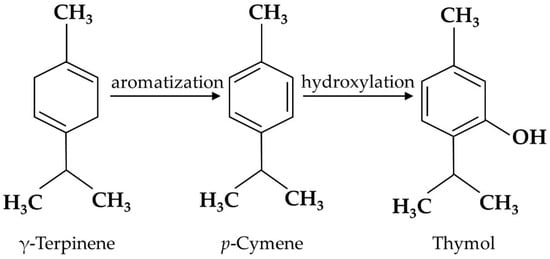
Thymol is the secondary metabolite produced by the aromatization of γ-terpinene to
p-cymene, followed by the hydroxylation of
p-cymene in plants [
19] (
Figure 1), including
Thymus zygis [
20],
Thymbra capitata [
21],
Thymus vulgaris [
22],
Satureja thymbra [
23],
Nigella sativa seeds [
24], and
Monarda didyma [
25]. Pure thymol has low solubility in water, high volatility, and a strong bitter/irritating taste [
26]; thus, it is usually encapsulated in electrospun nanofibers to enhance its water solubility and high temperature stability [
27]. Emulsification is also used for thymol processing. Both encapsulation and emulsification have been shown to improve the anti-oxidant activity of thymol [
28].
Thymol administered orally can be rapidly absorbed in the stomach and small intestines, and then transported to various organs via the circulation system in animals [
29]. Thymol can be metabolized to thymol sulfate and thymol glucuronide by sulfation and glucuronidation in the intestines, liver, kidney, and other organs, respectively [
30]. Thymol and its metabolites reach the maximum concentration in the blood 30 min after oral administration and then are slowly eliminated in about 24 h [
26]. They also present in the lungs, kidneys, mucosa of the small and large intestines, and other organs, suggesting that they may function directly in these organs. It is difficult to determine which compound is the active form of thymol, because thymol metabolites can be deconjugated to thymol locally and export its pharmacological activity in this way [
31]. Recently, scientists have focused on the pharmacological activities of thymol.
Thymol-containing plants have long been used in traditional Chinese medicine due to its pharmacological properties. Thymol acts as a potent inhibitor of the release of inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and IL-8 [
32]. Thymol enhances anti-oxidative capacity to alleviate OS in different tissues [
33]. As a spectrum anti-bacterial agent, thymol reduces the activities of microorganisms belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae, Streptococcus, and Saccharomycetaceae families, involving membrane rupture, inhibition of biofilm formation, and other pathways [
34,
35]. Thymol shows anti-viral potential to inhibit virus colonization, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-298), by docking with the S1 receptor-binding domain of spike glycoprotein [
36]. Thymol also exhibits other pharmacological functions, such as analgesia, anti-malarial, and anti-fungal properties [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41].
3. Thymol Protects Intestinal Barrier Function against IBD
The intestinal barrier, mainly composed of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) and immune cells, maintains the balance between the luminal contents and mucosa. The disturbance of this balance has been associated with gastrointestinal diseases, such as IBD [
42]. Although the exact pathogenesis of IBD remains unclear, a “leaky gut” with impaired intestinal barrier function is the main feature. The intestinal barrier is the first line of defense against pathogen infection, and injury to the intestinal barrier aggravates the disease. Thus, understanding how thymol protects the intestinal barrier is important for relieving IBD.
Thymol has exhibited a protective function for the intestinal barrier in both in vivo and in vitro studies, as illustrated in
Table 1, and its specific mechanism is shown in
Figure 2. Thymol attenuates weaning stress-induced diarrheal and intestinal barrier dysfunction in weanling pigs by reducing the serum diamine oxidase level, an indicator of intestinal integrity, and increasing the expression of the tight junction protein zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and occludins [
43]. Thymol alleviates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced intestinal damage and increases tight junction claudin-3 expression [
44]. Increased plasma endotoxin and D-lactic acid levels are markers of increased intestinal permeability. The latest study found that dietary thymol reduced the plasma endotoxin and D-lactic acid concentrations on days 7 and 14 post-weaning [
45]. The intestinal mucus layer is the first line of defense maintaining bacterial symbiosis with the host and preventing bacterial penetration into epithelial cells [
46]. Thymol increases mucus secretion to relieve ethanol-induced ulcer mucosal damage in rats [
47]. In IPEC-J2 cells, thymol alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced decrease in trans-epithelial electrical resistance (TEER), indicating an increase in the integrity of the single cell layer [
48]. In Caco-2 cells, thymol increases the integrity of the tight junction and up-regulates cyclooxygenase-1 (COX1) activity to maintain GIT homeostasis, which is beneficial for intestinal health [
49]. In addition, thymol changes the expressions of 120 and 59 genes in the oxyntic and pyloric mucosa, respectively, which are associated with gastric epithelium proliferation and maturation activities in weaned pigs [
29].
Figure 2. Action of thymol to protect intestinal barrier function. Pathogen infection in the intestinal lumen reduces mucus secretion and the expressions of tight junction proteins, and increases intestinal permeability, resulting in a “leaky gut”, which increases the risk of intestinal disease. Thymol has been shown to defend against pathogen invasion, promote mucus secretion, and enhance intestinal barrier integrity.
Table 1. Protective function of thymol on the intestinal barrier.
4. Thymol Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation in IBD
The dysregulation of innate and adaptive immune responses leads to chronic intestinal inflammation in IBD patients [
51,
52,
53]. Transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) is the key mediator regulating the inflammatory response. The activation of NF-κB signaling induces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), inductible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), interleukin (IL-1β), and IL-6 [
54]. The over-production and accumulation of inflammatory cytokines cause intestinal epithelial apoptosis and the disruption of intestinal homeostasis, resulting in the dysfunction of the intestinal epithelial barrier in IBD patients [
55]. Currently, the suppression of inflammation is the mainstay of IBD treatment.
Thymol shows strong anti-inflammatory properties in in vivo and in vitro studies [
56]. A schematic diagram of thymol’s action is depicted in
Figure 3. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are the main sensors used to detect various dangerous signals and activate innate immune responses. The classic TLR signaling pathway activates NF-κB to regulate the expressions of a series of cytokines [
57]. In mice and macrophages, thymol inhibits TLR4 expression and then inhibits the activation of NF-κB signaling, which reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β [
58,
59]. NF-κB is a master mediator of inflammatory responses. Inactive NF-κB binds to IκB, an inhibitory subunit of NF-κB, and presents in the cytoplasm. When activated by a variety of signals, such as cytokine receptors and pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs), IκB is phosphorylated and degraded to release RelA (p65) from the NF-κB complex. p65 is then translocated to the nucleus to induce pro-inflammatory cytokine expression as a transcription factor [
60]. Thymol has been shown to inhibit NF-κB activation by reducing p65 translocation and abundance in the colons of acetic acid-induced colitis rats and in LPS-activated macrophages, respectively, with decreased cytokine production [
61,
62]. The activation of NF-κB induces the expressions of iNOS and COX-2, which further promote vigorous inflammation. In ulcerative colitis rats, thymol reduces the COX-2 expression and nitric oxide (NO) levels produced by iNOS in the rats’ colon [
63]. These studies showed the anti-inflammatory function of thymol through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Figure 3. Mechanism of thymol in relieving inflammation. Cells receive various stimuli and activate IκB kinases (IκKs) through the TLR4 signaling pathway, and then IκB proteins are phosphorylated, ubiquitinated, and degraded, and NF-κB dimers are released. The NF-κB dimer is then further activated through various post-translational modifications and translocated into the nucleus to bind to target genes to promote pro-inflammatory gene transcription. In addition, by activating the MAPKs family, it can promote the expression of c-jun terminal kinases (JNK) 1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and p38 for activation, thereby promoting the nuclear entry of activator protein 1 (AP-1) to regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory genes. Thymol inhibits the dissociation of the IκB protein and NF-κB dimer and the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway to relieve inflammation.
Studies have reported that proteins in the MAPK family, such as JNK1/2, p38α, and ERK, are activated in the colonic mucosa of IBD patients [
71]. The suppression of the MAPK signaling pathway is an approach for alleviating inflammation and thus IBD [
71]. It has been reported that thymol inhibits p38 phosphorylation and interferes with the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway to maintain the immune balance [
64]. Thymol also suppresses LPS-induced activation of p-p38, p-JNK, and p-ERK, and correspondingly inhibits the production of NO, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, and other inflammatory cytokines [
72]. Therefore, thymol can also reduce the inflammatory response by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway.
Cytokines are synthesized and secreted by activated immune cells, such as macrophages, T cells, B cells, dendritic cells (DCs), and natural killer cells. Among them, the regulatory T cell (Treg) is essential to control autoimmunity. Treg is defined by the expression of CD4, CD25, and transcription factor forkhead box P3 (Foxp3) [
73]. Thymol promotes the differentiation of naïve T cells to CD4
+CD25
+Foxp3
+ Treg cells and induces Foxp3 expression [
74]. Meanwhile, thymol also maintains the balance of the Th1/Tregs and Th17/Tregs ratios to prevent autoimmunity as a result of suppressed inflammation [
74,
75]. Additionally, thymol exerts inhibitory effects on DCs’ maturation and T cell activation [
76]. Although thymol has influenced the immune cell population in some studies, more information is required on how thymol modulates immune cell differentiation and whether the changes in the immune cell population by thymol contribute to the relief of IBD.