The principle of least action – or, more accurately, the principle of stationary action – is a variational principle that, when applied to the action of a mechanical system, can be used to obtain the equations of motion for that system. It was historically called "least" because its solution requires finding the path of motion in space that has the least value. The principle can be used to derive Newtonian, Lagrangian and Hamiltonian equations of motion, and even general relativity (see Einstein–Hilbert action). In relativity, a different action must be minimized or maximized. The classical mechanics and electromagnetic expressions are a consequence of quantum mechanics. The stationary action method helped in the development of quantum mechanics. In 1933, the physicist Paul Dirac demonstrated how this principle can be used in quantum calculations by discerning the quantum mechanical underpinning of the principle in the quantum interference of amplitudes. Subsequently Julian Schwinger and Richard Feynman independently applied this principle in quantum electrodynamics. The principle remains central in modern physics and mathematics, being applied in thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, the theory of relativity, quantum mechanics, particle physics, and string theory and is a focus of modern mathematical investigation in Morse theory. Maupertuis' principle and Hamilton's principle exemplify the principle of stationary action. The action principle is preceded by earlier ideas in optics. In Ancient Greece , Euclid wrote in his Catoptrica that, for the path of light reflecting from a mirror, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Hero of Alexandria later showed that this path was the shortest length and least time. Scholars often credit Pierre Louis Maupertuis for formulating the principle of least action because he wrote about it in 1744 and 1746. However, Leonhard Euler discussed the principle in 1744,[ and evidence shows that Gottfried Leibniz preceded both by 39 years.
- variational principle
- electrodynamics
- string theory
1. General Statement
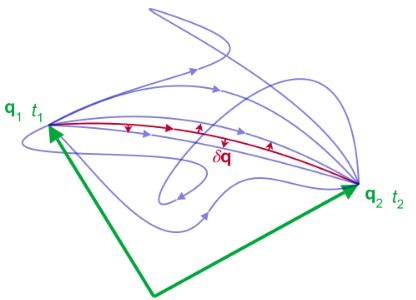
The starting point is the action, denoted [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{S} }[/math] (calligraphic S), of a physical system. It is defined as the integral of the Lagrangian L between two instants of time t1 and t2 – technically a functional of the N generalized coordinates q = (q1, q2, ... , qN) which define the configuration of the system:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{q} : \mathbf{R} \to \mathbf{R}^N }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{S}[\mathbf{q}, t_1, t_2] = \int_{t_1}^{t_2} L(\mathbf{q}(t),\mathbf{\dot{q}}(t), t) dt }[/math]
where the dot denotes the time derivative, and t is time.
Mathematically the principle is[2][3]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \delta \mathcal{S} = 0 , }[/math]
where δ (lowercase Greek delta) means a small change. In words this reads:[1]
- The path taken by the system between times t1 and t2 and configurations q1 and q2 is the one for which the action is stationary (no change) to first order.
Stationary action is not always a minimum, despite the historical name of least action.[4][5]:19-6 It is a minimum principle for sufficiently short, finite segments in the path.[6]
In applications the statement and definition of action are taken together:[7]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \delta \int_{t_1}^{t_2} L(\mathbf{q}, \mathbf{\dot{q}},t) dt = 0 . }[/math]
The action and Lagrangian both contain the dynamics of the system for all times. The term "path" simply refers to a curve traced out by the system in terms of the coordinates in the configuration space, i.e. the curve q(t), parameterized by time (see also parametric equation for this concept).
2. Origins, Statements, and Controversy
2.1. Fermat
In the 1600s, Pierre de Fermat postulated that "light travels between two given points along the path of shortest time," which is known as the principle of least time or Fermat's principle.[3]
2.2. Maupertuis
Credit for the formulation of the principle of least action is commonly given to Pierre Louis Maupertuis, who felt that "Nature is thrifty in all its actions", and applied the principle broadly:
The laws of movement and of rest deduced from this principle being precisely the same as those observed in nature, we can admire the application of it to all phenomena. The movement of animals, the vegetative growth of plants ... are only its consequences; and the spectacle of the universe becomes so much the grander, so much more beautiful, the worthier of its Author, when one knows that a small number of laws, most wisely established, suffice for all movements.—Pierre Louis Maupertuis[8]
This notion of Maupertuis, although somewhat deterministic today, does capture much of the essence of mechanics.
In application to physics, Maupertuis suggested that the quantity to be minimized was the product of the duration (time) of movement within a system by the "vis viva",
[math]\displaystyle{ \delta \int 2T(t) dt=0 }[/math]
which is the integral of twice what we now call the kinetic energy T of the system.
2.3. Euler
Leonhard Euler gave a formulation of the action principle in 1744, in very recognizable terms, in the Additamentum 2 to his Methodus Inveniendi Lineas Curvas Maximi Minive Proprietate Gaudentes. Beginning with the second paragraph:
| “ | Let the mass of the projectile be M, and let its speed be v while being moved over an infinitesimal distance ds. The body will have a momentum Mv that, when multiplied by the distance ds, will give Mv ds, the momentum of the body integrated over the distance ds. Now I assert that the curve thus described by the body to be the curve (from among all other curves connecting the same endpoints) that minimizes
or, provided that M is constant along the path,
|
” |
| — Leonhard Euler[9][10] | ||
As Euler states, ∫Mvds is the integral of the momentum over distance travelled, which, in modern notation, equals the abbreviated or reduced action
[math]\displaystyle{ \delta\int p\,dq=0 }[/math]
Thus, Euler made an equivalent and (apparently) independent statement of the variational principle in the same year as Maupertuis, albeit slightly later. Curiously, Euler did not claim any priority, as the following episode shows.
Disputed priority
Maupertuis' priority was disputed in 1751 by the mathematician Samuel König, who claimed that it had been invented by Gottfried Leibniz in 1707. Although similar to many of Leibniz's arguments, the principle itself has not been documented in Leibniz's works. König himself showed a copy of a 1707 letter from Leibniz to Jacob Hermann with the principle, but the original letter has been lost. In contentious proceedings, König was accused of forgery,[11] and even the King of Prussia entered the debate, defending Maupertuis (the head of his Academy), while Voltaire defended König.
Euler, rather than claiming priority, was a staunch defender of Maupertuis, and Euler himself prosecuted König for forgery before the Berlin Academy on 13 April 1752.[11] The claims of forgery were re-examined 150 years later, and archival work by C.I. Gerhardt in 1898[12] and W. Kabitz in 1913[13] uncovered other copies of the letter, and three others cited by König, in the Bernoulli archives.
3. Further Development
Euler continued to write on the topic; in his Réflexions sur quelques loix générales de la nature (1748), he called the quantity "effort". His expression corresponds to what we would now call potential energy, so that his statement of least action in statics is equivalent to the principle that a system of bodies at rest will adopt a configuration that minimizes total potential energy.
3.1. Lagrange and Hamilton
Much of the calculus of variations was stated by Joseph-Louis Lagrange in 1760[14][15] and he proceeded to apply this to problems in dynamics. In Mécanique analytique (1788) Lagrange derived the general equations of motion of a mechanical body.[16] William Rowan Hamilton in 1834 and 1835[17] applied the variational principle to the classical Lagrangian function
- [math]\displaystyle{ L=T-V }[/math]
to obtain the Euler–Lagrange equations in their present form.
3.2. Jacobi and Morse
In 1842, Carl Gustav Jacobi tackled the problem of whether the variational principle always found minima as opposed to other stationary points (maxima or stationary saddle points); most of his work focused on geodesics on two-dimensional surfaces.[18] The first clear general statements were given by Marston Morse in the 1920s and 1930s,[19] leading to what is now known as Morse theory. For example, Morse showed that the number of conjugate points in a trajectory equalled the number of negative eigenvalues in the second variation of the Lagrangian.
3.3. Gauss and Hertz
Other extremal principles of classical mechanics have been formulated, such as Gauss's principle of least constraint and its corollary, Hertz's principle of least curvature.
4. Disputes about Possible Teleological Aspects
The mathematical equivalence of the differential equations of motion and their integral counterpart has important philosophical implications. The differential equations are statements about quantities localized to a single point in space or single moment of time. For example, Newton's second law
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F}=m\mathbf{a} }[/math]
states that the instantaneous force F applied to a mass m produces an acceleration a at the same instant. By contrast, the action principle is not localized to a point; rather, it involves integrals over an interval of time and (for fields) an extended region of space. Moreover, in the usual formulation of classical action principles, the initial and final states of the system are fixed, e.g.,
- Given that the particle begins at position x1 at time t1 and ends at position x2 at time t2, the physical trajectory that connects these two endpoints is an extremum of the action integral.
In particular, the fixing of the final state has been interpreted as giving the action principle a teleological character which has been controversial historically. However, according to W. Yourgrau and S. Mandelstam, the teleological approach... presupposes that the variational principles themselves have mathematical characteristics which they de facto do not possess[20] In addition, some critics maintain this apparent teleology occurs because of the way in which the question was asked. By specifying some but not all aspects of both the initial and final conditions (the positions but not the velocities) we are making some inferences about the initial conditions from the final conditions, and it is this "backward" inference that can be seen as a teleological explanation. Teleology can also be overcome if we consider the classical description as a limiting case of the quantum formalism of path integration, in which stationary paths are obtained as a result of interference of amplitudes along all possible paths.[5]
The short story Story of Your Life by the speculative fiction writer Ted Chiang contains visual depictions of Fermat's Principle along with a discussion of its teleological dimension. Keith Devlin's The Math Instinct contains a chapter, "Elvis the Welsh Corgi Who Can Do Calculus" that discusses the calculus "embedded" in some animals as they solve the "least time" problem in actual situations.
The content is sourced from: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Physics:Principle_of_least_action
References
- R. Penrose (2007). The Road to Reality. Vintage books. p. 474. ISBN 0-679-77631-1.
- Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition), R.G. Lerner, G.L. Trigg, VHC publishers, 1991, ISBN (Verlagsgesellschaft) 3-527-26954-1, ISBN (VHC Inc.) 0-89573-752-3
- Analytical Mechanics, L.N. Hand, J.D. Finch, Cambridge University Press, 2008, ISBN:978-0-521-57572-0
- Goodman, Bernard (1993). "Action". in Parker, S. P.. McGraw-Hill Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 22. ISBN 0-07-051400-3. https://archive.org/details/mcgrawhillencycl1993park/page/22/mode/2up.
- Chapter 19 of Volume II, Feynman R, Leighton R, and Sands M. The Feynman Lectures on Physics . 3 volumes 1964, 1966. Library of Congress Catalog Card No. 63-20717. ISBN:0-201-02115-3 (1970 paperback three-volume set); ISBN:0-201-50064-7 (1989 commemorative hardcover three-volume set); ISBN:0-8053-9045-6 (2006 the definitive edition (2nd printing); hardcover)
- Stehle, Philip M. (1993). "Least-action principle". in Parker, S. P.. McGraw-Hill Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 670. ISBN 0-07-051400-3. https://archive.org/details/mcgrawhillencycl1993park/page/670/mode/2up.
- Classical Mechanics, T.W.B. Kibble, European Physics Series, McGraw-Hill (UK), 1973, ISBN:0-07-084018-0
- Chris Davis. Idle theory (1998) http://www.idlex.freeserve.co.uk/idle/evolution/ref/leastact.html
- Leonhard Euler, Methodus Inveniendi Lineas Curvas Maximi Minive Proprietate Gaudentes. (1744) Bousquet, Lausanne & Geneva. 320 pages. Reprinted in Leonhardi Euleri Opera Omnia: Series I vol 24. (1952) C. Cartheodory (ed.) Orell Fuessli, Zurich. Scanned copy of complete text at The Euler Archive, Dartmouth. http://math.dartmouth.edu/~euler/pages/E065.html
- Euler, Additamentum II (external link), ibid. (English translation) http://math.dartmouth.edu/~euler/docs/originals/E065h
- J J O'Connor and E F Robertson, "The Berlin Academy and forgery", (2003), at The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive. http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/history/HistTopics/Forgery_2.html
- Gerhardt CI. (1898) "Über die vier Briefe von Leibniz, die Samuel König in dem Appel au public, Leide MDCCLIII, veröffentlicht hat", Sitzungsberichte der Königlich Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, I, 419–427.
- Kabitz W. (1913) "Über eine in Gotha aufgefundene Abschrift des von S. König in seinem Streite mit Maupertuis und der Akademie veröffentlichten, seinerzeit für unecht erklärten Leibnizbriefes", Sitzungsberichte der Königlich Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, II, 632–638.
- D. J. Struik, ed (1969). A Source Book in Mathematics, 1200–1800. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press. pp. 406–413
- Kline, Morris (1972). Mathematical Thought from Ancient to Modern Times. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-501496-0. https://archive.org/details/mathematicalthou0000unse. pp. 582-589
- Lagrange, Joseph-Louis (1788). Mécanique Analytique. p. 226
- W. R. Hamilton, "On a General Method in Dynamics", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Part I (1834) p.247-308; Part II (1835) p. 95-144. (From the collection Sir William Rowan Hamilton (1805–1865): Mathematical Papers edited by David R. Wilkins, School of Mathematics, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland. (2000); also reviewed as On a General Method in Dynamics) http://www.emis.de/classics/Hamilton/GenMeth.pdf
- G.C.J. Jacobi, Vorlesungen über Dynamik, gehalten an der Universität Königsberg im Wintersemester 1842–1843. A. Clebsch (ed.) (1866); Reimer; Berlin. 290 pages, available online Œuvres complètes volume 8 at Gallica-Math from the Gallica Bibliothèque nationale de France. http://math-doc.ujf-grenoble.fr/cgi-bin/oeitem?id=OE_JACOBI__8_1_0
- Marston Morse (1934). "The Calculus of Variations in the Large", American Mathematical Society Colloquium Publication 18; New York.
- Stöltzner, Michael (1994). "Action Principles and Teleology". Inside Versus Outside. Berlin: Springer. pp. 33–62. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-48647-0_3. ISBN 978-3-642-48649-4. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007%2F978-3-642-48647-0_3
