Shanghai has an extensive public transport system, largely based on buses, trolley buses, taxis, and a rapidly expanding metro system. Shanghai has invested heavily in public transportation before and after the 2010 World Expo, including the construction of the Hongqiao transportation hub of high-speed rail, air, metro and bus routes. Public transport is the major mode of transport in Shanghai as limitations on car purchases were introduced in 1994 in order to limit the growth of automobile traffic and alleviate congestion. New private cars cannot be driven without a license plate, which are sold in monthly license plate auctions which is only accessible for locally registered residents and those who have paid social insurance or individual income taxes for over three years. Around 9,500 license plates are auctioned each month, and the average price is about CN¥89,600 (US$12,739) in 2019. Shanghai (population of 25 million) has over four million cars on the road, the fifth-largest number of any Chinese city. Despite this the city remains plagued by congestion and vehicle pollution. The results of the "2011 Shanghai Public Transport Passenger Flow Survey" released by the Municipal Transportation and Port Bureau showed that the city's public transport travel time was gradually reduced. The average travel distance of public transport in 2011 was 8.5 kilometers, the travel time 50.8 minutes per trip and the travel cost of public transport is gradually reduced: in 2011, the cost of rail transit was 2.4 yuan per trip, down 14% from 2005; the cost of bus and tram trips was 1.8 yuan, down 5% from 2005. Metro accounted for 33% of the public transport passenger volume. In 2018 the public transportation system handled a total of 16.05 million rides on average each day, among which 10.17 million (63%) were made via the Metro and 5.76 million (36%) via buses. Shanghai expressway traffic volume was 1.215 million vehicles on an average day.
- public transportation
- private cars
- public transport
1. Airports
Shanghai is served by two airports: Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport and Shanghai Pudong International Airport. Pudong International Airport is the primary international airport, while Hongqiao International Airport mainly operates domestic flights with limited short-haul international flights.
Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport opened in May 1923 and was the only primary airport of Shanghai. During the 1990s, the expansion of Hongqiao Airport to meet growing demand became impossible as the surrounding urban area was developing significantly, and an alternative to assume all international flights had to be sought. Shanghai Pudong International Airport opened on 1 October 1999. In 2019 Shanghai Pudong International Airport was the second busiest airport in China with 76 million passengers and Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport was the eight busiest airport in China with 45 million passengers (source: List of the busiest airports in China).
2. Long Distance Rail
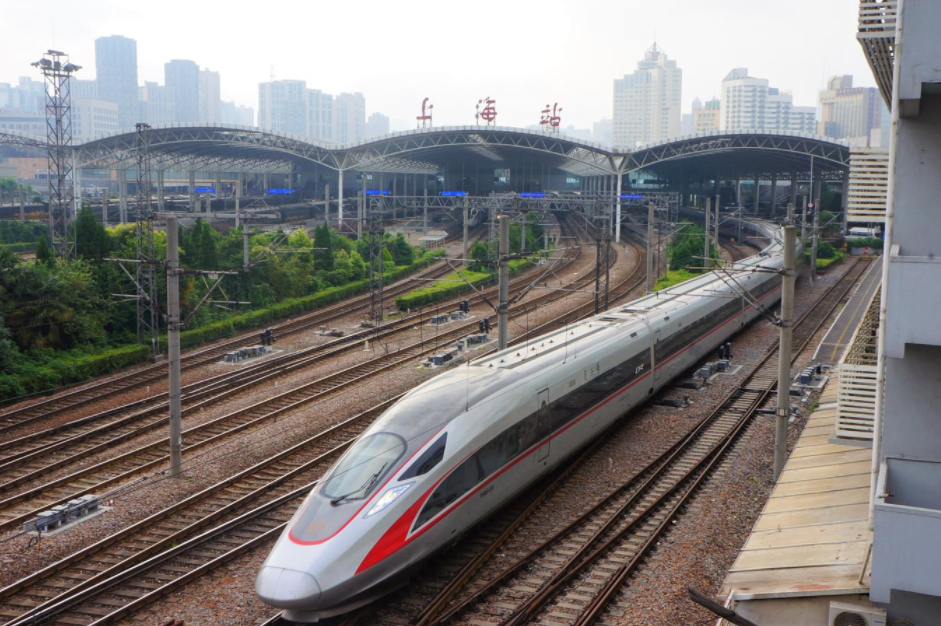

2.1. High Speed Rail
Shanghai has four major railway stations: Shanghai railway station, Shanghai South railway station, Shanghai West railway station, and Shanghai Hongqiao railway station.[1] All are connected to the metro network and serve as hubs in the railway network of China.
Shanghai has four high-speed railways (HSRs): Beijing–Shanghai HSR (overlaps with Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger railway) (opened in 2011), Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway, Shanghai–Kunming HSR, and Shanghai–Nantong railway. One HSR is under construction: Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou HSR.[2][3]
2.2. Conventional Rail
Built in 1876, the Woosung railway was the first railway in Shanghai and the first railway in operation in China[4] By 1909, Shanghai–Nanjing railway and Shanghai–Hangzhou railway were in service.[5][6] (As of October 2019), the two railways have been integrated into two main railways in China: Beijing–Shanghai railway (or Jinghu Railway passing through Nanjing) and Shanghai–Kunming railway (or Huhang Railway passing through Hangzhou), respectively.[7]
3. Shanghai Rail Transit
-
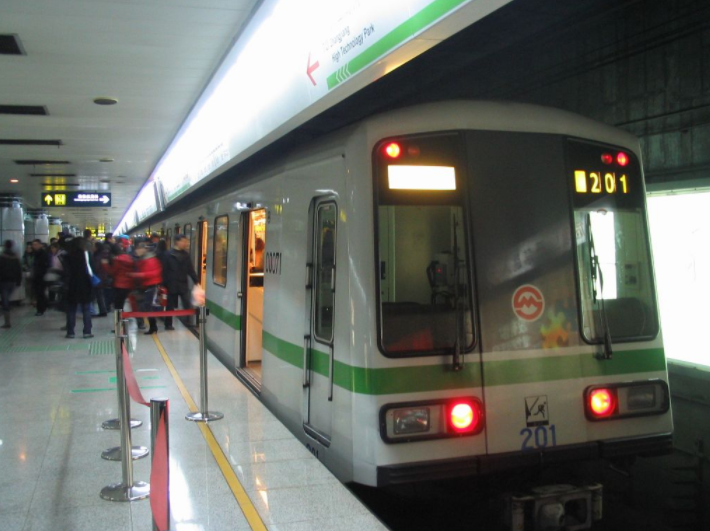

Shanghai Metro Line 2 train passes through People's Square station. https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?curid=1637972
-
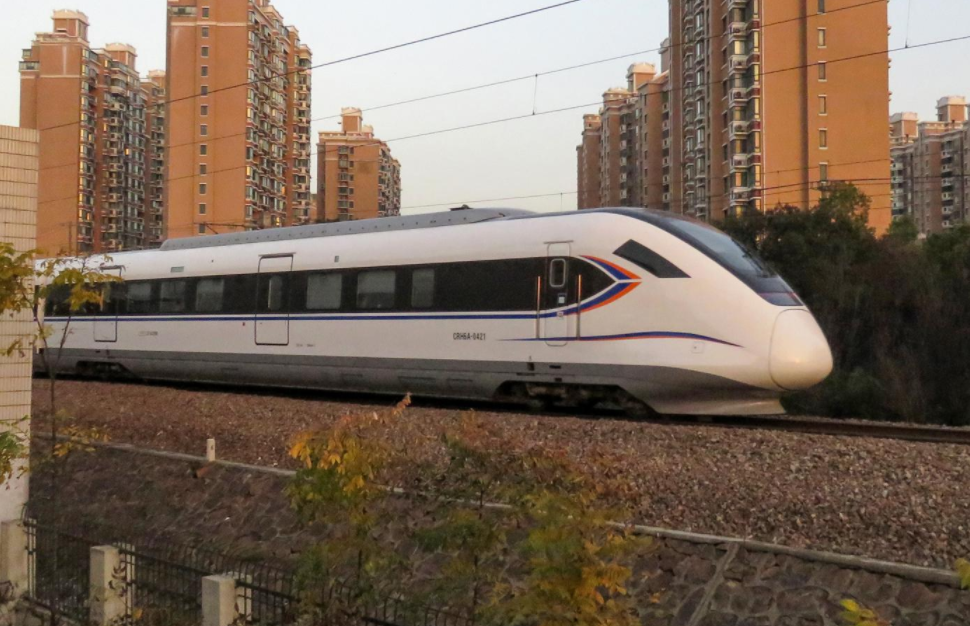

CRH6A train running on Jinshan Railway. https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?curid=1781999
-
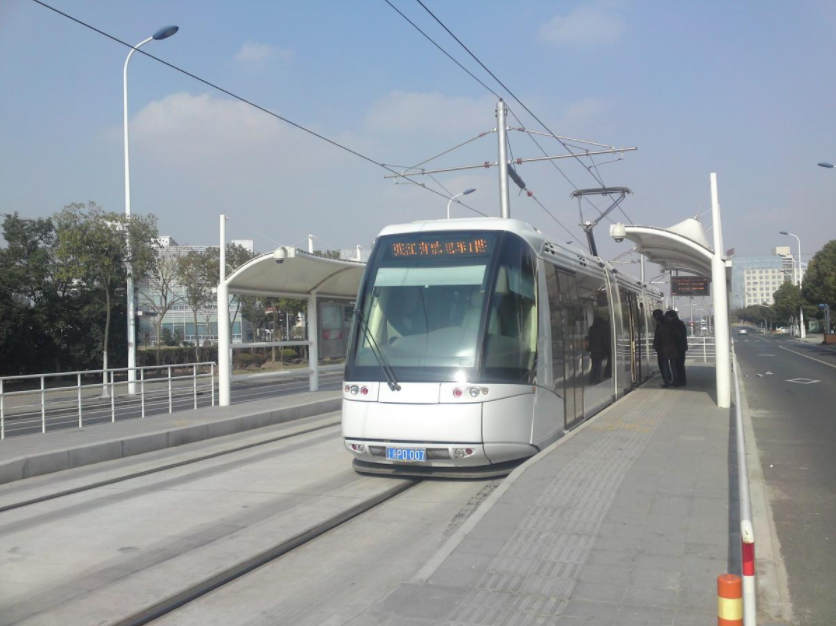

Zhangjiang Tram enters station. https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?curid=1191295
-
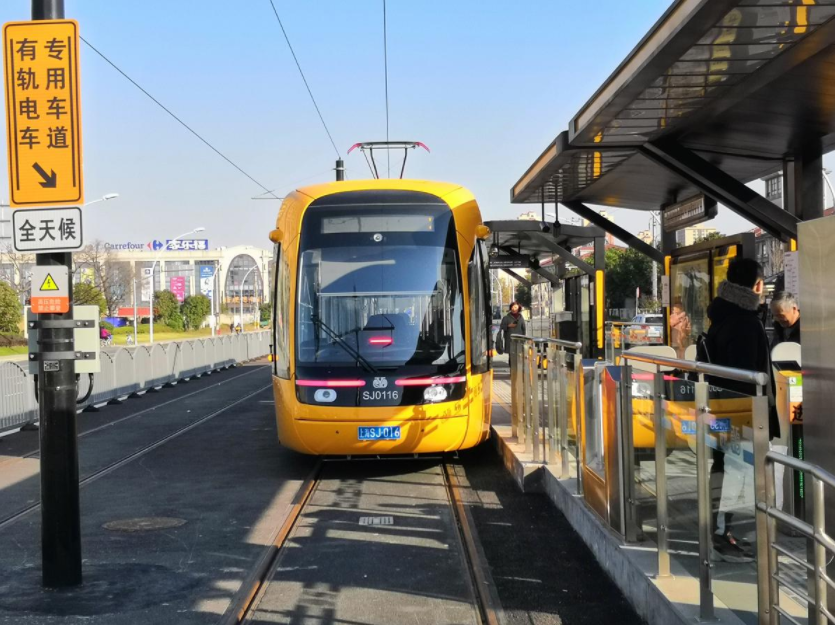

Songjiang Tram line 1 vehicle passes through Canghua Road Station. https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?curid=1766542
-
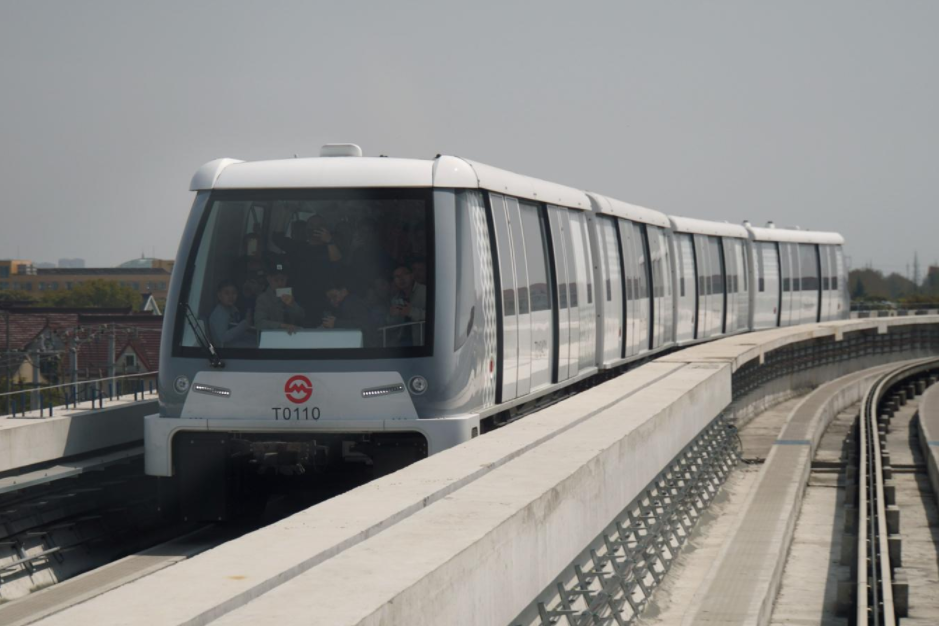

Pujiang line during operation. https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?curid=1451561
-
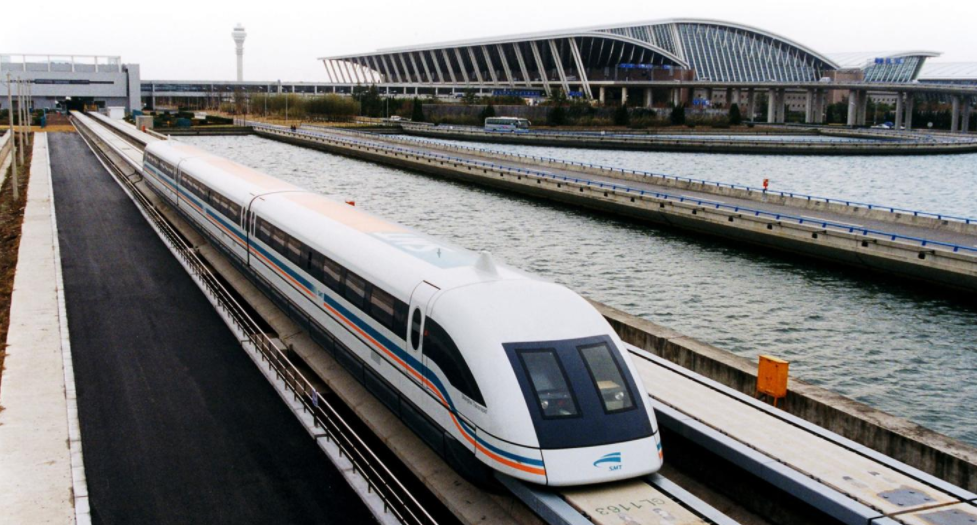

Shanghai maglev train leaves Shanghai Pudong International Airport. https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?curid=1590699
The Shanghai Metro is the biggest component of the Shanghai metropolitan rail transit network, together with the Shanghai maglev train, the Zhangjiang Tram, the Songjiang Tram, and the commuter rail Jinshan railway operated by China Railway Shanghai Group.
| Shanghai metropolitan rail transit network | Common- cement | Latest extension | Number of lines | System length | Number of stations | Operator(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR Commuter rail
(Shanghai Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway) |
2012 | 1 | 56.4 km (35.0 mi) | 8 | China Railway Shanghai Group | |
| Shanghai maglev train | 2002 | 1 | 29.5 km (18.3 mi) | 2 | Shanghai Maglev Transportation Development Co., Ltd. | |
| Shanghai metro | 1993 | 2021 | 19 | 802 km (498.3 mi) | 506 | Shanghai Shentong Metro Group Co., Ltd.;
Kunshan Rail Transit; and Shanghai Maglev Transportation Development Co., Ltd. |
| Shanghai Pudong Airport APM | 2019 | 2 | 3.5 km (2.2 mi) | 4 | Shanghai Keolis | |
| Zhangjiang Tram | 2009 | 1 | 9.8 km (6.1 mi) | 15 | Shanghai Pudong Modern Rail Transit Co., Ltd. | |
| Songjiang Tram | 2018 | 2019 | 2 | 39.4 km (24.5 mi) | 42 | Shanghai Songjiang Tram Investment and Operation Co., Ltd.; Shanghai Keolis |
| Total | 26 | 941 km (585 mi) | 577 | |||
3.1. High-Volume Railway System

Shanghai Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway
Shanghai Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway currently consists only of the Jinshan Railway, also known as Jinshan Line, opened on September 28, 2012, passing through Xuhui, Minhang, Songjiang, and Jinshan districts of Shanghai, with a total length of 56.4 km and 8 stations.[8][9][10] This line is operated by the China Railway Shanghai Group. Three further lines are under construction, namely the Airport Link line, Jiamin line and Lianggang Express. On the Pudong railway passenger service is currently suspended and is planned to be duplicated and electrified before passenger service will resume.
The daily operating time of the Jinshan Line is from 6:00[11] to 21:55.[12] On weekdays, there is another direct train from Shanghai South Station at 5:30. It takes 32 to 60 minutes from the starting station, Jinshanwei Station, to the final station, Shanghai South Station, depending on the number of stops on the way.
The starting fare is 3 yuan, and the full fare is 10 yuan.[9][13][14] Jinshan Line is one of the Shanghai suburban railway lines. In addition to paper tickets, passengers can also use Shanghai Public Transport Card,[15] near-field communication (NFC), and mobile phone boarding code[16] to enter the station. Contrary to China Railway trains, it operates on turn-up-and-go (board any train, no capacity limits, operates outside the national ID-ticketing (实名制) policy). The transfer discount policy for Shanghai public transport service is applicable in this line.[9][17][18]

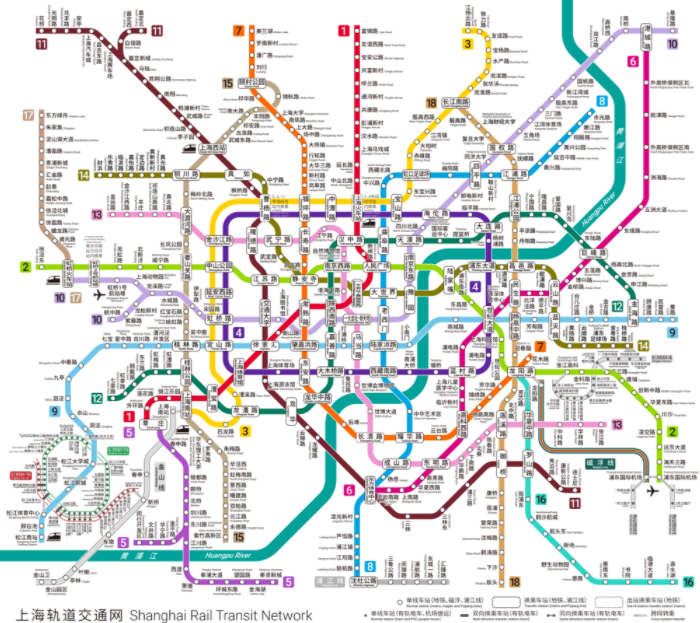
Maglev
Shanghai Maglev Line was opened on December 31, 2002, (Commercial operation started in 2003). The Shanghai maglev train, first commercial Maglev railway in the world, was constructed by Transrapid of Germany in cooperation with the Shanghai municipality and the Shanghai Maglev Transportation Development Co (SMT). It is operated by Shanghai Maglev Transportation Development Co., Ltd.
The length is 29.5 km km and there are two stations in Pudong: Longyang Road and Pudong International Airport. The trip takes 7 minutes and 21 seconds and reaches a maximum speed of 431 km/h (267.8 mph). Normal operating speeds usually reach 431 km/h, but during a test run, the Maglev has been shown to reach a top speed of 501 km/h. The daily service hours are from 6:40[19] to 21:42.[20] Except for the 15-minute interval between the first two trains from Template:Stl Station, the interval for other trains is 20 minutes.[21] An ordinary one-way ticket is 50 yuan, and the passenger holding an air ticket or Shanghai Public Transport Card can enjoy a 20% discount (40 yuan).

Shanghai Metro
Shanghai Metro was opened on May 28, 1993[22] and is one of the busiest urban rail transit systems in the world,[23][24] providing public transport services to 14 municipal districts[25] in Shanghai and Kunshan City in Jiangsu Province. The daily operating hours of Shanghai Metro are approximately from 5:00 to 24:00.[26] On workdays about 12 million people used the subway in 2021, accounting for 70 percent of all users of the city's public transportation network.[27]
As of December 2021, the Shanghai Metro rapid-transit system has 19 lines (numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 and Pujiang Line). Several other lines are under construction. It is the longest metro system in the world with 802 km of metro lines.[28]
Except the Pujiang Line, the other eighteen lines of the Shanghai Metro[29] are all heavy rails. These lines are operated by Shanghai Shentong Metro Group Co., Ltd., except the Huaqiao section of Line 11, which is operated by Kunshan Rail Transit Co., Ltd. The Pujiang Line is a rubber-tyred system which was opened on March 31, 2018, with a total length of 6.69 km and 6 stations. It is operated by Shanghai Keolis.
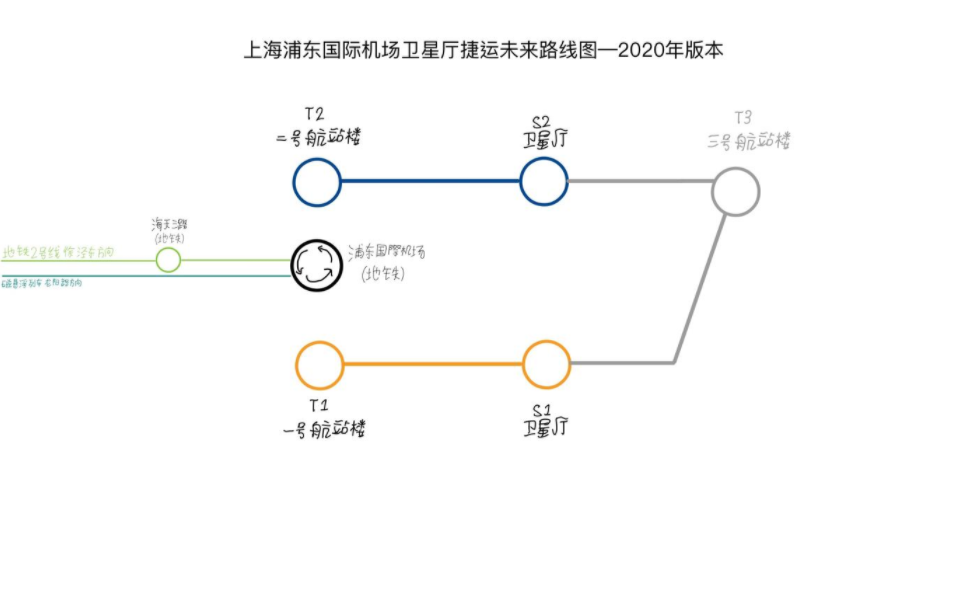
Shanghai Pudong Airport APM
Shanghai Pudong Airport APM is a People Mover opened on September 16, 2019, using A-type metro train system with four cars, runs inside Shanghai Pudong International Airport, including the East Line and the West Line. The operating section of the East Line is 1.65 km long, connecting Terminal 2 and Satellite 2, and the operating section of the West Line is 1.86 km long, connecting Terminal 1 and Satellite 1. Shanghai Keolis operates this transit system.
Trams
First tram line in service was in 1908, phased out after 1963 and were closed in 1975. A modern tram line opened in 2010: Zhangjiang Tram. Another tram system known as the Songjiang Tram was first opened in 2018 which currently has two lines (T1 & T2) that serves the Songjiang District. One tram line is running in Shanghai Movie Park for tourists.
Historic trams (1908-1975)
With the first tram line been in service in 1908, trams were once popular in Shanghai in the early 20th century. The first line ran from the Jing'an Temple to Bund (the route itself now lives on as part of trolleybus route 20 after the line was cancelled). By 1925, there were 328 tramcars and 14 routes operated by Chinese, French, and British companies collaboratively,[30] all of which were nationalized after the PRC's victory in 1949.
Trams in Shanghai were originally phased out after 1963, many tram lines were either dismantled or replaced by trolleybus or motorbus lines;[31] the last tram line was closed and demolished on December 1, 1975.[32]
Zhangjiang Tram
Zhangjiang Tram was opened on December 31, 2009. The whole line is located in Shanghai's Pudong New Area. It is about 10 km long and has 15 stations.[33][34] Zhangjiang tram adopts the French Translohr tram system, with low floor, monorail guidance, rubber wheels, three carriages, and a maximum capacity of about 167 passengers.[35] TEDA Modern Guided Rail Tram in Tianjin uses the same transit system. The line is operated by Shanghai Pudong Modern Rail Transit Co., Ltd., with daily operating hours from 5:45 to 23:00, and a full fare of 2 yuan for the whole line. The transfer discount policy for Shanghai public transport service is applicable in this line.
File:Songjiang Tram Line T2 entering Ronghui Road Station.webm
Songjiang Tram
Songjiang Tram was opened on December 26, 2018, passing through the Songjiang and Minhang districts of Shanghai. It has two lines operated by Shanghai Songjiang Tram Investment Operation Co., Ltd., and Shanghai Keolis, with a total length of about 30 km.[36][37][38] Songjiang tram uses the French Alstom Citadis 302 tramcar, with five carriages and a maximum capacity of about 300 passengers.[37] Chengdu Tram Line 2 uses the same vehicle model. The fare for 10 km or less is 2 yuan. For more than 10 km, the fare increases by 1 yuan for every 10 km.[37] The transfer discount policy for Shanghai public transport service is applicable in this line.
4. Bus

Shanghai has one of the world's most extensive bus systems with nearly one thousand bus lines, operated by numerous transportation companies. Opened in 1914, Shanghai has the world's oldest continuously operating trolley bus system, with 13 routes in operation in 2017. Not all of Shanghai's bus routes are numbered - some have names exclusively in Chinese.[39] Bus fares are usually ¥2, sometimes higher or lower, while Metro fares run from ¥3 to ¥16 depending on distance.
Shanghai has expanded its eco-friendly bus fleet in the 2010s. The goal was to have to 3,000 units by 2015 and to increase the percentage of its new energy buses to its total bus fleet to 30%. From 2014, the number of energy-saving and environmentally friendly buses should account for over 60% of its newly purchased bus fleet.[40]
In 2018, there were 1,543 bus routes. Bus-only lanes reached 363.7 kilometers.[41]
5. Taxi
Before the rapid expansion of the metro, driving a taxi used to be well-paid. Nowadays, it is hard to find people willing to work long hours in a taxi, with the profit margin for each cab much smaller than before.[27] Taxi transportation in Shanghai are offered by 6 major taxi groups.
- 强生出租 (Qiangsheng Taxi) is the biggest taxi company in Shanghai, they operate green and yellow taxis. They also operate a small fleet of accessible golden "London Taxis", making them the only company in Shanghai to operate accessible taxis.
- 海博出租 (Haibo Taxi) operate blue taxis. They operate a small fleet of Roewe all-electric taxis.
- 大众出租 (People's Taxi) operate light cyan taxis over Shanghai. They are the official taxi carrier of the 2010 Shanghai EXPO
- 锦江出租 (Jinjiang Taxi) is a subsidiary of the Shanghai Jinjiang International holdings. They operate white taxis all across Shanghai.
- 蓝色联盟 (Blue Alliance) is a major taxi group consisting of about 15 smaller taxi companies, they operate under the brand Blue Alliance, but all have their own branding on the back of the for-hire sign. They operate dark blue taxis in central Shanghai.
- 法兰红 (French Red) is another taxi group consisting of about 10 smaller taxi companies. They function the same as Blue Alliance, and operate orange taxis in central Shanghai.
Taxi fare is regulated by Shanghai Government.[42]

| Regulated taxi fare | Daytime 5am to 11pm | Night 11pm-5am +30% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First 3 km | ¥14 (sedan) - ¥18 (MPV) | ¥18.2 (sedan) - ¥23.4 (MPV) | |
| Standard rate: -weekdays 7pm-7am -weekends |
Peak +5%: -weekdays 7am-10am -weekdays 4pm-7pm |
Daytime -5%: -weekdays 10am-4pm |
|
| 3–15 km | ¥2.7/km | ¥2.835/km | ¥2.565/km |
| More than 15 km +50% | ¥4.05/km | ¥4.25/km | ¥3.85/km |
Waiting/low speed has a charge for every 4 minutes equal to that for 1.5 km:
- When the car speed is under 12 km/h;
- If the passenger asks the taxi driver to park somewhere while waiting for him or her.
Holiday surcharge:
- 10 yuan for each ride during the Spring Festival holiday;
- 5 yuan for each ride during the National Day and Labor Day holidays and if the Mid-Autumn Festival holiday happens to join the National Day holiday.
This means that if you take a taxi for 15 km, with the first 3 km charged at 16 yuan and with no surcharge for waiting time, you will pay 50 yuan during morning and evening hours on weekdays, about 46 yuan between 10am to 4pm on the same days, and 48.4 yuan otherwise.
6. Transportation Card
All public transport within Shanghai can be paid for using the contactless Shanghai Public Transportation Card (SPTC). With this card the holder can benefit from the transfer discount policy: when the cardholder takes a different suburban/bus/metro/tram within a 120-minute period from first touch-in, the second trip is discounted by 1 RMB.
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Public_transport_in_Shanghai
References
- "Error: no |title= specified when using {{Cite web}}" (in zh). 2 April 2019. http://www.mafengwo.cn/travel-news/220572.html.
- "Error: no |title= specified when using {{Cite web}}" (in zh). 24 December 2012. http://news.huochepiao.com/2012-12/2012122419242969.htm.
- (in zh). 15 July 2019. http://hz.fccs.com/news/5531232.html.
- "Songhu Railway". Office of Shanghai Chronicles. http://www.shtong.gov.cn/node2/node82288/node82292/node82361/userobject1ai111346.html.
- "Error: no |title= specified when using {{Cite web}}" (in zh). Jiangsu People's Government. http://jssdfz.jiangsu.gov.cn/szbook/slsz/tlp/default.htm.
- "Error: no |title= specified when using {{Cite web}}" (in zh). Office of Shanghai Chronicles. 25 December 2003. http://www.shtong.gov.cn/newsite/node2/node2245/node68716/node68721/node68756/node68828/userobject1ai66529.html.
- 辞海编辑委员会, ed (1989). Shanghai Lexicographical Publishing House. p. 2353.
- 新华社. "上海首条快速市域铁路--金山铁路正式开通试运营". 中国政府网. http://www.gov.cn/jrzg/2012-09/28/content_2235245.htm.
- "上海市举行金山铁路建设开通和运营有关情况新闻发布会". www.scio.gov.cn. http://www.scio.gov.cn/xwfbh/gssxwfbh/xwfbh/shanghai/Document/1221504/1221504.htm. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- "金山铁路9月28日试运营[图文_滨海如画_上海金山"]. www.jinshan.gov.cn. https://www.jinshan.gov.cn/jsrh-bhrh/20201011/785585.html. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- Depart from Jinshanwei Station and stop at each station.
- Depart from Jinshanwei Station without stopping midway.
- "时刻表查询". 上海申通地铁集团有限公司. http://service.shmetro.com/hcskb/index.htm.
- "上海金山铁路:市域铁路的"样板" - 科技新闻传播 科技知识普及". www.zghy.org.cn. https://www.zghy.org.cn/item/198062947230994432. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- Physical or virtual card.
- Through apps from Shanghai Public Transport Card, QuickPass, WeChat, Alipay, etc.
- 东方网. "上海金山铁路明天起能用手机乘车码啦!(附问答)". 上海热线. https://news.online.sh.cn/news/gb/content/2020-08/27/content_9631735.htm.
- "金山铁路可刷乘车码 两小时内换乘市内公交优惠-新华网". www.sh.xinhuanet.com. http://www.sh.xinhuanet.com/2020-08/30/c_139328273.htm. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- Depart from Longyang Road Station.
- Depart from Pudong International Airport Station.
- "最新活动". 上海磁浮交通发展有限公司. http://www.smtdc.com/cn/xwzx_xq.html?id=75.
- "Shanghai Subway - Metro". UrbanRail.Net. http://www.urbanrail.net/as/shan/shanghai.htm.
- "上海地铁". 上海申通地铁集团有限公司. http://www.shmetro.com/.
- "2019年上海市国民经济和社会发展统计公报". 上海市统计局. http://tjj.sh.gov.cn/tjgb/20200329/05f0f4abb2d448a69e4517f6a6448819.html.
- Shanghai metro extends to every core urban district as well as neighbouring suburban districts except Jinshan and the rural Chongming Districts. It serves Huangpu, Xuhui, Changning, Jing’an, Putuo, Hongkou, Yangpu, Minhang, Baoshan, Jiading, Pudong New Area, Songjiang, Qingpu, and Fengxian.
- There are certain differences in each line.
- Yanlin, Wang (January 5, 2022). "Subway expansion a delight, with care also taken for those left in slow lane". Shine. https://www.shine.cn/opinion/2201050454/.
- "上海地铁". http://www.shmetro.com/node49/201412/con113908.htm.
- "上海地铁网络示意图". 上海申通地铁集团有限公司. http://service.shmetro.com/yxxlt/index.htm.
- Warr, Anne (2007). Shanghai Architecture. The Watermark Press. ISBN 978-0-949284-76-1.
- "Archived copy" (in zh). Office of Shanghai Chronicles. 5 September 2003. http://www.shtong.gov.cn/Newsite/node2/node2245/node64620/node64630/node64705/node64711/userobject1ai58515.html.
- "Archived copy" (in zh). Office of Shanghai Chronicles. 30 December 2002. http://www.shtong.gov.cn/Newsite/node2/node2245/node4516/node55031/node55112/node55128/userobject1ai42410.html.
- 中国政府采购网. "上海浦东现代有轨交通有限公司2017年度-2019年度张江有轨电车"四电"系统维护保障及运行管理项目中标公告". 中华人民共和国财政部. http://www.ccgp.gov.cn/cggg/dfgg/zbgg/201611/t20161114_7573592.htm.
- "张江有轨电车31号通车 营业时间与二号线衔接_新浪上海_新浪网". sh.sina.com.cn. http://sh.sina.com.cn/news/s/2009-12-30/0819127953.html. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- "[新闻晨报与2号线"零换乘" 张江有轨 电车五六月份试通车[图]"]. wm600.eastday.com. http://wm600.eastday.com/w/20090206/u1a533038.html. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- "上海松江有轨电车一期示范线正式开通试运营-中新社上海" (in zh-CN). www.sh.chinanews.com. http://www.sh.chinanews.com/shms/2018-12-26/50349.shtml. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- "刚刚!松江有轨电车开动啦!你关心的问题都在这里↓". baijiahao.baidu.com. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1620875688793069588&wfr=spider&for=pc. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- 上海松江有轨电车投资运营有限公司. "上海松江有轨电车投资运营有限公司招聘公告". 上海市松江区人民政府. http://www.songjiang.gov.cn/xwzx/002004/002004001/20190227/4781e5a1-67e0-4e8b-8e36-e3843f273077.html.
- "Personal Cars and China (2003)". http://darwin.nap.edu/books/030908492X/html/223.html.
- Dang. "New Energy Buses to Receive a Maximum of 550,000 RMB Subsidies in Shanghai". chinabuses. https://www.chinabuses.org/news/2014/0605/article_8141.html.
- We, Xu; Ya, Zhou; Huihao, Tang. "Shanghai Basic Facts 2019". Information Office of Shanghai Municipality Shanghai Municipal Statistics Bureau, Zhongxi Book Company. http://www.shanghai.gov.cn/english2019/pdf/2019-ShanghaiBasicFacts.pdf.
- Huizhi, Chen (January 4, 2022). "No more smooth ride amid selective hike in city cab fares". Shine. https://www.shine.cn/news/metro/2201040419/.
