Perylene has had a tremendous impact in the history of material research for the molecular semiconductors. Among numerous derivatives of this polyaromatic hydrocarbon, perylene diimide (PDI) represents a promising class of organic materials envisioned as non-fullerene acceptors (NFAs) for the practical organic photovoltaic (OPV) applications due to their enhanced photo- and thermal stability and remarkably high electron affinity, some of which realize band-like transport properties. The present review guides some of the representative achievements in the development of rationally designed PDI systems, highlighting synthetic methodologies based on bay-functionalization strategies for creating well-designed molecular nanostructures and structure-performance relationship of perylene-based small molecular acceptors (SMAs) for the photovoltaic outcomes.
- perylene
- non-fullerene acceptor
- organic solar cell
1. Discovery of Perylene Dyes
Perylene, a primitive type of polyaromatic hydrocarbon comprising five benzene rings, has had a tremendous impact on the history of material research for the molecular semiconductors, since the discovery of electrical conductivity of perylene-bromine charge-transfer (CT) complex by Akamatsu, Inokuchi, and Matsunaga in 1954 [1]. Because of the electron-rich nature, the native perylene acts as an electron donor, playing a p-type semiconductor material in contact with electron-deficient molecules such as bromine. At this consideration, one may expand the potential molecular diversity around the perylene scaffold to find an electron-accepting counterpart by introducing electron-withdrawing elements into the aromatic nucleus [2].
Representative examples of such molecules include 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic acid (PTCA) and its dianhydride (PTCDA), which contain carboxylic functionalities at the so-called peri positions (Figure 1). According to the literature, PTCA has appeared as a vat dye in a US patent published in 1924 [3], while PTCDA has been available later in 1933 [4]. These compounds have been manufactured by oxidative coupling of naphthalene 1,8-dicarboxylic acid or its derivatives such as a 1,8-monoimide variant, which the contemporary production by commercial suppliers still relies on [5]. Here, it is of interest to note that a monoimide derivative of PTCA has been incidentally obtained as a consequence of incomplete conversion to the desired product through the synthetic process [6]. Afterward, diimide derivatives of PTCA, which we simply call perylene diimides (PDIs), have been intentionally produced by condensation of PTCA with amines to dye cotton and wool fabrics with Bordeaux-red shades as described in a US patent published in 1923 [7], ten years after the first discovery in 1913 by Kardos [8][9]. This type of reaction has been applied to the synthesis of different electron-deficient perylene systems, namely perylenetetracarboxylic dibenzimidazoles (PTCBIs), wherein 1,2-diamines undergo imidation and the following imination into benzimidazoles that adopt extended π-conjugation in the planar perylene systems [10]. Because of high thermal and chemical stability, these perylene derivatives were employed as a robust coloring matter in the early stages.
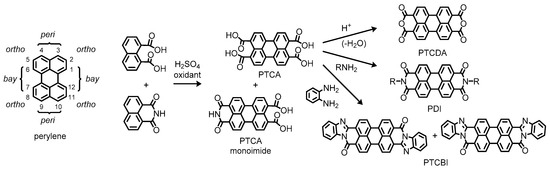
Figure 1. Chemical structures of perylene and related compounds. Positional prefixes for the perylene ring system are indicated in the left side of the figure.
2. Application for Organic Photovoltaics
Later on, researchers and engineers have widely applied these materials in the areas of organic molecular electronics. Among these applications, particularly worthy of note is the use of the perylene dyes as important constituents in organic photovoltaics (OPVs) [11]. The OPV devices, which potentially employ organic semiconductor materials for light-harvesting to facilitate charge separations, have been developed since the late 1950s [12]. In earlier studies, researchers have made a primitive type of OPVs based on a single-layer structure, wherein phthalocyanines gave a small but significant level of photovoltaic performance [13]. Despite the prominent success, the poor efficiency of photocurrent generation has been a major problem for the single-layer devices. One of the biggest breakthroughs to resolve this issue has been achieved by the invention of organic–organic heterojunction systems innovated by Tang (Figure 2) [14]. In his work, he set up a two-layer organic cell made through sequential vacuum evaporation of copper phthalocyanine (CuPc) and PTCBI onto an indium tin oxide (ITO) substrate. The work has demonstrated that the PTCBI layer obviously served as an electron-acceptor, extracting electrons from CuPc at their interfaces, to enhance the photovoltaic performance, demonstrating that the nature of organic–organic interfaces is the principal determinant of photovoltaic properties.
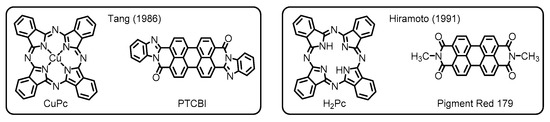
Figure 2. Chemical structures of organic semiconductor materials employed in the primitive organic photovoltaics (OPVs) developed by Tang and Hiramoto. Adapted from references [14][15].
The innovative contribution to the next evolution of the OPV technologies has been made by Hiramoto and coworkers, who first established the design concept of bulk heterojunction (BHJ) blends. Their OPV devices have been fabricated with sublimated metal-free phthalocyanine (H2Pc) donor and N,N’-dimethyl-substituted PDI (Pigment Red 179) acceptor to deposit three organic layers, which contain an interlayer (i-layer) of co-deposited donor/acceptor pigments between homogeneous layers of the two respective constituents. This work has ascertained that the pigment mixing enlarges the donor/acceptor interface to dramatically improve the photogeneration efficiency (Figure 2) [15]. The development of the three-layered p-i-n structure, where p and n denote the donor and acceptor layers, respectively, has emphasized the importance of the BHJ active layer to overcome the limitations of OPV performance for the conventional planar heterojunction (PHJ) systems.
3. Development of Organic Photovoltaic Technology
In the next stage, significant progress has been made in the fabrication protocol by Yu, Heeger, and coworkers. They adopted a solution process with the aim of developing practical and cost-effective technologies. This alternative way allows one to use non-sublimable organic semiconductors such as conjugated polymers and thermally less robust molecules [16]. Furthermore, the work has highlighted the potential utility of buckminsterfullerene (C60) derivatives as the electron acceptor (i.e., n-type semiconductor) because of their high electron conductivity. In the actual systems, two types of soluble phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl esters, namely [6,6]- and [5,6]-PC61BMs, were employed to fabricate the BHJ blend films with a donor of poly(2-methoxy-5-(2’-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylene vinylene), denoted as MEH-PPV, which were deposited by spin-cast from xylene and 1,2-dichlorobenzene solutions (Figure 3). Accordingly, the solution-processed devices provided comparably high efficiencies with regard to carrier collection and energy conversion, as has also been demonstrated in self-organized discotic liquid crystals composed of hexaphenyl-substituted hexabenzocoronene (HBC-PhC12) and N,N’-bis(1-ethylpropyl)-substituted PDI by Friend, Müllen, and coworkers [17]. Because of the superior versatility of organic materials and good processability combined with low-cost operation, the solution processing method has been accepted as the standard technique for contemporary OPV devices [18].
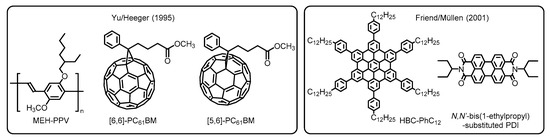
Figure 3. Chemical structures of organic semiconductor materials employed in the primitive OPVs developed by Yu/Heeger and Friend/ Müllen. Adapted from refs [16][17].
Thus, the OPV technology has recently emerged as credible and prominent future power sources, because of the economic and environmental advantages to offer low production disposal costs for processing hazardous-element-free materials, unlike the inorganic and perovskite counterparts [19][20]. Furthermore, the technological applications of the solution processing methods provide attractive options to fabricate semitransparent devices that allow for harnessing solar power through colored windows and roofs of buildings and vehicles [21]. The commercial scale levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) represents a measure of power sources to compare different methods of electricity generation. According to this estimate, mass-manufactured OPV modules with the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 5% and the operating life time of 5 years are predicted to produce an LCOE under $0.13/kWh, which is comparable to that of the current coal-based electricity generating systems [22]. It deserves to be mentioned that the OPVs, being compatible with large-scale roll-to-roll print manufacturing when fabricated on plastic substrates, combine additional advantages of flexibility and light weight, making them suitable as a next-generation avenue for generating portable and renewable energies [23][24].
4. Non-Fullerene Acceptors for Organic Solar Cells
As described above, the selection of organic semiconductors is crucial for the development of high-performance organic solar cells (OSCs). In contrast to a wide variety of the p-type semiconductor donor materials available nowadays, there is a very limited option of the n-type counterparts [25][26]. As a matter of fact, the current OSCs are being made with π-conjugated donor polymers that exhibit efficient hole transporting properties and good chemical compatibility with small molecular acceptors (SMAs) to tailor microcrystalline film morphologies of the polymer/SMA BHJ blends [27]. The earlier efforts have focused on the use of the fullerene-based materials as a potential SMA, mainly because of their excellent electron transport properties with high chemical stability, accompanied by favorable polymer compatibilities [28]. Despite the highly productive results obtained in many research works, the design-to-device approach based on fullerene acceptors suffers from inherent poor absorbance in the UV-visible region and limited tunability in terms of synthetic flexibility, cost efficiency, and amenability to scale-up manufacturing [29].
Thus, non-fullerene acceptors (NFAs) have recently emerged as promising alternatives to the conventional fullerene-based acceptors [30]. Researchers have synthesized a vast number of rationally designed NFAs with superior light-harvesting ability in the visible and near-infrared (NIR) regions, which have realized dramatically improved PCEs [31]. Indeed, the highest PCE of the state-of-the-art OSC based on Y6 has already reached over 17%, when coupled with complementary polymeric donor PM6 (Figure 4) [32][33]. Further research efforts with a Y6 derivative have made the most successful achievement in this field with remarkably enhanced PCE approaching 18% [34]. However, these types of NFA materials still face performance degradation because of their susceptibility to moisture and oxygen, offering less long-term durability [35][36] and suffer from synthetic complexity [32]. Therefore, it is highly desired to find chemically robust alternatives that perform well under a range of circumstances. At this point, the perylene-based NFAs have been envisioned as the other candidate for the practical OPV applications because of their enhanced photostability, thermal stability, and remarkably high electron affinity, some of which realize band-like transport properties [37][38][39].
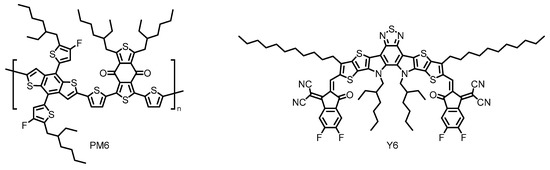
Figure 4. Chemical structures of polymeric donor PM6 and small molecular acceptor Y6 employed in the state-of-the-art organic solar cells (OSC). Adapted from ref [32].
5. Chemical Modification of Perylene Systems
Chemical modification of the perylene backbones, such as PTCDA and PDI, produces rich structural diversity to offer a broad range of functional properties [40]. The chemical modification is classified into functionalization at so-called bay (1,6,7,12-) positions and ortho (2,5,8,11-) positions (Figure 1). Although recent efforts in the ortho-functionalization endowed the perylene-based materials with a wide structural and functional diversity, such processes may be ineffective to tune the electronic properties of the perylene π-systems, because the ortho carbon atoms have inherent poor reactivity and relatively small contribution of the frontier molecular orbitals (FMOs) which determine the photophysical properties of the perylene nucleus [41][42].
Instead, bay-functionalization is more suitable for fine-tuning of optical and electronic properties of the perylene π-system, because the bay-carbons possess more electronic density of the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) to facilitate electrophilic substitution reactions and alteration of the electronic properties of the perylene π-system [43][44]. Conventional methods for the bay-functionalization rely on halogenation of the perylene nucleus [45]. The halogenation makes the perylene π-systems reactive toward nucleophiles, enabling introduction of functional groups at the bay positions [46]. Nevertheless, only limited methods are available for the halogenation reactions, most of which have low controllability with regard to precise location and number of incorporated halogen atoms [47]. As a matter of fact, conventional bay-halogenations require excess chlorine or bromine to yield highly substituted products such as 1,6,7,12-tetrachloride derivatives or inseparable mixtures of 1,7- and 1,6-dibromide ones, respectively (Figure 5) [48][49]. Such a different reactivity can be ascribed to the size of the two halogen atoms; the larger bromine atom prevents further bay-bromination at the opposite shores to afford the dibrominates as regioisomeric mixtures [50].
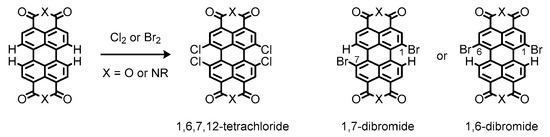
Figure 5. Chemical structures of halogenated perylenes readily available from commercial sources.
6. Synthetic Issues on Perylene Dyes
With this in mind, it is expected that controlling the course of bromination at one of the four bay positions becomes a key process to access monosubstituted perylenes available for various applications and further chemical modification. However, inherent insolubility of the planar perylene molecules has hampered synthesis of the monobromides with practically acceptable yields, thereby causing major limitations in rational design of perylene-based materials [51]. To address this issue, many researchers have utilized the “swallow-tail”-like branched alkyl chains on the nitrogen atoms of the imide groups, which bring significant steric hindrance to effectively weaken the excessive degree of π-stacking and crystallinity [52]. Indeed, the use of the “swallow-tail” substituents solves the solubility problem, enabling efficient monobromination with yields of as high as 57% upon treatment with bromine in dichloromethane (DCM) [53]. With the aid of this strategy, a diverse range of new molecular systems containing the swallow-tailed PDIs have been designed as efficient NFA materials for the OPV applications [54].
In contrast to the synthetic benefits of the solubilizing effects, flexible and bulky nature of the branched alkyl chains causes inevitable degradation of crystallinity or intermolecular interaction, which may cause detrimental effects in OSC performances [55]. On this basis, it is reasonable to find the molecular structures possessing both high solubility and crystallinity for creating ideal perylene-based NFAs. Thus, more flexible and efficient approach to supply the precisely activated perylene materials, independent of structural properties of the side chains, will be the key to achieving the diversity-oriented synthesis of novel highly efficient NFAs. In this regard, operating with more soluble perylene tetracarboxylic esters (PTEs) followed by conducting saponification and imidation to PDIs may represent an alternative strategy to address the above concerns [56]. The objective of this review is to highlight the significant progresses on the development of a diverse range of designed perylene systems as NFA materials. With the intention to clarify what progress has been achieved by structural arrangement of the perylene units in the OPV technology, the primary subject of this review focuses on the perylene-based SMAs developed through bay-functionalization strategies [57].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ma13092148
References
- Akamatsu, H.; Inokuchi, H.; Matsunaga, Y. Electrical Conductivity of the Perylene-Bromine Complex. Nature 1954, 173, 168–169.
- Wonneberger, H.; Reichelt, H.; Zagranyarski, Y.; Li, C.; Müllen, K.; Chen, L. Functionalisation of the Peri-Positions of Perylene and Naphthalene Monoimide via Versatile Building Blocks. US Patent US 9630973B2, 25 April 2017.
- Schmidt, M.P.; Neugebauer, W. Perylenetetracarboxylic Acids and Derivatives. US Patent US 1506545A, 26 August 1924.
- Pongratz, A. Process of Manufacturing Perylene Tetracarboxylic Acid Anhydride. US Patent US 1917153, 4 July 1933.
- Francis, E.M.; Simonsen, J.L. 111.Derivatives of Naphthalomethylimide. J. Chem. Soc. 1935, 496–499.
- Kalle & Co. AG. Process of Producing Perylenetetracarboxylic Acids or Their Mono-Imides. Patent GB 221008, 1 September 1924.
- Kalle & Co. AG. Process for Producing Vat Colouring-Matters. Patent GB 201786, 9 August 1923.
- Kardos, M. Verfahren zur Darstellung eines Küpenfarbstoffes der Naphtalinreihe. Deutsches Reichspatent DE276357, 14 June 1913.
- Kardos, M. Verfahren zur Darstellung eines Küpenfarbstoffes der Naphtalinreihe. Deutsches Reichspatent DE276956, 10 October 1913.
- Cullinan, J.F.; Lyte, L.D. Acid Treatment of Heterocyclic Imide and Imidazole Vat Dyestuffs. US Patent US 2473015, 14 June 1949.
- Li, C.; Wonneberger, H. Perylene Imides for Organic Photovoltaics: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 613–636.
- Spanggaard, H.; Krebs, F.C. A Brief History of the Development of Organic and Polymeric Photovoltaics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2004, 83, 125–146.
- Kearns, D.; Calvin, M. Photovoltaic Effect and Photoconductivity in Laminated Organic Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 29, 950.
- Tang, C.W. Two-Layer Organic Photovoltaic Cell. App. Phys. Lett. 1986, 48, 183–185.
- Hiramoto, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Yokoyama, M. Three-Layered Organic Solar Cell with a Photoactive Interlayer of Codeposited Pigments. App. Phys. Lett. 1991, 58, 1062–1064.
- Yu, G.; Gao, J.; Hummelen, J.C.; Wudl, F.; Heeger, A.J. Polymer Photovoltaic Cells: Enhanced Efficiencies via a Network of Internal Donor-Acceptor Heterojunctions. Science 1995, 270, 1789–1791.
- Schmidt-Mende, L.; Fechtenkötter, A.; Müllen, K.; Moons, E.; Friend, R.H.; MacKenzie, J.D. Self-Organized Discotic Liquid Crystals for High-Efficiency Organic Photovoltaics. Science 2001, 293, 1119–1122.
- Brus, V.V.; Lee, J.; Luginbuhl, B.; Ko, S.J.; Bazan, G.C.; Nguyen, T.Q. Solution-Processed Semitransparent Organic Photovoltaics: From Molecular Design to Device Performance. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900904.
- Burke, D.J.; Lipomi, D.J. Green Chemistry for Organic Solar Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2053–2066.
- Deng, R.; Chang, N.L.; Ouyang, Z.; Chong, C.M. A Techno-Economic Review of Silicon Photovoltaic Module Recycling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 109, 532–550.
- Lee, J.; Ko, S.-J.; Lee, H.; Huang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Seifrid, M.; Vollbrecht, J.; Brus, V.V.; Karki, A.; Wang, H.; et al. Side-Chain Engineering of Nonfullerene Acceptors for Near-Infrared Organic Photodetectors and Photovoltaics. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1401–1409.
- Mulligan, C.J.; Bilen, C.; Zhou, X.; Belcher, W.J.; Dastoor, P.C. Levelised Cost of Electricity for Organic Photovoltaics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 133, 26–31.
- Hashemi, S.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Aberle, A. Recent Progress in Flexible-Wearable Solar Cells for Self-Powered Electronic Devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 685–743.
- Darling, S.B.; You, F. The Case for Organic Photovoltaics. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17633–17648.
- Fu, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Polymer Donors for High-Performance Non-Fullerene Organic Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1433–7851.
- Sonar, P.; Fong Lim, J.P.; Chan, K.L. Organic Non-Fullerene Acceptors for Organic Photovoltaics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1558–1574.
- Mishra, A.; Bäuerle, P. Small Molecule Organic Semiconductors on the Move: Promises for Future Solar Energy Technology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1433–7851.
- Naveed, H.B.; Zhou, K.; Ma, W. Interfacial and Bulk Nanostructures Control Loss of Charges in Organic Solar Cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2904–2915.
- Collavini, S.; Delgado, J.L. Fullerenes: The Stars of Photovoltaics. Sustain. Energ. Fuels 2018, 2, 2480–2493.
- Duan, L.; Elumalai, N.K.; Zhang, Y.; Uddin, A. Progress in Non-Fullerene Acceptor Based Organic Solar Cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 193, 22–65.
- Wang, H.; Cao, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, R.; Yang, L.; Tang, W. Molecular Engineering of Central Fused-Ring Cores of Non-Fullerene Acceptors for High-Efficiency Organic Solar Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 2050–7488.
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, G.; Yip, H.-L.; Lau, T.-K.; Lu, X.; Zhu, C.; Peng, H.; Johnson, P.A.; et al. Single-Junction Organic Solar Cell with over 15% Efficiency Using Fused-Ring Acceptor with Electron-Deficient Core. Joule 2019, 3, 1140–1151.
- Liu, L.; Kan, Y.; Gao, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Jiu, T.; Jen, A.-K.-Y.; Li, Y. Graphdiyne Derivative as Multifunctional Solid Additive in Binary Organic Solar Cells with 17.3% Efficiency and High Reproductivity. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907604.
- Cui, Y.; Yao, H.; Zhang, J.; Xian, K.; Zhang, T.; Hong, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, K.; An, C.; et al. Single-Junction Organic Photovoltaic Cells with Approaching 18% Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2020, 1908205.
- Speller, E.M.; Clarke, A.J.; Luke, J.; Lee, H.K.H.; Durrant, J.R.; Li, N.; Wang, T.; Wong, H.C.; Kim, J.-S.; Tsoi, W.C.; et al. From Fullerene Acceptors to Non-Fullerene Acceptors: Prospects and Challenges in the Stability of Organic Solar Cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 2050–7488.
- Wadsworth, A.; Moser, M.; Marks, A.; Little, M.S.; Gasparini, N.; Brabec, C.J.; Baran, D.; McCulloch, I. Critical Review of The Molecular Design Progress in Non-Fullerene Electron Acceptors Towards Commercially Viable Organic Solar Cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1596–1625.
- Jones, B.A.; Ahrens, M.J.; Yoon, M.-H.; Facchetti, A.; Marks, T.J.; Wasielewski, M.R. High-Mobility Air-Stable n-Type Semiconductors with Processing Versatility: Dicyanoperylene-3,4:9,10-Bis(dicarboximides). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6363–6366.
- Minder, N.A.; Ono, S.; Chen, Z.; Facchetti, A.; Morpurgo, A.F. Band-Like Electron Transport in Organic Transistors and Implication of the Molecular Structure for Performance Optimization. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 503–508.
- Jiang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yang, M.; Zhan, C.; Xie, Z.; Verpoort, F.; Xiao, S. Taking the Place of Perylene Diimide: Perylene Tetracarboxylic Tetraester as a Building Block for Polymeric Acceptors to Achieve Higher Open Circuit Voltage in All-Polymer Bulk Heterojunction Solar Cells. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 5612–5620.
- Avlasevich, Y.; Li, C.; Müllen, K. Synthesis and Applications of Core-Enlarged Perylene Dyes. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 3814–3826.
- Nakazono, S.; Easwaramoorthi, S.; Kim, D.; Shinokubo, H.; Osuka, A. Synthesis of Arylated Perylene Bisimides through C−H Bond Cleavage under Ruthenium Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5426–5429.
- Clikeman, T.T.; Bukovsky, E.V.; Wang, X.-B.; Chen, Y.-S.; Rumbles, G.; Strauss, S.H.; Boltalina, O.V. Core Perylene Diimide Designs via Direct Bay- and ortho-(Poly)trifluoromethylation: Synthesis, Isolation, X-ray Structures, Optical and Electronic Properties. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 6641–6654.
- Dey, S.; Efimov, A.; Lemmetyinen, H. Diaryl-Substituted Perylene Bis(imides): Synthesis, Separation, Characterization and Comparison of Electrochemical and Optical Properties of 1,7- and 1,6-Regioisomer. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2367–2374.
- Weil, T.; Vosch, T.; Hofkens, J.; Peneva, K.; Müllen, K. The Rylene Colorant Family—Tailored Nanoemitters for Photonics Research and Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9068–9093.
- Nowak-Król, A.; Würthner, F. Progress in the Synthesis of Perylene Bisimide Dyes. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 1272–1318.
- Würthner, F. Perylene Bisimide Dyes as Versatile Building Blocks for Functional Supramolecular Architectures. Chem. Commun. 2004, 14, 1564–1579.
- Huang, C.; Barlow, S.; Marder, S.R. Perylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxylic Acid Diimides: Synthesis, Physical Properties, and Use in Organic Electronics. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 2386–2407.
- Dubey, R.K.; Westerveld, N.; Grozema, F.C.; Sudhölter, E.J.R.; Jager, W.F. Facile Synthesis of Pure 1,6,7,12-Tetrachloroperylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxy Bisanhydride and Bisimide. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1882–1885.
- Böhm, A.; Arms, H.; Henning, G.; Blaschka, P. (BASF AG) 1,7-Diaroxy-oder-Arylthiosubstituierte Perylen-3,4,9,10-Tetracarbonsäuren, deren Dianhydride und Diimide. Germain Patent DE 19547209A1, 19 June 1997.
- Würthner, F.; Stepanenko, V.; Chen, Z.; Saha-Möller, C.R.; Kocher, N.; Stalke, D. Preparation and Characterization of Regioisomerically Pure 1,7-Disubstituted Perylene Bisimide Dyes. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 7933–7939.
- Würthner, F.; Saha-Möller, C.R.; Fimmel, B.; Ogi, S.; Leowanawat, P.; Schmidt, D. Perylene Bisimide Dye Assemblies as Archetype Functional Supramolecular Materials. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 962–1052.
- Balakrishnan, K.; Datar, A.; Naddo, T.; Huang, J.; Oitker, R.; Yen, M.; Zhao, J.; Zang, L. Effect of Side-Chain Substituents on Self-Assembly of Perylene Diimide Molecules: Morphology Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7390–7398.
- Rajasingh, P.; Cohen, R.; Shirman, E.; Shimon, L.J.W.; Rybtchinski, B. Selective Bromination of Perylene Diimides under Mild Conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 5973–5979.
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, X. Non-Fullerene Small Molecule Acceptors Based on Perylene Diimides. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17604–17622.
- Izawa, S.; Shintaku, N.; Kikuchi, M.; Hiramoto, M. Importance of Interfacial Crystallinity to Reduce Open-Circuit Voltage Loss in Organic Solar Cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 153301.
- Vollbrecht , J.; Bock, H.; Wiebeler, C.; Schumacher, S.; Kitzerow, H. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Obtained by Lateral Core Extension of Mesogenic Perylenes: Absorption and Optoelectronic Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 12026–12031.
- Lütke Eversloh, C.; Li, C.; Müllen, K. Core-Extended Perylene Tetracarboxdiimides: The Homologous Series of Coronene Tetracarboxdiimides. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4148–4150.
