Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Engineering, Industrial
GSCM involves environmental concerns in supply chain activities to minimize ecological impacts. The aim of GSCM is to find a balance between economic and environmental activities. GSCM deals with the concept of sustainability of the entire supply chain network along with providing green products or services to customers.
- green supply chain management
- multiobjective optimization
- mathematical model
1. Introduction
The notion of supply chain management (SCM) was introduced in the early 1980s [1]. However, it received immense attention from researchers and industries in the mid-1990s [1]. SCM consists of a network or organizations that involve upstream and downstream relations in various operations, producing value in the form of products and services with less expenditure [2]. Supply chain management integrates design, planning, and procurement with logistics activities to maximize profit and increase customer satisfaction. Today, environmental issues are receiving attention along with economic concerns to protect the Earth from global warming, maintain ecological balance, and reduce severe health problems. Therefore, SCM not only evolves around financial circumstances but also includes sustainability in the primary decision-making processes. SCM coupled with environmental factors is also known as the green supply chain management (GSCM) concept [3]. Ensuring green culture is the key for an organization to sustain itself in the competitive global market.
GSCM involves environmental concerns in supply chain activities to minimize ecological impacts [3]. The aim of GSCM is to find a balance between economic and environmental activities. GSCM deals with the concept of sustainability of the entire supply chain network along with providing green products or services to customers [4]. GSCM has been established as an essential discipline in the academic world and a separate branch of sustainability [5]. Maditati et al. (2018) presented the most cited definitions of GSCM and sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) [6]. The concept of GSCM evolved in the early 1990s when environmental issues became a burning question around the globe [7]. Several aspects, including waste management, natural resources, and efficient network systems of green supply chain management, have become potential research interests in academia. Over the past few years, the literature review in this area has expanded around green design, green operations, green manufacturing, reverse logistics, and waste management [5,6,7,8,9].
Some of the critical environmental aspects of the green supply chain are noticeable in the green design (engineering and marketing), green procurement practices (environment-friendly raw material, recycled material), and transportation (CO2 reduction and minimization of fuel consumption). However, implementing the green concept is one of the biggest challenges for enterprises since it often requires additional investment. A supply chain structure becomes more complex when the economic, social, and environmental aspects are incorporated into supply chain performance analysis. Thus, finding the right balance between the economic, social, and environmental issues during decision making is the top priority for many organizations.
To overcome the challenges mentioned, employing multiobjective optimization (MOO) techniques is suitable to formulate and analyze supply chain network design. The MOO problem deals with multiple conflicting objectives simultaneously. Usually, there is no single optimum solution for MOO problems. Instead, a set of non-dominated solutions, known as Pareto optimal solutions, are generated by solving the MOO problems [10]. A trade-off between social, economic, and environmental issues can be analyzed through MOO. Based on the decisionmaker’s preference, the optimal solution is chosen from the Pareto solution sets. Thus, the decisionmakers (DM) need expertise in the problem domain.
There are tremendous opportunities to apply MOO approaches in green supply chain applications to analyze economic, social, and environmental aspects. Current research has shown significant applications of MOO techniques in decision-making phases such as green supply chain network design in the agricultural [11], packaging [12], biofuel [13], or biodiesel [14] industries. Jayamartha et al. [15] reviewed MOO for sustainable supply chain and logistics applications from 1999 to 2019. This paper serves as an extension of their review and discusses in more detail how several MOO approaches are formulated and solved. Different types of MOO techniques, such as classical [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23], evolutionary [16,24,25,26,27,28], and interactive [29,30] methods, have been applied in GSCM application depending on the size and complexity of the problem or the attributions from the decisionmakers. Moreover, some researchers have incorporated uncertain parameters in the decision-making phases. In short, this literature provides an overview of the present studies for the applications of MOO techniques in GSCM.
2. Green Supply Chain Management
Green supply chain management integrates environmental factors into different supply chain activities, including product design, material sourcing and selection, manufacturing procedures, transportation to the end users, and management of the green product’s end of life [31,32]. Green design involves designing products with minimum material or energy consumption [33]. The green design also incorporates the reuse, recovery, or recycling of products or parts [34]. In addition, the green design also considers the negative impacts on the environment in a product’s life cycle. Green manufacturing minimizes waste and pollution during production activities [35,36]. Green logistics includes environment-friendly transportation, distribution, and alternative fuel options [37,38]. In short, environmental, social, and economic aspects are considered the objectives in measuring the performance of GSCM [4,39,40], as shown in Figure 1.
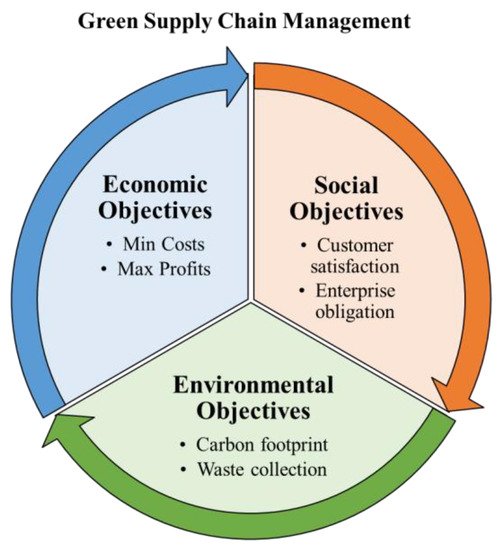
Figure 1. Three objectives of green supply chain management.
Green supply chain management can improve environmental performance, although the relationship depends on organizational capacity [41]. However, the relationship between environmental and economic performance is often conflicting in nature [42,43]. In many cases, enterprises would often like to maximize profits and minimize carbon emissions. However, maximizing profits by increasing supply chain activities often produces higher carbon emissions. It is essential to understand the relationship between social aspects, green supply chain management, and operational performance [44]. Enterprises often struggle to understand the direct link between green supply chain management adoption and the subsequent enhanced performance in operational, economic, or environmental areas. Thus, adopting green culture on a broad scale is often challenging to implement efficiently.
Before discussing MOO model development, different structures of the green supply chain are described. The model formulation includes certain model assumptions, notations regarding parameters, and decision variables. The mathematical model formulation is carried out considering several factors, including the conditions of the parameters. Generally, the entire model is formulated based on a deterministic assumption of parameters. However, in many cases, the parameters may be uncertain. The structure of the model formulation differs depending on the nature of the parameters. Finally, solution methods are implied to solve MOO problems to improve green supply chain performance. The solution methods may vary, considering the complexity of the problem and the decisionmakers’ preferences. The classical, evolutionary, and interactive methods are three broad categories of solution approaches.
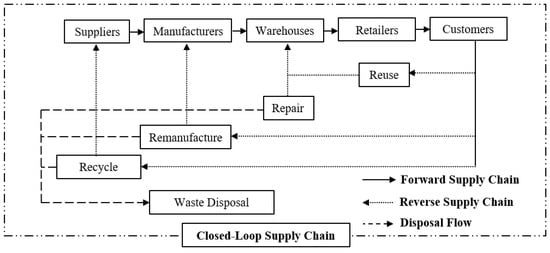
In order to design a green supply chain network, the first step is to choose a specific supply chain structure. Material and information flow between different domains of a supply chain network is required to be identified for multiobjective model formulation. Various supply chain structures are introduced in this section that are generally considered during the green model formulation. Figure 3 represents the overall structure of the forward, reverse, and closed-loop supply chain in one frame. Three types of supply chain structures are described in the following subsections.
2.1. Forward Supply Chain
The forward supply chain starts with delivering raw materials for manufacturing goods in a factory and ends with delivering goods to the end users. It is rather straightforward and encompasses all possible entities to satisfy customer requirements, such as suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, retailers, and customers [45,46]. In a typical forward supply chain structure, customers are the final entity of the process. Over the past few decades, the facility allocation problem in forward logistics has been considered a well-recognized topic by many researchers. A comprehensive summary of the modeling approaches in the forward supply chain over the past 15 years, where sustainability has been incorporated into the value chain, can be found in Refs. [47,48]. Thus, the modeling approaches for the forward supply chains are not elaborated further.
2.2. Reverse Supply Chain
The reverse supply chain deals with the practices and operations necessary to process the reuse of materials [50,51]. The prime objective of reverse logistics is to manage the backward flow in the current supply chain network. The reverse supply chain begins with collecting the used products from the customers and managing end-of-life products through decisions such as recycling, remanufacturing, repairing, and disposal [52]. Based on the American Reverse Logistics Executive Council’s definition, reverse logistics is ‘‘The process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, cost-effective flow of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods, and related information from the point of consumption to the point of origin for the purpose of recapturing value or proper disposal’’ [52,53]. The reverse logistics ensure an efficient reverse flow of the material from the point of consumption to the point of origin [46].
Reverse logistics are used in diverse fields, including the electronics, chemical, and medical industries [54]. While reverse logistics provide an excellent opportunity for remanufacturing the returned products, the entire process of recovering the product is extremely challenging. Collecting the product from the customer to the recovery center is highly expensive for companies. As a result, efficient network design is vital in reverse logistics. The reverse logistics starts with product return from the consumer end. Once the product condition is identified, the product is sent to the return collection centers. Ideally, products are inspected to categorize into fix, resell, repair, and recycle types. In the repair area, either the product is repaired or the sellable parts are sold. Similarly, the product is sent to the recycling area if any components or products are not fixable. The spare parts are collected either for reselling or waste material. Figure 4 highlights the major steps in a general reverse logistics flowchart.
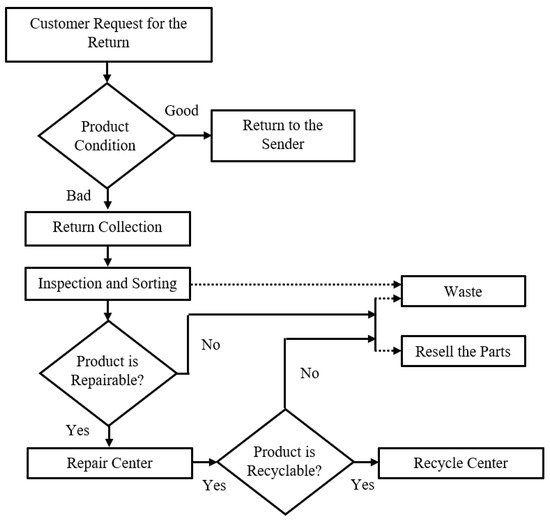
Figure 4. A flowchart of major steps in reverse logistics.
Several literature sources have addressed various supply chain aspects while discussing the concept of reverse logistics. Linton et al. [55] highlighted the interaction between sustainability and the supply chain by handling product design, product end of life, and the recovery process of end-of-life products. The review paper by Rubio et al. [56] summarized the literature on reverse logistics published between 1995 and 2005 and covered areas such as recovery, distribution of end-of-life products, production, and inventory management. Additionally, Pokharel and Mutha [57] reviewed major features of reverse logistics such as product acquisition, pricing, and collection of the used product.
2.3. Closed-Loop Supply Chain
Closed-loop supply chain combines both forward and reverse networks. The closed-loop supply chain deals with recovering the final product from the customers and creates added value by reusing the entire product or some parts of the product [58]. According to Kumar et al. [59], a closed-loop supply chain deals with the customer demand in the forward supply chain and manages the product’s end of life in reverse logistics. The closed-loop supply chain prioritizes efficient supply chain management aiming at reuse, remanufacture, recycling, and disposal. Figure 3 provides a collective overview of a closed-loop supply chain where forward and reverse supply flow are combined.
Several aspects of the closed-loop supply chain are still under observation. Researchers such as Schenkel et al. [60] showed ways to create values using a closed-loop supply chain. The value creation for the environment includes creating green products, processes, and markets, whereas the economic perspective provides cost and risk minimization. Customer value includes serving the customer better via return practices and services [61]. Finally, information value ensures the overall improvement of the forward and reverse supply chain, life cycle information, and product performance [62,63]. Additionally, researchers have also addressed the industrial challenges and uncertainties related to the remanufacturing system [64]. Therefore, studies are conducted regarding the performance improvement methods of the closed-loop supply chain. Asif et al. [65] highlighted that the performance of the closed-loop supply chain can be improved using a resource-conservative manufacturing approach.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/su141912790
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!