Ras Al Khaimah (RAK) (Arabic: رَأْس ٱلْخَيْمَة; IPA: [raʔs lˈxajma]), also spelled as Ras al Khaimah or Ras al-Khaimah, is one of the seven emirates that make up the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The city of Ras Al Khaimah, sometimes simply abbreviated to RAK City, is the capital of the emirate and home to most of the emirate's residents. It is linked to the medieval trading port of Julfar.[lower-alpha 1] Its name in English means "top of the tent". The emirate borders Oman's exclave of Musandam, and occupies part of the same peninsula. It covers an area of 2,486 km2 (960 sq mi) and has 64 km (40 mi) of beach coastline. As of 2015, the emirate had a population of about 345,000, of which about 31% were Emirati citizens. RAK city has two main areas - the Old Town and Nakheel - on either side of a creek that is home to mangroves and is framed by the North-Western Hajar Mountains. The emirate also consists of several villages and new gated residential developments, such as Al Hamra Village and Mina Al Arab. The emirate is served by Ras Al Khaimah International Airport. Its geography consists of a northern part (where Ras Al Khaimah City and most towns are situated) and a large southerly inland exclave (near the Dubai exclave of Hatta), and a few small islands in the Persian Gulf. Ras Al Khaimah has the most fertile soil in the country, due to a larger share of rainfall and underground water streams from the Hajar.
- small islands
- al-khaimah
- nakheel
1. History
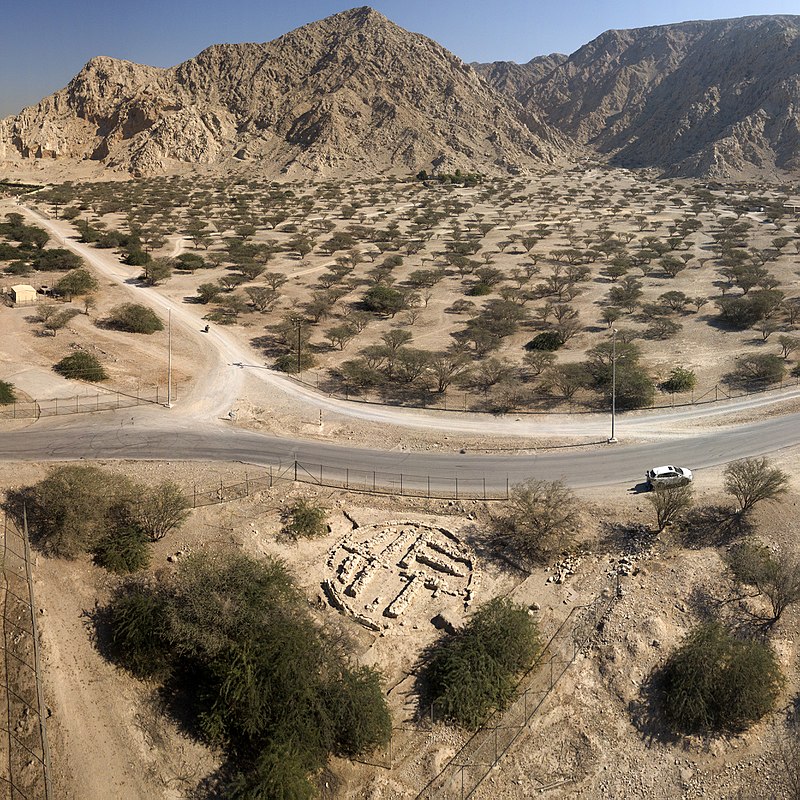 A tomb from the Umm al-Nar culture in Ras Al Khaimah. By Sahil.latheef - Self-photographed, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=68438314
A tomb from the Umm al-Nar culture in Ras Al Khaimah. By Sahil.latheef - Self-photographed, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=68438314Ras Al Khaimah has been the site of continuous human habitation for 7,000 years, one of the few places in the country[1] and the world where this is the case,[2] and there are many historical and archaeological sites throughout the emirate - local sources cite 1,000[3] - dating from different time periods, including remnants of the Umm Al Nar Culture (3rd millennium BC).[4] The area of Shimal contains both Umm Al Nar and Wadi Suq burials and a number of notable finds, including one grave that contained no fewer than 18 fine bronze arrowheads.
1.1. Pirate Coast
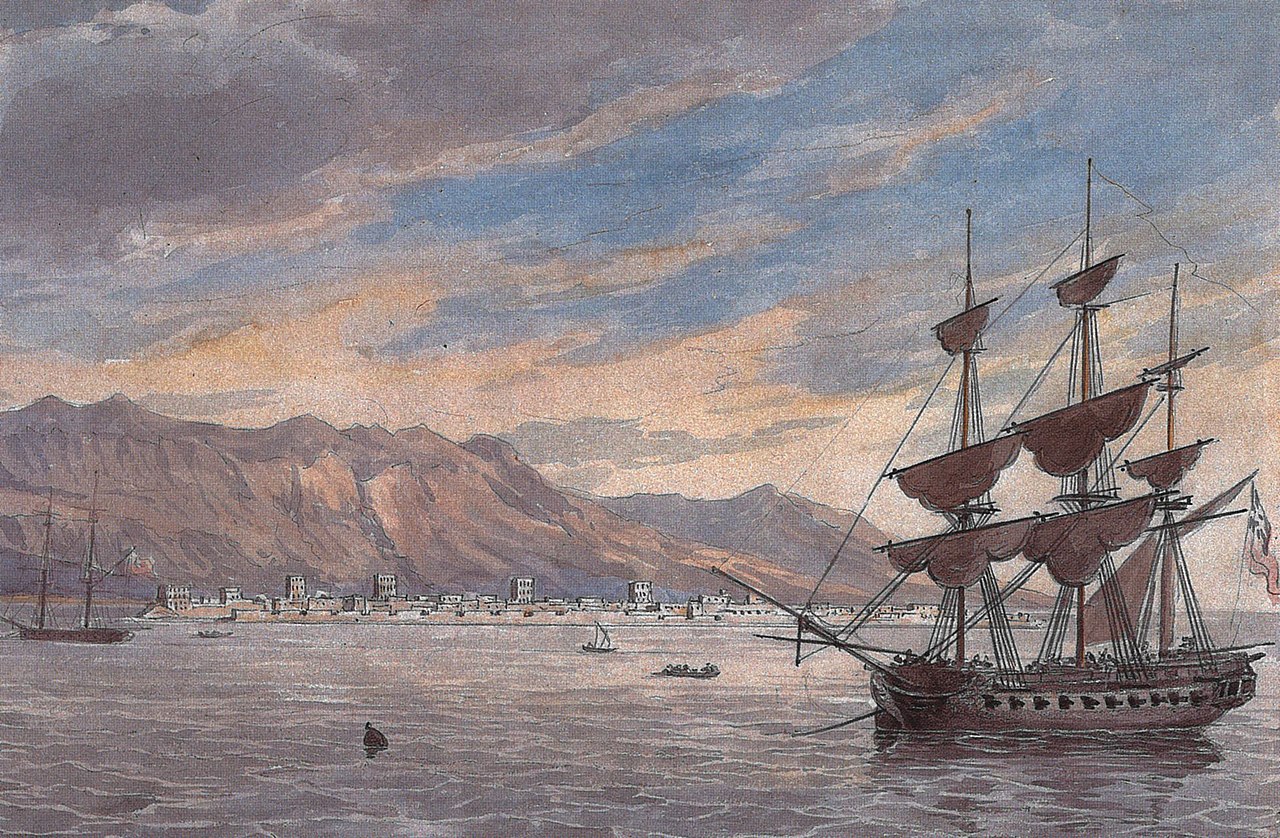 A painting depicting the British Expeditionary Force of 1809 off the coast of Ras Al Khaimah in 1809. By Charles Hamilton - The Myth of Arab Piracy in the Gulf, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=73438474
A painting depicting the British Expeditionary Force of 1809 off the coast of Ras Al Khaimah in 1809. By Charles Hamilton - The Myth of Arab Piracy in the Gulf, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=73438474There is considerable debate locally regarding the 18th-century charge of maritime piracy, attracting the United Kingdom label 'The Pirate Coast' to the Eastern Gulf. Local interpretations of the dispute with the British were that the British became increasingly aggressive in protecting their trade but this resulted in interference in locals' livelihoods, so they naturally took exception to it.[5] However, in the early 18th century, the Al Qasimi dynasty established itself in Ras Al Khaimah and Sharjah on the Arabian Peninsula, growing to become a significant maritime force with holdings on both the Persian and Arabian coasts that frequently came into conflict with British flagged shipping.
It was the Al Qasimi links to Persia that drew them to the attention of Ahmed bin Said, the Ruler of Muscat, who had wrested control of the coast and interior of Oman back from the Persian forces who had taken it under Nadir Shah and Mirza Taki Khan, the governor of Shiraz. Ahmed bin Said threw 12,000 men under the command of Kandhala bin Saif Al Suwaidi in an attack on Ras Al Khaimah which was met at Buraimi by 14,000 men of the Al Qasimi and Na'im. They were defeated, leading the garrison at Khor Fakkan, besieged by Ahmed bin Said, to surrender. He went on to take Khasab and then blockaded Ras Al Khaimah, Rams, Jazirat Al Hamra, Fasht and Sharjah. This led to all but Ras Al Khaimah suing for peace in 1763. The Sheikhs of Ras Al Khaimah submitted in 1771, but in 1775 revolted and re-took the towns on the West and East coast, consolidating their gains under the weak rule of Sultan bin Ahmed bin Saeed.[6] This longstanding war between the Al Qasimi and Muscat pitted them naturally against Muscat's ally – Britain.
In the aftermath of a series of attacks in 1808 off the coast of Sindh involving 50 Qasimi raiders and following the 1809 monsoon season, the British authorities in India decided to make a significant show of force against the Al Qasimi, in an effort not only to destroy their larger bases and as many ships as could be found, but also to counteract French encouragement of them from their embassies in Persia and Oman.[7] The British mounted the Persian Gulf campaign of 1809, in which the Al Qasimi fleet was largely destroyed. The British operation continued to Linga on the Persian coast which was, like the Greater and Lesser Tunbs islands, administered by the Al Qasimi.
By the morning of 14 November, the military expedition was over and the British forces returned to their ships, having suffered light casualties of five killed and 34 wounded. Arab losses are unknown, but were probably significant, while the damage done to the Al Qasimi fleets was severe: a significant portion of their vessels had been destroyed.[8]
1819 campaign
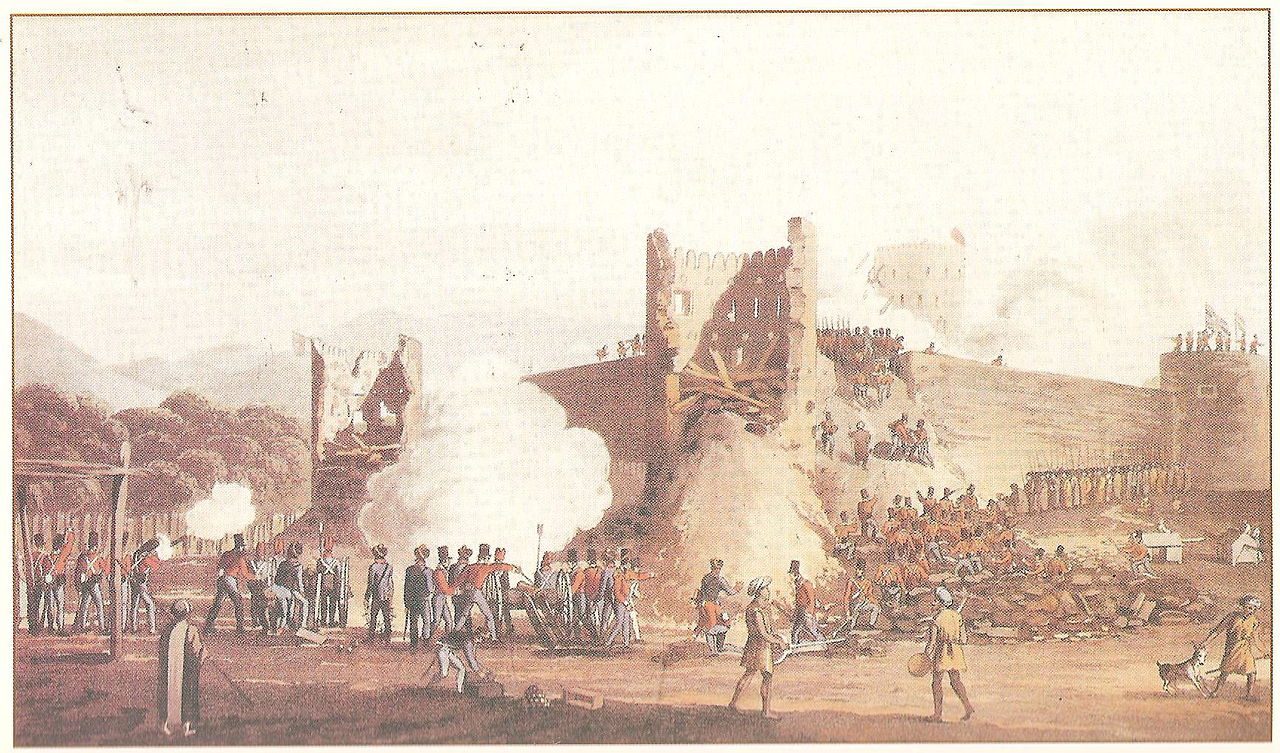 Ras Al Khaimah under attack by the British Expeditionary force of 1819 in December 1819. By رسام بريطاني توفي منذ أكثر من 100 عام - كتاب الصراع بين القواسم و الأنجليز في الخليج العربي (1800-1820) صفحة 88, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3771946
Ras Al Khaimah under attack by the British Expeditionary force of 1819 in December 1819. By رسام بريطاني توفي منذ أكثر من 100 عام - كتاب الصراع بين القواسم و الأنجليز في الخليج العربي (1800-1820) صفحة 88, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3771946With the 1809 campaign concluded without significant treaty concessions, an 1815 arrangement was made between the British and the Al Qasimi.[9] By 1819, it was clear the arrangement had broken down and so in November of that year, the British embarked on a second expedition against the Al Qasimi, led by Major-General William Keir Grant, voyaging to Ras Al Khaimah with a platoon of 3,000 soldiers. The British extended an offer to Said bin Sultan of Muscat in which he would be made the ruler of the Pirate Coast if he agreed to assist the British in their expedition. Obligingly, he sent a force of 600 men and two ships.[10][11]
The force gathered off the coast of Ras Al Khaimah on 25 and 26 November and, on 2 and 3 December, troops were landed south of the town and set up batteries of guns and mortars and, on 5 December, the town was bombarded from both land and sea. Continued bombardment took place over the following four days until, on the 9th, fortress and town of Ras Al Khaimah were stormed and found to be practically deserted. On the fall of Ras Al Khaimah, three cruisers were sent to blockade Rams to the North and this, too was found to be deserted and its inhabitants retired to the 'impregnable' hill-top fort of Dhayah.[12]
The British landed a force at Rams on 18 December, which fought its way inland through date plantations to the hilltop fort of Dhayah on the 19th. There, 398 men and another 400 women and children held out, without sanitation, water or effective cover from the sun, for three days under heavy fire from mortars and 12-pound cannon.
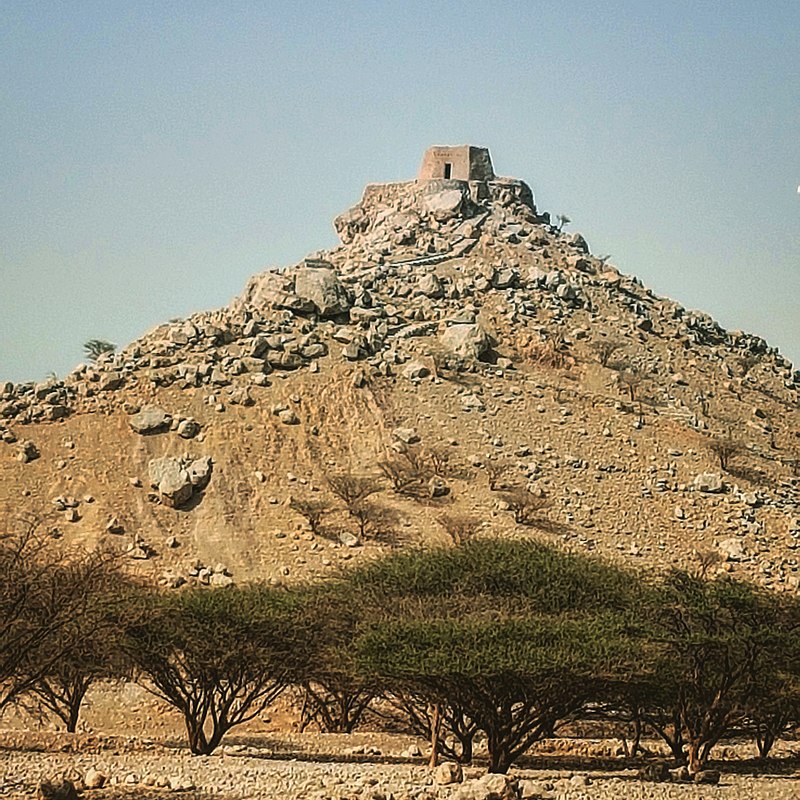 The hilltop fort of Dhayah. By Alexandermcnabb - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=73285828
The hilltop fort of Dhayah. By Alexandermcnabb - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=73285828The two 24-pound cannon from HMS Liverpool which had been used to bombard Ras Al Khaimah from the landward side were once again pressed into use and dragged across the plain from Rams, a journey of some four miles. Each of the guns weighed over 2 tonnes. After enduring two hours of sustained fire from the big guns, which breached the fort's walls, the last of the Al Qasimi surrendered at 10.30 on the morning of 22 December.[13]
1820 treaty
In January 1820, the British imposed the General Maritime Treaty of 1820 signed by Sheikh Sultan Bin Saqr Al Qasimi of Sharjah who was reinstated by the British in Ras Al Khaimah after the deposition of Hasan Bin Rahma Al Qasimi.[14] The treaty stipulated the end of piracy and slavery, and laid the foundation for the British protectorate over the Trucial States that lasted until December 1971. In 1869, Ras Al Khaimah became fully independent from neighbouring Sharjah. However, from September 1900 to 7 July 1921, it was re-incorporated into Sharjah; the last governor became its next independent ruler.
1.2. Annexation to the United Arab Emirates
On 10 February 1972,[15] Ras Al Khaimah, under the leadership of Sheikh Saqr bin Mohammad al-Qasimi, joined the United Arab Emirates.
1.3. Modern History
A partnership formed in 2020 between Ras Al Khaimah's Antiquities and Museums Department and two U.S. universities - University of South Alabama and Quinnipiac University in Connecticut - has led to 4,000-year-old human remains found in Shimal being studied for the first time.[16]
Wadi Suq era graves found at Seih Al Harf in the Emirate in October 2012 briefly held up the construction of the northern spur of the arterial E611 road.[17]
Ras Al Khaimah is linked with the medieval port and city of Julfar[18][19] and it overtook Julfar as the commercial center of the area in the late 16th century. Ras Al Khaimah was an independent settlement but it eventually grew to encapsulate the area known as Julfar.[20] By the end of the 16th century, Italian sources mention Ras Al Khaimah for the first time, after which the name Julfar fell out of usage.[21]
Archaeological evidence has demonstrated that the settlement known as Julfar shifted location over time as harbour channels silted up. Excavations of a sizable tell, which revealed remnants of a Sassanid era fortification, indicate that early Julfar was located in the north of the present city of Ras Al Khaimah,[22] not far from other sites of historical and archaeological interest such as the Pre-Islamic fort, 'Sheba's Palace' (Shimal Fort).
Hafit {Tuwwam} abounds in palm trees; it lies in the direction of Hajar {Al Hasa}, and the mosque is in the markets ... Dibba and Julfar, both in the direction of the Hajar, are close to the sea ...—Al-Muqaddasi, 985 CE.[19]
Like Dibba and the region of Tawam (which includes the modern city of Al Ain), this region witnessed events relevant to the history of Islam during the Umayyad and Abbasid eras.[19][22]
One of Ras Al Khaimah's most celebrated sons, Ibn Majid, was a seaman and navigator.
2. List of Rulers
Its rulers were:
- 1708–1731: Sheikh Rahma Al Qasimi
- 1731–1747: Sheikh Matar bin Butti Al Qasimi
- 1747–1777: Sheikh Rashid bin Matar Al Qasimi[23]
- 1777–1803: Sheikh Saqr bin Rashid Al Qasimi
- 1803–1809: Sheikh Sultan Bin Saqr Al Qasimi (1st time)[24]
- 1809–1814: Sheikh Hasan bin Ali Al Anezi
- 1814–1820: Sheikh Hassan bin Rahma Al Qasimi. In 1820 removed as ruler of RAK by British, recognised as Sheikh of Khatt and Falna. Signed General Maritime Treaty of 1820.
- 1820–1866: Sheikh Sultan Bin Saqr Al Qasimi (2nd time). In 1820 shifted capital to Sharjah.
- 1866 – 1868: Sheikh Khalid bin Sultan Al Qasimi (died 1868). Ruler of RAK.
- 14 April 1868 – 1869: Sheikh Salim bin Sultan Al Qasimi (18??–1919). Ruler of Sharjah and RAK.
- 1869 – August 1900: Sheikh Humaid bin Abdullah Al Qasimi (died 1900). Ruler of RAK.
- 1900 – 1914: Sheikh Saqr bin Khalid Al Qasimi
- 1914 –1921: Sheikh Khalid bin Ahmad Al Qasimi
- 10 July 1921 – Feb 1948: Sheikh Sultan bin Salim Al Qasimi
- 17 July 1948 – 27 October 2010: Sheikh Saqr bin Mohammed Al Qasimi (1918–2010)
- 27 October 2010 – current: Sheikh Saud bin Saqr Al Qasimi[25]
- The appointed heir presumptive is currently Mohammed bin Saud Al Qasimi, son of the current Ruler of the Emirate.
3. Population
 Sunset off the coast of Ras Al Khaimah beach. By Alexandermcnabb - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=73285828
Sunset off the coast of Ras Al Khaimah beach. By Alexandermcnabb - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=73285828In 1975, the total population of Ras Al Khaimah was 43,845 of which 29,613 were nationals and 14,232 were foreigners. This figure increased to 73,918 (39,148 locals; 34,770 foreigners) in 1980, 96,578 in 1985, 143,334 in 1995, and 210,063 in 2005. The total population, as of 2015, was estimated to be about 345,000 people, both Emiratis and expatriates.[26]
4. Towns and Settlements
Important towns, settlements and areas include:
- RAK City – The emirate's largest city and capital
- Al Jazirah Al Hamra – an old coastal town that is home to the Al Hamra Village development and an industrial zone
- Rams – a coastal town; in the past, a typical fishing and pearl-diving community
- Khor Khwair – an industrial zone, with the largest bulk-handling port in the Middle East[27][28]and numerous companies such as a cement factory
- Diqdaqah – a village known for agriculture activities
- Khatt – a village surrounded by mountains, famous for its thermal springs and palm gardens
- Masafi – a town in the south, on the border with Fujairah; well known for being a major supplier of bottled drinking water
- Huwaylat – a central village in the south
5. Landmarks
 Jebel Jais. By Ujjay Jayashankar - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=67949033
Jebel Jais. By Ujjay Jayashankar - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=67949033Notable landmarks in Ras Al Khaimah include:
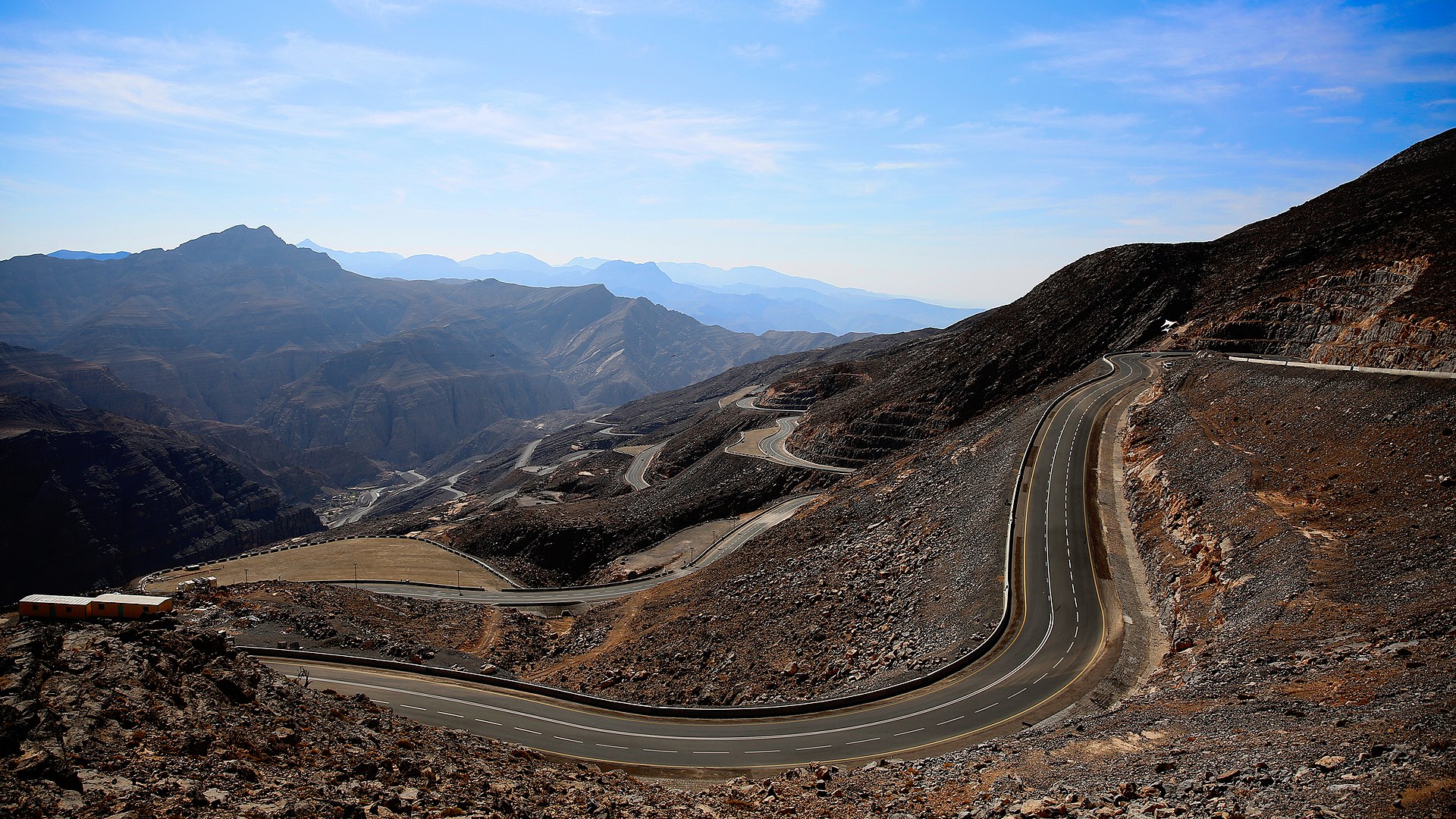 Jebel Jais is the highest mountain peak in the United Arab Emirates. By Stevenmccombe at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=74677804
Jebel Jais is the highest mountain peak in the United Arab Emirates. By Stevenmccombe at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=74677804- The National Museum of Ras Al Khaimah: housed in the former palace of the ruling Al Qasimi family, with exhibits on natural history, arts and crafts of previous centuries, and archaeology
- Dhayah Fort: the highest hilltop fort in the UAE and the last outpost of resistance to the British in 1819[29]
- Sheba's Palace: ruins of a medieval palace
- Al Falayah Fort: the former summer residence of the ruling Al Qasimi family
- Al Jazirah Al Hamra: an abandoned "ghost town" showing the preserved architecture of a 20th-century pearling port[30]
- The Old City and Souq: both traditional and modern shops as well as artisans' workshops
- Waldorf Astoria - Ras Al Khaimah
- Bu Shaqq tower
Dunes and landforms
- Jabal Jais, on the city's outskirts, is the highest peak in the UAE, at 1,934m, and is home to the world's longest zipline.[31]
6. Climate
Ras Al Khaimah's desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh) is hot and arid with very hot summers and mild winters. The average temperature is 12 to 25 °C (54 to 77 °F) in January and 29 to 43 °C (84 to 109 °F) in July. However, temperatures often reach 45 °C in the summer; the highest recorded temperature is 48.8 °C (119.8 °F). The humidity is usually high in the summer months. Rains and thunderstorms occur rarely, and only in winter. Snow has been reported in December 2004, January 2009 and February 2017[32] in the high mountains of Ras Al Khaimah. Temperatures as low as −5 °C (23 °F) have been measured at the peak of Jebel Jais, the highest mountain in the UAE.[33]
7. Economy
7.1. Main Economic Sectors
As one of the emirates that has never discovered oil, Ras Al Khaimah has focused on diversifying its economy and has had real success with its thriving industrial sector. It has one of the most diverse economies in the Gulf Cooperation Council region, with no one area exceeding more than 20% of total GDP.[34] The main economic sectors are the following:
- Real Estate – numerous residential areas, offices, commercial buildings have been built in Ras Al Khaimah and several major developments are ongoing. Major multi-purpose developments include Al Hamra Village and Mina Al Arab.
- Tourism – Ras Al Khaimah is a fast-growing tourist destination, with a focus on sun and sand vacations and also adventure tourism due to its mountains, which feature the longest zipline in the world, Jebel Jais Flight, and Jais Adventure Peak, a collection of adventure attractions such as Jais Sky Tour, Jebel Jais Viewing Deck Park and Jais Adventure Centre, which opened in February 2020.[35][36] It is home to five-star hotels and beach resorts including the Waldorf Astoria Ras Al Khaimah, the Ritz-Carlton Al Wadi and Beach resorts, the Cove Rotana and several Hilton hotels. In addition, it has a number of 4 and 3-star accommodation. In the pipeline is an Anantara resort, an InterContinental, a Marriott, Movenpick, a Rove hotel, an Avani resort and many more.[37][38] 2018 saw Ras Al Khaimah host the Arabian Hotel Investment Conference, the first time it had been hosted outside Dubai, and the event returned in 2019 to the newly built Al Hamra International Exhibition & Conference Centre.[39][40]
- Building materials – Ras Al Khaimah opened the UAE's first cement company in the early 1970s and is now the UAE's largest producer of cement. In the 1980s, the emirate formed Ras Al Khaimah Ceramics, which has become one of the world's largest ceramics producers. It is also home to Stevin Rock and RAK Rock, sister rock quarrying companies that collectively are among the largest quarrying companies in the world, providing 80 million tons of limestone to the construction sector annually.[41]
- Manufacturing and High-Tech Industry – In the 1980s, the emirate formed Julphar, the Persian Gulf region's first pharmaceuticals company. Julphar is now one of the Middle East and Africa's largest pharmaceutical manufacturers, producing more than a million boxes of medicine each day.[42] Ras Al Khaimah also became the first place in the Persian Gulf region to produce vehicles from a global manufacturer when Ashok Leyland started production in 2010. The Indian company now produces 12,400 vehicles a year from its base in the emirate.[43] Falcon Technologies International (FTI)[44] represents the high-tech industry and produces optical storage media (CDR, DVDR, BDR). In 2012, Innovative Composite Engineering was established in the Industrial Free-zone to manufacture high-end composite products (aerospace, construction parts).[45]
- Service sector – growing sector with RAKBANK, the UAE's No.1 small business bank[46], and RAK Insurance companies. In February 2020, RAKBANK posted profits of AED1,095.3 million for 2019, up 19.4% on the previous year, with total assets of AED57.1 billion.[47] RAK Economic Zone, the emirate's free zone and business set-up specialists, is home to more than 15,000 businesses from 100 countries operating in 50 sectors.[48]
- Agriculture and Fisheries – in the past, these were the main economic sectors of Ras Al Khaimah. Nowadays they are still significant, providing foodstuffs not only for the emirate but for the whole UAE.
7.2. Taxation and Companies Law
Taxation is legislated for by the UAE Federal Authorities and implemented across the seven Emirates of the UAE by the Federal Tax Authorities. In general, no income or wealth taxes are payable by individuals nor is corporation tax charged. In addition, there are no exchange controls or withholding taxes. However, a sales tax at 5% (VAT) was imposed in 2018 and import taxes apply in certain circumstances.[49]
Whilst a local partner or sponsor is typically required to do business, companies may be owned 100% by foreign investors in one of the many Free Trade Zones in Ras Al Khaimah which include Ras Al Khaimah Economic Zone, RAK Maritime City Free Trade Zone, RAK International Corporate Centre.[50] These zones provide trade and access to the Middle East, and wider markets in a variety of sectors including manufacturing and industry, education, consultancy and professional services, technology and aviation. Employment visas are available for these companies and, when approved, this type of company can own property. International, or "offshore" free zone companies are also available to be used for numerous business purposes, ranging from owning overseas financial and real estate assets, inheritance planning, setting up holding companies and special purpose vehicles and ship registration.[51]
8. Culture
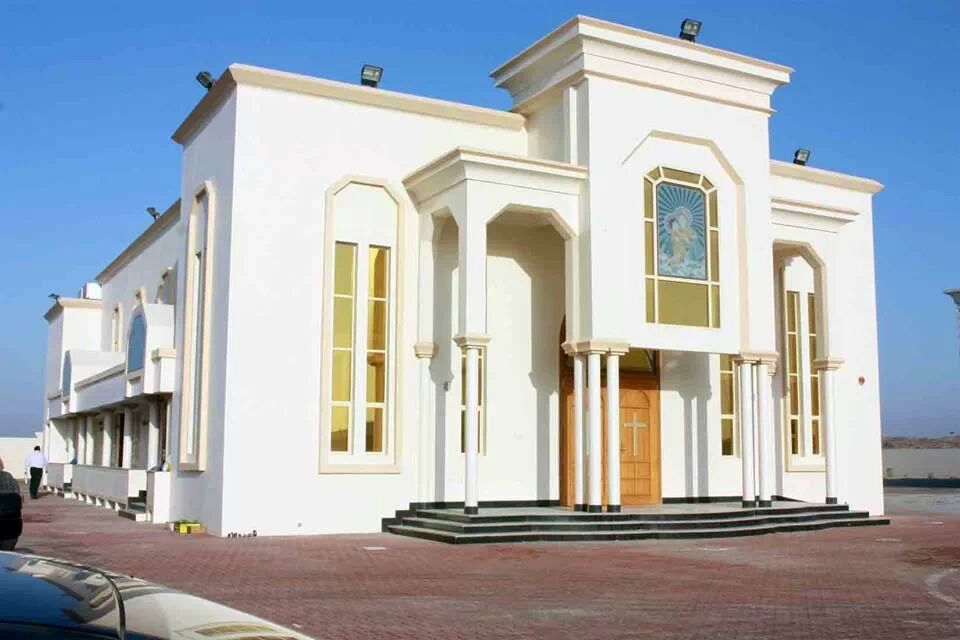
 Sheikh Zayed Mosque and St Mary's Orthodox Church. By Fadi Fayad Al Taoba, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=53139530. By Josephvarghese2005 - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=50412384
Sheikh Zayed Mosque and St Mary's Orthodox Church. By Fadi Fayad Al Taoba, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=53139530. By Josephvarghese2005 - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=50412384The UAE culture mainly revolves around the religion of Islam and traditional Arab culture. The influence of Islamic and Arab culture on its architecture, music, attire, cuisine and lifestyle are very prominent as well. Five times every day, Muslims are called to prayer from the minarets of mosques which are scattered around the country. Since 2006, the weekend has been Friday-Saturday, as a compromise between Friday's holiness to Muslims and the Western weekend of Saturday-Sunday.[52] A great majority of the population are non national citizens, coming from India, Pakistan, and a wide range of nations.
8.1. Community
The majority of mosques are Hanbali, Muwahhid Muslim or Salafi
8.2. Events
The annual Ras Al Khaimah Half Marathon, first held in 2007, resulted in a world record from Samuel Wanjiru in 2007 and the second fastest run of all time from Patrick Makau Musyoki in 2009.[53] Kenya's 19-year-old Stephen Kiprop won the 2019 edition of the half marathon in a course record-equaling 58 minutes and 42 seconds, the fastest time ever recorded by a teenager.[54]
In the 2020 iteration, Ethiopia's Ababel Yeshaneh broke the women's half marathon world record by 20 seconds with a time of 1:04:31, eclipsing the previous record of 1:04:51 set by Kenyan Joyciline Jepkosgei in Valencia in 2017.[55]
The UAE Awafi Festival is an annual cultural and heritage festival held in the Ras Al Khaimah desert. It is a three-week event, held in December or January, one attraction being a sand dune race. There is a heritage village with traditional food and dance, as well as shops for food and souvenirs.
The Terry Fox Run RAK is a yearly charity run organized in Ras Al Khaimah to support cancer research in the UAE.[56] The first event was organized in 2010 (short movie from 1st RAKTFR event). Participation in this event has grown from hundreds to thousands since its inception, averaging about 5,000 participants in recent years.
Ras Al Khaimah Fine Arts Festival is an annual event that has taken place since 2013, organised by the Al Qasimi Foundation for Policy Research.[57] It started with just 26 artists but by 2018 that number had grown to 84. The not-for-profit festival takes place every February-March and since 2019 has taken place at the redeveloped Al Jazirah Al Hamra Heritage Village.[58][59]
Each year, a number of events are lined up in Ras Al Khaimah to mark the United Arab Emirates' National Day, usually involving an air show by the Fursan Al Emarat aerobatics team and a free concert featuring some of the best singers in the Arab world.[60]
In 2018, Ras Al Khaimah became the new host for the season-ending tournament on the Challenge Tour, the second tier of European Tour golf. The "Road to Ras Al Khaimah" ends with the Ras Al Khaimah Challenge Tour Grand Final played at Al Hamra Golf Course.[61]
9. Infrastructure
Transportation
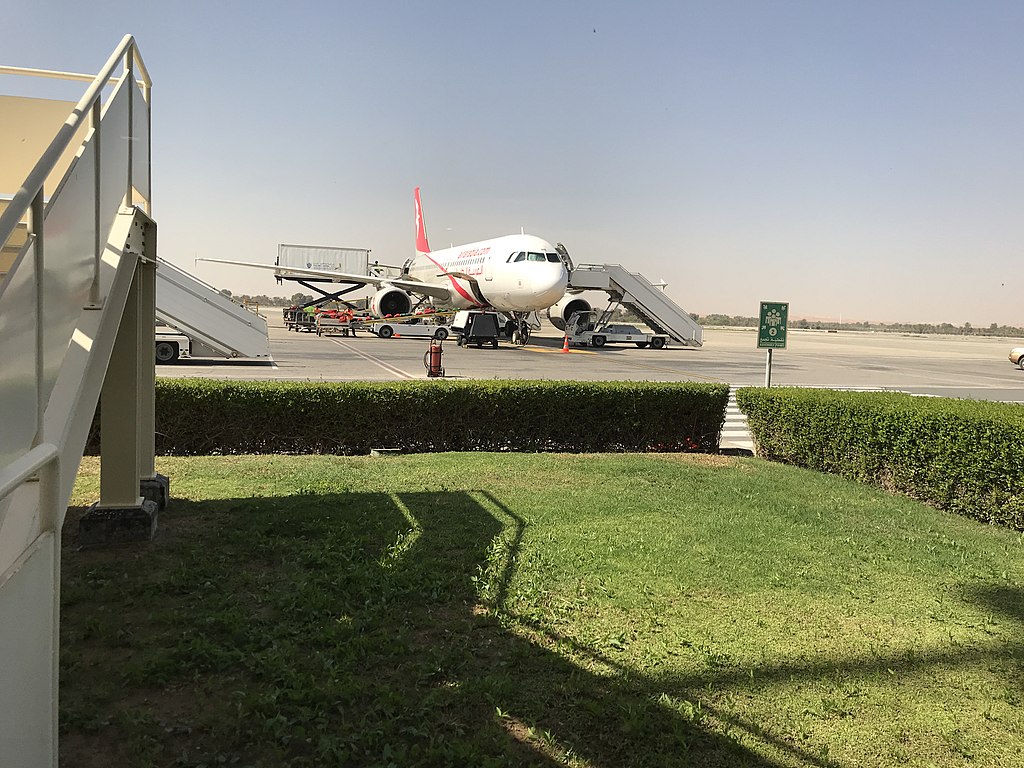 Ras Al Khaimah International Airport. By Hamza Izourane - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=67759550
Ras Al Khaimah International Airport. By Hamza Izourane - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=67759550Within Ras Al Khaimah city, the main mode of public transport are metered taxis, with public buses operating on long-haul routes and catering mainly to smaller towns (e.g. Sha`am, Rams, and Al Jazirah Al Hamra). A local bus service operated by RAK Transport Authority provides infrequent connections between Nakheel, Al Hamra and the airport.[62] In November 2019, RAK Transport Authority launched its five-year strategy for 2020–2025, part of which involved making its entire fleet of cars eco-friendly. At the time, 60% of its fleet of 850 taxis were already hybrid.[63][64]
Ras Al Khaimah is connected to the other emirates by taxis and buses which embark from the Bus station located at RAK Transport Authority Headquarters near the new Ras Al Khaimah Police Headquarters and opposite the Cove Rotana hotel.
The main highways linking Ras Al Khaimah with other emirates is Mohammed bin Zayed Road (E311) and Emirates Road (E611), both of which travel from Ras Al Khaimah through Umm Al Quwain, Ajman and Sharjah and onto Dubai and Abu Dhabi. These highways allow for journeys from Ras Al Khaimah to Dubai in under 45 minutes.
Dual carriageways connect major areas within the emirate, with one following the coast and another running inland towards the airport in the direction of Khatt, Masafi, Fujairah, Dhaid, and eventually Oman.
In July 2018, the first phase of the Ras Al Khaimah Ring Road opened, connecting the industrial areas of the mountainous north with the E311 to the south. The road has decreased the volume of industrial traffic through RAK City.[65] In spring 2013 work on the 32-kilometre (20 mi) RAK Ring Road was held up by a three-month rescue excavation after the discovery of megalithic tombs dating to the Wadi Suq period, from 2000 to 1600 BC.[66]
Saqr Port, located in the industrial area of Khor Khwair, is the emirate's main port, providing bulk and container services. It is the largest bulk-handling port in the Middle East.[67] It has eight deep-water berths, each 200 m (660 ft) long, is dredged to 12.2 m (40 ft) and has two "ro-ro" ramps plus specialised berths for handling bulk cement and aggregate. Other services include ship-handling, crew changes, and 40,000 m2 (430,000 sq ft) of covered storage, together with a vast open storage area. It is also the closest port in the UAE to Bandar Abbas, Iran, but there is no shipping from Saqr port to Bandar Abbas[clarification needed].
Ras Al Khaimah International Airport (RKT) offers cargo and passenger services to a variety of destinations covering the Middle East, North & East Africa, Central Asia, the Indian Subcontinent and Europe (to Luxembourg). It serves as a hub for low-cost carrier Air Arabia and, in May 2019, it was announced that direct flights operated by Pegasus airline would commence to Istanbul, Turkey, from Ras Al Khaimah in October 2019.[68]
SpiceJet, India's second largest carrier, announced in October, 2019 that RAK Airport would become its first overseas hub in a deal that brought with it direct flights from the Indian capital New Delhi to Ras Al Khaimah.[69]
On 17 February 2006, Space Adventures announced its plans to develop a $265 million commercial spaceport in Ras Al Khaimah for space tourism.[70] This plan has yet to be realized.
10. Notable People
- Saud bin Saqr Al Qasimi (Monarch)
- Saqr bin Mohammed Al Qasimi (Monarch)
- Al Hassan Saleh (Footballer)
- Ahmad ibn Mājid (Explorer)
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Finance:Emirate_of_Ras_Al_Khaimah
References
- See Al Ain and Tawam (region)
- "RAK Tourism Development Authority". https://en.rasalkhaimah.ae/ras-al-khaimah/history-of-ras-al-khaimah.
- "RAK drives home its heritage credentials". The National. 29 October 2014. http://www.thenational.ae/uae/heritage/rak-drives-home-its-heritage-credentials.
- "New archaeological site found in Ras Al Khaimah". GulfNews.com. 2013-02-11. http://gulfnews.com/news/gulf/uae/tourism/new-archaeological-site-found-in-ras-al-khaimah-1.1144557. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- Al-Qasimi, Sultan Muhammed; Shāriqah), Sulṭān ibn Muḥammad al-Qāsimī (Ruler of (1 January 1988). The Myth of Arab Piracy in the Gulf. Routledge. ISBN 9780415029735. https://books.google.com/books?id=2YTJmnISdOMC.
- Arabian Gulf Intelligence. Cambridge: Oleander Press. 1985. pp. 6–8. ISBN 9781909349964.
- James, William (2002) [1827]. The Naval History of Great Britain, Volume 5, 1808–1811. Conway Maritime Press. p. 204. ISBN 0-85177-909-3.
- Marshall, John (1823). "Samuel Leslie Esq.". Royal Naval Biography. Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown & Green. pp. 88–90. https://books.google.com/books?id=jWUBAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA87&lpg=PA87&dq=john+wainwright+ras+al#PPA87,M1.
- "'Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf. Vol I. Historical. Part IA & IB. J G Lorimer. 1915' [653 (796/1782)"]. qdl.qa. http://www.qdl.qa/en/archive/81055/vdc_100023575944.0x0000c5. Retrieved 13 January 2014. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "'Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf. Vol I. Historical. Part IA & IB. J G Lorimer. 1915' [659 (802/1782)"]. qdl.qa. http://www.qdl.qa/en/archive/81055/vdc_100023575945.0x000003. Retrieved 4 August 2015.
- Moorehead, John (1977). In Defiance of The Elements: A Personal View of Qatar. Quartet Books. p. 23. ISBN 9780704321496.
- Lorimer, John (1915). Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf. British Government, Bombay. pp. 666–670.
- Lorimer, John (1915). Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf. British Government, Bombay. pp. 668.
- Commins, David (2012-03-15). The Gulf States: A Modern History - David Commins - ßĘČ Google. ISBN 9781848852785. https://books.google.com/books?id=hxaKj3AjyfwC&lpg=PA79&dq=1835%20maritime%20peace&pg=PA78#v=onepage. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- Kourosh Ahmadi, Islands and International Politics in the Persian Gulf: The Abu Musa and Tunbs in Strategic Context (Routledge, 2008) p96
- "Bronze age bones from RAK to be studied for first time". https://www.thenational.ae/uae/heritage/bronze-age-bones-from-rak-to-be-studied-for-first-time-1.991414.
- "Ancient graves unearthed in RAK". GulfNews.com. 2013-04-05. http://gulfnews.com/news/gulf/uae/tourism/ancient-graves-unearthed-in-rak-1.1167035. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- Leech, Nick (2015-10-22). "The long read: has a lost Arab capital been found on the Oman-UAE border?". The National. https://www.thenational.ae/arts-culture/the-long-read-has-a-lost-arab-capital-been-found-on-the-oman-uae-border-1.4941.
- Morton, Michael Quentin (15 April 2016). Keepers of the Golden Shore: A History of the United Arab Emirates (1st ed.). London: Reaktion Books. ISBN 978-1-7802-3580-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=-oxfDQAAQBAJ&q=julfar#v=snippet. Retrieved 8 November 2016.
- Barbosa, Daurte (1918). The Book of Duarte Barbosa. Hakluyt Society. pp. 74.
- Fifty years of Emirates Archaeology (D.T. Potts and P. Hellyer, eds., 2012). https://www.academia.edu/1911251.
- Abed, Ibrahim; Hellyer, Peter (2001). The United Arab Emirates, A New Perspective. London: Trident Press Ltd.. pp. 74–90. ISBN 978-1-900724-47-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=QcMz3zV0qAMC&q=julfar#v=snippet.
- Lorimer, John (1915). Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf. British Government, Bombay. pp. 755.
- Lorimer, John (1915). Gazetteer of the Persian Gulf. British Government, Bombay. pp. 641.
- "Saud is Ras Al Khaimah ruler as UAE mourns Shaikh Saqr". Gulf News. 2010-10-27. http://gulfnews.com/news/gulf/uae/government/saud-is-ras-al-khaimah-ruler-as-uae-mourns-shaikh-saqr-1.702398.
- "RAK Government facts". https://www.rak.ae/wps/portal/rak/about/ras-al-khaimah/facts.
- "RAK Ports". https://www.rakports.ae/saqr-port.php.
- "Arabian Business". https://www.arabianbusiness.com/industries/transport/382883-ras-al-khaimah-signs-deal-to-develop-saqr-port.
- "Historic witness to RAK's defence". GulfNews.com. 2008-11-20. http://gulfnews.com/news/gulf/uae/heritage-culture/historic-witness-to-rak-s-defence-1.144297. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- Hawker, Ronald W. 'Tribe, house style, and the town layout of Jazirat al-Hamra, Ras al-Khaimah, UAE' in Proceedings of the Seminar for Arabian Studies, 2006
- "Jebel Jais". https://jebeljais.ae/.
- "Watch: Snowfall in UAE, temperature hits -2.2 degree". http://www.khaleejtimes.com/temperature-hits--1-degree-celsius-in-uae. Retrieved 2017-02-05.
- "Heavy snowfall on Ras Al Khaimah's Jebel Jais mountain cluster". http://gulfnews.com/news/uae/general/heavy-snowfall-on-ras-al-khaimah-s-jebel-jais-mountain-cluster-1.46663. Retrieved 2015-08-16.
- "Introduction to RAK - Economic Overview". http://www.rakinvest.ae/en/introductiontorak/economicoverview.aspx.
- "RAK Ruler hails tourism boom as he opens Jebel Jais adventure peak". https://www.thenational.ae/uae/rak-ruler-hails-tourism-boom-as-he-opens-jebel-jais-adventure-peak-1.977278.
- "Construction Commences on Ras Al Khaimah's Latest Adventure Products at the Toroverde Adventure Park". https://en.raktda.com/news-and-media/press-releases/2018/11/8/construction-commences-on-ras-al-khaimah-s-latest-adventure-products-at-the-toroverde-adventure-park-a3895.
- "New RAK resort revealed". https://www.arabianbusiness.com/new-rak-resort-revealed-668715.html.
- "Ras Al Khaimah sets new target of 3m tourists annually by 2025". https://www.arabianbusiness.com/travel-hospitality/407456-ras-al-khaimah-chases-3m-tourists-annually-by-2025.
- "AHIC 2019 kicks off with 'Day of Disruption' in Ras Al Khaimah". https://www.hospitalitynet.org/news/4092844.html.
- "AHIC returns to Ras Al Khaimah for the 15th edition in 2019". http://www.hoteliermiddleeast.com/34369-ahic-returns-to-ras-al-khaimah-for-the-15th-edition-in-2019/.
- "About Stevin Rock". https://www.linkedin.com/company/stevinrockllc/about/.
- "What We Do". http://www.julphar.net/en/about-us/what-we-do.
- "Ashok Leyland lifts capacity at RAK bus plant". https://gulfnews.com/business/ashok-leyland-lifts-capacity-at-rak-bus-plant-1.1683801.
- "FTI". http://falconrak.com/.
- "About Us". Composites.ae. http://composites.ae/index.php/about-us. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- "RAKBANK CEO on FY earnings, SME lending, consolidation". https://www.bloomberg.com/news/videos/2019-01-31/rakbank-ceo-on-fy-earnings-sme-lending-consolidation-video.
- "RAKBank 2019 net profit at Dh1.09b". https://gulfnews.com/business/banking/rakbank-2019-net-profit-at-dh109b-1.69505014.
- "About Us". https://rakez.com/About/Rakez.
- "Value Added Tax (VAT)". https://u.ae/en/information-and-services/finance-and-investment/taxation/valueaddedtaxvat.
- "RAKEZ FAQs". https://rakez.com/Faq.
- "About RAKICC". https://www.rakicc.com/about-us/.
- Jonathan Sheikh-Miller. "UAE Weekend Switchover". AMEinfo. Archived from the original on 12 February 2011. https://web.archive.org/web/20110212191741/http://www.ameinfo.com/95027.html. Retrieved 22 March 2010.
- Fairlie, Greg (2010-02-10). Fast times in store as a field of 10 sub-60 men announced for Ras al-Khaimah Half Marathon. IAAF. Retrieved on 2010-02-11. http://www.iaaf.org/LRR10/news/newsid=55529.html
- "Athletics: Kenyan teenager Kiprop wins RAK half marathon" (in en). Reuters. 8 February 2019. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-athletics-marathon/athletics-kenyan-teenager-kiprop-wins-rak-half-marathon-idUSKCN1PX197.
- "Yeshaneh Ababel smashes half marathon world record in Ras Al Khaimah". https://www.thenational.ae/sport/other-sport/yeshaneh-ababel-smashes-half-marathon-world-record-in-ras-al-khaimah-1.982666.
- "Facebook". Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/group.php?gid=252308532325&v=wall&ref=mf. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- "The Sheikh Saud bin Saqr Al Qasimi Foundation - Al Qasimi Foundation". http://www.alqasimifoundation.com/en/home.
- "Mission and Vision". http://rakfinearts.ae/index/en/mission-and-vision/.
- "WHY YOU NEED TO BE AT RAS AL KHAIMAH FINE ARTS FESTIVAL". https://www.graziame.com/culture/why-you-need-to-be-at-ras-al-khaimah-fine-arts-festival.
- "National Day celebrations". https://en.raktda.com/news-and-media/press-releases/2017/11/16/ras-al-khaimah-serves-up-wealth-of-national-day-family-celebrations-a3664.
- "RAKTDA and Challenge Tour chiefs hail inaugural Ras Al Khaimah Challenge Tour Grand Final". http://www.europeantour.com/challengetour/news/newsid=360899.html.
- "Transport : Taxi/Bus". Government of Ras Al Khaimah. http://rak.ae/en/web/rakportal/visitors-transport.
- "Taxis in Ras Al Khaimah to be eco-friendly by 2024". https://www.khaleejtimes.com/uae/ras-al-khaimah/taxis-in-ras-al-khaimah-to-be-eco-friendly-by-2024.
- "59% OF THE TAXI FLEET IN RAK IS HYBRID". https://www.raktransport.ae/news/59-of-the-taxi-fleet-in-rak-is-hybrid/.
- "Ras Al Khaimah opens phase 1 of $111m ring road project". https://www.arabianbusiness.com/transport/400636-ras-al-khaimah-opens-phase-1-of-111m-ring-road-project.
- "Archaeologists make last ditch attempt to rescue remains of pre-historic tombs in RAK | The National". Thenational.ae. 2013-04-13. http://www.thenational.ae/news/uae-news/heritage/archaeologists-make-last-ditch-attempt-to-rescue-remains-of-pre-historic-tombs-in-rak. Retrieved 2013-09-15.
- "About Us". https://rakports.ae/about-us/.
- "Direct Flights to Commence Between Istanbul and Ras Al Khaimah". https://www.transportandlogisticsme.com/smart-air-freight/2019/04/30/direct-flights-to-commence-between-istanbul-and-ras-al-khaimah.
- "SpiceJet to set up hub in Ras Al Khaimah". https://gulfnews.com/business/aviation/spicejet-to-set-up-hub-in-ras-al-khaimah-1.67327496.
- "News : Press Releases". Space Adventures. Archived from the original on 2013-11-12. https://web.archive.org/web/20131112052250/http://www.spaceadventures.com/index.cfm?fuseaction=news.viewnews&newsid=111. Retrieved 2013-09-15.

