Neohumanism is a holistic philosophical theory proposed by the Indian spiritual teacher Prabhat Ranjan Sarkar (1921 – 1990) to promote individual and collective progress. In this philosophy universalism plays a central role. It claims to elevate humanism to level of universalism. It claims not to have any grouping intention.
- neohumanism
- universalism
- spiritual
1. History
Sarkar detailed Neohumanism in his 1982 book The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism.[1]
In 1987, Sarkar published Neohumanism in a Nutshell (parts 1 and 2). They contain more discourses on Neohumanism, from various times that he discussed it.[2][3]
2. Definition
Neohumanism has three stages of development.[4]
- The first stage of Neohumanism is spiritual practice to enhance the physical, mental, and spiritual well-being of the practitioner. The stage of spiritual practice indirectly benefits society through the social service that is part of spiritual practice.
- The second stage of Neohumanism is spiritual principle (or essence). Its impact is mainly in the mental and spiritual realms, both individual and collective. According to Neohumanism, practice of rationality and adherence to the principle of social equality (especially when combined with protospiritualistic mentality) will not only strengthen individual minds but also the collective human mind to the point that humanity as a whole can withstand the destructive impact of geosentiment and sociosentiment and the ruthless exploiters who capitalize on those sentiments.
- The third and final stage of Neohumanism is spiritual mission. According to Neohumanism, when an individual's existential nucleus (soul) merges with the "Cosmic Existential Nucleus", she/he attains the consummation of her/his existence. Neohumanism asserts that this supreme status ensures the future of not only the human world but also of the animal and plant worlds as well.
3. Concepts
List of Neohumanism's key concepts in alphabetical order.
3.1. Devotion
According to neohumanism, love for the Supreme (devotion) is the highest and most valuable treasure of humanity. It automatically results in universalism. However, neohumanism deems devotion to be a very tender inner asset, frequently assailed by materialism and other onslaughts from the external world. To preserve this treasure, Sarkar submits neohumanism as a practical philosophy that provides a protective fence for devotion by (1) establishing harmony between the spiritual and material worlds (2) providing perennial inspiration for the onward march of society.[1]
3.2. Dogma
Neohumanism defines dogma as a mental prison. In other words, a dogma is any concept (belief) that one is expected to accept without question. Neohumanism perceives such conduct as fundamentally contrary to human nature, which includes a constant quest for mental expansion. Hence, the position of neohumanism on dogma is that all dogma must be eradicated.[5]
3.3. Exploitation
Neohumanism discourages both geosentiment and sociosentiment, because both tend to be injurious to society. However, neohumanism observes that, of the two, sociosentiment is more pernicious. Under the influence of sociosentiment, one group of people are driven to exploit a second group of people, that second group of people are driven to exploit a third group of people, and so on.[6]
According to Neohumanism, there are many types of exploitation. Though Neohumanism contends that exploitation is initiated in the psychic arena—for instance by infusing inferiority complex based on language or color—this inevitably expresses as economic exploitation, which may manifest in either of two forms:
- Politico-economic exploitation occurs when an imperialist nation or group engages in economic exploitation through the use of brute force to impose direct political control over another nation or group. For example, under the British Empire, the United Kingdom variously ruled the nations it conquered through three political mechanisms: direct rule, viceroys, and governor-generals.
- Psycho-economic exploitation occurs when direct political control is not or is no longer feasible (often due to military logistics). At such times, the imperialist nation or group engages in economic exploitation by injecting fear and inferiority complexes in the minds of the people that they would colonize.
A common name for psycho-economic exploitation is neocolonialism. However, Neohumanism observes that there is nothing new about psycho-economic exploitation. Wherever politico-economic exploitation takes place, it is invariably accompanied by psychic exploitation, the goal of which being to make the colonized people more docile. In other words, according to Neohumanism, in both politico-economic exploitation and psycho-economic exploitation, psychic exploitation is the foundation.[6] Neohumanism asserts that when politico-economic exploitation is combined with psycho-economic exploitation, the likely social devastation is much greater.[6]
Exploiters
In nature, there is a mainstream, and there is also positive and negative deviation from the mainstream. This is true for all species of living beings. Neohumanism classifies this deviation for plants, animals, and humans. When a living being substantially deviates from the mainstream in a constructive fashion, neohumanism describes that being as remarkable, good, or blissful (depending on whether the structure of that being is of a plant, animal, or human respectively). Conversely, when a living being substantially deviates from the mainstream in a destructive fashion, neohumanism describes that being as notorious, bad, or demonic (depending on whether the structure of that being is of a plant, animal, or human respectively).[7] In respect to exploitation, our main concern is with human structures, specifically those human structures with genius that is exercised for destructive purpose, demons in human form/framework (DHFs).
DHFs are geniuses, and so they are exceptionally devious. They know how to pander to and play on the geosentiments and sociosentiments of the common people, who rarely think deeply. But truth does not remain hidden forever. So whenever a particular abuse of geosentiment or sociosentiment is about to get exposed or that particular geosentiment or sociosentiment is likely to lose popularity, DHFs switch to a different sentiment. Neohumanism designates the adaptive art of conveniently switching sentiments as metamorphosed sentimental strategy.[7]
According to neohumanism, DHFs wreak great havoc upon this world.[7] Because of their adeptness at metamorphosed sentimental strategy, Sarkar also sometimes refers to DHFs as human chameleons. Like chameleons, DHFs are often very difficult to spot. Nevertheless, Sarkar insists that it is the duty of all neohumanists to identify the DHFs. Not only must neohumanists identify the DHFs, but they must also expose them.[7]
3.4. Humanism (general)
According to neohumanism, the radius of geosentiment and sociosentiment may be relatively short or long. In other words, they both have a minimal and maximal expression (geosentiment or sociosentiment minimitis and maximitis). With respect to sociosentiment, its minimal expression (sociosentiment minimitis) is the attraction felt toward one's nuclear family. That minimal sociosentiment may be extended to embrace a larger community, for example, a city, a state, a nation, an ethnicity, a religious group, and so on. When sociosentiment extends beyond nationalism and internationalism, theoretically embracing all human beings, that is sociosentiment maximitis. According to Sarkar, general (or ordinary) humanism is essentially sociosentiment maximitis.[8]
Pseudohumanism
Neohumanism is of the view that general or ordinary humanism is a distorted humanism that has done and is still doing harm in the world. According to neohumanism, in so far as humanism expanded sociosentiment, it was a positive trend; but in so far as it sets limits on the expansion of the underlying spirit of humanism, love, it has been and continues to be counterproductive.
According to neohumanism, there is a tendency for general humanists to substitute pity for love. Sarkar said this type of pseudohumanism inevitably fosters intra-human conflict.
3.5. Humanity
Neohumanism rejects the classic definition of human being as "rational animal", which first appeared in Aristotle's Metaphysics insisting that human beings have characteristics distinct from animals. It considers human life to be an ideological flow, characterized by identification with and commitment to an ideology.[9]
3.6. Inspiration (Motivation)
According to neohumanism, the impetus (inspiration or motivation) for human movement - human dynamism - may be either of two conflicting principles: the principle of selfish pleasure (átma-sukha tattva) or the principle of social equality (sama-samája tattva).
Selfish pleasure
According to neohumanism, selfishness is a socially divisive mental ailment. Those who promote or accept the dogmas founded on the principle of selfish pleasure typically do so in order to secure their own vested interests.[10]
Social equality
The concept of egalitarianism has been in circulation for thousands of years. Over time, the concept has become broader and more sophisticated. Recently, various studies have been conducted with results that endorse the tremendous importance of having a more equitable society (see, for example, The Spirit Level: Why More Equal Societies Almost Always Do Better by Richard G. Wilkinson and Kate Pickett). Neohumanism promotes egalitarianism by asserting the principle of social equality and rejecting all dogma and superstition.[11] According to neohumanism, realization of the principle of social equality is a natural consequence of spiritual practice (especially meditation founded on yogic morality, Yama-Niyama[12]). However, realization of this principle is not the final stage of neohumanism, because application of a principle is somewhat mechanical. In the final stage of neohumanism, the human being's life is transformed into a blissful mission of love (see the third stage of neohumanism).
3.7. Internationalism
Many general humanists support the concept of internationalism. Neohumanism observes that internationalism does not even rise to the standard of ordinary humanism. Indeed, it poses the same sort of risk to global peace as nationalism. Sarkar explains the problem as follows:
Suppose I was working for a particular nation, but now I am working for all nations. When I admit the existence of nations and say that I am working for all nations, then it is neither humanism nor universalism – it is merely internationalism. When I use the term "internationalism", I am admitting the existence of separate nations, and along with this I must naturally also think, within the nations, of the people's five fundamental requirements of life (food, clothes, education, shelter, and medical care). But when I discover that one nation is trying to thrive on the life-blood of another, I oppose it, and this opposition ultimately leads to world war. So internationalism is not the solution either.[4]
From the perspective of neohumanism, the League of Nations could not prevent World War II, and the United Nations cannot prevent a World War III. Only a world government could ensure peace on this planet.
3.8. Mental Illness
According to neohumanism, the major cause of mental disorder is a lack of harmony between the rhythm and speed of the inner world and the outer world. In modern times, humanity has made great progress in the intellectual sphere. But, for most people, the speed of that intellectual progress is not well reflected in the external world (for example, a rising standard of living). Similarly, the patterns of thought for most persons (their internal psychic rhythm) is quite different from the external rhythm of the objective world. These disparities naturally cause clash, and that clash is felt even more in the psychic realm than the physical realm. Neohumanism asserts that this is the reason why many human beings lose their mental balance.[1]
3.9. Mental Modes
According to neohumanism, in addition to various activities like thinking and remembering, mind has three modes of functioning: instinct, sentiment, and rationality.[13]

- Instinct: The position of neohumanism on instinct is somewhat conventional. All living beings, developed and undeveloped, have innate instincts. Many if not most such instincts incite behavior that increases the likelihood of self-preservation of an organism or a species. So, for example, mosquitoes suck blood, and human babies drink their mother's milk. Neohumanism takes note of the fact that life feeds on life,[14] but insists that human beings must employ rationality in the selection of food.[15] In short, neohumanism recognizes the fact that human beings are motivated to some extent by instinct, but neohumanism expects human beings to rely more on rationality so that any needlessly destructive impact of instinct (and sentiment) is curtailed.
- Sentiment: Regarding sentiment, neohumanism broadens the perspective. According to neohumanism, undeveloped minds operate only on instinct; whereas, in more developed minds (including human minds), sentiment also functions and tends to exceed instinct. Goaded by sentiment, mind runs blindly after what it likes (or away from what it does not like). A sentimental being does not ask questions about propriety or even employ common sense. Accordingly, sentiment poses the risk that an irrational course of action may be adopted - a course of action that could destroy not just the sentimental individual but also an entire family or social group.
- Discrimination: Discrimination occurs when a conscious decision is taken regarding the appropriate course of action. A tiger stalks its prey and attacks from a selected vantage point. This is discrimination. A robber enters a house and calculates which room to plunder first, based on most likely gain. This is discrimination. A reasoned decision regarding pros and cons is taken. When discrimination goes one step further, considering a choice between right and wrong (proper and improper), then conscience (viveka) is invoked. At that point, discrimination rises to the level of rationality. Compared to instinct and sentiment, discrimination is a slow process. It takes more time to exercise discrimination.
3.10. Protopsychospirituality
Protopsychospirituality (also known as protospiritualistic mentality) is a type of thinking whereby one remembers that everything and everyone with whom one comes in contact is a manifestation of Supreme Consciousness (Parama Brahma). Before and after doing any action, if one remembers that all existential phenomena emanate from and return to the Supreme (Cosmic) Existential Nucleus, a benevolent mode of thinking naturally arises within the mind. In that state of mind, one cannot contemplate doing harm to others. Neohumanism asserts that a protospiritualistic mentality is essential for identifying some exceptionally devious exploiters. Identification becomes possible when the person with a protospiritualistic mentality notes that her/his benevolent mode of thinking is not reflected in the actions of the exploiter.[7]
3.11. Pseudoculture
Culture generally refers to the refinements in human expressions. Everyone eats. However, to eat only after washing one's hands is commonly deemed to be part of the culture of eating. According to neohumanism, human culture is one, but there are variations in its expression. For example, humans, being social creatures, typically like to communicate; but, depending on locality, different languages are used. Neohumanism observes that whenever one group of people has sought to economically exploit another group of people, the former group simultaneously attempted to destroy the local cultural expressions of the latter group. This has been done through the imposition of pseudoculture. Examples of the imposition of pseudoculture are the forced acceptance of an imperialist ruler's language, religious dogma, style of dress, style of eating, political forms, historical perspectives, and artistic expressions.
Pseudoculture is imposed by various means from brute force to the mass media to public education. Often, the standard of refinement in pseudoculture is less than that which it replaces. But regardless of the standard of refinement, the end result is that the cultural backbone of the colonized society is broken. Psychologically crippled, the colonized people lose the will and the power to protest against exploitation. Instead, they tend to deem it just and proper to hand over much of their national wealth to the exploiters.[16]
3.12. Rationality
Philosophers have defined rationality in various ways. Some of those definitions could equally apply to animals or even plants. Neohumanism offers a new and precise definition of rationality that calls for a standard of mentality that is not discernible in any species other than human beings. According to neohumanism, rationality (also known as rationalistic mentality) is a three-stage process of discrimination that begins with adequate study to assimilate all relevant facts, proceeds to analyze the pros and cons of an action, and ends with a decision in favor of only a blissful auxiliary (practical action that furthers the welfare of all).[17]
3.13. Religion
Prabhat Ranjan Sarkar
Throughout history, religion has had a domineering influence on the human mind. According to neohumanism, all religions are based on dogma, and the propagation of that religious dogma has been instrumental in the creation of satellite groups. Some religious persons and priests propagate the damaging dogma of religion unwittingly. When such persons are made to understand their mistake, some admit their error and rectify themselves. Others, however, refuse to do so, fearing that the admission of error would injure their prestige. The latter group of persons thereby join the ranks of conscious agents of injustice.[18]

3.14. Sentiments
According to neohumanism, two types of sentiment are common to human beings (in both an individual and collective sense): geosentiment and sociosentiment.[19] Both sentiments have a minimal and a maximal expression (geosentiment or sociosentiment minimitis and maximitis). As with any sentiment, both geosentiment and sociosentiment may have good uses, but there is also great risk of harm (harm to others and harm to oneself). Neohumanism observes that those who would exploit other human beings for their own selfish gain (exploiters) typically employ these two types of sentiment, often shifting or transforming sentiments whenever convenient.
Geosentiment
Geosentiment is the attraction felt toward one's own home, city, or country. Its minimal expression (geosentiment minimitis) is love for one's home (house, homestead, or the like). The maximal expression of geosentiment (geosentiment maximitis) is love for one's country. In theory, one might feel love for the entire planet, but today such an expression of geosentiment would be very rare, possibly non-existent. In the future, when interplanetary travel becomes commonplace, geosentiment maximitis may expand.
Geosentiment presents in many forms: geopolitics, geoeconomics, geopatriotism, georeligion, and so on. For example, georeligion would associate a religion or a religious group with a specific territory. So, the belief that God has granted a particular territory to a particular group of people is an example of georeligion. Similarly, the belief that prayer must be carried out facing in a specific direction is another expression of georeligion. Such type of beliefs (geosentiments) may prove harmless or harmful, depending on circumstances. According to neohumanism, the potential for harm in geosentiment can be curbed through the cultivation of a rationalistic mentality.[20]
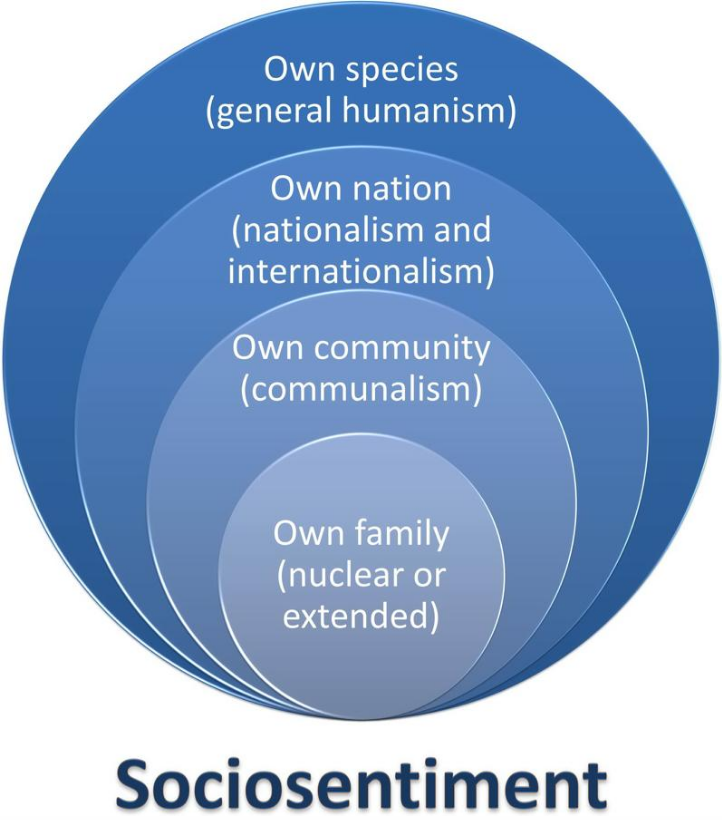
Sociosentiment
Sociosentiment is the attraction felt toward one's own family, nation, or other social grouping (linguistic, religious, political, and so on). Its minimal expression (sociosentiment minimitis) is the attraction felt toward one's nuclear family. That minimal sociosentiment may be extended to embrace a larger community, for example, a city, a state, a nation, an ethnicity, a religious group, and so on. When sociosentiment extends beyond nationalism and internationalism, theoretically embracing all human beings, that is sociosentiment maximitis. According to Sarkar, general (or ordinary) humanism is essentially sociosentiment maximitis.[8]
Sociosentiment presents itself in many forms: sociopolitics, socioeconomics, sociopatriotism, socioreligion, and so on. For example, sociopatriotism might express itself as jingoism with declarations like "my country, right or wrong" or "my country over all others". Socioeconomics might express itself in the form of an imperialist attempt to create colonies or satellite states.
Compared to geosentiment, sociosentiment has the capacity to do - and has done - much greater harm in the world. Sociosentiment can also be more difficult to recognize. As such, rationality might not be adequate to offset the dangers of sociosentiment. To overcome sociosentiment, neohumanism prescribes an additional tool, protopsychospirituality.[21]
3.15. Social Justice
Neohumanism extends the concept of society to include all living beings. Unlike most other theories, past or present, neohumanism distinguishes between human society and society (in its broadest or universal sense).
In respect to the universal society, the stance of neohumanism corresponds to the spirit of the third fundamental principle of PROUT. The physical, mental, and spiritual potential of each and every living being should be developed to the maximum. This means that humans should not only respect and protect the rights of the non-human creatures but also actively promote their welfare and happiness.
Regarding human society, neohumanism asserts that no one should be left to lag behind. In a healthy human society, no one should suffer from oppression. Every problem - big or small, individual or collective - should be taken as a problem of the entire humanity.[22] So, for example, neohumanism is claimed to oppose any form of social discrimination based on race or sex, and support women's rights. Neohumanism makes men responsible for acting in support of those rights.[23]
The concern of neohumanism for social justice extends even to relatively minor but intractable matters. So, for example, though it pertains only to grammar, the male bias of the English language should not continue. When the pronoun 'he' can mean 'he' or 'she' and when 'man' can mean 'man' or 'woman', should not the same be the case with 'she' and 'woman'? Either English must have neutral words or the meaning of existing words must change. Though such type of change generally takes a while to implement, neohumanism insists that it be done.
3.16. Social Progress
As with PROUT, neohumanism views social progress as a condition in which the welfare and happiness of the entire society is increased. Neohumanism considers the individual and the society to be an inalienable concomitance. Unlike other philosophical theories that would satisfice or allegedly optimize social well-being through principles like the lesser of two evils principle or the greatest good for the greatest number, neohumanism measures progress on the basis of improvements in the poorest sectors of society. According to neohumanism, what is genuinely good for the individual is also good for the society; and what is genuinely good for the society is also good for the individual.
Neohumanism distinguishes two ways in which social progress may be effected: evolution and revolution.
- Evolution brings gradual and specific change.
- Revolution brings rapid and comprehensive change.
Of the two systems, neohumanism greatly prefers revolution.[24]
Neohumanism distinguishes four types of people who take a stance on the subject of social change: reactionaries, reformists, vocal revolutionaries, and revolutionaries.
- Reactionaries openly oppose change. Neohumanism respects their honesty but deems such persons to be suffering from a fear complex.[25]
- Reformists promote some miscellaneous fixes. According to neohumanism, such persons outwardly claim to want change, but their inner desire is to perpetuate the machinery of exploitation. The contradictory nature of reformism may manifest as a pseudoreformist strategy.[26]
- Vocal revolutionaries (also referred to as pseudorevolutionaries) are similar to reformists but even less forthright. They pretend to want revolutionary change, but their tall talk is belied by their action.[27]
- Revolutionaries are forthright about their vision of a new society and unrelenting in their effort to materialize that vision.
According to neohumanism, revolutionaries are the true well-wishers of society. As such, neohumanism asserts that only the revolutionaries can effect significant social progress.
3.17. Universalism
Neohumanism's concept of universalism is non-religious. It is a type of love that extends to all beings of this universe, animate and even inanimate. From the perspective of Neohumanism, such a viewpoint is the ultimate outcome of the principle of 'social equality and 'protopsychospirituality'.[7]
3.18. Value Systems
According to neohumanism, the human-centered utilitarian approach of general humanism is problematic in that it allows the possibility of cruelty to animals and plants. Such type of cruelty inevitably fosters inter-creature clash. Neohumanism extends this analysis by observing that cruelty has a tendency to become habitual. In other words, what a human does today to an animal, that same human may do tomorrow to another human being. Hence, according to neohumanism, general humanism may also foster intra-human clash. To offset the anthropic bias of general humanism and to reduce the potential for conflict, neohumanism posits two types of value: utility value and existential value.[28]
Existential value and utility value
According to neohumanism, until now, people have tended to think primarily in terms of utility value, typically the utility that another entity has for oneself or one's nation. So, for example, when horses were a primary means of transportation, the utility value of horses to human beings was very great. Today, with more efficient and comfortable means of transportation, horses have lost most of their utility value for humans. Accordingly, Sarkar argues that the status of horses in modern society is much reduced. But neohumanism insists that horses also have existential value. The existential value of a horse to itself is no less than the existential value of a human being to itself. In terms of the existential value one holds for one's own existence, all beings are said to be equal. Neohumanism would give greater importance to this existential value than to utility value.[28] Sarkar said: "Who says that those creatures who have lost their immediate utility value have no right to exist? No one has the moral right to say this.[28]
4. Applied Neohumanism
- Renaissance Universal (RU) - an organization for intellectuals. It promotes science, 'rationality, 'social equality, and 'universalism' to solve problems confronting humanity and to expand our mental horizon.[29]
- Renaissance Artists and Writers Association (RAWA) (a department of Renaissance Universal) seeks to inspire, unite, and uplift humanity through the fine arts and literature. RAWA organized performances and competitions for Prabhat Samgiita.[30] The slogan of RAWA is "art for service and blessedness". This is in stark contrast to the oft-heard slogan, "art for art's sake".[31][32]
- Ananda Marga schools: A of Ananda Marga Pracaraka Samgha, is education. Ananda Marga schools (from kindergartens to universities) have been established[33]http://gurukul.edu/newsletter/issue33/ananda-marga-school-kulu-india/[34] [35]
- Ananda Marga Universal Relief Team (AMURT) and its sister organization, Ananda Marga Universal Relief Team (Ladies) or AMURTEL - is a disaster relief organization. It has long-term projects through a department known as AMUPRESO (Ananda Marga Universal Permanent Relief Society).[36]
- Prevention of Cruelty to Animals and Plants - has a wide scope including animals and plants.[37][38]
5. Critiques
In a recent book,[39] Helen Crovetto asserts that there is a "dramatic" number of correlations between Ananda Marga and Mark Juergensmeyer's "description of religious groups inclined toward terrorism". Crovetto mentions here the imagery of "cosmic war" that appears in Sarkar's writings, and Crovetto repeatedly references language that seems to "satanize" opponents, for example, the term demon in human form that is part of the terminology of neohumanism. After considerable analysis, Crovetto concludes that it is probably more appropriate to describe the followers of Sarkar as revolutionary rather than terrorist. As such, Crovetto classifies them as "revolutionary sociospiritual utopians".
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Philosophy:Neohumanism
References
- When the underlying spirit of humanism is extended to everything, animate and inanimate, in this universe – I have designated this as "neohumanism". This neohumanism will elevate humanism to universalism, the cult of love for all created beings of this universe. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Devotional Sentiment and Neohumanism (Discourse 1)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- "Neo- Humanism in a Nutshell - 1". Ananda Marga. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. https://web.archive.org/web/20160304093145/http://ampublications.org/product-detail.php?proid=33&mode=addtocart. Retrieved 15 January 2013.
- "Neo- Humanism in a Nutshell - 2". Ananda Marga. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. https://web.archive.org/web/20160304101630/http://ampublications.org/product-detail.php?proid=34. Retrieved 15 January 2013.
- Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Neohumanism Is the Ultimate Shelter (Discourse 11)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- The snares of dogma will have to be shattered to pieces; the iron prison gates of dogma will have to be crushed to dust. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Bondages and Solutions (Discourse 2)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Now, in sociosentiment, it happens that a certain group exploits another, and that exploited group in turn exploits a third. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Exploitation and Pseudoculture (Discourse 7)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Whenever people, after performing some activity, think of the Nucleus of the circum-rotarian universe, their minds become all-pervasive. Such people can never think of harming others; rather they will think only of universal welfare. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "An Ideology for a New Generation (Discourse 10)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Now, this sociosentiment, in its stage of excellencio or in theory maximitis, is called "humanism." Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Pseudohumanism (Discourse 8)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Shrii Shrii Anandamurti, "The Glory of Human Dharma", 21 February 1979, Bhopal. Published in Ananda Vacanamrtam Part 8, Ananda Marga Publications, 1987.
- All the social, economic and geographical forces that normally motivate human beings are guided by dogma; and this dogma in its turn is entirely based on átma-sukha tattva [the principle of selfish pleasure]. Human beings yield to this dogma with the sole intention of attaining selfish pleasures; even educated people knowingly submit to dogma. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Sama-Samája Tattva (Discourse 6)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- The endeavor to advance towards the ultimate reality by forming a society free from all inequalities, with everyone of the human race moving in unison, is called sama-samája tattva [the principle of social equality]... We must totally reject all those hypocritical ideas which are contrary to this sama-samája tattva, and we must welcome all those ideas which will help human beings to be established in it. All opposing theories must be removed mercilessly, just like thorns from our path. And in this process we must not give indulgence to any dogmas or supernatural ideas. This should be the task of today’s human beings; all people should combine their efforts and strive unitedly to accomplish that end. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Sama-Samája Tattva (Discourse 6)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Shrii Shrii Anandamurti, A Guide to Human Conduct. Fourth Paperback Edition, 2004, Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:9788172521035.
- Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Geo-Sentiment (Discourse 3)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- It is true that living creatures are the food for other living beings (jiivah jiivasya bhojanam); and indeed, the vegetables that we eat every day also have living cells in them. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Devotional Sentiment and Neohumanism (Discourse 1)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Once I read in a certain book that a great saint used to live only on locusts dipped in honey. That saint did not seriously consider that those little locusts also had vital life force throbbing in them... This concern for the vital rhythm throbbing in other human creatures has driven people to the fold of humanism, has made them humanists. Now, if the same human sentiment is extended to include all creatures of this universe, then and only then can human existence be said to have attained its final consummation. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Devotional Sentiment and Neohumanism (Discourse 1)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- This exploitation in the cultural sphere is accomplished by the propagation of pseudoculture. Every honest, virtuous, rational person must fight against this pseudoculture, and inspire others to do the same. If this is not done, the future of humanity will be sealed. It is proper for human beings to struggle for political freedom, for social emancipation; but if their cultural backbone is broken, then all their struggles will end in nothing – like offering ghee into a fire that has died out. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Exploitation and Pseudoculture (Discourse 7)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- In the first stage you study; in the second you analyze the positive and negative sides; and in the third stage you arrive at "blissful or non-blissful, auxiliary or non-auxiliary". When you complete this whole process of logical reasoning, the outcome is your "awakened conscience". This state of awakened conscience is what is called "rationalistic mentality". Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Awakened Conscience (Discourse 9)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Exploitation and Pseudoculture (Discourse 7)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Bondages and Solutions (Discourse 2)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Geosentiment (Discourse 3)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- What is the way to counteract this sociosentiment? The only way to eliminate it is to develop protospiritualistic mentality. The basis of this protospiritualistic mentality is sama-samája tattva [the principle of social equality]. When people understand this principle from the core of their hearts, they spontaneously develop protospiritualistic mentality, protospiritualistic psychic structure. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Bondages and Solutions (Discourse 2)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Spread out the sermons of amity amongst the humanity. Remind one and all that the establishment of human excellence does not lie in hypocrisy but in simplicity and sincerity. Make them all realize that every individual human problem, whether big or small, is the problem of universal humanity. Make them also understand that the origin as well as the finality of the entire humanity is one and the same. Shrii Shrii Anandamurti, 1982 January 1. Ánanda Váńii Saḿgraha. Compilation from 1956-1990, Ananda Marga Publications.
- In every sphere of life men have either substantially limited the rights of women, or made the ability of women to exercise their rights subject to the whims and caprices of men... The main point of the discussion is this: those who take advantage of people’s simplicity or ignorance are veritable demons in human form, and those who deceive people by exploiting their sentiments of sacrifice are even worse than demons... If at all a movement is required, it must be implemented by men themselves. Today men should consider the needs of women and gradually restore to women the rights which women once entrusted to men out of feelings of helplessness or in response to their heartfelt sentiments. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1959). Human Society Part 1. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-120-0.
- Now, those who are courageous enough to speak out this truth in clear language – those who say, "Shatter this bondage of limitation!" – their path is called the path of revolution. And those who say, "Everything will be done gradually... why so much haste?" – their path is called the path of evolution. They can never accomplish any glorious task. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Exploitation and Pseudoculture (Discourse 7)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- There are still others who say straightforwardly, "No, no, how can I contradict the way followed by my ancestors – my father, my grandfather?" They are reactionaries. They suffer from a mental disease. They are afraid to accept the new; they suffer from fear complex. They utter high-sounding phrases, but their hearts are filled with fear complexes. Not that they are terribly reprehensible. They say outwardly: "We are just doing the same as our ancestors did." But their ancestors used to wear wooden sandals instead of shoes, and shawls instead of tailored shirts, eat guŕ [raw sugar] instead of refined sugar, and drink water from wells instead of from taps. Do they follow this also? Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Exploitation and Pseudoculture (Discourse 7)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- The reformists say, "Let us go slowly on the path of reform." But actually they intend that the process of exploitation should continue without interruption. There were many reformists in the world, but in reality they did not want the welfare of the society; they only wanted to perpetuate the process of exploitation by bringing about some patchwork improvements. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Exploitation and Pseudoculture (Discourse 7)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- I have branded these people as "vocal revolutionaries". They deliver long lectures against exploitation, but they do the opposite in practice. Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Exploitation and Pseudoculture (Discourse 7)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- Sarkar, Prabhat Ranjan (1982). "Pseudohumanism (Discourse 8)" of The Liberation of Intellect: Neohumanism. Kolkata: Ananda Marga Publications. ISBN:81-7252-168-5.
- http://www.ru.org/ru.html
- http://www.thestatesman.net/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&show=archive&id=385734&catid=47&year=2011&month=10&day=7
- http://rawa.asia/mp3/info/rawa-structure.html
- http://www.hindu.com/thehindu/mp/2002/08/26/stories/2002082600070400.htm
- . The education system is also known as Neohumanist Education under Ananda Marga Gurukula the board of education for Neohumanist schools in the world.
- http://www.ru.org/economics/peace-for-a-troubled-world-neo-humanist-education.html
- Sil, Milly (2016). "NEO-HUMANISM AND PROUT: ALTERNATIVE PEDAGOGY". https://appliedsentience.com/2016/05/31/neo-humanism-and-prout-alternative-pedagogy/.
- http://www.rurapuk.com/volunteers.html
- http://pcap.amps.org/about.htm
- Anandamurtijii, Shrii Shrii (Apr 28, 2014). "PCAP - Prevention of Cruelty to Animals and PLants Eco Quiz". Wellness Blog on Speakingtree.in. Times of India Group. http://www.speakingtree.in/spiritual-blogs/masters/wellness/pcap-prevention-of-cruelty-to-animals-and-plants-eco-quiz. Retrieved 12 May 2014.
- Lewis, James R. Violence and New Religious Movements. Oxford University Press, 2011. ISBN:0199735611.
