Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Chemistry, Organic
Thienothiophenes (TT), formed by two annulated thiophene rings, represent fully the planar system, whose embedding into a molecular architecture can significantly improve/alter the fundamental properties of organic, π-conjugated materials.
- thieno[3,2-b]thiophene
- thieno[2,3-b]thiophene
- synthesis
1. Introduction
Nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur represent the traditional triad of elements incorporated within the molecular structure of organic compounds, while only sulphur is capable to accommodate electrons in d atomic orbitals. Due to this electronic feature, sulfur possesses unique binding possibilities and can be integrated into a π-conjugated system. These are typically found in organic push–pull chromophores [1,2,3] and active substances of various (opto)electronic and photonic devices [4,5,6]. The simplest five-membered sulphur-based heteroaromatic compound, known since 19th century [7], is thiophene. It is found in many functional materials (e.g., poly-3-hexylthiophene or poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) [8]). Thiophene derivatives are often used as semiconducting [9], light-harvesting [10] or electroluminescent [11] substances. Electronic communication and intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) across molecules built from thiophene units, mostly depend on their connectivity and structural arrangement. A large dihedral angle and non-planar arrangement are general obstacles hindering the efficient ICT. On the contrary, thienothiophenes (TT), formed by two annulated thiophene rings, represent fully the planar system, whose embedding into a molecular architecture can significantly improve/alter the fundamental properties of organic, π-conjugated materials. Principally, there are four TT isomers differing in mutual orientation of both cycles (Figure 1) [12]. Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene 1 and thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2 are the most stable derivatives, as compared to thieno[3,4-b]thiophene 3 and the very unstable thieno[3,4-c]thiophene 4.
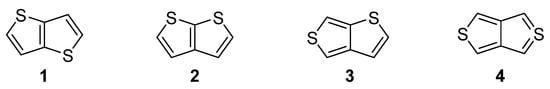
Figure 1. Molecular structure of four possible TT isomers 1–4.
Thieno[3,2-b]thiophene 1 or its structural analogue thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2, can serve as an auxiliary electron-donor unit [13] or π-linker mediating the ICT between the donor and acceptor [14]. The latter can be considered as a suitable alternative to commonly used π-linkers (e.g., 1,4-phenylene or 2,5-thienylene [15]) (Figure 2).
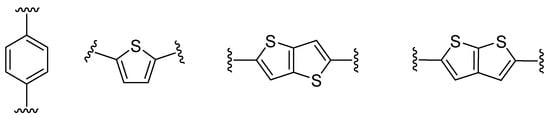
Figure 2. π-Linker examples commonly used in push–pull molecules.
The main limitation of thienothiophenes is instability of the unsubstituted isomers 3 and 4 preventing their facile preparation. Moreover, a successful synthetic method towards TTs 1 and 2 depends mostly on the attained overall yield, the number of reaction steps and the availability of the used starting materials. The method should be also operationally easy and should proceed via stable intermediates. Methods 1–14, listed below and their comparison, summarized in Table 1, review the current synthetic state-of-the-art towards 1 and 2.
Based on the aforementioned structural features and consequent properties, TT derivatives found wide applications across material sciences. TTs were applied as an active emissive layer of organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) [16]. The colour of the emitted light in the OLED fundamentally depends on the level of the highest/lowest (un)occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO/LUMO) of the used organic emitter. Hence, the colour can be easily adjusted by the structural variation of the organic chromophore, (e.g., by embedding TT moiety). The opposite physical principle to OLEDs is found in organic solar cells (OSCs) converting light energy into the electricity. For instance, thienothiophene derivatives were used in bulk heterojunction solar cells (BHJ) [17]. The dye sensitized solar cell (DSSC) represents another type of OSC, where TTs were also investigated [18].
2. Synthesis
2.1. Synthesis of Thieno[3,2-b]hiophene 1
The current literature reports six principal synthetic routes towards thieno[3,2-b]thiophene 1, which were sorted into Methods 1–6, as discussed in the following text.
2.1.1. Method 1
The first synthetic approach outlined in Scheme 1, consists of a four-step reaction sequence entitled Method 1 [24,25,26,27,28]. 3-bromothiophene 5 was selectively lithiated at position 2 using LDA and the formed lithium species was trapped by the reaction with N-formylpiperidine [24,25,28] or N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) [26], affording aldehyde 6. It further underwent a cyclization with ethyl thioglycolate, in the presence of potassium carbonate as a base. Both C=C and C-S bonds in 7 were established within this step. Using lithium or sodium hydroxide, ester 7 was hydrolysed to carboxylic acid 8, which underwent a final decarboxylation, accomplished either by Cu/quinoline [25] or Cu2O/N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) [28]. The overall yield of this reaction sequence is about 50%.
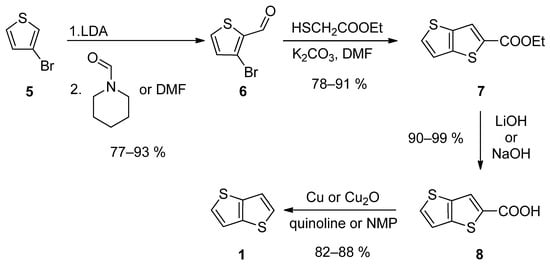
Scheme 1. Four-step Method 1.
2.1.2. Method 2
This method also starts from 3-bromothiophene 5 and involves three main reaction steps (Scheme 2) [29,30,31]. The lithiation of 5 and subsequent reaction with elementary sulphur afforded in-situ thiolate intermediate, which further substituted halogen atom in either potassium chloroacetate [29,30] or potassium bromoacetate [31] to give carboxylic acid 9. The subsequent cyclization can be performed in two ways. The first one involves acid-catalysed (H2SO4) cyclization [29,30], while Leriche et al. [31] prepared the corresponding acyl chloride first, which underwent the subsequent intramolecular Friedel–Crafts acylation. The formed ketone 10 was reduced to the intermediate alcohol 11, either by NaBH4 [29,31] or LiAlH4 [30]. Alcohol 11 forms 1 by the subsequent acid work up. This reaction sequence affords 1 in the 36% overall yield.
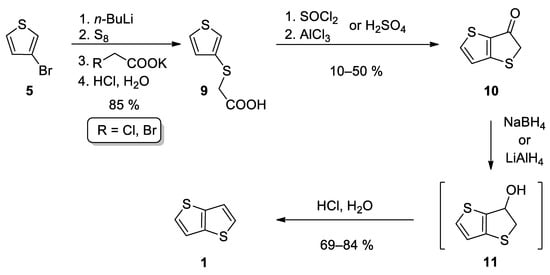
Scheme 2. Synthesis of 1 according to Method 2.
2.1.3. Method 3
TT 1 can be also prepared by a two-step synthesis via acetal 13, as a key precursor (Scheme 3). It can be prepared either from 3-bromothiophene 5 or thiophene-3-thiol 14 [32,33]. The lithiation of 5 provided intermediate 3-lithiumthiophene, which reacted with disulfide 12 [33]. Alternatively, thiolate generated by deprotonation of the starting thiophene-3-thiol 14, substitutes bromine in 2,2-diethoxyethylbromide [32]. The final cyclization of 13 to 1 was assisted either by poly(4-styrene)sulphonic acid (PSSA) or phosphorous oxide [32,33]. The overall yields were 12% [32] and 67% [33], respectively.
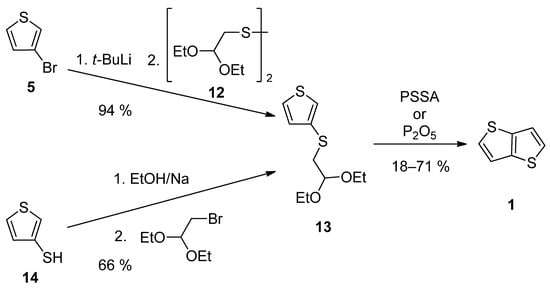
Scheme 3. Preparation of 1 via acetal 13—Method 3.
2.1.4. Method 4
A comprehensive eight-step synthetic sequence towards TT 1 has been reported by Schroth et al. [34] (Scheme 4). The starting 3-bromothiophene 5 was converted to sulphide 15 via lithiation and the reaction with dibenzyldisulphide. The further synthetic steps involved the preparation of alkyne 18, either via the Vilsmeier–Haack formylation (15–16), the Corey–Fuchs dibromoolefination (16–17) and treatment with n-BuLi or the bromination with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), affording 19 with the subsequent Sonogashira cross-coupling (19–20) and the final deprotection of the formed acetylene with sodium hydroxide. The next joint step is an addition of benzylthiol and the replacement of two benzyl groups in 21, by the acetyl groups by lithium 1-(N,N-dimethylamino)naphtalenide (LDMAN) and acetyl chloride. Thioester 22 underwent an alkaline hydrolysis and oxidation affording bisulphide intermediate 23, which rearranged to 1 under the irradiation with daylight. The overall yield of Method 4 is 2% for pathway, using the Vilsmeier–Haack formylation. Considering the pathway containing the Sonogashira reaction, the overall yield toward the final intermediate 23, is 6%. The yield of the last photochemical reaction step is given in the literature.
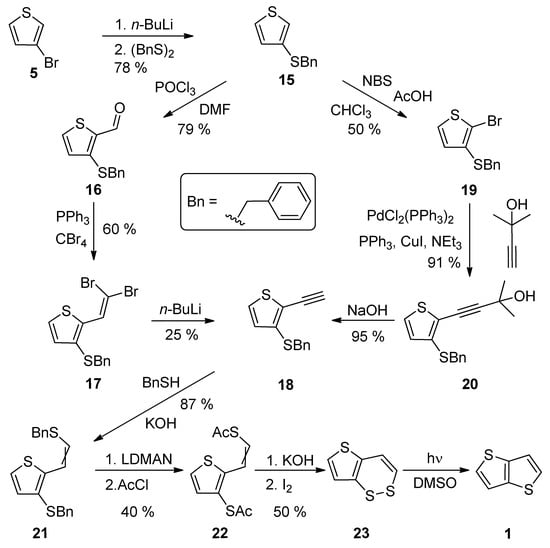
Scheme 4. Synthesis of thieno[3,2-b]thiophene 1 via Method 4.
2.1.5. Method 5
3-Bromothiophene-2-carbaldehyde 6 was used in a three-step synthetic pathway (Scheme 5) [35]. The bromine atom in 6 was substituted with the aid of sodium tert-butylthiolate to aldehyde 24, which underwent the Seyferth–Gilbert homologization, using dimethyl-1-diazo-2-oxo-phenylethylphosphonate. In the final step, the terminal alkyne 25 was cyclized to target 1 under the catalysis of gold(I) chloride with an overall yield of 48%.
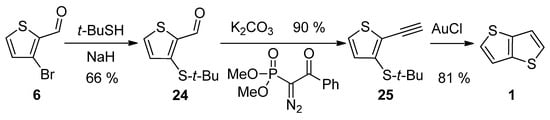
Scheme 5. Method 5, starting from 3-bromothiophene-2-carbaldehyde.
2.1.6. Method 6
The last of the six synthetic pathways towards TT 1 utilizes a selective Sonogashira cross-coupling of 3-bromo-2-iodothiophene 26 and trimethylsilyl(TMS)acetylene (Scheme 6) [36]. The TMS-terminated alkyne 27 further underwent reduction with di(iso-butyl)aluminium hydride (DIBAL) and bromination with NBS. The resulting dibromo derivative 28 was lithiated to 29, which subsequently reacted with bis(phenylsulphonyl)sulphide. The final TMS-group removal by tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) afforded 1. The yields of the particular reaction steps are not given in the literature.
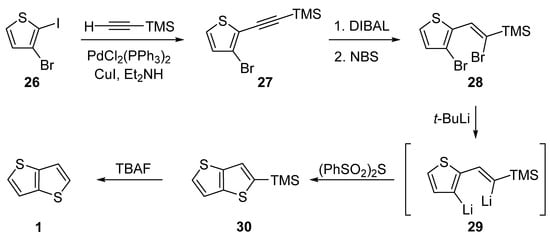
Scheme 6. Selective Sonogashira cross-coupling in the synthesis of 1 (Method 6).
2.2. Synthesis of Thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2
Methods 7–14 represent the currently available synthetic pathways to thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2.
2.2.1. Method 7
1-Methoxy-1-en-3-yne 31 was utilized in Method 7 (Scheme 7) [37,38,39,40]. Its TMS-protection, lithiation (33) and methylation with iodomethane afforded diyne 34. These transformations can be also performed as a one-pot reaction [39]. The final step(s) involved three in-situ potassium intermediates 35–37. The first allene 35 is generated by treating 34 with the superbase LiC-KOR. Further reaction with carbon disulfide afforded 36, which provided diyne-bis(thiolate) 37, by adding LiC-KOR again. The cyclization of diyne-bis(thiolate) 37 in the presence of hexamethylphosphoric acid triamide (HMPA) yielded the target TT 2 in a 40% overall yield.
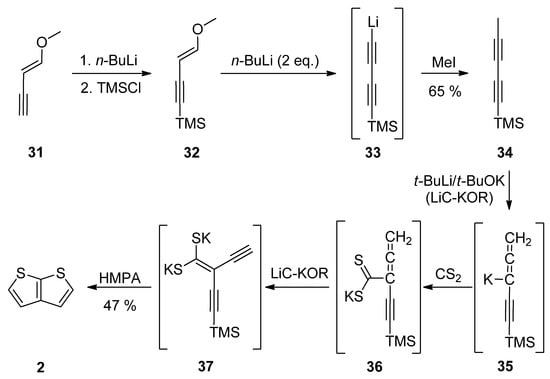
Scheme 7. Preparation of 2 via the cyclization of diyne-bis(thiolate)—Method 7.
2.2.2. Method 8
Similarly to the key intermediate of Method 7—diyne-bis(thiolate) 37, Method 8 utilizes dicyano-bis(thiolate) 38 (Scheme 8) [41], which was prepared from malononitrile and carbon disulphide. Its reaction with two ethyl-bromoacetates provided the tetrasubstituted TT derivative 39. The amino groups at positions 3 and 4 were removed by diazotization (40) and the reaction with hypophosphorous acid towards molecule 41. The esters were hydrolysed and the corresponding dicarboxylic acid 42 underwent the final decarboxylation to the unsubstituted thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2 in a 30% overall yield.
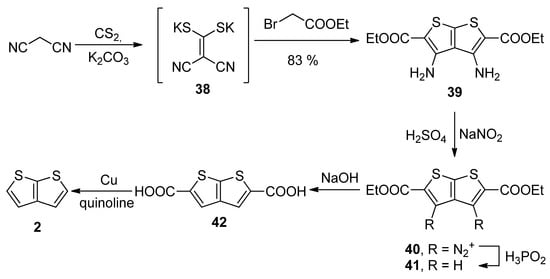
Scheme 8. Preparation of 2 via the cyclization of dicyano-bis(thiolate)—Method 8.
2.2.3. Method 9
Gas phase one-step synthesis starting from allyl(thiophen-2-yl)sulphide 43 is shown in Scheme 9 [42]. The sulphide 43 was thermally cleaved, providing the radical 44, which subsequently reacted with acetylene. In the last step, the formed (thiophen-2-yl)vinylsulphide radical 45 cyclized to thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2, as a major product (25% yield) at 460 °C.
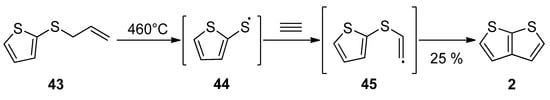
Scheme 9. Gas phase reaction of allyl(thiophen-2-yl)sulphide to TT 2—Method 9.
2.2.4. Method 10
One of the oldest synthetic attempts towards TT 2, is depicted in Scheme 10 [43,44,45,46]. Among other side products, a gas phase condensation of acetylene with various mixtures of sulphane, hydrogen or elementary sulphur at 600 °C afforded 2 with an unspecified yield. Hence, the synthetic utilization of this procedure is rather low.
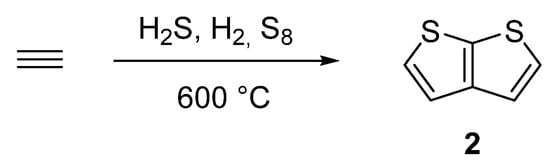
Scheme 10. Gas phase cyclization of acetylene to thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2—Method 10.
2.2.5. Method 11
Another older procedure reported the preparation of thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2 from aconitic acid 46a [47] or the structurally related citric acid 46b (Method 11, Scheme 11) [48,49,50]. Both acids can be cyclized to 2 in the presence of elementary sulphur and phosphorous sulphides, such as P2S3 or P4S3. However, the yields of this procedure were not given.
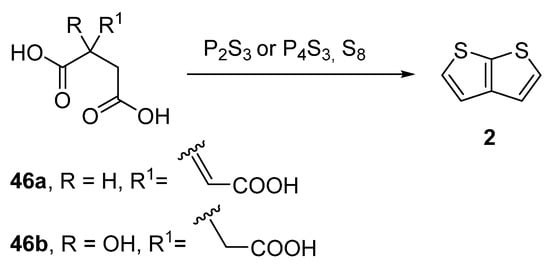
Scheme 11. Cyclization of aconitic and citric acids to 2—Method 11.
2.2.6. Method 12
Method 12 towards 2, is a similar reaction pathway to Method 6 (see Scheme 6 and Scheme 12) used for the construction of 1 [36]. Both methods differ in the halide substitution of the starting thiophene 47 vs. 26. Starting from 2-bromo-3-iodothiophene 47 and involving the Sonogashira reaction, reduction, bromination, lithiation, cyclization and the TMS-group removal, TT derivative 2 can be prepared in an 18% overall yield (Scheme 12).
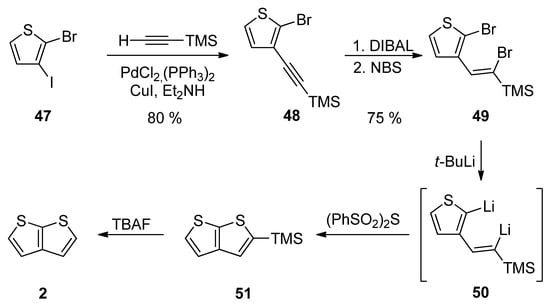
Scheme 12. Sonogashira reaction in preparation of 2—Method 12.
2.2.7. Method 13
This method, utilizing acetal 53, is analogous to Method 3 working with acetal 13 (see Scheme 3 and Scheme 13) [32,51]. The starting 2-sulphanylthiophene 52 replaced the bromine atom in 1,1-dimethoxyethylbromide as S-nucleophile in the presence of potassium carbonate [51] or sodium ethanolate [32]. The formed acetal 53 was cyclized to 2, using phosphorous oxide [32] or polyphosphoric acid (PPA) [51]. The overall yield of this reaction sequence is 7%.
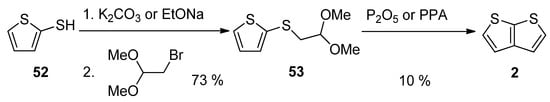
Scheme 13. Cyclization of acetal 53—Method 13.
2.2.8. Method 14
Thiophene-3-carbaldehyde 54 has been utilized as a suitable starting material within our synthetic approach to 2 (Scheme 14) [28]. The aldehyde was firstly converted to acetal 55, which was lithiated, reacted with elementary sulphur and the produced S-nucleophile reacted with methyl-bromoacetate to intermediate 56. The deprotection of formyl group (57) allowed the cyclization to the thienothiophene scaffold in the presence of 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU). The resulting ester 58 was hydrolysed to carboxylic acid 59, which underwent decarboxylation to target thieno[2,3-b]thiophene 2. This procedure provides 2 in 13% overall yield.
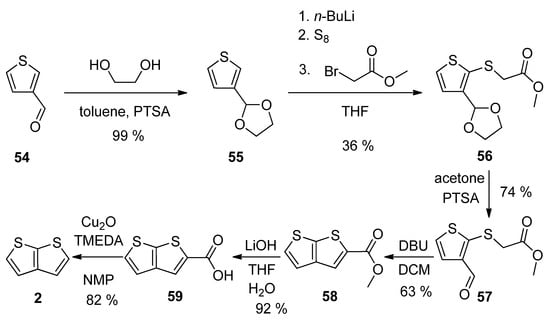
Scheme 14. Method 14, starting from thiophene-3-carbaldehyde.
All six listed synthetic methods towards TT 1, start from the 3-monosubstituted or 2,3-disubstituted thiophene heterocycle, while the second ring is created during the synthesis. The sulphur atom is mostly incorporated through the reactions based on the nucleophilic aromatic substitution mechanism, with the exception of Method 6, where sulphur is inserted within the cyclization step. The prepared intermediates are cyclized via addition-elimination (Method 1–3) or by the triple bond reduction (Method 4 and 5). The achieved overall yields and the number of reaction steps are summarized in Table 1. Considering the number of involved steps and the overall yield, Method 3 (2/67%) seems to be the best synthetic route. However, the used reagents are rather unavailable and expensive, which makes Method 3 economically less feasible, similarly to Method 5 (3/48%). The four-step Method 1, with the 50% overall yield, commercially available reagents and feasible chemical transformation, is probably the most rational synthetic approach towards TT 1.
Table 1. The summary of the reviewed synthetic methods.
| Method | Target TT Molecule | Number of Steps | Overall Yield [%] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 50 | [24,25,26,27,28] |
| 2 | 1 | 4 | 36 | [29,30,31] |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 12/67 | [32,33] |
| 4 | 1 | 8 | - | [34] |
| 5 | 1 | 3 | 48 | [35] |
| 6 | 1 | 4 | - | [36] |
| 7 | 2 | 4 | 40 | [37,38,39,40] |
| 8 | 2 | 4 | 30 | [41] |
| 9 | 2 | 1 | 25 | [42] |
| 10 | 2 | 1 | - | [43,44,45,46] |
| 11 | 2 | 1 | - | [47,48,49,50] |
| 12 | 2 | 4 | 18 | [36] |
| 13 | 2 | 2 | 7 | [32,51] |
| 14 | 2 | 6 | 13 | [28] |
Methods 7–14 towards TT 2 are very different in the used starting compounds, often with a simple molecular structure (e.g., malononitrile (Method 8), carbon disulphide (Method 7 and 8) or acetylene (Method 10)). Some synthetic routes (Method 9 and 12–14) use substituted thiophenes analogously to TT 1. Except carbon disulphide, sulphur is incorporated from simple substances, such as sulphane, various sulphides or elementary sulphur. At the first sight, the highest overall yield (40%) was found for the four-step Method 7. However, the commercial availability of the starting compound 31 makes it less useful. One-step syntheses (Method 9–11) seem to be tempting, but the gas phase reactions (Method 9 and 10) at high temperatures (460 or 600 °C, respectively) and obtained complex mixtures are rather unfit for a gram-scale preparation of TT 2. Furthermore, there are no yields given for Methods 10 and 11. Methods 12 and 13 work with expensive reagents and provide a very low yield of 2. Our developed strategy (Method 14) operates with easy steps, uses only commercially available and inexpensive reagents, and TT 2 can be isolated in a 13% overall yield after six steps.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/org3040029
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
