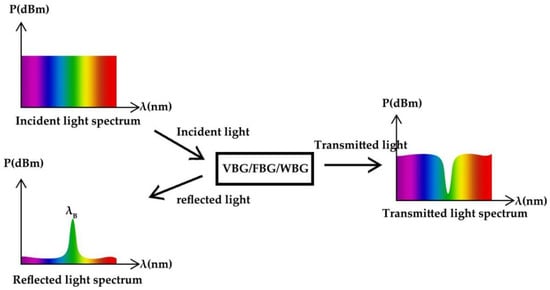
The structures of BG-ECSLs can be mainly divided into the VBG structure, FBG structure and WBG structure. This paper mainly discusses the research progress of VBG structure, FBG structure and WBG structure of BG-ECSLs. BG-ECSLs have a long history. Since the 1970s, in order to make Bragg grating in fiber and other materials, people have carried out a lot of research on the effect of UV radiation damage in silica, germanium-doped silicon glass and other materials. Nowadays, there are many kinds of Bragg grating, and the application fields are also very wide. Due to the unique characteristics and potential application prospects of Bragg grating, since the first batch of BG-ECSLs came out, a large number of companies have studied and continuously optimized the performance of BG-ECSLs. At present, Coherent, OptiGrate, DILAS and so on are well-known in the world. Among them, the United States, Germany, France, Sweden, Canada, Japan and other countries have certain technical advantages in the development of BG-ECSLs. In China, there are also a large number of companies and research institutions developing relevant cutting-edge technologies, such as Wuhan National Laboratory of Optoelectronics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Precision Instruments, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, etc. BG-ECSLs can be widely used in optical communication, biotechnology, environmental detection, material processing and other fields and has potential application prospects in high-precision detection, quantum communication system and other fields.
3. Applications
BG-ECSLs can be widely used in optical communication, gas detection, coherent light detection, synthetic aperture Lidar, spectral gas sensing and other fields and has potential application prospects in underwater optical communication, spaceborne carbon dioxide detection Lidar, biomedical imaging system, high-speed long-distance quantum communication system, etc. [
103,
104,
105]. In this paper, the principle of BG-ECSLs is described, and the research achievements and latest progress in this field in the past ten years are reviewed. As shown in
Table 4, the linewidth of VBG-ECSLs is in the range of kHz-THz (generally in the order of kHz-GHz), the SMSR is in the range of 16~57 dB and the tuning range is in the order of GHz (most of them are tens of picometers). The narrowest linewidth can be as low as 2 kHz while having SMSR up to 57 dB, but the continuous tunable range is small, only 0.063 nm. The maximum tuning range is 1.9 nm. The linewidth of FBG-ECSLs is in the range of kHz~GHz and that of SMSR is in the range of 25~82 dB. The tuning range is in the order of GHz and THz (from tens of picometers to tens of nanometers, and the tuning range is better than that of VBG-ECSLs). The narrowest linewidth can be as low as 125 Hz while having a continuous tunable range of 0.8nm. The maximum SMSR is 82 dB with a narrow linewidth of 16 kHz. The maximum continuous tuning range is 48 nm. The linewidth of WBG-ECSLs is in the range of KHz~GHz, and that of SMSR is in the range of 15~82 dB. The tuning range is in the order of GHz and THz (from hundreds of picometers to tens of nanometers, the tuning range is better than FBG-ECSLs). The narrowest linewidth can be as low as 320 Hz, and the SMSR can be greater than 55 dB. The maximum SMSR is greater than 60 dB, and the linewidth is less than 17 kHz, which can be continuously tuned to 20.2 GHz. The maximum tuning range is 81.8 nm. From the characteristics of commercial BG-ECSLs products, it is not difficult to find that VBG-ECSLs can obtain relatively large output power, while FBG-ECSLs and WBG-ECSLs can obtain a relatively wide tuning range, and the tuning range of WBG-ECSLs is larger, because commercial products are highly targeted (most of them are aimed at a certain module in a certain application or even a certain band). In order to meet the parameter requirements of their application field, most companies do not pursue performances with a low parameter impact on the field. For the application of DWDM, the company pursues parameters such as tuning range, linewidth, output power, SMSR, etc. when conducting research on commercial products, but some parameters cannot obtain the optimal values at the same time. For example, according to Formula (2), if the linewidth is narrower, the output power will be lower. Therefore, in the design of products, it is necessary to meet the requirements of the primary parameters (tuning range), combined with the existing technology, comprehensive consideration of production costs, product stability and other factors to adopt the optimal choice.
The advantages of VBG-ECSLs are the simple structure of the outer cavity and the lack of moving parts, thus providing maximum mechanical stability and reliability. and the center wavelength of the outer cavity structure can be adjusted by tilting the angle of the VBG or changing the cavity length. It plays an important role in biomedicine, optical data storage, synthetic aperture Lidar, quantum optical sensors and other fields. FBG-ECSLs can compress the linewidth of narrow lasers more efficiently, even to the sub-kHz magnitude. It has the advantages of simple and compact structures, narrow linewidths, good stability and a certain tuning ability, and the production cost is low, so the manufacturing process is more mature. However, due to the small refractive index, the large size and large material absorption loss of FBG material itself, it is not conducive to improving the output power of ECSL. Therefore, FBG-ECSLS is suitable for a narrow linewidth, but the tuning range and power requirements are not high. It can be widely used in optical fiber sensing, spectral gas sensing, optical coherence tomography and other fields and has potential application prospects in underwater optical communication, microwave photonics, spaceborne carbon dioxide detection Lidar, ground–starlight Doppler ranging and so on. WBG-ECSLs can not only narrow the linewidth but also maintain good SMSR and tuning capability. Compared with VBG-ECSLs and FBG-ECSLs, WBG-ECSLs have excellent comprehensive performances, which not only have narrow linewidth characteristics but can also maintain a relatively large tuning range and SMSR. Moreover, due to the particularity (good thermal stability) of waveguide materials (Si, SiO2 and Si3N4), WBG-ECSLs has a smaller central wavelength offset with the temperature. The work performance is more stable. Moreover, waveguide has the advantages of a simple structure, small size, low noise and low manufacturing cost, which can be combined with CMOS technology for large-scale production. Through the selection of gain media, materials, integrated devices, new external cavity structure design and optimization of Bragg waveguide structure, so as to improve the coupling efficiency and reduce the waveguide loss, so as to achieve a narrower linewidth, wider tuning range, higher SMSR, lower noise, low-cost and small-volume performance WBG-ECSLs. In general, with the continuous maturation of silicon chip designs and process platforms, the types of external cavity feedback components based on SiO2, Si3N4 and other materials have become more diverse. By introducing the WBG structure, the linewidth of WBG-ECSLs can be compressed, and the coherence of the output can be improved. In addition, the wavelength tuning range of WBG-ECSLs can also be significantly increased. WBG-ECSLs can be widely used in gas detection, coherent optical communication, wavelength division multiplexing system and other fields and have potential applications in multicomponent detection, multi-atom cooling, high-precision spectral detection, biomedical imaging system, high-speed long-distance quantum communication system and so on.
At present, due to the late start and technical blockade, the research on BG-ECSLs still has a certain gap with the international top level. Therefore, the key technologies (epitaxial growth, etching, etc. [
106]) should be continuously broken through in the future research, and the device structure should be optimized [
107]. The internal cavity (gain chip) optimizes the chip structure. The external cavity (Bragg grating and other optical feedback components [
93,
108,
109]) adjust the structure of the existing optical components and design the optical feedback components with a better performance. In general, WBG-ECSLs are a potential approach for laser output with integration, small size, narrow linewidth, wide tuning range, stable spectral output and high side-mode rejection ratio. Using WBG as an optical feedback element is still the mainstream direction of BG-ECSLs.