This is a list of known oxidation states of the chemical elements, excluding nonintegral values. The most common states appear in bold. The table is based on that of Greenwood and Earnshaw, with additions noted. Oxidation state 0, which occurs for all elements, is implied by the column with the symbol of the element. The format of the table, which was devised by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1889, shows the periodicity of the oxidation states of the elements.
- nonintegral
- oxidation states
- oxidation
1. List
| Z | Element | Negative oxidation states |
Positive oxidation states |
Group | Notes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −5 | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | +9 | ||||
| 1 | hydrogen | −1 | H | +1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 2 | helium | He | 18 | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | lithium | Li | +1 | 1 | [1] | |||||||||||||
| 4 | beryllium | Be | +1 | +2 | 2 | [2] | ||||||||||||
| 5 | boron | −5 | −1 | B | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [3][4] | |||||||||
| 6 | carbon | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | C | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | |||||||
| 7 | nitrogen | −3 | −2 | −1 | N | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | |||||||
| 8 | oxygen | −2 | −1 | O | +1 | +2 | 16 | |||||||||||
| 9 | fluorine | −1 | F | 17 | ||||||||||||||
| 10 | neon | Ne | 18 | |||||||||||||||
| 11 | sodium | −1 | Na | +1 | 1 | [1] | ||||||||||||
| 12 | magnesium | Mg | +1 | +2 | 2 | [5] | ||||||||||||
| 13 | aluminium | −2 | −1 | Al | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [6][7][8] | |||||||||
| 14 | silicon | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | Si | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | |||||||
| 15 | phosphorus | −3 | −2 | −1 | P | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | |||||||
| 16 | sulfur | −2 | −1 | S | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | |||||||
| 17 | chlorine | −1 | Cl | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 17 | [9] | ||||||
| 18 | argon | Ar | 18 | |||||||||||||||
| 19 | potassium | −1 | K | +1 | 1 | [1] | ||||||||||||
| 20 | calcium | Ca | +1 | +2 | 2 | [10] | ||||||||||||
| 21 | scandium | Sc | +1 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [11][12] | |||||||||||
| 22 | titanium | −2 | −1 | Ti | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [13][14][15] | ||||||||
| 23 | vanadium | −3 | −1 | V | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [14] | |||||||
| 24 | chromium | −4 | −2 | −1 | Cr | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [14] | |||||
| 25 | manganese | −3 | −2 | −1 | Mn | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | |||||
| 26 | iron | −4 | −2 | −1 | Fe | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 8 | [16][17][18] | ||||
| 27 | cobalt | −3 | −1 | Co | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 9 | [14] | |||||||
| 28 | nickel | −2 | −1 | Ni | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 10 | [19] | ||||||||
| 29 | copper | −2 | Cu | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 11 | [18] | |||||||||
| 30 | zinc | −2 | Zn | +1 | +2 | 12 | [18][20] | |||||||||||
| 31 | gallium | −5 | −4 | −2 | −1 | Ga | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [7][21] | |||||||
| 32 | germanium | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | Ge | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [22] | ||||||
| 33 | arsenic | −3 | −2 | −1 | As | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [7][23][24] | ||||||
| 34 | selenium | −2 | −1 | Se | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [25][26][27][28] | ||||||
| 35 | bromine | −1 | Br | +1 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +7 | 17 | |||||||||
| 36 | krypton | Kr | +2 | 18 | ||||||||||||||
| 37 | rubidium | −1 | Rb | +1 | 1 | [1] | ||||||||||||
| 38 | strontium | Sr | +1 | +2 | 2 | [29] | ||||||||||||
| 39 | yttrium | Y | +1 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [30][31] | |||||||||||
| 40 | zirconium | −2 | Zr | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [14][32] | |||||||||
| 41 | niobium | −3 | −1 | Nb | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [14][33] | |||||||
| 42 | molybdenum | −4 | −2 | −1 | Mo | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [14] | |||||
| 43 | technetium | −3 | −1 | Tc | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | ||||||
| 44 | ruthenium | −4 | −2 | Ru | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | 8 | [14][18] | ||||
| 45 | rhodium | −3 | −1 | Rh | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 9 | [14] | ||||||
| 46 | palladium | Pd | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 10 | [34][35] | ||||||||||
| 47 | silver | −2 | −1 | Ag | +1 | +2 | +3 | 11 | [18][36] | |||||||||
| 48 | cadmium | −2 | Cd | +1 | +2 | 12 | [18][37] | |||||||||||
| 49 | indium | −5 | −2 | −1 | In | +1 | +2 | +3 | 13 | [7][38][39] | ||||||||
| 50 | tin | −4 | −3 | −2 | −1 | Sn | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [7][40][41] | ||||||
| 51 | antimony | −3 | −2 | −1 | Sb | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [7][42][43][44] | ||||||
| 52 | tellurium | −2 | −1 | Te | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [7][45][46][47] | ||||||
| 53 | iodine | −1 | I | +1 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 17 | [48][49] | |||||||
| 54 | xenon | Xe | +2 | +4 | +6 | +8 | 18 | [50] | ||||||||||
| 55 | caesium | −1 | Cs | +1 | 1 | [1] | ||||||||||||
| 56 | barium | Ba | +1 | +2 | 2 | [51] | ||||||||||||
| 57 | lanthanum | La | +1 | +2 | +3 | 3 | [52] | |||||||||||
| 58 | cerium | Ce | +2 | +3 | +4 | |||||||||||||
| 59 | praseodymium | Pr | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | [53][54] | |||||||||||
| 60 | neodymium | Nd | +2 | +3 | +4 | [55] | ||||||||||||
| 61 | promethium | Pm | +2 | +3 | [56] | |||||||||||||
| 62 | samarium | Sm | +2 | +3 | ||||||||||||||
| 63 | europium | Eu | +2 | +3 | ||||||||||||||
| 64 | gadolinium | Gd | +1 | +2 | +3 | |||||||||||||
| 65 | terbium | Tb | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | [56] | |||||||||||
| 66 | dysprosium | Dy | +2 | +3 | +4 | [57] | ||||||||||||
| 67 | holmium | Ho | +2 | +3 | [56] | |||||||||||||
| 68 | erbium | Er | +2 | +3 | [56] | |||||||||||||
| 69 | thulium | Tm | +2 | +3 | ||||||||||||||
| 70 | ytterbium | Yb | +2 | +3 | ||||||||||||||
| 71 | lutetium | Lu | +2 | +3 | [56] | |||||||||||||
| 72 | hafnium | −2 | Hf | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 4 | [14][58] | |||||||||
| 73 | tantalum | −3 | −1 | Ta | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 5 | [14][33] | |||||||
| 74 | tungsten | −4 | −2 | −1 | W | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 6 | [14] | |||||
| 75 | rhenium | −3 | −1 | Re | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | 7 | ||||||
| 76 | osmium | −4 | −2 | −1 | Os | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | 8 | [18][59] | |||
| 77 | iridium | −3 | −1 | Ir | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | +8 | +9 | 9 | [60][61][62][63] | |||
| 79 | gold | −3 | −2 | −1 | Au | +1 | +2 | +3 | +5 | 11 | [18] | |||||||
| 80 | mercury | −2 | Hg | +1 | +2 | 12 | [18][64] | |||||||||||
| 82 | lead | −4 | −2 | −1 | Pb | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 14 | [7][65][66] | |||||||
| 83 | bismuth | −3 | −2 | −1 | Bi | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | 15 | [67][68][69][70] | ||||||
| 84 | polonium | −2 | Po | +2 | +4 | +5 | +6 | 16 | [71] | |||||||||
| 85 | astatine | −1 | At | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 | 17 | ||||||||||
| 86 | radon | Rn | +2 | +6 | 18 | [72][73][74] | ||||||||||||
| 87 | francium | Fr | +1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 88 | radium | Ra | +2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| 89 | actinium | Ac | +3 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| 90 | thorium | Th | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | [75][76] | |||||||||||
| 91 | protactinium | Pa | +3 | +4 | +5 | |||||||||||||
| 92 | uranium | U | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | [77][78] | |||||||||
| 93 | neptunium | Np | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | [79] | |||||||||
| 94 | plutonium | Pu | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | [80] | |||||||||
| 95 | americium | Am | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | +7 | [81] | |||||||||
| 96 | curium | Cm | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 | [82][83][84] | |||||||||||
| 97 | berkelium | Bk | +3 | +4 | +5 | [82] | ||||||||||||
| 98 | californium | Cf | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | [82] | |||||||||||
| 99 | einsteinium | Es | +2 | +3 | +4 | [85] | ||||||||||||
| 100 | fermium | Fm | +2 | +3 | ||||||||||||||
| 101 | mendelevium | Md | +2 | +3 | ||||||||||||||
| 102 | nobelium | No | +2 | +3 | ||||||||||||||
| 103 | lawrencium | Lr | +3 | |||||||||||||||
| 104 | rutherfordium | Rf | +4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| 105 | dubnium | Db | +5 | 5 | [86] | |||||||||||||
| 106 | seaborgium | Sg | +6 | 6 | [87] | |||||||||||||
| 107 | bohrium | Bh | +7 | 7 | [88] | |||||||||||||
| 108 | hassium | Hs | +8 | 8 | [89] | |||||||||||||
| 109 | meitnerium | Mt | 9 | |||||||||||||||
| 110 | darmstadtium | Ds | 10 | |||||||||||||||
| 111 | roentgenium | Rg | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| 112 | copernicium | Cn | +2 | 12 | [90] | |||||||||||||
| 113 | nihonium | Nh | 13 | |||||||||||||||
| 114 | flerovium | Fl | 14 | |||||||||||||||
| 115 | moscovium | Mc | 15 | |||||||||||||||
| 116 | livermorium | Lv | 16 | |||||||||||||||
| 117 | tennessine | Ts | 17 | |||||||||||||||
| 118 | oganesson | Og | 18 | |||||||||||||||
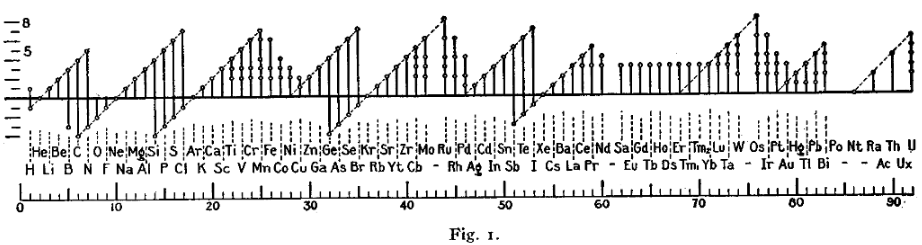
A figure with a similar format (shown below) was used by Irving Langmuir in 1919 in one of the early papers about the octet rule.[91] The periodicity of the oxidation states was one of the pieces of evidence that led Langmuir to adopt the rule.
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:List_of_oxidation_states_of_the_elements
References
- null
- Be(I) has been observed in beryllium monohydride (BeH); see Shayesteh, A.; Tereszchuk, K.; Bernath, P. F.; Colin, R. (2003). "Infrared Emission Spectra of BeH and BeD". J. Chem. Phys. 118 (3): 1158. doi:10.1063/1.1528606. Bibcode: 2003JChPh.118.1158S. Archived from the original on 2007-12-02. https://web.archive.org/web/20071202130342/http://bernath.uwaterloo.ca/media/252.pdf. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- B(−1) has been observed in magnesium diboride (MgB2), see James Keeler, Peter Wothers (2014). Chemical Structure and Reactivity: An Integrated Approach. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199604135. https://books.google.com/books?id=2RgbAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA315&lpg=PA315#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- B(−5) has been observed in Al3BC, see Melanie Schroeder. "Eigenschaften von borreichen Boriden und Scandium-Aluminium-Oxid-Carbiden" (in de). p. 139. https://www.deutsche-digitale-bibliothek.de/binary/KKUKEQ5AXZBNJVU7NJCHZB4UXT2HAGJE/full/1.pdf.
- Low valent magnesium compounds with Mg(I) have been obtained using bulky ligands; see Green, S. P.; Jones C.; Stasch A. (December 2007). "Stable Magnesium(I) Compounds with Mg-Mg Bonds". Science 318 (5857): 1754–1757. doi:10.1126/science.1150856. PMID 17991827. Bibcode: 2007Sci...318.1754G. https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscience.1150856
- Al(II) has been observed in aluminium(II) oxide (AlO); see D. C. Tyte (1964). "Red (B2Π–A2σ) Band System of Aluminium Monoxide". Nature 202 (4930): 383–384. doi:10.1038/202383a0. Bibcode: 1964Natur.202..383T. , and in dialanes (R2Al—AlR2); see Uhl, Werner "Organoelement Compounds Possessing Al—Al, Ga—Ga, In—In, and Tl—Tl Single Bonds" Advances in Organometallic Chemistry Volume 51, 2004, Pages 53–108. doi:10.1016/S0065-3055(03)51002-4 https://doi.org/10.1016%2FS0065-3055%2803%2951002-4
- Negative oxidation states of p-block metals (Al, Ga, In, Sn, Tl, Pb, Bi, Po) and metalloids (Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, At) may occur in Zintl phases, see: [1], p. 259 and [2] (both in German).
- Al(−2) has been observed in Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3, see Wemdorff, Marco; Röhr, Caroline (2007). "Sr14[Al42[Ge]3: Eine Zintl-Phase mit isolierten [Ge]4–- und [Al4]8–-Anionen / Sr14[Al4]2[Ge]3: A Zintl Phase with Isolated [Ge]4–- and [Al4]8– Anions"] (in de). Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B 62 (10): 1227. doi:10.1515/znb-2007-1001. http://www.degruyter.com/view/j/znb.2007.62.issue-10/znb-2007-1001/znb-2007-1001.xml.
- The equilibrium Cl2O6⇌2ClO3 is mentioned by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but it has been refuted, see Lopez, Maria; Juan E. Sicre (1990). "Physicochemical properties of chlorine oxides. 1. Composition, ultraviolet spectrum, and kinetics of the thermolysis of gaseous dichlorine hexoxide". J. Phys. Chem. 94 (9): 3860–3863. doi:10.1021/j100372a094. , and Cl2O6 is actually chlorine(V,VII) oxide. However, ClO3 has been observed, see Grothe, Hinrich; Willner, Helge (1994). "Chlorine Trioxide: Spectroscopic Properties, Molecular Structure, and Photochemical Behavior". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 33 (14): 1482–1484. doi:10.1002/anie.199414821. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fj100372a094
- Ca(I) has been observed; see Krieck, Sven; Görls, Helmar; Westerhausen, Matthias (2010). "Mechanistic Elucidation of the Formation of the Inverse Ca(I) Sandwich Complex [(thf)3Ca(μ-C6H3-1,3,5-Ph3)Ca(thf)3] and Stability of Aryl-Substituted Phenylcalcium Complexes". Journal of the American Chemical Society 132 (35): 12492–501. doi:10.1021/ja105534w. PMID 20718434. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fja105534w
- Sc(I) has been observed; see Polly L. Arnold; F. Geoffrey; N. Cloke; Peter B. Hitchcock; John F. Nixon (1996). "The First Example of a Formal Scandium(I) Complex: Synthesis and Molecular Structure of a 22-Electron Scandium Triple Decker Incorporating the Novel 1,3,5-Triphosphabenzene Ring". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118 (32): 7630–7631. doi:10.1021/ja961253o. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fja961253o
- Sc(II) has been observed; see Woen, David H.; Chen, Guo P.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Boyle, Timothy J.; Furche, Filipp; Evans, William J. (January 2017). "Solution Synthesis, Structure, and CO Reduction Reactivity of a Scandium(II) Complex". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 56 (8): 2050–2053. doi:10.1002/anie.201611758. PMID 28097771. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fanie.201611758
- Ti(I) has been observed in [Ti(η6-1,3,5-C6H3iPr3)2][BAr4] (Ar = C6H5, p-C6H4F, 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2); see Fausto Calderazzo, Isabella Ferri, Guido Pampaloni, Ulli Englert, Malcolm L. H. Green (1997). "Synthesis of [Ti(η6-1,3,5-C6H3iPr3)2][BAr4] (Ar = C6H5, p-C6H4F, 3,5-C6H3(CF3)2), the First Titanium(I) Derivatives". Organometallics 16 (14): 3100–3101. doi:10.1021/om970155o. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fom970155o
- Ti(−2), V(−3), Cr(−4), Co(−3), Zr(−2), Nb(−3), Mo(−4), Ru(−2), Rh(−3), Hf(−2), Ta(−3), and W(−4) occur in anionic binary metal carbonyls; see [3], p. 4 (in German); [4], pp. 97–100; [5], p. 239
- Ti(−1) has been reported in [Ti(bipy)3]−, but was later shown to be Ti(+3); see Bowman, A. C.; England, J.; Sprouls, S.; Weihemüller, T.; Wieghardt, K. (2013). "Electronic structures of homoleptic [tris(2,2'-bipyridine)M]n complexes of the early transition metals (M = Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta; n = 1+, 0, 1-, 2-, 3-): an experimental and density functional theoretical study". Inorganic Chemistry 52 (4): 2242–56. doi:10.1021/ic302799s. PMID 23387926. However, Ti(−1) occurs in [Ti(η-C6H6]− and [Ti(η-C6H5CH3)]−, see Bandy, J. A.; Berry, A.; Green, M. L. H.; Perutz, R. N.; Prout, K.; Verpeautz, J.-N. (1984). "Synthesis of anionic sandwich compounds: [Ti(η-C6H5R)2]– and the crystal structure of [K(18-crown-6)(µ-H)Mo(η-C5H5)2]". Inorganic Chemistry 52 (4): 729–731. doi:10.1039/C39840000729. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fic302799s
- Fe(VII) has been observed in [FeO4]−; see Lu, Jun-Bo; Jian, Jiwen; Huang, Wei; Lin, Hailu; Zhou, Mingfei (2016). "Experimental and theoretical identification of the Fe(VII) oxidation state in FeO4−". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 18 (45): 31125–31131. doi:10.1039/C6CP06753K. PMID 27812577. Bibcode: 2016PCCP...1831125L. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/cp/c6cp06753k#!divAbstract.
- Fe(VIII) has been reported; see Yurii D. Perfiliev; Virender K. Sharma (2008). "Higher Oxidation States of Iron in Solid State: Synthesis and Their Mössbauer Characterization – Ferrates – ACS Symposium Series (ACS Publications)". Platinum Metals Review 48 (4): 157–158. doi:10.1595/147106704X10801. However, its existence has been disputed. https://dx.doi.org/10.1595%2F147106704X10801
- Fe(−4), Ru(−4), and Os(−4) have been observed in metal-rich compounds containing octahedral complexes [MIn6−xSnx]; Pt(−3) (as a dimeric anion [Pt–Pt]6−), Cu(−2), Zn(−2), Ag(−2), Cd(−2), Au(−2), and Hg(−2) have been observed (as dimeric and monomeric anions; dimeric ions were initially reported to be [T–T]2− for Zn, Cd, Hg, but later shown to be [T–T]4− for all these elements) in La2Pt2In, La2Cu2In, Ca5Au3, Ca5Ag3, Ca5Hg3, Sr5Cd3, Ca5Zn3(structure (AE2+)5(T–T)4−T2−⋅4e−), Yb3Ag2, Ca5Au4, and Ca3Hg2; Au(–3) has been observed in ScAuSn and in other 18-electron half-Heusler compounds. See Changhoon Lee; Myung-Hwan Whangbo (2008). "Late transition metal anions acting as p-metal elements". Solid State Sciences 10 (4): 444–449. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2007.12.001. Bibcode: 2008SSSci..10..444K. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1293255807003883. and Changhoon Lee; Myung-Hwan Whangbo; Jürgen Köhler (2010). "Analysis of Electronic Structures and Chemical Bonding of Metal-rich Compounds. 2. Presence of Dimer (T–T)4– and Isolated T2– Anions in the Polar Intermetallic Cr5B3-Type Compounds AE5T3 (AE = Ca, Sr; T = Au, Ag, Hg, Cd, Zn)". Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 636 (1): 36–40. doi:10.1002/zaac.200900421.
- Ni(−2) has been observed in Li2[Ni(1,5-COD)2], see Jonas, Klaus (1975). "Dilithium-Nickel-Olefin Complexes. Novel Bimetal Complexes Containing a Transition Metal and a Main Group Metal". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 14 (11): 752–753. doi:10.1002/anie.197507521. and Ellis, John E. (2006). "Adventures with Substances Containing Metals in Negative Oxidation States". Inorganic Chemistry 45 (8): 3167–86. doi:10.1021/ic052110i. PMID 16602773. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fanie.197507521
- Zn(I) has been observed in decamethyldizincocene (Zn2(η5–C5Me5)2); see Resa, I.; Carmona, E.; Gutierrez-Puebla, E.; Monge, A. (2004). "Decamethyldizincocene, a Stable Compound of Zn(I) with a Zn-Zn Bond". Science 305 (5687): 1136–8. doi:10.1126/science.1101356. PMID 15326350. Bibcode: 2004Sci...305.1136R. https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscience.1101356
- Ga(−2), Ga(−4), and Ga(−5) have been observed in the magnesium gallides MgGa, Mg2Ga, and Mg5Ga2, respectively; see Patrick Hofmann. "Colture. Ein Programm zur interaktiven Visualisierung von Festkörperstrukturen sowie Synthese, Struktur und Eigenschaften von binären und ternären Alkali- und Erdalkalimetallgalliden" (in de). p. 72. http://www.uni-kassel.de/upress/online/frei/978-3-7281-2597-2.volltext.frei.pdf.
- Ge(−1), Ge(−2), and Ge(−3) have been observed in germanides; see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). "Germanium" (in German). Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 953–959. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9. .
- As(I) has been observed in arsenic(I) iodide (AsI); see Ellis, Bobby D.; MacDonald, Charles L. B. (2004). "Stabilized Arsenic(I) Iodide: A Ready Source of Arsenic Iodide Fragments and a Useful Reagent for the Generation of Clusters". Inorganic Chemistry 43 (19): 5981–6. doi:10.1021/ic049281s. PMID 15360247. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fic049281s
- As(IV) has been observed in arsenic(IV) hydroxide (As(OH)4) and HAsO−3; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Bielski, Benon H. J.; Sehested, K. (1989). "Arsenic(IV). A pulse-radiolysis study". Inorganic Chemistry 28 (14): 2717–24. doi:10.1021/ic00313a007. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fic00313a007
- Se(−1) has been observed in diselenides(2−) (Se22−).
- Se(I) has been observed in selenium(I) chloride (Se2Cl2); see "Selenium : Selenium(I) chloride compound data". WebElements.com. http://www.webelements.com/webelements/compounds/text/Se/Cl2Se2-10025680.html. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- Se(III) has been observed in Se2NBr3; see Lau, Carsten; Neumüller, Bernhard; Vyboishchikov, Sergei F.; Frenking, Gernot; Dehnicke, Kurt; Hiller, Wolfgang; Herker, Martin (1996). "Se2NBr3, Se2NCl5, Se2NCl−6: New Nitride Halides of Selenium(III) and Selenium(IV)". Chemistry: A European Journal 2 (11): 1393–1396. doi:10.1002/chem.19960021108. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fchem.19960021108
- Se(V) has been observed in SeO2−3 and HSeO2−4; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, K. (1986). "Selenium(V). A pulse radiolysis study". Inorganic Chemistry 90 (21): 5460–4. doi:10.1021/j100412a112. http://orbit.dtu.dk/en/publications/seleniumv-a-pulse-radiolysis-study(01d1260d-45a3-4a09-8316-e6f6b4993561).html.
- Sr(I) has been observed in strontium monofluoride (SrF); see P. Colarusso et al. (1996). "High-Resolution Infrared Emission Spectrum of Strontium Monofluoride". Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy 175 (1): 158–171. doi:10.1006/jmsp.1996.0019. Bibcode: 1996JMoSp.175..158C. Archived from the original on 2012-03-08. https://web.archive.org/web/20120308063843/http://bernath.uwaterloo.ca/media/149.pdf.
- Y(I) has been observed in yttrium(I) bromide (YBr); see "Yttrium: yttrium(I) bromide compound data". OpenMOPAC.net. Archived from the original on 2011-07-23. https://web.archive.org/web/20110723233118/http://www.openmopac.net/data_normal/yttrium%28i%29%20bromide_jmol.html. Retrieved 2007-12-10.
- Y(II) has been observed in [(18-crown-6)K][(C5H4SiMe3)3Y]; see MacDonald, M. R.; Ziller, J. W.; Evans, W. J. (2011). "Synthesis of a Crystalline Molecular Complex of Y2+, [(18-crown-6)K][(C5H4SiMe3)3Y]". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133 (40): 15914–17. doi:10.1021/ja207151y. PMID 21919538. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fja207151y
- Zr(−1) has been reported in [Zr(bipy)3]− (see Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 960. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8. and Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). "Zirconium" (in German). Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1413. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9. ), but was later shown to be Zr(+4); see Bowman, A. C.; England, J.; Sprouls, S.; Weihemüller, T.; Wieghardt, K. (2013). "Electronic structures of homoleptic [tris(2,2'-bipyridine)M]n complexes of the early transition metals (M = Sc, Y, Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta; n = 1+, 0, 1-, 2-, 3-): an experimental and density functional theoretical study". Inorganic Chemistry 52 (4): 2242–56. doi:10.1021/ic302799s. PMID 23387926. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fic302799s
- Nb(I) and Ta(I) occur in CpNb(CO)4 and CpTa(CO)4, see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1995). "Tantal" (in German). Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (101 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1430. ISBN 978-3-11-012641-9. and King, R. Bruce (1969). Transition-Metal Organometallic Chemistry: An Introduction. Academic Press. pp. 11. ISBN 978-0-32-315996-8.
- Pd(I) has been observed; see Crabtree, R. H. (2002). "CHEMISTRY: A New Oxidation State for Pd?". Science 295 (5553): 288–289. doi:10.1126/science.1067921. PMID 11786632. https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscience.1067921
- Pd(III) has been observed; see Powers, D. C.; Ritter, T. (2011). Palladium(III) in Synthesis and Catalysis. Topics in Organometallic Chemistry. 35. 129–156. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17429-2_6. ISBN 978-3-642-17428-5. http://www.chem.harvard.edu/groups/ritter/pdf/2011-129t.pdf.
- The Ag− ion has been observed in metal ammonia solutions: see Tran, N. E.; Lagowski, J. J. (2001). "Metal Ammonia Solutions: Solutions Containing Argentide Ions". Inorganic Chemistry 40 (5): 1067–68. doi:10.1021/ic000333x. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fic000333x
- Cd(I) has been observed in cadmium(I) tetrachloroaluminate (Cd2(AlCl4)2); see Holleman, Arnold F.; Wiberg, Egon; Wiberg, Nils (1985). "Cadmium" (in German). Lehrbuch der Anorganischen Chemie (91–100 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1056–1057. ISBN 978-3-11-007511-3.
- In(–5) has been observed in La3InGe, see Guloy, A. M.; Corbett, J. D. (1996). "Synthesis, Structure, and Bonding of Two Lanthanum Indium Germanides with Novel Structures and Properties". Inorganic Chemistry 35 (9): 2616–22. doi:10.1021/ic951378e. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fic951378e
- In(−2) has been observed in Na2In, see [6], p. 69.
- 3.0.co;2-u. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12379848. Retrieved 2015-02-23. " id="ref_40">Sn(−3) has been observed in [Sn2]6−, e.g. in (Ba2)4+(Mg4)8+Sn4−(Sn2)6−Sn2− (with square (Sn2−)n sheets), see Papoian, Garegin A.; Hoffmann, Roald (2000). "Hypervalent Bonding in One, Two, and Three Dimensions: Extending the Zintl–Klemm Concept to Nonclassical Electron-Rich Networks". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000 (39): 2408–2448. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20000717)39:14<2408::aid-anie2408>3.0.co;2-u. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12379848. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- Sn(I) and Sn(III) have been observed in organotin compounds
- Sb(−2) has been observed in [Sb2]4−, e.g. in RbBa4[Sb2][Sb][O], see Boss, Michael; Petri, Denis; Pickhard, Frank; Zönnchen, Peter; Röhr, Caroline (2005). "Neue Barium-Antimonid-Oxide mit den Zintl-Ionen [Sb]3−, [Sb2]4− und 1∞[Sbn]n− / New Barium Antimonide Oxides containing Zintl Ions [Sb]3−, [Sb2]4− and 1∞[Sbn]n−" (in de). Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 631 (6–7): 1181–1190. doi:10.1002/zaac.200400546. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fzaac.200400546
- Sb(I) and Sb(II) have been observed in organoantimony compounds; for Sb(I), see Šimon, Petr; de Proft, Frank; Jambor, Roman; Růžička, Aleš; Dostál, Libor (2010). "Monomeric Organoantimony(I) and Organobismuth(I) Compounds Stabilized by an NCN Chelating Ligand: Syntheses and Structures". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 49 (32): 5468–5471. doi:10.1002/anie.201002209. PMID 20602393. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fanie.201002209
- Sb(IV) has been observed in [SbCl6]2−, see Nobuyoshi Shinohara; Masaaki Ohsima (2000). "Production of Sb(IV) Chloro Complex by Flash Photolysis of the Corresponding Sb(III) and Sb(V) Complexes in CH3CN and CHCl3". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 73 (7): 1599–1604. doi:10.1246/bcsj.73.1599. https://dx.doi.org/10.1246%2Fbcsj.73.1599
- Te(I) has been observed in tellurium iodide (TeI), see "Tellurium: tellurium iodide". WebElements.com. http://www.webelements.com/compounds/tellurium/tellurium_iodide.html. Retrieved 2015-02-23.
- Te(III) has been observed in [Te(N(SiMe3)2)2]+, see Heinze, Thorsten; Roesky, Herbert W.; Pauer, Frank; Stalke, Dietmar; Sheldrick, George M. (1991). "Synthesis and Structure of the First Tellurium(III) Radical Cation". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 30 (12): 1678. doi:10.1002/anie.199116771. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237225046. Retrieved 2015-02-23. .
- Te(V) is mentioned by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but they do not give any example of a Te(V) compound. What was long thought to be ditellurium decafluoride (Te2F10) is actually bis(pentafluorotelluryl) oxide, F5TeOTeF5: see Watkins, P. M. (1974). "Ditellurium decafluoride - A Continuing Myth". Journal of Chemical Education 51 (9): 520–521. doi:10.1021/ed051p520. However, Te(V) has been observed in H2TeO−4, TeO−3, HTeO2−4, and TeO3−4; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, K. (2001). "Tellurium(V). A Pulse Radiolysis Study". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 105 (27): 6637–45. doi:10.1021/jp010577i. Bibcode: 2001JPCA..105.6637K. http://orbit.dtu.dk/en/publications/tellurium-5-a-pulse-radiolysis-study(58c2417f-34c0-436d-8a46-211f3d752423).html.
- I(IV) has been observed in iodine dioxide (IO2); see Pauling, Linus (1988). "Oxygen Compounds of Nonmetallic Elements". General Chemistry (3rd ed.). Dover Publications, Inc.. p. 259. ISBN 978-0-486-65622-9.
- I(VI) has been observed in IO3, IO42−, H5IO6−, H2IO52−, H4IO62−, and HIO53−; see Kläning, Ulrik K.; Sehested, Knud; Wolff, Thomas (1981). "Laser flash photolysis and pulse radiolysis of iodate and periodate in aqueous solution. Properties of iodine(VI)". J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1 77 (7): 1707–18. doi:10.1039/F19817701707. https://dx.doi.org/10.1039%2FF19817701707
- Xe(I) has been reported in xenon hexafluoroplatinate and xenon hexafluororhodate (see Pauling, Linus (1988). General Chemistry (3rd ed.). Dover Publications, Inc.. p. 250. ISBN 978-0-486-65622-9. ), however these compounds were later found to contain Xe(II).
- Ba(I) has been observed in barium monofluoride (BaF); see P. Colarusso et al. (1995). "High-Resolution Fourier Transform Infrared Emission Spectrum of Barium Monofluoride". Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy 170: 59. doi:10.1006/jmsp.1996.0019. Bibcode: 1996JMoSp.175..158C. Archived from the original on 2005-03-10. https://web.archive.org/web/20050310180822/http://bernath.uwaterloo.ca/media/126.pdf.
- La(I) has been observed in lanthanum monohydride (LaH); see Ram, R. S.; Bernath, P. F. (1996). "Fourier Transform Emission Spectroscopy of New Infrared Systems of LaH and LaD". Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy 104 (17): 6444. doi:10.1063/1.471365. Bibcode: 1996JChPh.104.6444R. Archived from the original on 2005-03-10. https://web.archive.org/web/20050310194449/http://bernath.uwaterloo.ca/media/143.pdf.
- Pr(V) has been observed in [PrO2]+; see Zhang, Qingnan; Hu, Shu-Xian; Qu, Hui; Su, Jing; Wang, Guanjun; Lu, Jun-Bo; Chen, Mohua; Zhou, Mingfei et al. (2016-06-06). "Pentavalent Lanthanide Compounds: Formation and Characterization of Praseodymium(V) Oxides". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 55 (24): 6896–6900. doi:10.1002/anie.201602196. ISSN 1521-3773. PMID 27100273. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fanie.201602196
- Hu, Shu-Xian; Jian, Jiwen; Su, Jing; Wu, Xuan; Li, Jun; Zhou, Mingfei (2017). "Pentavalent lanthanide nitride-oxides: NPrO and NPrO− complexes with NPr triple bonds" (in en). Chemical Science 8 (5): 4035–4043. doi:10.1039/C7SC00710H. ISSN 2041-6520. PMID 28580119. PMC 5434915. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2017/SC/C7SC00710H#!divAbstract.
- Nd(IV) has been observed in unstable solid state compounds; see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils, ed., Inorganic Chemistry, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- All the lanthanides (La–Lu) in the +2 oxidation state have been observed (except La, Gd, Lu) in dilute, solid solutions of dihalides of these elements in alkaline earth dihalides (see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils, ed., Inorganic Chemistry, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5 ) and (except Pm) in organometallic molecular complexes, see Lanthanides Topple Assumptions and Meyer, G. (2014). "All the Lanthanides Do It and Even Uranium Does Oxidation State +2". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 53 (14): 3550–51. doi:10.1002/anie.201311325. PMID 24616202. . Additionally, all the lanthanides (La–Lu) form dihydrides (LnH2), dicarbides (LnC2), monosulfides (LnS), monoselenides (LnSe), and monotellurides (LnTe), but for most elements these compounds have Ln3+ ions with electrons delocalized into conduction bands, e. g. Ln3+(H−)2(e−). http://cen.acs.org/articles/91/i24/Lanthanides-Topple-Assumptions.html
- Dy(IV) has been observed in unstable solid state compounds; see Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils, ed., Inorganic Chemistry, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- Hf(I) has been observed in hafnium monobromide (HfBr), see Marek, G.S.; Troyanov, S.I.; Tsirel'nikov, V.I. (1979). "Кристаллическое строение и термодинамические характеристики монобромидов циркония и гафния / Crystal structure and thermodynamic characteristics of monobromides of zirconium and hafnium" (in ru). Журнал неорганической химии / Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry 24 (4): 890–893. https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:11520917.
- Os(−1) has been observed in Na2[Os4(CO)13]; see Krause, J.; Siriwardane, Upali; Salupo, Terese A.; Wermer, Joseph R.; Knoeppel, David W.; Shore, Sheldon G. (1993). "Preparation of [Os3(CO)11]2− and its reactions with Os3(CO)12; structures of [Et4N] [HOs3(CO)11] and H2OsS4(CO)". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 454: 263–271. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(93)83250-Y. and Carter, Willie J.; Kelland, John W.; Okrasinski, Stanley J.; Warner, Keith E.; Norton, Jack R. (1982). "Mononuclear hydrido alkyl carbonyl complexes of osmium and their polynuclear derivatives". Inorganic Chemistry 21 (11): 3955–3960. doi:10.1021/ic00141a019. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2F0022-328X%2893%2983250-Y
- Ir(−3) has been observed in Ir(CO)33−; see Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1117. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Ir(VII) has been observed in [(η2-O2)IrO2]+; see C&EN: Iridium dressed to the nines. http://2014.cenmag.org/iridium-dressed-to-the-nines/
- Ir(VIII) has been observed in iridium tetroxide (IrO4); see Gong, Yu; Zhou, Mingfei; Kaupp, Martin; Riedel, Sebastian (2009). "Formation and Characterization of the Iridium Tetroxide Molecule with Iridium in the Oxidation State +VIII". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 48 (42): 7879–7883. doi:10.1002/anie.200902733. PMID 19593837. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fanie.200902733
- Ir(IX) has been observed in IrO+4; see Wang, Guanjun; Zhou, Mingfei; Goettel, James T.; Schrobilgen, Gary G.; Su, Jing; Li, Jun; Schlöder, Tobias; Riedel, Sebastian (21 August 2014). "Identification of an iridium-containing compound with a formal oxidation state of IX". Nature 514 (7523): 475–477. doi:10.1038/nature13795. PMID 25341786. Bibcode: 2014Natur.514..475W. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038%2Fnature13795
- Hg(IV) has been reported in mercury(IV) fluoride (HgF4); see Xuefang Wang; Lester Andrews; Sebastian Riedel; Martin Kaupp (2007). "Mercury Is a Transition Metal: The First Experimental Evidence for HgF4". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46 (44): 8371–8375. doi:10.1002/anie.200703710. PMID 17899620. However, it could not be confirmed by later experiments; see Is mercury a transition metal? http://www2.hull.ac.uk/science/chemistry/research/inorganicmaterials/mercurytransitionmaterial.aspx
- Pb(−2) has been observed in BaPb, see Ferro, Riccardo (2008). Nicholas C. Norman. ed. Intermetallic Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 505. ISBN 978-0-08-044099-6. and Todorov, Iliya; Sevov, Slavi C. (2004). "Heavy-Metal Aromatic Rings: Cyclopentadienyl Anion Analogues Sn56− and Pb56− in the Zintl Phases Na8BaPb6, Na8BaSn6, and Na8EuSn6". Inorganic Chemistry 43 (20): 6490–94. doi:10.1021/ic000333x. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fic000333x
- Pb(+1) and Pb(+3) have been observed in organolead compounds, e.g. hexamethyldiplumbane Pb2(CH3)6; for Pb(I), see Siew-Peng Chia; Hong-Wei Xi; Yongxin Li; Kok Hwa Lim; Cheuk-Wai So (2013). "A Base-Stabilized Lead(I) Dimer and an Aromatic Plumbylidenide Anion". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52 (24): 6298–6301. doi:10.1002/anie.201301954. PMID 23629949. . https://dx.doi.org/10.1002%2Fanie.201301954
- Bi(−2) and Bi(−1) occur in Zintl phases, e.g. (Ca2+)22[Bi4]4−([Bi2]4−)4[Bi3−]8; see Ponou, Siméon (2006). "Germanides, Germanide-Tungstate Double Salts and Substitution Effects in Zintl Phases". Technische Universität München. Lehrstuhl für Anorganische Chemie mit Schwerpunkt Neue Materialien. p. 68. http://d-nb.info/985527676/34?origin=publication_detailSim.
- Bi(I) has been observed in bismuth monobromide (BiBr) and bismuth monoiodide (BiI); see Godfrey, S. M.; McAuliffe, C. A.; Mackie, A. G.; Pritchard, R. G. (1998). Nicholas C. Norman. ed. Chemistry of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Springer. pp. 67–84. ISBN 978-0-7514-0389-3.
- Bi(+2) has been observed in dibismuthines (R2Bi—BiR2), see Arthur J. Ashe III (1990). Thermochromic Distibines and Dibismuthines. 30. 77–97. doi:10.1016/S0065-3055(08)60499-2. ISBN 9780120311309. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2FS0065-3055%2808%2960499-2
- Bi(IV) has been observed; see A. I. Aleksandrov, I. E. Makarov (1987). "Formation of Bi(II) and Bi(IV) in aqueous hydrochloric solutions of Bi(III)". Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science 36 (2): 217–220. doi:10.1007/BF00959349. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2FBF00959349
- Po(V) has been observed in dioxidopolonium(1+) (PoO+2); see Thayer, John S. (2010). "Relativistic Effects and the Chemistry of the Heavier Main Group Elements". Relativistic Methods for Chemists. p. 78. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9975-5_2. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2F978-1-4020-9975-5_2
- Rn(II) has been observed in radon difluoride (RnF2); see Stein, L. (1970). "Ionic Radon Solution". Science 168 (3929): 362–4. doi:10.1126/science.168.3929.362. PMID 17809133. Bibcode: 1970Sci...168..362S. and Kenneth S. Pitzer (1975). "Fluorides of radon and element 118". J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. (18): 760b – 761. doi:10.1039/C3975000760b. https://dx.doi.org/10.1126%2Fscience.168.3929.362
- Rn(IV) is reported by Greenwood and Earnshaw, but is not known to exist; see Sykes, A. G. (1998). "Recent Advances in Noble-Gas Chemistry". Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. 46. Academic Press. pp. 91–93. ISBN 978-0-12-023646-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=6iqXRtz6p3QC. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- Rn(VI) is known in radon trioxide (RnO3); see Sykes, A. G. (1998). "Recent Advances in Noble-Gas Chemistry". Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. 46. Academic Press. pp. 91–93. ISBN 978-0-12-023646-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=6iqXRtz6p3QC. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- Th(I) is known in thorium(I) bromide (ThBr); see Wickleder, Mathias S.; Fourest, Blandine; Dorhout, Peter K. (2006). "Thorium". in Morss, Lester R.; Edelstein, Norman M.; Fuger, Jean. The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements. 3 (3rd ed.). Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Springer. pp. 52–160. doi:10.1007/1-4020-3598-5_3. ISBN 978-1-4020-3555-5. http://radchem.nevada.edu/classes/rdch710/files/thorium.pdf.
- Th(II) and Th(III) are observed in [ThII{η5-C5H3(SiMe3)2}3]− and [ThIII{η5-C5H3(SiMe3)2}3], see Langeslay, Ryan R.; Fieser, Megan E.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Furche, Philip; Evans, William J. (2015). "Synthesis, structure, and reactivity of crystalline molecular complexes of the {[C5H3(SiMe3)23Th}1− anion containing thorium in the formal +2 oxidation state"]. Chem. Sci. 6 (1): 517–521. doi:10.1039/C4SC03033H. PMID 29560172. PMC 5811171. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2015/SC/C4SC03033H#!divAbstract. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- U(I) has been observed in uranium monofluoride (UF) and uranium monochloride (UCl), see Sykes, A. G. (1990). "Compounds of Thorium and Uranium". Advances in Inorganic Chemistry. 34. Academic Press. pp. 87–88. ISBN 978-0-12-023634-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=MZRm6E9LmgMC. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- U(II) has been observed in [K(2.2.2-Cryptand)][(C5H4SiMe3)3U], see MacDonald, Matthew R.; Fieser, Megan E.; Bates, Jefferson E.; Ziller, Joseph W.; Furche, Filipp; Evans, William J. (2013). "Identification of the +2 Oxidation State for Uranium in a Crystalline Molecular Complex, [K(2.2.2-Cryptand)][(C5H4SiMe3)3U]". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 (36): 13310–13313. doi:10.1021/ja406791t. PMID 23984753. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fja406791t
- Np(II) has been observed, see Dutkiewicz, Michał S.; Apostolidis, Christos; Walter, Olaf; Arnold, Polly L (2017). "Reduction chemistry of neptunium cyclopentadienide complexes: from structure to understanding". Chem. Sci. 8 (4): 2553–2561. doi:10.1039/C7SC00034K. PMID 28553487. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=5431675
- Pu(II) has been observed in −; see Windorff, Cory J.; Chen, Guo P; Cross, Justin N; Evans, William J.; Furche, Filipp; Gaunt, Andrew J.; Janicke, Michael T.; Kozimor, Stosh A. et al. (2017). "Identification of the Formal +2 Oxidation State of Plutonium: Synthesis and Characterization of −". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 (11): 3970–3973. doi:10.1021/jacs.7b00706. PMID 28235179. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fjacs.7b00706
- Am(VII) has been observed in AmO5−6; see Americium, Das Periodensystem der Elemente für den Schulgebrauch (The periodic table of elements for schools) chemie-master.de (in German), Retrieved 28 November 2010 and Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1265. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8. http://www.chemie-master.de/FrameHandler.php?loc=http://www.chemie-master.de/pse/pse.php?modul=Am
- Cm(V), Bk(V), and Cf(V) have been observed in BkO2+, CfO2+, CmO2(NO3)2−, BkO2(NO3)2−, and CfO2(NO3)2−; see Dau, Phuong Diem; Vasiliu, Monica; Peterson, Kirk A; Dixon, David A; Gibsoon, John K (October 2017). "Remarkably High Stability of Late Actinide Dioxide Cations: Extending Chemistry to Pentavalent Berkelium and Californium". Chemistry - A European Journal 23 (68): 17369–17378. doi:10.1002/chem.201704193. PMID 29024093. http://www.escholarship.org/uc/item/1mk7j6ps. and Kovács, Attila; Dau, Phuong D.; Marçalo, Joaquim; Gibson, John K. (2018). "Pentavalent Curium, Berkelium, and Californium in Nitrate Complexes: Extending Actinide Chemistry and Oxidation States". Inorg. Chem. 57 (15): 9453–9467. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01450. PMID 30040397. .
- Cm(VI) has been observed in curium trioxide (CmO3) and dioxidocurium(2+) (CmO2+2); see Domanov, V. P.; Lobanov, Yu. V. (October 2011). "Formation of volatile curium(VI) trioxide CmO3". Radiochemistry 53 (5): 453–6. doi:10.1134/S1066362211050018. https://dx.doi.org/10.1134%2FS1066362211050018
- Cm(VIII) has been reported to possibly occur in curium tetroxide (CmO4); see Domanov, V. P. (January 2013). "Possibility of generation of octavalent curium in the gas phase in the form of volatile tetraoxide CmO4". Radiochemistry 55 (1): 46–51. doi:10.1134/S1066362213010098. However, new experiments seem to indicate its nonexistence: Zaitsevskii, Andréi; Schwarz, W H Eugen (April 2014). "Structures and stability of AnO4 isomers, An = Pu, Am, and Cm: a relativistic density functional study". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2014 (16): 8997–9001. doi:10.1039/c4cp00235k. PMID 24695756. Bibcode: 2014PCCP...16.8997Z. https://dx.doi.org/10.1134%2FS1066362213010098
- Es(IV) is known in einsteinium(IV) fluoride (EsF4); see Kleinschmidt, P (1994). "Thermochemistry of the actinides". Journal of Alloys and Compounds 213–214: 169–172. doi:10.1016/0925-8388(94)90898-2. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016%2F0925-8388%2894%2990898-2
- Db(V) has been observed in dubnium pentachloride (DbCl5); see H. W. Gäggeler (2007). "Gas Phase Chemistry of Superheavy Elements". Paul Scherrer Institute. pp. 26–28. Archived from the original on 2012-02-20. https://web.archive.org/web/20120220090755/http://lch.web.psi.ch/files/lectures/TexasA%26M/TexasA%26M.pdf.
- Sg(VI) has been observed in seaborgium oxide hydroxide (SgO2(OH)2); see Huebener, S.; Taut, S.; Vahle, A.; Dressler, R.; Eichler, B.; Gäggeler, H. W.; Jost, D.T.; Piguet, D. et al. (2001). "Physico-chemical characterization of seaborgium as oxide hydroxide". Radiochim. Acta 89 (11–12_2001): 737–741. doi:10.1524/ract.2001.89.11-12.737. Archived from the original on 2014-10-25. https://web.archive.org/web/20141025201143/http://www-w2k.gsi.de/kernchemie/images/pdf_Artikel/Radiochim_Acta_89_737_2001.pdf.
- Bh(VII) has been observed in bohrium oxychloride (BhO3Cl); see "Gas chemical investigation of bohrium (Bh, element 107)" , Eichler et al., GSI Annual Report 2000. Retrieved on 2008-02-29 http://www.gsi.de/informationen/wti/library/scientificreport2000/Chemistry/9/r_eichler_jb2000.pdf
- Hs(VIII) has been observed in hassium tetroxide (HsO4); see "Chemistry of Hassium" (PDF). 2002. http://www.gsi.de/documents/DOC-2003-Jun-29-2.pdf. Retrieved 2007-01-31.
- Cn(II) has been observed in copernicium selenide (CnSe); see "Annual Report 2015: Laboratory of Radiochemistry and Environmental Chemistry". Paul Scherrer Institute. 2015. p. 3. https://www.psi.ch/luc/AnnualReportsEN/PSI_LCH_AnnualReport2015.pdf.
- Langmuir, Irving (1919). "The arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 41 (6): 868–934. doi:10.1021/ja02227a002. https://dx.doi.org/10.1021%2Fja02227a002