A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks instead of being slaughtered to harvest animal products. Some are beasts of burden (draught animals) that provide transportation (e.g. riding horses and camels) and aid in physical labor (e.g. oxens and elephants), while others are service animals trained to execute certain specialized tasks (e.g. hunting and guide dogs, messenger pigeons and fishing cormorants). They may also be used for milking or herding. Some, at the end of their working lives, may also be used for meat or other products such as leather. The history of working animals may predate agriculture, with dogs used by our hunter-gatherer ancestors. Around the world, millions of animals work in relationship with their owners. Domesticated species are often bred for different uses and conditions, especially horses and working dogs. Working animals are usually raised on farms, though some are still captured from the wild, such as dolphins and some Asian elephants. People have found uses for a wide variety of abilities in animals, and even industrialised societies use many animals for work. People use the strength of horses, elephants, and oxen to pull carts and move loads. Police forces use dogs for finding illegal substances and assisting in apprehending wanted persons, others use dogs to find game or search for missing or trapped people. People use various animals — camels, donkeys, horses, dogs, etc.—for transport, either for riding or to pull wagons and sleds. Other animals, including dogs and monkeys, help disabled people. On rare occasions, wild animals are not only tamed, but trained to perform work—though often solely for novelty or entertainment, as such animals tend to lack the trustworthiness and mild temper of true domesticated working animals. Conversely, not all domesticated animals are working animals. For example, while cats may catch mice, it is an instinctive behaviour, not one that can be trained by human intervention. Other domesticated animals, such as sheep or rabbits, may have agricultural uses for meat, hides and wool, but are not suitable for work. Finally, small domestic pets, such as most small birds (other than certain types of pigeon) are generally incapable of performing work other than providing companionship.
- wild animals
- domesticated animals
- working animals
1. Roles and Specializations
1.1. Transportation
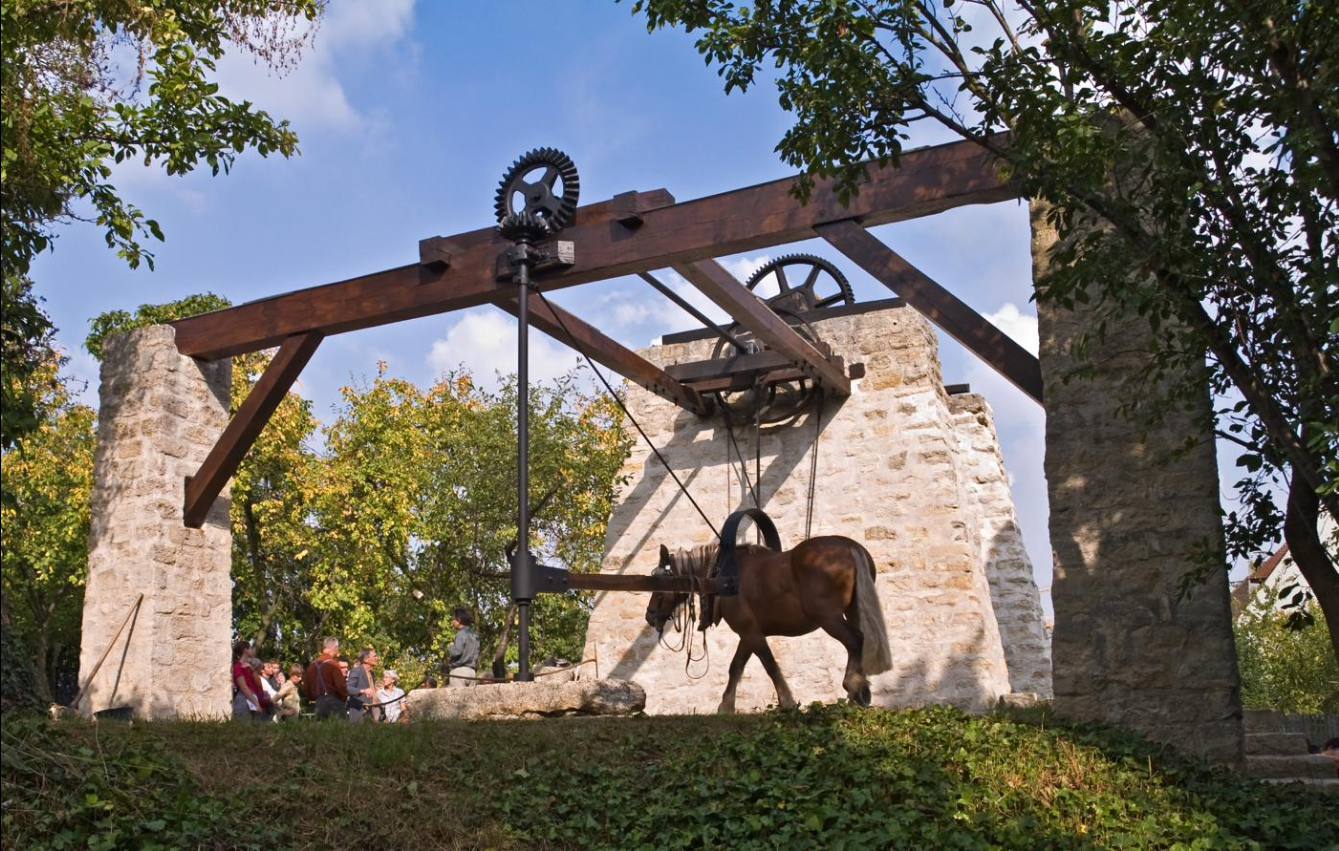

Some animals are used due to sheer physical strength in tasks such as ploughing or logging. Such animals are grouped as a draught or draft animals. Others may be used as pack animals, for animal-powered transport, the movement of people and goods. Together, these are sometimes called beasts of burden. Some animals are ridden by people on their backs and are known as mounts. Alternatively, one or more animals in harness may be used to pull vehicles.
Riding animals or mounts
They mainly include equines such as horses, donkeys, and mules; bovines such as cattle, water buffalo, and yak. In some places, elephants, llamas and camels are also used. Dromedary camels are in arid areas of Australia, North Africa and the Middle East; the less common Bactrian camel inhabits central and East Asia; both are used as working animals. On occasion, reindeer, though usually driven, may be ridden.
Certain wild animals have been tamed and used for riding, usually for novelty purposes, including the zebra and the ostrich. Some mythical creatures are believed to act as divine mounts, such as garuda in Hinduism (See vahana for divine mounts in Hinduism) and the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology.
Pack animals
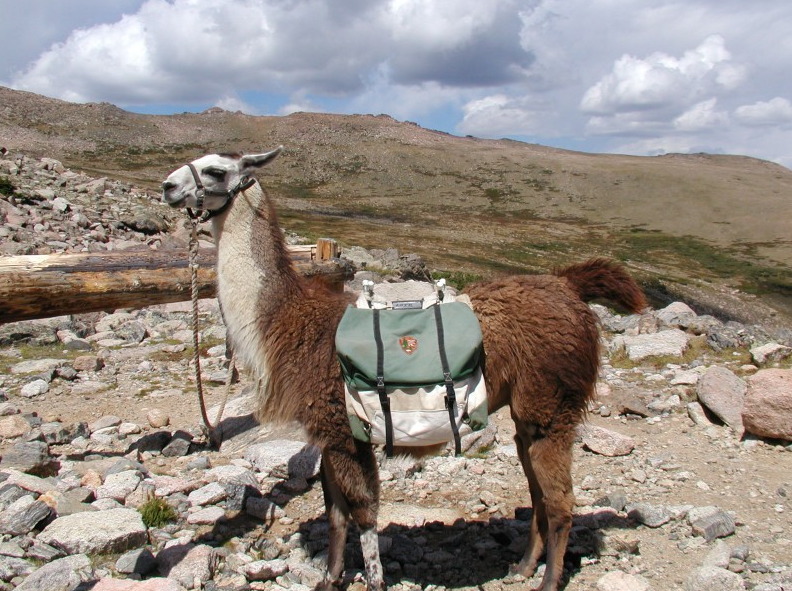

Pack animals may be of the same species as mounts or harness animals, though animals such as horses, mules, donkeys, reindeer and both types of camel may have individual bloodlines or breeds that have been selectively bred for packing. Additional species are only used to carry loads, including llamas in the Andes.
Domesticated cattle and yaks are also used as pack animals. Other species used to carry cargo include dogs and pack goats.
Draft animals
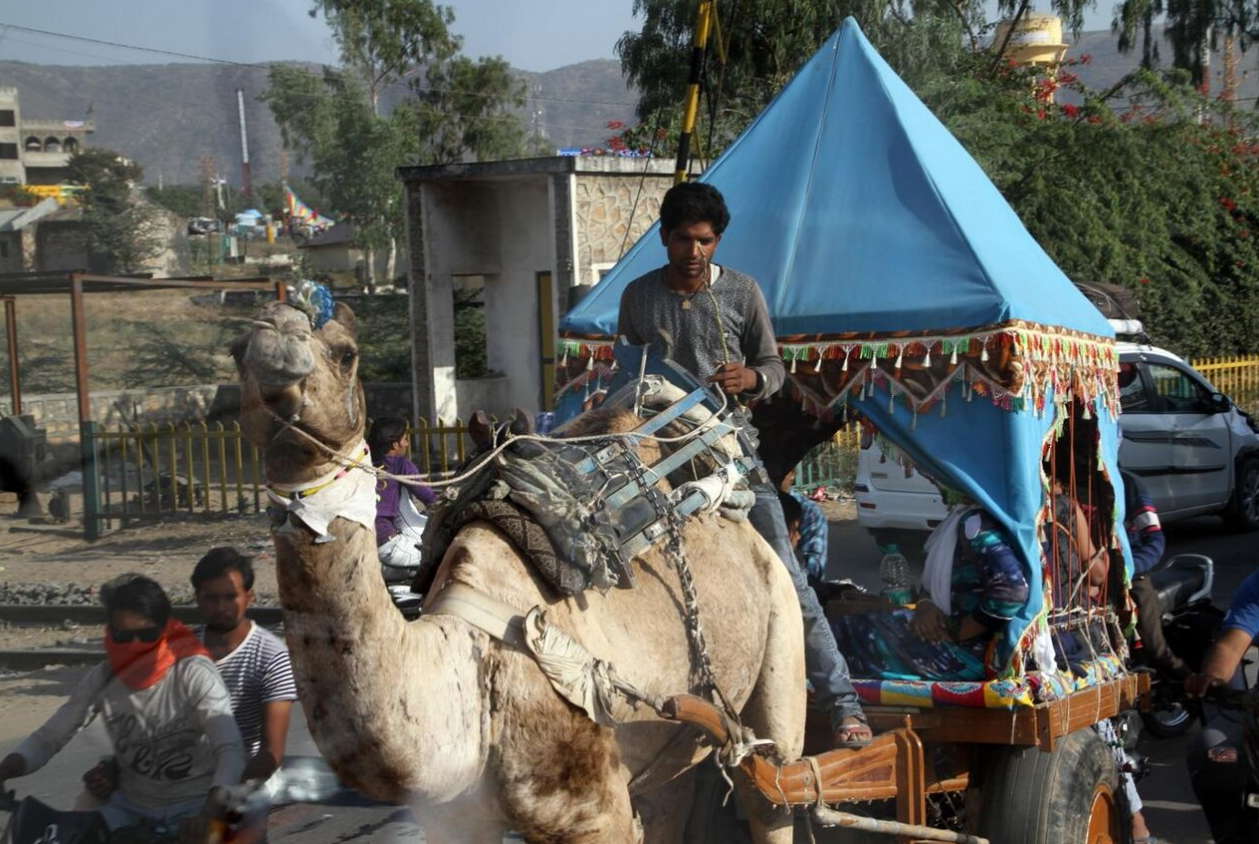
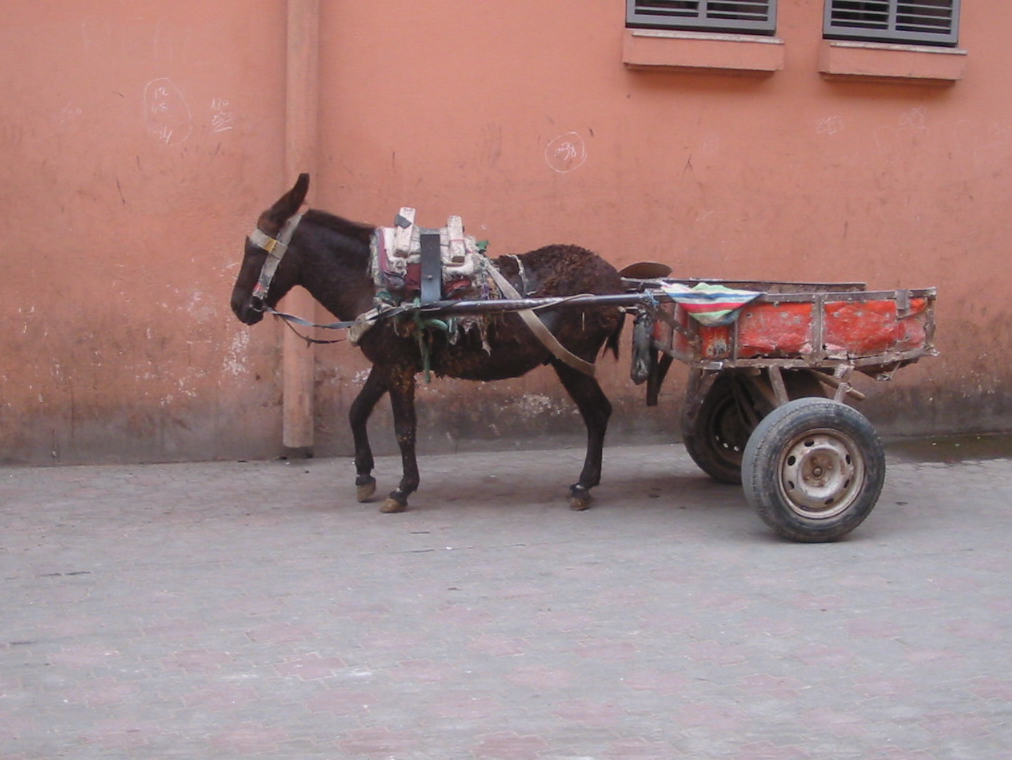

An intermediate use is as draft animals, harnessed singly or in teams, to pull sleds, wheeled vehicles or ploughs.
- Oxen are slow but strong, and have been used in a yoke since ancient times: the earliest surviving vehicle, Puabi's Sumerian sledge, was ox-drawn; an acre was originally defined as the area a span of oxen could plow in a day. The water buffalo and carabao, domesticated water buffalo, pull wagons and ploughs in Southeast Asia and the Philippines .
- Draught or draft horses are commonly used in harness for heavy work. Several breeds of medium-weight horses are used to pull lighter wheeled carts, carriages and buggies when a certain amount of speed or style is desirable.
- Mules are considered tough and strong, with harness capacity dependent on the type of horse mare used to produce the mule foal. Because they are a hybrid animal and usually are infertile, separate breeding programs must also be maintained.
- Ponies and donkeys are often used to pull carts and small wagons. Historically, ponies were commonly used in mining to pull ore carts.
- Dogs are used for pulling light carts or, particularly, sleds (e.g. sled dogs such as huskies) for both recreation and working purposes.
- Goats also can perform light harness work in front of carts
- Reindeer are used in the Arctic and sub-Arctic Nordic countries and Siberia. During World War II, the Red Army deployed deer transportation battalions on the Eastern Front.[1] In the twenty-first century, Russian soldiers continue to train with reindeer sleds in winter.[2] In traditional festive legend, Santa Claus's reindeer pull a sleigh through the night sky to help Santa Claus deliver gifts to children on Christmas Eve.
- Elephants are still used for logging in Southeast Asia.
- Less often, camels and llamas have been trained to harness. According to Juan Ignacio Molina the Dutch captain Joris van Spilbergen observed the use of chiliquenes (a llama type) by native Mapuches of Mocha Island as plough animals in 1614.[3]
Assorted wild animals have, on occasion, been tamed and trained to harness, including zebras and even moose.
1.2. Guard Animals
As some domesticated animals display extremely protective or territorial behaviour, certain breeds and species can be utilised to guard property, including dogs, geese, llamas and alpacas.
1.3. Powering Fixed Machinery
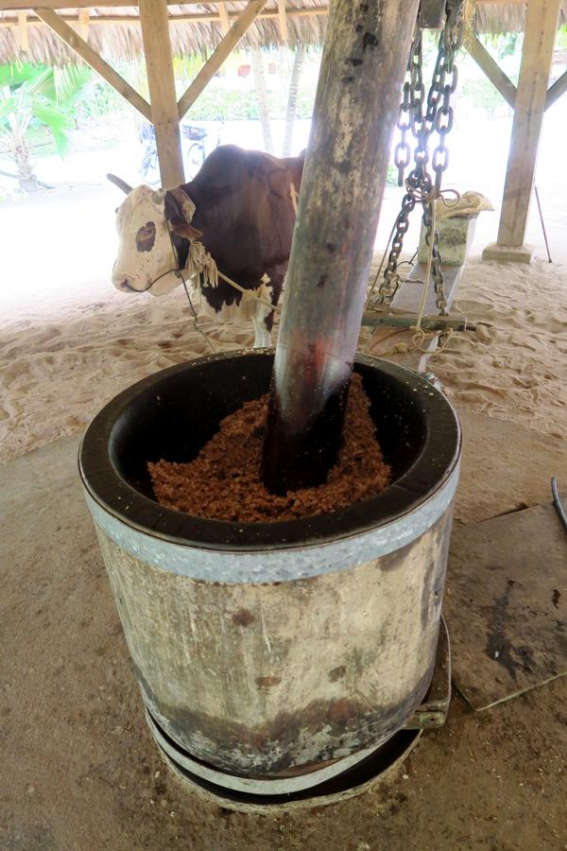

Working draught animals may power fixed machinery using a treadmill and have been used throughout history to power a winch to raise water from a well. Turnspit dogs were formerly used to power roasting jacks for roasting meat.
1.4. Treatment Animals
Working as a form of biological treatment for the environment. Animals such as Asian carps were imported to the U.S. in 1970s to control algae, weed, and parasite growth in aquatic farms, weeds in canal systems, and as one form of sewage treatment.[4]
1.5. Searching and Retrieving
Hunting

As predatory species are naturally equipped to catch prey, this is a further use for animals and birds. This can be done either for sustenance, sport, or to reduce the population of undesired animals that are considered harmful to crops, livestock or the environment.
- Hounds and other dogs are used to kill and fetch prey. Certain breeds have been bred for this task such as pointers and setters.
- Mousers (domestic cats used for hunting small rodents and birds) are one of the oldest working animals having protected food supplies from pests since the foundation of human agriculture.
- Caracals are sometimes used as hunting animals in some parts of the Middle East, although they are normally kept as pets.
- Cheetahs that have been tamed but not domesticated have been used by humans for chasing down prey.
- Ferrets prey on creatures living in burrows, such as rabbits.
- In falconry, birds of prey are used as hunters in the air.
- Aquatic birds, such as cormorants in China, can be used to catch fish.
Humans
- Search and rescue dogs, with their highly developed sense of smell, are used to locate humans, such as escaped prisoners, a thief or people lost in remote areas. They are used also to find people who are trapped, such as in avalanches or collapsed buildings.
- Dogs can also be used to look for dead people.
- Searchers use horses in remote areas to cover large areas of rugged terrain. The horse's natural awareness of their surroundings often alerts human handlers to the presence of something unusual, including lost hikers or hunters. Like some dogs, some horses are trained to follow scent. The use of horses in search and rescue is known as Mounted search and rescue.
- Animals can be used to detect the presence of pathogens and patients carrying infectious diseases. Dogs[5][6][7][8] and bees[9] have been trained to detect COVID-19 infections.
Foods
- Dogs and pigs, with a better sense of smell than humans, can assist with gathering by finding valuable products, such as truffles (a very expensive subterranean fungus). Frenchmen typically use truffle hogs, while Italians mainly use dogs.
- Monkeys are trained to pick coconuts from palm trees, a job many human workers consider as too dangerous.[10]
Contraband
- Detection dogs, commonly employed by law enforcement authorities, are trained to use their senses to detect illegal drugs, explosives, currency, and contraband electronics such as illicit mobile phones, among other things.[11] The sense most used by detection dogs is smell, hence such dogs are also commonly known as 'sniffer dogs'. For this task, dogs may sometimes be used remotely from the suspect item, for example via the Remote Air Sampling for Canine Olfaction ('RASCO') system.[12]
1.6. Interfacing and Organization
Assistance animals
- The best-known example is the guide dog or seeing eye dog for blind people. See also service dog. Miniature horses are also occasionally used for this purpose as well.
- Trained dogs and African, Asian, and American monkeys, such as capuchin monkeys have been taught to provide other functions for impaired people, such as opening mail and minor household tasks of the same like.
Herding

- A very close working relationship exists between a stockman or shepherd, a herding dog, and the herd (or mob) of sheep or cattle. Cattle and sheep herders in other parts of the world also use various dog breeds.
- Certain breeds of horses also have an innate "cow sense" that allows them to effectively carry a rider to the right place at the right time to muster (gather or round up) livestock. See stock horse; cutting horse
2. Employers
2.1. Police and Military
The defensive and offensive capabilities of animals (such as fangs and claws) can be used to protect or to attack humans.
- The guard dog barks or attacks, to warn of an intruder
- War elephants were trained for battle in ancient times and are still used for military transport today.
- Military uses of horses have changed over the millennia but still continue, including for police work.
- Dolphins and sea lions carry markers to attach to mines as well as patrolling harbors.
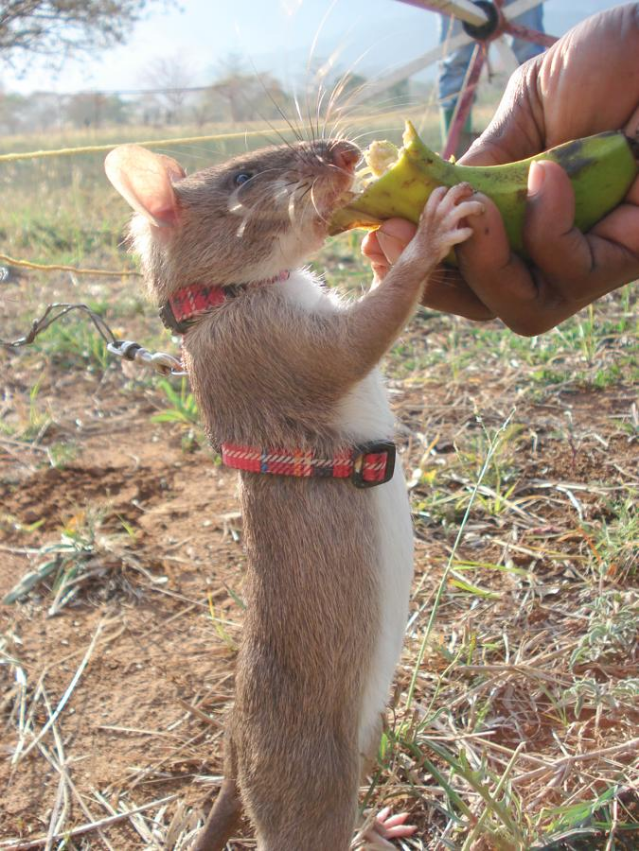
- On land, dogs can be trained to find landmines. Rats, which are lighter and less of a risk to set the mines off, have recently been used more frequently.[13] Detection rats such as those trained by APOPO can also be taught to identify diseases, especially pulmonary tuberculosis.[14]

- Homing pigeons transport material, usually messages on small pieces of paper, by air.
3. Legal Status
In some jurisdictions, certain working animals are afforded greater legal rights than other animals. One such common example is police dogs, which are often afforded additional protections and the same memorial services as human officers.
India law have provision for the in loco parentis for implementing animal welfare laws. Under the India law the non-human entities such as animals, deities, trusts, charitable organizations, corporate, managing bodies, etc. and several other non-human entitles have been given the status of the "legal person" with legal rights and duties, such as to sue and be sued, to own and transfer the property, to pay taxes, etc. In court cases regarding animals, the animals have the status of "legal person" and humans have the legal duty to act as "loco parentis" towards animals welfare like a parent has towards the minor children. In a case of cow-smuggling, the Punjab and Haryana High Court mandated that "entire animal kingdom including avian and aquatic" species has a "distinct legal persona with corresponding rights, duties, and liabilities of a living person" and humans are "loco parentis" while laying out the norms for animal welfare, veterinary treatment, fodder and shelter, e.g. animal drawn carriages must not have more than four humans, and load carrying animals must not be loaded beyond the specified limits and those limits must be halved when animals have to carry the load up a slope. A court while deciding the "Animal Welfare Board of India vs Nagaraja" case in 2014 mandated that animals are also entitled to the fundamental right to freedom[15] enshrined in the Article 21 of Constitution of India i.e. right to life, personal liberty and the right to die with dignity (passive euthanasia). In another case, a court in Uttarakhand state mandated that animals have the same rights as humans.[16]
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Biology:Working_animal
References
- Андрей Зайцев (8 May 2013). "Error: no |title= specified when using {{Cite web}}" (in ru). Мурман. http://murman.rfn.ru/rnews.html?id=1072121&cid=7.
- "Russian soldiers train in sub-zero temperatures with reindeer". BBC. 4 February 2016. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-35487449.
- The Geographical, Natural and Civil History of Chili, Pages 15 and 16, Volume II https://books.google.com/books?id=F4oIAAAAQAAJ
- "Asian Carp Overview". 24 June 2019. https://www.nps.gov/miss/learn/nature/ascarpover.htm.
- Davis, Nicola (25 September 2020). "'Any breed could do it': dogs might be a Covid tester's best friend". The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/sep/25/any-breed-could-do-it-dogs-might-be-covid-testers-best-friend.
- Else, Holly (23 November 2020). "Can dogs smell COVID? Here's what the science says" (in en). Nature: pp. 530–531. doi:10.1038/d41586-020-03149-9. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-020-03149-9.
- Jendrny, Paula; Schulz, Claudia; Twele, Friederike; Meller, Sebastian; von Köckritz-Blickwede, Maren; Osterhaus, Albertus Dominicus Marcellinus Erasmus; Ebbers, Janek; Pilchová, Veronika et al. (23 July 2020). "Scent dog identification of samples from COVID-19 patients – a pilot study". BMC Infectious Diseases 20 (1): 536. doi:10.1186/s12879-020-05281-3. ISSN 1471-2334. PMID 32703188. Available under CC BY 4.0. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
- Grandjean, DominiqueExpression error: Unrecognized word "et". (10 December 2020). "Can the detection dog alert on COVID-19 positive persons by sniffing axillary sweat samples? A proof-of-concept study" (in en). PLOS ONE 15 (12): e0243122. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0243122. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 33301539. Bibcode: 2020PLoSO..1543122G. Available under CC BY 4.0. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
- "Bees in the Netherlands trained to detect COVID-19 infections". Reuters. 2021-05-06. https://www.reuters.com/lifestyle/oddly-enough/bees-netherlands-trained-detect-covid-19-infections-2021-05-06/.
- Nelson, Dean (20 February 2012). "Monkeys to be trained to pick coconuts". The Daily Telegraph. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/india/9093553/Monkeys-to-be-trained-to-pick-coconuts.html.
- Jenkins, Austin (22 July 2009). "KPLU: Dogs Used to Sniff Out Cell Phones in NW Prisons". Publicbroadcasting.net. http://www.publicbroadcasting.net/kplu/news.newsmain/article/0/1/1533129/KPLU.Local.News/Dogs.Used.to.Sniff.Out.Cell.Phones.in.NW.Prisons.
- Remote Air Sampling for Canine Olfaction Published in: Proceedings IEEE 35th Annual 2001 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology, accessed 8 March 2021 DOI: 10.1109/CCST.2001.962819 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/962819
- Bees, Giant African Rats Used to Sniff Landmines. In National Geographic, 10 February 2004. Webpage found 12 March 2010. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/02/0210_040210_minerats.html
- APOPO, Dutch organization that raises and trains detection rats for worldwide use. See also HeroRAT. http://www.apopo.org/
- Democratic Politics Class 9. NCERT.
- Birds to holy rivers: A list of everything India considers “legal persons”, Quartz (publication), September 2019. https://qz.com/india/1636326/who-apart-from-human-beings-are-legal-persons-in-india/
