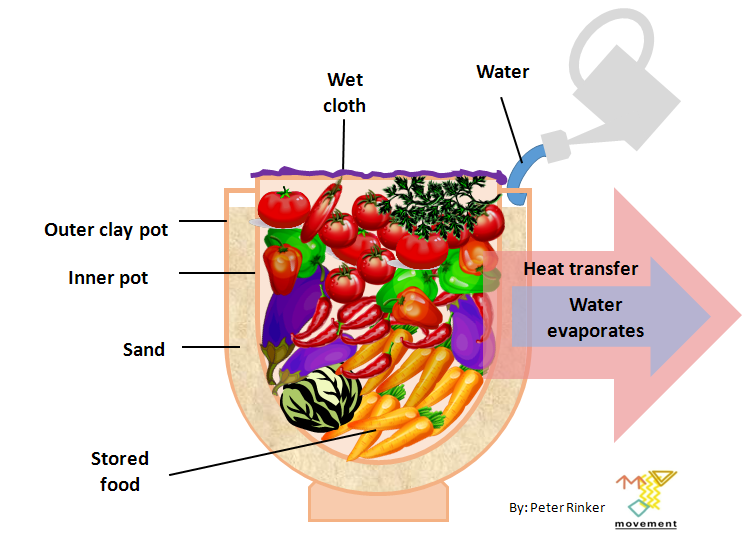
A pot-in-pot refrigerator, clay pot cooler or zeer (Arabic: زير) is an evaporative cooling refrigeration device which does not use electricity. It uses a porous outer earthenware pot (lined with wet sand) containing an inner pot (which can be glazed to prevent penetration by the liquid) within which the food is placed. The evaporation of the outer liquid draws heat from the inner pot. The device can cool any substance, and requires only a flow of relatively dry air and a source of water.
- evaporative cooling
- clay pot
- refrigeration
1. History
There is some evidence that evaporative cooling was used as early as the Old Kingdom of Egypt, around 2500 B.C. Frescos show slaves fanning water jars, which would increase air flow around the porous jars and aid evaporation, cooling the contents.[1] These jars exist even today and are called "zeer", hence the name of the pot cooler.
Many earthenware pots were discovered in Indus Valley Civilization around 3000 BC which were probably used for storing as well as cooling water similar to the present-day ghara and matki used in India and Pakistan.[2]
Despite being developed in Northern Africa, the technology appears to have been forgotten with the advent of modern electrical refrigerators. However, in the Indian Subcontinent, ghara, matka and surahi, which are different types of earthenware water pots are used to cool water.[3] In Spain, botijos are popular. A botijo is a porous clay container used to keep and to cool water; they have been in use for centuries, and are still relatively widespread. Botijos are favored most by the low Mediterranean climate; locally, the cooling effect is known as "botijo effect".[4][5]
In the 1890s gold miners in Australia developed the Coolgardie safe, based on the same principles.
In rural northern Nigeria in the 1990s Mohamed Bah Abba developed the Pot-in-Pot Preservation Cooling System, consisting of a small earthenware pot placed inside a larger one, and the space between the two filled with moist sand. The inner pot is filled with fruit, vegetables or soft drinks and covered with a wet cloth.
Abba, who hails from a family of potmakers, tapped into the large unemployed local workforce and hired skilled pot makers to mass-produce the first batch of 5,000 Pot-in-Pots.[6] He received the Rolex Award for Enterprise in 2001 and used his $75,000 award to make the invention available throughout Nigeria.[7] Abba devised an educational campaign tailored to village life and the illiterate population featuring a video-recorded play by local actors to dramatise the benefits of the desert refrigerator. The pots sell at 40 US cents a pair.[6]
After the millennium several international NGOs started to work on the dissemination of this technology in various African countries: Practical Action in Sudan and Humanity first in Gambia and Movement e.V. in Burkina Faso.[8]
Extensive research has also been done in Mali by D-Lab in partnership with World Vegetable Center. [9]
2. Construction
A zeer is constructed by placing a clay pot within a larger clay pot with wet sand in between the pots and a wet cloth on top.[10]
The device cools as the water evaporates, allowing refrigeration in hot, dry climate. It must be placed in a dry, ventilated space for the water to evaporate effectively towards the outside. Evaporative coolers tend to perform poorly or not at all in climates with high ambient humidity, since the water is not able to evaporate well under these conditions.
If there is an impermeable separation layer between the food and the porous pots, undrinkable water such as seawater can be used to drive the cooling process, without contaminating the food. This is useful in arid locations near the ocean where drinkable water is a limited commodity, and can be accomplished by using a pot that has waterproof glaze or cement [11] applied to the inner wall where the food is stored.
Extended operation is possible if the pots are able to draw water from a storage container, such as an inverted airtight jar, or if the pots are placed in a shallow pool of water. A strap can be used to tie the inner pot down instead of using sand to prevent it from floating.
Alternatives to the Pot-in-Pot construction include various versions of a simple Pot-in-Dish. For larger storage capacity, evaporative cooling chambers (ECCs) can be constructed from a double walled brick structure with a straw and wood cover. The same basic operating principles apply. Detailed information on construction materials and methods can be found in the D-Lab best practices guide. [12]
3. Operating Conditions
Several key considerations are important for determining if an evaporative cooling device will provide effective cooling and storage. ECCs and clay pot coolers provide the most benefits when they are used in low humidity climates (less than 40% relative humidity), the temperature is relatively hot (maximum daily temperature greater than 25 °C), water is available to add to the device between one and three times per day, and the device can be located in a shady and well-ventilated area. If any of these key criteria cannot be met at the time when improved vegetable storage is needed, then ECCs or clay pot coolers may not provide sufficient benefits to justify their use. [12]
4. Effectiveness
The effectiveness of evaporative cooling varies with the temperature, humidity and airflow. Given a constant flow of cool dry air, evaporative cooling can achieve temperatures as low as the wet bulb temperature, the 100% humidity condition at the given temperature. Documented tables [13]show the minimum temperature that can be achieved at different starting temperatures and percent humidities.
To determine the effectiveness of evaporative cooling chambers for specific uses it is helpful to evaluate the following questions:
What type of vegetables or other products are in need of improved storage?
ECCs or clay pot coolers provide benefits if post-harvest vegetable spoilage is the result of exposure to high temperatures, low humidity, animals, or insects. Some examples of vegetables that are particularly vulnerable to these conditions include eggplants, tomatoes, leafy greens, peppers, and okra. See the “Conclusions and Additional Resources” section of the Best Practices Guide [12] for a more complete list of vegetables that can benefit from storage in an evaporative cooling device. Non- electric evaporative cooling devices – such as ECCs and clay pot coolers – are not suitable for items that require sustained temperatures below 20 °C (medicine, meat, and dairy products) or foods that require a low humidity environment (onions, coffee, garlic, millet, and other grains).
What volume of vegetables needs to be stored at any one time?
It is necessary to estimate the volume of vegetables in need of improved storage at any given time to determine the appropriate size of the evaporative cooling device. If the vegetables can fit into a clay pot with a capacity of 150 liters or less, then a clay pot cooler is most appropriate. Individuals or groups that need to store larger amounts of vegetables can consider an ECC. A brick ECC can be designed to accommodate the storage volumes between roughly 500 and 5,000 liters, see the “Construction of Evaporative Cooling Chambers” section of the Best Practices Guide. [12]
How often is improved vegetable storage needed?
Variations in the need for improved vegetable storage can arise due to seasonal growing and harvest cycles, vegetable production surpluses relative to local demand, and climate variations. It is important to determine if proper operating conditions exist for evaporative cooling to effectively provide benefits during the time when vegetable storage is needed, and if the need for improved vegetable storage is frequent enough that the value an ECC or clay pot cooler can provide is greater than its cost.
5. Impact
Pot-in-pot refrigeration has had multiple positive impacts on the population that uses them beyond the simple ability to keep food fresh for longer periods of time and decreasing instances of food-related disease.[10]
- Increased profits from food sales: As there is no rush to sell food to avoid spoilage, farmers are able to sell their produce on demand and can command higher prices.
- Increased opportunities for women: Women can sell food directly from their homes, decreasing their dependence on their husbands as sole providers. Also, because girls traditionally take food to market to sell, and because food in the zeer stays fresh long enough that they can go to market once a week rather than once a day, there is more time for them to attend school.
- Rural employment opportunities: Farmers are able to support themselves with their increased profits at market, slowing the move into cities. Also, the creation of the pots themselves generates job opportunities.
- Increased diet variety because food is available for longer into the year.
- The ability to store vaccines and medicines that would otherwise be unavailable in areas without refrigeration facilities.[14]
A zeer costs about 150 naira (approximately US$1.00 in 2011) to make in Nigeria, and they sell for 180-200 naira (US$1.20 to US$1.30 in 2011).
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Pot-in-pot_refrigerator
References
- Evans, Lisa. "The Advent of Mechanical Refrigeration Alters Daily Life and National Economies Throughout the World".
- George F. Dales, Jonathan M. Kenoyer, Leslie Alcock. Excavations at Mohenjo Daro, Pakistan: the pottery
- prkhitman (2009-06-27). "Cold water in rural India : matka(earthen ware) |". fuel efficiency.org. http://www.fuelefficiency.org/?q=node/132. Retrieved 2012-02-09.
- "The Origin of the Botijo". Universidad de Valladolid. http://www.urcomante.uva.es/Urcopedia/Ing-Botijo.php. Retrieved 2012-02-09.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 April 2016. https://web.archive.org/web/20160406053141/http://www.museucantir.org/documents/8_Guide_english.pdf. Retrieved 2016-08-21.
- Soin, Kanwaljit. "The Art of Pottery in Nigeria". UWEC. http://www.uwec.edu/geography/ivogeler/w111/articles/pots.htm. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- Anon (2001). "Best inventions of 2001: Food Cooling System". Time: Lists. Time. http://content.time.com/time/specials/packages/article/0,28804,1936165_1936254_1936632,00.html. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- Rinker, Peter (2014-04-15). The clay pot cooler – an appropriate cooling technology. Movement e.V.. p. 2. https://movement-verein.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/informationen_projekte_clay_pot_cooler_2014_en.pdf. Retrieved 2016-12-26.
- Eric Verploegen, Ousmane Sanogo, Takemore Chagomoka. Evaporative Cooling Technologies for Improved Vegetable Storage in Mali. http://d-lab.mit.edu/sites/default/files/Evaporative%20Cooling%20Technologies%20for%20Improved%20Vegetable%20Storage%20in%20Mali%20-%20Appendix.pdf.
- "How a zeer pot fridge makes food last longer". Practical Action website. http://practicalaction.org/zeer-pot-fridge. Retrieved 2010-12-24.
- "The clay pot cooler – an appropriate cooling technology". Peter Rinker / Movement website. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. https://web.archive.org/web/20140714185554/http://www.movement-verein.org/downloads/Movement_Clay-pot-cooler_english.pdf. Retrieved 2014-06-17.
- Eric Verploegen, Peter Rinker, Kukom Edoh Ognakossan. Evaporative Cooling Best Practices, Producing and using evaporative cooling chambers and clay pot coolers. http://d-lab.mit.edu/sites/default/files/Evaporative%20Cooling%20Best%20Practices%20Guide.pdf.
- http://rebuildingcivilization.com/content/build-evaporative-refrigerator-no-moving-parts-no-electricity
- Abraham, Martin A. A. "The Twelve Principles of Green Engineering". Sustainability Science and Engineering: Defining Principles (Google ebook ed.). Elsevier. pp. 30, 31. https://books.google.com/books?id=YgSD_2QpGKoC&pg=PA30&lpg=PA30&dq=earthenware+cooling+device&source=bl&ots=60zoRXu2Of&sig=l6qZTwkGeyqZzIWaU8SmPX58Pc4&hl=en&sa=X&ei=e1vHUoLwM4GrhQfvnoCgCQ&ved=0CEsQ6AEwATgK#v=onepage&q=earthenware%20cooling%20device&f=false. Retrieved 4 January 2014.