This timeline of human prehistory comprises the time from the first appearance of Homo sapiens in Africa 300,000 years ago to the invention of writing and the beginning of history, 5,000 years ago. It thus covers the time from the Middle Paleolithic (Old Stone Age) to the very beginnings of world history. All dates are approximate subject to revision based on new discoveries or analyses.
- paleolithic
- prehistory
- timeline
1. Middle Paleolithic
- 315,000 years ago: approximate date of appearance of Homo sapiens (Jebel Irhoud, Morocco).
- 270,000 years ago: age of Y-DNA haplogroup A00 ("Y-chromosomal Adam").
- 250,000 years ago: first appearance of Homo neanderthalensis (Saccopastore skulls).
- 250,000–200,000 years ago: modern human presence in West Asia (Misliya cave).
- 230,000–150,000 years ago: age of mt-DNA haplogroup L ("Mitochondrial Eve").
- 210,000 years ago: modern human presence in southeast Europe (Apidima, Greece).[1]
- 195,000 years ago: Omo remains (Ethiopia).[2]
- 170,000 years ago: humans are wearing clothing by this date.[3]
- 160,000 years ago: Homo sapiens idaltu.
- 150,000 years ago: Peopling of Africa: Khoisanid separation, age of mtDNA haplogroup L0.
- 125,000 years ago: peak of the Eemian interglacial period.
- 120,000 years ago: It is possible that SE Australian Aboriginal people were cooking on hearths. Charcoal and Burnt Stone Feature #1 (CBS1) located within coastal dune sediments at Moyjil (Point Ritchie), Warrnambool, that independent geomorphic and OSL dating indicates is of Last Interglacial age (~120,000 years ago). [1]
- 120,000–90,000 years ago: Abbassia Pluvial in North Africa—the Sahara desert region is wet and fertile.
- 120,000–75,000 years ago: Khoisanid back-migration from Southern Africa to East Africa.[4]
- 100,000 years ago: Earliest structures in the world (sandstone blocks set in a semi-circle with an oval foundation) built in Egypt close to Wadi Halfa near the modern border with Sudan.[5]
- 82,000 years ago: small perforated seashell beads from Taforalt in Morocco are the earliest evidence of personal adornment found anywhere in the world.[6]
- 80,000–70,000 years ago: Recent African origin: separation of sub-Saharan Africans and non-Africans.
- 75,000 years ago: Toba Volcano supereruption that may have contributed to human populations being lowered to about 15,000 people.[7]
- 70,000 years ago: earliest example of abstract art or symbolic art from Blombos Cave, South Africa—stones engraved with grid or cross-hatch patterns.[8]
- 67,000–40,000 years ago: Neanderthal admixture to Eurasians.
- 50,000 years ago: earliest sewing needle found. Made and used by Denisovans.[9]
- 50,000–30,000 years ago: Mousterian Pluvial in North Africa. The Sahara desert region is wet and fertile. Later Stone Age begins in Africa.
- 45,000–43,000 years ago: European early modern humans.[10]
2. Upper Paleolithic
"Epipaleolithic" or "Mesolithic" are terms for a transitional period between the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution in Old World (Eurasian) cultures.
- 45,000–40,000 years ago: Châtelperronian cultures in France.[11]
- 42,000 years ago: Paleolithic flutes in Germany.[12]
- 42,000 years ago: earliest evidence of advanced deep sea fishing technology at the Jerimalai cave site in East Timor—demonstrates high-level maritime skills and by implication the technology needed to make ocean crossings to reach Australia and other islands, as they were catching and consuming large numbers of big deep sea fish such as tuna.[13][14]
- 41,000 years ago: Denisova hominin lives in the Altai Mountains.
- 40,000 years ago: extinction of Homo neanderthalensis.[11]
- 40,000 years ago: Aurignacian culture begins in Europe.[15]
- 40,000 years ago: oldest known figurative art the zoomorphic Löwenmensch figurine.[16]
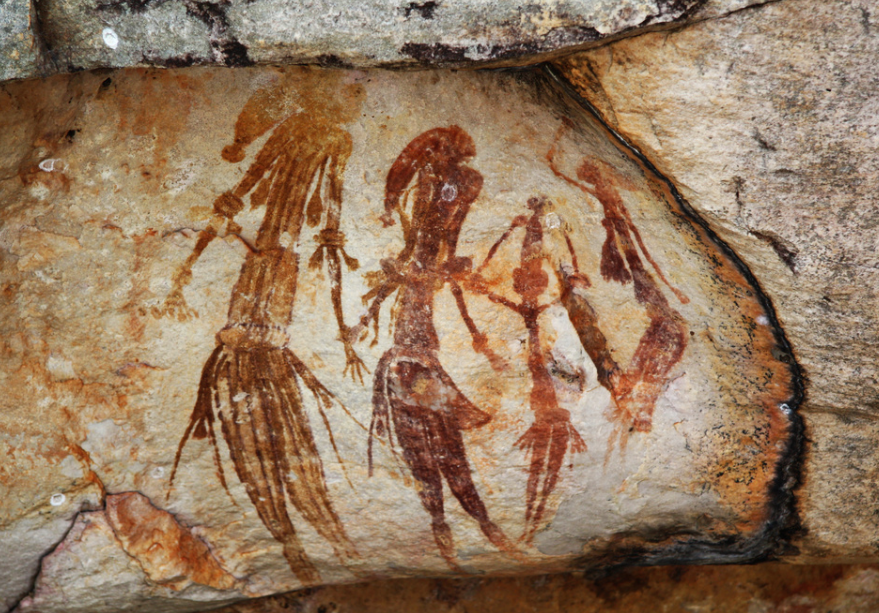

- 40,000–30,000 years ago: First human settlements formed by Aboriginal Australians in several areas which are today the cities of Sydney,[17] Perth[18] and Melbourne.[19]
- 40,000–20,000 years ago: oldest known ritual cremation, the Mungo Lady, in Lake Mungo, Australia.
- 35,000 years ago: oldest known figurative art of a human figure as opposed to a zoomorphic figure (Venus of Hohle Fels).
- 33,000 years ago: oldest known domesticated dog skulls show they existed in both Europe and Siberia by this time.[20][21]
- 31,000–16,000 years ago: Last Glacial Maximum (peak at 26,500 years ago).
- 30,000 years ago: rock paintings tradition begins in Bhimbetka rock shelters in India , which presently as a collection is the densest known concentration of rock art. In an area about 10 km2, there are about 800 rock shelters of which 500 contain paintings.[22]
- 29,000 years ago: The earliest ovens found.
- 28,500 years ago: New Guinea is populated by colonists from Asia or Australia.[23]
- 28,000 years ago: oldest known twisted rope.
- 28,000–24,000 years ago: oldest known pottery—used to make figurines rather than cooking or storage vessels (Venus of Dolní Věstonice).
- 28,000–20,000 years ago: Gravettian period in Europe. Harpoons and saws invented.
- 26,000 years ago: people around the world use fibers to make baby carriers, clothes, bags, baskets, and nets.
- 25,000 years ago: a hamlet consisting of huts built of rocks and of mammoth bones is founded in what is now Dolní Věstonice in Moravia in the Czech Republic. This is the oldest human permanent settlement that has yet been found by archaeologists.
- 24,000 years ago: Evidence suggests humans living in Alaska and Yukon North America.[24]
- 21,000 years ago: artifacts suggest early human activity occurred in Canberra, the capital city of Australia.[25]
- 20,000 years ago: Kebaran culture in the Levant: beginning of the Epipalaeolithic in the Levant
- 20,000 years ago: oldest pottery storage or cooking vessels from China.
- 20,000–10,000 years ago: Khoisanid expansion to Central Africa.[4]
- 20,000–19,000 years ago: earliest pottery use, in Xianren Cave, China.
- 18,000–12,000 years ago: Though estimations vary widely, it is believed by scholars that Afro-Asiatic was spoken as a single language around this time period.[26]
- 16,000–14,000 years ago: Minatogawa Man (Proto-Mongoloid phenotype) in Okinawa, Japan
- 16,000–13,000 years ago: first human migration into North America.
- 16,000–11,000 years ago: Caucasian Hunter-Gatherer expansion to Europe.
- 16,000 years ago: Wisent (European bison) sculpted in clay deep inside the cave now known as Le Tuc d'Audoubert in the French Pyrenees near what is now the border of Spain.
- 15,000–14,700 years ago (13,000 BC to 12,700 BC): Earliest supposed date for the domestication of the pig.
- 14,800 years ago: The Humid Period begins in North Africa. The region that would later become the Sahara is wet and fertile, and the aquifers are full.[27]
- 14,500–11,500: Red Deer Cave people in China, possible late survival of archaic or archaic-modern hybrid humans.
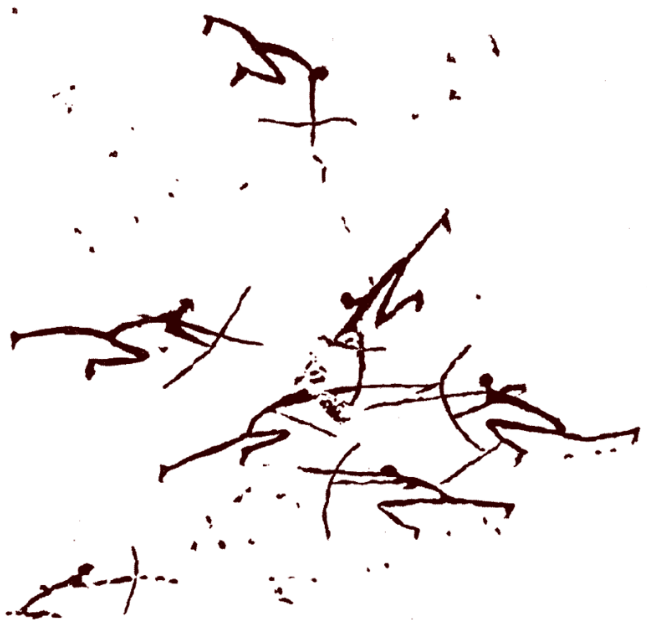

- 14,000–12,000 years ago: Oldest evidence for prehistoric warfare (Jebel Sahaba massacre, Natufian culture).
- 13,000–10,000 years ago: Late Glacial Maximum, end of the Last glacial period, climate warms, glaciers recede.
- 13,000 years ago: A major water outbreak occurs on Lake Agassiz, which at the time could have been the size of the current Black Sea and the largest lake on Earth. Much of the lake is drained in the Arctic Ocean through the Mackenzie River.
- 13,000–11,000 years ago: Earliest dates suggested for the domestication of the sheep.
- 12,900–11,700 years ago: the Younger Dryas was a period of sudden cooling and return to glacial conditions.
- 12,000 years ago: Jericho has evidence of settlement dating back to 10,000 BC. Jericho was a popular camping ground for Natufian hunter-gatherer groups, who left a scattering of crescent microlith tools behind them.[28]
- 12,000 years ago: Earliest dates suggested for the domestication of the goat.
3. Holocene
The terms "Neolithic" and "Bronze Age" are culture-specific and are mostly limited to cultures of the Old World. Many populations of the New World remain in the Mesolithic cultural stage until European contact in the modern period.
- 11,600 years ago (9,600 BC): An abrupt period of global warming accelerates the glacial retreat; taken as the beginning of the Holocene geological epoch.
- 11,200–11,000 years ago: Meltwater pulse 1B, a sudden rise of sea level by 7.5 m within about 160 years.
- 11,000 years ago (9,000 BC): Earliest date recorded for construction of temenoi ceremonial structures at Göbekli Tepe in southern Turkey, as possibly the oldest surviving proto-religious site on Earth.[29]
- 11,000 years ago (9,000 BC): Emergence of Jericho, which is now one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Giant short-faced bears and giant ground sloths go extinct. Equidae goes extinct in North America.
- 10,500 years ago (8,500 BC): Earliest supposed date for the domestication of cattle.
- 10,000 years ago (8,000 BC): The Quaternary extinction event, which has been ongoing since the mid-Pleistocene, concludes. Many of the ice age megafauna go extinct, including the megatherium, woolly rhinoceros, Irish elk, cave bear, cave lion, and the last of the sabre-toothed cats. The mammoth goes extinct in Eurasia and North America, but is preserved in small island populations until ~1650 BC.
- 10,800–9,000 years ago: Byblos appears to have been settled during the PPNB period, approximately 8800 to 7000 BC. Neolithic remains of some buildings can be observed at the site.[30][31]
- 10,000–8,000 years ago (8000 BC to 6000 BC): The post-glacial sea level rise decelerates, slowing the submersion of landmasses that had taken place over the previous 10,000 years.
- 10,000–9,000 years ago (8000 BC to 7000 BC): In northern Mesopotamia, now northern Iraq, cultivation of barley and wheat begins. At first they are used for beer, gruel, and soup, eventually for bread.[32] In early agriculture at this time, the planting stick is used, but it is replaced by a primitive plow in subsequent centuries.[33] Around this time, a round stone tower, now preserved to about 8.5 meters high and 8.5 meters in diameter is built in Jericho.[34]
- 10,000–5,000 years ago (8,000–3,000 BC) Identical ancestors point: sometime in this period lived the latest subgroup of human population consisting of those that were all common ancestors of all present day humans, the rest having no present day descendants.[35]
- 9,500–5,500 years ago: Neolithic Subpluvial in North Africa. The Sahara desert region supports a savanna-like environment. Lake Chad is larger than the current Caspian Sea. An African culture develops across the current Sahel region.
- 9,500 years ago (7500 BC): Çatalhöyük urban settlement founded in Anatolia. Earliest supposed date for the domestication of the cat.
- 9,200 years ago: First human settlement in Amman, Jordan; 'Ain Ghazal Neolithic settlement was built spanning over an area of 15 hectares.[36]
- 9,000 years ago (7000 BC): Jiahu culture began in China.
- 9,000 years ago: large first fish fermentation in southern Sweden.[37]
- 8,200–8,000 years ago: 8.2 kiloyear event: a sudden decrease of global temperatures, probably caused by the final collapse of the Laurentide Ice Sheet, which leads to drier conditions in East Africa and Mesopotamia.
- 8,200–7,600 years ago (6200–5600 BC): sudden rise in sea level (Meltwater pulse 1C) by 6.5 m in less than 140 years; this concludes the early Holocene sea level rise and sea level remains largely stable throughout the Neolithic.[38]
- 8,000–5,000 years ago: (6000 BC–3000 BC) development of proto-writing in China, Southeast Europe (Vinca symbols) and West Asia (proto-literate cuneiform).
- 8,000 years ago: Evidence of habitation at the current site of Aleppo dates to about c. 8,000 years ago, although excavations at Tell Qaramel, 25 kilometers north of the city show the area was inhabited about 13,000 years ago,[39] Carbon-14 dating at Tell Ramad, on the outskirts of Damascus, suggests that the site may have been occupied since the second half of the seventh millennium BC, possibly around 6300 BC.[40] However, evidence of settlement in the wider Barada basin dating back to 9000 BC exists.[41]
- 7,500 years ago (5500 BC): Copper smelting in evidence in Pločnik and other locations.
- 7,200–6,000 years ago: 5200–4000 BC:Għar Dalam phase on Malta. First farming settlements on the island.[42][43]
- 6300 or 6350 years ago: Akahoya eruption creates the Kikai Caldera and ends the earliest homogeneous Jomon culture in Japan. When the Jomon culture recovers, it shows regional differences.[44]
- 6,100–5,800 years ago: 4100–3800 BC: Żebbuġ phase. Malta.
- 6,070–6,000 years ago (4050–4000 BC): Trypillian build in Nebelivka (Ukraine ) settlement which reached 15,000–18,000 inhabitants.[45][46]
- 6,500 years ago: The oldest known gold hoard deposited at Varna Necropolis, Bulgaria.
- 6,000 years ago (4000 BC): Civilizations develop in the Mesopotamia/Fertile Crescent region (around the location of modern-day Iraq). Earliest supposed dates for the domestication of the horse and for the domestication of the chicken, invention of the potter's wheel.
3.1. 4th Millennium BC
- 5,800 years ago: (3840 to 3800 BC): The Post Track and Sweet Track causeways are constructed in the Somerset Levels.
- 5,800 years ago (3800 BC): Trypillian build in Talianki (Ukraine ) settlement which reached 15,600–21,000 inhabitants.[47]
- 5,800–5,600 years ago: (3800–3600 BC): Mġarr phase A short transitional period in Malta's prehistory. It is characterized by pottery consisting of mainly curved lines.
- 5,700 years ago (3800 to 3600 BC): mass graves at Tell Brak in Syria.
- 5,700 years ago (3700 BC): Trypillian build in Maidanets (Ukraine ) settlement which reached 12,000–46,000 inhabitants,[48] and built 3-storey building.[49]
- 5,700 years ago: (3700 to 3600 BC): Minoan culture begins on Crete.
- 5,600–5,200 years ago (3600–3200 BC): Ġgantija phase on Malta. Characterized by a change in the way the prehistoric inhabitants of Malta lived.
- 5,500 years ago: (3600 to 3500 BC): Uruk period in Sumer. First evidence of mummification in Egypt.
- 5,500: oldest known depiction of a wheeled vehicle (Bronocice pot, Funnelbeaker culture)
- 5,500 years ago: Earliest conjectured date for the still-undeciphered Indus script.
- 5,500 years ago: End of the African humid period possibly linked to the Piora Oscillation: a rapid and intense aridification event, which probably started the current Sahara Desert dry phase and a population increase in the Nile Valley due to migrations from nearby regions. It is also believed this event contributed to the end of the Ubaid period in Mesopotamia.
- 5,300 years ago: (3300 BC): Bronze Age begins in the Near East[50] Newgrange is built in Ireland. Ness of Brodgar is built in Orkney[51] Hakra Phase of the Indus Valley Civilisation begins in the Indian subcontinent.
- 5,300–5,000 years ago (3300–3000 BC): Saflieni phase in Maltese prehistory.
3.2. 3rd Millennium BC
- 5,000 years ago: Settlement of Skara Brae built in Orkney.[52]
- 4,600 years ago: (2600 BC): Writing is developed in Sumer and Egypt, triggering the beginning of recorded history.
4. Post-Historical Prehistories
- 3,800 years ago (1800 BC): Currently undeciphered Minoan script (Linear A) and Cypro-Minoan script developed on Crete and Cyprus.
- 3,450 years ago (1450 BC): Mycenean Greece, first deciphered writing in Europe
- 3,200 years ago (1200 BC): Oracle bone script, first written records in Old Chinese
- 3,050–2,800 years ago: Alphabetic writing; the Phoenician alphabet spreads around the Mediterranean
- 2,300 years ago: Maya writing, the only known full writing system developed in the Americas, emerges.
- 2,260 years ago (260 BC): Earliest deciphered written records in South Asia (Middle Indo-Aryan)
- 1800s AD: Undeciphered Rongorongo script on Easter Island may mark the latest independent development of writing.
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/History:Timeline_of_human_prehistory
References
- Harvati, K., Röding, C., Bosman, A. M., Karakostis, F. A., Grün, R., Stringer, C., ... & Gorgoulis, V. G. (2019). Apidima Cave fossils provide earliest evidence of Homo sapiens in Eurasia. Nature, 571(7766), 500-504.
- Erin Wayman (11 January 2012). "Meet the Contenders for Earliest Modern Human". smithsonian.com. http://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/meet-the-contenders-for-earliest-modern-human-17801455/.
- "Lice DNA study shows humans first wore clothes 170,000 years ago". ScienceDaily. 7 January 2011. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/01/110106164616.htm.
- Rito T, Richards MB, Fernandes V, Alshamali F, Cerny V, Pereira L, Soares P., "The first modern human dispersals across Africa", PLoS One 2013 Nov 13; 8(11):e80031. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080031. "By ~130 ka two distinct groups of anatomically modern humans co-existed in Africa: broadly, the ancestors of many modern-day Khoe and San populations in the south and a second central/eastern African group that includes the ancestors of most extant worldwide populations. Early modern human dispersals correlate with climate changes, particularly the tropical African “megadroughts” of MIS 5 (marine isotope stage 5, 135–75 ka) which paradoxically may have facilitated expansions in central and eastern Africa, ultimately triggering the dispersal out of Africa of people carrying haplogroup L3 – 60 ka. Two south to east migrations are discernible within haplogroup L0. One, between 120 and 75 ka, represents the first unambiguous long-range modern human dispersal detected by mtDNA and might have allowed the dispersal of several markers of modernity. A second one, within the last 20 ka signalled by L0d, may have been responsible for the spread of southern click-consonant languages to eastern Africa, contrary to the view that these eastern examples constitute relics of an ancient, much wider distribution." https://doi.org/10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0080031
- "Ancient Egypt Online – Lower Paleolithic". https://www.ancientegyptonline.co.uk/paleolithic.html. Retrieved 2019-01-20.
- "World's Oldest Manufactured Beads Are Older Than Previously Thought". Science Daily. 7 May 2009. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/05/090505163021.htm. Retrieved 2013-11-22.
- "Mount Toba Eruption – Ancient Humans Unscathed, Study Claims". http://anthropology.net/2007/07/06/mount-toba-eruption-ancient-humans-unscathed-study-claims/. Retrieved 2008-04-20.
- "'Oldest' prehistoric art unearthed". BBC News. 10 January 2002. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/1753326.stm.
- "World's oldest needle found in Siberian cave that stitches together human history". Siberian Times. 23 August 2016. http://siberiantimes.com/science/casestudy/news/n0711-worlds-oldest-needle-found-in-siberian-cave-that-stitches-together-human-history/.
- John Noble Wilford (3 November 2011). "Fossil Teeth Put Humans in Europe Earlier Than Thought". The New York Times: p. A4. https://www.nytimes.com/2011/11/03/science/fossil-teeth-put-humans-in-europe-earlier-than-thought.html.
- Tom Higham et al. (21 August 2014). "The timing and spatiotemporal patterning of Neanderthal disappearance". Nature 512 (7514): 306–09. doi:10.1038/nature13621. PMID 25143113. Bibcode: 2014Natur.512..306H. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038%2Fnature13621
- Earliest music instruments found, BBC News, 25 May 2012 https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-18196349
- Corbyn, Zoë (24 November 2011). "Archaeologists land world's oldest fish hook". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2011.9461. http://www.nature.com/news/archaeologists-land-world-s-oldest-fish-hook-1.9461. Retrieved 22 October 2014.
- O'Connor, Sue; Ono, Rintaro (25 November 2011). "Pelagic Fishing at 42,000 Years Before the Present and the Maritime Skills of Modern Humans". Science 334 (6059): 1117–21. doi:10.1126/science.1207703. PMID 22116883. Bibcode: 2011Sci...334.1117O. https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscience.1207703
- William E. Banks; Francesco d'Errico; João Zilhão (2013). "Revisiting the chronology of the Proto-Aurignacian and the Early Aurignacian in Europe: A reply to Higham et al.'s comments on Banks et al.". Journal of Human Evolution 65 (6): 810–17. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.08.004. PMID 24095637. https://www.academia.edu/4669550.
- Martin Bailey Ice Age Lion Man is world's earliest figurative sculpture The Art Newspaper, 31 January 2013, accessed 1 February 2013 http://old.theartnewspaper.com/articles/Ice-Age-Lion-Man-is-worlds-earliest-figurative-sculpture/28595
- "Aboriginal people and place". Sydney Barani. 2013. http://www.sydneybarani.com.au/sites/aboriginal-people-and-place/. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- Sandra Bowdler. "Human settlement". in D. Denoon. The Pleistocene Pacific. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 41–50. http://www.archaeology.arts.uwa.edu.au/staff/bowdler__research_interests/the_pleistocene_pacific. Retrieved 26 February 2008.
- Gary Presland, The First Residents of Melbourne's Western Region, (revised edition), Harriland Press, 1997. ISBN:0-646-33150-7. Presland says on page 1: "There is some evidence to show that people were living in the Maribyrnong River valley, near present day Keilor, about 40,000 years ago."
- Elizabeth Landau (14 November 2013). "Dogs first domesticated in Europe, study says". CNN. http://edition.cnn.com/2013/11/14/health/dogs-domesticated-europe/.
- "Ancient domesticated dog skull found in Siberian cave: 33,000 years old". ScienceDaily. 24 January 2012. https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/01/120123152528.htm.
- "Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka". World Heritage Site. Archived from the original on 8 March 2007. https://web.archive.org/web/20070308082739/https://whc.unesco.org/pg.cfm?cid=31&id_site=925. Retrieved 2007-02-15.
- James Trager, The People's Chronology, 1994, ISBN:0-8050-3134-0
- "Earliest Human Presence in North America Dated to the Last Glacial Maximum: New Radiocarbon Dates from Bluefish Caves, Canada", Lauriane Bourgeon ,Ariane Burke,Thomas Higham, Published: January 6, 2017 https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0169486
- Flood, J. M.; David, B.; Magee, J.; English, B. (1987). "Birrigai: a Pleistocene site in the south eastern highlands". Archaeology in Oceania 22: 9–22. doi:10.1002/j.1834-4453.1987.tb00159.x. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fj.1834-4453.1987.tb00159.x
- Ehret, Christopher (1995). Reconstructing Proto-Afroasiatic (Proto-Afrasian): vowels, tone, consonants, and vocabulary. University of California Press. ISBN:0-520-09799-8
- "Shift from Savannah to Sahara was Gradual", by Kenneth Chang, The New York Times , 9 May 2008. https://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/The%20New%20York%20Times
- Mithen, Steven (2006). After the ice: a global human history, 20,000–5000 BC (1st Harvard University Press pbk. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-674-01999-7.
- Curry, Andrew (November 2008). Gobekli Tepe: The World's First Temple?. Smithsonian.com. http://www.smithsonianmag.com/history-archaeology/gobekli-tepe.html. Retrieved 2 August 2013.
- E.J. Peltenburg; Alexander Wasse; Council for British Research in the Levant (2004). Garfinkel, Yosef., "Néolithique" and "Énéolithique" Byblos in Southern Levantine Context* in Neolithic revolution: new perspectives on southwest Asia in light of recent discoveries on Cyprus. Oxbow Books. ISBN 978-1-84217-132-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=6mKBAAAAMAAJ. Retrieved 18 January 2012.
- Vogel, J.C. and Waterbolk, H.T., "Groningen Radiocarbon Dates X", Radiocarbon, 14, 6–110 / 105, 1972.
- Kiple, Kenneth F. and Ornelas, Kriemhild Coneè, eds., The Cambridge World History of Food, Cambridge University Press, 2000, p. 83
- "No-Till: The Quiet Revolution", by David Huggins and John Reganold, Scientific American, July 2008, pp. 70–77.
- Fagan, Brian M, ed. The Oxford Companion to Archaeology, Oxford University Press, Oxford 1996 ISBN:978-0-521-40216-3 p 363
- https://tedlab.mit.edu/~dr/Papers/Rohde-MRCA-two.pdf On the Common Ancestors of All Living Humans
- Scarre, Chris, ed (2005). The Human Past. Thames & Hudson. p. 222.
- "Signs of early settlement in the Nordic region date back to the cradle of civilisation". 2016-02-08. https://www.lunduniversity.lu.se/article/signs-of-early-settlement-in-the-nordic-region-date-back-to-the-cradle-of-civilisation.
- Blanchon, P. (2011b) Backstepping. In: Hopley, D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Modern Coral Reefs: Structure, form and process. Springer-Verlag Earth Science Series, pp. 77–84. ISBN:978-90-481-2638-5. Blanchon, P., and Shaw, J. (1995) Reef drowning during the last deglaciation: evidence for catastrophic sea-level rise and icesheet collapse. Geology, 23:4–8.
- Bryan Nelson (4 August 2015). "12 oldest continuously inhabited cities". Mother Nature Network. https://www.mnn.com/lifestyle/eco-tourism/stories/12-oldest-continuously-inhabited-cities. (3. Aleppo, Syria.)
- Moore, A.M.T. The Neolithic of the Levant. Oxford: Oxford University, 1978. 192–98.
- Burns 2005, p. 2
- "Zebbug Phase". http://www.maltavoyager.com/moa/areas/zebbug.htm.
- "The prehistoric archaeology of the temples of Malta". Bradshaw Foundation. http://www.bradshawfoundation.com/malta/.
- The Impact of Volcanic Eruptions on Human Society from an Archaeological Perspective https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jaqua1957/30/5/30_5_427/_article/-char/en
- Thomas K. Harper. "The effect of climatic variability on population dynamics of the Cucuteni-Tripolye cultural complex and the rise of the Western Tripolye giant-settlements". http://www.chronikajournal.com/resources/Harper.pdf. Retrieved 2016-11-14.
- Müller, Johannes; Rassmann, Knut; Videiko, Mykhailo (2016-01-22). Trypillia Mega-Sites and European Prehistory: 4100–3400 BCE. p. 347. ISBN 978-1317247913. https://books.google.com/?id=-3twCwAAQBAJ&pg=PT347&lpg=PT347&dq=Taljanky+15,600%E2%80%9321,000#v=onepage&q=Taljanky%2015%2C600%E2%80%9321%2C000&f=false. Retrieved 2016-11-14.
- Müller, Johannes; Rassmann, Knut; Videiko, Mykhailo (22 January 2016). Trypillia Mega-Sites and European Prehistory: 4100–3400 BCE. Routledge. ISBN 978-1317247913. https://books.google.com/?id=-3twCwAAQBAJ&pg=PT347&lpg=PT347&dq=Taljanky%2015,600%E2%80%9321,000#v=onepage&q=Taljanky%2015,600%E2%80%9321,000&f=false. Retrieved 13 November 2016.
- Müller, Johannes. High precision Tripolye settlement plans, demographic estimations and settlement organization. https://www.academia.edu/8641305. Retrieved 13 November 2016.
- "ДОСЛІДИ З ТРИПІЛЬСЬКОГО ДОМОБУДІВНИЦТВА". http://www.inst-ukr.lviv.ua/files/11/07chaban.pdf. Retrieved 2016-11-14.
- Kristiansen & Larsson 2005
- Towers, Roy; Card, Nick; Edmonds, Mark (2015). The Ness of Brodgar. Kirkwall, UK: Archaeology Institute, University of the Higlands and Islands. ISBN 978-0-9932757-0-8.
- Childe, V. Gordon; Clarke, D. V. (1983). Skara Brae. Edinburgh: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. ISBN:0-11-491755-8.
