Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system originally developed by Sun Microsystems. It superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993. In 2010, after the Sun acquisition by Oracle, it was renamed Oracle Solaris. Solaris is known for its scalability, especially on SPARC systems, and for originating many innovative features such as DTrace, ZFS and Time Slider. Solaris supports SPARC and x86-64 workstations and servers from Oracle and other vendors. Solaris is registered as compliant with the Single UNIX Specification. Historically, Solaris was developed as proprietary software. In June 2005, Sun Microsystems released most of the codebase under the CDDL license, and founded the OpenSolaris open-source project. With OpenSolaris, Sun wanted to build a developer and user community around the software. After the acquisition of Sun Microsystems in January 2010, Oracle decided to discontinue the OpenSolaris distribution and the development model. In August 2010, Oracle discontinued providing public updates to the source code of the Solaris kernel, effectively turning Solaris 11 back into a closed source proprietary operating system. Following that, OpenSolaris was forked as illumos and is alive through several illumos distributions. In 2011, the Solaris 11 kernel source code leaked to BitTorrent. However, through the Oracle Technology Network (OTN), industry partners can still gain access to the in-development Solaris source code. Solaris is developed under a proprietary development model, and only the source for open-source components of Solaris 11 is available for download from Oracle.
- solaris
- opensolaris
- scalability
1. History
In 1987, AT&T Corporation and Sun announced that they were collaborating on a project to merge the most popular Unix variants on the market at that time: Berkeley Software Distribution, UNIX System V, and Xenix. This became Unix System V Release 4 (SVR4).[1]
On September 4, 1991, Sun announced that it would replace its existing BSD-derived Unix, SunOS 4, with one based on SVR4. This was identified internally as SunOS 5, but a new marketing name was introduced at the same time: Solaris 2.[2] The justification for this new overbrand was that it encompassed not only SunOS, but also the OpenWindows graphical user interface and Open Network Computing (ONC) functionality.
Although SunOS 4.1.x micro releases were retroactively named Solaris 1 by Sun, the Solaris name is used almost exclusively to refer only to the releases based on SVR4-derived SunOS 5.0 and later.[3]
For releases based on SunOS 5, the SunOS minor version is included in the Solaris release number. For example, Solaris 2.4 incorporates SunOS 5.4. After Solaris 2.6, the 2. was dropped from the release name, so Solaris 7 incorporates SunOS 5.7, and the latest release SunOS 5.11 forms the core of Solaris 11.4.
Although SunSoft stated in its initial Solaris 2 press release their intent to eventually support both SPARC and x86 systems, the first two Solaris 2 releases, 2.0 and 2.1, were SPARC-only. An x86 version of Solaris 2.1 was released in June 1993, about 6 months after the SPARC version, as a desktop and uniprocessor workgroup server operating system. It included the Wabi emulator to support Windows applications.[4] At the time, Sun also offered the Interactive Unix system that it had acquired from Interactive Systems Corporation.[5] In 1994, Sun released Solaris 2.4, supporting both SPARC and x86 systems from a unified source code base.
On September 2, 2017, Simon Phipps, a former Sun Microsystems employee not hired by Oracle in the acquisition, reported on Twitter that Oracle had laid off the Solaris core development staff, which many interpreted as sign that Oracle no longer intended to support future development of the platform.[6] While Oracle did have a large layoff of Solaris development engineering staff, development continues today of which Solaris 11.4 was released in 2018.[7][8]
2. Supported Architectures
Solaris uses a common code base for the platforms it supports: SPARC and i86pc (which includes both x86 and x86-64).[9]
Solaris has a reputation for being well-suited to symmetric multiprocessing, supporting a large number of CPUs.[10] It has historically been tightly integrated with Sun's SPARC hardware (including support for 64-bit SPARC applications since Solaris 7), with which it is marketed as a combined package. This has led to more reliable systems, but at a cost premium compared to commodity PC hardware. However, it has supported x86 systems since Solaris 2.1 and 64-bit x86 applications since Solaris 10, allowing Sun to capitalize on the availability of commodity 64-bit CPUs based on the x86-64 architecture. Sun has heavily marketed Solaris for use with both its own "x64" workstations and servers based on AMD Opteron and Intel Xeon processors, as well as x86 systems manufactured by companies such as Dell, Hewlett-Packard, and IBM. As of 2009, the following vendors support Solaris for their x86 server systems:
- Dell – will "test, certify, and optimize Solaris and OpenSolaris on its rack and blade servers and offer them as one of several choices in the overall Dell software menu"[11]
- Intel[12]
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise[13] – distributes and provides software technical support for Solaris on BL, DL, and SL platforms
- Fujitsu Siemens[14]
As of July 2010, Dell and HP certify and resell Oracle Solaris, Oracle Enterprise Linux and Oracle VM on their respective x86 platforms,[15] and IBM stopped direct support for Solaris on x64 kit.
2.1. Other Platforms
Solaris 2.5.1 included support for the PowerPC platform (PowerPC Reference Platform), but the port was canceled before the Solaris 2.6 release.[16] In January 2006, a community of developers at Blastwave began work on a PowerPC port which they named Polaris.[17] In October 2006, an OpenSolaris community project based on the Blastwave efforts and Sun Labs' Project Pulsar,[18] which re-integrated the relevant parts from Solaris 2.5.1 into OpenSolaris,[16] announced its first official source code release.[19]
A port of Solaris to the Intel Itanium architecture was announced in 1997 but never brought to market.[20]
On November 28, 2007, IBM, Sun, and Sine Nomine Associates demonstrated a preview of OpenSolaris for System z running on an IBM System z mainframe under z/VM,[21] called Sirius (in analogy to the Polaris project, and also due to the primary developer's Australian nationality: HMS Sirius of 1786 was a ship of the First Fleet to Australia ). On October 17, 2008, a prototype release of Sirius was made available[22] and on November 19 the same year, IBM authorized the use of Sirius on System z Integrated Facility for Linux (IFL) processors.[23]
Solaris also supports the Linux platform application binary interface (ABI), allowing Solaris to run native Linux binaries on x86 systems. This feature is called Solaris Containers for Linux Applications (SCLA), based on the branded zones functionality introduced in Solaris 10 8/07.[24]
3. Installation and Usage Options
Solaris can be installed from various pre-packaged software groups, ranging from a minimalistic Reduced Network Support to a complete Entire Plus OEM. Installation of Solaris is not necessary for an individual to use the system. Additional software, like Apache, MySQL, etc. can be installed as well in a packaged form from sunfreeware[25] and OpenCSW.[26] Solaris can be installed from physical media or a network for use on a desktop or server, or be used without installing on a desktop or server.
4. Desktop Environments
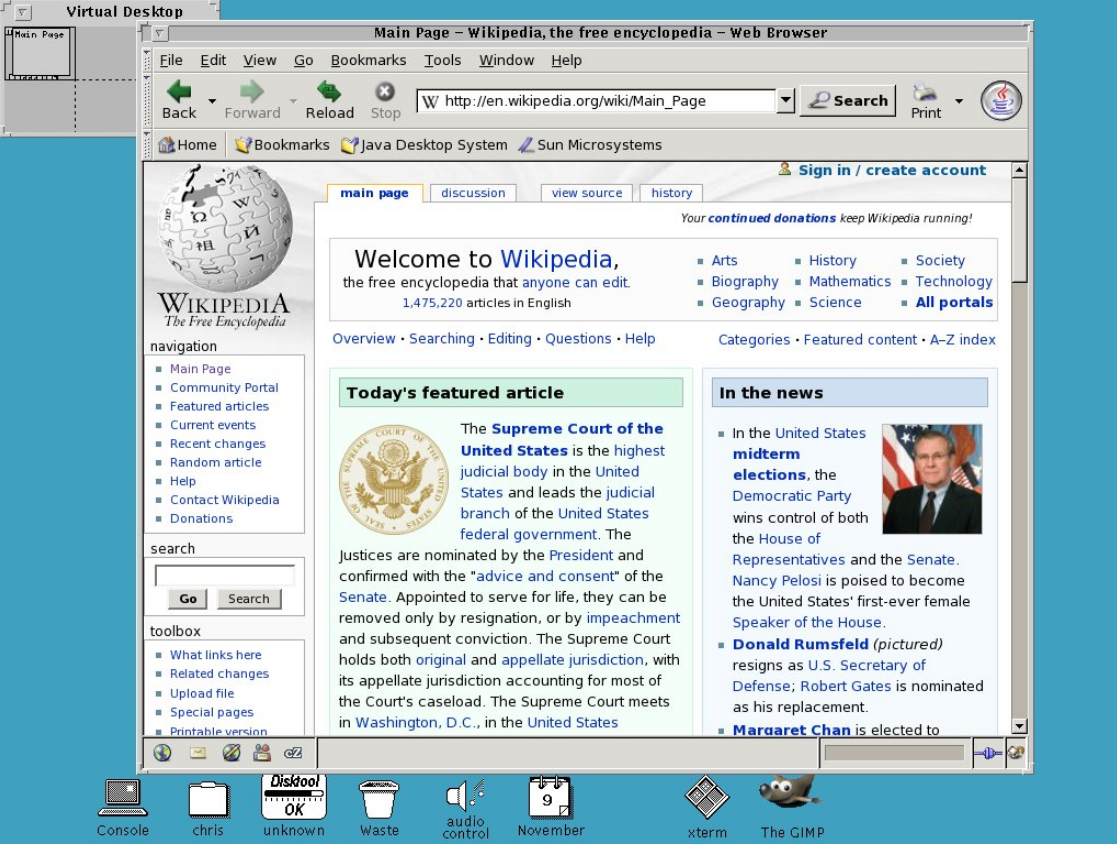
Early releases of Solaris used OpenWindows as the standard desktop environment. In Solaris 2.0 to 2.2, OpenWindows supported both NeWS and X applications, and provided backward compatibility for SunView applications from Sun's older desktop environment. NeWS allowed applications to be built in an object-oriented way using PostScript, a common printing language released in 1982. The X Window System originated from MIT's Project Athena in 1984 and allowed for the display of an application to be disconnected from the machine where the application was running, separated by a network connection. Sun's original bundled SunView application suite was ported to X.
Sun later dropped support for legacy SunView applications and NeWS with OpenWindows 3.3, which shipped with Solaris 2.3, and switched to X11R5 with Display Postscript support. The graphical look and feel remained based upon OPEN LOOK. OpenWindows 3.6.2 was the last release under Solaris 8. The OPEN LOOK Window Manager (olwm) with other OPEN LOOK specific applications were dropped in Solaris 9, but support libraries were still bundled, providing long term binary backwards compatibility with existing applications. The OPEN LOOK Virtual Window Manager (olvwm) can still be downloaded for Solaris from sunfreeware and works on releases as recent as Solaris 10.
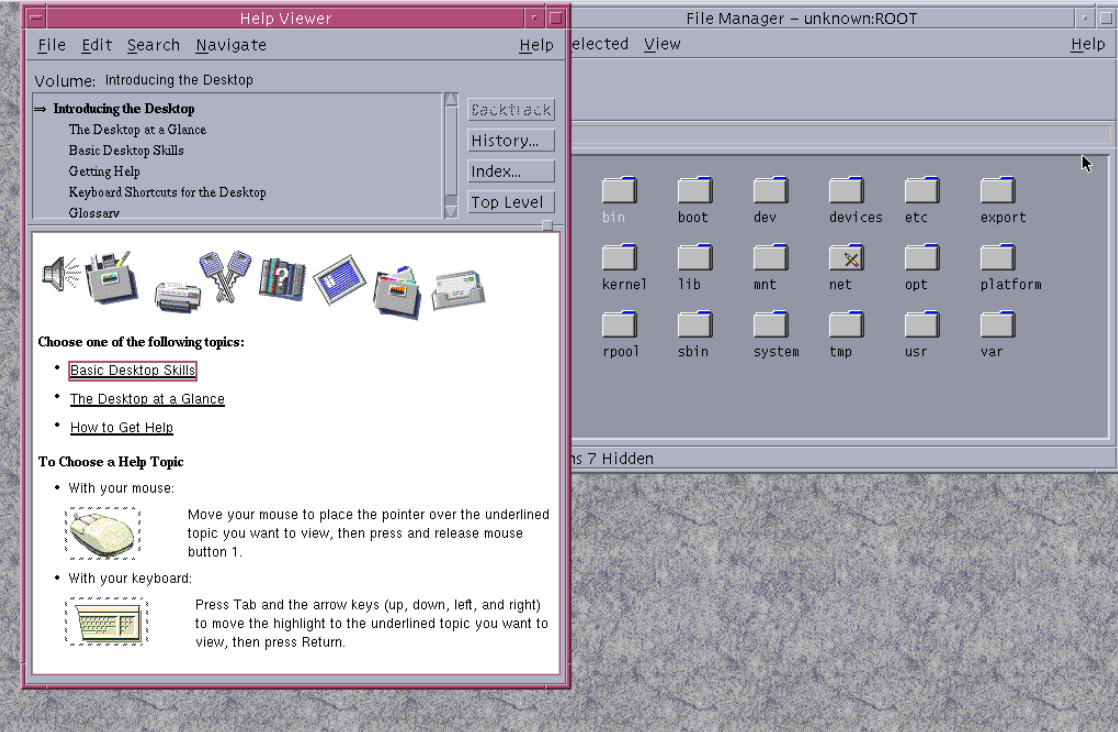
Sun and other Unix vendors created an industry alliance to standardize Unix desktops. As a member of the Common Open Software Environment (COSE) initiative, Sun helped co-develop the Common Desktop Environment (CDE). This was an initiative to create a standard Unix desktop environment. Each vendor contributed different components: Hewlett-Packard contributed the window manager, IBM provided the file manager, and Sun provided the e-mail and calendar facilities as well as drag-and-drop support (ToolTalk). This new desktop environment was based upon the Motif look and feel and the old OPEN LOOK desktop environment was considered legacy. CDE unified Unix desktops across multiple open system vendors. CDE was available as an unbundled add-on for Solaris 2.4 and 2.5, and was included in Solaris 2.6 through 10.
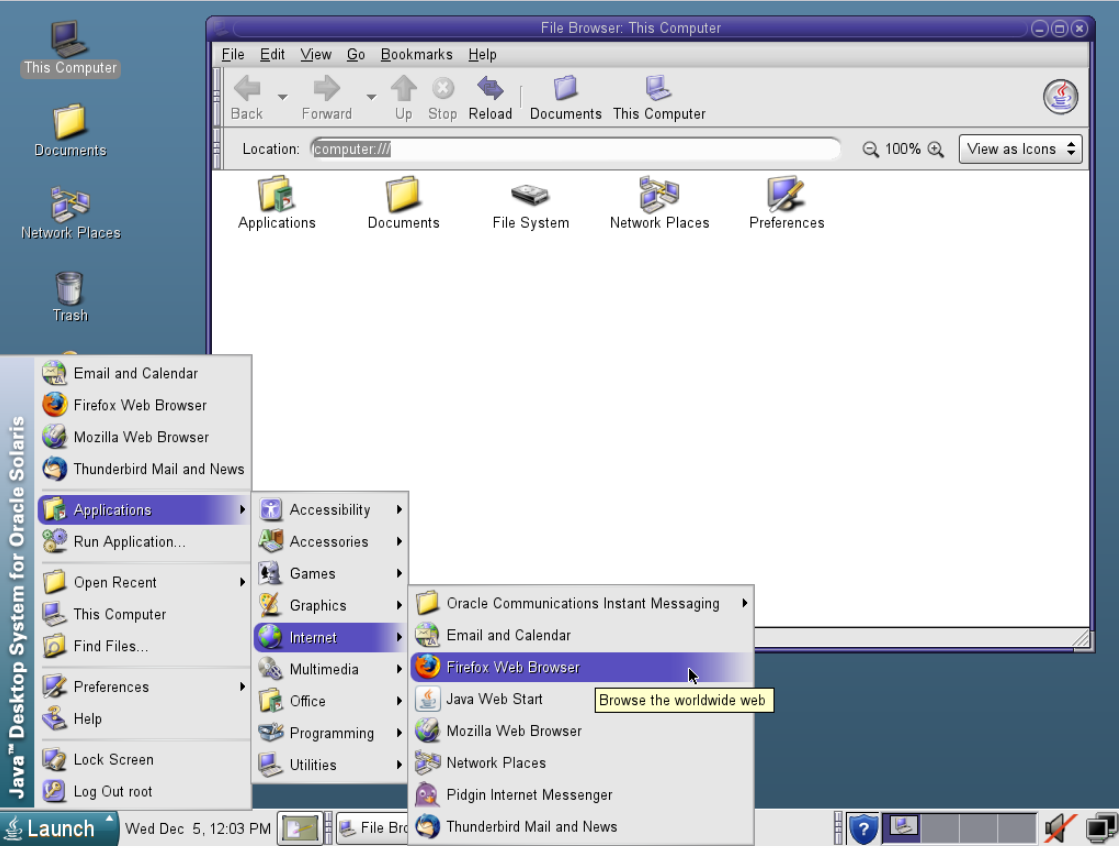
In 2001, Sun issued a preview release of the open-source desktop environment GNOME 1.4, based on the GTK+ toolkit, for Solaris 8.[27] Solaris 9 8/03 introduced GNOME 2.0 as an alternative to CDE. Solaris 10 includes Sun's Java Desktop System (JDS), which is based on GNOME and comes with a large set of applications, including StarOffice, Sun's office suite. Sun describes JDS as a "major component" of Solaris 10.[28] The Java Desktop System is not included in Solaris 11 which instead ships with a stock version of GNOME.[29] Likewise, CDE applications are no longer included in Solaris 11, but many libraries remain for binary backwards compatibility.
The open source desktop environments KDE and Xfce, along with numerous other window managers, also compile and run on recent versions of Solaris.
Sun was investing in a new desktop environment called Project Looking Glass since 2003. The project has been inactive since late 2006.[30]
5. License
Traditional operating system license (1982 to 2004)
For versions up to 2005 (Solaris 9), Solaris was licensed under a license that permitted a customer to buy licenses in bulk, and install the software on any machine up to a maximum number. The key license grant was:
License to Use. Customer is granted a non-exclusive and non-transferable license ("License") for the use of the accompanying binary software in machine-readable form, together with accompanying documentation ("Software"), by the number of users and the class of computer hardware for which the corresponding fee has been paid.
In addition, the license provided a "License to Develop" granting rights to create derivative works, restricted copying to only a single archival copy, disclaimer of warranties, and the like. The license varied only little through 2004.
Open source (2005 until March 2010)
From 2005–10, Sun began to release the source code for development builds of Solaris under the Common Development and Distribution License (CDDL) via the OpenSolaris project. This code was based on the work being done for the post-Solaris 10 release (code-named "Nevada"; eventually released as Oracle Solaris 11). As the project progressed, it grew to encompass most of the necessary code to compile an entire release, with a few exceptions.[31]
Post-Oracle closed source (March 2010 to present)
When Sun was acquired by Oracle in 2010, the OpenSolaris project was discontinued after the board became unhappy with Oracle's stance on the project.[32] In March 2010, the previously freely available Solaris 10 was placed under a restrictive license that limited the use, modification and redistribution of the operating system.[33] The license allowed the user to download the operating system free of charge, through the Oracle Technology Network, and use it for a 90-day trial period. After that trial period had expired the user would then have to purchase a support contract from Oracle to continue using the operating system.
With the release of Solaris 11 in 2011, the license terms changed again. The new license allows Solaris 10 and Solaris 11 to be downloaded free of charge from the Oracle Technology Network and used without a support contract indefinitely; however, the license only expressly permits the user to use Solaris as a development platform and expressly forbids commercial and "production" use.[34] Educational use is permitted in some circumstances. From the OTN license:
If You are an educational institution vested with the power to confer official high school, associate, bachelor, master and/or doctorate degrees, or local equivalent, ("Degree(s)"), You may also use the Programs as part of Your educational curriculum for students enrolled in Your Degree program(s) solely as required for the conferral of such Degree (collectively "Educational Use").
When Solaris is used without a support contract it can be upgraded to each new "point release"; however, a support contract is required for access to patches and updates that are released monthly.[35]
6. Version History

Notable features of Solaris include DTrace, Doors, Service Management Facility, Solaris Containers, Solaris Multiplexed I/O, Solaris Volume Manager, ZFS, and Solaris Trusted Extensions.
Updates to Solaris versions are periodically issued. In the past, these were named after the month and year of their release, such as "Solaris 10 1/13"; as of Solaris 11, sequential update numbers are appended to the release name with a period, such as "Oracle Solaris 11.4".
In ascending order, the following versions of Solaris have been released:
{{{2}}}
| Solaris version | SunOS version | Release date | End of support[36] | License form | Major new features | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPARC | x86 | |||||
| 1.x | 4.1.x | 1991–1994 | – | September 2003 | Traditional license | SunOS 4 rebranded as Solaris 1 for marketing purposes. See SunOS article for more information. |
| 2.0 | 5.0 | June 1992 | – | January 1999 | Traditional license | Preliminary release (primarily available to developers only), support for only the sun4c architecture. First appearance of NIS+.[37] |
| 2.1 | 5.1 | December 1992 | May 1993 | April 1999 | Traditional license | Support for sun4 and sun4m architectures added; first Solaris x86 release. First Solaris 2 release to support SMP. |
| 2.2 | 5.2 | May 1993 | – | May 1999 | Traditional license | SPARC-only release. First to support sun4d architecture. First to support multithreading libraries (UI threads API in libthread).[38] |
| 2.3 | 5.3 | November 1993 | – | June 2002 | Traditional license | SPARC-only release. OpenWindows 3.3 switches from NeWS to Display PostScript and drops SunView support. Support added for autofs and CacheFS filesystems. |
| 2.4 | 5.4 | November 1994 | September 2003 | Traditional license | First unified SPARC/x86 release. Includes OSF/Motif runtime support. | |
| 2.5 | 5.5 | November 1995 | December 2003 | Traditional license | First to support UltraSPARC and include CDE, NFSv3 and NFS/TCP. Dropped sun4 (VMEbus) support. POSIX.1c-1995 pthreads added. Doors added but undocumented.[39] | |
| 2.5.1 | 5.5.1 | May 1996 | September 2005 | Traditional license | The only Solaris release that supports PowerPC;[40] Ultra Enterprise support added; user and group IDs (uid_t, gid_t) expanded to 32 bits,[41] also included processor sets[42] and early resource management technologies. | |
| 2.6 | 5.6 | July 1997 | July 2006 | Traditional license | Includes Kerberos 5, PAM, TrueType fonts, WebNFS, large file support, enhanced procfs. SPARCserver 600MP series support dropped.[43] | |
| 7 | 5.7 | November 1998 | August 2008 | Traditional license | The first 64-bit UltraSPARC release. Added native support for file system meta-data logging (UFS logging). Dropped MCA support on x86 platform. Sun dropped the prefix "2." in the Solaris version number, leaving "Solaris 7." Last update was Solaris 7 11/99.[44] | |
| 8 | 5.8 | February 2000 | March 2012 | Traditional license | Includes Multipath I/O, Solstice DiskSuite,[45] IPMP, first support for IPv6 and IPsec (manual keying only), mdb Modular Debugger. Introduced Role-Based Access Control (RBAC); sun4c support removed. Last update is Solaris 8 2/04.[46] | |
| 9 | 5.9 | May 28, 2002 | January 10, 2003 | October 2014 | Traditional license | iPlanet Directory Server, Resource Manager, extended file attributes, IKE IPsec keying, and Linux compatibility added; OpenWindows dropped, sun4d support removed. Most current update is Solaris 9 9/05 HW.[47] |
| 10 | 5.10 | January 31, 2005 (2005-01-31) | January 2024 | before Oracle acquisition in March 2010, open source under CDDL after March 2010, Post-Oracle closed source |
Includes x86-64 (AMD64/Intel 64) support, DTrace (Dynamic Tracing), Solaris Containers, Service Management Facility (SMF) which replaces init.d scripts, NFSv4. Least privilege security model. Support for sun4m and UltraSPARC I processors removed. Support for EISA-based PCs removed. Adds Java Desktop System (based on GNOME) as default desktop.[48]
|
|
| 11 Express 2010.11 | 5.11 | November 15, 2010 (2010-11-15) | November 2011 | Post-Oracle closed source | Adds new packaging system (IPS – Image Packaging System) and associated tools, ZFS (only) for boot, 1 GB RAM min., x86, Solaris 10 Containers, network virtualization and QoS, virtual consoles, ZFS encryption and deduplication, fast reboot,[59] updated GNOME. Removed Xsun, CDE,[60] and the /usr/ucb BSD-compatible commands |
|
| 11 | 5.11 | November 9, 2011 (2011-11-09) | ? | Post-Oracle closed source | New features and enhancements (compared to Solaris 10) in software packaging, network virtualization, server virtualization, storage, security and hardware support:
|
|
| 11.1 | 5.11 | October 3, 2012 (2012-10-03) | ? | Post-Oracle closed source | New features and enhancements:[62][63][64]
|
|
| 11.2 | 5.11 | April 29, 2014 (2014-04-29) | ? | Post-Oracle closed source | New features and enhancements:[66]
|
|
| 11.3 | 5.11 | October 26, 2015 (2015-10-26) | October 2020 | Post-Oracle closed source | New features and enhancements:[68]
|
|
| 11.4 | 5.11 | August 28, 2018 (2018-08-28) | November 2034 | Post-Oracle closed source | New features and enhancements:[69]
|
|
Template:Timeline Solaris
A more comprehensive summary of some Solaris versions is also available.[72] Solaris releases are also described in the Solaris 2 FAQ.[73]
7. Development Release
The underlying Solaris codebase has been under continuous development since work began in the late 1980s on what was eventually released as Solaris 2.0. Each version such as Solaris 10 is based on a snapshot of this development codebase, taken near the time of its release, which is then maintained as a derived project. Updates to that project are built and delivered several times a year until the next official release comes out.
The Solaris version under development by Sun since the release of Solaris 10 in 2005, was codenamed Nevada, and is derived from what is now the OpenSolaris codebase.
In 2003, an addition to the Solaris development process was initiated. Under the program name Software Express for Solaris (or just Solaris Express), a binary release based on the current development basis was made available for download on a monthly basis, allowing anyone to try out new features and test the quality and stability of the OS as it progressed to the release of the next official Solaris version.[74] A later change to this program introduced a quarterly release model with support available, renamed Solaris Express Developer Edition (SXDE).
In 2007, Sun announced Project Indiana with several goals, including providing an open source binary distribution of the OpenSolaris project, replacing SXDE.[75] The first release of this distribution was OpenSolaris 2008.05.
The Solaris Express Community Edition (SXCE) was intended specifically for OpenSolaris developers.[76] It was updated every two weeks until it was discontinued in January 2010, with a recommendation that users migrate to the OpenSolaris distribution.[77] Although the download license seen when downloading the image files indicates its use is limited to personal, educational and evaluation purposes, the license acceptance form displayed when the user actually installs from these images lists additional uses including commercial and production environments.
SXCE releases terminated with build 130 and OpenSolaris releases terminated with build 134 a few weeks later. The next release of OpenSolaris based on build 134 was due in March 2010, but it was never fully released, though the packages were made available on the package repository. Instead, Oracle renamed the binary distribution Solaris 11 Express, changed the license terms and released build 151a as 2010.11 in November 2010.
8. Open Source Derivatives
Current
- illumos – A fully open source fork of the project, started in 2010 by a community of Sun OpenSolaris engineers and Nexenta OS. Note that OpenSolaris was not 100% open source: Some drivers and some libraries were property of other companies that Sun (now Oracle) licensed and was not able to release.
- OpenIndiana – A project under the illumos umbrella aiming "... to become the de facto OpenSolaris distribution installed on production servers where security and bug fixes are required free of charge."[78]
- SchilliX[79] – The first LiveCD released after OpenSolaris code was opened to public.
- napp-it[80] – A webmanaged ZFS storage appliance based on Solaris and the free forks like OmniOS with a Free and Pro edition.
- NexentaStor – Optimized for storage workloads, based on Nexenta OS.
- Dyson – illumos kernel with GNU userland and packages from Debian. Strives to become an official Debian port.
- SmartOS – Virtualization centered derivative from Joyent.
Discontinued
- OpenSolaris – A project initiated by Sun Microsystems, discontinued after the acquisition by Oracle.
- Nexenta OS (discontinued October 31, 2012) – First distribution based on Ubuntu userland with Solaris-derived kernel.[81]
- StormOS (discontinued September 14, 2012[82]) – A lightweight desktop OS based on Nexenta OS and Xfce.
- MartUX[83][84] – The first SPARC distribution of OpenSolaris, with an alpha prototype released by Martin Bochnig in April 2006. It was distributed as a Live CD but is later available only on DVD as it has had the Blastwave community software added.[85] Its goal was to become a desktop operating system. The first SPARC release was a small Live CD, released as marTux_0.2 Live CD[86] in summer of 2006, the first straight OpenSolaris distribution for SPARC (not to be confused with GNOME metacity theme). It was later re-branded as MartUX and the next releases included full SPARC installers in addition to the Live media. Much later, MartUX was re-branded as OpenSXCE when it moved to the first OpenSolaris release to support both SPARC and Intel architectures after Sun was acquired by Oracle.[87]
- MilaX – A small Live CD/Live USB[88][89] with minimal set of packages to fit a 90 MB image.
- EON ZFS Storage[90] – A NAS implementation targeted at embedded systems.
- Jaris OS – Live DVD and also installable.[91] Pronounced according to the IPA but in English as Yah-Rees. This distribution has been heavily modified to fully support a version of Wine called Madoris that can install and run Windows programs at native speed. Jaris stands for "Japanese Solaris". Madoris is a combination of the Japanese word for Windows "mado" and Solaris.
- OpenSXCE – An OpenSolaris distribution release for both 32-bit and 64-bit x86 platforms and SPARC microprocessors, initially produced from OpenSolaris source code repository, ported to the illumos source code repository to form OpenIndiana's first[92] SPARC distribution.[93] Notably, the first OpenSolaris distribution with illumos source for SPARC based upon OpenIndiana, OpenSXCE finally moved to a new source code repository, based upon DilOS.
9. Reception
- Robert Lipschutz and Gregg Harrington from PCMag reviewed Solaris 9 in 2002:[94]
| “ | All in all, Sun has stayed the course with Solaris 9. While its more user-friendly management is welcome, that probably won't be enough to win over converts. What may is the platform's reliability, flexibility, and power. | ” |
- Robert Lipschutz also reviewed Solaris 10:[95]
| “ | Be that as it may, since the Solaris 10 download is free, it behooves any IT manager to load it on an extra server and at least give it a try. | ” |
- Tom Henderson reviewed Solaris 10 for Network World:[96]
| “ | Solaris 10 provides a flexible background for securely dividing system resources, providing performance guarantees and tracking usage for these containers. Creating basic containers and populating them with user applications and resources is simple. But some cases may require quite a bit of fine-tuning. | ” |
- Robert Escue for OSNews:[97]
| “ | I think that Sun has put some really nice touches on Solaris 10 that make it a better operating system for both administrators and users. The security enhancements are a long time coming, but are worth the wait. Is Solaris 10 perfect, in a word no it is not. But for most uses, including a desktop OS I think Solaris 10 is a huge improvement over previous releases. | ” |
- Thomas Greene for The Register:[98]
| “ | We've had fun with Solaris 10. It's got virtues that we definitely admire. What it needs to compete with Linux will be easier to bring about than what it's already got. It could become a Linux killer, or at least a serious competitor on Linux's turf. The only question is whether Sun has the will to see it through. | ” |
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Software:Solaris_(operating_system)
References
- Salus, Peter (1994). A Quarter Century of Unix. Addison-Wesley. pp. 199–200. ISBN 0-201-54777-5.
- "SunSoft introduces first shrink-wrapped distributed computing solution: Solaris" (Press release). Sun Microsystems, Inc. September 4, 1991. Retrieved August 7, 2007. http://www.sun.com/aboutsun/media/presskits/25years/pr.html#solaris
- "What are SunOS and Solaris?". Knowledge Base. Indiana University Technology Services. May 20, 2013. http://kb.iu.edu/data/agjq.html. Retrieved November 10, 2014.
- Taylor, Noel-Marie; Wallace, Mark (June 15, 1993). "Solaris 2.1: The Rise of a New Sun?". PC Magazine: pp. 243–244. https://books.google.com/books?id=jMKfH6i9OcYC&pg=PA244.
- Vaughan-Nichols, Steven J. (June 15, 1993). "Interactive Unix". PC Magazine: p. 240. https://books.google.com/books?id=jMKfH6i9OcYC&pg=PA240.
- Varghese, Sam. "Bye, bye Solaris, it was a nice ride while it lasted" (in en-gb). https://www.itwire.com/open-sauce/79738-bye,-bye-solaris,-it-was-a-nice-ride-while-it-lasted.html.
- Lynn, Scott. "Continuous Delivery, Really?". https://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/continuous-delivery,-really.
- Lynn, Scott. "2017 in Review and Looking ahead to 2018". https://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/2017-in-review-and-looking-ahead-to-2018.
- "Solaris OS: Hardware Compatibility Lists". BigAdmin System Administration Portal. Sun Microsystems, Inc.. http://sun.com/bigadmin/hcl. Retrieved December 12, 2006.
- Vance, Ashlee (April 19, 2002). "Sun rethinks Solaris on Intel". Infoworld (IDG). Archived from the original on October 12, 2007. https://web.archive.org/web/20071012153147/http://infoworld.com/articles/hn/xml/02/04/19/020419hnsecretsix.html. Retrieved December 11, 2006. "Neither Microsoft Windows nor Linux can match Solaris in this type of high-end architecture, said Tony Iams, an analyst at Port Chester, N.Y., research company D.H. Brown and Associates. "Solaris has earned its reputation over a long period of time," Iams said. "They have been working on high-end scalability features for 10 years, and that's the only way you can get solid results.""
- "Dell to Offer Sun's Solaris, OpenSolaris in Servers". eWeek. November 14, 2007. http://www.eweek.com/article2/0%2C1895%2C2216876%2C00.asp. Retrieved November 14, 2007.
- "Intel Carrier Grade Platforms Certified for Sun Solaris" (Press release). Intel Corp. July 16, 2007. Retrieved August 16, 2007. http://www.intel.com/pressroom/archive/releases/20070716corp_b.htm
- "Oracle Solaris Certification and Support" (Press release). Hewlett Packard Enterprise. 2019. Retrieved February 3, 2019. http://h17007.www1.hpe.com/us/en/enterprise/servers/supportmatrix/solaris.aspx
- "Sun Microsystems and Fujitsu Siemens Computers Power PRIMERGY Servers with Solaris Operating System" (Press release). Sun Microsystems. Retrieved June 10, 2008. http://www.sun.com/aboutsun/pr/2008-06/sunflash.20080610.2.xml
- "Dell and HP to Certify and Resell All Three Oracle Operating Systems – Oracle Solaris, Oracle Enterprise Linux and Oracle VM – on Their x86 Server Computers". DailyFinance. http://www.dailyfinance.com/rtn/pr/dell-and-hp-to-certify-and-resell-all-three-oracle-operating-systems-oracle-solaris-oracle-enterprise-linux-and-oracle-vm-on-their-x86-server-computers/rfid352819358/?channel=pf. Retrieved July 29, 2010.
- "Kickstarting OpenSolaris on PowerPC". OpenSolaris Project. Archived from the original on February 29, 2012. https://web.archive.org/web/20120229133259/http://hub.opensolaris.org/bin/view/Project+ppc-dev/kickstart.
- "OpenSolaris Community Creates Kernel for Power Chips". ITJungle. Archived from the original on April 5, 2012. https://web.archive.org/web/20120405144010/http://www.itjungle.com/tfh/tfh011606-story02.html.
- "Embedded Solaris on PowerPC". Sun Research. Archived from the original on June 27, 2006. https://web.archive.org/web/20060627042251/http://research.sun.com/spotlight/2006/2006-06-14-SolarisPPC.html.
- "PowerPC at OpenSolaris". OpenSolaris Project. Archived from the original on February 29, 2012. https://web.archive.org/web/20120229133135/http://hub.opensolaris.org/bin/view/Community+Group+power_pc/WebHome. Retrieved October 4, 2007.
- "Sun to deliver enterprise-class solaris for intel's merced processor" (Press release). Intel Corporation, Sun Microsystems, Inc. December 16, 1997. Retrieved September 10, 2006. http://www.sun.com/smi/Press/sunflash/1997-12/sunflash.971216.3.xml
- "OpenSolaris Runs on IBM Mainframe" (Press release). IBM. November 30, 2007. Retrieved January 21, 2018. https://www-03.ibm.com/press/us/en/pressrelease/22718.wss
- "OpenSolaris Project: Systemz". OpenSolaris Project. Archived from the original on August 25, 2009. https://web.archive.org/web/20090825162814/http://opensolaris.org/os/project/systemz/.
- "IBM authorizes OpenSolaris on mainframes". The Register. November 24, 2008. https://www.theregister.co.uk/2008/11/24/ibm_authorizes_mainframe_opensolaris/. Retrieved November 24, 2008.
- "BrandZ/SCLA FAQ". OpenSolaris Project. Archived from the original on October 4, 2006. https://archive.today/20061004053007/http://www.opensolaris.org/os/community/brandz/brandz_lae_faq/. Retrieved September 10, 2006.
- "Sunfreeware Package List". Sunfreeware. http://sunfreeware.com. Retrieved November 24, 2014.
- "OpenCSW Package List". OpenCSW. http://www.opencsw.org/packages. Retrieved November 24, 2014.
- Mannina, Scott (May 23, 2001). "Sun Announces GNOME 1.4 for Solaris". http://mail.gnome.org/archives/gnome-announce-list/2001-May/msg00046.html. Retrieved February 9, 2009.
- "Sun Java Desktop System". Sun Microsystems Inc. May 22, 2006. http://www.sun.com/software/javadesktopsystem/. Retrieved March 10, 2007.
- "Oracle Solaris 11 Desktop Feature Summary - Transitioning From Oracle Solaris 10 to Oracle Solaris 11". Oracle Corporation. March 1, 2011. http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/html/E24456/desktop-123.html. Retrieved November 24, 2014.
- "Project Looking Glass Homepage". Archived from the original on July 12, 2007. https://web.archive.org/web/20070712044749/https://lg3d-core.dev.java.net/. Retrieved January 6, 2010.
- "What source code does the OpenSolaris project include?". OpenSolaris FAQ. OpenSolaris Project. http://hub.opensolaris.org/bin/view/Main/general_faq#HWhatsourcecodedoestheOpenSolarisprojectinclude. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
- "Oracle Has Killed OpenSolaris". Techie Buzz. August 14, 2010. http://techie-buzz.com/foss/oracle-has-killed-opensolaris.html. Retrieved July 17, 2013.
- Paul, Ryan (March 30, 2010). "Solaris 10 no longer free as in beer, now a 90-day trial". https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2010/03/solaris-10-no-longer-free-as-in-beer-now-a-90-day-trial. Retrieved July 17, 2013.
- "Oracle Technology Network Developer License Terms for Oracle Solaris, Oracle Solaris Cluster and Oracle Solaris Express". Oracle Corporation. July 13, 2011. http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/licenses/solaris-cluster-express-license-167852.html. Retrieved July 17, 2013.
- "How to Update to Oracle Solaris 11.1 Using the Image Packaging System". Oracle Corporation. November 30, 2012. http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/servers-storage-admin/howto-update-11dot1-ips-1866781.html. Retrieved July 17, 2013.
- "Lifetime Support Policies, see Oracle and Sun System Software and Operating Systems (PDF)". Oracle Corporation. http://www.oracle.com/us/support/lifetime-support/index.html. Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- Demetrios Stellas (September 3, 1992). "SUMMARY: Solaris 2.0 vs 2.1". Sun Managers mailing list. Archived from the original on October 4, 2006. https://web.archive.org/web/20061004080321/http://www.sunmanagers.org/archives/1992/1133.html. Retrieved September 10, 2006.
- "Multithreading in the Solaris Operating Environment" (PDF). Sun Microsystems. May 17, 2002. http://home.mit.bme.hu/~meszaros/edu/oprendszerek/segedlet/unix/2_folyamatok_es_utemezes/solaris_multithread.pdf. Retrieved August 19, 2012.
- "Solaris 2.5". OCF Solaris History. Archived from the original on November 18, 2005. https://web.archive.org/web/20051118141731/http://www.ocf.berkeley.edu/solaris/versions/solaris/2.5.html.
- There was a later PPC port with help from Sun, based on OpenSolaris that was withdrawn because the related hardware could not be produced in a RoHS compliant variant
- "Solaris 2.5.1". OCF Solaris History. Archived from the original on September 12, 2005. https://web.archive.org/web/20050912194850/http://www.ocf.berkeley.edu/solaris/versions/solaris/2.5.1.html.
- Matthias Laux (June 2001). "Solaris Processor Sets Made Easy". Sun Microsystems Inc. http://developers.sun.com/solaris/articles/solaris_processor.html. Retrieved March 10, 2007.
- "Solaris 2.6". OCF Solaris History. Archived from the original on November 13, 2005. https://web.archive.org/web/20051113144231/http://www.ocf.berkeley.edu/solaris/versions/solaris/2.6.html.
- "Solaris 7". OCF Solaris History. Archived from the original on September 7, 2005. https://web.archive.org/web/20050907220232/http://www.ocf.berkeley.edu/solaris/versions/solaris/2.7.html.
- "Solaris 8 Operating Environment Data Sheet". Sun Microsystems. Archived from the original on August 3, 2009. https://web.archive.org/web/20090803063632/http://www.sun.com/software/solaris/8/ds/ds-sol8oe/index.xml. Retrieved November 24, 2014.
- "Solaris 8". SunOS & Solaris Version History (OCF Solaris History). UC Berkeley Open Computing Facility. Archived from the original on September 7, 2006. https://web.archive.org/web/20060907000356/http://www.ocf.berkeley.edu/solaris/versions/solaris/8.html. Retrieved September 10, 2006.
- "Solairis Operating System - Releases". Oracle. http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/solaris/overview/releases-jsp-140987.html. Retrieved February 4, 2015.
- "Solaris 10 What's New". Sun Microsystems. http://docs.sun.com/app/docs/doc/817-0547.
- "SAMBA and SWAT in Solaris 10 Update 4 (Solaris 10 8/07)". As Good A Place As Any: Tim Thomas' Blog. Archived from the original on March 12, 2008. https://web.archive.org/web/20080312212825/http://blogs.sun.com/timthomas/entry/samba_and_swat_in_solaris. Retrieved December 1, 2007.
- "Introducing Enhanced Intel SpeedStep to Solaris". Archived from the original on May 1, 2008. https://web.archive.org/web/20080501125300/http://blogs.sun.com/mhaywood/entry/introducing_speedstep_on_solaris. Retrieved May 6, 2008.
- "AMD PowerNow! for Solaris". Sun Microsystems. http://blogs.sun.com/mhaywood/entry/powernow_for_solaris. Retrieved May 6, 2008.
- "General FAQs for Solaris 10". Sun Microsystems. http://www.sun.com/software/solaris/faqs_general.jsp. Retrieved October 23, 2008.
- "Solaris 10 10/09 What's New". Sun Microsystems. http://docs.sun.com/app/docs/doc/821-0382. Retrieved October 9, 2009.
- "Oracle Solaris 10 9/10 What's New". Oracle Corporation. http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E18752_01/html/821-1840/index.html. Retrieved September 8, 2010.
- "Oracle Solaris 10 8/11 What's New". Oracle Corporation. http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23823_01/html/821-2730/index.html. Retrieved August 12, 2011.
- "Oracle Solaris 10 8/11 Released". Oracle Corporation. https://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/entry/oracle_solaris_10_8_11. Retrieved September 28, 2012.
- "Oracle Solaris 10 1/13 What's New". http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E26505_01/html/E27003/index.html. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- "Introducing Oracle Solaris 10 1/13". Oracle Corporation. https://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/entry/introducing_oracle_solaris_10_1. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- Sun Microsystems. "x86: Introducing Fast Reboot". Archived from the original on August 16, 2011. https://web.archive.org/web/20110816095353/http://dlc.sun.com/osol/docs/content/SYSADV1/ghsbc.html. Retrieved August 20, 2011.
- "Transitioning From Oracle® Solaris 10 to Oracle Solaris 11". Oracle Corporation. March 2012. https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/pdf/E24456.pdf. Retrieved August 19, 2012.
- "Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, 11/11 Release". Oracle Corporation. July 1, 2012. http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/. Retrieved August 19, 2012.
- "Announcing Oracle Solaris 11.1". Oracle Corporation. April 18, 2013. http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/solaris11/overview/solaris11-1-1845817.html. Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- "Announcing Oracle Solaris 11.1 – solaris blog". Oracle Corporation. April 18, 2013. http://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/entry/announcing_oracle_solaris_11_1. Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- "Oracle Solaris 11.1 Blog Post Roundup". Oracle Corporation. April 18, 2013. http://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/entry/oracle_solaris_11_1_blog. Retrieved April 18, 2013.
- "Oracle Solaris 11.1 — What's New". Oracle. March 21, 2013. http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/solaris11/documentation/solaris11-1-whatsnew-1732377.pdf.
- "Oracle Introduces Oracle Solaris 11.2—Engineered for Cloud" (Press release). Oracle Corporation. April 29, 2014. http://www.oracle.com/us/corporate/pressrelease/solaris-11-2-042914
- Foster, Tim (April 30, 2014). "IPS changes in Solaris 11.2". http://timsfoster.wordpress.com/2014/04/30/ips-changes-in-solaris-11-2/.
- "What's New in Oracle® Solaris 11.3" (Press release). Oracle Corporation. October 2015. https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E53394_01/html/E54847/index.html
- "What's New in Oracle® Solaris 11.4" (Press release). Oracle Corporation. August 2018. https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E37838_01/html/E60974/index.html
- "Oracle Solaris 11.3 Support (Doc ID 2382427.1)". 2020-03-09. https://support.oracle.com/knowledge/Sun%20Microsystems/2382427_1.html.
- Coopersmith, Alan. "Using GNOME 3 in Oracle Solaris 11.4". Oracle Solaris Blog. https://blogs.oracle.com/solaris/using-gnome-3-in-oracle-solaris-114.
- "SunOS & Solaris Version History". UC Berkeley Open Computing Facility. Archived from the original on July 8, 2006. https://web.archive.org/web/20060708215337/http://www.ocf.berkeley.edu/solaris/versions. Retrieved September 10, 2006.
- Casper Dik (April 26, 2005). "What machines does Solaris 2.x run on?". Solaris 2 FAQ. Archived from the original on September 1, 2006. https://web.archive.org/web/20060901012636/http://www.science.uva.nl/pub/solaris/solaris2/Q1.5.html. Retrieved September 10, 2006.
- "10 New Network Services Components Featured in Sun's Java Enterprise System; New Software Express Program Accelerates Customer Access to Future Technologies" (Press release). Sun Microsystems. September 16, 2003. Retrieved August 16, 2008. http://www.sun.com/smi/Press/sunflash/2003-09/sunflash.20030916.5.xml
- Robert Baty (July 31, 2007). "Project Indiana". Sun Microsystems. http://sun.com/featured-articles/2007-0731/feature/. Retrieved December 1, 2007.
- "Operating System/Networking (ON) Download Center". OpenSolaris web site. Archived from the original on December 10, 2006. https://web.archive.org/web/20061210234421/http://opensolaris.org/os/downloads/on/. Retrieved December 12, 2006.
- Derek Cicero (January 6, 2010). "Update on SXCE". Sun Microsystems. Archived from the original on March 12, 2010. https://web.archive.org/web/20100312151007/http://mail.opensolaris.org/pipermail/opensolaris-announce/2010-January/001356.html. Retrieved March 21, 2010.
- Frequently Asked Questions, OpenIndiana, http://wiki.openindiana.org:8080/display/oi/Frequently+Asked+Questions, retrieved 2012-12-29
- Preliminary Release, Jörg Schilling, 2017-01-17, http://schillix.sourceforge.net/, retrieved 2017-09-09
- napp-it ZFS server appliance, http://www.napp-it.org/index_en.html, retrieved 2012-12-29
- DownloadMirrors - Nexenta Project Wiki, archived from the original on 2010-04-05, https://web.archive.org/web/20100405120551/http://www.nexenta.org/os/DownloadMirrors
- StormOS is dead. Long live osdyson, stormos.org, 2012-09-14, archived from the original on 2013-10-10, https://web.archive.org/web/20131010001228/http://www.stormos.org/node/2378
- Preliminary Release, Martin Bochnig, 2012-09-27, http://openindiana.org/pipermail/openindiana-discuss/2012-September/009792.html, retrieved 2014-02-13
- pavroo (2016-06-14), MartUX, https://archiveos.org/MartUX/, retrieved 2018-02-02
- "Blastwave Open Source Sun Software". September 20, 2006. http://www.blastwave.org/.
- Preliminary SPARC 4u Release, Martin Bochnig, 2006-09-13, archived on 2006-09-20. Error: If you specify |archivedate=, you must also specify |archiveurl=, http://www.martux.org/, retrieved 2014-02-13
- OpenSXCE 2013.01 http://netmgt.blogspot.com/2013/03/tab-update-opensxce-march-3013.html
- MilaX, Alexander R. Eremin, http://www.milax.org/, retrieved 2012-12-29
- pavroo (2015-08-11), MilaX, https://archiveos.org/milax/, retrieved 2018-02-02
- EON ZFS Storage, http://sites.google.com/site/eonstorage/, retrieved 2012-12-29
- Project Jaris, archived from the original on July 22, 2011, https://web.archive.org/web/20110722111050/http://jaris.jp/
- 151a0 (and soon to be last) http://openindiana.org/pipermail/openindiana-discuss/2012-September/009792.html
- pavroo (January 8, 2016), OpenSXCE, https://archiveos.org/opensxce/, retrieved 2018-02-02
- Solaris 9 Operating Environment (final beta) reviewed by PC Magazine https://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,10432,00.asp
- Solaris 10 Review & Rating | PCMag.com https://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,1781190,00.asp
- Solaris 10 heads for Linux territory | NetworkWorld https://www.networkworld.com/article/2318756/software/solaris-10-heads-for-linux-territory.html
- Review of Solaris 10, OSNews http://www.osnews.com/story/9865
- Sun's Linux killer shows promise • The Register https://www.theregister.co.uk/2005/08/16/solaris_x86_not_too_shabby/
