Fungi and nematodes are among the most abundant organisms in soil habitats. They provide essential ecosystem services and play crucial roles for maintaining the stability of food-webs and for facilitating nutrient cycling. As two of the very abundant groups of organisms, depending on the specific species, fungi and nematodes interact with each other in multiple ways either directly or indirectly. Directly, they can interact with each other mutualistically to helping each other survive and reproduce, antagonistically to cause damage and/or kill each other, and as commensals. Indirectly, they may be interact with each other through other organisms. Both biotic and abiotic factors can impact the direction and magnitude of fungal-nematode interactions.
- Nematode
- Fungi
- nematophagous fungi
- plant parasitic nematodes
- nematode-trapping fungi
1. Introduction
Ecosystems consist of many types of organisms, including different types of microscopic organisms such as bacteria, archaea, protozoa, fungi, and small animals such as nematodes. Together, these organisms interact with each other and with macroscopic organisms such as plants and large animals to perform ecosystem functions. Their interactions happen in multiple ways, can be direct or indirect, involving two or more partners, and occur through different mechanisms such as predation, parasitism, mutualism, or competition. These interactions are critical for maintaining ecosystem balance [1].
Fungi and nematodes are among the most abundant organisms in the terrestrial ecosystem. The phylum Nematoda, also known as the roundworms, is the second largest phylum in the animal kingdom, encompassing an estimated 500,000 species [2] Ninety percent of terrestrial nematodes reside in the top 15 cm of soil, and they play an important role in the nitrogen cycle by way of nitrogen mineralization. Nematodes do not decompose organic matter but instead are parasitic or free-living organisms that feed on living materials [3]. On the other hand, fungi are the principal decomposers of dead organic matter; they perform fundamental roles in nutrient cycling in the ecosystem. Although fungi may look like plants, they are in fact evolutionarily more closely related to animals than to plants. Both fungi and nematodes (as well as all animals) are heterotrophs. They are commonly found co-existing in a diversity of natural and man-made ecosystems, especially in the rhizosphere of plants, including crops, with significant impacts on agriculture and forestry. Consequently, interactions among fungi and nematodes have attracted significant attention.
Nematode and fungi arose about 550–600 million years ago (mya) and 1050 mya, respectively. They likely co-existed and interacted with each other in soils before plants colonized terrestrial habitats about 450 mya [4][5]. The co-existence and interactions between nematodes and fungi, whether antagonistic or mutualistic, direct or indirect, are fundamental for understanding their ecosystem effects and their potential manipulations in agriculture. An important long-term goal in agriculture pest and pathogen management is to identify novel control strategies against phytophagous nematodes and soil-borne fungal pathogens, to help increase both the quality and quantity of agricultural products. Here, we summarize our current knowledge of the interactions between nematodes and fungi. Specifically, we focus on the interactions between these two groups of organisms that have shown both antagonistic and mutualistic interactions to each other, either directly or indirectly (Figure 1). We note that the nature of their interactions can vary greatly among the different fungal and nematode species. Furthermore, the interactions between two organisms are not static but can be impacted by environmental factors to influence both the type and magnitude of their interactions [6].
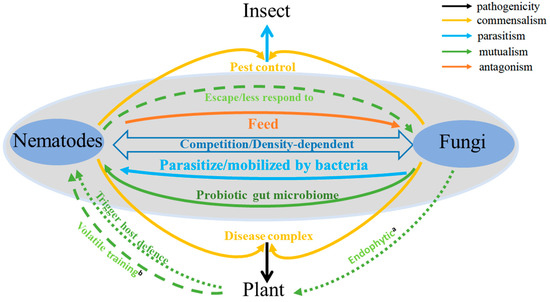
Figure 1. Fungi-nematode interactions in soil. a: Endophytic fungi trigger host plant defense against plant pathogenic nematodes (PPNs). b: Plants help nematodes escape fungal attacks through volatile training.
2. Applications of Our Understanding in Fungi–Nematode Interactions in Agriculture: The Control of Phytophagous Nematodes and Soilborne Fungal Pathogens
The rhizosphere contains a complex of biological and ecological processes. A better understanding of fungi–nematode complexes could benefit the development of ecologically based management tools to control important plant pathogen and crop pests. Discoveries of antagonistic interactions between nematodes and some rhizospheric microorganisms can provide the basis for developing control strategies to enhance plant defense against soil-borne plant pathogens and root-knot nematode parasites, including Meloidogyne spp., etc. Below we discuss a few potential approaches.
2.1. Nematodes as Biocontrol Agents against Plant Pathogenic Fungi
Because fungal-feeding nematodes can be attracted to and actively feed on plant pathogenic fungi, these nematodes can potentially be used to reduce the load of fungal plant pathogens and minimize the effects of these fungal pathogens on crops.
Some species of the nematode genus Aphelenchoides feed on the cytoplasm of fungal hyphae by piercing and sucking using a strong stylet [7]. When mixed with the mycopathogenetic fungus Trichoderma spp., these nematodes are able to feed on two plant fungal pathogens, namely Botrytis cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [6], and the combination of T. harzianum and Aphelenchoides nematode treatment resulted in the best disease control efficiency against fungal diseases [8]. One species in this nematode genus, Aphelenchoides hylurgi is able to parasitize both virulent and hypovirulent strains of the fungus Cryphonectria parasitica, the causal agent of chestnut blight [9]. Furthermore, the nematodes were also able to spread propagules of the hypovirulent strain, thus increasing the efficacy of biological control under field conditions. Another fungal-feeding nematode, Aphelenchus avenae, also showed strong abilities to reduce pathogen loads of two root-rot fungi in corn [10], Rhizoctonia solani and Fusarium solani [11][12], as well as one root-rot fungus, Fusarium oxysporum, in beans and peas [13]. However, fungivorous nematodes are often not discriminatory in their food fungal choice. They can also feed on fungi with potential beneficial effects to plants. For example, Trichoderma harzianum, an extensively studied biocontrol agent against the sclerotium-forming fungus, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, is also a favorite food for the fungivorous nematode Aphelenchoides saprophilus. Consequently, A. saprophilus can reduce the biocontrol efficiency of T. harzianum against S. sclerotiorum [14].
At present, most fungivorous nematodes reported in the literature are those that are easy to propagate in large numbers and can be stored in a dormant stage (anhydrobiosis) for a relatively long time. They have so far not been extensively applied to agriculture or horticulture fields in the form of nematode applications. This is mainly due to the high costs associated with the production, storage, and distribution of fungivorous nematodes for commercial applications. One way to realize such commercial potential is to combine fungivorous nematodes with other agricultural practices such as crop rotation and the application of other biocontrol agents to reduce the costs and maximize the benefits.
2.2. Biocontrol of Nematodes with Nematophagous Fungi
It is estimated that, worldwide, plant parasitic nematodes (PPNs) cause a combined >$150 billion worth of damages to agriculture each year [15]. From an ecological perspective, this group of nematodes is one of many components in the ecosystem that interact with other organisms, contributing to the maintenance and stability of the soil food-web. Over the last 30 years, our understanding of microbial diversity and the multitrophic interactions that are manifested in the rhizosphere, as well as biological control systems as they apply to nematodes, has improved tremendously. Indeed, several environmentally benign strategies have been developed for PPN management. Among PPNs, the root-knot nematodes (RKNs; Meloidogyne spp.) represent the most severe challenges to crop production. In a summary of the biocontrol methods evaluated between 2015 and April 2020, 10 microfungi and 3 mushroom species were tested for their effectiveness in controlling RKNs [16]. However, most studies were conducted in laboratories and greenhouse settings and their efficacies in the field are not known. Converting the laboratory successes into equally effective field applications represents the next step of the challenge.
2.2.1. Potential for the Discovery of Novel Candidates
It has been estimated that the number of culturable fungal species is between 2.2 and 3.8 million. On the basis of a 1:8.8 ratio between the numbers of cultured fungal species and the number of fungal operational taxonomic units estimated based on metagenome sequencing, there would be approximately 12 million fungal species on earth [17][18]. At present, only ~1.2% (140,000) of these have been described [19]. Thus, many new fungi with potential nematophagous activities await discovery. Even among the known culturable fungi, new compounds with novel mechanisms of nematode-parasite action have been continuously found. For example, in the fungus Pleurotus ostreatus, anthelmintic compounds were recently isolated and showed potent activity against a wide range of nematode species. It is possible that there are many novel fungi and novel fungal compounds effective at controlling parasitic nematodes of plants, animals, and humans [20].
Over the last few years, high-throughput sequencing of the universal barcode locus for fungi (18S, ITS rDNA) has revealed great potential for identifying fungi in many ecological niches. However, the fungal community comparisons between niches with different nematodes, especially those with different phytopathogenic nematodes, have been very limited. Microbiome studies of such ecological niches could help reveal the microbial diversities responsible for the differential distributions of phytopathogenic nematodes and assist in developing holistic management strategies with multi-target modes of action to control these pests. Integration of microfluidics, robotics, and machine learning technologies in interaction studies in microcosms between the microbiome and nematodes could provide novel ways to capitalize on our knowledge about the core microbiomes of pest nematodes. Such knowledge could help increase control efficiency and stress-resistance of biocontrol applications [21]. On the other hand, novel molecular markers could be developed to analyze the parasitic activities and population dynamics of nematophagous fungi. Such tools could allow us monitoring these fungi and their activities in agricultural fields.
2.2.2. Development and Integration of New Methods
To achieve successful and reproducible biological control, we must understand the ecological interactions affecting the control agent and the target. Modern technologies can help us achieve such goals. For example, real-time quantitative PCR provides an effective way to quantify and track biocontrol agents after they are applied to soil [22]. Similarly, genetic modifications of the biocontrol agents could be used to help the organisms overexpress traits involved in pathogenicity or nematocidal activity [23][24].
Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of using combinations of treatments, including various cultural practices (like soil solarization and soil amendment), chemical nematicides, and biological agents in controlling PPN populations under various conditions [25]. These studies have revealed that soil physical chemical properties can have a significant influence on their control efficacies. Thus, attention should be paid to develop biocontrol protocols that are specific for targeting ecological niches.
The use of nematophagous fungi as endophytes, i.e., rhizosphere colonization by biocontrol agents, is a promising strategy for implementing biocontrol of plant-parasitic nematodes. Endophytes should be relatively easy to apply as inoculants to seeds or seedlings and could therefore be established in the root system before nematodes are attracted to roots [26].
Finally, the unpredictability and relatively low efficacy of nematode antagonists against PPN in field conditions are major obstacles for the application of biocontrol agents for managing plant-parasitic nematodes. Part of the reasons for the differences between laboratory-based and field-based trial results may be related to the intrinsic mechanisms regulating ecosystem stability in field conditions. Application of a large number of a specific organism would disturb the balance of interactions among organisms in native niches, with the target interaction between the applied biocontrol agent and PPN in the field not realized. Thus, understanding how organismal interactions in native niches are regulated could help us develop better applications that take into account native agricultural ecosystems to ultimately produce sustainable methods of crop protection while maintaining biodiversity. Studies that evaluate the effects of coadministration of multiple partners such as nematophagous fungi, mycoparasites of plant pathogens, and plant growth promotors could help generate significant data to allow a systems approach in developing biocontrol measures to minimize the effects of nematode pests and fungal pathogens on agricultural crops [27][28].
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/jof6040206
References
- Topalovic, O.; Heuer, H. Plant-nematode interactions assisted by microbes in the rhizosphere. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2019, 30, 75–88.
- Bongers, T.; Bongers, M. Functional diversity of nematodes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1998, 10, 239–251.
- Burros, L. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 11th ed.; Nyle, C.B., Ray, R.W., Eds.; Prentice Hall Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 740.
- Hassani, M.A.; Durán, P.; Hacquard, S. Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont. Microbiome 2018, 6, 58.
- Van Megen, H.; Elsen, S.V.D.; Holterman, M.; Karssen, G.; Mooyman, P.; Bongers, T.; Holovachov, O.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. A phylogenetic tree of nematode based on about 1200 full-length small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Nematology 2009, 11, 927–950.
- Ragozzino, A.; D’Errico, G. Interactions between nematodes and fungi: A concise review. Redia 2011, 94, 123–125.
- Barron, G.; Dierkes, Y. Nematophagous fungi: Hohenbuehelia the perfect state of nematoctonus. Can. J. Bot. 1977, 55, 3054–3062.
- Jun, O.-K.; Kim, Y.H. Aphelenchus avenae and antagonistic fungi as biological control agents of pythium spp. Plant Pathol. J. 2004, 20, 271–276.
- Griffin, G.; Eisenback, J.; Yancey, M.; Templeton, J. Aphelenchoides hylurgi as a carrier of white, Hypovirulent Cryphonectria parasitica and its possible role in hypovirulence spread on blight-controlled American Chestnut trees. J. Nematol. 2009, 41, 267–273.
- Nickle, W.; McIntosh, P. Studies on the feeding and reproduction of seven mycophagous nematodes on Rhizoctonia, Fusarium, and Verticillium. Nematologica 1968, 14, 11–12.
- De la Cruz, R.G.; Knudsen, G.R.; Carta, L.K.; Newcombe, G. Either low inoculum or a multi-trophic interaction can reduce the ability of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum to kill an invasive plant. Rhizosphere 2018, 5, 76–80.
- De la Cruz, R.G.; Knudsen, G.R.; Dandurand, L.-M.C. Colonisation of sclerotia of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by a fungivorous nematode. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 1166–1170.
- Barnes, G. Aphelenchus avenae, a Potential biological control agent for root rot fungi. Plant Dis. 1981, 65, 423.
- Knudsen, G.R.; Kim, T.G.; Bae, Y.-S.; Dandurand, L.M.C. Use of quantitative real-time pcr to unravel ecological complexity in a biological control system. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 237–244.
- Li, J.; Zou, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, X.; Niu, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, K.Q. Molecular mechanisms of nematode-nematophagous microbe interactions: Basis for biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 67–95.
- Forghani, F.; Hajihassani, A. Recent advances in the development of environmentally benign treatments to control root-knot nematodes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1125.
- Wu, B.; Hussain, M.; Zhang, W.; Stadler, M.; Liu, X.; Xiang, M. Current insights into fungal species diversity and perspective on naming the environmental DNA sequences of fungi. Mycology 2019, 10, 127–140.
- Hawksworth, D.; Lücking, R. Fungal diversity revisited: 2.2 to 3.8 million species. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 79–95.
- Xu, J. Fungal species concepts in the genomics era. Genome 2020, 63, 459–468.
- Lee, C.-H.; Chang, H.-W.; Yang, C.-T.; Wali, N.; Shie, J.-J.; Hsueh, Y.-P. Sensory cilia as the Achilles heel of nematodes when attacked by carnivorous mushrooms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6014–6022.
- Toju, H.; Peay, K.; Yamamichi, M.; Narisawa, K.; Hiruma, K.; Naito, K.; Fukuda, S.; Ushio, M.; Nakaoka, S.; Onoda, Y.; et al. Core microbiomes for sustainable agroecosystems. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 247–257.
- Zhang, L.; Yang, E.; Xiang, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. Population dynamics and biocontrol efficacy of the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis as affected by stage of the soybean cyst nematode. Biol. Control 2008, 47, 244–249.
- Su, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Feng, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yang, J. Trapping devices of nematode-trapping fungi: Formation, evolution, and genomic perspectives. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 357–368.
- Liang, L.M.; Zou, C.G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, K.Q. Signal pathways involved in microbe—Nematode interactions provide new insights into the biocontrol of plant-parasitic nematodes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180317.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Hyde, K. The ecology of nematophagous fungi in natural environments. In Nematode-Trapping Fungi; Zhang, K.-Q., Hyde, K.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 211–229.
- Escudero, N.; Lopez-Llorca, L. Effects on plant growth and root-knot nematode infection of an endophytic GFP transformant of the nematophagous fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia. Symbiosis 2012, 57, 33–42.
- Luns, F.; Assis, R.; Silva, L.; Ferraz, C.; Braga, F.; Araújo, J. Coadministration of Nematophagous Fungi for Biological Control over Nematodes in Bovine in the South-Eastern Brazil. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–6.
- Baron Cozentino, N.; Souza-Pollo, A.; Rigobelo, E. Purpureocillium lilacinum and Metarhizium marquandii as plant growth-promoting fungi. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9005.
- Hsueh, Y.P.; Gronquist, M.R.; Schwarz, E.M.; Nath, R.D.; Lee, C.H.; Gharib, S.; Schroeder, F.C.; Sternberg, P.W. Nematophagous fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora mimics olfactory cues of sex and food to lure its nematode prey. eLife 2017, 6, 79.
- Liu, X.; Xiang, M.; Che, Y. The living strategy of nematophagous fungi. Mycoscience 2009, 50, 20–25.
- Li, J.; Zou, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, X.; Niu, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, K.Q. Molecular mechanisms of nematode-nematophagous microbe interactions: Basis for biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 67–95.
- Jiang, X.; Xiang, M.; Liu, X. Nematode-trapping fungi. In The Fungai Kingdom; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 5.
- Yang, Y.; Yang, E.; An, Z.; Liu, X. Evolution of nematode-trapping cells of predatory fungi of the Orbiliaceae based on evidence from rRNA-encoding DNA and multiprotein sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8379–8384.
- Zhang, K.Q.; Hyde, K.D. Nematode-Trapping Fungi; Zhang, K.Q., Hyde, K.D., Eds.; Springer Science & Business: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 23.
- Persmark, L.; Nordbring-Hertz, B. Conidial trap formation of nematode-trapping fungi in soil and soil extracts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1997, 22, 313–323.
- Li, L.; Yang, M.; Qu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J.; Liang, L.; Zhang, K. Nematode-trapping fungi and fungus-associated bacteria interactions: The role of bacterial diketopiperazines and biofilms on Arthrobotrys oligospora surface in hyphal morphogenesis. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 3827–3839.
- Barron, G.; Dierkes, Y. Nematophagous fungi: Hohenbuehelia the perfect state of nematoctonus. Can. J. Bot. 1977, 55, 3054–3062.
- Drechsler, C. Four phycomycetes destructive to nematodes and rhizopods. Mycologia 1941, 33, 248–269.
- Gray, N. Nematophagous fungi with particular reference to their ecology. Biol. Rev. 1987, 62, 245–304.
- Tzean, S. Nematophagous resupinate basidiomycetous fungi. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 1015–1020.
- Luo, H.; Liu, Y.; Fang, L.; Li, X.; Tang, N.; Zhang, K. Coprinus comatus damages nematode cuticles mechanically with spiny balls and produces potent toxins to immobilize nematodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3916–3923.
- Luo, H.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, K. Acanthocytes of Stropharia rugosoannulata function as a nematode-attacking device. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2982–2987.
- Beakes, G.; Glockling, S. Injection tube differentiation in gun cells of a Haptoglossa species which infects nematodes. Fung. Genet. Biol. 1998, 24, 45–68.
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Ji, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Zou, C.-G.; Xu, J.; Ren, Y.; Mi, Q.; Wu, J.; et al. Genomic and proteomic analyses of the fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora provide insights into nematode-trap formation. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002179.
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, X.; Xiang, M. Genome studies on nematophagous and entomogenous fungi in China. J. Fungi 2016, 2, 9.
- Larriba, E.; Jaime, M.; Carbonell-Caballero, J.; Conesa, A.; Dopazo, J.; Nislow, C.; Martín-Nieto, J.; Lopez-Llorca, L. Sequencing and functional analysis of the genome of a nematode egg-parasitic fungus, Pochonia chlamydosporia. Fung. Genet. Biol. 2014, 65, 69–80.
- Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Lai, Y.; Xiang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Drechslerella stenobrocha genome illustrates the mechanism of constricting rings and the origin of nematode predation in fungi. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 114.
- Lai, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, X.; Xiaoling, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, N.; Shu, C.; Yunpeng, W.; Wang, C.; Bushley, K.; et al. Comparative genomics and transcriptomics analyses reveal divergent lifestyle features of nematode endoparasitic fungus Hirsutella minnesotensis. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 11, 3077–3093.
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.Z.; Fang, M.L.; Deng, C.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yu, Z.F.; Xu, J.P. Comparative analyses of mitochondrial genomes provide evolutionary insights into nematode-trapping fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 617.
- Nordbring-Hertz, B. Scanning electron microscopy of the nematode-trapping organs in Arthrobotrys oligospora. Physiol. Plant. 1972, 26, 279–284.
- Veenhuis, D.M.; van Wijk, C.; Wyss, U.; Nordbring-Hertz, B.; Harder, W. Significance of electron dense microbodies in trap cells of the nematophagous fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Anton. Leeuw. 1989, 56, 251–261.
- Xie, M.H.; Bai, N.; Yang, J.L.; Jiang, K.X.; Zhou, D.X.; Zhao, Y.N.; Li, D.N.; Niu, X.M.; Zhang, K.Q.; Yang, J.K. Protein kinase Ime2 is required for mycelial growth, conidiation, osmoregulation, and pathogenicity in nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3065.
- Tunlid, A.; Johansson, T.; Nordbring-Hertz, B. Surface polymers of the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1991, 137, 1231–1240.
- Johnstone, I.L. The cuticle of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: A complex collagen structure. Bioessays 1994, 16, 171–178.
- Yang, J.K.; Tian, B.Y.; Liang, L.M.; Zhang, K.Q. Extracellular enzymes and the pathogenesis of nematophagous fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 21–31.
- Li, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.K.; Dong, L.Q.; Tian, B.Y.; Yu, Z.F.; Liang, L.M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.Q. New insights into the evolution of subtilisin-like serine protease genes in Pezizomycotina. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 68.
- Nordbring-Hertz, B.; Mattiasson, B. Action of a nematode-trapping fungus shows lectin-mediated host-microorganism interaction. Nature 1979, 281, 477–479.
- Rosen, S.; Ek, B.; Rask, L.; Tunlid, A. Purification and Characterization of a Surface Lectin from the Nematode-Trapping Fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1992, 138, 2663–2672.
- Liu, M.; Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Tian, D.; Tang, K.; Xu, T.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M. Structural insights into the fungi-nematodes interaction mediated by fucose-specific lectin AofleA from Arthrobotrys oligospora. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 783–793.
- Liang, L.M.; Shen, R.F.; Mo, Y.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Ji, X.L.; Zhang, K.Q. A proposed adhesin AoMad1 helps nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora recognizing host signals for life-style switching. Fung. Genet. Biol. 2015, 81, 172–181.
- Youssar, L.; Wernet, V.; Hensel, N.; Yu, X.; Hildebrand, H.G.; Schreckenberger, B.; Kriegler, M.; Hetzer, B.; Frankino, P.; Dillin, A.; et al. Intercellular communication is required for trap formation in the nematode-trapping fungus Duddingtonia flagrans. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008029.
- Wang, B.L.; Chen, Y.H.; He, J.N.; Xue, H.X.; Yan, N.; Zeng, Z.J.; Bennett, J.W.; Zhang, K.Q.; Niu, X.M. Integrated metabolomics and morphogenesis reveal volatile signaling of the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84.
- Liang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.-Q. The nitrate assimilation pathway is involved in the trap formation of Arthrobotrys oligospora, a nematode-trapping fungus. Fung. Genet. Biol. 2016, 92, 33–39.
- Chen, Y.L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, K.Q.; Zou, C.G. Autophagy is required for trap formation in the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 511–517.
- Tunlid, A.; Rosén, S.; Ek, B.; Rask, L. Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiology 1994, 140, 1687–1695.
- Yang, J.; Le, C.; Liang, L.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, K.-Q. Cloning and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys conoides. Arch. Microbiol. 2007, 188, 167–174.
- Wang, R.B.; Yang, J.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.Q. Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode-trapping fungus Dactylella shizishanna. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 589–594.
- Yang, J.; Liang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Le, C.; Zhang, L.; Ye, F.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, K.-Q. Purification and cloning of a novel serine protease from the nematode-trapping fungus Dactylellina varietas and its potential roles in infection against nematodes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 557–565.
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.-Q. Characterization of an extracellular protease and its cDNA from the nematode-trapping fungus Monacrosporium microscaphoides. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 130–139.
- Yang, J.-K.; Ye, F.-P.; Mi, Q.-L.; Tang, S.-Q.; Le, C.; Yang, J. Purification and cloning of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode-trapping fungus Monacrosporium cystosporium. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 852–858.
- Lebrigand, K.; He, L.D.; Thakur, N.; Arguel, M.J.; Polanowska, J.; Henrissat, B.; Record, E.; Magdelenat, G.; Barbe, V.; Raffaele, S.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of Drechmeria coniospora reveals core and specific genetic requirements for fungal endoparasitism of nematodes. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006017.
- Jansson, H.-B.; Jeyaprakash, A.; Zuckerman, B. Differential adhesion and infection of nematodes by the endo-parasitic fungus Meria coniospora (Deuteromycetes). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 552–555.
- Zuckerman, B.; Dicklow, M.B.; Coles, G.; Jansson, H.-B. Cryopreservation studies on the nematophagous fungus Drechmeria coniospora. Revue Nematol. 1988, 11, 327–331.
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Guo, Q.; Fokkens, L.; Miskei, M.; Pócsi, I.; Zhang, W.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; et al. Insights into adaptations to a near-obligate nematode endoparasitic lifestyle from the finished genome of Drechmeria coniospora. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23122.
- Wang, R.; Dong, L.; He, R.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liangjian, Q.; Zhang, Y.-A. Comparative genomic analyses reveal the features for adaptation to nematodes in fungi. DNA Res. 2018, 25, 245–256.
- Wang, Y.-L.; Li, L.-F.; Li, D.-X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Niu, X. Yellow pigment aurovertins mediate interactions between the pathogenic fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia and its nematode host. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6577–6587.
- Lopez-Llorca, L.; Olivares-Bernabeu, C.; Salinas, J.; Jansson, H.-B.; Kolattukudy, P. Pre-penetration events in fungal parasitism of nematode eggs. Mycol. Res. 2002, 106, 499–506.
- Huang, X.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, K. Extracellular enzymes serving as virulence factors in nematophagous fungi involved in infection of the host. Res. Microbiol. 2005, 155, 811–816.
- Lee, C.-H.; Chang, H.-W.; Yang, C.-T.; Wali, N.; Shie, J.-J.; Hsueh, Y.-P. Sensory cilia as the Achilles heel of nematodes when attacked by carnivorous mushrooms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6014–6022.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Hyde, K. The ecology of nematophagous fungi in natural environments. In Nematode-Trapping Fungi; Zhang, K.-Q., Hyde, K.D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 211–229.
- Jansson, H.-B. Predacity by nematophagous fungi and its relation to the attraction of nematodes. Microb. Ecol. 1982, 8, 233–240.
- McCallum, K.; Garsin, D. The role of reactive oxygen species in modulating the Caenorhabditis elegans immune response. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005923.
- Couillault, C.; Pujol, N.; Reboul, J.; Ehret-Sabatier, L.; Guichou, J.-F.; Kohara, Y.; Ewbank, J. TLR-independent control of innate immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans by the TIR domain adaptor protein TIR-1, an ortholog of human SARM. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 488–494.
- Pujol, N.; Zugasti, O.; Wong, D.; Couillault, C.; Kurz, C.; Schulenburg, H.; Ewbank, J. Anti-fungal innate immunity in C. elegans is enhanced by evolutionary diversification of antimicrobial peptides. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000105.
- Zou, C.-G.; Tu, Q.; Niu, J.; Ji, X.-L.; Zhang, K.-Q. The DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor functions as a regulator of epidermal innate immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003660.
- Nag, P.; Aggarwal, P.; Ghosh, S.; Narula, K.; Tayal, R.; Maheshwari, N.; Chakraborty, N.; Chakraborty, S. Interplay of neuronal and non-neuronal genes regulates intestinal DAF-16-mediated immune response during Fusarium infection of Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17073.
- Singh, U.B.; Sahu, A.; Sahu, N.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, R.K.; Renu; Singh, D.P.; Jaiswal, R.K.; Sarma, B.K.; Singh, H.B.; et al. Can endophytic Arthrobotrys oligospora modulate accumulation of defence related biomolecules and induced systemic resistance in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) against root knot disease caused by Meloidogyne incognita. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 63, 45–56.
- Dijksterhuis, J.; Sjollema, K.; Veenhuis, D.M.; Harder, W. Competitive interactions between two nematophagous fungi during infection and digestion of the nematode Panagrellus redivivus. Mycol. Res. 1994, 98, 1458–1462.
- El-Borai Kora, F.; Stuart, R.; Campos-Herrera, R.; Pathak, E.; Duncan, L. Entomopathogenic nematodes, root weevil larvae, and dynamic interactions among soil texture, plant growth, herbivory, and predation. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 109, 134–142.
- Alexander, M. Why microbial predators and parasites do not eliminate their prey and hosts. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 1981, 35, 113–133.
- Phillips, A.J.; Mangel, M. Density-dependent host-pathogen dynamics in soil microcosms. Ecology 1992, 73, 495–506.
- Jaffee, B.; Muldoon, A. Numerical responses of the nematophagous fungi Hirsutella rhossiliensis, Monacrosporium cionopagum, and M. ellipsosporum. Mycologia 1995, 87, 643–650.
- Jaffee, B.A.; Innis, T.M. Sampling strategies for detection of density-dependent parasitism of soil-borne nematodes by nematophagous fungi. Rev. Nematol. 1991, 14, 147–150.
- Jaffee, B.; Gaspard, J.; Ferris, H.; Muldoon, A. Quantification of parasitism of the soil-borne nematode Criconemella xenoplax by the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 631–636.
- Pathak, E.; Campos-Herrera, R.; El-Borai, F.; Duncan, L. Spatial relationships between entomopathogenic nematodes and nematophagous fungi in Florida citrus orchards. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 144, 37–46.
- Costa, S.; Kerry, B.; Bardgett, R.; Davies, K. Interactions between nematodes and their microbial enemies in coastal sand dunes. Oecologia 2012, 170, 1053–1066.
- Pathak, E.; El-Borai Kora, F.; Campos-Herrera, R.; Johnson, E.; Stuart, R.; Graham, J.; Duncan, L. Use of real-time PCR to discriminate predatory and saprophagous behavior by nematophagous fungi. Fung. Biol. 2012, 116, 563–573.
- Jaffuel, G.; Mäder, P.; Blanco-Pérez, R.; Chiriboga Morales, X.; Fliessbach, A.; Turlings, T.; Campos-Herrera, R. Prevalence and activity of entomopathogenic nematodes and their antagonists in soils that are subject to different agricultural practices. Agr. Ecosys. Environ. 2016, 230, 329–340.
- Duncan, L.W.; Stuart, R.; El-Borai Kora, F.; Campos-Herrera, R.; Pathak, E.; Giurcanu, M.; Graham, J.H. Modifying orchard planting sites conserves entomopathogenic nematodes, reduces weevil herbivory and increases citrus tree growth, survival and fruit yield. Biol. Control 2013, 64, 26–36.
- Atkinson, G.F. Some diseases of cotton. Ala. Agric. Exp. Stn. Bull. 1892, 41, 61–65.
- Lacey, L.; Grzywacz, D.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.; Frutos, R.; Brownbridge, M.; Goettel, M. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Back to the future. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 1–41.
- Ansari, M.; Shah, F.; Tirry, L.; Moens, M. Field trials against Hoplia philanthus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) with a combination of an entomopathogenic nematode and the fungus Metarhizium anisopliae CLO 53. Biol. Control 2006, 39, 453–459.
- Wu, S.-Y.; El-Borai, F.; Graham, J.; Duncan, L. The saprophytic fungus Fusarium solani increases the insecticidal efficacy of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema diaprepesi. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 159, 87–94.
- Ansari, M.; Shah, F.; Butt, T. Combined use of entomopathogenic nematodes and Metarhizium anisopliae as a new approach for black vine weevil, Otiorhynchus sulcatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) control. Entomo. Exp. Appl. 2008, 129, 340–347.
- Navarro, P.; Ii, J.; Stock, S.P. Interactions between the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis sonorensis (Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae) and the saprobic fungus Fusarium oxysporum (Ascomycota: Hypocreales). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 115, 41–47.
- Carneiro, F.; Ramalho, M.; Pereira, M. Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. phaseoli and Meloidogyne incognita interaction in common bean. Crop. Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 271–274.
- El-Shennawy, M.Z.; Khalifa, E.Z.; Ammar, M.M.; Mousa, E.M.; Hafez, S.L. Biological control of the disease complex on potato caused by root-knot nematode and Fusarium wilt fungus. Nematol. Medit. 2012, 40, 169–172.
- Alhazmi, A.; Al-Nadary, S.N. Interaction between Meloidogyne incognita and Rhizoctonia solani on green beans. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 27, 570–574.
- Parkunan, V.; Timper, P.; Ji, P. Lack of influence of Meloidogyne incognita on resistance of bell pepper cultivars to Phytophthora capsici. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 38, 1–7.
- Wanjohi, W.J.; Wafula, G.O.; Macharia, C.M. Integrated management of Fusarium wilt-root knot nematode complex on tomato in central highlands of Kenya. Sustain. Agric. Res. 2018, 7, 8.
- Hajji-Hedfi, L.; M’Hamdi-Boughalleb, N.; Horrigue-Raouani, N. Fungal diversity in rhizosphere of root-knot nematode infected tomatoes in Tunisia. Symbiosis 2019, 79, 171–181.
- Beyan, A. Response of tomato genotypes to Meloidogyne javanica and Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici co-infestation under glasshouse conditions. Pak. J. Nematol. 2019, 37, 63–82.
- Alfadhl, F. Efficacy of some control agents in controlling seedling decline in figs caused by disease complex of Meloidogyne incognita and Fusarium solani. Plant Soil 2019, 17, 323–330.
- Keinath, A.P.; Wechter, W.P.; Rutter, W.B.; Agudelo, P.A. Cucurbit Rootstocks Resistant to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum Remain Resistant When Coinfected by Meloidogyne incognita in the Field. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1383–1390.
- Scherlach, K.; Hertweck, C. Mediators of mutualistic microbe—Microbe interactions. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 303–308.
- Khan, M.; Siddiqui, Z.A. Interactions of Meloidogyne incognita, Ralstonia solanacearum and Phomopsis vexans on eggplant in sand mix and fly ash mix soils. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 177–184.
- Ahmad, L.; Siddiqui, Z.A.; Abd_Allah, E.F. Effects of interaction of Meloidogyne incognita, Alternaria dauci and Rhizoctonia solani on the growth, chlorophyll, carotenoid and proline contents of carrot in three types of soil. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Plant Soil Sci. 2019, 69, 324–331.
- Björsell, P.; Edin, E.; Viketoft, M. Interactions between some plant-parasitic nematodes and Rhizoctonia solani in potato fields. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 151–154.
- Memari, Z.; Karimi, J.; Kamali, S.; Goldansaz, S.; Hosseini, M. Are entomopathogenic nematodes effective biological control agents against the carob moth, Ectomyelois ceratoniae? J. Nematol. 2016, 48, 261–267.
- Wu, S.-Y.; Duncan, L. Recruitment of an insect and its nematode natural enemy by olfactory cues from a saprophytic fungus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 144, 107781.
- Back, M.; Haydock, P.; Jenkinson, P. Disease complexes involving plant parasitic nematodes and soilborne pathogens. Plant Pathol. 2002, 51, 683–697.
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Salem, H.H. Initial fungal infection reduce the penetration and reproduction rate of Steinernema riobravae in Galleria mellonella. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. A, Entomol. 2019, 12, 101–109.
- Martinuz, A.; Zewdu, G.; Ludwig, N.; Grundler, F.; Sikora, R.; Schouten, A. The application of Arabidopsis thaliana in studying tripartite interactions among plants, beneficial fungal endophytes and biotrophic plant-parasitic nematodes. Planta 2014, 241, 1015–1025.
- Martinez-Medina, A.; Fernandez, I.; Lok, G.B.; Pozo, M.J.; Pieterse, C.M.; Van Wees, S.C. Shifting from priming of salicylic acid- to jasmonic acid-regulated defences by Trichoderma protects tomato against the root knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1363–1377.
- Schouten, A. Mechanisms involved in nematode control by endophytic fungi. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2016, 54, 121–142.
- Khan, A.; Williams, K.; Nevalainen, H. Effects of Paecilomyces lilacinus protease and chitinase on the eggshell structures and hatching of Meloidogyne javanica juveniles. Biol. Control 2004, 31, 346–352.
- Zhou, W.; Wheeler, T.A.; Starr, J.L.; Valencia, C.U.; Sword, G.A. A fungal endophyte defensive symbiosis affects plant-nematode interactions in cotton. Plant Soil 2016, 422, 251–266.
- Singh, U.; Sahu, P.; Singh, S.; Malviya, D.; Chaurasia, R.; Sharma, S.; Saxena, A. Drechslerella dactyloides and Dactylaria brochopaga mediated induction of defense related mediator molecules in tomato plants pre-challenged with Meloidogyne incognita. Indian Phytopathol. 2019, 72, 309–320.
- Larriba, E.; Jaime, M.; Nislow, C.; Martín-Nieto, J.; Lopez-Llorca, L. Endophytic colonization of barley (Hordeum vulgare) roots by the nematophagous fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia reveals plant growth promotion and a general defense and stress transcriptomic response. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 665–678.
- Terhonen, E.; Sipari, N.; Asiegbu, F. Inhibition of phytopathogens by fungal root endophytes of Norway spruce. Biol. Control 2016, 99, 53–63.
- Escudero, N.; Lopez-Moya, F.; Ghahremani, Z.; Zavala-González, E.; Alaguero-Cordovilla, A.; Ros Ibáñez, C.; Lacasa, A.; Sorribas, F.; Lopez-Llorca, L. Chitosan increases tomato root colonization by Pochonia chlamydosporia and their combination reduces root-knot nematode damage. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1415.
- Strom, N.; Hu, W.; Haarith, D.; Chen, S.; Bushley, K. Corn and soybean host root endophytic fungi with toxicity toward the soybean cyst nematode. Phytopathology 2019, 110, 603–614.
- Torto, B.; Cortada, L.; Murungi, L.; Haukeland, S.; Coyne, D. Management of cyst and root knot nematodes: A chemical ecology perspective. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8672–8678.
- Hallmann, J.; Sikoraand, R.A. Endophytic fungi. In Biological Control of Plant-Parasitic Nematodes; Spiegel, K.D.A.Y., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 227–258.
- Vos, C.; Tesfahun, A.; Panis, B.; De Waele, D.; Elsen, A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi induce systemic resistance in tomato against the sedentary nematode Meloidogyne incognita and the migratory nematode Pratylenchus penetrans. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 61, 1–6.
- Grundler, F.; Schnibbe, L.; Wyss, U. In vitro studies on the behaviour of second-stage juveniles of Heterodera schachtii (Nematoda: Heteroderidae) in response to host plant root exudates. Parasitology 1991, 103, 149–155.
- Kirwa, H.; Murungi, L.; Beck, J.; Torto, B. Elicitation of differential responses in the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita to tomato root exudate cytokinin, flavonoids, and alkaloids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11291–11300.
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A renaissance of elicitors: Perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–406.
- Srinivasan, J.; Kaplan, F.; Ajredini, R.; Zachariah, C.; Alborn, H.; Teal, P.; Malik, R.; Edison, A.; Sternberg, P.; Schroeder, F. A blend of small molecules regulates both mating and development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2008, 454, 1115–1118.
- Srinivasan, J.; von Reuss, S.; Bose, N.; Zaslaver, A.; Mahanti, P.; Ho, M.; O’Doherty, O.; Edison, A.; Sternberg, P.; Schroeder, F. A modular library of small molecule signals regulates social behaviors in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001237.
- Zhao, L.; Ahmad, F.; Lu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wickham, J.; Sun, J. Ascarosides promote the prevalence of ophiostomatoid fungi and an invasive pathogenic nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Chem. Ecol. 2018, 44, 1–10.
- Zhang, H.X.; Tan, J.L.; Wei, L.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, C.P.; Wu, D.K.; Zhu, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.Q.; Niu, X.M. Morphology regulatory metabolites from Arthrobotrys oligospora. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1419–1423.
- Su, H.N.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.Q.; Li, G.H. Induction of trap formation in nematode-trapping fungi by bacteria-released ammonia. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 349–353.
- Willett, D.; Alborn, H.; Duncan, L.; Stelinski, L. Social networks of educated nematodes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14388.
- Willett, D.; Alborn, H.; Stelinski, L. Multitrophic effects of belowground parasitoid learning. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2067.
- Dirksen, P.; Marsh, S.; Braker, I.; Heitland, N.; Wagner, S.; Nakad, R.; Mader, S.; Petersen, C.; Kowallik, V.; Rosenstiel, P.; et al. The native microbiome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: Gateway to a new host-microbiome model. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 38.
- Toju, H.; Tanaka, Y. Consortia of anti-nematode fungi and bacteria in the rhizosphere of soybean plants attacked by root-knot nematodes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181693.
- Hamid, M.I.; Hussain, M.; Yunpeng, W.; Xiaoling, Z.; Xiang, M.; Liu, X. Successive soybean-monoculture cropping assembles rhizosphere microbial communities for the soil suppression of soybean cyst nematode. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fiw222.
- Tian, B.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, K.-Q. Metagenomic insights into communities, functions of endophytes, and their associates with infection by root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita, in tomato roots. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17087.
- Xiao, G.; Ying, S.-h.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Z.-L.; Zhang, S.; Xie, X.-Q.; Shang, Y.; Stleger, R.; Zhao, G.-P.; Wang, C.; et al. Genomic perspectives on the evolution of fungal entomopathogenicity in Beauveria bassiana. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 483.
- Chanthala, L.; Kurrey, N.; Appaiah, A.; Rao, R. Probiotic yeasts inhibit virulence of non-albicans Candida Species. mBio 2019, 10, e02307–e02319.
- Haarith, D.; Kim, D.-G.; Strom, N.; Chen, S.; Bushley, K. In vitro screening of a culturable soybean cyst nematode cyst mycobiome for potential biological control agents and biopesticides. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 1388–1397.
- Jun, O.-K.; Kim, Y.H. Aphelenchus avenae and antagonistic fungi as biological control agents of pythium spp. Plant Pathol. J. 2004, 20, 271–276.
- Griffin, G.; Eisenback, J.; Yancey, M.; Templeton, J. Aphelenchoides hylurgi as a carrier of white, Hypovirulent Cryphonectria parasitica and its possible role in hypovirulence spread on blight-controlled American Chestnut trees. J. Nematol. 2009, 41, 267–273.
- Nickle, W.; McIntosh, P. Studies on the feeding and reproduction of seven mycophagous nematodes on Rhizoctonia, Fusarium, and Verticillium. Nematologica 1968, 14, 11–12.
- De la Cruz, R.G.; Knudsen, G.R.; Carta, L.K.; Newcombe, G. Either low inoculum or a multi-trophic interaction can reduce the ability of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum to kill an invasive plant. Rhizosphere 2018, 5, 76–80.
- De la Cruz, R.G.; Knudsen, G.R.; Dandurand, L.-M.C. Colonisation of sclerotia of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by a fungivorous nematode. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 1166–1170.
- Barnes, G. Aphelenchus avenae, a Potential biological control agent for root rot fungi. Plant Dis. 1981, 65, 423.
- Knudsen, G.R.; Kim, T.G.; Bae, Y.-S.; Dandurand, L.M.C. Use of quantitative real-time pcr to unravel ecological complexity in a biological control system. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 237–244.
- Forghani, F.; Hajihassani, A. Recent advances in the development of environmentally benign treatments to control root-knot nematodes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1125.
- Wu, B.; Hussain, M.; Zhang, W.; Stadler, M.; Liu, X.; Xiang, M. Current insights into fungal species diversity and perspective on naming the environmental DNA sequences of fungi. Mycology 2019, 10, 127–140.
- Hawksworth, D.; Lücking, R. Fungal diversity revisited: 2.2 to 3.8 million species. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5, 79–95.
- Xu, J. Fungal species concepts in the genomics era. Genome 2020, 63, 459–468.
- Toju, H.; Peay, K.; Yamamichi, M.; Narisawa, K.; Hiruma, K.; Naito, K.; Fukuda, S.; Ushio, M.; Nakaoka, S.; Onoda, Y.; et al. Core microbiomes for sustainable agroecosystems. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 247–257.
- Zhang, L.; Yang, E.; Xiang, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. Population dynamics and biocontrol efficacy of the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis as affected by stage of the soybean cyst nematode. Biol. Control 2008, 47, 244–249.
- Liang, L.M.; Zou, C.G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, K.Q. Signal pathways involved in microbe—Nematode interactions provide new insights into the biocontrol of plant-parasitic nematodes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180317.
- Escudero, N.; Lopez-Llorca, L. Effects on plant growth and root-knot nematode infection of an endophytic GFP transformant of the nematophagous fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia. Symbiosis 2012, 57, 33–42.
- Luns, F.; Assis, R.; Silva, L.; Ferraz, C.; Braga, F.; Araújo, J. Coadministration of Nematophagous Fungi for Biological Control over Nematodes in Bovine in the South-Eastern Brazil. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–6.
- Baron Cozentino, N.; Souza-Pollo, A.; Rigobelo, E. Purpureocillium lilacinum and Metarhizium marquandii as plant growth-promoting fungi. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9005.
