Aegerolysins are remarkable proteins. They are distributed over the tree of life, being relatively widespread in fungi and bacteria, but also present in some insects, plants, protozoa, and viruses. Their function, in particular, is intriguing. Aegerolysin proteins are involved in various interactions by recognizing a molecular receptor in the target organism. Despite their abundance in cells of certain developmental stages and their presence in secretomes, only a few aegerolysins have been studied in detail. Formation of pores with various larger non-aegerolysin-like protein partners is one of the possible responses of the aegerolysin-producing organism in competitive exclusion of other organisms from the ecological niche.
- aegerolysins
- bacteria
- fungi
- insecticidal
- lipid binding
- lifestyle
- membrane-attack complex/perforin domain (MACPF)
- pore forming proteins
1. Introduction
2. Aegerolysins
| Organism Name | Other Names | Taxonomy | Lifestyle/Niche | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungi | ||||
| Pleurotus ostreatus | Oyster mushroom Hiratake |
Agaricomycotina Agaricales |
Saprotroph White rot Nematocidal |
[12] |
| Pleurotus eryngii | King oyster or trumpet or brown mushroom Boletus of the steppes French horn mushroom Aliʻi oyster |
Agaricomycotina Agaricales |
Saprotroph Grassland-litter decomposer Facultatively biotrophic Nematocidal |
[13] |
| Cyclocybe aegerita | Agrocybe aegerita Poplar mushroom Tea tree mushroom Cha shu gu Yanagi-matsutake Sword-belt mushroom Velvet pioppini |
Agaricomycotina Agaricales |
Saprotroph Weak white rot on hardwoods Facultatively pathogenic |
[14] |
| Moniliophthora perniciosa | Crinipellis perniciosa Witches’ broom disease |
Agaricomycotina Agaricales |
Hemibiotrophic plant pathogen Broad range of host |
[15] |
| Lignosus rhinocerotis | Tiger milk mushroom | Agaricomycotina Polyporales |
Saprotroph White rot |
[16] |
| Neosartorya fumigata | Aspergillus fumigatus | Eurotimycetes Eurotiales |
Saprotroph Ubiquitous in soil and compost Human (opportunistic) pathogen |
[17][18][19][20] |
| Aspergillus niger | Eurotimycetes Eurotiales |
Saprotroph Ubiquitous in soil and compost Human opportunistic pathogen |
[17][18][21][22][23][24] | |
| Aspergillus terreus | Eurotimycetes Eurotiales |
Saprotroph Human opportunistic pathogen |
[17][18][25] | |
| Aspergillus oryzae | Eurotimycetes Eurotiales |
Saprotroph | [17][18][26] | |
| Beauveria bassiana | Sordariomycetes Hypocreales |
Entomopathogen Endophyte Soil and insects |
[27][28] | |
| Hypocrea atroviridis | Trichoderma atroviride | Sordariomycetes Hypocreales |
Mycoparasitic (including oomycetes) Cosmopolitan, soil |
[29][30][31][32] |
| Alternaria geisen | Black spot of Japanese pear | Dothideomycetes Pleosporales |
Plant pathogen | [33][34] |
| Bacteria | ||||
| Bacillus thuringiensis | Firmicutes | Ubiquitous opportunistic pathogen on vertebrates, plants, insects, nematodes, mollusks, protozoan, animal, and human parasites. Soils, grain dusts, dead insects, water Aerobic and spore-forming |
[35][36] | |
| Paraclostridium bifermentans subsp. malaysia |
Clostridium bifermentans subsp. malaysia |
Firmicutes | Anaerobic, forming endospores Mosquito larvicidal |
[37] |
| Alcaligenes faecalis | Proteobacteria | Soil, water, environments associated with humans Human opportunistic pathogen Nematocidal |
[38] | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Proteobacteria | Ubiquitous opportunistic pathogen on: humans, vertebrates, plants, and insects |
[39][40][41][42][43] | |
| Insecta | ||||
| Chrysodeixis includens | Pseudoplusia includes | Lepidoptera Noctuidae |
Plant pest (defoliator) Larvae feed on a wide range of plants |
[44][45] |
| Viria | ||||
| Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 6a1 | Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 2c | Varidnaviria Ascoviridae |
Obligate pathogen Pseudoplusia includens moth larvae |
[44][46][47][48] |
3. Aegerolysin Binary Partner Proteins
| Short Name | Aegerolysin/ Structure |
Membrane Receptor |
Function | Partner Protein Short Name | Partner Protein/ Structure |
Organism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PlyA | Pleurotolysin A PDB ID: 4OEBA |
SM/Chol | n.d. | PlyB | Pleurotolysin B PDB ID: 4OEJ Membrane embedded PlyA/PlyB pore PDB ID: 4V2T |
Pleurotus ostreatus | [56][57] |
| OlyA | Ostreolysin A | SM/Chol CPE/Chol Lipid rafts |
Involvement in mushroom fruiting Anticancer (+PlyB) |
PlyB | Pleurotolysin B PDB ID: 4OEJ |
Pleurotus ostreatus | [58][59][60][61][62][63][64][65][66][67][68][69][70][71][72][73] |
| OlyA6 | Ostreolysin A6 PDB ID: 6MYJ |
SM/Chol CPE/Chol CAEP/POPC/Chol Lipid rafts |
Insecticidal (+PlyB) | PlyB | Pleurotolysin B PDB ID: 4OEJ |
Pleurotus ostreatus | [53][68][74][75][76][77][78][79][80][81][82] |
| rOly | Recombinant ostreolysin | Lipid rafts? | Antiproliferative Pro-apoptotic |
n.d. | n.d. | Pleurotus ostreatus | [83][84][85] |
| PlyA2 | Pe.PlyA/Pleurotolysin A2 | SM/Chol CPE/Chol CPE Lipid rafts |
Insecticidal (+PlyB) |
EryB | Erylysin B | Pleurotus eryngii | [12][68][78][86][87][88][89] |
| EryA | Erylysin A | CPE/Chol CL/DPPC/Chol |
Insecticidal (+PlyB) Inhibition of cytokinesis |
No | No | Pleurotus eryngii | [53][68][89][90][91] |
| Aa-Pri1 | Aegerolysin Aa-Pri1 | n.d. | No | No | Agrocybe aegerita | [58][92] | |
| MpPRIA1 | Putative aegerolysin | n.d. | MpPLYB? | n.d. | Moniliophthora perniciosa | [93] | |
| MpPRIA2 | Putative aegerolysin | n.d. | MpPLYB? | n.d. | Moniliophthora perniciosa | [93] | |
| GME7309 | GME7309_g aegerolysin-domain-containing protein | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | Lignosus rhinocerotis | [94] | |
| Asp-HS | Asp-hemolysin | Oxidized low-density lipoproteins | Cytotoxic effects on murine macrophages and vascular endothelial cells Induce cytokine genes |
Asp-HSB | n.d. | Aspergillus fumigatus | [95][96][97][98][99][100][101][102][103] |
| Asp-HS-like | Asp hemolysin-like | n.d. | n.d. | No | No | Aspergillus fumigatus |
[102] |
| NigA1 | Nigerolysin A1 | n.d. | n.d. | No | No | Aspergillus niger | [104][105] |
| NigA2 | Nigerolysin A2 | CPE/Chol | n.d. | NigB1 | Nigerolysin B1 | Aspergillus niger | [104][105] |
| Ter | Terrelysin | n.d. | n.d. | No | No | Aspergillus terreus | [25][106][107] |
| AoHlyA | Aspergillus oryzae hemolysin | n.d. | n.d. | No | No | Aspergillus oryzae | [108][109][110] |
| BlyA | Beauveriolysin A | SM/Chol CPE/Chol |
n.d. | BlyB | Beauveriolysin B | Beauveria bassiana | [54] |
| Agl1 | Trichoderma atroviride aegerolysin | Conidiation Antagonism |
n.d. | No | No | Trichoderma atroviride | [111] |
| L152 | Alternaria geisen aegerolysin | n.d. | n.d. | L152B | n.d. | Alternaria geisen | [33] |
| Cry34Ab1 (Gpp34Ab1) |
13.6 kDa Insecticidal crystal protein PDB ID: 4JOX |
Unknown protein receptor | Insecticidal (+Cry34Ab1) |
Cry35Ab1 (Tpp35Ab1) |
43.8 kDa insecticidal crystal protein PDB ID: 4JP0 |
Bacillus thuringiensis | [36][49][50][112][113][114][115][116][117] |
| Cbm17.1 | Hemolysin-like protein Cbm17.1 | n.d. | Insecticidal (+Cry16Aa/Cry17Aa/ Cbm17.2) |
Cry16Aa, Cry17Aa, Cbm17.2 | Pesticidal crystal-like protein Cry16Aa and Cry17Aa, Hemolysin-like protein Cbm17.2 | Clostridium bifermentans | [37][118][119] |
| Cbm17.2 | Hemolysin-like protein Cbm17.2 | n.d. | Insecticidal (+Cry16Aa/Cry17Aa/ Cbm17.1) |
Cry16Aa, Cry17Aa, Cbm17.2 | Pesticidal crystal-like protein Cry16Aa and Cry17Aa, Hemolysin-like protein Cbm17.1 | Clostridium bifermentans | [37][118][119] |
| AfIP-1A | Two-component insecticidal protein 16 kDa unit PDB ID: 5V3S |
Unknown protein receptor AfIP-1A/AfIP-1B membrane pore |
n.d. | AfIP-1B | Two-component insecticidal protein 77 kDa unit |
Alcaligenes faecalis | [51][120] |
| RahU | RahU protein PDB ID: 6ZC1 |
CPE/Chol | n.d. | No | No | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [121][122] |
| P23 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | No | No | Pseudoplusia includes | [45] |
| TnAV2cgp029 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | No | No | Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 2c | [46][47][123][124][125] |
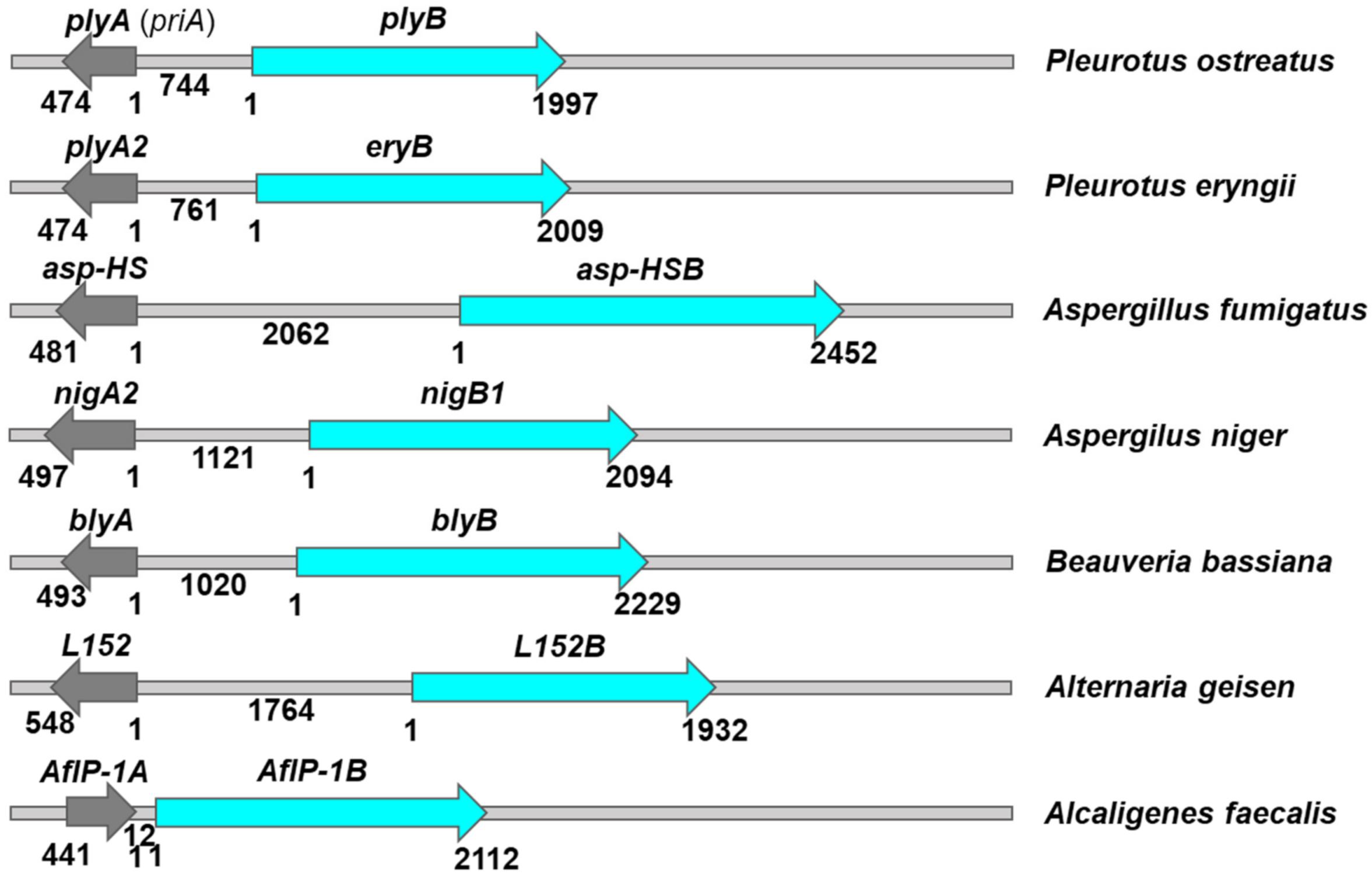
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/toxins14090629
References
- Berne, S.; Lah, L.; Sepčić, K. Aegerolysins: Structure, function, and putative biological role. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 694–706.
- Butala, M.; Novak, M.; Kraševec, N.; Skočaj, M.; Veranič, P.; Maček, P.; Sepčić, K. Aegerolysins: Lipid-binding proteins with versatile functions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 142–151.
- Nayak, A.P.; Green, B.J.; Beezhold, D.H. Fungal hemolysins. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 1–16.
- Novak, M.; Kraševec, N.; Skočaj, M.; Maček, P.; Anderluh, G.; Sepčić, K. Fungal aegerolysin-like proteins: Distribution, activities, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 601–610.
- Ota, K.; Butala, M.; Viero, G.; Dalla Serra, M.; Sepčić, K.; Maček, P. Fungal MACPF-like proteins and aegerolysins: Bi-component pore-forming proteins? In Sub-Cellular Biochemistry; Anderluh, G., Gilbert, R., Eds.; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 80, pp. 271–291. ISBN 978-94-017-8880-9.
- Yamaji-Hasegawa, A.; Hullin-Matsuda, F.; Greimel, P.; Kobayashi, T. Pore-forming toxins: Properties, diversity, and uses as tools to image sphingomyelin and ceramide phosphoethanolamine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 576–592.
- Kishimoto, T.; Ishitsuka, R.; Kobayashi, T. Detectors for evaluating the cellular landscape of sphingomyelin- and cholesterol-rich membrane domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 812–829.
- Hullin-Matsuda, F.; Makino, A.; Murate, M.; Kobayashi, T. Probing phosphoethanolamine-containing lipids in membranes with duramycin/cinnamycin and aegerolysin proteins. Biochimie 2016, 130, 81–90.
- Hullin-Matsuda, F.; Murate, M.; Kobayashi, T. Protein probes to visualize sphingomyelin and ceramide phosphoethanolamine. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 216, 132–141.
- Panevska, A.; Skočaj, M.; Modic, Š.; Razinger, J.; Sepčić, K. Aegerolysins from the fungal genus Pleurotus—Bioinsecticidal proteins with multiple potential applications. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107474.
- Grundner, M.; Panevska, A.; Sepčić, K.; Skočaj, M. What can mushroom proteins teach us about lipid rafts? Membranes 2021, 11, 264.
- Lee, C.-H.; Chang, H.-W.; Yang, C.-T.; Wali, N.; Shie, J.-J.; Hsueh, Y.-P. Sensory cilia as the Achilles heel of nematodes when attacked by carnivorous mushrooms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6014–6022.
- Zervakis, G.I.; Ntougias, S.; Gargano, M.L.; Besi, M.I.; Polemis, E.; Typas, M.A.; Venturella, G. A reappraisal of the Pleurotus eryngii complex—New species and taxonomic combinations based on the application of a polyphasic approach, and an identification key to Pleurotus taxa associated with Apiaceae plants. Fungal Biol. 2014, 118, 814–834.
- Gupta, D.K.; Rühl, M.; Mishra, B.; Kleofas, V.; Hofrichter, M.; Herzog, R.; Pecyna, M.J.; Sharma, R.; Kellner, H.; Hennicke, F.; et al. The genome sequence of the commercially cultivated mushroom Agrocybe aegerita reveals a conserved repertoire of fruiting-related genes and a versatile suite of biopolymer-degrading enzymes. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 48.
- Meinhardt, L.W.; Rincones, J.; Bailey, B.A.; Aime, M.C.; Griffith, G.W.; Zhang, D.; Pereira, G.A.G. Moniliophthora perniciosa, the causal agent of witches’ broom disease of cacao: What’s new from this old foe? Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 577–588.
- Fung, S.-Y.; Tan, C.-S. Tiger milk mushroom (the Lignosus trinity) in Malaysia: A medicinal treasure trove. In Medicinal Mushrooms; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 349–369.
- de Vries, R.P.; Riley, R.; Wiebenga, A.; Aguilar-Osorio, G.; Amillis, S.; Uchima, C.A.; Anderluh, G.; Asadollahi, M.; Askin, M.; Barry, K.; et al. Comparative genomics reveals high biological diversity and specific adaptations in the industrially and medically important fungal genus Aspergillus. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 28.
- Abdel-Azeem, A.M.; Salem, F.M.; Abdel-Azeem, M.A.; Nafady, N.A.; Mohesien, M.T.; Soliman, E.A. Biodiversity of the genus Aspergillus in different habitats. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 3–28.
- Nierman, W.C.; Pain, A.; Anderson, M.J.; Wortman, J.R.; Kim, H.S.; Arroyo, J.; Berriman, M.; Abe, K.; Archer, D.B.; Bermejo, C.; et al. Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 2005, 438, 1151–1156.
- Mullins, J.; Harvey, R.; Seaton, A. Sources and incidence of airborne Aspergillus fumigatus (Fres). Clin. Exp. Allergy 1976, 6, 209–217.
- Schuster, E.; Dunn-Coleman, N.; Frisvad, J.C.; Van Dijjck, P. On the safety of Aspergillus niger—A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 426–435.
- Perrone, G.; Susca, A.; Cozzi, G.; Ehrlich, K.; Varga, J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Meijer, M.; Noonim, P.; Mahakarnchanakul, W.; Samson, R.A. Biodiversity of Aspergillus species in some important agricultural products. Stud. Mycol. 2007, 59, 53–66.
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Safety Evaluation of Certain Mycotoxins in Food/Prepared by the Fifty-Sixth Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives: Rome, Italy, 2001.
- Pel, H.J.; de Winde, J.H.; Archer, D.B.; Dyer, P.S.; Hofmann, G.; Schaap, P.J.; Turner, G.; de Vries, R.P.; Albang, R.; Albermann, K.; et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 221–231.
- Nayak, A.P.; Blachere, F.M.; Hettick, J.M.; Lukomski, S.; Schmechel, D.; Beezhold, D.H. Characterization of recombinant terrelysin, a hemolysin of Aspergillus terreus. Mycopathologia 2011, 171, 23–34.
- Machida, M.; Yamada, O.; Gomi, K. Genomics of Aspergillus oryzae: Learning from the history of koji mold and exploration of its future. DNA Res. 2008, 15, 173–183.
- Vega, F.E.; Goettel, M.S.; Blackwell, M.; Chandler, D.; Jackson, M.A.; Keller, S.; Koike, M.; Maniania, N.K.; Monzón, A.; Ownley, B.H.; et al. Fungal entomopathogens: New insights on their ecology. Fungal Ecol. 2009, 2, 149–159.
- Rasool, S.; Vidkjær, N.H.; Hooshmand, K.; Jensen, B.; Fomsgaard, I.S.; Meyling, N.V. Seed inoculations with entomopathogenic fungi affect aphid populations coinciding with modulation of plant secondary metabolite profiles across plant families. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1715–1727.
- Druzhinina, I.S.; Kubicek, C.P. Ecological Genomics of Trichoderma. In The Ecological Genomics of Fungi; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 89–116.
- Druzhinina, I.S.; Seidl-Seiboth, V.; Herrera-Estrella, A.; Horwitz, B.A.; Kenerley, C.M.; Monte, E.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Zeilinger, S.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Kubicek, C.P. Trichoderma: The genomics of opportunistic success. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 749–759.
- Atanasova, L.; Le Crom, S.L.; Gruber, S.; Coulpier, F.; Seidl-Seiboth, V.; Kubicek, C.P.; Druzhinina, I.S. Comparative transcriptomics reveals different strategies of Trichodermamycoparasitism. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 121.
- Atanasova, L. Ecophysiology of Trichoderma in Genomic Perspective. In Biotechnology and Biology of Trichoderma; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 25–40.
- Roberts, R.G.; Bischoff, J.F.; Reymond, S.T. Differential gene expression in Alternaria gaisen exposed to dark and light. Mycol. Prog. 2011, 11, 373–382.
- Simmons, E.G.; Roberts, R.G. Alternaria themes and variations (73). Mycotaxon 1993, 48, 109–140.
- Argôlo-Filho, R.; Loguercio, L. Bacillus thuringiensis is an environmental pathogen and host-specificity has developed as an adaptation to human-generated ecological niches. Insects 2013, 5, 62–91.
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; Caballero, P. Bacillus thuringiensis toxins: An overview of their biocidal activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3296–3325.
- Qureshi, N.; Chawla, S.; Likitvivatanavong, S.; Lee, H.L.; Gill, S.S. The Cry Toxin operon of Clostridium bifermentans subsp. malaysia is highly toxic to Aedes larval mosquitoes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5689–5697.
- Ju, S.; Lin, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; Sun, M. Alcaligenes faecalis ZD02, a Novel Nematicidal Bacterium with an Extracellular Serine Protease Virulence Factor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2112–2120.
- Finlay, B.B. Bacterial Disease in Diverse Hosts. Cell 1999, 96, 315–318.
- Chieda, Y.; Iiyama, K.; Yasunaga-Aoki, C.; Lee, J.M.; Kusakabe, T.; Shimizu, S. Pathogenicity of gacA mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01 in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 181–186.
- Sousa, A.; Pereira, M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa diversification during infection development in cystic fibrosis lungs—A review. Pathogens 2014, 3, 680–703.
- Starkey, M.; Rahme, L.G. Modeling Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis in plant hosts. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 117–124.
- Bano, N.; Musarrat, J. Characterization of a new Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain NJ-15 as a potential biocontrol agent. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 46, 324–328.
- Specht, A.; Sosa-Gómez, D.R.; Roque-Specht, V.F.; Valduga, E.; Gonzatti, F.; Schuh, S.M.; Carneiro, E. Biotic potential and life tables of Chrysodeixis includens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), Rachiplusia nu, and Trichoplusia ni on soybean and forage turnip. J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 8.
- Zhang, S.; Clark, K.D.; Strand, M.R. The protein P23 identifies capsule-forming plasmatocytes in the moth Pseudoplusia includens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 501–510.
- Cheng, X.-W.; Wang, L.; Carner, G.R.; Arif, B.M. Characterization of three ascovirus isolates from cotton insects. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 89, 193–202.
- Wang, L.; Xue, J.; Seaborn, C.P.; Arif, B.M.; Cheng, X.-W. Sequence and organization of the Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 2c (Ascoviridae) genome. Virology 2006, 354, 167–177.
- Stasiak, K.; Renault, S.; Federici, B.A.; Bigot, Y. Characteristics of pathogenic and mutualistic relationships of ascoviruses in field populations of parasitoid wasps. J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 103–115.
- Kelker, M.S.; Berry, C.; Evans, S.L.; Pai, R.; McCaskill, D.G.; Wang, N.X.; Russell, J.C.; Baker, M.D.; Yang, C.; Pflugrath, J.W.; et al. Structural and biophysical characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal proteins Cry34Ab1 and Cry35Ab1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112555.
- Moellenbeck, D.J.; Peters, M.L.; Bing, J.W.; Rouse, J.R.; Higgins, L.S.; Sims, L.; Nevshemal, T.; Marshall, L.; Ellis, R.T.; Bystrak, P.G.; et al. Insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis protect corn from corn rootworms. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 668–672.
- Yalpani, N.; Altier, D.; Barry, J.; Kassa, A.; Nowatzki, T.M.; Sethi, A.; Zhao, J.-Z.; Diehn, S.; Crane, V.; Sandahl, G.; et al. An Alcaligenes strain emulates Bacillus thuringiensis producing a binary protein that kills corn rootworm through a mechanism similar to Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3063.
- Lukoyanova, N.; Kondos, S.C.; Farabella, I.; Law, R.H.P.; Reboul, C.F.; Caradoc-Davies, T.T.; Spicer, B.A.; Kleifeld, O.; Traore, D.A.K.; Ekkel, S.M.; et al. Conformational changes during pore formation by the perforin-related protein pleurotolysin. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002049.
- Milijaš Jotić, M.; Panevska, A.; Iacovache, I.; Kostanjšek, R.; Mravinec, M.; Skočaj, M.; Zuber, B.; Pavšič, A.; Razinger, J.; Modic, Š.; et al. Dissecting out the molecular mechanism of insecticidal activity of ostreolysin A6/pleurotolysin B complexes on western corn rootworm. Toxins 2021, 13, 455.
- Kraševec, N.; Panevska, A.; Lemež, Š.; Razinger, J.; Sepčić, K.; Anderluh, G.; Podobnik, M. Lipid-Binding aegerolysin from biocontrol fungus Beauveria bassiana. Toxins 2021, 13, 820.
- Zaitseva, J.; Vaknin, D.; Krebs, C.; Doroghazi, J.; Milam, S.L.; Balasubramanian, D.; Duck, N.B.; Freigang, J. Structure–function characterization of an insecticidal protein GNIP1Aa, a member of an MACPF and β-tripod families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2897–2906.
- Tomita, T.; Noguchi, K.; Mimuro, H.; Ukaji, F.; Ito, K.; Sugawara-Tomita, N.; Hashimoto, Y. Pleurotolysin, a novel sphingomyelin-specific two-component cytolysin from the edible mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus, assembles into a transmembrane pore complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26975–26982.
- Huang, G.; Voorspoels, A.; Versloot, R.C.A.; Van Der Heide, N.J.; Carlon, E.; Willems, K.; Maglia, G. PlyAB nanopores detect single amino acid differences in folded haemoglobin from blood. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202206227.
- Berne, S.; Križaj, I.; Pohleven, F.; Turk, T.; Maček, P.; Sepčić, K. Pleurotus and Agrocybe hemolysins, new proteins hypothetically involved in fungal fruiting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1570, 153–159.
- Maličev, E.; Chowdhury, H.H.; Maček, P.; Sepčić, K. Effect of ostreolysin, an Asp-hemolysin isoform, on human chondrocytes and osteoblasts, and possible role of Asp-hemolysin in pathogenesis. Med. Mycol. 2007, 45, 123–130.
- Sepčić, K.; Berne, S.; Rebolj, K.; Batista, U.; Plemenitaš, A.; Šentjurc, M.; Maček, P. Ostreolysin, a pore-forming protein from the oyster mushroom, interacts specifically with membrane cholesterol-rich lipid domains. FEBS Lett. 2004, 575, 81–85.
- Vidic, I.; Berne, S.; Drobne, D.; Maček, P.; Frangež, R.; Turk, T.; Štrus, J.; Sepčić, K. Temporal and spatial expression of ostreolysin during development of the oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus). Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 377–382.
- Rebolj, K.; Sepčić, K. Ostreolysin, a cytolytic protein from culinary-medicinal oyster mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus (Jacq.: Fr.) P. Kumm. (Agaricomycetideae), and its potential use in medicine and biotechnology. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2008, 10, 293–302.
- Rebolj, K.; Bakrač, B.; Garvas, M.; Ota, K.; Šentjurc, M.; Potrich, C.; Coraiola, M.; Tomazzolli, R.; Serra, M.D.; Maček, P.; et al. EPR and FTIR studies reveal the importance of highly ordered sterol-enriched membrane domains for ostreolysin activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 891–902.
- Rebolj, K.; Ulrih, N.P.; Maček, P.; Sepčić, K. Steroid structural requirements for interaction of ostreolysin, a lipid-raft binding cytolysin, with lipid monolayers and bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 1662–1670.
- Chowdhury, H.H.; Rebolj, K.; Kreft, M.; Zorec, R.; Maček, P.; Sepčić, K. Lysophospholipids prevent binding of a cytolytic protein ostreolysin to cholesterol-enriched membrane domains. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1345–1356.
- Sepčić, K.; Berne, S.; Potrich, C.; Turk, T.; Maček, P.; Menestrina, G. Interaction of ostreolysin, a cytolytic protein from the edible mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus, with lipid membranes and modulation by lysophospholipids. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 1199–1210.
- Resnik, N.; Repnik, U.; Kreft, M.E.; Sepčić, K.; Maček, P.; Turk, B.; Veranič, P. Highly selective anti-cancer activity of cholesterol-interacting agents methyl-β-cyclodextrin and ostreolysin A/pleurotolysin B protein complex on urothelial cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137878.
- Bhat, H.B.; Ishitsuka, R.; Inaba, T.; Murate, M.; Abe, M.; Makino, A.; Kohyama-Koganeya, A.; Nagao, K.; Kurahashi, A.; Kishimoto, T.; et al. Evaluation of aegerolysins as novel tools to detect and visualize ceramide phosphoethanolamine, a major sphingolipid in invertebrates. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 3920–3934.
- Juntes, P.; Rebolj, K.; Sepčić, K.; Maček, P.; Cecilija Žužek, M.; Cestnik, V.; Frangež, R. Ostreolysin induces sustained contraction of porcine coronary arteries and endothelial dysfunction in middle- and large-sized vessels. Toxicon 2009, 54, 784–792.
- Rebolj, K.; Batista, U.; Sepčić, K.; Cestnik, V.; Maček, P.; Frangež, R. Ostreolysin affects rat aorta ring tension and endothelial cell viability in vitro. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1211–1213.
- Žužek, M.C.; Maček, P.; Sepčić, K.; Cestnik, V.; Frangež, R. Toxic and lethal effects of ostreolysin, a cytolytic protein from edible oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus), in rodents. Toxicon 2006, 48, 264–271.
- Berne, S.; Pohleven, J.; Vidic, I.; Rebolj, K.; Pohleven, F.; Turk, T.; Maček, P.; Sonnenberg, A.; Sepčić, K. Ostreolysin enhances fruiting initiation in the oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus). Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 1431–1436.
- Berne, S.; Sepčić, K.; Anderluh, G.; Turk, T.; Maček, P.; Poklar Ulrih, N. Effect of pH on the pore forming activity and conformational stability of ostreolysin, a lipid raft-binding protein from the edible mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 11137–11147.
- Ota, K.; Leonardi, A.; Mikelj, M.; Skočaj, M.; Wohlschlager, T.; Künzler, M.; Aebi, M.; Narat, M.; Križaj, I.; Anderluh, G.; et al. Membrane cholesterol and sphingomyelin, and ostreolysin A are obligatory for pore-formation by a MACPF/CDC-like pore-forming protein, pleurotolysin B. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1855–1864.
- Endapally, S.; Frias, D.; Grzemska, M.; Gay, A.; Tomchick, D.R.; Radhakrishnan, A. Molecular discrimination between two conformations of sphingomyelin in plasma membranes. Cell 2019, 176, 1040–1053.e17.
- Skočaj, M.; Resnik, N.; Grundner, M.; Ota, K.; Rojko, N.; Hodnik, V.; Anderluh, G.; Sobota, A.A.; Maček, P.; Veranič, P.; et al. Tracking cholesterol/sphingomyelin-rich membrane domains with the ostreolysin A-mCherry protein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92783.
- Skočaj, M.; Yu, Y.; Grundner, M.; Resnik, N.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Leonardi, A.; Križaj, I.; Guella, G.; Maček, P.; Kreft Erdani, M.; et al. Characterisation of plasmalemmal shedding of vesicles induced by the cholesterol/sphingomyelin binding protein, ostreolysin A-mCherry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 2882–2893.
- Panevska, A.; Hodnik, V.; Skočaj, M.; Novak, M.; Modic, Š.; Pavlic, I.; Podržaj, S.; Zarić, M.; Resnik, N.; Maček, P.; et al. Pore-forming protein complexes from Pleurotus mushrooms kill western corn rootworm and Colorado potato beetle through targeting membrane ceramide phosphoethanolamine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5073.
- Novak, M.; Krpan, T.; Panevska, A.; Shewell, L.K.; Day, C.J.; Jennings, M.P.; Guella, G.; Sepčić, K. Binding specificity of ostreolysin A6 towards Sf9 insect cell lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183307.
- Panevska, A.; Glavan, G.; Jemec Kokalj, A.; Kukuljan, V.; Trobec, T.; Žužek, M.C.M.C.; Vrecl, M.; Drobne, D.; Frangež, R.; Sepčić, K.; et al. Effects of bioinsecticidal aegerolysin-based cytolytic complexes on non-target organisms. Toxins 2021, 13, 457.
- Landi, N.; Grundner, M.; Ragucci, S.; Pavšič, M.; Mravinec, M.; Pedone, P.V.; Sepčić, K.; Di Maro, A. Characterization and cytotoxic activity of ribotoxin-like proteins from the edible mushroom Pleurotus eryngii. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133655.
- Balbi, T.; Trenti, F.; Panevska, A.; Bajc, G.; Guella, G.; Ciacci, C.; Canonico, B.; Canesi, L.; Sepčić, K. Ceramide aminoethylphosphonate as a new molecular target for pore-forming aegerolysin-based protein complexes. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 902706.
- Nimri, L.; Spivak, O.; Tal, D.; Schälling, D.; Peri, I.; Graeve, L.; Salame, T.M.; Yarden, O.; Hadar, Y.; Schwartz, B. A recombinant fungal compound induces anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28854–28864.
- Oren, T.; Nimri, L.; Yehuda-Shnaidman, E.; Staikin, K.; Hadar, Y.; Friedler, A.; Amartely, H.; Slutzki, M.; Di Pizio, A.; Niv, M.Y.; et al. Recombinant ostreolysin induces brown fat-like phenotype in HIB-1B cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700057.
- Nimri, L.; Staikin, K.; Peri, I.; Yehuda-Shnaidman, E.; Schwartz, B. Ostreolysin induces browning of adipocytes and ameliorates hepatic steatosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1990–2000.
- Ngai, P.H.K.; Ng, T.B.B. A hemolysin from the mushroom Pleurotus eryngii. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 1185–1191.
- Bhat, H.B.; Kishimoto, T.; Abe, M.; Makino, A.; Inaba, T.; Murate, M.; Dohmae, N.; Kurahashi, A.; Nishibori, K.; Fujimori, F.; et al. Binding of a pleurotolysin ortholog from Pleurotus eryngii to sphingomyelin and cholesterol-rich membrane domains. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2933–2943.
- Kurahashi, A.; Sato, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishibori, K.; Fujimori, F. Homologous genes, Pe.pleurotolysin A and Pe.ostreolysin, are both specifically and highly expressed in primordia and young fruiting bodies of Pleurotus eryngii. Mycoscience 2014, 55, 113–117.
- Shibata, T.; Kudou, M.; Hoshi, Y.; Kudo, A.; Nanashima, N.; Miyairi, K. Isolation and characterization of a novel two-component hemolysin, erylysin A and B, from an edible mushroom, Pleurotus eryngii. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1436–1442.
- Grundner, M.; Munjaković, H.; Tori, T.; Sepčić, K.; Gašperšič, R.; Oblak, Č.; Seme, K.; Guella, G.; Trenti, F.; Skočaj, M. Ceramide phosphoethanolamine as a possible marker of periodontal disease. Membranes 2022, 12, 655.
- Sakihara, T.; Takiguchi, N.; Uzawa, H.; Serizawa, R.; Kobayashi, T. Erylysin A inhibits cytokinesis in Escherichia coli by binding with cardiolipin. J. Biochem. 2021, 170, 369–377.
- Fernandez Espinar, M.T.; Labarere, J.; Labarère, J. Cloning and sequencing of the Aa-Pri1 gene specifically expressed during fruiting initiation in the edible mushroom Agrocybe aegerita, and analysis of the predicted amino-acid sequence. Curr. Genet. 1997, 32, 420–424.
- Pires, A.B.L.; Gramacho, K.P.; Silva, D.C.; Góes-Neto, A.; Silva, M.M.; Muniz-Sobrinho, J.S.; Porto, R.F.; Villela-Dias, C.; Brendel, M.; Cascardo, J.C.M.; et al. Early development of Moniliophthora perniciosa basidiomata and developmentally regulated genes. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 158.
- Yap, H.-Y.Y.; Fung, S.-Y.; Ng, S.-T.; Tan, C.-S.; Tan, N.-H. Genome-based proteomic analysis of Lignosus rhinocerotis (Cooke) Ryvarden sclerotium. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 23–31.
- Iwata, K.; Matsuda, A.; Wakabayashi, K.; Fununaga, N.; Fukunaga, N. Endotoxin-like substance from Aspergillus fumigatus. Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. 1962, 3, 66–73.
- Sakaguchi, O.; Shimada, H.; Yokota, K. Proceedings: Purification and characteristics of hemolytic toxin from Aspergillus fumigatus. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1975, 28, 328–331.
- Ebina, K.; Yokota, K.; Sakaguchi, O. Studies on toxin of Aspergillus fumigatus. XIV. Relationship between Asp-hemolysin and experimental infection for mice. Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. 1982, 23, 246–252.
- Ebina, K.; Sakagami, H.; Yokota, K.; Kondo, H. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding Asp-hemolysin from Aspergillus fumigatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1219, 148–150.
- Kudo, Y.; Fukuchi, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Ebina, K.; Yokota, K. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein-binding specificity of Asp-hemolysin from Aspergillus fumigatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2001, 1568, 183–188.
- Kumagai, T.; Nagata, T.; Kudo, Y.; Fukuchi, Y.; Ebina, K.; Yokota, K. Cytotoxic activity and cytokine gene induction of Asp-hemolysin to murine macrophages. Jpn. J. Med. Mycol. 1999, 40, 217–222.
- Kumagai, T.; Nagata, T.; Kudo, Y.; Fukuchi, Y.; Ebina, K.; Yokota, K. Cytotoxic activity and cytokine gene induction of Asp-hemolysin to vascular endothelial cells. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 121, 271–275.
- Wartenberg, D.; Lapp, K.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Dahse, H.-M.; Kniemeyer, O.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A. Secretome analysis of Aspergillus fumigatus reveals Asp-hemolysin as a major secreted protein. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 602–611.
- Rementeria, A.; López-Molina, N.; Ludwig, A.; Vivanco, A.B.; Bikandi, J.; Pontón, J.; Garaizar, J. Genes y moléculas implicados en la virulencia de Aspergillus fumigatus. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2005, 22, 1–23.
- Novak, M.; Čepin, U.; Hodnik, V.; Narat, M.; Jamnik, M.; Kraševec, N.; Sepčić, K.; Anderluh, G. Functional studies of aegerolysin and MACPF-like proteins in Aspergillus niger. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 112, 1253–1269.
- Kraševec, N.; Novak, M.; Barat, S.; Skočaj, M.; Sepčić, K.; Anderluh, G. Unconventional secretion of nigerolysins A from Aspergillus species. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1973.
- Nayak, A.P.; Green, B.J.; Janotka, E.; Hettick, J.M.; Friend, S.; Vesper, S.J.; Schmechel, D.; Beezhold, D.H. Monoclonal antibodies to hyphal exoantigens derived from the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus terreus. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1568–1576.
- Nayak, A.P.; Green, B.J.; Friend, S.; Beezhold, D.H. Development of monoclonal antibodies to recombinant terrelysin and characterization of expression in Aspergillus terreus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 489–499.
- Bando, H.; Hisada, H.; Ishida, H.; Hata, Y.; Katakura, Y.; Kondo, A. Isolation of a novel promoter for efficient protein expression by Aspergillus oryzae in solid-state culture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 561–569.
- Hisada, H.; Tsutsumi, H.; Ishida, H.; Hata, Y. High production of llama variable heavy-chain antibody fragment (VHH) fused to various reader proteins by Aspergillus oryzae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 761–766.
- Yamada, R.; Yoshie, T.; Wakai, S.; Asai-Nakashima, N.; Okazaki, F.; Ogino, C.; Hisada, H.; Tsutsumi, H.; Hata, Y.; Kondo, A. Aspergillus oryzae-based cell factory for direct kojic acid production from cellulose. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 71.
- Dubey, M.; Jensen, D.F.; Karlsson, M. Functional characterization of the AGL1 aegerolysin in the mycoparasitic fungus Trichoderma atroviride reveals a role in conidiation and antagonism. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2021, 296, 131–140.
- Pigott, C.R.; Ellar, D.J. Role of receptors in Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin activity. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 255–281.
- Humphreys, M.J.; Berry, C. Variants of theBacillus sphaericus binary toxins: Implications for differential toxicity of strains. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1998, 71, 184–185.
- Narva, K.E.; Wang, N.X.; Herman, R. Safety considerations derived from Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 structure and function. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 142, 27–33.
- Masson, L.; Schwab, G.; Mazza, A.; Brousseau, R.; Potvin, L.; Schwartz, J.-L. A novel Bacillus thuringiensis (PS149B1) containing a Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 binary toxin specific for the eestern corn rootworm Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte forms ion channels in lipid membranes. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 12349–12357.
- Li, H.; Olson, M.; Lin, G.; Hey, T.; Tan, S.Y.; Narva, K.E. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry34Ab1/Cry35Ab1 interactions with western corn rootworm midgut membrane binding sites. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53079.
- Wang, H.; Eyun, S.; Arora, K.; Tan, S.; Gandra, P.; Moriyama, E.; Khajuria, C.; Jurzenski, J.; Li, H.; Donahue, M.; et al. Patterns of gene expression in western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera) neonates, challenged with Cry34Ab1, Cry35Ab1 and Cry34/35Ab1, based on next-generation sequencing. Toxins 2017, 9, 124.
- Barloy, F.; Lecadet, M.M.; Delécluse, A. Cloning and sequencing of three new putative toxin genes from Clostridium bifermentans CH18. Gene 1998, 211, 293–299.
- Barloy, F.; Delécluse, A.; Nicolas, L.; Lecadet, M.M. Cloning and expression of the first anaerobic toxin gene from Clostridium bifermentans subsp. malaysia, encoding a new mosquitocidal protein with homologies to Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 3099–3105.
- Pérez Ortega, C.; Leininger, C.; Barry, J.; Poland, B.; Yalpani, N.; Altier, D.; Nelson, M.E.; Lu, A.L. Coordinated binding of a two-component insecticidal protein from Alcaligenes faecalis to western corn rootworm midgut tissue. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 183, 107597.
- Miklavič, Š.; Kogovšek, P.; Hodnik, V.; Korošec, J.; Kladnik, A.; Anderluh, G.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; Maček, P.; Butala, M.; Miklavič, S.; et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa RhlR-controlled aegerolysin RahU is a low-affinity rhamnolipid-binding protein. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv069.
- Kočar, E.; Lenarčič, T.; Hodnik, V.; Panevska, A.; Huang, Y.; Bajc, G.; Kostanjšek, R.; Naren, A.P.A.P.; Maček, P.; Anderluh, G.; et al. Crystal structure of RahU, an aegerolysin protein from the human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and its interaction with membrane ceramide phosphorylethanolamine. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6572.
- Cui, L.; Cheng, X.; Li, L.; Li, J. Identification of Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 2c virion structural proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2194–2197.
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Xian, W.-F.; Xue, J.; Wei, Y.-L.; Cheng, X.-W.; Wang, X. Complete genome sequence of a renamed isolate, Trichoplusia ni Ascovirus 6b, from the United States. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00148-18.
- Zaghloul, H.A.H.; Hice, R.; Arensburger, P.; Federici, B.A. Early in vivo transcriptome of Trichoplusia ni ascovirus core genes. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001737.
- Anderluh, G.; Kisovec, M.; Kraševec, N.; Gilbert, R.J.C. Distribution of MACPF/CDC Proteins. Subcell. Biochem. 2014, 80, 7–30.
- Schnepf, H.E.; Lee, S.; Dojillo, J.A.; Burmeister, P.; Fencil, K.; Morera, L.; Nygaard, L.; Narva, K.E.; Wolt, J.D. Characterization of Cry34/Cry35 binary insecticidal proteins from diverse Bacillus thuringiensis strain collections. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1765–1774.
- Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt toxins and their potential for insect control. Toxicon 2007, 49, 423–435.
- Alfaro, M.; Castanera, R.; Lavín, J.L.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Oguiza, J.A.; Ramírez, L.; Pisabarro, A.G. Comparative and transcriptional analysis of the predicted secretome in the lignocellulose-degrading basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4710–4726.
- Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; Barrasa, J.M.; Sánchez-García, M.; Camarero, S.; Miyauchi, S.; Serrano, A.; Linde, D.; Babiker, R.; Drula, E.; Ayuso-Fernández, I.; et al. Genomic analysis enlightens Agaricales lifestyle evolution and increasing peroxidase diversity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 1428–1446.
- Xiao, G.; Ying, S.-H.; Zheng, P.; Wang, Z.-L.; Zhang, S.; Xie, X.-Q.; Shang, Y.; St. Leger, R.J.; Zhao, G.-P.; Wang, C.; et al. Genomic perspectives on the evolution of fungal entomopathogenicity in Beauveria bassiana. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 483.
- Dang, H.X.; Pryor, B.; Peever, T.; Lawrence, C.B. The Alternaria genomes database: A comprehensive resource for a fungal genus comprised of saprophytes, plant pathogens, and allergenic species. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 239.
