In celestial mechanics, the Lagrangian points (/ləˈɡrɑːndʒiən/ also Lagrange points, L-points, or libration points) are the points near two large bodies in orbit where a smaller object will maintain its position relative to the large orbiting bodies. At other locations, a small object would go into its own orbit around one of the large bodies, but at the Lagrangian points the gravitational forces of the two large bodies, the centripetal force of orbital motion, and (for certain points) the Coriolis acceleration all match up in a way that cause the small object to maintain a stable or nearly stable position relative to the large bodies. There are five such points, labeled L1 to L5, all in the orbital plane of the two large bodies, for each given combination of two orbital bodies. For instance, there are five Lagrangian points L1 to L5 for the Sun–Earth system, and in a similar way there are five different Lagrangian points for the Earth–Moon system. L1, L2, and L3 are on the line through the centers of the two large bodies, while L4 and L5 each act as the third vertex of an equilateral triangle formed with the centers of the two large bodies. L4 and L5 are stable, which implies that objects can orbit around them in a rotating coordinate system tied to the two large bodies. Several planets have trojan satellites near their L4 and L5 points with respect to the Sun. Jupiter has more than a million of these trojans. Artificial satellites have been placed at L1 and L2 with respect to the Sun and Earth, and with respect to the Earth and the Moon. The Lagrangian points have been proposed for uses in space exploration.
- equilateral
- centripetal
- small object
1. History
The three collinear Lagrange points (L1, L2, L3) were discovered by Leonhard Euler a few years before Joseph-Louis Lagrange discovered the remaining two.[1][2]
In 1772, Lagrange published an "Essay on the three-body problem". In the first chapter he considered the general three-body problem. From that, in the second chapter, he demonstrated two special constant-pattern solutions, the collinear and the equilateral, for any three masses, with circular orbits.[3]
2. Lagrange Points
The five Lagrangian points are labeled and defined as follows:
2.1. L1 Point
The L1 point lies on the line defined by the two large masses M1 and M2, and between them. It is the point where the gravitational attraction of M2 partially cancels M1's gravitational attraction. An object that orbits the Sun more closely than Earth would normally have a shorter orbital period than Earth, but that ignores the effect of Earth's own gravitational pull. If the object is directly between Earth and the Sun, then Earth's gravity counteracts some of the Sun's pull on the object, and therefore increases the orbital period of the object. The closer to Earth the object is, the greater this effect is. At the L1 point, the orbital period of the object becomes exactly equal to Earth's orbital period. L1 is about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, or 0.01 au, 1/100th the distance to the Sun.[4]
2.2. L2 Point
The L2 point lies on the line through the two large masses, beyond the smaller of the two. Here, the gravitational forces of the two large masses balance the centrifugal effect on a body at L2. On the opposite side of Earth from the Sun, the orbital period of an object would normally be greater than that of Earth. The extra pull of Earth's gravity decreases the orbital period of the object, and at the L2 point that orbital period becomes equal to Earth's. Like L1, L2 is about 1.5 million kilometers or 0.01 au from Earth.
2.3. L3 Point
The L3 point lies on the line defined by the two large masses, beyond the larger of the two. Within the Sun–Earth system, the L3 point exists on the opposite side of the Sun, a little outside Earth's orbit and slightly further from the Sun than Earth is. This placement occurs because the Sun is also affected by Earth's gravity and so orbits around the two bodies' barycenter, which is well inside the body of the Sun. An object at Earth's distance from the Sun would have an orbital period of one year if only the Sun's gravity is considered. But an object on the opposite side of the Sun from Earth and directly in line with both "feels" Earth's gravity adding slightly to the Sun's and therefore must orbit a little further from the Sun in order to have the same 1-year period. It is at the L3 point that the combined pull of Earth and Sun causes the object to orbit with the same period as Earth, in effect orbiting an Earth+Sun mass with the Earth-Sun barycenter at one focus of its orbit.
2.4. L4 and L5 Points
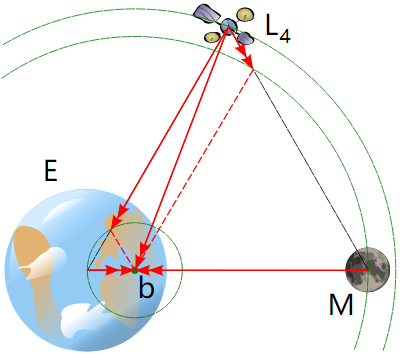
The L4 and L5 points lie at the third corners of the two equilateral triangles in the plane of orbit whose common base is the line between the centers of the two masses, such that the point lies behind (L5) or ahead (L4) of the smaller mass with regard to its orbit around the larger mass.
The triangular points (L4 and L5) are stable equilibria, provided that the ratio of M1/M2 is greater than 24.96.[5][6] This is the case for the Sun–Earth system, the Sun–Jupiter system, and, by a smaller margin, the Earth–Moon system. When a body at these points is perturbed, it moves away from the point, but the factor opposite of that which is increased or decreased by the perturbation (either gravity or angular momentum-induced speed) will also increase or decrease, bending the object's path into a stable, kidney bean-shaped orbit around the point (as seen in the corotating frame of reference).
In contrast to L4 and L5, where stable equilibrium exists, the points L1, L2, and L3 are positions of unstable equilibrium. Any object orbiting at L1, L2, or L3 will tend to fall out of orbit; it is therefore rare to find natural objects there, and spacecraft inhabiting these areas must employ station keeping in order to maintain their position.
3. Natural Objects at Lagrangian Points
It is common to find objects at or orbiting the L4 and L5 points of natural orbital systems. These are commonly called "trojans". In the 20th century, asteroids discovered orbiting at the Sun–Jupiter L4 and L5 points were named after characters from Homer's Iliad. Asteroids at the L4 point, which leads Jupiter, are referred to as the "Greek camp", whereas those at the L5 point are referred to as the "Trojan camp".
Other examples of natural objects orbiting at Lagrange points:
- The Sun–Earth L4 and L5 points contain interplanetary dust and at least one asteroid, 2010 TK7, detected in October 2010 by Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) and announced during July 2011.[7][8]
- The Earth–Moon L4 and L5 points contain interplanetary dust in what are called Kordylewski clouds. Although the Hiten spacecraft's Munich Dust Counter (MDC) detected no increase in dust during its passes through these points in 1992, their presence was confirmed in 2018 by a team of Hungarian astronomers and physicists.[9][10] Stability at these specific points is greatly complicated by solar gravitational influence.[11]
- Recent observations suggest that the Sun–Neptune L4 and L5 points, known as the Neptune trojans, may be very thickly populated,[12] containing large bodies an order of magnitude more numerous than the Jupiter trojans.
- Several asteroids also orbit near the Sun–Jupiter L3 point, called the Hilda family.
- The Saturnian moon Tethys has two smaller moons in its L4 and L5 points, Telesto and Calypso. The Saturnian moon Dione also has two Lagrangian co-orbitals, Helene at its L4 point and Polydeuces at L5. The moons wander azimuthally about the Lagrangian points, with Polydeuces describing the largest deviations, moving up to 32° away from the Saturn–Dione L5 point. Tethys and Dione are hundreds of times more massive than their "escorts" (see the moons' articles for exact diameter figures; masses are not known in several cases), and Saturn is far more massive still, which makes the overall system stable.
- One version of the giant impact hypothesis suggests that an object named Theia formed at the Sun–Earth L4 or L5 point and crashed into Earth after its orbit destabilized, forming the Moon.
- Mars has four known co-orbital asteroids (5261 Eureka, 1999 UJ7, 1998 VF31, and 2007 NS2), all at its Lagrangian points.
- Earth's companion object 3753 Cruithne is in a relationship with Earth that is somewhat trojan-like, but that is different from a true trojan. Cruithne occupies one of two regular solar orbits, one of them slightly smaller and faster than Earth's, and the other slightly larger and slower. It periodically alternates between these two orbits due to close encounters with Earth. When it is in the smaller, faster orbit and approaches Earth, it gains orbital energy from Earth and moves up into the larger, slower orbit. It then falls farther and farther behind Earth, and eventually Earth approaches it from the other direction. Then Cruithne gives up orbital energy to Earth, and drops back into the smaller orbit, thus beginning the cycle anew. The cycle has no noticeable impact on the length of the year, because Earth's mass is over 20 billion (2×1010) times more than that of 3753 Cruithne.
- Epimetheus and Janus, satellites of Saturn, have a similar relationship, though they are of similar masses and so actually exchange orbits with each other periodically. (Janus is roughly 4 times more massive but still light enough for its orbit to be altered.) Another similar configuration is known as orbital resonance, in which orbiting bodies tend to have periods of a simple integer ratio, due to their interaction.
- In a binary star system, the Roche lobe has its apex located at L1; if a star overflows its Roche lobe, then it will lose matter to its companion star.
4. Mathematical Details
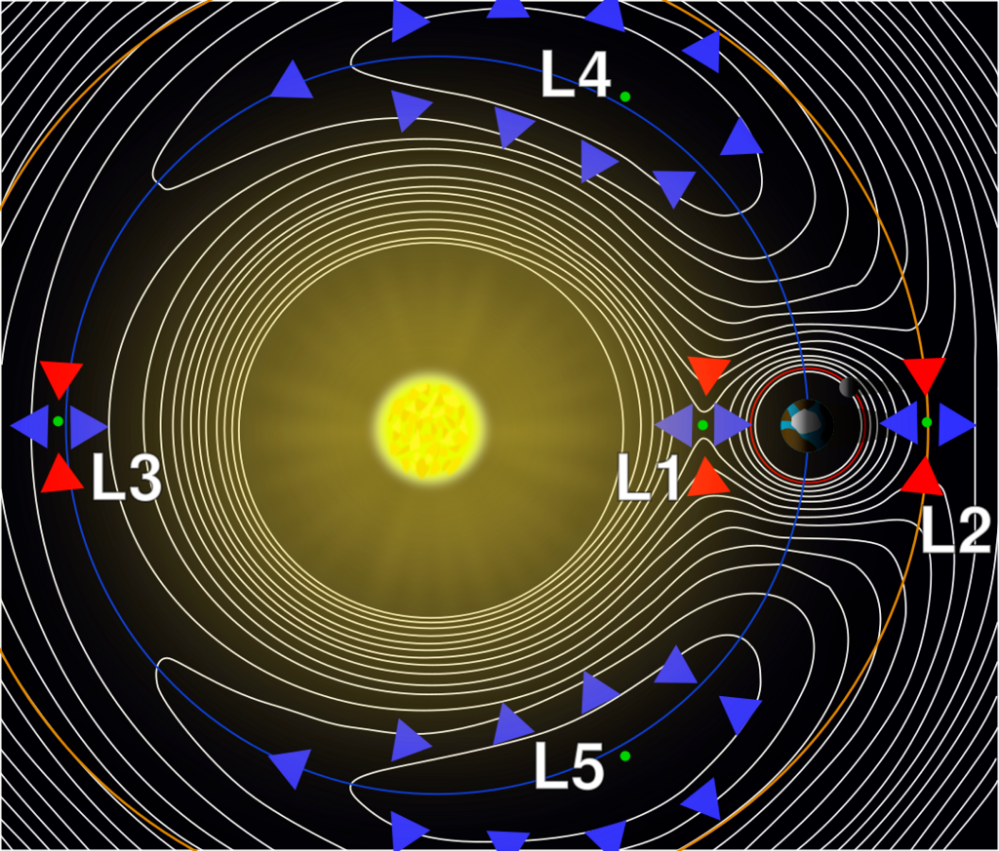
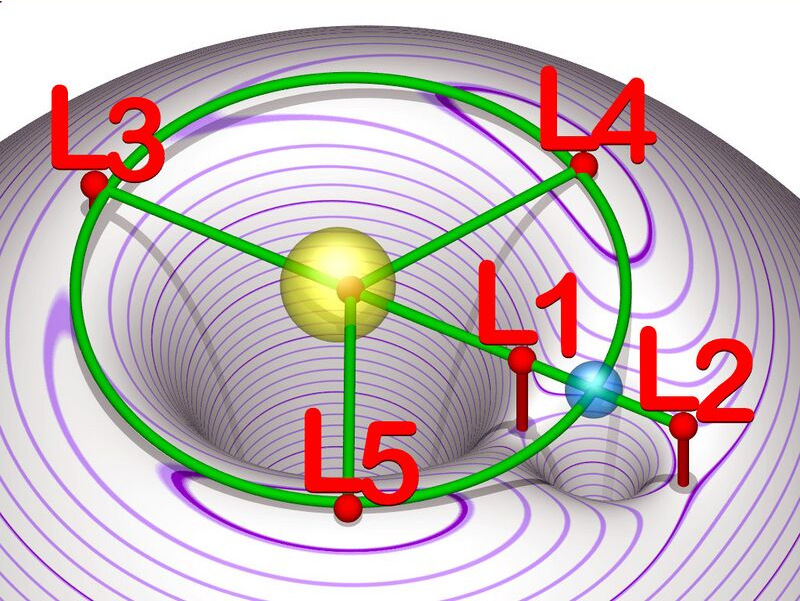
Click for animation.
Lagrangian points are the constant-pattern solutions of the restricted three-body problem. For example, given two massive bodies in orbits around their common barycenter, there are five positions in space where a third body, of comparatively negligible mass, could be placed so as to maintain its position relative to the two massive bodies. As seen in a rotating reference frame that matches the angular velocity of the two co-orbiting bodies, the gravitational fields of two massive bodies combined providing the centripetal force at the Lagrangian points, allowing the smaller third body to be relatively stationary with respect to the first two.[14]
4.1. L1
The location of L1 is the solution to the following equation, gravitation providing the centripetal force:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{M_1}{(R-r)^2}=\frac{M_2}{r^2}+\left(\frac{M_1}{M_1+M_2}R-r\right)\frac{M_1+M_2}{R^3} }[/math]
where r is the distance of the L1 point from the smaller object, R is the distance between the two main objects, and M1 and M2 are the masses of the large and small object, respectively. (The quantity in parentheses on the right is the distance of L1 from the center of mass.) Solving this for r involves solving a quintic function, but if the mass of the smaller object (M2) is much smaller than the mass of the larger object (M1) then L1 and L2 are at approximately equal distances r from the smaller object, equal to the radius of the Hill sphere, given by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ r \approx R \sqrt[3]{\frac{M_2}{3 M_1}} }[/math]
This distance can be described as being such that the orbital period, corresponding to a circular orbit with this distance as radius around M2 in the absence of M1, is that of M2 around M1, divided by √3 ≈ 1.73:
- [math]\displaystyle{ T_{s,M_2}(r) = \frac{T_{M_2,M_1}(R)}{\sqrt{3}}. }[/math]
4.2. L2
The location of L2 is the solution to the following equation, gravitation providing the centripetal force:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{M_1}{(R+r)^2}+\frac{M_2}{r^2}=\left(\frac{M_1}{M_1+M_2}R+r\right)\frac{M_1+M_2}{R^3} }[/math]
with parameters defined as for the L1 case. Again, if the mass of the smaller object (M2) is much smaller than the mass of the larger object (M1) then L2 is at approximately the radius of the Hill sphere, given by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ r \approx R \sqrt[3]{\frac{M_2}{3 M_1}} }[/math]
4.3. L3
The location of L3 is the solution to the following equation, gravitation providing the centripetal force:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{M_1}{\left(R-r\right)^2}+\frac{M_2}{\left(2R-r\right)^2}=\left(\frac{M_2}{M_1+M_2}R+R-r\right)\frac{M_1+M_2}{R^3} }[/math]
with parameters M1,2 and R defined as for the L1 and L2 cases, and r now indicates the distance of L3 from the position of the smaller object, if it were rotated 180 degrees about the larger object. If the mass of the smaller object (M2) is much smaller than the mass of the larger object (M1) then:[15]
- [math]\displaystyle{ r\approx R\frac{7M_2}{12 M_1} }[/math]
4.4. L4 and L5
The reason these points are in balance is that, at L4 and L5, the distances to the two masses are equal. Accordingly, the gravitational forces from the two massive bodies are in the same ratio as the masses of the two bodies, and so the resultant force acts through the barycenter of the system; additionally, the geometry of the triangle ensures that the resultant acceleration is to the distance from the barycenter in the same ratio as for the two massive bodies. The barycenter being both the center of mass and center of rotation of the three-body system, this resultant force is exactly that required to keep the smaller body at the Lagrange point in orbital equilibrium with the other two larger bodies of system. (Indeed, the third body need not have negligible mass.) The general triangular configuration was discovered by Lagrange in work on the three-body problem.
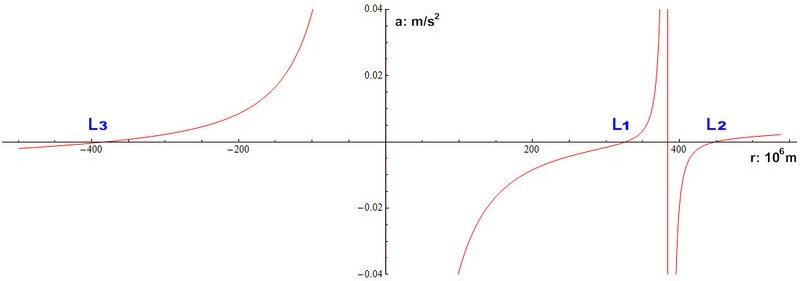
4.5. Radial Acceleration
The radial acceleration a of an object in orbit at a point along the line passing through both bodies is given by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ a=-\frac{G M_1}{r^2}\sgn(r)+\frac{G M_2}{(R-r)^2}\sgn(R-r)+\frac{G\bigl((M_1+M_2) r-M_2 R\bigr)}{R^3} }[/math]
where r is the distance from the large body M1 and sgn(x) is the sign function of x. The terms in this function represent respectively: force from M1; force from M2; and centrifugal force. The points L3, L1, L2 occur where the acceleration is zero — see chart at right.
5. Stability
Although the L1, L2, and L3 points are nominally unstable, there are (unstable) periodic orbits called "halo" orbits around these points in a three-body system. A full n-body dynamical system such as the Solar System does not contain these periodic orbits, but does contain quasi-periodic (i.e. bounded but not precisely repeating) orbits following Lissajous-curve trajectories. These quasi-periodic Lissajous orbits are what most of Lagrangian-point space missions have used until now. Although they are not perfectly stable, a modest effort of station keeping keeps a spacecraft in a desired Lissajous orbit for a long time. Also, for Sun–Earth-L1 missions, it is preferable for the spacecraft to be in a large-amplitude (100,000–200,000 km or 62,000–124,000 mi) Lissajous orbit around L1 than to stay at L1, because the line between Sun and Earth has increased solar interference on Earth–spacecraft communications. Similarly, a large-amplitude Lissajous orbit around L2 keeps a probe out of Earth's shadow and therefore ensures continuous illumination of its solar panels.
The L4 and L5 points are stable provided that the mass of the primary body (e.g. the Earth) is at least 25[5] times the mass of the secondary body (e.g. the Moon).[16][17] The Earth is over 81 times the mass of the Moon (the Moon is 1.23% of the mass of the Earth[18]). Although the L4 and L5 points are found at the top of a "hill", as in the effective potential contour plot above, they are nonetheless stable. The reason for the stability is a second-order effect: as a body moves away from the exact Lagrange position, Coriolis acceleration (which depends on the velocity of an orbiting object and cannot be modeled as a contour map)[17] curves the trajectory into a path around (rather than away from) the point.[17][19]
6. Solar System Values
This table lists sample values of L1, L2, and L3 within the solar system. Calculations assume the two bodies orbit in a perfect circle with separation equal to the semimajor axis and no other bodies are nearby. Distances are measured from the larger body's center of mass with L3 showing a negative location. The percentage columns show how the distances compare to the semimajor axis. E.g. for the Moon, L1 is located 326400 km from Earth's center, which is 84.9% of the Earth–Moon distance or 15.1% in front of the Moon; L2 is located 448900 km from Earth's center, which is 116.8% of the Earth–Moon distance or 16.8% beyond the Moon; and L3 is located −381700 km from Earth's center, which is 99.3% of the Earth–Moon distance or 0.7084% in front of the Moon's 'negative' position.
| Body pair | Semimajor axis (SMA) | L1 | 1 − L1/SMA (%) | L2 | L2/SMA − 1 (%) | L3 | 1 + L3/SMA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth–Moon | 3.844×108 m | 3.2639×108 m | 15.09 | 4.489×108 m | 16.78 | −3.8168×108 m | 0.7084 |
| Sun–Mercury | 5.7909×1010 m | 5.7689×1010 m | 0.3806 | 5.813×1010 m | 0.3815 | −5.7909×1010 m | 0.000009683 |
| Sun–Venus | 1.0821×1011 m | 1.072×1011 m | 0.9315 | 1.0922×1011 m | 0.9373 | −1.0821×1011 m | 0.0001428 |
| Sun–Earth | 1.496×1011 m | 1.4811×1011 m | 0.997 | 1.511×1011 m | 1.004 | −1.496×1011 m | 0.0001752 |
| Sun–Mars | 2.2794×1011 m | 2.2686×1011 m | 0.4748 | 2.2903×1011 m | 0.4763 | −2.2794×1011 m | 0.00001882 |
| Sun–Jupiter | 7.7834×1011 m | 7.2645×1011 m | 6.667 | 8.3265×1011 m | 6.978 | −7.7791×1011 m | 0.05563 |
| Sun–Saturn | 1.4267×1012 m | 1.3625×1012 m | 4.496 | 1.4928×1012 m | 4.635 | −1.4264×1012 m | 0.01667 |
| Sun–Uranus | 2.8707×1012 m | 2.8011×1012 m | 2.421 | 2.9413×1012 m | 2.461 | −2.8706×1012 m | 0.002546 |
| Sun–Neptune | 4.4984×1012 m | 4.3834×1012 m | 2.557 | 4.6154×1012 m | 2.602 | −4.4983×1012 m | 0.003004 |
7. Spaceflight Applications
7.1. Sun–Earth
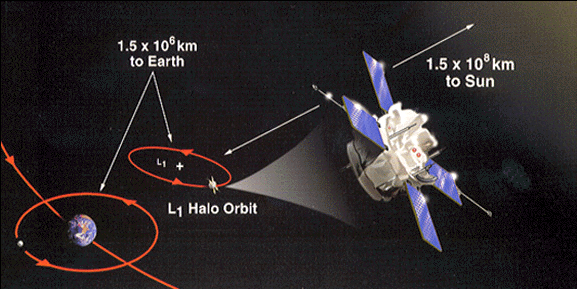
Sun–Earth L1 is suited for making observations of the Sun–Earth system. Objects here are never shadowed by Earth or the Moon and, if observing Earth, always view the sunlit hemisphere. The first mission of this type was the 1978 International Sun Earth Explorer 3 (ISEE-3) mission used as an interplanetary early warning storm monitor for solar disturbances.[20] Since June 2015, DSCOVR has orbited the L1 point. Conversely it is also useful for space-based solar telescopes, because it provides an uninterrupted view of the Sun and any space weather (including the solar wind and coronal mass ejections) reaches L1 a few hours before Earth. Solar telescopes currently located around L1 include the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory and Advanced Composition Explorer.
Sun–Earth L2 is a good spot for space-based observatories. Because an object around L2 will maintain the same relative position with respect to the Sun and Earth, shielding and calibration are much simpler. It is, however, slightly beyond the reach of Earth's umbra,[21] so solar radiation is not completely blocked at L2. Spacecraft generally orbit around L2, avoiding partial eclipses of the Sun to maintain a constant temperature. From locations near L2, the Sun, Earth and Moon are relatively close together in the sky; this means that a large sunshade with the telescope on the dark-side can allow the telescope to cool passively to around 50 K – this is especially helpful for infrared astronomy and observations of the cosmic microwave background. The James Webb Space Telescope is due to be positioned at L2.
Sun–Earth L3 was a popular place to put a "Counter-Earth" in pulp science fiction and comic books. Once space-based observation became possible via satellites[22] and probes, it was shown to hold no such object. The Sun–Earth L3 is unstable and could not contain a natural object, large or small, for very long. This is because the gravitational forces of the other planets are stronger than that of Earth (Venus, for example, comes within 0.3 AU of this L3 every 20 months).
A spacecraft orbiting near Sun–Earth L3 would be able to closely monitor the evolution of active sunspot regions before they rotate into a geoeffective position, so that a 7-day early warning could be issued by the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center. Moreover, a satellite near Sun–Earth L3 would provide very important observations not only for Earth forecasts, but also for deep space support (Mars predictions and for manned mission to near-Earth asteroids). In 2010, spacecraft transfer trajectories to Sun–Earth L3 were studied and several designs were considered.[23]
Missions to Lagrangian points generally orbit the points rather than occupy them directly.
Another interesting and useful property of the collinear Lagrangian points and their associated Lissajous orbits is that they serve as "gateways" to control the chaotic trajectories of the Interplanetary Transport Network.
7.2. Earth–Moon
Earth–Moon L1 allows comparatively easy access to Lunar and Earth orbits with minimal change in velocity and this has as an advantage to position a half-way manned space station intended to help transport cargo and personnel to the Moon and back.
Earth–Moon L2 has been used for a communications satellite covering the Moon's far side, for example, Queqiao, launched in 2018[24], and would be "an ideal location" for a propellant depot as part of the proposed depot-based space transportation architecture.[25]
7.3. Sun–Venus
Scientists at the B612 Foundation were[26] planning to use Venus's L3 point to position their planned Sentinel telescope, which aimed to look back towards Earth's orbit and compile a catalogue of near-Earth asteroids.[27]
7.4. Sun–Mars
In 2017, Nasa proposed the idea of positioning a magnetic dipole shield at the Sun–Mars L1 point for use as an artificial magnetosphere for Mars.[28] The idea is that this would protect the planet's atmosphere from the Sun's radiation and solar winds.
8. Lagrangian Spacecraft and Missions
8.1. Spacecraft at Sun–Earth L1
International Sun Earth Explorer 3 (ISEE-3) began its mission at the Sun–Earth L1 before leaving to intercept a comet in 1982. The Sun–Earth L1 is also the point to which the Reboot ISEE-3 mission was attempting to return the craft as the first phase of a recovery mission (as of September 25, 2014 all efforts have failed and contact was lost).[29]
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is stationed in a halo orbit at L1, and the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in a Lissajous orbit. WIND is also at L1.
Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR), launched on 11 February 2015, began orbiting L1 on 8 June 2015 to study the solar wind and its effects on Earth.[30] DSCOVR is unofficially known as GORESAT, because it carries a camera always oriented to Earth and capturing full-frame photos of the planet similar to the Blue Marble. This concept was proposed by then-Vice President of the United States Al Gore in 1998[31] and was a centerpiece in his film An Inconvenient Truth.[32]
LISA Pathfinder (LPF) was launched on 3 December 2015, and arrived at L1 on 22 January 2016, where, among other experiments, it tested the technology needed by (e)LISA to detect gravitational waves. LISA Pathfinder used an instrument consisting of two small gold alloy cubes.
8.2. Spacecraft at Sun–Earth L2
Spacecraft at the Sun–Earth L2 point are in a Lissajous orbit until decommissioned, when they are sent into a heliocentric graveyard orbit.
- 1 October 2001 – October 2010: Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe[33]
- November 2003 – April 2004: WIND, then it returned to Earth orbit before going to L1 where it still remains
- July 2009 – 29 April 2013: Herschel Space Telescope[34]
- 3 July 2009 – 21 October 2013: Planck Space Observatory
- 25 August 2011 – April 2012: Chang'e 2,[35][36] from where it travelled to 4179 Toutatis and then into deep space
- January 2014: Gaia Space Observatory
- 2019: Spektr-RG X-Ray Observatory
- 2020: Euclid Space Telescope
- 2021: James Webb Space Telescope will use a halo orbit
- 2024: Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (WFIRST) will use a halo orbit
- 2031: Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics (ATHENA) will use a halo orbit
8.3. Spacecraft at Earth–Moon L2
- Chang'e 5-T1 experimental spacecraft DFH-3A "service module" was sent to the Earth-Moon L2 lunar Lissajous orbit on 13 January 2015, where it used the remaining 800 kg of fuel to test maneuvers key to future lunar missions.[37]
- Queqiao entered orbit around the Earth–Moon L2 on 14 June 2018. It serves as a relay satellite for the Chang'e 4 lunar far-side lander, which cannot communicate directly with Earth.
8.4. Past and Current Missions
| Unflown or planned mission | Mission en route or in progress (including mission extensions) | Mission at Lagrangian point completed successfully (or partially successfully) |
| Mission | Lagrangian point | Agency | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| International Sun–Earth Explorer 3 (ISEE-3) | Sun–Earth L1 | NASA | |
| Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) | Sun–Earth L1 | NASA | Launched 1997. Has fuel to orbit near L1 until 2024. Operational (As of 2019).[38] |
| Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) | Sun–Earth L1 | NASA | Launched on 11 February 2015. Planned successor of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) satellite. In safe mode (As of 2019), but is planned to reboot.[39] |
| LISA Pathfinder (LPF) | Sun–Earth L1 | ESA, NASA | Launched one day behind revised schedule (planned for the 100th anniversary of the publication of Einstein's General Theory of Relativity), on 3 December 2015. Arrived at L1 on 22 January 2016.[40] LISA Pathfinder was deactivated on 30 June 2017.[41] |
| Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) | Sun–Earth L1 | ESA, NASA | Orbiting near L1 since 1996. Operational (As of 2020).[42] |
| WIND | Sun–Earth L1 | NASA | Arrived at L1 in 2004 with fuel for 60 years. Operational (As of 2019).[43] |
| Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) | Sun–Earth L2 | NASA | Arrived at L2 in 2001. Mission ended 2010,[44] then sent to solar orbit outside L2.[45] |
| Herschel Space Telescope | Sun–Earth L2 | ESA | Arrived at L2 July 2009. Ceased operation on 29 April 2013; will be moved to a heliocentric orbit.[46][47] |
| Planck Space Observatory | Sun–Earth L2 | ESA | Arrived at L2 July 2009. Mission ended on 23 October 2013; Planck has been moved to a heliocentric parking orbit.[48] |
| Chang'e 2 | Sun–Earth L2 | CNSA | Arrived in August 2011 after completing a lunar mission before departing en route to asteroid 4179 Toutatis in April 2012.[36] |
| ARTEMIS mission extension of THEMIS | Earth–Moon L1 and L2 | NASA | Mission consists of two spacecraft, which were the first spacecraft to reach Earth–Moon Lagrangian points. Both moved through Earth–Moon Lagrangian points, and are now in lunar orbit.[49][50] |
| WIND | Sun–Earth L2 | NASA | Arrived at L2 in November 2003 and departed April 2004. |
| Gaia Space Observatory | Sun–Earth L2 | ESA | Launched 19 December 2013.[51] Operational (As of 2020).[52] |
| Chang'e 5-T1 Service Module | Earth–Moon L2 | CNSA | Launched on 23 October 2014, arrived at L2 halo orbit on 13 January 2015.[37] |
| Queqiao | Earth–Moon L2 | CNSA | Launched on 21 May 2018, arrived at L2 halo orbit on June 14.[53] |
| Spektr-RG | Sun–Earth L2 | IKI RAN DLR |
Launched 13 July 2019. Roentgen and Gamma space observatory. En route to L2 point. |
8.5. Future and Proposed Missions
| Mission | Lagrangian point | Agency | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Lunar Far-Side Communication Satellites" | Earth–Moon L2 | NASA | Proposed in 1968 for communications on the far side of the Moon during the Apollo program, mainly to enable an Apollo landing on the far side—neither the satellites nor the landing were ever realized.[54] |
| Space colonization and manufacturing | Earth–Moon L4 or L5 | — | First proposed in 1974 by Gerard K. O'Neill[55] and subsequently advocated by the L5 Society. |
| EQUULEUS | Earth–Moon L2 | University of Tokyo, JAXA | 6U CubeSat, launch planned in 2019 as a secondary payload onboard SLS Artemis 1.[56] |
| James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) | Sun–Earth L2 | NASA, ESA, CSA | (As of 2018), launch is planned for 2021.[57] |
| Euclid | Sun–Earth L2 | ESA, NASA | (As of 2013), launch is planned in 2020.[58] |
| Aditya-L1 | Sun–Earth L1 | ISRO | Launch planned for 2021; it will be going to a point 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth, from where it will observe the Sun constantly and study the solar corona, the region around the Sun's surface.[59] |
| Demonstration and Experiment of Space Technology for INterplanetary voYage (DESTINY) |
Earth–Moon L2 | JAXA | Candidate for JAXA's next "Competitively-Chosen Medium-Sized Focused Mission", possible launch in the early 2020s.[60] |
| Exploration Gateway Platform | Earth–Moon L2[61] | NASA | Proposed in 2011.[62] |
| Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (WFIRST) | Sun–Earth L2 | NASA, USDOE | (As of 2013), in a "pre-formulation" phase until at least early 2016; possible launch in the early 2020s.[63] |
| LiteBIRD | Sun–Earth L2[64] | JAXA, NASA | (As of 2015), one of two finalists for JAXA's next "Strategic Large Mission"; would be launched in 2024 if selected.[65] |
| Planetary Transits and Oscillations of stars (PLATO) | Sun–Earth L2 | ESA | Planned for launch in 2024 for an initial six-year mission.[66] |
| Space Infrared Telescope for Cosmology and Astrophysics (SPICA) |
Sun–Earth L2 | JAXA, ESA, SRON | (As of 2015), awaiting approval from both Japanese and European side, launch proposed for 2025.[67] |
| Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics (ATHENA) |
Sun–Earth L2 | ESA | Launch planned for 2028.[68] |
| Spektr-M | Sun–Earth L2 | Roscosmos | Possible launch after 2027. [69] |
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Astronomy:Lagrangian_point
References
- Koon, W. S.; Lo, M. W.; Marsden, J. E.; Ross, S. D. (2006). Dynamical Systems, the Three-Body Problem, and Space Mission Design. p. 9. http://www.cds.caltech.edu/~marsden/books/Mission_Design.html. Retrieved 2008-06-09. (16MB)
- Euler, Leonhard (1765). De motu rectilineo trium corporum se mutuo attrahentium. http://www.math.dartmouth.edu/~euler/docs/originals/E327.pdf.
- Lagrange, Joseph-Louis (1867–92). "Tome 6, Chapitre II: Essai sur le problème des trois corps" (in fr). Œuvres de Lagrange. Gauthier-Villars. pp. 229–334. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k229225j/f231.image.r=Oeuvres+de+Lagrange.langFR.
- Cornish, Neil J.. "The Lagrangian Points". http://www.physics.montana.edu/faculty/cornish/lagrange.pdf. Retrieved 15 Dec 2015.
- Actually 25 + √621/2 ≈ 24.9599357944
- "The Lagrange Points". http://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/media/ContentMedia/lagrange.pdf. , Neil J. Cornish with input from Jeremy Goodman
- Choi 2011-07-27T17:06:00Z, Charles Q.. "First Asteroid Companion of Earth Discovered at Last". https://www.space.com/12443-earth-asteroid-companion-discovered-2010-tk7.html.
- "NASA - NASA's Wise Mission Finds First Trojan Asteroid Sharing Earth's Orbit". https://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2011/jul/HQ_11-247_WISE_Trojan.html.
- Slíz-Balogh, Judit; Barta, András; Horváth, Gábor (2018). "Celestial mechanics and polarization optics of the Kordylewski dust cloud in the Earth-Moon Lagrange point L5 - Part I. Three-dimensional celestial mechanical modelling of dust cloud formation". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 480 (4): 5550–5559. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2049. Bibcode: 2018MNRAS.480.5550S. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fmnras%2Fsty2049
- Slíz-Balogh, Judit; Barta, András; Horváth, Gábor (2019). "Celestial mechanics and polarization optics of the Kordylewski dust cloud in the Earth-Moon Lagrange point L5. Part II. Imaging polarimetric observation: new evidence for the existence of Kordylewski dust cloud". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 482 (1): 762–770. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2630. Bibcode: 2019MNRAS.482..762S. https://dx.doi.org/10.1093%2Fmnras%2Fsty2630
- Freitas, Robert; Valdes, Francisco (1980). "A Search for Natural or Artificial Objects Located at the Earth–Moon Libration Points". Icarus 42 (3): 442–447. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(80)90106-2. Bibcode: 1980Icar...42..442F. http://www.rfreitas.com/Astro/SearchIcarus1980.htm.
- "List Of Neptune Trojans". Minor Planet Center. Archived from the original on 2011-07-25. https://web.archive.org/web/20110725075646/http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/iau/lists/NeptuneTrojans.html. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- Seidov, Zakir F. (March 1, 2004). "The Roche Problem: Some Analytics". The Astrophysical Journal 603 (1): 283–284. doi:10.1086/381315. Bibcode: 2004ApJ...603..283S. https://dx.doi.org/10.1086%2F381315
- "Lagrange Points" by Enrique Zeleny, Wolfram Demonstrations Project. http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/LagrangePoints/
- "Widnall, Lecture L18 - Exploring the Neighborhood: the Restricted Three-Body Problem". https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/aeronautics-and-astronautics/16-07-dynamics-fall-2009/lecture-notes/MIT16_07F09_Lec18.pdf.
- Fitzpatrick, Richard. "Stability of Lagrange Points". University of Texas. http://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/336k/Newtonhtml/node126.html.
- Greenspan, Thomas (January 7, 2014). "Stability of the Lagrange Points, L4 and L5". http://www.math.cornell.edu/~templier/junior/final_paper/Thomas_Greenspan-Stability_of_Lagrange_points.pdf.
- Pitjeva, E.V.; Standish, E.M. (2009-04-01). "Proposals for the masses of the three largest asteroids, the Moon-Earth mass ratio and the Astronomical Unit". Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy 103 (4): 365–372. doi:10.1007/s10569-009-9203-8. Bibcode: 2009CeMDA.103..365P. https://zenodo.org/record/1000691.
- Cacolici, Gianna Nicole , et al., "Stability of Lagrange Points: James Webb Space Telescope", University of Arizona. Retrieved 17 Sept. 2018. http://math.arizona.edu/~gabitov/teaching/141/math_485/Final_Report/Lagrange_Final_Report.pdf
- "ISEE-3/ICE". Solar System Exploration. NASA. http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/profile.cfm?MCode=ISEEICE. Retrieved August 8, 2015.
- Angular size of the Sun at 1 AU + 1.5 million kilometres: 31.6′, angular size of Earth at 1.5 million kilometres: 29.3′
- STEREO mission description by NASA, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stereo/main/index.html#.UuG0NxDb-kk
- Tantardini, Marco; Fantino, Elena; Ren, Yuan; Pergola, Pierpaolo; Gómez, Gerard; Masdemont, Josep J. (2010). "Spacecraft trajectories to the L3 point of the Sun–Earth three-body problem". Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy 108 (3): 215–232. doi:10.1007/s10569-010-9299-x. Bibcode: 2010CeMDA.108..215T. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00568378/file/PEER_stage2_10.1007%252Fs10569-010-9299-x.pdf.
- Jones, Andrew (2018-06-14). "Chang'e-4 relay satellite enters halo orbit around Earth-Moon L2, microsatellite in lunar orbit". SpaceNews. https://spacenews.com/change-4-relay-satellite-enters-halo-orbit-around-earth-moon-l2-microsatellite-in-lunar-orbit/.
- Zegler, Frank; Kutter, Bernard (2010-09-02). "Evolving to a Depot-Based Space Transportation Architecture". AIAA SPACE 2010 Conference & Exposition. AIAA. p. 4. http://www.ulalaunch.com/uploads/docs/Published_Papers/Exploration/DepotBasedTransportationArchitecture2010.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-25. "L2 is in deep space far away from any planetary surface and hence the thermal, micrometeoroid, and atomic oxygen environments are vastly superior to those in LEO. Thermodynamic stasis and extended hardware life are far easier to obtain without these punishing conditions seen in LEO. L2 is not just a great gateway—it is a great place to store propellants. ... L2 is an ideal location to store propellants and cargos: it is close, high energy, and cold. More importantly, it allows the continuous onward movement of propellants from LEO depots, thus suppressing their size and effectively minimizing the near-Earth boiloff penalties."
- "B612 studying smallsat missions to search for near Earth objects". June 20, 2017. https://spacenews.com/b612-studying-smallsat-missions-to-search-for-near-earth-objects/.
- "The Sentinel Mission". B612 Foundation. https://b612foundation.org/sentinel-mission/.
- "NASA proposes a magnetic shield to protect Mars' atmosphere". https://phys.org/news/2017-03-nasa-magnetic-shield-mars-atmosphere.html.
- "ISEE-3 is in Safe Mode". Space College. 25 September 2014. "The ground stations listening to ISEE-3 have not been able to obtain a signal since Tuesday the 16th"
- US Department of Commerce, NOAA Satallites and Information Service. "NOAA's Satellite and Information Service (NESDIS)". Archived from the original on 2015-06-08. https://web.archive.org/web/20150608182042/http://www.nesdis.noaa.gov/news_archives/DSCOVR_L1_orbit.html.
- "At long last: Al Gore's satellite dream blasts off". USA TODAY. 7 February 2015. https://www.usatoday.com/story/tech/2015/02/07/goresat-gore-satellite-deep-space-climate/23013283/.
- Mellow, Craig (August 2014). "Al Gore's Satellite". Air & Space/Smithsonian. Retrieved December 12, 2014.
- "Mission Complete! WMAP Fires Its Thrusters For The Last Time". http://news.discovery.com/space/mission-complete-wmap-fires-its-thrusters-for-the-last-time.html.
- Toobin, Adam (2013-06-19). "Herschel Space Telescope Shut Down For Good, ESA Announces". Huffington Post. http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2013/06/19/herschel-telescope-shut-down-esa_n_3461962.html.
- Lakdawalla, Emily (14 June 2012). "Chang'e 2 has departed Earth's neighborhood for.....asteroid Toutatis!?". http://www.planetary.org/blogs/emily-lakdawalla/2012/20120614-change-2-toutatis.html. Retrieved 15 June 2012.
- Lakdawalla, Emily (15 June 2012). "Update on yesterday's post about Chang'e 2 going to Toutatis". Planetary Society. http://www.planetary.org/blogs/emily-lakdawalla/2012/06150926-change2-update.html. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- "Chang'e 5 Test Mission Updates". http://www.spaceflight101.com/change-5-test-mission-updates.html. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
- "ACE MAG Spectrograms: 1 day starting 2019/3/15 (2019 074)". http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=0&YEAR=2019&MONTH=3&DAY=15&DOY=-1.
- "Software fix planned to restore DSCOVR" (in en-US). 2019-10-01. https://spacenews.com/software-fix-planned-to-restore-dscovr/.
- "LISA Pathfinder factsheet". ESA. 11 June 2012. http://www.esa.int/esaSC/SEMQSBWO4HD_index_0.html. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- "LISA Pathfinder Will Concludee Trailblazing Mission". ESA. 20 June 2017. http://sci.esa.int/lisa-pathfinder/59238-lisa-pathfinder-to-conclude-trailblazing-mission/.
- "The Very Latest SOHO Images". https://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/data/realtime-images.html.
- Tran, Lina (2019-10-31). "25 Years of Science in the Solar Wind". http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2019/25-years-of-science-in-the-solar-wind.
- "WMAP Facts". NASA. http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/news/facts.html. Retrieved 2013-03-18.
- http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/news/events.html WMAP Ceases Communications
- "Herschel Factsheet". European Space Agency. 17 April 2009. http://www.esa.int/esaSC/SEMA539YFDD_index_0.html. Retrieved 2009-05-12.
- "Herschel space telescope finishes mission". BBC news. 29 April 2013. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-21934520.
- "Last command sent to ESA's Planck space telescope". European Space Agency. October 23, 2013. http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Science/Planck/Last_command_sent_to_ESA_s_Planck_space_telescope. Retrieved October 23, 2013.
- Fox, Karen C.. "First ARTEMIS Spacecraft Successfully Enters Lunar Orbit". The Sun-Earth Connection: Heliophysics. NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/artemis/news/P1-lunarOrbit.html.
- Hendrix, Susan. "Second ARTEMIS Spacecraft Successfully Enters Lunar Orbit". The Sun-Earth Connection: Heliophysics. NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/artemis/news/P2-lunarOrbit.html.
- "Worldwide launch schedule". Spaceflight Now. 27 November 2013. Archived from the original on 30 May 2010. https://web.archive.org/web/20100530232910/http://www.spaceflightnow.com/tracking/index.html.
- "ESA Science & Technology - Fact Sheet". https://sci.esa.int/web/gaia/-/47354-fact-sheet.
- Jones, Andrew (21 May 2018). "China launches Queqiao relay satellite to support Chang'e 4 lunar far side landing mission". GBTimes. https://gbtimes.com/china-launches-queqiao-relay-satellite-to-support-change-4-lunar-far-side-landing-mission.
- Schmid, P. E. (June 1968). "Lunar Far-Side Communication Satellites". NASA. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19680015886_1968015886.pdf. Retrieved 2008-07-16.
- O'Neill, Gerard K. (September 1974). "The Colonization of Space". Physics Today 27 (9): 32–40. doi:10.1063/1.3128863. Bibcode: 1974PhT....27i..32O. http://www.nss.org/settlement/physicstoday.htm.
- "Extended Tisserand graph and multiple lunar swing-by design with Sun perturbation". JAXA. 3 March 2016. https://indico.esa.int/indico/event/111/session/29/contribution/102/material/slides/2.pdf. Retrieved 2016-06-07.
- "Jim Bridenstine on Twitter" (in en). https://twitter.com/JimBridenstine/status/1012008010150006786.
- "NASA Officially Joins ESA's 'Dark Universe' Mission". JPL/NASA. 24 January 2013. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2013-033. Retrieved 12 April 2013.
- Aravind, Indulekha (15 November 2014). "After Mars Mission, what is Isro planning next?". http://www.business-standard.com/article/beyond-business/man-in-space-and-other-plans-114111401887_1.html.
- "DESTINYについて " (in Japanese). http://destiny.isas.jaxa.jp/about.html.
- "NASA teams evaluating ISS-built Exploration Platform roadmap". June 15, 2012. https://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2012/06/nasa-teams-evaluating-iss-built-exploration-platform-roadmap/.
- Bergin, Chris (December 2011). "Exploration Gateway Platform hosting Reusable Lunar Lander proposed". NASA Spaceflight.com. http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2011/12/exploration-gateway-platform-hosting-reusable-lunar-lander-proposed/. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
- Hertz, Paul (2013-06-04), NASA Astrophysics presentation to American Astronomical Society, https://science.nasa.gov/media/medialibrary/2013/06/04/AAS_TownHall_2013-06_V7A_for_posting.pdf, retrieved 2013-09-10
- Masahashi, Hazumi (1 September 2015). "LiteBIRD" (PDF). indico.cern. https://indico.cern.ch/event/376392/contribution/17/attachments/1147595/1645901/20150901_Hazumi_LiteBIRD_Florence_final.pdf#page=10.
- "宇宙科学・探査分野工程表の取り組み状況について その3" (in Japanese). Space Policy Committee. 13 October 2015. http://www8.cao.go.jp/space/comittee/27-kagaku/kagaku-dai3/siryou4-3.pdf.
- "ESA selects planet-hunting PLATO mission". ESA. 19 February 2014. http://sci.esa.int/plato/53707-esa-selects-planet-hunting-plato-mission/. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- Shibai, Hiroshi (2014-12-31), SPICA, http://cor.gsfc.nasa.gov/copag/aas_jan2015/SPICA_COPAG_4Jan2015.pdf, retrieved 2015-02-24
- "ESA Science & Technology: Athena to study the hot and energetic Universe". ESA. 27 June 2014. http://sci.esa.int/cosmic-vision/54241-athena-to-study-the-hot-and-energetic-universe/. Retrieved 23 August 2014.
- "В РАН рассказали, когда состоится запуск космического телескопа "Спектр-М"". РИА Новости. 2019-06-29. https://ria.ru/20190629/1556035673.html. Retrieved 2019-07-13.
