Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Materials Science, Biomaterials
Among carbon-based nanomaterials, carbon dots (CDs) have received a surge of interest in recent years due to their attractive features such as tunable photoluminescence, cost effectiveness, nontoxic renewable resources, quick and direct reactions, chemical and superior water solubility, good cell-membrane permeability, and simple operation. CDs and their composites have a large potential for sensing contaminants present in physical systems such as water resources as well as biological systems. Tuning the properties of CDs is a very important subject.
- N-CDs
- metal-based CDs composites
- properties
1. Introduction
The rapid increase in the world population has caused a sharp rise in environmental pollution. The most alarming example is water pollution involving the scarcity of potable water due to the discharge of various types of pollutants such as phenolic compounds, inorganic materials, heavy metals, pesticides, and pathogenic microorganisms [1,2,3], that come from industries such as paper, printing, food processing, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic. This is an increasingly serious problem causing fatal diseases in the world [4,5,6]. The identification of inorganic and organic contaminants in various sectors, such as environmental monitoring, chemical and biological analysis, healthcare, and food safety, is crucial [7,8,9].
Several techniques for monitoring of water quality and detection of contaminants are popular, including conventional instrumental laboratory-based analysis, such as mass spectrometry, electrochemical methods, and gas chromatography. The prospective advantages of the laboratory-based analytical methods have been recognised for a long time, but studies show that they are not very efficient for on-site monitoring applications. With the technical improvements in analytical chemistry, new techniques are available for real-time detection such as, advanced spectroscopy, model-based event detection and water quality sensors [10,11].
In this regard, the introduction of sensor technology is attracting considerable attention. Sensors are classified into chemical, and biosensors based on their nature of sensing including the qualitative and quantitative analysis of a specific type of sample with the help of spectroscopic, electrochemical, and photoluminescence properties of the systems [12]. The chemical sensor involves the detection of metal ions and other molecules in the physical systems such as water resources, while biosensors sense molecules of biological importance [13,14].
In the last decade, a significant amount of attention has been given to “nanotechnology”, particularly in the field of sensors. It is one of the most essential technologies encompassing discoveries and inventions in numerous fields, such as chemistry, biology, medicine, physics, chemistry, and engineering. Richard P. Feynman (1959) first coined the word “nanotechnology” [15]. It is made of two words “nano” and “technology”. The word “nano” originated from the ancient Greek word νᾶνος (nános) meaning dwarf [16]. Thus, nanotechnology is the branch of technology where the manipulation of matter takes place on an atomic and molecular scale within at least 1 to 100 nm. Nanoparticles are the basic tools of nanotechnology. Particles with the size within the nano dimensions are known as nanoparticles (NPs) and the materials consisting of these particles are called nanomaterials [17]. The NPs can be 0D, 1D, 2D, and 3D depending on their shapes. A nanocomposite is a combination of the best properties of two or more different materials, in which one of the components has at least one dimension that is around 10−9 m (1 nm) [18,19]. In this regard, carbon materials, including fullerenes, nanofibers, graphene oxide (GO), and other carbonaceous nanomaterials have drawn significant attention due to a number of notable characteristics, such as electrical conductivity, chemical reactivity, and photocatalytic properties [20].
In recent years, carbon-based sensors have been reported to play a crucial role in chemical sensing and biological sensing. Carbon “quantum dots” (CQDs) or carbon dots (CDs) represent the carbonaceous family with incredible properties and advantageous features to overcome the shortcomings of common traditional metal-based quantum dots (QDs) such as metal oxides (TiO2, ZnO), and inorganic QDs (ZnO-PbS). Their shortcomings include high-carcinogenic toxicity, reactivity, cost, and low biocompatibility, hindering their extensive use and making them responsible for serious health and environmental problems [21,22]. Generally, CDs are spherical carbon NPs in which carbon atoms are sp2 hybridised with diameters of less than 10 nm [23,24]. CDs have a large number of -OH and -COOH and -NH2 and other groups on their surfaces, which give them outstanding photophysical and chemical properties, together with excellent biocompatibility, negligible toxicity, short response times, considerable aqueous solubility, cell-membrane permeability, and cost effectiveness with good quantum yield (Φ) [25,26,27]. Hence CDs show great importance in different fields, including bioimaging [28], energy harvesting [29], biosensing [30], drug delivery [31], and photocatalysis [32]. The efficiency of CDs significantly improves with the introduction of a heteroatom (N, S, B, P, F, Br, etc.) or transition metal (Zn, Cu, Mg, Ag, Au, etc.) [33,34] through the process of doping and formation of composites of CDs with difference matrices such as metal, metal oxide, polymer, and carbon-based materials (graphene, GO) compared to individual CDs and without CDs [35,36,37,38].
2. Carbon Sources for the Preparation of Carbon Dots
CDs can be synthesised from a good number of precursor materials coming from both natural (organic) and chemical (inorganic) sources (Figure 2). The properties of CDs rely on the source materials used for synthesis. For instance, fluorescent CDs exhibit relatively lower Φ when prepared from chemical sources [39], compared to organic carbon sources, such as organic compounds, organic natural products, and biomass waste. Natural sources are more popular for the synthesis of CDs because they are heterogeneous, biodegradable, and bio-organic substances mainly composed of biopolymers such as cellulose (30–60%), hemicelluloses (20–40%), lignin (15–25%), ash, and proteins [40,41]. Renewable, ecofriendly, abundant, and innocuous carbon sources show excellent optical properties and low cytotoxicity. However, most of the natural resources in the form of biomass waste are currently discarded, landfilled, or openly burned, which not only leads to a waste of resources but also causes some environmental problems threatening human life [42,43,44].
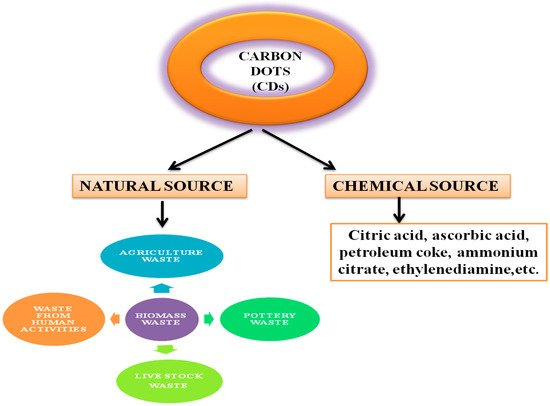
Figure 2. Natural and chemical sources of precursors used in the synthesis of CDs.
3. Methods of Preparation of CDs
CDs can be prepared by both top-down and bottom-up approaches (Figure 3). The former involves the rupture or cleaving of bulk carbonaceous materials into small materials by physical, chemical, or electrochemical means, including electrochemical synthesis [45], laser ablation [46], arc discharge [47], or chemical oxidation [48]. The top-down method is associated with the advantages of an abundance of raw materials, a large-scale production, and a simple mode of operation. This method, however, also suffers from the drawbacks of low yield, the requirement of special equipment, and use of nonselective chemical cutting method. Thus, the bottom-up method is preferred. It is an easy method and involves carbonization, that is, small molecules are chemically fused in a stepwise way, using microwave [49], ultrasonication [50] and hydrothermal methods [51]. The hydrothermal method has been the most popular method, due to its associated advantages, such as ease and convenience of the procedure, simple operation, cost effectiveness and ecofriendliness, which have rendered it to be considered as a green method [44]. Conventionally, CDs are synthesised by surface functionalization of carbon nanoparticles with organic and polymeric molecules. CDs synthesised using this method often require high-operational temperatures, the use of volatile organic solvents or alkaline and acidic conditions. Sun and coworkers reported the synthesis of CDs by laser ablation of a carbon target, prepared by hot-pressing a mixture of graphite powder and cement, followed by stepwise baking, curing, and annealing, in the presence of water vapor with argon as a carrier gas at 900 °C and 75 k [46]. The treated sample was not photoluminescent, but upon the surface passivation, by attaching simple organic species to the acid-treated carbon particles, typically at 120 °C, for 72 h, bright luminescence emissions could be observed. A similar method was used, and photoluminescent CDs were produced by surface passivation, by Cao et al. [52] and in these cases, the optical properties were widely varying but were less controllable. The experimental conditions also made them environmentally unfriendly [46,52]. Given the natural concerns about environmental sustainability, greener approaches to CD synthesis are urgently needed [53,54].
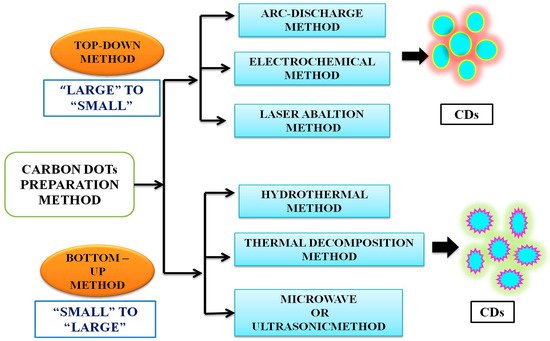
Figure 3. Common top-down and bottom-up approaches to synthesize carbon dots. The details of these methods are available in recent textbooks.
Both chemical and natural sources are based either on top-down or bottom-up strategies. As noted earlier, the top-down method involves harsh experimental conditions (e.g., strong acid and arc discharge), tedious operation steps, with expensive equipment usually employed, yielding CDs with low Φ, which greatly limits their practical application [55,56,57]. The bottom-up approach is based on the polymerisation reaction of small molecules aiming at the formation of nanoscale CDs. The green synthesis of CDs using the bottom-up approach involves hydrothermal and solvothermal combustion, and template-assisted, microwave, and ultrasonic methods, etc. Among them, hydrothermal methods are the most frequently used due to their advantages, such as low cost, high yields, ease of operation, simple equipment requirements, and their ecofriendly nature [58,59]. The bottom-up synthetic route thus appears promising and is more appealing as it uses “green precursors” (that is, renewable natural resources or their derivatives or precursors made from waste materials of biomass). In contrast, chemical precursors refer to chemical species, such as citric acid, ethylene, etc. [54,60].
CDs can be used as fluorescent chemical sensors for measuring several analytes found in water bodies, such as different types of chemical species such as pesticides and heavy metal ions such as As, Hg, and Cd. CDs find important applications in the quantification of biological molecules and intracellular metal ions (such as Fe3+, Hg2+, Na+, and K+), vitamins, enzymes, nucleic acids, proteins, H2O2, glucose, L-cysteine, and galactose, among others [61,62,63]. The exceptional sensing ability of CDs toward a range of substrates has been exploited and a significant role of CDs was noted in a number of biological processes, such as regulation of metalloenzymes, gene expression, energy generation, and neurotransmission in biological systems [53,54,60].
CDs are excellent sensors due to their novel characteristics, such as high sensitivity, intrinsic fluorescent properties, low cost, ecofriendliness, quick response, negligible cytotoxicity, and easy preparation method. Thus, they serve as appropriate energy materials or electron acceptors and donors and are a hot topic in modern research. The sensing of CDs generally occurs as a result of a change in their fluorescence behaviour through various means, such as the inner-filter effect, photoinduced electron and charge transfer, and resonance energy transfer [64,65]. Figure 4 displays the progress data for CDs from 2004 to 2020 [66,67]. A nearly exponential rise is observed within the reported time frame.
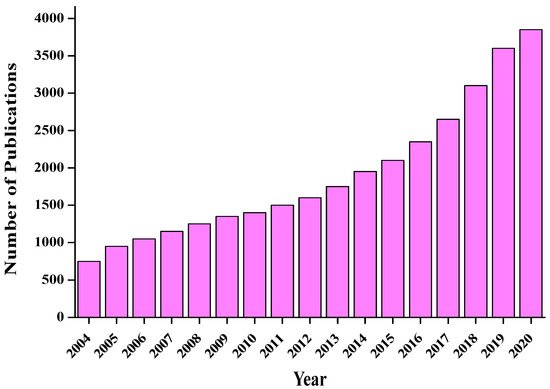
Figure 4. The number of publications related to CDs. A surge of interest in recent years is observed.
4. Properties of Carbon Dots
4.1. Structural Properties
CDs are commonly sphere-like three-dimensional (3D) clusters of 2–10 nm, composed of C, N, O, and H atoms [68]. The proportions of these elements vary, depending on the carbon source used to produce them through different approaches (generally carbohydrates, proteins, and other biomolecules are employed). The inside parts of these clusters are surrounded by mostly sp3 hybridised and a small portion of sp2 hybridised carbon atoms, along with disordered carbons, which result in an amorphous nature [69,70]. Codoping, surface passivation, and some other treatments improve the water solubility of CDs, allowing more applications [71,72]. Due to low toxicity and biocompatibility, CDs can enter cells without any difficulty via endocytosis, and have extensive relevance in deep-tissue and cell imaging. Raman spectroscopy is widely used for the identification of functional groups and spectral characteristics of the molecular structures of samples [73,74].
4.2. Optical Properties
4.2.1. Absorbance
CDs show broad and strong absorption bands in the ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) region. The absorption spectra vary for CDs synthesised from different sources with various approaches. Water-soluble CDs show a light yellow colour in aqueous solution. Many functional groups present on the surface of CDs cause different types of transitions, such as π-π* transition of C=C and C=N bonds observed at 220~270 nm, while a shoulder peak is observed due to the n-π* transition of C−O and C=O bonds at around 280~350 nm [75,76]. Upon increasing the synthesis temperature, the latter band becomes broader and weaker [77].
4.2.2. Fluorescence Properties
One of the most exceptional features of CDs is their fluorescence properties, which include fluorescence emission, narrow emission, wide excitation, size- or excitation wavelength-dependent fluorescence emission, strong resistance to photobleaching, and upconversion luminescence [78,79]. Zhang et al. [78] reported the influence of organic solvents on the fluorescence emission peak position of CDs. Different organic solvents create different types of defects on the surface of CDs, which initiate different emission sites responsible for intensifying the fluorescence emission spectrum of the materials.
4.2.3. Upconversion Photoluminescence
Upconversion photoluminescence (PL) is one of the most appealing optical features of CDs, affected by surface defects, quantum size, or confinement effects. It is a kind of tunable PL [80]. In tunable PL phenomenon, CDs show excitation-dependent PL along with strong emission, which rapidly decline from blue-wavelength to red-wavelength region. The upconversion phenomenon, on the other hand, involves emission of photon at shorter wavelengths than the excitation wavelength, which is attained by absorbing two or more photons [79,80,81,82]. CDs prepared from the natural sources show special upconversion fluorescence, with an emission wavelength shorter than the excitation wavelength, instead of traditional down-conversion fluorescence [83]. Two types of accepted mechanisms of antistokes photoluminescence and multiphoton active processes are usually used to explain upconversion fluorescence [84]. Sun et al. [85] reported that S and N codoped CDs prepared from hair fibres exhibit upconversion fluorescence behaviour. Wu et al. [86] demonstrated the upconversion phenomenon of CDs prepared from walnut shells by introducing an electronic transition process model. According to this model, the phenomenon occurs due to the gap between the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest occupied molecular orbital (LUMO). The HOMO–LUMO gap decreases as the particle size of CDs increases. The electrons at the π orbitals (HOMO) of carbine are excited after the absorption of low-energy radiation with wavelengths >600 nm and jump into the excited state with higher energy (LUMO). The electrons in this state return back to the ground σ state and release a huge amount of energy in the form of radiation and, consequently, upconversion luminescence takes place.
4.2.4. Electrochemiluminescence
The electrochemiluminescence (ECL) of CDs plays an excellent role in the clinical diagnosis of intracellular toxic elements, even in ultratrace amounts, due to the high sensitivity and simple mode-of-action of this technique. Some of the numerous novel luminescent materials used so far include iridium complexes [87], fluorescent dyes, and noble-metal nanoclusters [88,89,90]. The conventional techniques for detection, on the other hand, include atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) [91], electrochemistry [92], fluorescence [93], and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [94], which are time consuming. Electrochemical or chemical approaches applied for the synthesis of CDs for ECL applications yield CDs with oxygen-rich functional groups, such as carbonyl (C=O), carboxyl (-COOH), hydroxyl (-OH) and epoxy or ether (R−O−R) [95,96]. These lead to formation of defects and serve as chemically reactive sites, responsible for the degradation of large carbonaceous substances into smaller fragments [97]. While both oxidized and reduced CDs, having different ECL behaviours, are produced using the bottom-up method, negligible or weak ECL behaviour is exhibited by reduced CDs. Strong ECL emission is obtained from oxidized CDs. The oxygen-containing functional groups present on the surface of the CDs produce electrogenerated CDs•− radicals with the help of K2S2O8, where S2O82− produces the strongly oxidizing SO4•− radicals by electrochemical reduction. After CDs•− react with SO4•− radicals through electron-transfer annihilation, an excited state for ECL emission is generated [98,99].
4.3. Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility
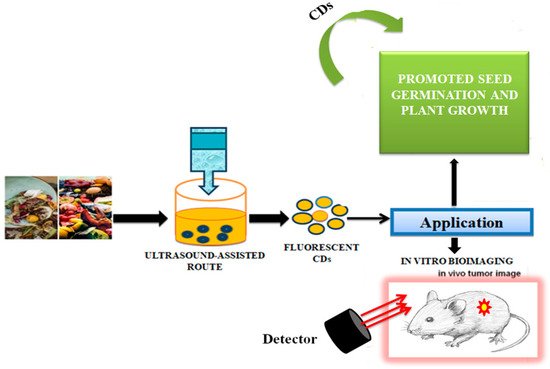
CDs synthesised from green routes, using cost-effective and renewable sources, such as fruits, vegetables, and different types of waste are excellent alternatives. The unique properties of those CDs, such as good biocompatibility, low toxicity, high-water solubility, catalytic behaviour, and electrical conductivity make them useful as biosensors in biomedical applications, especially in biolabelling, DNA-sensing microbial control, and drug-delivery studies, metal sensing, drug delivery, and energy storage [100,101]. Jhansi et al. [102] studied the biocompatible properties of CDs through an in vitro cytotoxicity test on L6 normal rat myoblast cells by using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Arul et al. [103] reported that fluorescent nitrogen-doped CDs (N-CDs) could be prepared from kiwi fruit (Actinidia deliciosa) extract by a one-step hydrothermal method using aqueous ammonia. Due to low cytotoxicity, N-CDs were tested against L-929 (Lympho blastoid-929) and MCF-7 (Michigan Cancer Foundation-7) cells and interestingly, they exhibited anticancer activity. N-CDs also catalysed the degradation of carcinogenic agents such as rhodamine-B (RhB), a xanthene-based dye released from paper, textiles, paint, and leather industries, being applied as an illegal food additive, staining fluorescent dye and as a tracer dye using NaBH4. Park et al. [104] proposed simple adjustable experimental conditions such as ultrasonic power and the optimal proportion of solvents and reaction time for a large-scale preparation of water-soluble CDs from food-waste-derived carbon sources. The ultrasound-assisted route led to the production of 120 g CDs produced from 100 kg of food waste mixture, which were highly water soluble, photostable, photoluminescent, and with low cytotoxicity, and which could be used for in vitro bioimaging and promotion of seed germination and plant growth (Figure 5).

Figure 5. Synthesis of carbon dots from the waste food. The CDs were successfully used for in vivo tumour imaging, as described in [104].
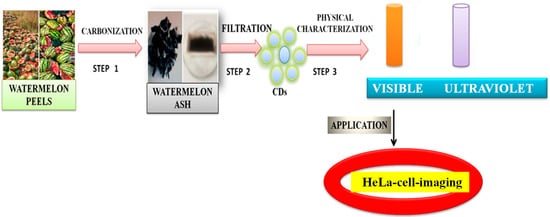
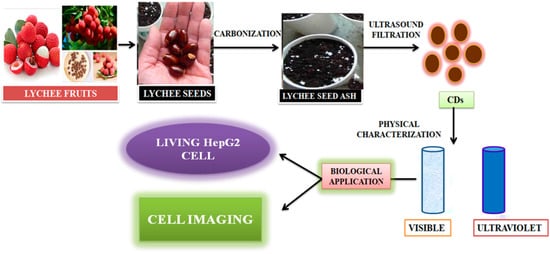
Zhou et al. [105] achieved large-scale production of CDs by pyrolysis of watermelon-peel waste under a low temperature and followed by filtration. The obtained CDs showed strong-blue luminescence, excellent water solubility, good stability in solutions with a wide range of pH and high salinity. The as-prepared carbon dots were successfully used in HeLa cell imaging (Figure 6). Similarly, CDs with low inherent cytotoxicity could also be produced from lychee seeds by pyrolysis, and CDs with a Φ of 10.6% could be used in fluorescence imaging of living HepG2 cells (Figure 7) [106].

Figure 6. Synthesis of carbon dots from the watermelon peels. The CDs were successfully applied to HeLa cell imaging, as described in [105].

Figure 7. Synthesis of carbon dots from lychee seeds. The CDS were used for fluorescence imaging of living HepG2 cells, as described in [106].
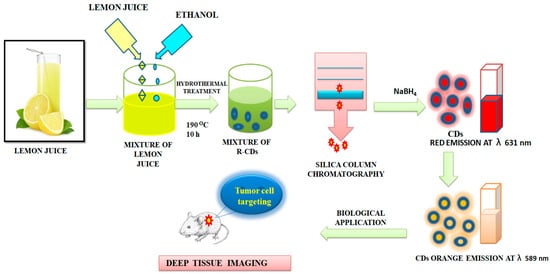
Ding et al. [107] reported the preparation of red-emitting C-dots (R-CDs) from lemon juice using a hydrothermal method, followed by purification using silica column chromatography. The CDs exhibited Φ of 28% and an excitation-independent red emission maximum at 631 nm could be observed. The reduced R-CDs showed very negligible cytotoxicity. The surface states of R-CDs were crucial. The reduced R-CDs showed orange emission maxima at 589 nm and could be used in deep-tissue imaging as represented in Figure 8. Oh et al. [108] and Bilal et al. [109] reported the metacellular analysis of QDs. Table 1 lists cytotoxicity and the detection-limit range of a number of QDs and CDs to depict an overall scenario. Although due to the variation in the preparative method and precursors, it is difficult to have a realistic comparison, this would serve as a screenshot of the development in this arena.

Figure 8. Synthesis of carbon dots from the lemon juice. The CDs were used for deep-tissue imaging, as described in [107].
Table 1. Cytotoxicity and detection-limit range of QDs and CDs.
| Quantum Dots vs. Carbon Dots | Source | Method | Cytotoxicity and Detection-Limit Range | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdTe QDs | CdCl2, NaBH4, tellurium powder, phosphate buffered saline tablets | Electrochemical method | 118 ± 49 μg/mL with the help of electrochemical assay 157 ± 31 μg/mL by MTT cytotoxicity assay |
[110] |
| InPZnS QDs | InPZnS alloy core and a thin ZnS shell | Heating Up Method | 70 nM of QDs responsible for cytotoxic effect on environmental health on 72 h exposure | [111] |
| Indium-based QDs | In and Zn content and implementing a more robust outer shell | Heating Up Method | 12.5 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg QDs generally collected in the liver as well as the spleen | [112] |
| InZnP and InZnPS QD | Indium myristate, ZnSt2 | Precipitation Method | 6.25–200 nM upon 24 h exposure | [113] |
| CDs | Onion waste | Hydrothermal method | 0.31 μM | [114] |
| CDs | ZrCl2, trinitrophenol (TNP), 2,4-dinitrophenol, 4-nitrophenol, phenol, Polyvinylpyrrolidone, acetic acid, citric acid | Hydrothermal Method |
0.01–20.0 μM at a low-detection limit of 3.5 nM | [115] |
| CDs | Gelatin | Hydrothermal Method |
1−75 μmol/L | [116] |
| CDs | Carbohydrate | Hydrothermal Method |
0 to 1 × 103 | [117] |
| CDs | DEA | Microwave Method |
5.0 × 10−2 to 8.0 | [118] |
| CDs | Catechol | Hydrothermal Method |
1 × 10−2 to 25 | [119] |
| CDs | Citric acid | Hydrothermal Method |
8.0 × 10−2 to 50 | [120] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/nano12193434
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
