome in Pancreatic Carcinogenesis
2. Diagnostic Aspects of the Microbiome in PDAC
2.1. Difficulties in Establishing Screening Tools for PDAC
2.2. The Orointestinal Microbiome as PDAC Biomarker
| Year | Authors | Study Design; Country of Conduction | Sample Type | Detection Method | Number of Patients | Change in Bacterial Composition | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | Farrell et al. | Prospective study; USA | Saliva | Microarray, qRT-PCR | 38 PC 27 CP 38 HC |
Neisseria elongata, Streptococcus mitis increased in PC cases | [3] |
| 2013 | Lin et al. | Cross-sectional study; USA | Oral wash samples | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (NGS) | 13 PC 3 CP 12 HC |
Bacteroides increased in PC cases as compared with HC; Corynebacterium, Aggregatibacter decreased in PC cases as compared with HC |
[8] |
| 2013 | Michaud et al. | Prospective study; European countries | Blood | Immunoblot array | 405 PC 416 HC |
Plasma IgG against Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 53978 increased in PC cases | [9] |
| 2015 | Torres et al. | Cross-sectional study; USA | Saliva | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V4 region) (NGS); qRT-PCR | 8 PC 78 other diseases (including pancreatic disease, non-pancreatic digestive disease/cancer, and non-digestive disease/cancer) 22 HC |
Leptotrichia:Porphyromonas ratio increased in PC cases; Neisseria, Aggregatibacter decreased in PC cases |
[10] |
| 2016 | Fan et al. | Case-control study; USA | Oral wash samples | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 361 PDAC 371 HC |
Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans increased in PDAC cases; Leptotrichia decreased in PDAC cases |
[5] |
| 2017 | Ren et al. | Prospective study; China | Feces | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V5 region) (NGS) | 85 PC 57 HC |
Veillonella, Klebsiella, Selenomonas, LPS-producing bacteria (Prevotella, Hallella, Enterobacter, Cronobacter) increased in PC cases; Bifidobacterium, butyrate-producing bacteria (Coprococcus, Clostridium IV, Blautia, Flavonifractor, Anaerostipes bifidum, Butyricicoccus, Dorea, Gemmiger) decreased in PC cases |
[11] |
| 2017 | Olson et al. | Cross-sectional study; USA | Saliva | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V4–V5 region) (NGS) | 40 PDAC 39 IPMN 58 HC |
Firmicutes (e.g., Streptococcus) increased in PDAC cases; Proteobacteria (e.g., Haemophilus, Neisseria) decreased in PDAC cases as compared with HC |
[12] |
| 2018 | Pushalkar et al. | Case-control study; USA | Rectal swabs | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 32 PDAC 31 HC |
Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Fusobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Synergistetes, Euryarchaeota increased in PDAC cases | [13] |
| 2018 | Mei et al. | Case-control study; China | Duodenal mucosa | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 14 PC (pancreatic head cancer) 14 HC |
Acinetobacter, Aquabacterium, Oceanobacillus, Rahnella, Massilia, Delftia, Deinococcus, Sphingobium increased in PC cases; Porphyromonas, Paenibacillus, Enhydrobacter, Escherichia, Shigella, Pseudomonas decreased in PC cases |
[14] |
| 2019 | Lu et al. | Case- control study; China | Tongue coat samples | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 30 PC (pancreatic head cancer) 25 HC |
Leptotrichia, Fusobacterium, Rothia, Actinomyces, Corynebacterium, Atopobium, Peptostreptococcus, Catonella, Oribacterium, Filifactor, Campylobacter, Moraxella, Tannerella increased in PC cases; Haemophilus, Porphyromonas, Paraprevotella decreased in PC cases |
[15] |
| 2019 | del Castillo et al. | Cross-sectional study; USA | Tissue samples (pancreatic duct, duodenum, pancreas); swabs (bile duct, jejunum, stomach); feces |
16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 39 PC 12 periampullary cancer 18 non-cancer pancreatic conditions 8 non-cancer gastrointestinal conditions 34 HC |
Porphyromonas, Prevotella, Selenomonas, Gemella, Fusobacterium spp. increased in cancer cases as compared with non-cancer cases; Lactobacillus decreased in cancer cases as compared with non-cancer cases |
[16] |
| 2019 | Half et al. | Case-control study; Israel | Feces | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 30 PDAC 6 pre-cancerous lesions 16 NAFLD 13 HC |
Veillonellaceae, Akkermansia, Odoribacter increased in PDAC cases as compared with HC; Clostridiacea, Erysipelotrichaeceae, Ruminococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Anaerostipes decreased in PDAC cases as compared with HC |
[17] |
| 2020 | Vogtmann et al. | Case-control study; Iran | Saliva | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V4 region) (NGS) | 273 PDAC 285 HC |
Enterobacteriaceae, Lachnospiraceae G7, Bacteroidaceae, Staphylococcaceae increased in PDAC cases; Haemophilus decreased in PDAC cases |
[18] |
| 2020 | Sun et al. | Case-control study; China | Saliva | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 10 PC 17 BPD 10 HC |
Fusobacteria (e.g., Fusobacterium periodonticum), Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes increased in PC cases; Proteobacteria (e.g., Neisseria mucosa) decreased in PC cases |
[19] |
| 2020 | Kohi et al. | Case-control study; USA | Duodenal fluid | 16S and 18S rRNA amplicon sequencing (16S V3–V4 rRNA region, 18S ITS1 rRNA region) (NGS) | 74 PDAC 98 pancreatic cysts 134 HC |
Fusobacterium, Bifidobacterium genera, Enterococcus increased in PDAC cases as compared with HC; Escherichia/Shigella, Enterococcus, Clostridium sensu stricto 1, Bifidobacterium increased in PDAC cases as compared with pancreatic cysts; Fusobacterium, Rothia, Neisseria increased in PDAC cases with short-term survival |
[20] |
| 2020 | Wei et al. | Case- control study; China | Saliva | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V3–V4 region) (NGS) | 41 PDAC 69 HC |
Leptotrichia, Actinomyces, Lachnospiraceae, Micrococcaceae, Solobacterium, Coriobacteriaceae, Moraxellaceae, Streptococcus, Rothia, Peptostreptococcus, Oribacterium increased in PDAC cases; Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fusobacteriaceae, Campylobacter, Spirochaetaceae, Veillonella, Neisseria, Selenomona, Tannerella forsythia, Prevotella intermedia decreased in PDAC cases |
[21] |
| 2021 | Zhou et al. | Case-control study; China | Feces | Metagenomic shotgun sequencing (NGS) | 32 PDAC 32 AIP 32 HC |
Gammaproteobacteria (e.g., Escherichia coli), Veillonella (V. atypica, V. parvula, V. dispar), Clostridium (e.g., Clostridium bolteae, Clostridium symbiosum), Fusobacterium nucleatum, Streptococcus parasanguinis, Prevotella stercorea increased in PDAC cases as compared with HC; Butyrate-producing bacteria (Eubacterium rectale, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Roseburia intestinalis, Coprococcus), Ruminococcus, Dialister succinatiphilus decreased in PDAC cases as compared with HC |
[22] |
| 2021 | Matsukawa et al. | Case-control study; Japan | Feces | Whole-genome sequencing (including PCR) (NGS) | 24 PC (thereof 22 PDAC) 18 HC |
Klebsiella pneumoniae, Clostridium bolteae, Clostridium symbiosum, Streptococcus mutans, Alistipes shahii, Bacteroides, Parabacteroides, Lactobacillus increased in PC cases | [23] |
| 2021 | Sugimoto et al. | Case-control study; Japan | Duodenal fluid | 16S rRNA terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism method (5’ FAM-labeled 516F and 1510R primers) | 22 benign pancreaticobiliary diseases (thereof 16 BPD) 12 pancreaticobiliary cancer (thereof 9 PC) |
Bifidobacterium, Clostridium cluster XVIII increased in PC cases as compared with BPD | [24] |
| 2022 | Petrick et al. | Prospective study; USA | Oral wash samples | Metagenomic shotgun sequencing (NGS) | 148 PDAC (thereof 122 of African Americans, 26 of Caucasians) 441 HC (thereof 354 of African Americans, 87 of Caucasians) |
No significant changes in PDAC cases among African Americans; Porphyromonas gingivalis increased in PDAC cases among Caucasians; Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, Tannerella forsythia increased in PDAC cases among never-smokers |
[25] |
| 2022 | Kartal et al. | Case- control study; Spain, Germany | Saliva | Metagenomic shotgun sequencing (NGS) (43 PDAC, 12 CP, 45 HC) 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V4 region) (NGS) (59 PDAC, 28 CP, 55 HC) |
59 PDAC 28 CP 55 HC (Spanish cohort only) |
No significant changes in PDAC cases | [4] |
| Feces | Metagenomic shotgun sequencing (NGS) (101 PDAC, 29 CP, 82 HC) 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (V4 region) (NGS) (51 PDAC, 23 CP, 46 HC) |
101 PDAC 29 CP 82 HC (thereof 57 PDAC, 29 CP and 50 HC from Spanish cohort; 44 PDAC and 32 HC from German cohort) |
Streptococcus, Akkermansia, Veillonella atypica, Fusobacterium nucleatum/hwasookii, Alloscardovia omnicolens increased in PDAC cases as compared with HC; Romboutsia timonensis, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Bacteroides coprocola, Bifidobacterium bifidum decreased in PDAC cases as compared with HC |
||||
| 2022 | Guo et al. | Case-control study; China | Feces | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing (27F, 1492R primer) (NGS) | 36 resectable PDAC 36 unresectable PDAC |
Pseudonocardia, Cloacibacterium, Mucispirillum, Anaerotruncus increased in unresectable PDAC cases; Alistipes, Anaerostipes, Faecalibacterium, Parvimonas decreased in unresectable PDAC cases |
[26] |
| 2022 | Nagata et al. | Case-control study; Japan, Spain, Germany | Saliva | Metagenomic shotgun sequencing (NGS) | 90 PDAC 280 HC (thereof 47 PDAC and 235 HC from Japanese cohort; others from Kartal et al., 2022) |
Firmicutes (unknown Firmicutes, Dialister and Solobacterium spp.), Prevotella spp. (Prevotella pallens, Prevotella sp. C561) increased in PDAC cases among Japanese cohort; Streptococcus spp. (e.g., Streptococcus salivarius, Streptococcus thermophilus, Streptococcus australis) decreased in PDAC cases among Japanese cohort; No significant changes in PDAC cases among Spanish cohort; No correlation for oral species between the Japanese and Spanish datasets |
[27] |
| Feces | Metagenomic shotgun sequencing (NGS) | 144 PDAC 65 CP 150 IPMN 317 HC (thereof 43 PDAC, 65 CP, 150 IPMN and 235 HC from Japanese cohort; others from Kartal et al., 2022) |
Streptococcus oralis, Streptococcus vestibularis, Streptococcus anginosus, Veillonella atypica, Veillonella parvula, Actinomyces spp., Clostridium symbiosum, unknown Mogibacterium, Clostridium clostridioforme increased in PDAC cases as compared with HC among Japanese cohort; Unknown Lachnospiraceae, Eubacterium ventriosum, unknown Butyricicoccus, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii decreased in PDAC cases as compared with HC among Japanese cohort; Clostridium symbiosum, Streptococcus oralis, unknown Mogibacterium increased in PDAC cases as compared with IPMN and CP among Japanese cohort; Significant correlation for gut species between the Japanese and Spanish datasets and between the Japanese and German datasets; Streptococcus spp. (S. anginosus and S. oralis), Veillonella spp. (V. parvula and V. atypica) increased in PDAC cases among all three cohorts; Faecalibacterium prausnitzii decreased in PDAC cases among all three cohorts |
2.3. Blood-Derived Microbial Signatures as PDAC Biomarker
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cancers14235974
References
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Biological Agents. ARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Biological Agents. A Review of Human Carcinogens. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 100, pp. 1–441.
- Chhoda, A.; Lu, L.; Clerkin, B.M.; Risch, H.; Farrell, J.J. Current Approaches to Pancreatic Cancer Screening. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 22–35.
- Farrell, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Chia, D.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Paster, B.J.; Joshipura, K.; Wong, D.T.W. Variations of Oral Microbiota Are Associated with Pancreatic Diseases Including Pancreatic Cancer. Gut 2012, 61, 582–588.
- Kartal, E.; Schmidt, T.S.B.; Molina-Montes, E.; Rodríguez-Perales, S.; Wirbel, J.; Maistrenko, O.M.; Akanni, W.A.; Alhamwe, B.A.; Alves, R.J.; Carrato, A.; et al. A Faecal Microbiota Signature with High Specificity for Pancreatic Cancer. Gut 2022, 71, 1359–1372.
- Fan, X.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Abnet, C.C.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Miller, G.; et al. Human Oral Microbiome and Prospective Risk for Pancreatic Cancer: A Population-Based Nested Case-Control Study. Gut 2016, 67, 120–127.
- Stasiewicz, M.; Kwaśniewski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Microbial Associations with Pancreatic Cancer: A New Frontier in Biomarkers. Cancers 2021, 13, 3784.
- Bukin, Y.S.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Morozov, I.V.; Bukin, S.V.; Zakharenko, A.S.; Zemskaya, T.I. The Effect of 16S RRNA Region Choice on Bacterial Community Metabarcoding Results. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 190007.
- Lin, I.-H.; Wu, J.; Cohen, S.; Chen, C.; Bryk, D.; Marr, M.; Melis, M.; Newman, E.; Pachter, H.; Alekseyenko, A.; et al. Abstract 101: Pilot Study of Oral Microbiome and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 101.
- Michaud, D.S.; Izard, J.; Wilhelm-Benartzi, C.S.; You, D.-H.; Grote, V.A.; Tjønneland, A.; Dahm, C.C.; Overvad, K.; Jenab, M.; Fedirko, V.; et al. Plasma Antibodies to Oral Bacteria and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in a Large European Prospective Cohort Study. Gut 2013, 62, 1764–1770.
- Torres, P.J.; Fletcher, E.M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Bouvet, M.; Doran, K.S.; Kelley, S.T. Characterization of the Salivary Microbiome in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1373.
- Ren, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xie, H.; Li, A.; Lu, H.; Xu, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Cui, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Gut Microbial Profile Analysis by MiSeq Sequencing of Pancreatic Carcinoma Patients in China. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95176–95191.
- Olson, S.H.; Satagopan, J.; Xu, Y.; Ling, L.; Leong, S.; Orlow, I.; Saldia, A.; Li, P.; Nunes, P.; Madonia, V.; et al. The Oral Microbiota in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer, Patients with IPMNs, and Controls: A Pilot Study. Cancer Causes Control 2017, 28, 959–969.
- Pushalkar, S.; Hundeyin, M.; Daley, D.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Kurz, E.; Mishra, A.; Mohan, N.; Aykut, B.; Usyk, M.; Torres, L.E.; et al. The Pancreatic Cancer Microbiome Promotes Oncogenesis by Induction of Innate and Adaptive Immune Suppression. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 403–416.
- Mei, Q.-X.; Huang, C.-L.; Luo, S.-Z.; Zhang, X.-M.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, Y.-Y. Characterization of the Duodenal Bacterial Microbiota in Patients with Pancreatic Head Cancer vs. Healthy Controls. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 438–445.
- Lu, H.; Ren, Z.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Yang, J.; Luo, Q.; Zhou, K.; et al. Tongue Coating Microbiome Data Distinguish Patients with Pancreatic Head Cancer from Healthy Controls. J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1563409.
- Del Castillo, E.; Meier, R.; Chung, M.; Koestler, D.C.; Chen, T.; Paster, B.J.; Charpentier, K.P.; Kelsey, K.T.; Izard, J.; Michaud, D.S. The Microbiomes of Pancreatic and Duodenum Tissue Overlap and Are Highly Subject Specific but Differ between Pancreatic Cancer and Noncancer Subjects. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 370–383.
- Half, E.; Keren, N.; Reshef, L.; Dorfman, T.; Lachter, I.; Kluger, Y.; Reshef, N.; Knobler, H.; Maor, Y.; Stein, A.; et al. Fecal Microbiome Signatures of Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16801.
- Vogtmann, E.; Han, Y.; Caporaso, J.G.; Bokulich, N.; Mohamadkhani, A.; Moayyedkazemi, A.; Hua, X.; Kamangar, F.; Wan, Y.; Suman, S.; et al. Oral Microbial Community Composition Is Associated with Pancreatic Cancer: A Case-Control Study in Iran. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 797–806.
- Sun, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, R.; Ren, X.; Wang, H.; Zou, L. Characterization of Oral Microbiome and Exploration of Potential Biomarkers in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, e4712498.
- Kohi, S.; Macgregor-Das, A.; Dbouk, M.; Yoshida, T.; Chuidian, M.; Abe, T.; Borges, M.; Lennon, A.M.; Shin, E.J.; Canto, M.I.; et al. Alterations in the Duodenal Fluid Microbiome of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e196–e227.
- Wei, A.-L.; Li, M.; Li, G.-Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.-M.; Li, Z.-L.; Yuan, J.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zhou, L.-L.; Li, K.; et al. Oral Microbiome and Pancreatic Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 7679–7692.
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Ren, R.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; et al. The Fecal Microbiota of Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Autoimmune Pancreatitis Characterized by Metagenomic Sequencing. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 215.
- Matsukawa, H.; Iida, N.; Kitamura, K.; Terashima, T.; Seishima, J.; Makino, I.; Kannon, T.; Hosomichi, K.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Dysbiotic Gut Microbiota in Pancreatic Cancer Patients Form Correlation Networks with the Oral Microbiota and Prognostic Factors. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3163–3175.
- Sugimoto, M.; Abe, K.; Takagi, T.; Suzuki, R.; Konno, N.; Asama, H.; Sato, Y.; Irie, H.; Watanabe, K.; Nakamura, J.; et al. Dysbiosis of the Duodenal Microbiota as a Diagnostic Marker for Pancreaticobiliary Cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 2088–2100.
- Petrick, J.L.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Michaud, D.S.; Cai, Q.; Gerlovin, H.; Signorello, L.B.; Wolpin, B.M.; Ruiz-Narváez, E.A.; Long, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. The Oral Microbiome in Relation to Pancreatic Cancer Risk in African Americans. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 287–296.
- Guo, X.; Hu, Z.; Rong, S.; Xie, G.; Nie, G.; Liu, X.; Jin, G. Integrative Analysis of Metabolome and Gut Microbiota in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 1555–1564.
- Nagata, N.; Nishijima, S.; Kojima, Y.; Hisada, Y.; Imbe, K.; Miyoshi-Akiyama, T.; Suda, W.; Kimura, M.; Aoki, R.; Sekine, K.; et al. Metagenomic Identification of Microbial Signatures Predicting Pancreatic Cancer From a Multinational Study. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 222–238.
- Xie, J.; Li, Q.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Hoecke, L.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. The Tremendous Biomedical Potential of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1173–1194.
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Yuan, H.; Liang, F.; Liu, J.; Tang, W. Extracellular Vesicles in Inter-Kingdom Communication in Gastrointestinal Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1087–1103.
- Jahromi, L.P.; Fuhrmann, G. Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles: Understanding Biology Promotes Applications as Nanopharmaceuticals. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 125–140.
- Kim, S.I.; Kang, N.; Leem, S.; Yang, J.; Jo, H.; Lee, M.; Kim, H.S.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Kim, Y.-K.; Park, T.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Serum Microbe-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Diagnostic Models to Differentiate Ovarian Cancer and Benign Ovarian Tumor. Cancers 2020, 12, 1309.
- Kim, J.R.; Han, K.; Han, Y.; Kang, N.; Shin, T.-S.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.; Kwon, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-K.; et al. Microbiome Markers of Pancreatic Cancer Based on Bacteria-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Acquired from Blood Samples: A Retrospective Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 219.
- Poore, G.D.; Kopylova, E.; Zhu, Q.; Carpenter, C.; Fraraccio, S.; Wandro, S.; Kosciolek, T.; Janssen, S.; Metcalf, J.; Song, S.J.; et al. Microbiome Analyses of Blood and Tissues Suggest Cancer Diagnostic Approach. Nature 2020, 579, 567–574.
